Outcomes of Chronic Phase Chronic Myeloid Leukemia after Treatment with Multiple Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patients’ Characteristics
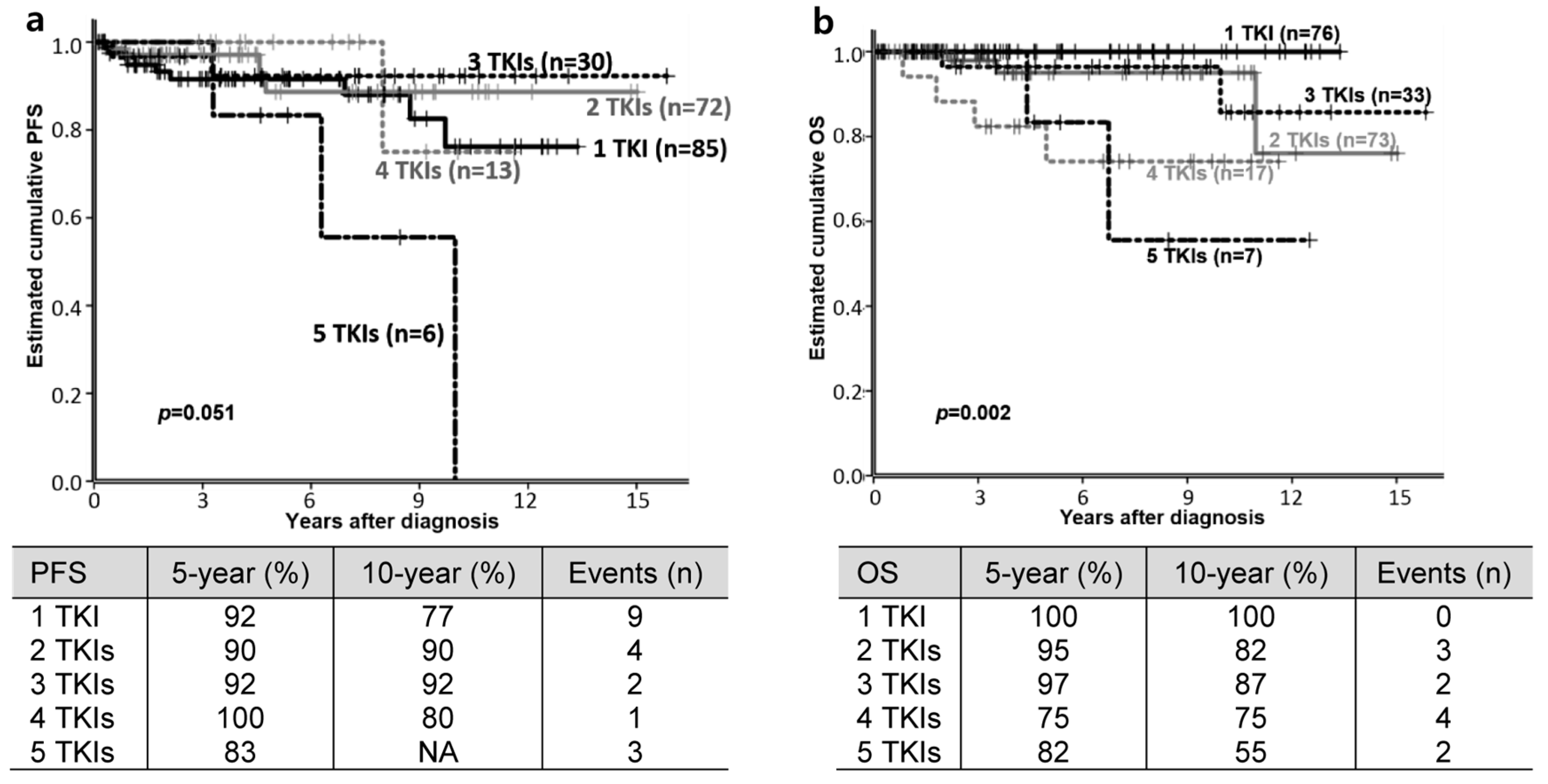
3.2. Clinical Outcomes
3.3. Outcomes According to First-Line TKI: IM vs. NG-TKI
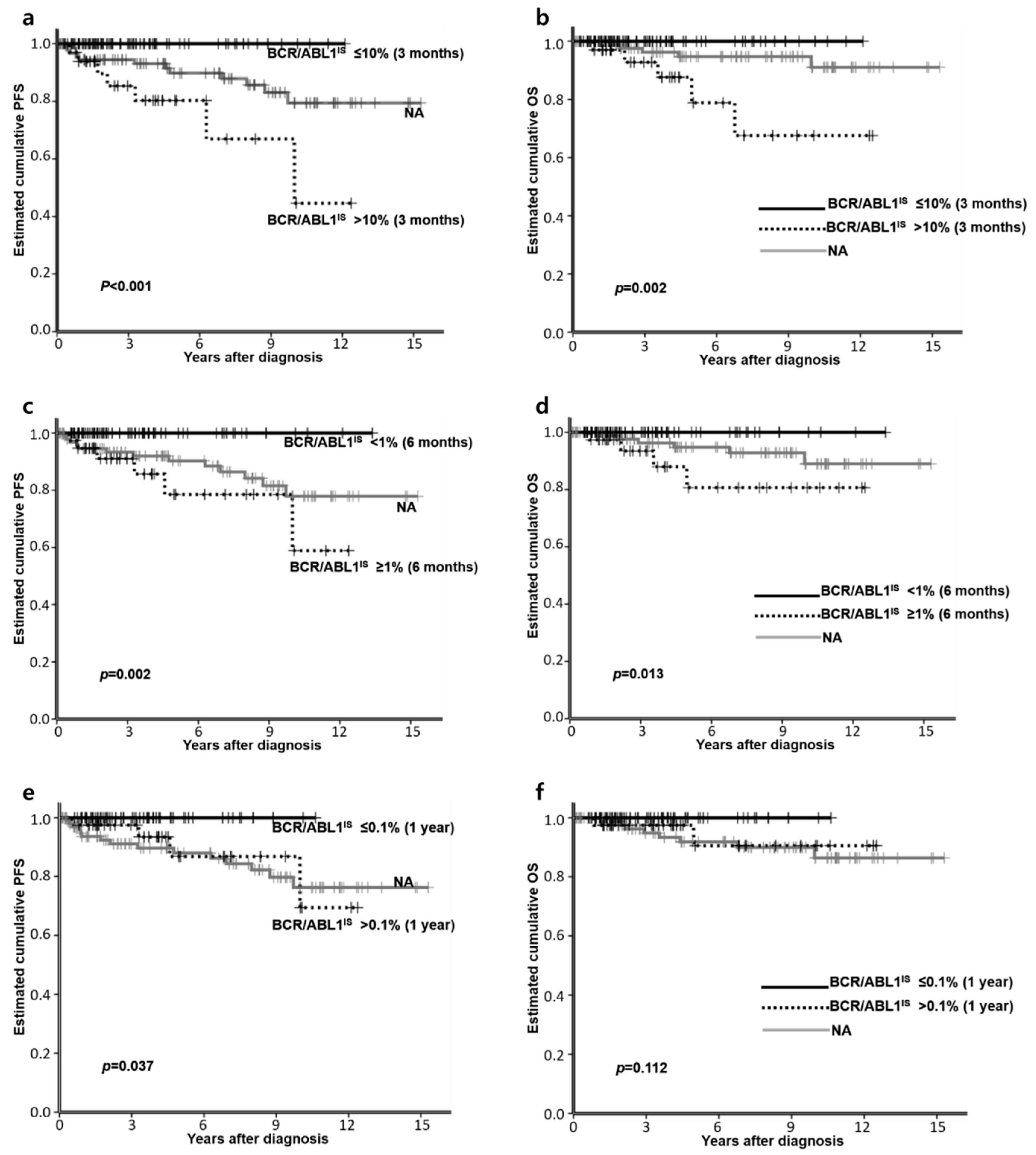
3.4. Factors Affecting PFS or OS
3.5. TKI Discontinuation
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Faderl, S.; Talpaz, M.; Estrov, Z.; O’Brien, S.; Kurzrock, R.; Kantarjian, H.M. The biology of chronic myeloid leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 341, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bower, H.; Bjorkholm, M.; Dickman, P.W.; Hoglund, M.; Lambert, P.C.; Andersson, T.M. Life expectancy of patients with chronic myeloid leukemia approaches the life expectancy of the general population. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 2851–2857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haznedaroglu, I.C. Current concerns of undertreatment and overtreatment in chronic myeloid leukemia based on european leukemianet 2013 recommendations. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2013, 14, 2005–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cortes, J.E.; Kim, D.W.; Pinilla-Ibarz, J.; le Coutre, P.; Paquette, R.; Chuah, C.; Nicolini, F.E.; Apperley, J.F.; Khoury, H.J.; Talpaz, M.; et al. A phase 2 trial of ponatinib in philadelphia chromosome-positive leukemias. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 1783–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo Rossi, A.; Breccia, M.; Abruzzese, E.; Castagnetti, F.; Luciano, L.; Gozzini, A.; Annunziata, M.; Martino, B.; Stagno, F.; Cavazzini, F.; et al. Outcome of 82 chronic myeloid leukemia patients treated with nilotinib or dasatinib after failure of two prior tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Haematologica 2013, 98, 399–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klamova, H.; Faber, E.; Zackova, D.; Markova, M.; Voglova, J.; Cmunt, E.; Novakova, L.; Machova-Polakova, K.; Moravcova, J.; Dvorakova, D.; et al. Dasatinib in imatinib-resistant or -intolerant cml patients: Data from the clinical practice of 6 hematological centers in the czech republic. Neoplasma 2010, 57, 355–359. [Google Scholar]
