Immunoadsorption for Treatment of Patients with Suspected Alzheimer Dementia and Agonistic Autoantibodies against Alpha1a-Adrenoceptor—Rationale and Design of the IMAD Pilot Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
Rationale of the Clinical Investigation
2. Methods
2.1. Objectives
2.2. Patients
2.3. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
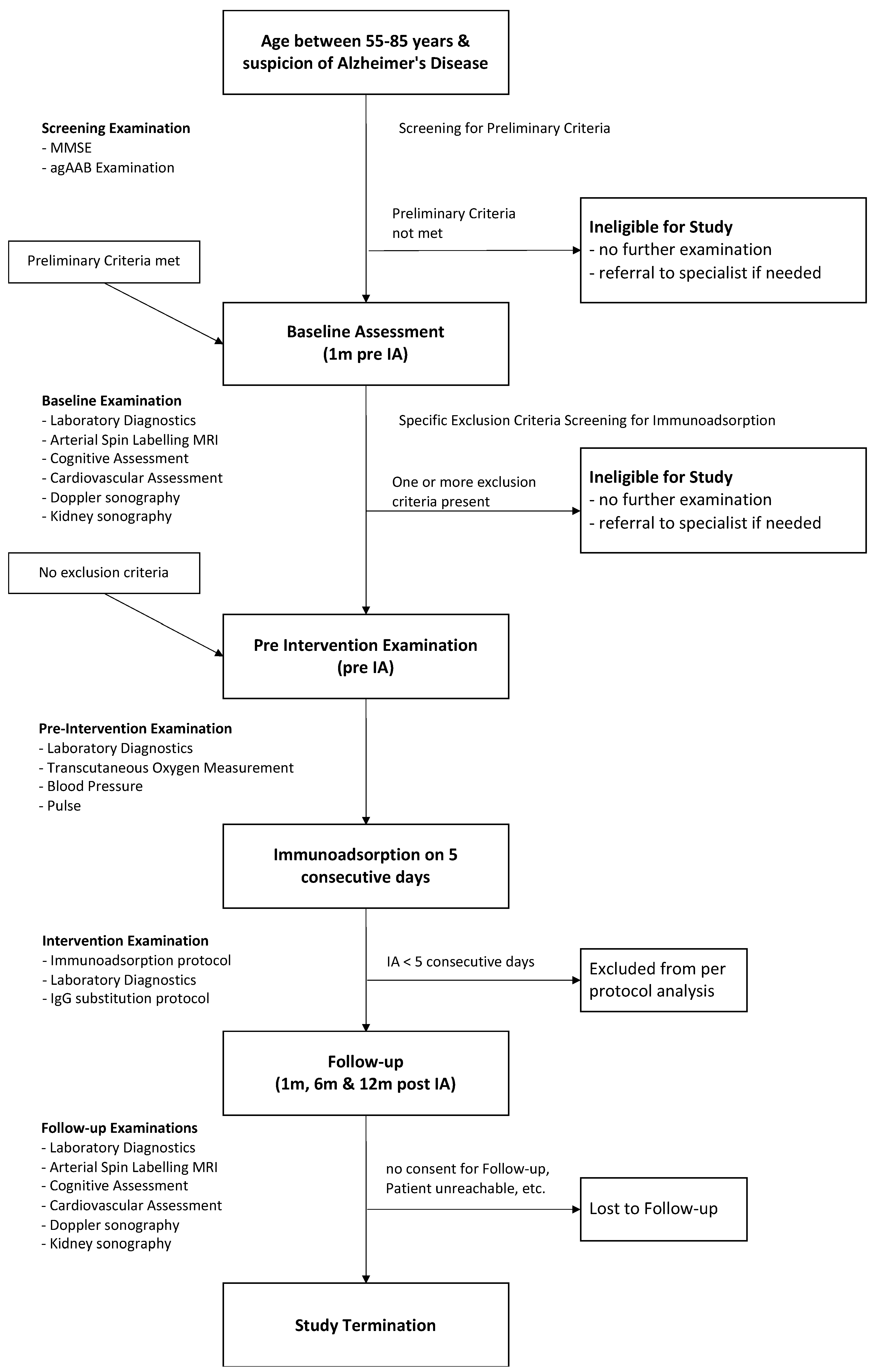
2.4. Study Design
2.5. Examinations and Assessments
2.5.1. Brain Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
MR Imaging Protocol
MR Image Analysis
2.5.2. Cognitive Assessment
Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE)
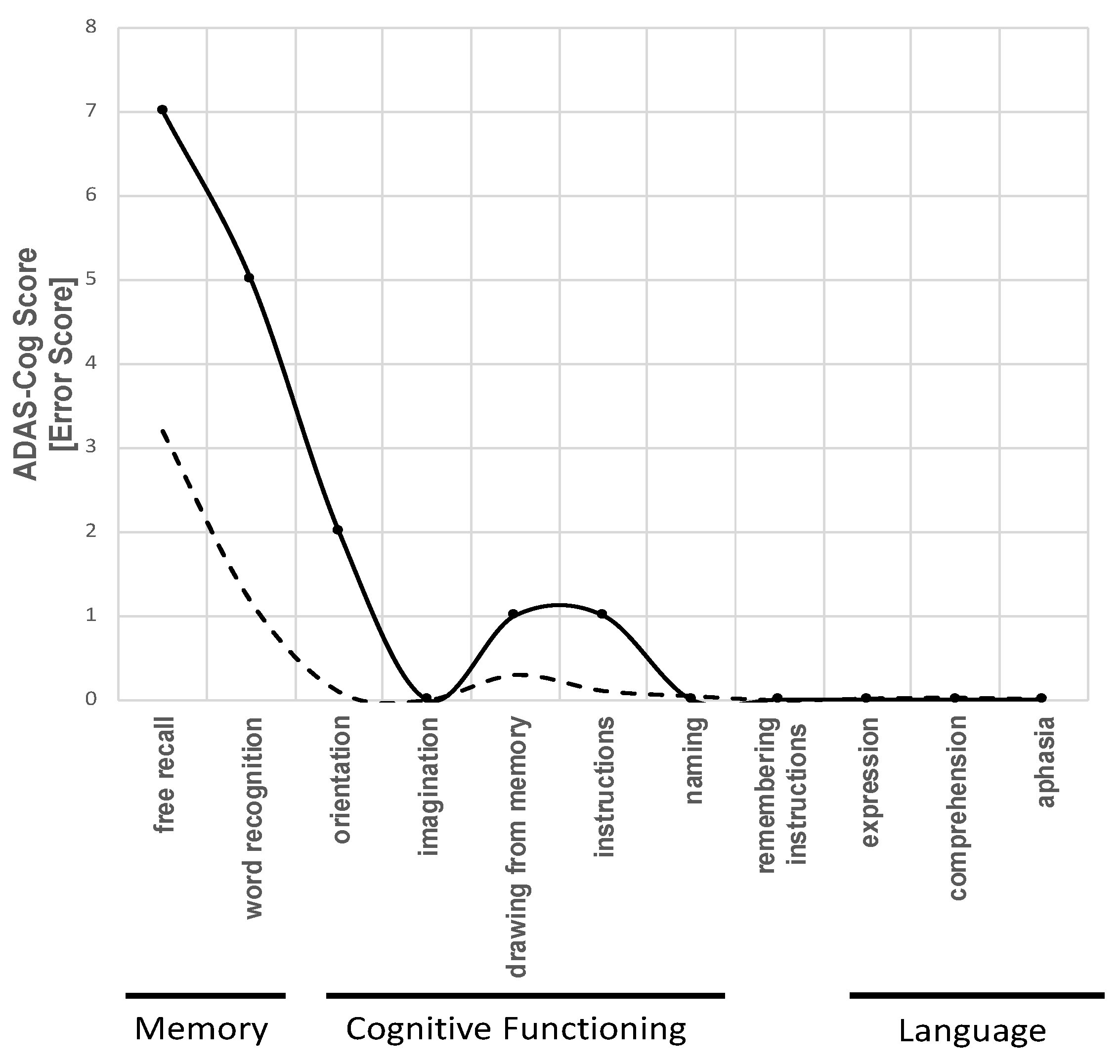
Alzheimer’s Disease Assessment Scale - Cognition (ADAS-Cog)
Verbal Learning and Memory Test (VLMT)
Benton Test
Geriatric Depression Scale (GDS)
2.5.3. Cardiovascular Examinations
Brachial Blood Pressure Measurement
Pulse-Wave Analysis and Central Hemodynamics
Digital Endothelial Vascular Function and Stiffness
Transcutaneous Oxygen Pressure (tcPO2)
Echocardiography
2.5.4. Kidney Function and Ultrasound
2.5.5. Ultrasound of the Extracranial Arteries
2.5.6. Blood and Urine Samples
2.5.7. Laboratory Parameters
2.5.8. Assessment of Autoantibodies
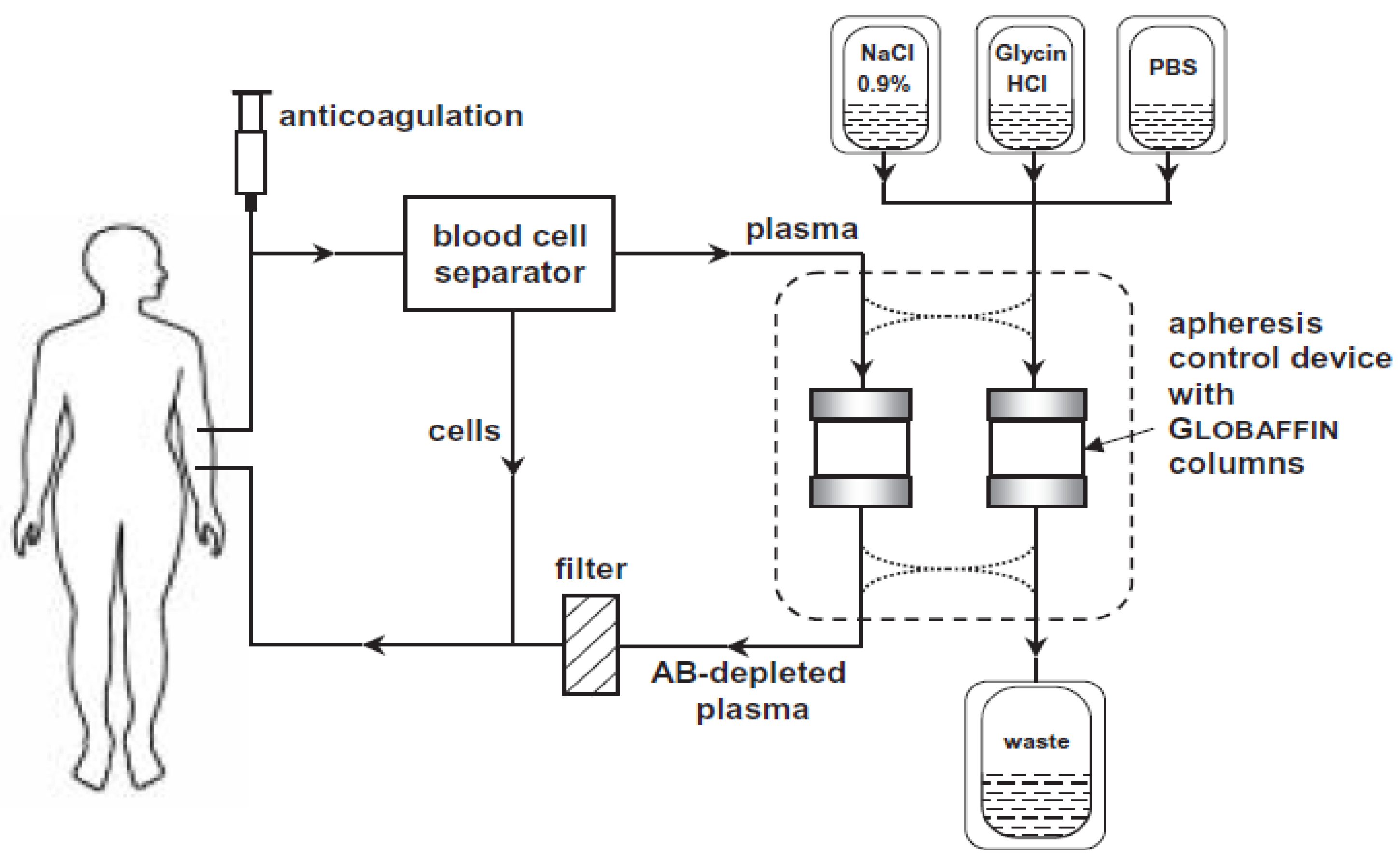
2.6. Intervention
2.7. Statistical Considerations
2.7.1. Statistical Analyses
2.7.2. Missing Data
2.7.3. Effect Size Consideration
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Parameter | Screening | Baseline | Immunoadsorption | Follow-Ups | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| d1 Pre-IA | d1 Post-IA | d2 Pre-IA | d2 Post-IA | d3 Pre-IA | d3 Post-IA | d4 Pre-IA | d4 Post-IA | d5 Pre-IA | d5 Post-IA | d6 Subst. | ||||
| agAB A1AR | X | X | ||||||||||||
| anti oxLDL | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | |||
| anti MPO | X | X | ||||||||||||
| anti PR3 | X | X | ||||||||||||
| anti GBM | X | X | ||||||||||||
| anti NMDA | X | |||||||||||||
| anti Amyloid ß | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||
| Neurogranin | X | X | ||||||||||||
| Oxidized low density lipoprotein (oxLDL) | X | X | ||||||||||||
| BAFF | X | X | ||||||||||||
| Leucocytes | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||
| Erythrocytes | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||
| Hemoglobin | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||
| Hematocrit | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||
| Platelets | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||
| Mean Platelet Volume | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||
| Platelet Distribution Width | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||
