Depth of Neuromuscular Block Is Not Associated with Abdominal Wall Distention or Surgical Conditions during Gynecologic Laparoscopic Operations. A Prospective Trial
Abstract
1. Introduction
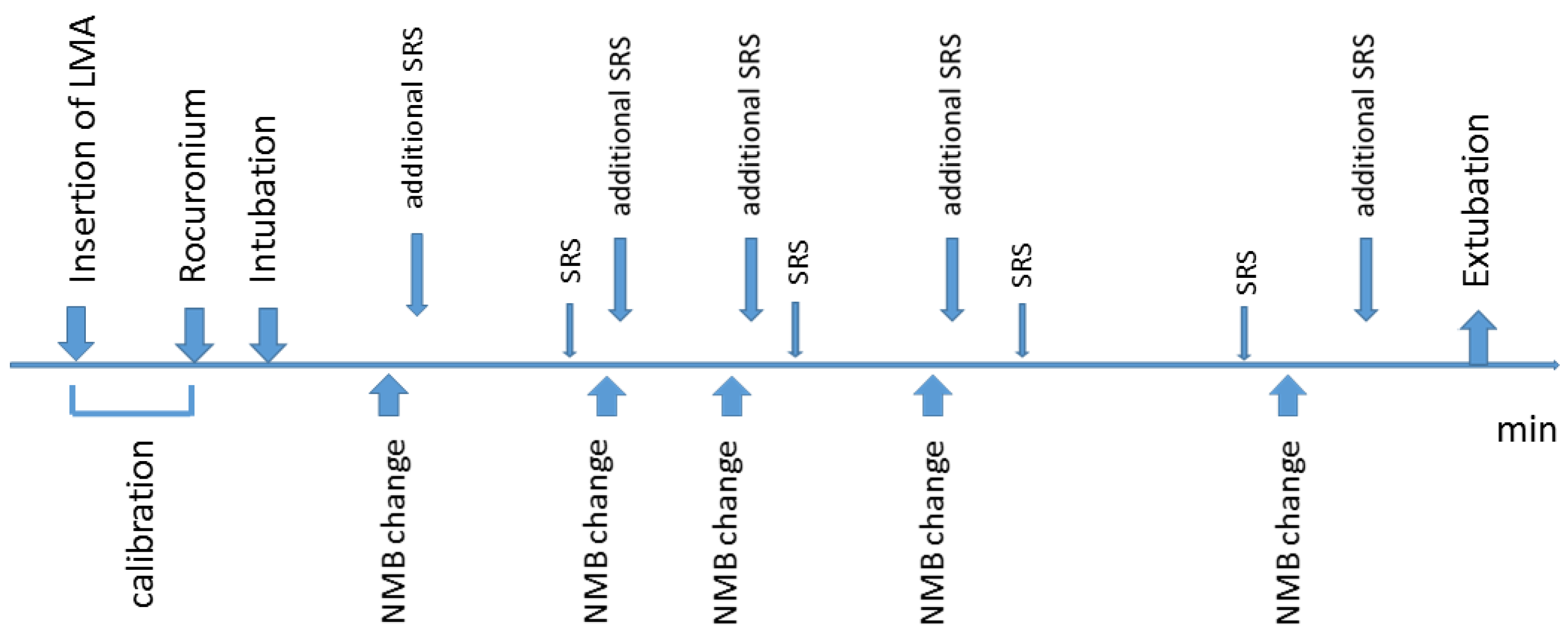
2. Experimental Section
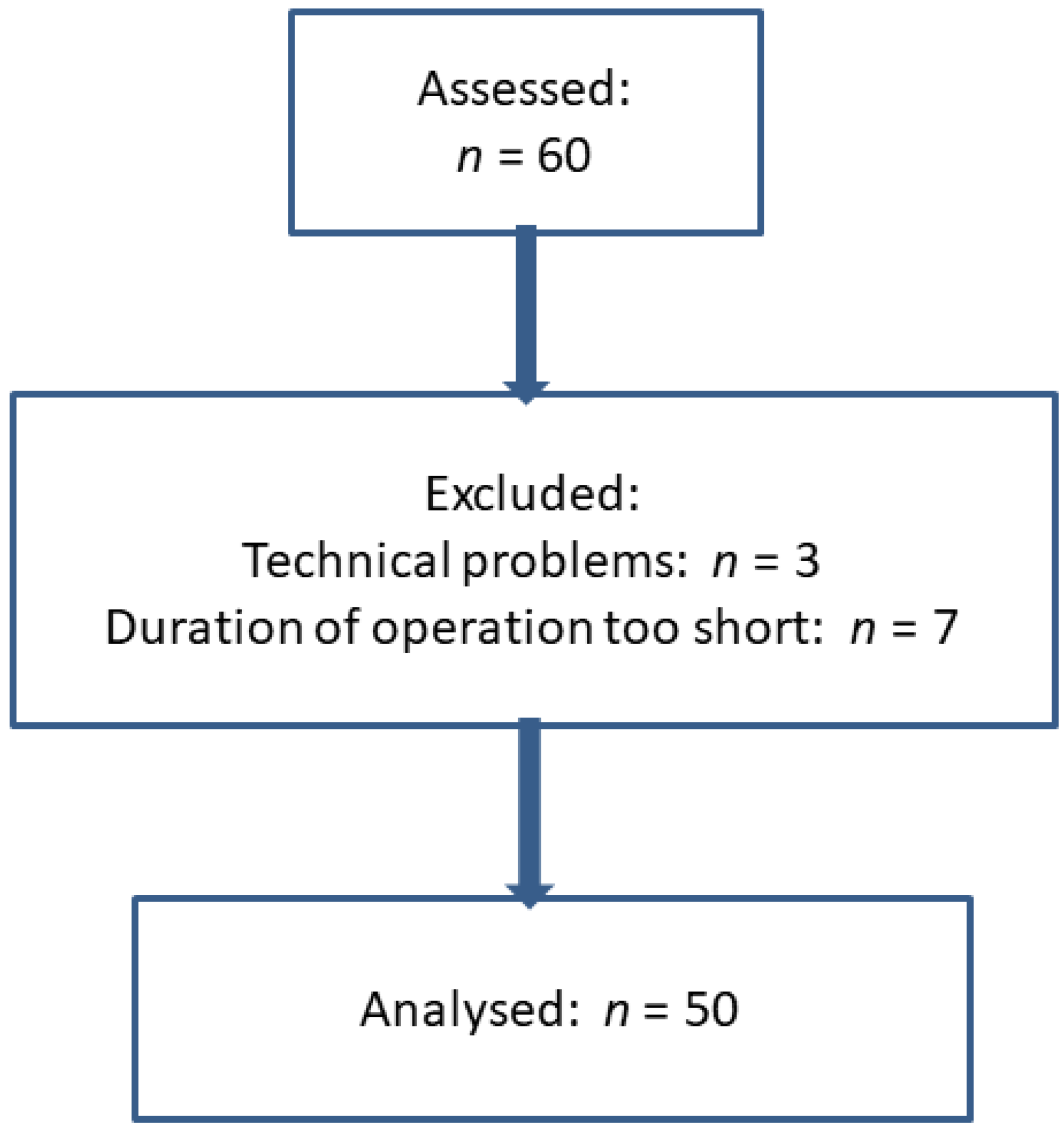
2.1. Patients
2.2. Anesthesia
2.3. SRS
2.4. Abdominal Wall Length
2.5. Statistics
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baete, S.; Vercruysse, G.; Vander, L.M.; De Vooght, P.; Van Melkebeek, J.; Dylst, D.; Beran, M.; Van Zundert, J.; Heylen, R.; Boer, W.; et al. The effect of deep versus moderate neuromuscular block on surgical conditions and postoperative respiratory function in bariatric laparoscopic surgery: A randomized, double blind clinical trial. Anesth. Analg. 2017, 124, 1469–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrio, J.; Errando, C.L.; San, M.G.; Salas, B.I.; Raga, J.; Carrion, J.L.; Garcia-Ramon, J.; Gallego, J. Effect of depth of neuromuscular blockade on the abdominal space during pneumoperitoneum establishment in laparoscopic surgery. J. Clin. Anesth. 2016, 34, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruintjes, M.H.; Van Helden, E.V.; Braat, A.E.; Dahan, A.; Scheffer, G.J.; Van Laarhoven, C.J.; Warle, M.C. Deep neuromuscular block to optimize surgical space conditions during laparoscopic surgery: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Br. J. Anaesth. 2017, 118, 834–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubois, P.E.; Putz, L.; Jamart, J.; Marotta, M.L.; Gourdin, M.; Donnez, O. Deep neuromuscular block improves surgical conditions during laparoscopic hysterectomy: A randomised controlled trial. Eur. J. Anaesthesiol. 2014, 31, 430–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindekaer, A.L.; Halvor, S.H.; Istre, O. Deep neuromuscular blockade leads to a larger intraabdominal volume during laparoscopy. J. Vis. Exp. 2013, 76, e50045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madsen, M.V.; Gatke, M.R.; Springborg, H.H.; Rosenberg, J.; Lund, J.; Istre, O. Optimising abdominal space with deep neuromuscular blockade in gynaecologic laparoscopy—A randomised, blinded crossover study. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 2015, 59, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen, M.V.; Istre, O.; Springborg, H.H.; Staehr-Rye, A.K.; Rosenberg, J.; Lund, J.; Gatke, M.R. Deep neuromuscular blockade and low insufflation pressure during laparoscopic hysterectomy. Dan. Med. J. 2017, 64, A5364. [Google Scholar]
