Evaluating the Association between Contrast Medium Dosage and Acute Kidney Injury in Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement Using Different Predictive Models
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
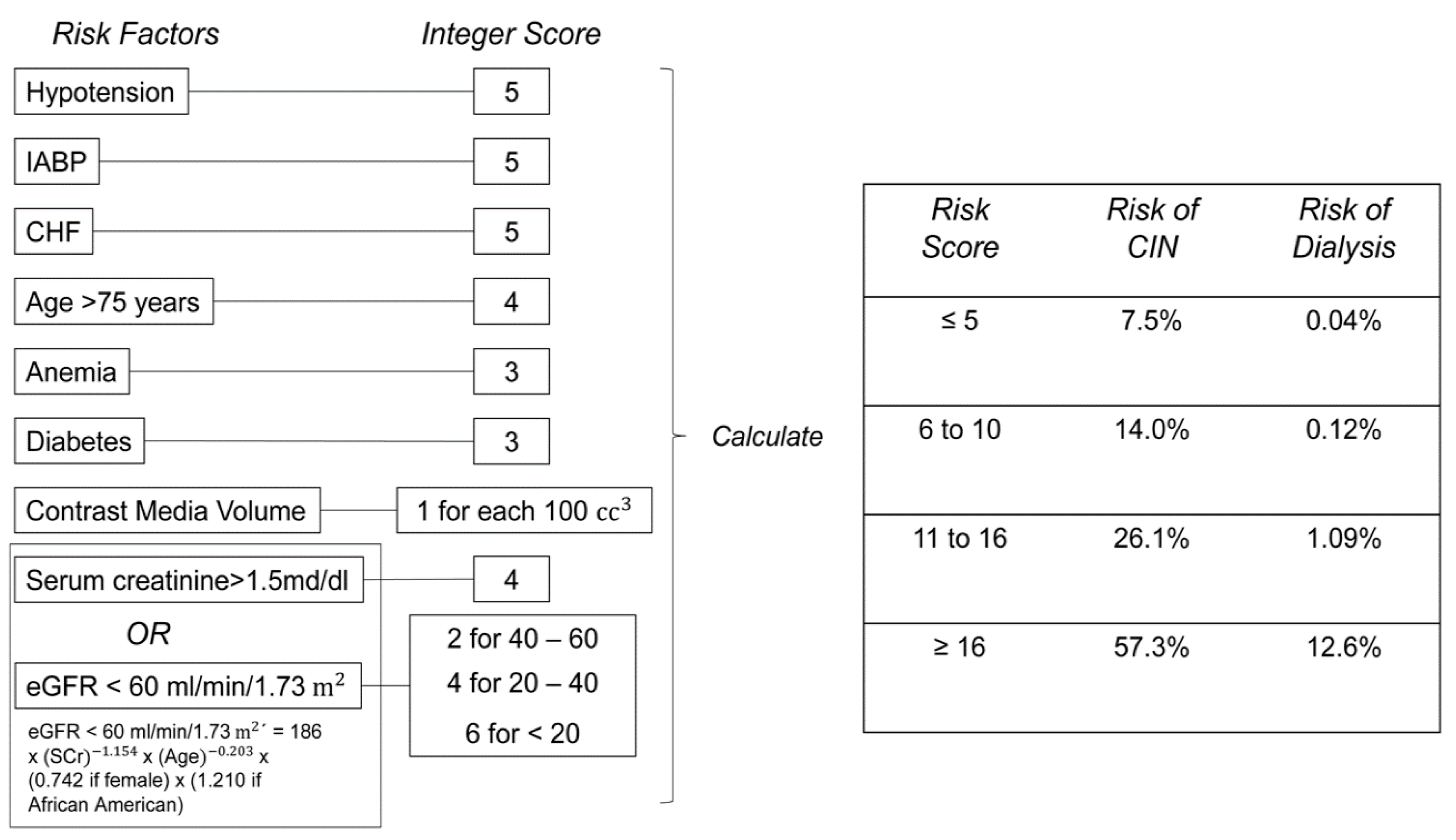
2.1. CM Volume Models
2.2. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
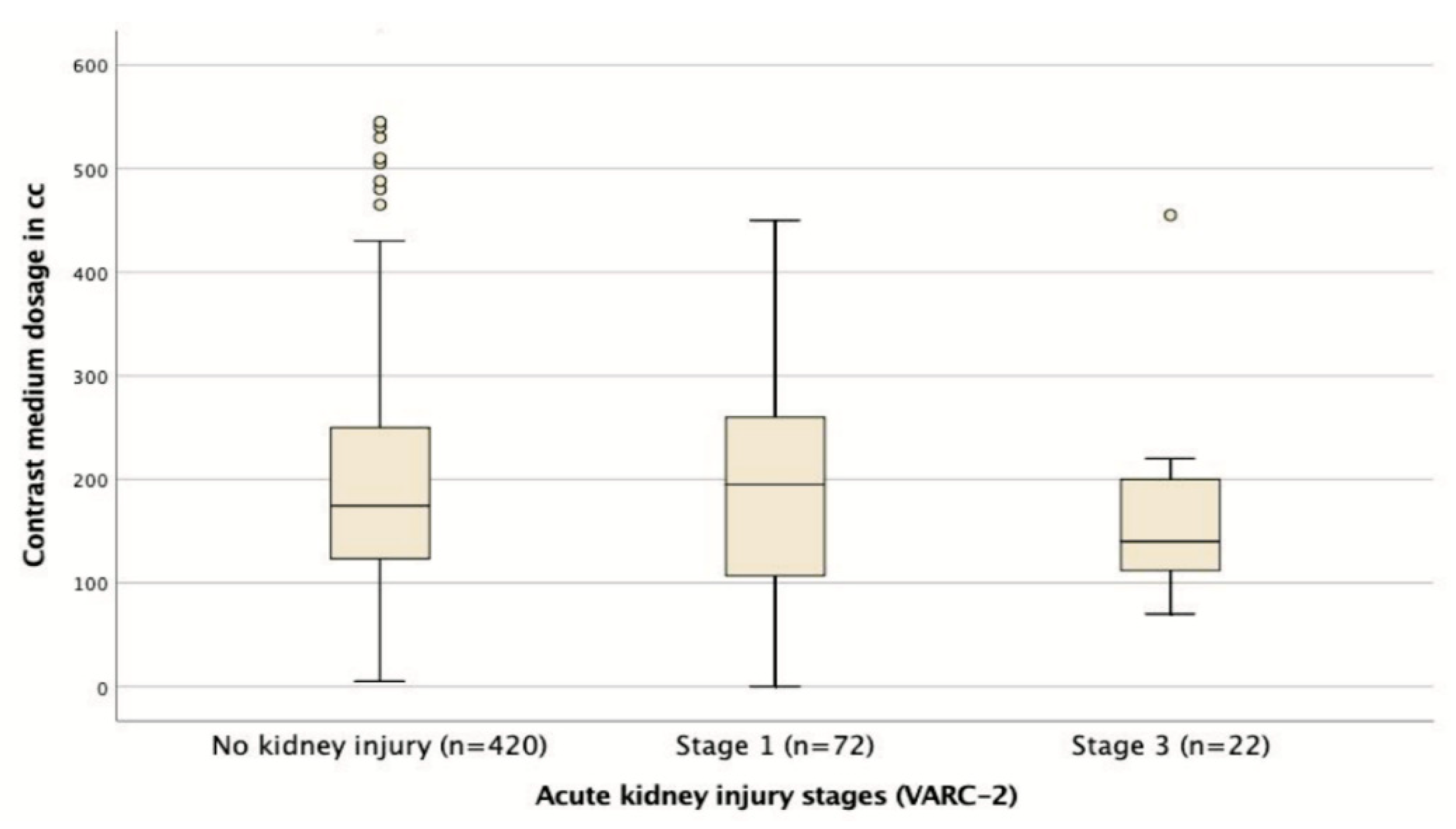
3.2. Procedural Characteristics
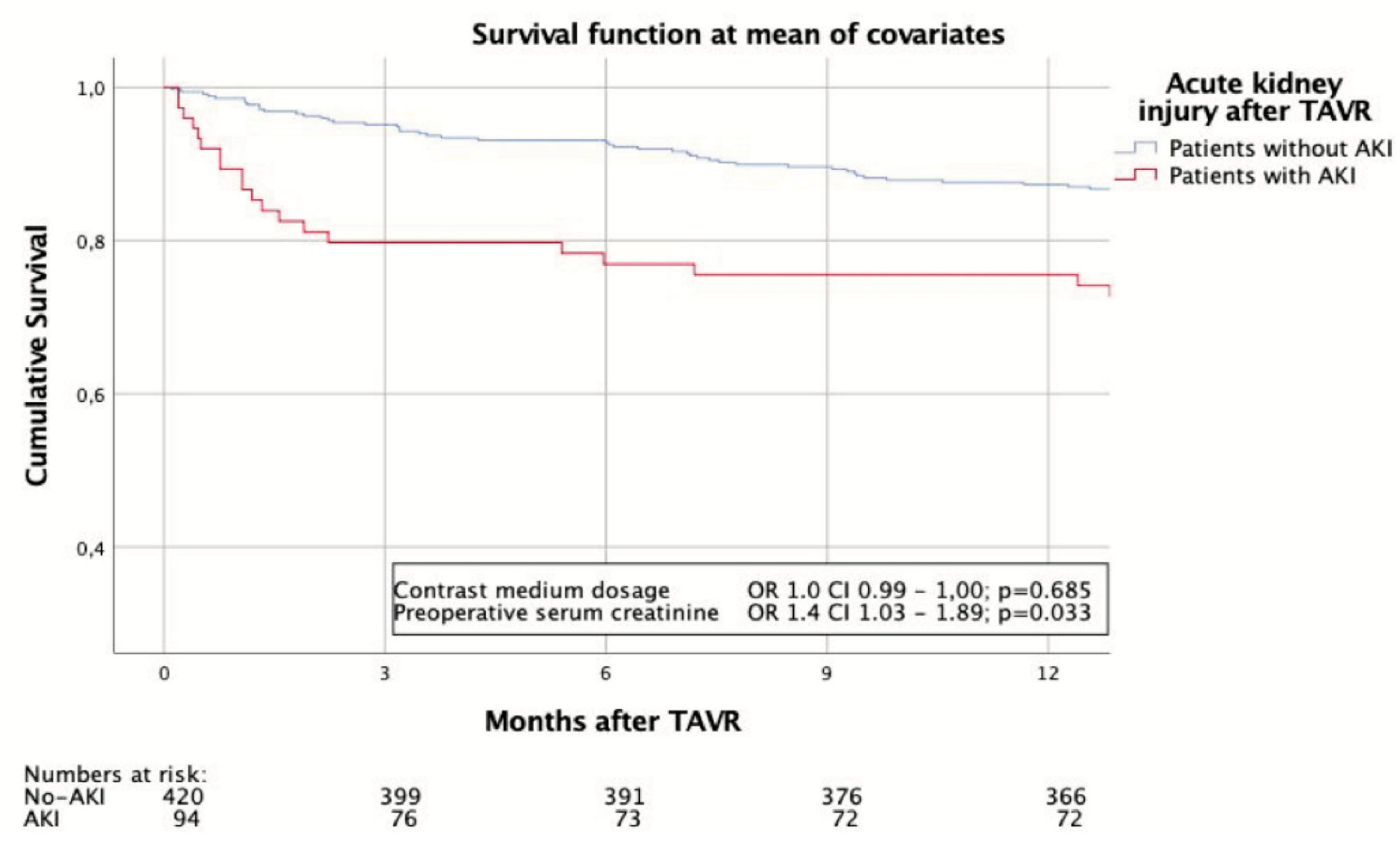
3.3. Adverse Events and Survival
3.4. Factors Associated with and Predictive of AKI
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barbash, I.M.; Ben-Dor, I.; Dvir, D.; Maluenda, G.; Xue, Z.; Torguson, R.; Satler, L.F.; Pichard, A.D.; Waksman, R. Incidence and predictors of acute kidney injury after transcatheter aortic valve replacement. Am. Heart J. 2012, 163, 1031–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elhmidi, Y.; Bleiziffer, S.; Deutsch, M.-A.; Krane, M.; Mazzitelli, D.; Lange, R.; Piazza, N. Acute kidney injury after transcatheter aortic valve implantation: Incidence, predictors and impact on mortality. Arch. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2014, 107, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aregger, F.; Wenaweser, P.; Hellige, G.J.; Kadner, A.; Carrel, T.; Windecker, S.; Frey, F.J. Risk of acute kidney injury in patients with severe aortic valve stenosis undergoing transcatheter valve replacement. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2009, 24, 2175–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gebauer, K.; Diller, G.-P.; Kaleschke, G.; Kerckhoff, G.; Malyar, N.; Meyborg, M.; Reinecke, H.; Baumgartner, H. The Risk of Acute Kidney Injury and Its Impact on 30-Day and Long-Term Mortality after Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation. Int. J. Nephrol. 2012, 2012, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.R.; Robb, J.F.; Block, C.A.; Schoolwerth, A.C.; Kaplan, A.V.; O’Connor, G.T.; Solomon, R.J.; Malenka, D.J. Does Safe Dosing of Iodinated Contrast Prevent Contrast-Induced Acute Kidney Injury? Circ. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2010, 3, 346–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freeman, R.V.; O’Donnell, M.; Share, D.; Meengs, W.L.; Kline-Rogers, E.; Clark, V.L.; DeFranco, A.C.; Eagle, K.A.; McGinnity, J.G.; Patel, K.; et al. Nephropathy requiring dialysis after percutaneous coronary intervention and the critical role of an adjusted contrast dose. Am. J. Cardiol. 