Gene Expression Patterns Distinguish Mortality Risk in Patients with Postsurgical Shock
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Patient Selection and Clinical Data
2.2. Sample Collection and RNA Extraction
2.3. Microarray Processing and Data Analysis
2.4. Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (qPCR)
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
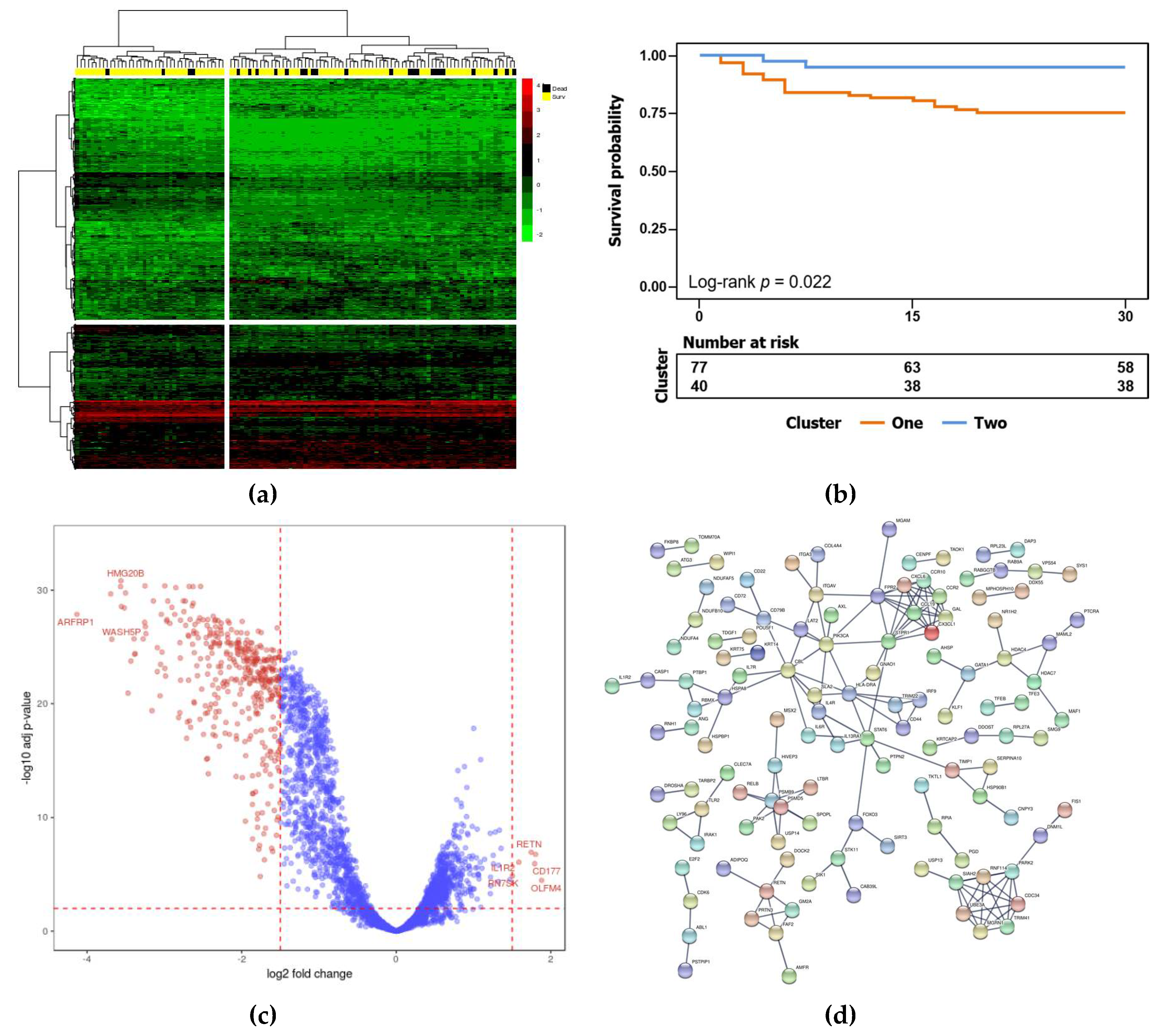
3.2. Identification of Biomarker Genes for Mortality Risk after Surgery
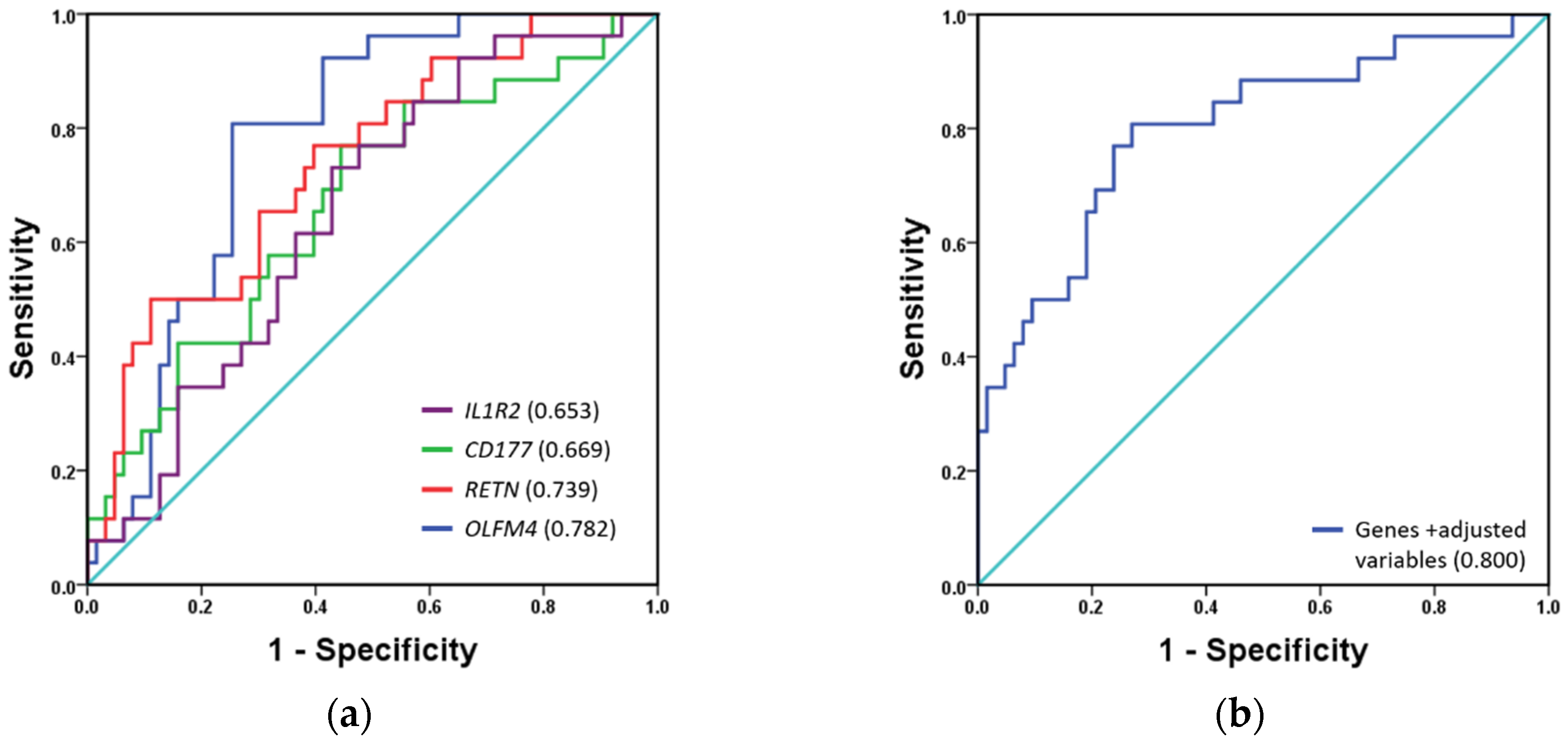
3.3. Validation of Biomarker Genes in the Validation Cohort
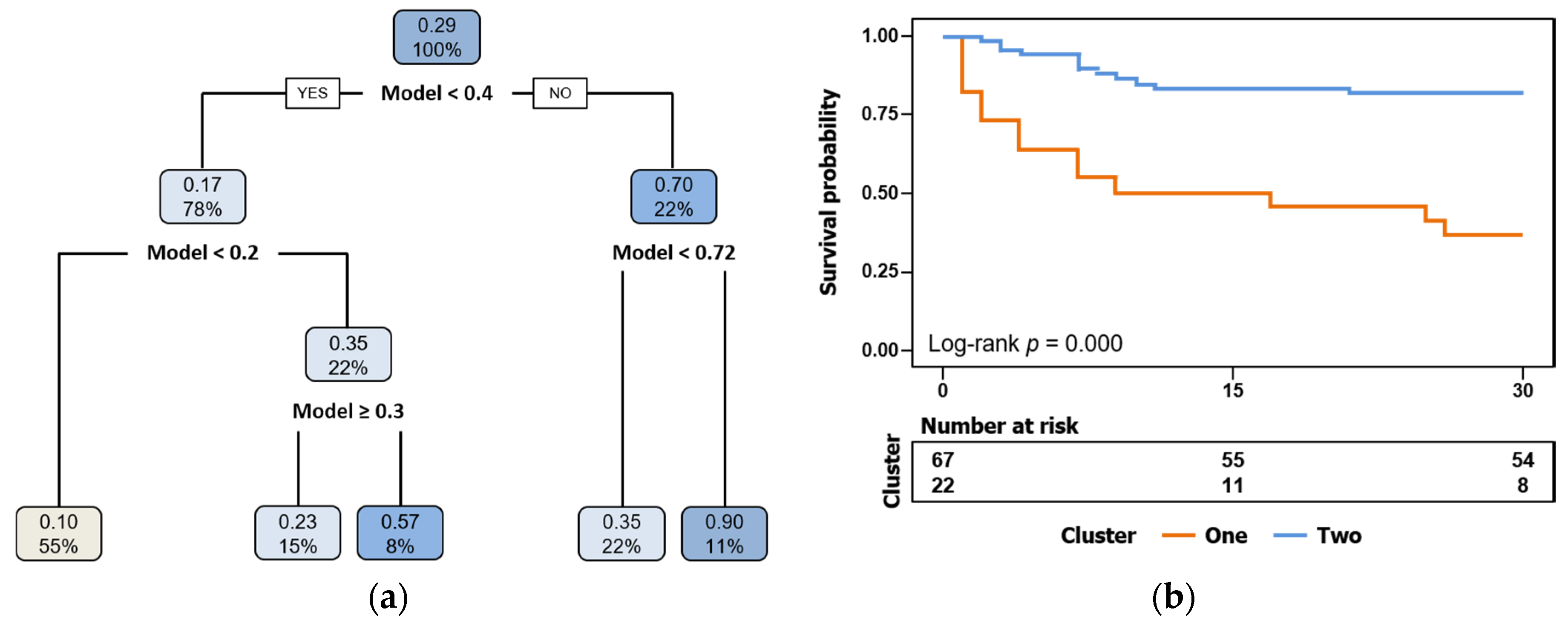
3.4. Mortality Prediction by Biomarkers Compared to Classical Risk Scales
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Graham, C.A.; Parke, T.R.J. Critical care in the emergency department: Shock and circulatory support. Emerg. Med. J. 2005, 22, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uzman, S.; Yilmaz, Y.; Toptas, M.; Akkoc, I.; Gul, Y.G.; Daskaya, H.; Toptas, Y. A