- Ongoren, S.; Eskazan, A.E.; Suzan, V.; Savci, S.; Erdogan Ozunal, I.; Berk, S.; Yalniz, F.F.; Elverdi, T.; Salihoglu, A.; Erbilgin, Y.; et al. Third-line treatment with second-generation tyrosine kinase inhibitors (dasatinib or nilotinib) in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia after two prior tkis: Real-life data on a single center experience along with the review of the literature. Hematol. Am. Soc. Hematol. Educ. Program 2017, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, N.P.; Rousselot, P.; Schiffer, C.; Rea, D.; Cortes, J.E.; Milone, J.; Mohamed, H.; Healey, D.; Kantarjian, H.; Hochhaus, A.; et al. Dasatinib in imatinib-resistant or -intolerant chronic-phase, chronic myeloid leukemia patients: 7-year follow-up of study ca180-034. Am. J. Hematol. 2016, 91, 869–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eghtedar, A.; Kantarjian, H.; Jabbour, E.; O’Brien, S.; Burton, E.; Garcia-Manero, G.; Verstovsek, S.; Ravandi, F.; Borthakur, G.; Konopleva, M.; et al. Outcome after failure of second generation tyrosine kinase inhibitors treatment as first-line therapy for patients with chronic myeloid leukemia. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2013, 13, 477–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, R.J.; Kantarjian, H.; O’Brien, S.; Quintás-Cardama, A.; Faderl, S.; Estrov, Z.; Cortes, J. The use of nilotinib or dasatinib after failure to 2 prior tyrosine kinase inhibitors: Long-term follow-up. Blood 2009, 114, 4361–4368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giles, F.J.; Abruzzese, E.; Rosti, G.; Kim, D.W.; Bhatia, R.; Bosly, A.; Goldberg, S.; Kam, G.L.; Jagasia, M.; Mendrek, W.; et al. Nilotinib is active in chronic and accelerated phase chronic myeloid leukemia following failure of imatinib and dasatinib therapy. Leukemia 2010, 24, 1299–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giles, F.J.; le Coutre, P.D.; Pinilla-Ibarz, J.; Larson, R.A.; Gattermann, N.; Ottmann, O.G.; Hochhaus, A.; Radich, J.P.; Saglio, G.; Hughes, T.P.; et al. Nilotinib in imatinib-resistant or imatinib-intolerant patients with chronic myeloid leukemia in chronic phase: 48-month follow-up results of a phase ii study. Leukemia 2013, 27, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brummendorf, T.H.; Cortes, J.E.; Khoury, H.J.; Kantarjian, H.M.; Kim, D.W.; Schafhausen, P.; Conlan, M.G.; Shapiro, M.; Turnbull, K.; Leip, E.; et al. Factors influencing long-term efficacy and tolerability of bosutinib in chronic phase chronic myeloid leukaemia resistant or intolerant to imatinib. Br. J. Haematol. 