- Martini, C.H.; Boon, M.; Bevers, R.F.; Aarts, L.P.; Dahan, A. Evaluation of surgical conditions during laparoscopic surgery in patients with moderate vs deep neuromuscular block. Br. J. Anaesth. 2014, 112, 498–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, J.; Herring, W.J.; Blobner, M.; Mulier, J.P.; Rahe-Meyer, N.; Woo, T.; Li, M.K.; Grobara, P.; Assaid, C.A.; Fennema, H.; et al. Deep neuromuscular blockade improves laparoscopic surgical conditions: A randomized, controlled study. Adv. Ther. 2017, 34, 925–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torensma, B.; Martini, C.H.; Boon, M.; Olofsen, E.; in ‘t Veld, B.; Liem, R.S.; Knook, M.T.; Swank, D.J.; Dahan, A. Deep neuromuscular block improves surgical conditions during bariatric surgery and reduces postoperative pain: A randomized double blind controlled trial. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0167907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Wijk, R.M.; Watts, R.W.; Ledowski, T.; Trochsler, M.; Moran, J.L.; Arenas, G.W. Deep neuromuscular block reduces intra-abdominal pressure requirements during laparoscopic cholecystectomy: A prospective observational study. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 2015, 59, 434–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin-Flores, M.; Gleed, R.D.; Basher, K.L.; Scarlett, J.M.; Campoy, L.; Kopman, A.F. TOF-Watch(R) monitor: Failure to calculate the train-of-four ratio in the absence of baseline calibration in anaesthetized dogs. Br. J. Anaesth. 2012, 108, 240–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuchs-Buder, T.; Claudius, C.; Skovgaard, L.T.; Eriksson, L.I.; Mirakhur, R.K.; Viby-Mogensen, J. Good clinical research practice in pharmacodynamic studies of neuromuscular blocking agents II: The Stockholm revision. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 2007, 51, 789–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozdemir-van Brunschot, D.M.D.; Braat, A.E.; Van der Jagt, M.F.P.; Scheffer, G.J.; Martini, C.H.; Langenhuijsen, J.F.; Dam, R.E.; Huurman, V.A.; Lam, D.; d’Ancona, F.C.; et al. Deep neuromuscular blockade improves surgical conditions during low-pressure pneumoperitoneum laparoscopic donor nephrectomy. Surg. Endosc. 