retrospective analysis of postoperative patients admitted to the intensive care unit. Hippokratia 2016, 20, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Goldhill, D.R.; Down, J.F. Are we operating as well as we can? Critical care to minimise postoperative mortality and morbidity. Anaesthesia 2008, 63, 689–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearse, R.M.; Moreno, R.P.; Bauer, P.; Pelosi, P.; Metnitz, P.; Spies, C.; Vallet, B.; Vincent, J.L.; Hoeft, A.; Rhodes, A. Mortality after surgery in Europe: A 7 day cohort study. Lancet 2012, 380, 1059–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerman, J.E.; Kramer, A.A.; Knaus, W.A. Changes in hospital mortality for United States intensive care unit admissions from 1988 to 2012. Crit. Care 2013, 17, R81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molina, J.A.; Seow, E.; Heng, B.H.; Chong, W.F.; Ho, B. Outcomes of direct and indirect medical intensive care unit admissions from the emergency department of an acute care hospital: A retrospective cohort study. BMJ Open 2014, 4, e005553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Wagenberg, L.; Witteveen, E.; Wieske, L.; Horn, J. Causes of mortality in ICU-acquired weakness. J. Intensive Care Med. 2020, 35, 293–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaieski, D.F.; Edwards, J.M.; Kallan, M.J.; Carr, B.G. Benchmarking the incidence and mortality of severe sepsis in the United States. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 41, 1167–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberti, C.; Brun-Buisson, C.; Burchardi, H.; Martin, C.; Goodman, S.; Artigas, A.; Sicignano, A.; Palazzo, M.; Moreno, R.; Boulmé, R.; et al. Epidemiology of sepsis and infection in ICU patients from an international multicenter cohort study. Intensive Care Med. 2002, 28, 108–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Care in Canadian ICUs. Available online: https://secure.cihi.ca/free_products/ICU_Report_EN.pdf (accessed on 7 February 2020).