2016, 172, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortes, J.E.; Khoury, H.J.; Kantarjian, H.M.; Lipton, J.H.; Kim, D.W.; Schafhausen, P.; Matczak, E.; Leip, E.; Noonan, K.; Brummendorf, T.H.; et al. Long-term bosutinib for chronic phase chronic myeloid leukemia after failure of imatinib plus dasatinib and/or nilotinib. Am. J. Hematol. 2016, 91, 1206–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochhaus, A.; Baccarani, M.; Silver, R.T.; Schiffer, C.; Apperley, J.F.; Cervantes, F.; Clark, R.E.; Cortes, J.E.; Deininger, M.W.; Guilhot, F.; et al. European leukemianet 2020 recommendations for treating chronic myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 2020, 34, 966–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swerdlow, S.H.; Campo, E.; Harris, N.L.; Jaffe, E.S.; Pileri, S.A.; Stein, H.; Thiele, J.; Vardiman, J.W. The World Health Organization (Who) Classification of Tumors of the Hematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues, 4th ed.; IARC Press: Lyon, France, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Baccarani, M.; Saglio, G.; Goldman, J.; Hochhaus, A.; Simonsson, B.; Appelbaum, F.; Apperley, J.; Cervantes, F.; Cortes, J.; Deininger, M.; et al. Evolving concepts in the management of chronic myeloid leukemia: Recommendations from an expert panel on behalf of the european leukemianet. Blood 2006, 108, 1809–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baccarani, M.; Deininger, M.W.; Rosti, G.; Hochhaus, A.; Soverini, S.; Apperley, J.F.; Cervantes, F.; Clark, R.E.; Cortes, J.E.; Guilhot, F.; et al. European leukemianet recommendations for the management of chronic myeloid leukemia: 2013. Blood 2013, 122, 872–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasford, J.; Baccarani, M.; Hoffmann, V.; Guilhot, J.; Saussele, S.; Rosti, G.; Guilhot, F.; Porkka, K.; Ossenkoppele, G.; Lindoerfer, D.; et al. Predicting complete cytogenetic response and subsequent progression-free survival in 2060 patients with cml on imatinib treatment: The eutos score. Blood 2011, 118, 686–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitelman, F. The cytogenetic scenario of chronic myeloid leukemia. Leuk. Lymphoma 1993, 11 (Suppl. 1), 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes, J.E.; Saglio, G.; Kantarjian, H.M.; Baccarani, M.; Mayer, J.; Boque, C.; Shah, N.P.; Chuah, C.; Casanova, L.; Bradley-Garelik, B.; et al. Final 5-year study results of dasision: The dasatinib versus imatinib study in treatment-naïve chronic myeloid leukemia patients trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 