| Lymphocytes | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||
| Prothrombin time (Quick) | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||
| International Normalized Ratio (INR) | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||
| Partial Thromboplastine Time (aPTT) | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||
| Mean Cell Volume (MCV) | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||
| Mean Cellular Hemogoblin (MCH) | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||
| Mean Cellular Hemoglobin Concentration (MCHC) | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||
| Red Blood Cell Distribution Curve | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||
| Red Blood Cell Distribution Width (RBCD) | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||
| Sodium | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||
| Potassium | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||
| Calcium | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||
| Phosphate | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||
| Glucose | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||
| Creatinine | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||
| Urea | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||
| Uric Acid | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||
| Total Cholesterol | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||
| High density lipoprotein (HDL)-Cholesterol | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||
| Low density lipoprotein (LDL)-Cholesterol | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||
| Total Triglyzeride | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||
| Alanine Aminotransferase | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||
| Aspartate Aminotransferase | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||
| γ-Glutamyl Transferase | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||
| Total Bilirubin | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||
| Lipase | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||
| C-reactive Protein (CRP) | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||
| Thyroid (TSH) | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||
| HbA1c | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||
| Albumin | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||
| Protein | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||
| Cystatin C | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||
| Fibrinogen | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||
| Complement C3 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||
| Complement C4 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||
| Factor VIII | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||
| Antithrombin | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||
| Immunoglobulin IgG1 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||
| Immunoglobulin IgG2 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||
| Immunoglobulin IgG3) | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||
| Immunoglobulin IgG4 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||
| Immunoglobulin M | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||
| Immunoglobulin A | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||
| Total Immunoglobulin G | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | |
| Total Immunoglobulin | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||
| Vitamin B12 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||
| 25-Hydroxy-Vitamin D | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||
| Folic Acid | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||
| Homocysteine | X | |||||||||||||
| Specific gravity (Urine) | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||
| pH (Urine) | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||
| Leucocytes (Urine) | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||
| Nitrite (Urine) | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||
| Protein (Urine) | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||
| Glucose (Urine) | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||
| Ketone (Urine) | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||
| Urobilinogen (Urine) | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||
| Bilirubin (Urine) | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||
| Erythrocytes/Blood (Urine) | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||
| U-Creatine (Urine) | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||
| U-Protein (Urine) | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||
| U-Albumin (Urine) | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||
References
- Prince, M. World Alzheimer Report the Global Impact of Dementia. An Analysis of Prevalence, Incidence, Cost and Trends; Alzheimer’s Disease International: London, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Eggink, E.; van Charante, E.P.M.; van Gool, W.A.; Richard, E. A Population Perspective on Prevention of Dementia. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Dementia-Key Facts. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/dementia (accessed on 27 May 2020).