- Breslow, M.J.; Badawi, O. Severity scoring in the critically ill: Part 1—Interpretation and accuracy of outcome prediction scoring systems. Chest 2012, 141, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Sun, X.; Hoshida, Y. Survival analysis tools in genomics research. Hum. Genom. 2014, 8, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chibon, F. Cancer gene expression signatures—The rise and fall? Eur. J. Cancer 2013, 49, 2000–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almansa, R.; Heredia-Rodríguez, M.; Gomez-Sanchez, E.; Andaluz-Ojeda, D.; Iglesias, V.; Rico, L.; Ortega, A.; Gomez-Pesquera, E.; Liu, P.; Aragón, M.; et al. Transcriptomic correlates of organ failure extent in sepsis. J. Infect. 2015, 70, 445–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sweeney, T.E.; Wong, H.R. Risk stratification and prognosis in sepsis: What have we learned from microarrays? Clin. Chest Med. 2016, 37, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davenport, E.E.; Burnham, K.L.; Radhakrishnan, J.; Humburg, P.; Hutton, P.; Mills, T.C.; Rautanen, A.; Gordon, A.C.; Garrard, C.; Hill, A.V.; et al. Genomic landscape of the individual host response and outcomes in sepsis: A prospective cohort study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2016, 4, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweeney, T.E.; Perumal, T.M.; Henao, R.; Nichols, M.; Howrylak, J.A.; Choi, A.M.; Bermejo-Martin, J.F.; Almansa, R.; Tamayo, E.; Davenport, E.E.; et al. A community approach to mortality prediction in sepsis via gene expression analysis. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonarow, G.C.; Adams, K.F., Jr.; Abraham, W.T.; Yancy, C.W.; Boscardin, W.J. Risk stratification for in-hospital mortality in acutely decompensated heart failure: Classification and regression tree analysis. JAMA 2005, 293, 572–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almansa, R.; Ortega, A.; Ávila-Alonso, A.; Heredia-Rodríguez, M.; Martín, S.; Benavides, D.; Martín-Fernandez, M.; Rico, L.; Aldecoa, C.; Rico, J.; et al. Quantification of immune dysregulation by next-generation polymerase chain reaction to improve sepsis diagnosis in surgical patients. Ann. Surg. 2019, 269, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metzeler, K.H.; Hummel, M.; Bloomfield, C.D.; Spiekermann, K.; Braess, J.; Sauerland, M.C.; Heinecke, A.; Radmacher, M.; Marcucci, G.; Whitman, S.P.; et al. An 86-probe-set gene-expression signature predicts survival in cytogenetically normal acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2008, 112, 4193–4201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Wang, Y.; Hang, B.; Zou, X.; Mao, J.H. A novel gene expression-based prognostic scoring system to predict survival in gastric cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 55343–55351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trépo, E.; Goossens, N.; Fujiwara, N.; Song, W.M.; Colaprico, A.; Marot, A.; Spahr, L.; Demetter, P.; Sempoux, C.; Im, G.Y.; et al. Combination of gene expression signature and model for end-stage liver disease score predicts survival of patients with severe alcoholic hepatitis. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, 965–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Z.; Shivakumar, P.; Mourya, R.; Gutta, S.; Bezerra, J.A. Gene expression signatures associated with survival times of pediatric patients with biliary atresia identify potential therapeutic agents. Gastroenterology 2019, 157, 1138–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, M.; Zhu, R.; Stephens, R.M. GradientScanSurv-An exhaustive association test method for gene expression data with censored survival outcome. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0207590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dellinger, R.P.; Levy, M.M.; Rhodes, A.; Annane, D.; Gerlach, H.; Opal, S.M.; Sevransky, J.E.; Sprung, C.L.; Douglas, I.S.; Jaeschke, R.; et al. Surviving sepsis campaign: International guidelines for management of severe sepsis and septic shock: 2012. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 41, 580–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Gene | Forward (5′-3′) | Reverse (5′-3′) | Efficiency |
|---|---|---|---|
| Actin | CCTTGCACATGCCGGAG | ACAGAGCCTCGCCTTTG | 87.2% |
| IL1R2 | GCATCTGTATTCTCAAAAACTCTGA | GGTGCTCTGTGGCTTCTG | 96.9% |
| CD177 | AAGAGATTACCAGCCACAGAC | GCTGAACTGTCCCAAACTG | 90.0% |
| RETN | GCCGGATTTGGTTAGCTGA | CATGGAGCACAGGGTCTTG | 99.7% |
| OLFM4 | TGCTGATGTTCACCACACC | CTGAAGACCAAGCTGAAAGAGT | 92.2% |
| Discovery Cohort | Validation Cohort | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Surviving (n = 88) | Non-Surviving (n = 29) | p | Surviving (n = 79) | Non-Surviving (n = 33) | p | |
| Characteristics | ||||||
| Age | 69.15 | 71.86 | 0.297 | 69.06 | 72.70 | 0.108 |
| Male (n (%)) | 55 (63) | 18 (62) | 0.967 | 50 (63) | 23 (70) | 0.517 |
| Comorbidities (n (%)) | ||||||
| High blood pressure | 64 (73) | 19 (66) | 0.458 | 46 (58) | 23 (70) | 0.255 |
| Chronic cardiovascular disease | 53 (60) | 14 (48) | 0.259 | 20 (25) | 10 (30) | 0.587 |
| Chronic respiratory disease | 14 (16) | 5 (17) | 0.866 | 14 (18) | 8 (24) | 0.428 |
| Chronic renal failure | 10 (11) | 6 (21) | 0.205 | 5 (6) | 3 (9) | 0.605 |
| Chronic hepatic failure | 3 (3) | 0 (0) | 0.314 | 1 (1) | 0 (0) | 0.516 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 25 (28) | 7 (24) | 0.655 | 16 (20) | 6 (18) | 0.801 |
| Cancer | 23 (26) | 5 (17) | 0.330 | 17 (22) | 9 (27) | 0.511 |
| Immunosuppression | 4 (5) | 1 (3) | 0.800 | 4 (5) | 0 (0) | 0.188 |
| Time course and outcome | ||||||
| Length of hospital stay | 30.51 | 18.31 | 0.011 | 37.22 | 12.21 | 0.000 |
| Length of ICU stay | 8.26 | 7.03 | 0.525 | 10.58 | 6.61 | 0.021 |
| Mortality (% (7 days)) | 0 (0) | 14 (48) | 0.000 | 0 (0) | 15 (45) | 0.000 |
| Mortality (% (15 days)) | 0 (0) | 21 (72) | 0.000 | 0 (0) | 28 (85) | 0.000 |
| Type of surgery (n (%)) | ||||||
| Cardiac surgery | 54 (61) | 14 (48) | 0.215 | 34 (43) | 15 (45) | 0.814 |
| General surgery | 26 (30) | 12 (41) | 0.238 | 35 (44) | 15 (45) | 0.911 |
| Others | 8 (9) | 3 (11) | 1.000 | 10 (13) | 3 (10) | 0.755 |
| Source of infection (n (%)) | ||||||
| Respiratory tract | 19 (22) | 9 (31) | 0.301 | 20 (25) | 8 (24) | 0.905 |
| Abdomen | 15 (17) | 5 (17) | 0.981 | 17 (22) | 8 (24) | 0.752 |
| Urinary tract | 12 (14) | 4 (14) | 0.983 | 13 (16) | 2 (6) | 0.141 |
| Surgical site | 22 (25) | 5 (17) | 0.390 | 21 (27) | 7 (21) | 0.550 |
| Bacteremia | 23 (26) | 7 (24) | 0.831 | 28 (35) | 7 (21) | 0.139 |
| Microbiology (n (%)) | ||||||
| Gram + | 42 (48) | 9 (31) | 0.116 | 43 (54) | 10 (30) | 0.020 |
| Gram − | 46 (52) | 14 (48) | 0.709 | 40 (51) | 13 (39) | 0.277 |
