Bilateral Simultaneous Breast Reconstruction with DIEP- and TMG Flaps: Head to Head Comparison, Risk and Complication Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Patients and Methods
2.1. Data Extraction
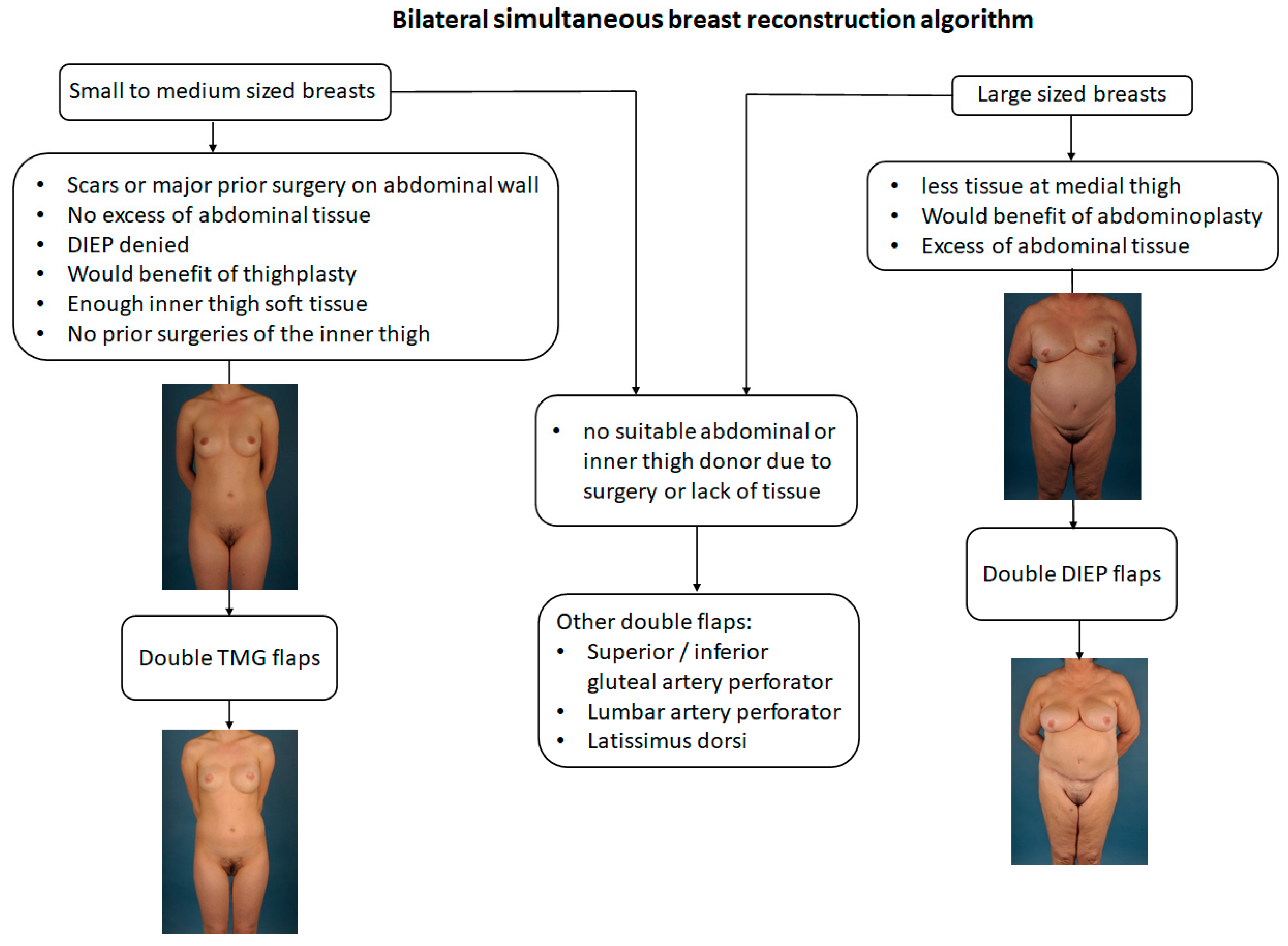
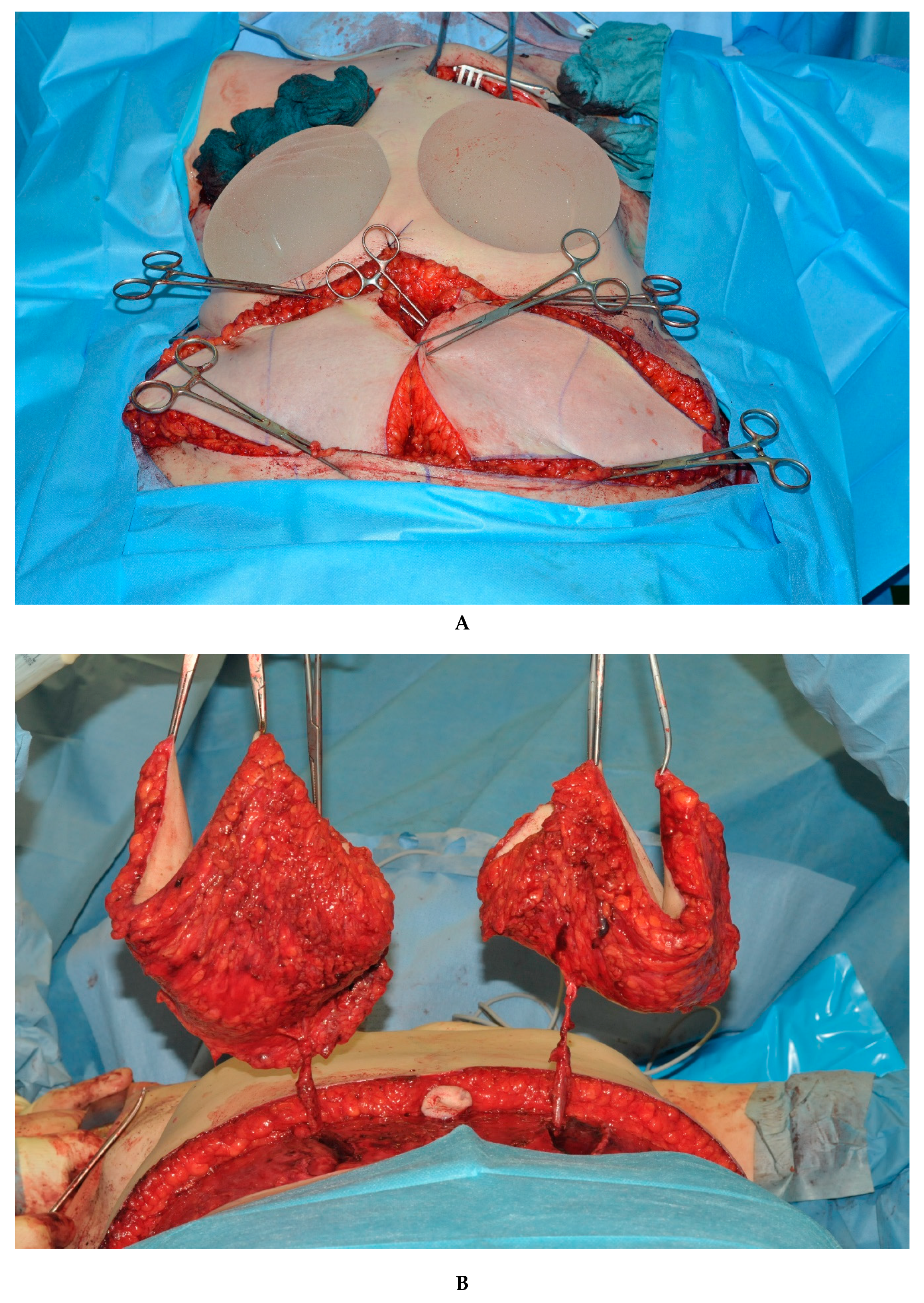
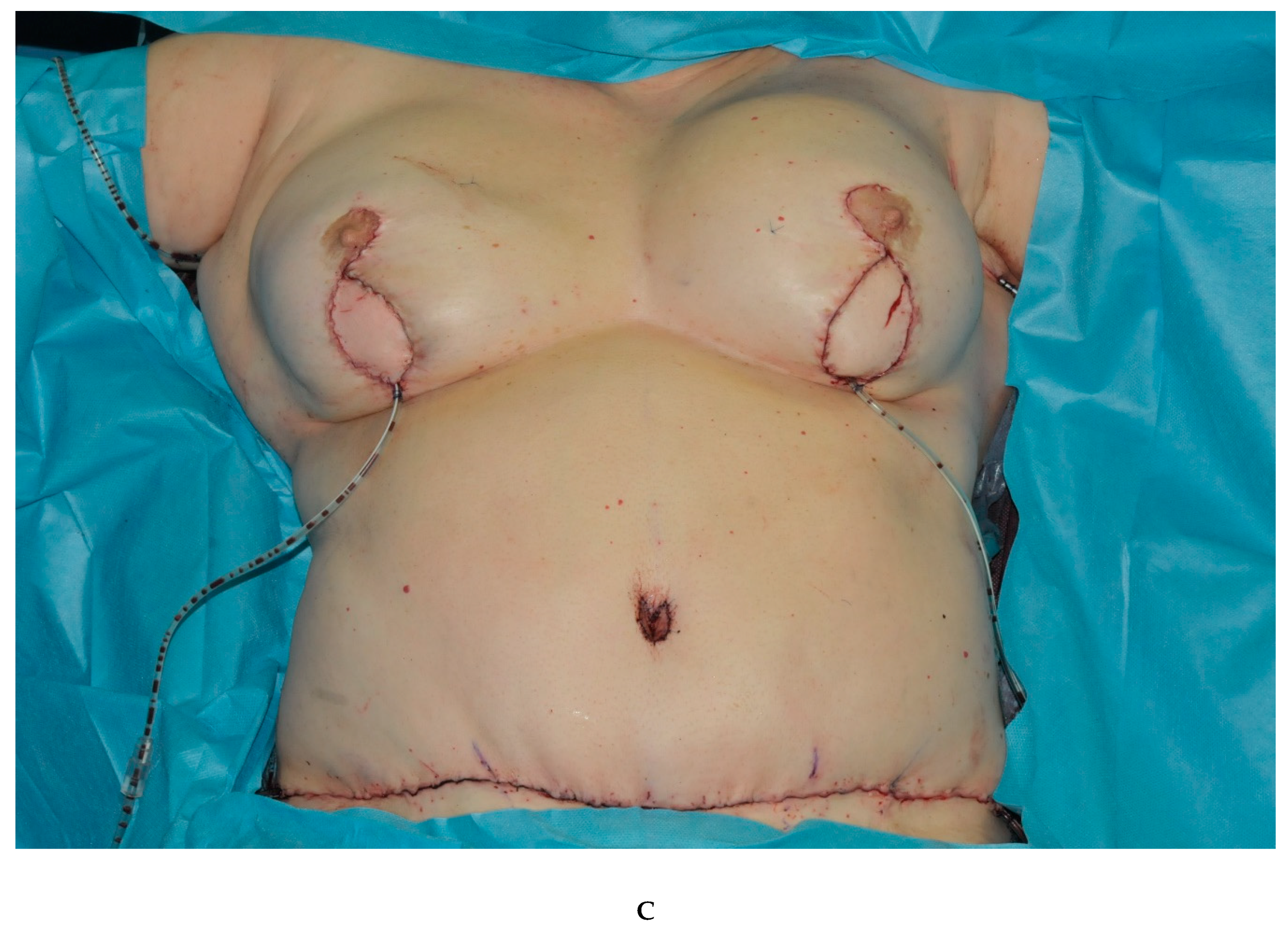
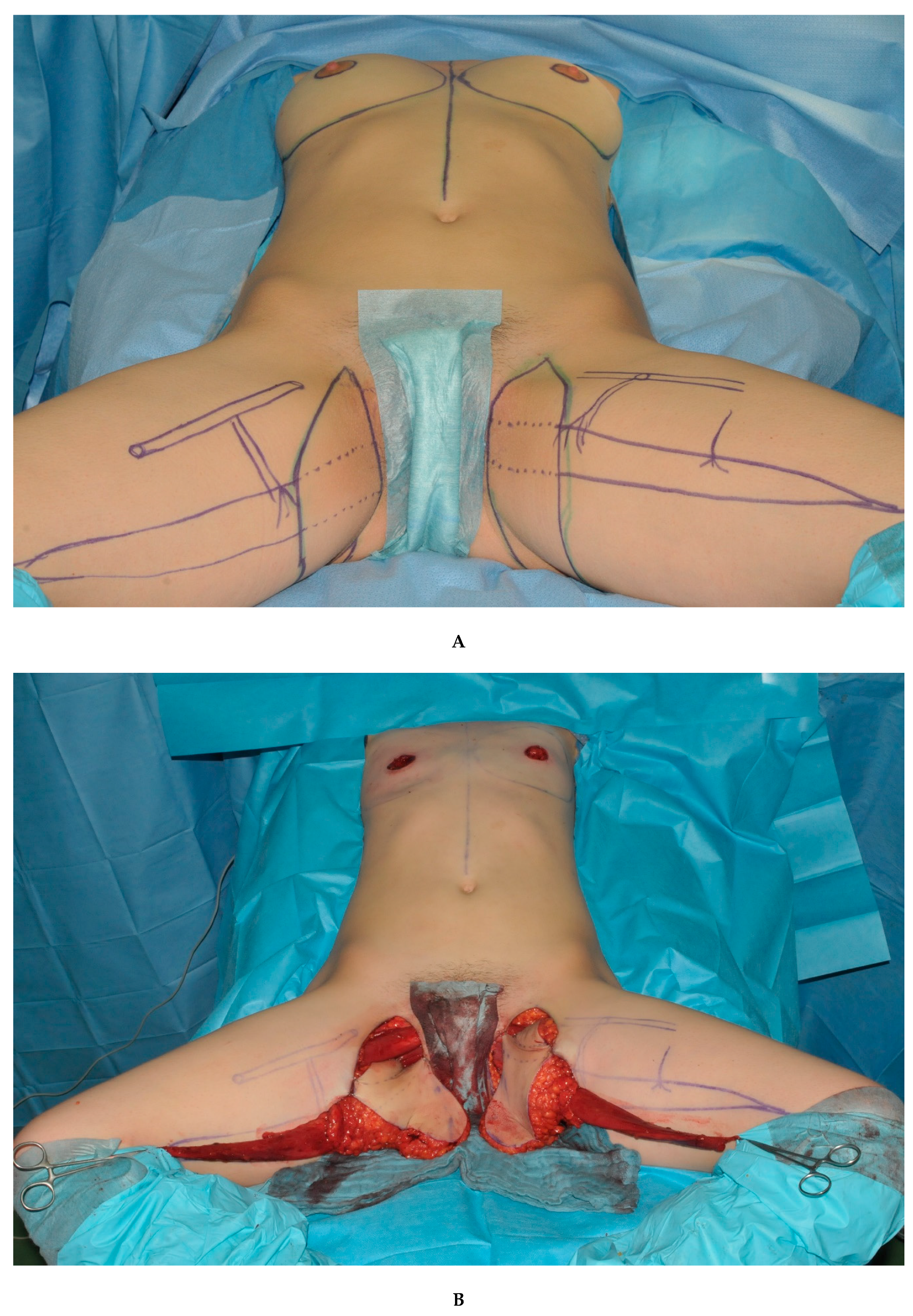
2.2. Surgical Approach
3. Statistics
4. Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hamdi, M.; Blondeel, P.; Van Landuyt, K.; Tondu, T.; Monstrey, S. Bilateral Autogenous Breast Reconstruction Using Perforator Free Flaps: A Single Center Experience. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2004, 114, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eisen, A.; Rebbeck, T.R.; Wood, W.C.; Weber, B.L. Prophylactic surgery in women with a hereditary to breast and ovarian cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2000, 18, 1980–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solomon, J.S.; Brunicardi, C.F.; Friedman, J.D. Evaluation and treatment of BRCA-positive patients. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2000, 105, 714–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Healy, C.; Allen, R.J. The evolution of perforator flap breast reconstruction: Twenty years after the first DIEP flap. J. Reconstr. Microsurg. 