2018, 32, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staehr-Rye, A.K.; Rasmussen, L.S.; Rosenberg, J.; Juul, P.; Lindekaer, A.L.; Riber, C.; Gatke, M.R. Surgical space conditions during low-pressure laparoscopic cholecystectomy with deep versus moderate neuromuscular blockade: A randomized clinical study. Anesth. Analg. 2014, 119, 1084–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boon, M.; Martini, C.H.; Aarts, L.P.H.J.; Dahan, A. The use of surgical rating scales for the evaluation of surgical working conditions during laparoscopic surgery: A scoping review. Surg. Endosc. 2019, 33, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, B.W.; Oh, A.Y.; Na, H.S.; Lee, H.J.; Kang, S.B.; Kim, D.W.; Seo, K.S. Effects of depth of neuromuscular block on surgical conditions during laparoscopic colorectal surgery: A randomised controlled trial. Anaesthesia 2018, 73, 1090–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, C.H.; Chung, S.H.; Kim, B.G.; Min, B.H.; Lee, S.C.; Oh, A.Y.; Jeon, Y.T.; Ryu, J.H. Comparison between the effects of deep and moderate neuromuscular blockade during transurethral resection of bladder tumor on endoscopic surgical condition and recovery profile: A prospective, randomized, and controlled trial. World J. Urol. 2019, 37, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen, M.V.; Scheppan, S.; Mork, E.; Kissmeyer, P.; Rosenberg, J.; Gatke, M.R. Influence of deep neuromuscular block on the surgeons assessment of surgical conditions during laparotomy: A randomized controlled double blinded trial with rocuronium and sugammadex. Br. J. Anaesth. 2017, 119, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soderstrom, C.M.; Borregaard, M.R.; Assadzadeh, S.; Folsgaard, S.; Rosenberg, J.; Gatke, M.R.; Madsen, M.V. Deep neuromuscular blockade and surgical conditions during laparoscopic ventral hernia repair: A randomised, blinded study. Eur. J. Anaesthesiol. 2018, 35, 876–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.K.; Son, Y.G.; Yoo, S.; Lim, T.; Kim, W.H.; Kim, J.T. Deep vs. Moderate neuromuscular blockade during laparoscopic surgery: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Anaesthesiol. 