- Vetrano, D.L.; Rizzuto, D.; Calderon-Larranaga, A.; Onder, G.; Welmer, A.K.; Bernabei, R.; Marengoni, A.; Fratiglioni, L. Trajectories of functional decline in older adults with neuropsychiatric and cardiovascular multimorbidity: A Swedish cohort study. PLoS Med. 2018, 15, e1002503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vetrano, D.L.; Rizzuto, D.; Calderon-Larranaga, A.; Onder, G.; Welmer, A.K.; Qiu, C.; Bernabei, R.; Marengoni, A.; Fratiglioni, L. Walking Speed Drives the Prognosis of Older Adults with Cardiovascular and Neuropsychiatric Multimorbidity. Am. J. Med. 2019, 132, 1207–1215 e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alzheimer’s Association. 2020 Alzheimer’s Disease Facts and Figures. Alzheimers Dement. 2020, 6, 391–460. [Google Scholar]
- Deutsche Gesellschaft für Psychiatrie, Psychotherapie und Nervenheilkunde (DGPPN); Deutsche Gesellschaft für Neurologie (DGN). S3-Leitlinie “Demenzen”. 2016. Available online: https://www.awmf.org/uploads/tx_szleitlinien/038-013l_S3-Demenzen-2016-07.pdf (accessed on 27 May 2020).
- Brier, M.R.; Gordon, B.; Friedrichsen, K.; McCarthy, J.; Stern, A.; Christensen, J.; Owen, C.; Aldea, P.; Su, Y.; Hassenstab, J.; et al. Tau and Abeta imaging, CSF measures, and cognition in Alzheimer’s disease. Sci. Transl. Med. 2016, 8, 338ra66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holtzman, D.M.; Carrillo, M.C.; Hendrix, J.A.; Bain, L.J.; Catafau, A.M.; Gault, L.M.; Goedert, M.; Mandelkow, E.; Mandelkow, E.M.; Miller, D.S.; et al. Tau: From research to clinical development. Alzheimers Dement. 2016, 12, 1033–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Dyck, C.H. Anti-Amyloid-beta Monoclonal Antibodies for Alzheimer’s Disease: Pitfalls and Promise. Biol. Psychiatry 2018, 83, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doody, R.S.; Thomas, R.G.; Farlow, M.; Iwatsubo, T.; Vellas, B.; Joffe, S.; Kieburtz, K.; Raman, R.; Sun, X.; Aisen, P.S.; et al. Phase 3 trials of solanezumab for mild-to-moderate Alzheimer’s disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salloway, S.; Sperling, R.; Fox, N.C.; Blennow, K.; Klunk, W.; Raskind, M.; Sabbagh, M.; Honig, L.S.; Porsteinsson, A.P.; Ferris, S.; et al. Two phase 3 trials of bapineuzumab in mild-to-moderate Alzheimer’s disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 322–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egan, M.F.; Kost, J.; Tariot, P.N.; Aisen, P.S.; Cummings, J.L.; Vellas, B.; Sur, C.; Mukai, Y.; Voss, T.; Furtek, C.; et al. Randomized Trial of Verubecestat for Mild-to-Moderate Alzheimer’s Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 1691–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuberas-Borros, G.; Roca, I.; Boada, M.; Tarraga, L.; Hernandez, I.; Buendia, M.; Rubio, L.; Torres, G.; Bittini, A.; Guzman-de-Villoria, J.A.; et al. Longitudinal Neuroimaging Analysis in Mild-Moderate Alzheimer’s Disease Patients Treated with Plasma Exchange with 5% Human Albumin. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2018, 61, 321–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boada, M.; Lopez, O.; unez, L.N.; Szczepiorkowski, Z.M.; Torres, M.; Grifols, C.; Paez, A. Plasma exchange for Alzheimer’s disease Management by Albumin Replacement (AMBAR) trial: Study design and progress. Alzheimers Dement. (N. Y.) 2019, 5, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitaguchi, N.; Kawaguchi, K.; Yamazaki, K.; Kawachi, H.; Sakata, M.; Kaneko, M.; Kato, M.; Sakai, K.; Ohashi, N.; Hasegawa, M.; et al. Adsorptive filtration systems for effective removal of blood amyloid beta: A potential therapy for Alzheimer’s disease. J. Artif. Organs. 2018, 21, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attems, J.K.; Jellinger, A. The overlap between vascular disease and Alzheimer’s disease–lessons from pathology. BMC Med. 2014, 12, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habes, M.; Erus, G.; Toledo, J.B.; Zhang, T.; Bryan, N.; Launer, L.J.; Rosseel, Y.; Janowitz, D.; Doshi, J.; van der Auwera, S.; et al. White matter hyperintensities and imaging patterns of brain ageing in the general population. Brain 2016, 139, 1164–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallukat, G.; Schimke, I. Agonistic autoantibodies directed against G-protein-coupled receptors and their relationship to cardiovascular diseases. Semin. Immunopathol. 2014, 36, 351–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabral-Marques, O.; Riemekasten, G. Functional autoantibodies targeting G protein-coupled receptors in rheumatic diseases. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2017, 13, 648–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakatake, N.; Sanders, J.; Richards, T.; Burne, P.; Barrett, C.; Pra, C.D.; Presotto, F.; Betterle, C.; Furmaniak, J.; Smith, B.R. Estimation of serum TSH receptor autoantibody concentration and affinity. Thyroid 2006, 16, 1077–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallukat, G.; Fu, M.L.; Magnusson, Y.; Hjalmarson, A.; Hoebeke, J.; Wollenberger, A. Agonistic effects of anti-peptide antibodies and autoantibodies directed against adrenergic and cholinergic receptors: Absence of desensitization. Blood Press. Suppl. 1996, 3, 31–36. [Google Scholar]