2014, 30, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldwin, B.J.; Schusterman, M.A.; Miller, M.J.; Kroll, S.S.; Wang, B.G. Bilateral Breast Reconstruction—Conventional Versus Free Tram. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1994, 93, 1410–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodin, F.; Schohn, T.; Dissaux, C.; Baratte, A.; Fiquet, C.; Bruant-Rodier, C. Bilateral simultaneous breast reconstruction with transverse musculocutaneous gracilis flaps. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthetic Surg. 2015, 68, e1–e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weichman, K.E.; Tanna, N.; Broer, P.N.; Wilson, S.; Azhar, H.; Karp, N.S.; Choi, M.; Ahn, C.Y.; Levine, J.P.; Allen Sr, R.J. Microsurgical breast reconstruction in thin patients: The impact of low body mass indices. J. Reconstr. Microsurg. 2015, 31, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wechselberger, G.; Schoeller, T. The transverse myocutaneous gracilis free flap: A valuable tissue source breast reconstruction. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2004, 114, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pülzl, P.; Schoeller, T.; Kleewein, K.; Wechselberger, G. Donor-site morbidity of the transverse musculocutaneous gracilis flap in autologous breast reconstruction: Short-term and long-term results. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2011, 128, 233e–242e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alderman, A.K.; Wilkins, E.G.; Lowery, J.C.; Kim, M.; Davis, J.A. Determinants of patient satisfaction in postmastectomy breast reconstruction. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2000, 106, 769–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdi, M.; Weiler-Mithoff, E.M.; Webster, M.H. Deep inferior epigastric perforator flap in breast reconstruction: Experience with the first 50 flaps. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1999, 103, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wade, R.G.; Razzano, S.; Sassoon, E.M.; Haywood, R.M.; Ali, R.S.; Figus, A. Complications in DIEP Flap Breast Reconstruction After Mastectomy for Breast Cancer: A Prospective Cohort Study Comparing Unilateral Versus Bilateral Reconstructions. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2017, 24, 1465–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Offodile, A.C., II; Aherrera, A.; Wenger, J.; Rajab, T.K.; Guo, L. Impact of increasing operative time on the incidence of early failure and complications following free tissue transfer? A risk factor analysis of 2,008 patients from the ACS-NSQIP database. Microsurgery 2017, 37, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craft, R.O.; Colakoglu, S.; Curtis, M.S.; Yueh, J.H.; Lee, B.S.; Tobias, A.M.; Lee, B.T. Patient satisfaction in unilateral and bilateral breast reconstruction [outcomes article]. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2011, 127, 1417–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaverien, M.V.; Butler, C.E. Complications in DIEP Flap Breast Reconstruction after Mastectomy for Breast Cancer: A Prospective Cohort Study Comparing Unilateral and Bilateral Reconstructions. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2017, 24, 1451–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomouk, T.; Mohan, A.T.; Azizi, A.; Conci, E.; Brickley, E.B.; Malata, C.M. Donor site morbidity in DIEP free flap breast reconstructions: A comparison of unilateral, bilateral, and bipedicled surgical procedure types. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthet. Surg. 2017, 70, 1505–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werdin, F.; Peek, A.; Martin, N.C.; Baumeister, S. Superior gluteal artery perforator flap in bilateral breast reconstruction. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2010, 64, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Frene, B.; Van Landuyt, K.O.E.N.R.A.A.D.; Hamdi, M.O.U.S.T.A.P.H.A.; Blondeel, P.; Roche, N.; Voet, D.; Monstrey, S. Free DIEAP and SGAP flap breast reconstruction after abdominal/gluteal liposuction. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthetic Surg. 2006, 59, 1031–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoeller, T.; Huemer, G.M.; Wechselberger, G. The transverse musculocutaneous gracilis flap for breast reconstruction: Guidelines for flap and patient selection. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2008, 122, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fansa, H.; Schirmer, S.; Warnecke, I.C.; Cervelli, A.; Frerichs, O. The transverse myocutaneous gracilis muscle flap: A fast and reliable method for breast reconstruction. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2008, 122, 1326–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buntic, R.F.; Horton, K.M.; Brooks, D.; Althubaiti, G.A. Transverse Upper Gracilis Flap as an Alternative to Abdominal Tissue Breast Reconstruction. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2011, 128, 607e–613e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vega, S.J.; Sandeen, S.N.; Bossert, R.P.; Perrone, A.; Ortiz, L.; Herrera, H. Gracilis myocutaneous free flap in autologous breast reconstruction. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2009, 124, 1400–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattah, A.; Figus, A.; Mathur, B.; Ramakrishnan, V.V. The transverse myocutaneous gracilis flap: Technical refinements. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthetic Surg. 2010, 63, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gill, P.S.; Hunt, J.P.; Guerra, A.B.; Dellacroce, F.J.; Sullivan, S.K.; Boraski, J.; Metzinger, S.E.; Dupin, C.L.; Allen, R.J. A 10-Year Retrospective Review of 758 DIEP Flaps for Breast Reconstruction. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2004, 113, 1153–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, S.S.; Parikh, P.M.; Goldstein, J.A.; Nahabedian, M.Y. Unilateral failures in bilateral microvascular breast reconstruction. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2010, 126, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, E.I.; Chang, E.I.; Soto-Miranda, M.A.; Zhang, H.; Nosrati, N.; Crosby, M.A.; Reece, G.P.; Robb, G.L.; Chang, D.W. Comprehensive Evaluation of Risk Factors and Management of Impending Flap Loss in 2138 Breast Free Flaps. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2016, 77, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.E.; Alkureishi, L.W.; Song, D.H. TUGs into VUGs and Friendly BUGs: Transforming the Gracilis Territory into the Best Secondary Breast Reconstructive Option. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2015, 136, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Table 1 | Total | Double DIEP | Double TMG |
|---|---|---|---|
| n = 119 | n = 76 | n = 43 | |
| Age-years | |||
| mean | 53 | 54.0 | 52.4 |
| standard deviation | 10 | 9.3 | 11.2 |
| BMI kg/m² | |||
| mean | 26.4 | 28.8 | 22.2 |
| standard deviation | 5.5 | 5.0 | 3.6 |
| Table 2 | Total | Double DIEP | Double TMG |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cut to suture time | |||
| mean | 473.5 | 476.4 | 468.5 |