2018, 35, 867–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuller, P.J.; Newell, S.; Strickland, P.A.; Barry, J.J. Response of bispectral index to neuromuscular block in awake volunteers. Br. J. Anaesth. 2015, 115 (Suppl. 1), i95–i103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unterbuchner, C.; Blobner, M. Deep neuromuscular blockade: Benefits and risks. Anaesthesist 2018, 67, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Combes, X.; Andriamifidy, L.; Dufresne, E.; Suen, P.; Sauvat, S.; Scherrer, E.; Feiss, P.; Marty, J.; Duvaldestin, P. Comparison of two induction regimens using or not using muscle relaxant: Impact on postoperative upper airway discomfort. Br. J. Anaesth. 2007, 99, 276–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mencke, T.; Echternach, M.; Kleinschmidt, S.; Lux, P.; Barth, V.; Plinkert, P.K.; Fuchs-Buder, T. Laryngeal morbidity and quality of tracheal intubation: A randomized controlled trial. Anesthesiology 2003, 98, 1049–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirmeier, E.; Eriksson, L.I.; Lewald, H.; Jonsson, F.M.; Hoeft, A.; Hollmann, M.; Meistelman, C.; Hunter, J.M.; Ulm, K.; Blobner, M. Post-anaesthesia pulmonary complications after use of muscle relaxants (POPULAR): A multicentre, prospective observational study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2019, 7, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variables: | Age (years) | Height (cm) | Weight (kg) | BMI (kg/cm2) | Rocuronium (mg) Initial Dose | Rocuronium (mg) Repetition |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean (SD) | 50.9 (13.4) | 167.4 (5.4) | 70.8 (13.9) | 25.2 (4.5) | 37.4 (3.8) | 17.9 (7.2) |
| Drugs | PTC = 0 | PTC = 1–5 | TOF 0–1 | TOF > 1 | TOFR > 90% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Propofol infusion: mg kg h−1 (mean (SD)) | 3.7 (0.7) | 3.8 (0.8) | 3.6 (0.8) | 3.8 (1.0) | 3.8 (0.9) |
| Remifentanil infusion: µg kg min−1 (mean (SD)) | 0.12 (0.03) | 0.13 (0.03) | 0.13 (0.03) | 0.14 (0.03) | 0.14 (0.04) |
| Sufentanil bolus: number | 12 | 14 | 3 | 12 | 3 |
| Sufentanil bolus: mg (mean (SD)) | 15.0 (7.1) | 11.1 (5.6) | 13.3 (5.8) | 10.0 (4.3) | 8.3 (2.9) |
| Rocuronium bolus: number | 0 | 0 | 5 | 1 | 0 |
| Rocuronium bolus: mg (mean (SD)) | - | - | 13 (4.5) | 10 | - |
| Variables: | PTC = 0 | PTC = 1–5 | TOF 0–1 | TOF > 1 | TOFR > 90% | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BIS | 41.6 (5.5) | 41.9 (6.3) | 41.3 (5.0) | 42.8 (5.5) | 43.5 (4.6) | n.s. |