- Karczewski, P.; Pohlmann, A.; Wagenhaus, B.; Wisbrun, N.; Hempel, P.; Lemke, B.; Kunze, R.; Niendorf, T.; Bimmler, M. Antibodies to the alpha1-adrenergic receptor cause vascular impairments in rat brain as demonstrated by magnetic resonance angiography. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e41602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- El Fassi, D.; Banga, J.P.; Gilbert, J.A.; Padoa, C.; Hegedus, L.; Nielsen, C.H. Treatment of Graves’ disease with rituximab specifically reduces the production of thyroid stimulating autoantibodies. Clin. Immunol. 2009, 130, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beyer, G.; Kuster, I.; Budde, C.; Wilhelm, E.; Hoene, A.; Evert, K.; Stracke, S.; Friesecke, S.; Mayerle, J.; Steveling, A. Hyperthyroid and acute tonsillitis in a 23-year-old woman. Internist (Berl.) 2016, 57, 717–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mawuenyega, K.G.; Sigurdson, W.; Ovod, V.; Munsell, L.; Kasten, T.; Morris, J.C.; Yarasheski, K.E.; Bateman, R.J. Decreased clearance of CNS beta-amyloid in Alzheimer’s disease. Science 2010, 330, 1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, M.L.; Herlitz, H.; Wallukat, G.; Hilme, E.; Hedner, T.; Hoebeke, J.; Hjalmarson, A. Functional autoimmune epitope on alpha 1-adrenergic receptors in patients with malignant hypertension. Lancet 1994, 344, 1660–1663. [Google Scholar]
- Wenzel, K.; Haase, H.; Wallukat, G.; Derer, W.; Bartel, S.; Homuth, V.; Herse, F.; Hubner, N.; Schulz, H.; Janczikowski, M.; et al. Potential relevance of alpha(1)-adrenergic receptor autoantibodies in refractory hypertension. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e3742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Cao, Z.; Wu, X.W.; Wu, H.K.; Ma, Y.; Wu, B.; Wang, W.Q.; Cheng, J.; Zhou, Z.H.; Tu, Y.C. Autoantibodies against AT1 and alpha1-adrenergic receptors predict arterial stiffness progression in normotensive subjects over a 5-year period. Clin. Sci. (Lond.) 2017, 131, 2947–2957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felix, S.B.; Beug, D.; Dörr, M. Immunoadsorption therapy in dilated cardiomyopathy. Expert. Rev. Cardiovasc. Ther. 2015, 13, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felix, S.B.; Staudt, A.; Dorffel, W.V.; Stangl, V.; Merkel, K.; Pohl, M.; Docke, W.D.; Morgera, S.; Neumayer, H.H.; Wernecke, K.D.; et al. Hemodynamic effects of immunoadsorption and subsequent immunoglobulin substitution in dilated cardiomyopathy: Three-month results from a randomized study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2000, 35, 1590–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herda, L.R.; Trimpert, C.; Nauke, U.; Landsberger, M.; Hummel, A.; Beug, D.; Kieback, A.; Dörr, M.; Empen, K.; Knebel, F.; et al. Effects of immunoadsorption and subsequent immunoglobulin G substitution on cardiopulmonary exercise capacity in patients with dilated cardiomyopathy. Am. Heart J. 2010, 159, 809–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staudt, A.; Schaper, F.; Stangl, V.; Plagemann, A.; Bohm, M.; Merkel, K.; Wallukat, G.; Wernecke, K.D.; Stangl, K.; Baumann, G.; et al. Immunohistological changes in dilated cardiomyopathy induced by immunoadsorption therapy and subsequent immunoglobulin substitution. Circulation 2001, 103, 2681–2686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staudt, A.; Hummel, A.; Ruppert, J.; Dörr, M.; Trimpert, C.; Birkenmeier, K.; Krieg, T.; Staudt, Y.; Felix, S.B. Immunoadsorption in dilated cardiomyopathy: 6-month results from a randomized study. Am. Heart J. 2006, 152, 712 e1-6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winters, J.L. Apheresis in the treatment of idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy. J. Clin. Apher. 2012, 27, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dandel, M.; Wallukat, G.; Englert, A.; Lehmkuhl, H.B.; Knosalla, C.; Hetzer, R. Long-term benefits of immunoadsorption in beta(1)-adrenoceptor autoantibody-positive transplant candidates with dilated cardiomyopathy. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2012, 14, 1374–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thyrian, J.R.; Hertel, J.; Schulze, L.N.; Dörr, M.; Prüss, H.; Hempel, P.; Bimmler, M.; Kunze, R.; Grabe, H.J.; Teipel, S.; et al. Prevalence and Determinants of Agonistic Autoantibodies Against alpha1-Adrenergic Receptors in Patients Screened Positive for Dementia: Results from the Population-Based DelpHi-Study. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2018, 64, 1091–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hempel, P.; Heinig, B.; Jerosch, C.; Decius, I.; Karczewski, P.; Kassner, U.; Kunze, R.; Steinhagen-Thiessen, E.; Bimmler, M. Immunoadsorption of Agonistic Autoantibodies Against alpha1-Adrenergic Receptors in Patients With Mild to Moderate Dementia. Ther. Apher. Dial. 2016, 20, 523–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jack, C.R.; Bennett, D.A., Jr.; Blennow, K.; Carrillo, M.C.; Dunn, B.; Haeberlein, S.B.; Holtzman, D.M.; Jagust, W.; Jessen, F.; Karlawish, J.; et al. NIA-AA Research Framework: Toward a biological definition of Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2018, 14, 535–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazekas, F.; Chawluk, J.B.; Alavi, A.; Hurtig, H.I.; Zimmerman, R.A. MR signal abnormalities at 1.5 T in Alzheimer’s dementia and normal aging. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 1987, 149, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheltens, P.; Launer, L.J.; Barkhof, F.; Weinstein, H.C.; van Gool, W.A. Visual assessment of medial temporal lobe atrophy on magnetic resonance imaging: Interobserver reliability. J. Neurol. 1995, 242, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leijenaar, J.F.; Ivan Maurik, S.; Kuijer, J.P.A.; van der Flier, W.M.; Scheltens, P.; Barkhof, F.; Prins, N.D. Lower cerebral blood flow in subjects with Alzheimer’s dementia, mild cognitive impairment, and subjective cognitive decline using two-dimensional phase-contrast magnetic resonance imaging. Alzheimers Dement. (Amst.) 2017, 9, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binnewijzend, M.A.; Kuijer, J.P.; Benedictus, M.R.; van der Flier, W.M.; Wink, A.M.; Wattjes, M.P.; van Berckel, B.N.; Scheltens, P.; Barkhof, F. Cerebral blood flow measured with 3D pseudocontinuous arterial spin-labeling MR imaging in Alzheimer disease and mild cognitive impairment: A marker for disease severity. Radiology 2013, 267, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asllani, I.; Borogovac, A.; Brown, T.R. Regression algorithm correcting for partial volume effects in arterial spin labeling MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. 2008, 60, 1362–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folstein, M.F.; Folstein, S.E.; McHugh, P.R. Mini-mental state. A practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. J. Psychiatr. Res. 1975, 12, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folstein, M.F.; Folstein, S.E.; White, T.; Messer, M.A. MMSE-2. Mini-Mental State Examination, 2nd ed.; PAR Inc.: Lutz, FL, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Rosen, W.G.; Mohs, R.C.; Davis, K.L. A new rating scale for Alzheimer’s disease. Am. J. Psychiatry 1984, 141, 1356–1364. [Google Scholar]
- Graham, N.L.; Emery, T.; Hodges, J.R. Distinctive cognitive profiles in Alzheimer’s disease and subcortical vascular dementia. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2004, 75, 61–71. [Google Scholar]
- Ihl, R.; Mohs, R.; Weyer, G. Alzheimer’s Disease Assessment Scale: ADAS; Beltz Test: Göttingen, Germany, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Stern, R.G.; Mohs, R.C.; Davidson, M.; Schmeidler, J.; Silverman, J.; Kramer-Ginsberg, E.; Searcey, T.; Bierer, L.; Davis, K.L. A longitudinal study of Alzheimer’s disease: Measurement, rate, and predictors of cognitive deterioration. Am. J. Psychiatry 1994, 151, 390–396. [Google Scholar]
- Helmstaedter, C.; Lendt, M.; Lux, S. VLMT: Verbaler Lern-und Merkfähigkeitstest; Beltz Test: Göttingen, Germany, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Yesavage, J.A. Geriatric depression scale. Psychopharmacol. Bull. 1988, 24, 709–711. [Google Scholar]