| standard deviation | 106.7 | 103.4 | 113.2 |
| p = 0.698 |
| Table 3 | Total | Double DIEP | Double TMG | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
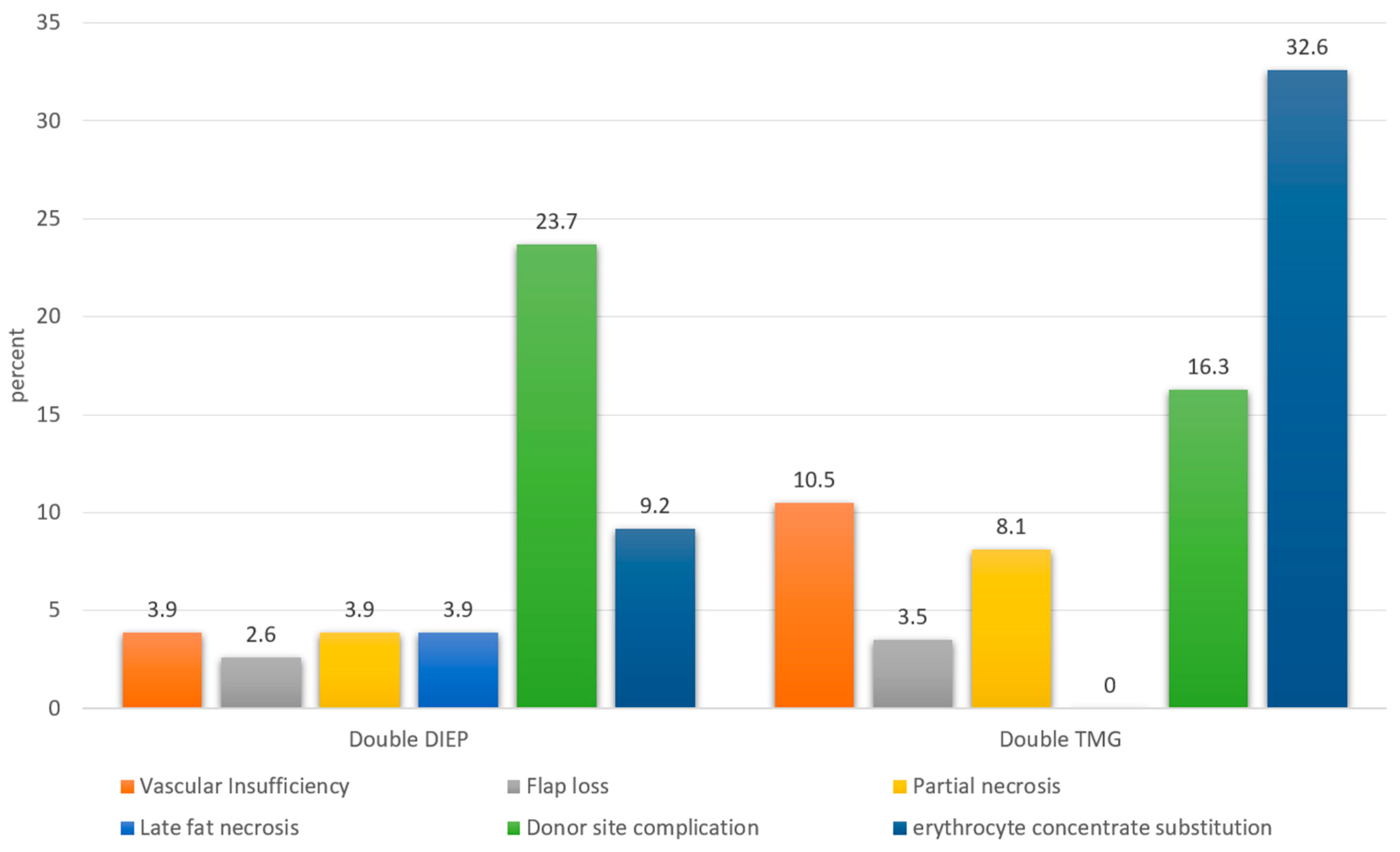
| vascular insufficiency | 15/238 (6.3 %) | 6/152 (3.9 %) | 9/86 (10.5 %) | 0.0468 |
| Relative Risk double TMG vs. double DIEP: | 2.65 | |||
| partial flap necrosis | 13/238 (5.5 %) | 6/152 (3.9 %) | 7/86 (8.1 %) | 0.1716 |
| Relative Risk double TMG vs. double DIEP: | 2.06 | |||
| flap loss | 7/238 (2.9 %) | 4/152 (2.6 %) | 3/86 (3.5 %) | 0.7071 |
| Relative Risk double TMG vs. double DIEP: | 1.33 | |||
| late fat necrosis | 6/238 (2.5 %) | 6/152 (3.9 %) | 0/86 (0.0 %) | 0.0898 |
| Relative Risk double TMG vs. double DIEP: | 0.00 | |||
| donor site complication | 25/119 (21.0 %) | 18/76 (23.7 %) | 7/43 (16.3 %) | 0.9075 |
| Relative Risk double DIEP vs. double TMG: | 1.45 | |||
| erythrocyte concentrate substitution | 21/119 (17.6 %) | 7/76 (9.2 %) | 14/43 (32.6 %) | 0.0013 |
| Relative Risk double TMG vs. double DIEP: | 3.53 |
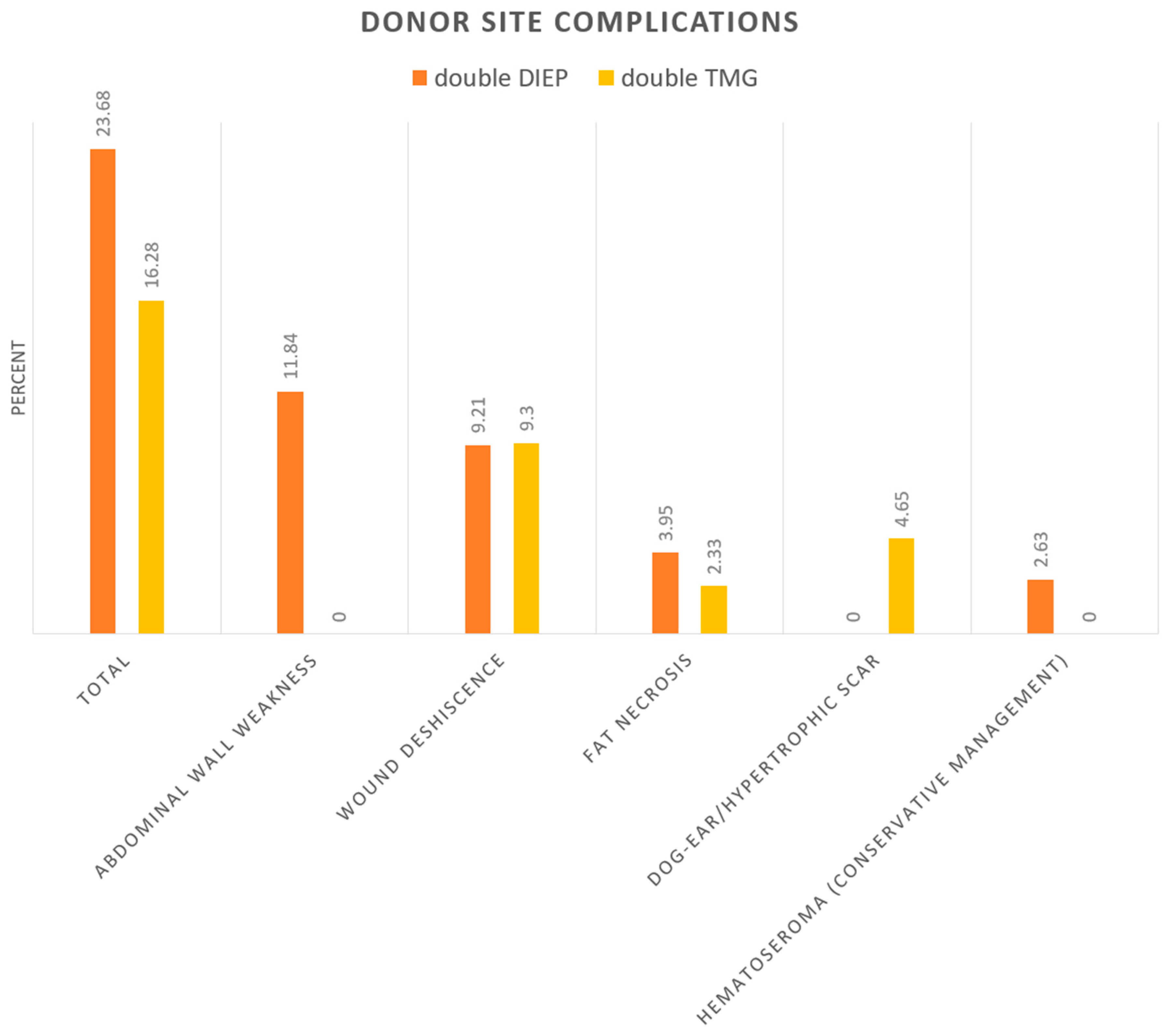
| Table 4 | Double DIEP (%) | Double TMG (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Total | 23.68 | 16.28 |
| abdominal wall weakness/Hernias | 11.84 | 0 |
| wound deshiscence | 9.21 | 9.3 |
| fat necrosis | 3.95 | 2.33 |
| dog-ear/hypertrophic scar | 0 | 4.65 |