2333–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochhaus, A.; Saglio, G.; Hughes, T.P.; Larson, R.A.; Kim, D.W.; Issaragrisil, S.; le Coutre, P.D.; Etienne, G.; Dorlhiac-Llacer, P.E.; Clark, R.E.; et al. Long-term benefits and risks of frontline nilotinib vs imatinib for chronic myeloid leukemia in chronic phase: 5-year update of the randomized enestnd trial. Leukemia 2016, 30, 1044–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hochhaus, A.; Larson, R.A.; Guilhot, F.; Radich, J.P.; Branford, S.; Hughes, T.P.; Baccarani, M.; Deininger, M.W.; Cervantes, F.; Fujihara, S.; et al. Long-term outcomes of imatinib treatment for chronic myeloid leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 917–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akosile, M.; Pierce, S.; Brandt, M.; Verstovsek, S.; Borthakur, G.; Kantarjian, H.; Ravandi, F.; Wierda, W.; Garcia-Manero, G.; Daver, N.; et al. Survival impact of patients (pts) with chronic myeloid leukemia (cml) due to failure from the use of one or more tyrosine kinase inhibitors (tki). Blood 2015, 126, 1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, J.H.; Winton, E.F.; Heffner, L.T.; Chen, Z.; Langston, A.A.; Hill, B.; Arellano, M.; El-Rassi, F.; Kim, A.; Jillella, A.; et al. Does the frequency of molecular monitoring after tyrosine kinase inhibitor discontinuation affect outcomes of patients with chronic myeloid leukemia? Cancer 2017, 123, 2482–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, E.Q.; Guerin, A.; Yu, A.P.; Bollu, V.K.; Guo, A.; Griffin, J.D. Retrospective real-world comparison of medical visits, costs, and adherence between nilotinib and dasatinib in chronic myeloid leukemia. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2010, 26, 2861–2869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabbour, E.; Cortes, J.; Nazha, A.; O’Brien, S.; Quintas-Cardama, A.; Pierce, S.; Garcia-Manero, G.; Kantarjian, H. Eutos score is not predictive for survival and outcome in patients with early chronic phase chronic myeloid leukemia treated with tyrosine kinase inhibitors: A single institution experience. Blood 2012, 119, 4524–4526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, E.; Iriyama, N.; Tokuhira, M.; Takaku, T.; Ishikawa, M.; Nakazato, T.; Sugimoto, K.J.; Fujita, H.; Fujioka, I.; Asou, N.; et al. Introduction of second-generation tyrosine kinase inhibitors may reduce the prognostic impact of high-risk patients, according to the european treatment and outcome study (eutos) score. Leuk. Lymphoma 