2002, 90, 1068–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehran, R.; Aymong, E.D.; Nikolsky, E.; Lasić, Z.; Iakovou, I.; Fahy, M.; Mintz, G.S.; Lansky, A.J.; Moses, J.W.; Stone, G.W.; et al. A simple risk score for prediction of contrast-induced nephropathy after percutaneous coronary intervention. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2004, 44, 1393–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, M.; Hayashida, K.; Mouillet, G.; Chevalier, B.; Meguro, K.; Watanabe, Y.; Dubois-Rande, J.-L.; Morice, M.-C.; Lefèvre, T.; Teiger, E. Renal Function–Based Contrast Dosing Predicts Acute Kidney Injury Following Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation. JACC Cardiovasc. Interv. 2013, 6, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhmidi, Y.; Bleiziffer, S.; Piazza, N.; Hutter, A.; Opitz, A.; Hettich, I.; Kornek, M.; Ruge, H.; Brockmann, G.; Mazzitelli, D.; et al. Incidence and predictors of acute kidney injury in patients undergoing transcatheter aortic valve implantation. Am. Heart J. 2011, 161, 735–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinning, J.-M.; Ghanem, A.; Steinhäuser, H.; Adenauer, V.; Hammerstingl, C.; Nickenig, G.; Werner, N. Renal Function as Predictor of Mortality in Patients After Percutaneous Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation. JACC Cardiovasc. Interv. 2010, 3, 1141–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saia, F.; Ciuca, C.; Taglieri, N.; Marrozzini, C.; Savini, C.; Bordoni, B.; Dall’Ara, G.; Moretti, C.; Pilato, E.; Martin-Suarez, S.; et al. Acute kidney injury following transcatheter aortic valve implantation: Incidence, predictors and clinical outcome. Int. J. Cardiol. 2013, 168, 1034–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Généreux, P.; Kodali, S.K.; Green, P.; Paradis, J.-M.; Daneault, B.; Rene, G.; Hueter, I.; Georges, I.; Kirtane, A.; Hahn, R.T.; et al. Incidence and Effect of Acute Kidney Injury After Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement Using the New Valve Academic Research Consortium Criteria. Am. J. Cardiol. 2013, 111, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuis, R.