| Hematoseroma (conservative management) | 2.63 | 0 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Weitgasser, L.; Schwaiger, K.; Medved, F.; Hamler, F.; Wechselberger, G.; Schoeller, T. Bilateral Simultaneous Breast Reconstruction with DIEP- and TMG Flaps: Head to Head Comparison, Risk and Complication Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2031. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9072031
Weitgasser L, Schwaiger K, Medved F, Hamler F, Wechselberger G, Schoeller T. Bilateral Simultaneous Breast Reconstruction with DIEP- and TMG Flaps: Head to Head Comparison, Risk and Complication Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2020; 9(7):2031. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9072031
Chicago/Turabian StyleWeitgasser, Laurenz, Karl Schwaiger, Fabian Medved, Felix Hamler, Gottfried Wechselberger, and Thomas Schoeller. 2020. "Bilateral Simultaneous Breast Reconstruction with DIEP- and TMG Flaps: Head to Head Comparison, Risk and Complication Analysis" Journal of Clinical Medicine 9, no. 7: 2031. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9072031
APA StyleWeitgasser, L., Schwaiger, K., Medved, F., Hamler, F., Wechselberger, G., & Schoeller, T. (2020). Bilateral Simultaneous Breast Reconstruction with DIEP- and TMG Flaps: Head to Head Comparison, Risk and Complication Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(7), 2031. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9072031