2017, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, V.S.; Baccarani, M.; Hasford, J.; Castagnetti, F.; Di Raimondo, F.; Casado, L.F.; Turkina, A.; Zackova, D.; Ossenkoppele, G.; Zaritskey, A.; et al. Treatment and outcome of 2904 cml patients from the eutos population-based registry. Leukemia 2017, 31, 593–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branford, S.; Yeung, D.T.; Ross, D.M.; Prime, J.A.; Field, C.R.; Altamura, H.K.; Yeoman, A.L.; Georgievski, J.; Jamison, B.A.; Phillis, S.; et al. Early molecular response and female sex strongly predict stable undetectable bcr-abl1, the criteria for imatinib discontinuation in patients with cml. Blood 2013, 121, 3818–3824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hehlmann, R.; Lauseker, M.; Saussele, S.; Pfirrmann, M.; Krause, S.; Kolb, H.J.; Neubauer, A.; Hossfeld, D.K.; Nerl, C.; Gratwohl, A.; et al. Assessment of imatinib as first-line treatment of chronic myeloid leukemia: 10-year survival results of the randomized cml study iv and impact of non-cml determinants. Leukemia 2017, 31, 2398–2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskazan, A.E.; Sadri, S.; Keskin, D.; Ayer, M.; Kantarcioglu, B.; Demirel, N.; Aydin, D.; Aydinli, F.; Yokus, O.; Ozunal, I.E.; et al. Outcomes of chronic myeloid leukemia patients with early molecular response at 3 and 6 months: A comparative analysis of generic imatinib and glivec. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2017, 17, 804–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marin, D.; Ibrahim, A.R.; Lucas, C.; Gerrard, G.; Wang, L.; Szydlo, R.M.; Clark, R.E.; Apperley, J.F.; Milojkovic, D.; Bua, M.; et al. Assessment of bcr-abl1 transcript levels at 3 months is the only requirement for predicting outcome for patients with chronic myeloid leukemia treated with tyrosine kinase inhibitors. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, P.; Kantarjian, H.; Nazha, A.; O’Brien, S.; Jabbour, E.; Romo, C.G.; Pierce, S.; Cardenas-Turanzas, M.; Verstovsek, S.; Borthakur, G.; et al. Early responses predict better outcomes in patients with newly diagnosed chronic myeloid leukemia: Results with four tyrosine kinase inhibitor modalities. Blood 2013, 121, 4867–4874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabbour, E.; Kantarjian, H.M.; Saglio, G.; Steegmann, J.L.; Shah, N.P.; Boque, C.; Chuah, C.; Pavlovsky, C.; Mayer, J.; Cortes, J.; et al. Early response with dasatinib or imatinib in chronic myeloid leukemia: 3-year follow-up from a randomized phase 3 trial (dasision). Blood 