-J.M.; Van Mieghem, N.M.; Tzikas, A.; Piazza, N.; Otten, A.M.; Cheng, J.; Van Domburg, R.; Betjes, M.G.H.; Serruys, P.W.; De Jaegere, P. Frequency, determinants, and prognostic effects of acute kidney injury and red blood cell transfusion in patients undergoing transcatheter aortic valve implantation. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2011, 77, 881–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Linden, A.; Kempfert, J.; Rastan, A.J.; Holzhey, D.M.; Blumenstein, J.; Schuler, G.; Mohr, F.W.; Walther, T. Risk of acute kidney injury after minimally invasive transapical aortic valve implantation in 270 patients. Eur. J. Cardio Thorac. Surg. 2011, 39, 835–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagur, R.; Webb, J.G.; Nietlispach, F.; Dumont, É.; De Larochellière, R.; Doyle, D.; Masson, J.-B.; Gutiérrez, M.J.; Clavel, M.-A.; Bertrand, O.F.; et al. Acute kidney injury following transcatheter aortic valve implantation: Predictive factors, prognostic value, and comparison with surgical aortic valve replacement. Eur. Heart J. 2009, 31, 865–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khawaja, M.Z.; Thomas, M.; Joshi, A.; Asrress, K.; Wilson, K.; Bolter, K.; Young, C.; Hancock, J.; Bapat, V.; Redwood, S. The effects of VARC-defined acute kidney injury after transcatheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI) using the Edwards bioprosthesis. EuroIntervention 2012, 8, 563–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davenport, M.S.; Khalatbari, S.; Cohan, R.H.; Dillman, J.R.; Myles, J.D.; Ellis, J.H. Contrast Material–induced Nephrotoxicity and Intravenous Low-Osmolality Iodinated Contrast Material: Risk Stratification by Using Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate. Radiology 2013, 268, 719–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonald, J.S.; McDonald, R.J.; Carter, R.E.; Katzberg, R.W.; Kallmes, D.F.; Williamson, E.E. Risk of Intravenous Contrast Material–mediated Acute Kidney Injury: A Propensity Score–matched Study Stratified by Baseline-estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate. Radiology 2014, 271, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, J.S.; McDonald, R.J.; Comin, J.; Williamson, E.E.; Katzberg, R.W.; Murad, M.H.; Kallmes, D.F. Frequency of Acute Kidney Injury Following Intravenous Contrast Medium Administration: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Radiology 2013, 267, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruce, R.J.; Djamali, A.; Shinki, K.; Michel, S.J.; Fine, J.P.; Pozniak, M.A. Background Fluctuation of Kidney Function Versus Contrast-Induced Nephrotoxicity. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2009, 192, 711–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, F.; Lev, M.; Levy, R.; Silva, G.; Ebril, M.; De Camargo, É.C.; Pomerantz, S.; Singhal, A.; Greer, D.; Ay, H.; et al. Functional Contrast-Enhanced CT for Evaluation of Acute Ischemic Stroke Does Not Increase the Risk of Contrast-Induced Nephropathy. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2009, 31, 817–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davenport, M.S.; Perazella, M.A.; Yee, J.; Dillman, J.R.; Fine, D.; McDonald, R.J.; Rodby, R.A.; Wang, C.L.; Weinreb, J.C. Use of Intravenous Iodinated Contrast Media in Patients with Kidney Disease: Consensus Statements from the American College of Radiology and the National Kidney Foundation. Radiology 2020, 294, 660–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wuest, W.; Anders, K.; Schuhbaeck, A.; May, M.S.; Gauss, S.; Marwan, M.; Arnold, M.; Ensminger, S.; Muschiol, G.; Daniel, W.G.; et al. Dual source multidetector CT-angiography before Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation (TAVI) using a high-pitch spiral acquisition mode. Eur. Radiol. 2011, 22, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leon, M.B.; Smith, C.R.; Mack, M.J.; Miller, D.C.; Moses, J.W.; Svensson, L.G.; Tuzcu, E.M.; Webb, J.G.; Fontana, G.P.; Makkar, R.R.; et al. Transcatheter Aortic-Valve Implantation for Aortic Stenosis in Patients Who Cannot Undergo Surgery. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 1597–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wild, C.; Puig, S. Nicht-Ionische Röntgenkontrastmittel—Klinische Relevanz Der Unterschiede Verschiedener Kontrastmittel; Institute of Technology Assessment: Vienna, Austria, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.; Chen, J.; Cheng, T.; Gindulyte, A.; He, J.; He, S.; Li, Q.; Shoemaker, B.A.; Thiessen, P.A.; Yu, B.; et al. PubChem 2019 update: Improved access to chemical data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 47, 