| BP syst (mm Hg) | 96.8 (18.2) | 105.6 (21.1) | 110.1 (18.0) * | 109.4 (16.6) * | 102.4 (15.7) | *: p < 0.001 vs. PTC = 0 |
| BP diast (mm Hg) | 56.6 (11.7) | 63.4 (13.7) * | 67.8 (10.1) * + | 65.6 (10.2) * + | 60.0 (7.7) | *: p < 0.001 vs. PTC = 0 +: p <0.008 vs. TOFR > 90% |
| HR | 56.1 (8.9) | 56.9 (8.1) | 58.3 (9.6) # | 57.4 (8.8) | 55.9 (8.8) | #: p < 0.05 vs. TOFR > 90% |
| Abdominal Wall Length | PTC = 0 | PTC = 1–5 | TOF 0–1 | TOF > 1 | TOFR > 90% | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Increase in mm: mean (SD) | 11.5 (4.6) | 11.5 (4.9) | 10.5 (4.5) | 11.1 (5.9) | 10.6 (5.2) | 0.17 |
| SRS | PTC = 0 | PTC = 1–5 | TOF 0–1 | TOF > 1 | TOFR > 90% | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SRS (mean (SD)) | 4.7 (0.5) | 4.6 (0.5) | 4.6 (0.5) | 4.6 (0.6) | 4.5 (0.5) * | *: p = 0.025 vs. PTC = 0 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Soltesz, S.; Mathes, A.; Anapolski, M.; Noé, K.G. Depth of Neuromuscular Block Is Not Associated with Abdominal Wall Distention or Surgical Conditions during Gynecologic Laparoscopic Operations. A Prospective Trial. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1078. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9041078
Soltesz S, Mathes A, Anapolski M, Noé KG. Depth of Neuromuscular Block Is Not Associated with Abdominal Wall Distention or Surgical Conditions during Gynecologic Laparoscopic Operations. A Prospective Trial. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2020; 9(4):1078. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9041078
Chicago/Turabian StyleSoltesz, Stefan, Alexander Mathes, Michael Anapolski, and Karl Guenter Noé. 2020. "Depth of Neuromuscular Block Is Not Associated with Abdominal Wall Distention or Surgical Conditions during Gynecologic Laparoscopic Operations. A Prospective Trial" Journal of Clinical Medicine 9, no. 4: 1078. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9041078
APA StyleSoltesz, S., Mathes, A., Anapolski, M., & Noé, K. G. (2020). Depth of Neuromuscular Block Is Not Associated with Abdominal Wall Distention or Surgical Conditions during Gynecologic Laparoscopic Operations. A Prospective Trial. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(4), 1078. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9041078