- Yesavage, J.A.; Brink, T.L.; Rose, T.L.; Lum, O.; Huang, V.; Adey, M.; Leirer, V.O. Development and validation of a geriatric depression screening scale: A preliminary report. J. Psychiatr. Res. 1982, 17, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volzke, H.; Alte, D.; Schmidt, C.O.; Radke, D.; Lorbeer, R.; Friedrich, N.; Aumann, N.; Lau, K.; Piontek, M.; Born, G.; et al. Cohort profile: The study of health in Pomerania. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2011, 40, 294–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, T.; Wassertheurer, S.; Rammer, M.; Maurer, E.; Hametner, B.; Mayer, C.C.; Kropf, J.; Eber, B. Validation of a brachial cuff-based method for estimating central systolic blood pressure. Hypertension 2011, 58, 825–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wassertheurer, S.; Kropf, J.; Weber, T.; van der Giet, M.; Baulmann, J.; Ammer, M.; Hametner, B.; Mayer, C.C.; Eber, B.; Magometschnigg, D. A new oscillometric method for pulse wave analysis: Comparison with a common tonometric method. J. Hum. Hypertens 2010, 24, 498–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamburg, N.M.; Keyes, M.J.; Larson, M.G.; Vasan, R.S.; Schnabel, R.; Pryde, M.M.; Mitchell, G.F.; Sheffy, J.; Vita, J.A.; Benjamin, E.J. Cross-sectional relations of digital vascular function to cardiovascular risk factors in the Framingham Heart Study. Circulation 2008, 117, 2467–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.; Dong, X.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Lu, D.; Wu, Q.; Liang, Z.; Yang, G.; Chen, B. Transcutaneous oxygen pressure (TcPO(2)): A novel diagnostic tool for peripheral neuropathy in type 2 diabetes patients. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2014, 105, 336–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recommendations for Cardiac Chamber Quantification by Echocardiography in Adults: An Update from the American Society of Echocardiography and the European Association of, Cardiovascular Imaging. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2016, 17, 412. [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, G.G.; Kursbuch, C. Ultraschall Nach den Richtlinien der DEGUM und der KVR, 6th ed.; Thieme: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Arning, C.; Widder, B.; von Reutern, G.M.; Stiegler, H.; Gortler, M. Revision of DEGUM ultrasound criteria for grading internal carotid artery stenoses and transfer to NASCET measurement. Ultraschall Med. 2010, 31, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabe, H.J.; Assel, H.; Bahls, T.; Dörr, M.; Endlich, K.; Endlich, N.; Erdmann, P.; Ewert, R.; Felix, S.B.; Fiene, B.; et al. Cohort profile: Greifswald approach to individualized medicine (GANI_MED). J. Transl. Med. 2014, 12, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karczewski, P.; Hempel, P.; Bimmler, M. Role of alpha1-adrenergic receptor antibodies in Alzheimer’s disease. Front. Biosci. (Landmark Ed.) 2018, 23, 2082–2089. [Google Scholar]
- Wallukat, G.A.W. Effects of the serum gamma globulin fraction of patients with allergic asthma and dilated cardiomyopathy on chronotropic beta adrenoceptor function in cultured neonatal rat heart myocytes. Biomed. Biochim. Acta 1987, 46, S634–S639. [Google Scholar]
- Wallukat, G.; Saravia, S.G.M.; Haberland, A.; Bartel, S.; Araujo, R.; Valda, G.; Duchen, D.; Ramirez, I.D.; Borges, A.C.; Schimke, I. Distinct patterns of autoantibodies against G-protein-coupled receptors in Chagas’ cardiomyopathy and megacolon. Their potential impact for early risk assessment in asymptomatic Chagas’ patients. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2010, 55, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallukat, G.; Prüss, H.; Muller, J.; Schimke, I. Functional autoantibodies in patients with different forms of dementia. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0192778. [Google Scholar]
- Davideit, H.; Haberland, A.; Bartel, S.; Schulze-Rothe, S.; Muller, J.; Wenzel, K. Determination of Agonistically Acting Autoantibodies to the Adrenergic Beta-1 Receptor by Cellular Bioassay. Methods Mol. Biol. 2019, 1901, 95–102. [Google Scholar]
- Ronspeck, W.; Brinckmann, R.; Egner, R.; Gebauer, F.; Winkler, D.; Jekow, P.; Wallukat, G.; Muller, J.; Kunze, R. Peptide based adsorbers for therapeutic immunoadsorption. Ther. Apher. Dial. 2003, 7, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Boada, M.; Anaya, F.; Ortiz, P.; Olazaran, J.; Shua-Haim, J.R.; Obisesan, T.O.; Hernandez, I.; Munoz, J.; Buendia, M.; Alegret, M.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Plasma Exchange with 5% Albumin to Modify Cerebrospinal Fluid and Plasma Amyloid-beta Concentrations and Cognition Outcomes in Alzheimer’s Disease Patients: A Multicenter, Randomized, Controlled Clinical Trial. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2017, 56, 129–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitaguchi, N.; Kawaguchi, K.; Nakai, S.; Murakami, K.; Ito, S.; Hoshino, H.; Hori, H.; Ohashi, A.; Shimano, Y.; Suzuki, N.; et al. Reduction of Alzheimer’s disease amyloid-beta in plasma by hemodialysis and its relation to cognitive functions. Blood Purif. 