1102–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levey, A.S.; Coresh, J.; Greene, T.; Stevens, L.A.; Zhang, Y.L.; Hendriksen, S.; Kusek, J.W.; Van Lente, F. Using Standardized Serum Creatinine Values in the Modification of Diet in Renal Disease Study Equation for Estimating Glomerular Filtration Rate. Ann. Intern. Med. 2006, 145, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kappetein, A.P.; Head, S.J.; Généreux, P.; Piazza, N.; Van Mieghem, N.M.; Blackstone, E.H.; Brott, T.G.; Cohen, D.J.; Cutlip, D.E.; Van Es, G.-A.; et al. Updated standardized endpoint definitions for transcatheter aortic valve implantation: The Valve Academic Research Consortium-2 consensus document. Eur. Heart J. 2012, 33, 2403–2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cigarroa, R.G.; Lange, R.A.; Williams, R.H.; Hillis, D. Dosing of contrast material to prevent contrast nephropathy in patients with renal disease. Am. J. Med. 1989, 86, 649–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thongprayoon, C.; Cheungpasitporn, W.; Podboy, A.; Gillaspie, E.A.; Greason, K.L.; Kashani, K. The effects of contrast media volume on acute kidney injury after transcatheter aortic valve replacement: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Evid. Based Med. 2016, 9, 188–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Najjar, M.; Salna, M.; George, I. Acute kidney injury after aortic valve replacement: Incidence, risk factors and outcomes. Expert Rev. Cardiovasc. Ther. 2015, 13, 301–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowhurst, J.A.; Savage, M.; Subban, V.; Incani, A.; Raffel, O.C.; Poon, K.; Murdoch, D.; Saireddy, R.; Clarke, A.; Aroney, C.; et al. Factors Contributing to Acute Kidney Injury and the Impact on Mortality in Patients Undergoing Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement. Heart Lung Circ. 2016, 25, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merchant, A.M.; Neyra, J.A.; Minhajuddin, A.; Wehrmann, L.E.; Mills, R.A.; Gualano, S.K.; Kumbhani, D.J.; Huffman, L.C.; Jessen, M.E.; Fox, A.A. Packed red blood cell transfusion associates with acute kidney injury after transcatheter aortic valve replacement. BMC Anesthesiol. 