2014, 123, 494–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perry, A.M.; Brunner, A.M.; Zou, T.; McGregor, K.L.; Amrein, P.C.; Hobbs, G.S.; Ballen, K.K.; Neuberg, D.S.; Fathi, A.T. Association between insurance status at diagnosis and overall survival in chronic myeloid leukemia: A population-based study. Cancer 2017, 123, 2561–2569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noens, L.; van Lierde, M.A.; De Bock, R.; Verhoef, G.; Zachee, P.; Berneman, Z.; Martiat, P.; Mineur, P.; Van Eygen, K.; MacDonald, K.; et al. Prevalence, determinants, and outcomes of nonadherence to imatinib therapy in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia: The adagio study. Blood 2009, 113, 5401–5411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| n | % | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Median Age at Diagnosis, Years (Range) | a 50 (11–88) | ||
| Sex | M/F | 105/101 | 51/49 |
| Race | African American | 56 | 27.2 |
| Asian | 5 | 2.4 | |
| Hispanic | 6 | 2.9 | |
| White | 106 | 51.5 | |
| Others | 3 | 1.5 | |
| Unknown or declined | 30 | 14.6 | |
| Risk (available, n = 110) | Sokal Low/Intermediate/High | 64/27/19 | 58.2/24.5/17.3 |
| Hasford Low/Intermediate/High | 66/38/6 | 60.0/34.5/5.5 | |
| EUTOS Low/High | 95/15 | 86.4/13.6 | |
| b Additional chromosomal abnormality (available, n = 173) | 12 | 6.9 | |
| Number of used TKI | 1 | 76 | 36.9 |
| 2 | 73 | 35.4 | |
| 3 | 33 | 16.0 | |
| 4 | 17 | 8.3 | |
| 5 | 7 | 3.4 | |
| 1st-line TKI (n = 206) | IM/DAS/NIL/BOS/PON | 145/43/13/4/1 | 70.4/20.9/6.3/1.9/0.5 |
| 2nd-line TKI (n = 130) | IM/DAS/NIL/BOS/PON/REB | 28/68/23/9/1/1 | 21.5/52.3/17.7/6.9/0.8/0.8 |
| 3rd-line TKI (n = 65) | IM/DAS/NIL/BOS/PON | 8/19/21/11/6 | 12.3/29.2/32.3/16.9/9.2 |
| 4th-line TKI (n = 30) | IM/DAS/NIL/BOS/PON/REB | 4/4/1/9/11/1 | 13.3/13.3/3.3/30.0/36.7/3.3 |
| 5th-line TKI (n = 10) | DAS/BOS/PON | 3/3/4 | 30.0/30.0/40.0 |
| Reason for TKI switch or discontinuation (239 events) | R | c 119 | 49.8 |
| I | c 104 | 43.5 | |
| O | c 16 | 6.7 | |
| Nivolumab | 3 | 1.5 | |
| Blinatumomab | 1 | 0.5 | |
| Chemotherapy | 12 | 5.8 | |
| HSCT | Allogeneic/Autologous | 8/1 | 3.9/0.5 |
| dABL domain mutation (n = 72) | Positive | 25 | 34.7 |
| n (%) | IM (n = 145) | NG-TKI (n = 61) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Switching TKIs | 93 (64.1) | 37 (60.7) | 0.639 | |
| Median follow up, months (range) | 80.9 (1.4–190.1) | 23.6 (1.7–64.6) | 0.000 | |
| BCR/ABL1IS at 3 months (n = 111) | ≤10% | 39 (59.1) | 39 (86.7) | 0.003 |