2011, 32, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trimpert, C.; Herda, L.R.; Eckerle, L.G.; Pohle, S.; Muller, C.; Landsberger, M.; Felix, S.B.; Staudt, A. Immunoadsorption in dilated cardiomyopathy: Long-term reduction of cardiodepressant antibodies. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2010, 40, 685–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, J.; Wallukat, G.; Dandel, M.; Bieda, H.; Brandes, K.; Spiegelsberger, S.; Nissen, E.; Kunze, R.; Hetzer, R. Immunoglobulin adsorption in patients with idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy. Circulation 2000, 101, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Criteria | |
|---|---|
| Inclusion |
|
| |
| |
| |
| |
| Exclusion |
|
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| Method | Parameter | Screening | Baseline | Follow-Ups | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arterial Spin Labelling MRI | Cerebral blood flow | X | X | ||
| MRI Basic protocol | Brain Volume, WMH, CBM; MTA | X | X | ||
| Time-of-flight MR angiography | Vessel anatomy and size | X | X | ||
| Diffusion Tensor Imaging | Fractional anisotropy | X | X | ||
| ADAS-Cog | Cognition | X | X | ||
| MMSE | Cognition | X | X | X | |
| GDS | Depression | X | X | ||
| VLMT | Cognition | X | X | ||
| Benton Test | Cognition | X | X | ||
| Brachial blood | Brachial blood pressure values | X | X | X | |
| Pulse wave analysis | Arterial stiffness, central hemodynamics | X | X | ||
| Digital endothelial vascular function and stiffness | Endothelial function and vascular stiffness | X | |||
| Echocardiography | Cardiac function and structure | X | |||
| Transcutaneous oxygen measurement | Oxygenation | X | X | ||
| Kidney sonography | Renal function | X | X | ||
| Doppler Sonography | Carotid Arteria blood flow | X | X | ||
| Liquor analytics | Tau/P-Tau | (X) | (X) | Optional | |
| Liquor analytics | ß-A40/42 | (X) | (X) | Optional |
| Test | Abbreviation | No Impairment | Severe Impairment | Normal Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mini-Mental State Examination | MMSE | 30 | 0 | 26–30 |
| Alzheimer’s Disease Assessment Scale—cognitive Scale | ADAS-Cog | 0 | 70 | 0–4 |
| Memory | 0 | 22 | - | |
| Cognitive Functioning | 0 | 28 | - | |
| Language | 0 | 15 | - | |
| Verbal Learning and Memory Test | VLMT | |||
| Learning | 75 | 0 | 48–75 | |
| Loss after Interference | 0 | 15 | - | |
| Loss after Delay | 0 | 15 | 0–3 | |
| Recognition | 0 | 15 | - | |
| Benton Test | Benton Test | |||
| Number Correct Score | 10 | 0 | - | |
| Error Score | 0 | - | - | |
| Geriatric Depression Scale | GDS | 0 | 15 | 0–5 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stracke, S.; Lange, S.; Bornmann, S.; Kock, H.; Schulze, L.; Klinger-König, J.; Böhm, S.; Vogelgesang, A.; von Podewils, F.; Föel, A.; et al. Immunoadsorption for Treatment of Patients with Suspected Alzheimer Dementia and Agonistic Autoantibodies against Alpha1a-Adrenoceptor—Rationale and Design of the IMAD Pilot Study. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1919. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9061919
Stracke S, Lange S, Bornmann S, Kock H, Schulze L, Klinger-König J, Böhm S, Vogelgesang A, von Podewils F, Föel A, et al. Immunoadsorption for Treatment of Patients with Suspected Alzheimer Dementia and Agonistic Autoantibodies against Alpha1a-Adrenoceptor—Rationale and Design of the IMAD Pilot Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2020; 9(6):1919. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9061919
Chicago/Turabian StyleStracke, Sylvia, Sandra Lange, Sarah Bornmann, Holger Kock, Lara Schulze, Johanna Klinger-König, Susanne Böhm, Antje Vogelgesang, Felix von Podewils, Agnes Föel, and et al. 2020. "Immunoadsorption for Treatment of Patients with Suspected Alzheimer Dementia and Agonistic Autoantibodies against Alpha1a-Adrenoceptor—Rationale and Design of the IMAD Pilot Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 9, no. 6: 1919. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9061919
APA StyleStracke, S., Lange, S., Bornmann, S., Kock, H., Schulze, L., Klinger-König, J., Böhm, S., Vogelgesang, A., von Podewils, F., Föel, A., Gross, S., Wenzel, K., Wallukat, G., Prüss, H., Dressel, A., Kunze, R., Grabe, H. J., Langner, S., & Dörr, M. (2020). Immunoadsorption for Treatment of Patients with Suspected Alzheimer Dementia and Agonistic Autoantibodies against Alpha1a-Adrenoceptor—Rationale and Design of the IMAD Pilot Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(6), 1919. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9061919