2019, 19, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fefer, P.; Bogdan, A.; Grossman, Y.; Berkovitch, A.; Brodov, Y.; Kuperstein, R.; Segev, A.; Guetta, V.; Barbash, I.M. Impact of Rapid Ventricular Pacing on Outcome After Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2018, 7, e009038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stratta, P.; Bozzola, C.; Quaglia, M. Pitfall in nephrology: Contrast nephropathy has to be differentiated from renal damage due to atheroembolic disease. J. Nephrol. 2012, 25, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aalaei-Andabili, S.H.; Pourafshar, N.; Bavry, A.A.; Klodell, C.T.; Anderson, R.D.; Karimi, A.; Petersen, J.W.; Beaver, T.M. Acute Kidney Injury After Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement. J. Card. Surg. 2016, 31, 416–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thongprayoon, C.; Cheungpasitporn, W.; Gillaspie, E.A.; Greason, K.L.; Kashani, K. Association of blood transfusion with acute kidney injury after transcatheter aortic valve replacement: A meta-analysis. World J. Nephrol. 2016, 5, 482–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thongprayoon, C.; Cheungpasitporn, W.; Srivali, N.; Kittanamongkolchai, W.; Greason, K.L.; Kashani, K. Incidence and risk factors of acute kidney injury following transcatheter aortic valve replacement. Nephrology 2016, 21, 1041–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almac, E.; Ince, C. The impact of storage on red cell function in blood transfusion. Best Pr. Res. Clin. Anaesthesiol. 2007, 21, 195–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karkouti, K. Transfusion and risk of acute kidney injury in cardiac surgery. Br. J. Anaesth. 2012, 109, i29–i38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldalati, O.; Keshavarzi, F.; Kaura, A.; Byrne, J.; Eskandari, M.; Deshpande, R.; Monaghan, M.; Wandler, O.; Dworakowski, R.; MacCarthy, P. Factors associated with safe early discharge after transcatheter aortic valve implantation. Cardiol. J. 2018, 25, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Rosendael, P.J.; Kamperidis, V.; Van Der Kley, F.; Katsanos, S.; Al Amri, I.; Regeer, M.V.; Schalij, M.J.; De Weger, A.; Marsan, N.A.; Bax, J.J.; et al. Atherosclerosis burden of the aortic valve and aorta and risk of acute kidney injury after transcatheter aortic valve implantation. J. Cardiovasc. Comput. Tomogr. 