| Fungi | 17 (19) | 5 (17) | 0.804 | 16 (20) | 7 (21) | 0.909 |
| Measurements at diagnosis (median (IQR)) | ||||||
| SOFA score | 7 (7) | 10 (3) | 0.000 | 9 (3) | 10 (3) | 0.351 |
| APACHE score | 13 (6) | 16 (6.5) | 0.000 | 13 (5) | 16 (3) | 0.006 |
| Total bilirubin (mg/dL) | 0.72 (1.56) | 0.99 (1.08) | 0.324 | 0.98 (1.67) | 1.27 (1.10) | 0.662 |
| Glucose (mg/dL) | 157 (65) | 159 (97) | 0.142 | 169 (76) | 193 (145) | 0.258 |
| Platelet count (cell/mm3) | 131,000 (96,250) | 100,000 (131,500) | 0.415 | 149,000 (163,250) | 123,000 (137,500) | 0.565 |
| INR | 1.36 (0.37) | 1.31 (0.49) | 0.989 | 1.33 (0.33) | 1.31 (0.49) | 0.325 |
| ScvO2 (%) | 72.30 (11.9) | 66.70 (17.1) | 0.007 | 70.90 (18.00) | 67.00 (19.10) | 0.334 |
| C-reactive protein (mg/L) | 107.80 (208.4) | 186.00 (228.4) | 0.012 | 208.60 (213.50) | 184.40 (241.60) | 0.417 |
| Procalcitonin (ng/mL) | 0.99 (9.82) | 5.24 (19.49) | 0.276 | 3.72 (23.10) | 8.02 (20.46) | 0.775 |
| Lactate (mM) | 3.11 (1.86) | 4.33 (5.50) | 0.004 | 2.89 (2.11) | 5.00 (5.00) | 0.003 |
| White Blood cells (cells/mm3) | 13,370 (10,540) | 13,560 (10,490) | 0.639 | 15,470 (11,960) | 15,350 (10,605) | 0.193 |
| Neutrophils (cells/mm3) | 11,738 (9803) | 12,319 (10,623) | 0.585 | 13,614 (11,310) | 12,921 (10,420) | 0.192 |
| Biomarker | Area | Asymptotic 95% Confidence Interval |
|---|---|---|
| SOFA score | 0.580 | 0.456–0.705 |
| APACHE score | 0.647 | 0.543–0.751 |
| Procalcitonin | 0.589 | 0.478–0.699 |
| C-reactive protein | 0.444 | 0.323–0.565 |
| White blood cells | 0.447 | 0.332–0.563 |
| Neutrophils | 0.446 | 0.332–0.560 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martínez-Paz, P.; Aragón-Camino, M.; Gómez-Sánchez, E.; Lorenzo-López, M.; Gómez-Pesquera, E.; López-Herrero, R.; Sánchez-Quirós, B.; de la Varga, O.; Tamayo-Velasco, Á.; Ortega-Loubon, C.; et al. Gene Expression Patterns Distinguish Mortality Risk in Patients with Postsurgical Shock. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1276. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9051276
Martínez-Paz P, Aragón-Camino M, Gómez-Sánchez E, Lorenzo-López M, Gómez-Pesquera E, López-Herrero R, Sánchez-Quirós B, de la Varga O, Tamayo-Velasco Á, Ortega-Loubon C, et al. Gene Expression Patterns Distinguish Mortality Risk in Patients with Postsurgical Shock. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2020; 9(5):1276. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9051276
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartínez-Paz, Pedro, Marta Aragón-Camino, Esther Gómez-Sánchez, Mario Lorenzo-López, Estefanía Gómez-Pesquera, Rocío López-Herrero, Belén Sánchez-Quirós, Olga de la Varga, Álvaro Tamayo-Velasco, Christian Ortega-Loubon, and et al. 2020. "Gene Expression Patterns Distinguish Mortality Risk in Patients with Postsurgical Shock" Journal of Clinical Medicine 9, no. 5: 1276. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9051276
APA StyleMartínez-Paz, P., Aragón-Camino, M., Gómez-Sánchez, E., Lorenzo-López, M., Gómez-Pesquera, E., López-Herrero, R., Sánchez-Quirós, B., de la Varga, O., Tamayo-Velasco, Á., Ortega-Loubon, C., García-Morán, E., Gonzalo-Benito, H., Heredia-Rodríguez, M., & Tamayo, E. (2020). Gene Expression Patterns Distinguish Mortality Risk in Patients with Postsurgical Shock. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(5), 1276. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9051276