| >10% | 27 (40.9) | 6 (13.3) | ||
| BCR/ABL1IS at 6 months (n = 106) | <1% | 36 (54.5) | 32 (80.0) | 0.012 |
| ≥1% | 30 (45.5) | 8 (20.0) | ||
| BCR/ABL1 at 1 year (n = 103) | ≤0.1% | 33 (51.6) | 30 (76.9) | 0.013 |
| >0.1% | 31 (48.4) | 9 (23.1) | ||
| The last BCR/ABL1IS <0.1 | 83 (57.2) | 43 (70.5) | 0.086 | |
| Disease progression | 17 (11.7) | 2 (3.3) | 0.066 | |
| Death | 9 (6.2) | 2 (3.3) | 0.513 | |
| TKI | 1 CMR, n (%) | 2 Additional CMR, n (%) | 3 Attempts of TKI Discontinuation, n (%) | 4 TKI Discontinuation, n (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st-line TKI (n = 206) | 69 (33.5) | - | 14 (6.8) | 7 (3.4) |
| 2nd-line TKI (n = 130) | 52 (40.0) | 41 (31.5) | 7 (5.4) | 5 (3.8) |
| 3rd-line TKI (n = 65) | 18 (27.7) | 8 (12.3) | 1 (1.5) | 1 (1.5) |
| 4th-line TKI (n = 30) | 8 (26.7) | 5 (16.7) | 3 (10.0) | 1 (3.3) |
| 5th-line TKI (n = 10) | 1 (10.0) | 1 | 0 | 0 (0) |
| Total (n = 206) | 124(60.2) | - | 25(12.1) | 14 (6.8) |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kong, J.H.; Winton, E.F.; Heffner, L.T.; Gaddh, M.; Hill, B.; Neely, J.; Hatcher, A.; Joseph, M.; Arellano, M.; El-Rassi, F.; et al. Outcomes of Chronic Phase Chronic Myeloid Leukemia after Treatment with Multiple Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1542. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9051542
Kong JH, Winton EF, Heffner LT, Gaddh M, Hill B, Neely J, Hatcher A, Joseph M, Arellano M, El-Rassi F, et al. Outcomes of Chronic Phase Chronic Myeloid Leukemia after Treatment with Multiple Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2020; 9(5):1542. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9051542
Chicago/Turabian StyleKong, Jee Hyun, Elliott F. Winton, Leonard T. Heffner, Manila Gaddh, Brittany Hill, Jessica Neely, Angela Hatcher, Meena Joseph, Martha Arellano, Fuad El-Rassi, and et al. 2020. "Outcomes of Chronic Phase Chronic Myeloid Leukemia after Treatment with Multiple Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors" Journal of Clinical Medicine 9, no. 5: 1542. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9051542
APA StyleKong, J. H., Winton, E. F., Heffner, L. T., Gaddh, M., Hill, B., Neely, J., Hatcher, A., Joseph, M., Arellano, M., El-Rassi, F., Kim, A., Khoury, J. H., & Kota, V. K. (2020). Outcomes of Chronic Phase Chronic Myeloid Leukemia after Treatment with Multiple Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(5), 1542. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9051542