2015, 9, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konigstein, M.; Ben-Assa, E.; Banai, S.; Shacham, Y.; Ziv-Baran, T.; Abramowitz, Y.; Steinvil, A.; Rubinow, E.L.; Havakuk, O.; Halkin, A.; et al. Periprocedural Bleeding, Acute Kidney Injury, and Long-term Mortality After Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation. Can. J. Cardiol. 2015, 31, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ACR Comittee on Drugs and Contrast Media. ACR Manual on Contrast Media; American College of Radiology: Reston, VA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Neumann, F.-J.; Sousa-Uva, M.; Ahlsson, A.; Alfonso, F.; Banning, A.P.; Benedetto, U.; Byrne, R.A.; Collet, J.-P.; Falk, V.; Head, S.J.; et al. 2018 ESC/EACTS Guidelines on myocardial revascularization. Eur. Heart J. 2018, 40, 87–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikoo, M.H.; Pakfetrat, M.; Malekmakan, L.; Salmanpour, Z.; Izadpanah, P. Comparison of normal saline, Ringer’s lactate, and sodium bicarbonate for prevention of contrast-induced nephropathy in patients with coronary angiography: A randomized double-blind clinical trial. Indian J. Nephrol. 2018, 29, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Overall n = 514 | AKI n = 94 | Non-AKI n = 420 | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Demographics | ||||
| Age, mean (±SD) | 81.3 (7.0) | 82.9 (5.5) | 81.0 (7.0) | 0.385 |
| Female, n (%) | 323 (62.8) | 61 (64.9) | 262 (62.4) | 0.370 |
| Body mass index kg/m2, median (IQR) | 25.9 (6.7) | 26.7 (7.4) | 24.7 (5.1) | 0.369 |
| Risk Profile | ||||
| EuroSCORE II, median (IQR) | 4.8 (6.0) | 6.6 (10.4) | 5.4 (6.2) | 0.103 |
| Logistic EuroSCORE, median (IQR) | 17.8 (20.4) | 21.6 (28.9) | 17.4 (19.6) | 0.032 |
| STS score, median (IQR) | 4.5 (3.3) | 5.8 (4.7) | 4.6 (3.2) | 0.288 |
| Incremental risk score, median (IQR) | 3 (8) | 3 (9) | 5 (11.5) | 0.889 |
| HAS-BLED score, median (IQR) | 1 (1) | 1 (1) | 1 (1) | 0.085 |
| CHADS-VASC Score, mean (±SD) | 5.3 (1.4) | 5.8 (1.4) | 5.2 (1.4) | 0.014 |
| Chronic health Conditions and Risk Factors | ||||
| Hypertension, n (%) | 443 (86.2) | 83 (88.3) | 360 (85.7) | 0.160 |
| Dyslipidaemia, n (%) | 302 (58.8) | 63 (67) | 239 (56.9) | 0.026 |
| Diabetes mellitus (IDDM), n (%) | 82 (16.0) | 23 (24.5) | 59 (14) | 0.012 |
| COPD, n (%) | 108 (21.0) | 15 (16.0) | 93 (22.1) | 0.209 |
| Peripheral vascular disease, n (%) | 100 (19.5) | 19 (20.2) | 81 (19.3) | 0.433 |
| Cerebrovascular accident, n (%) | 63 (12.3) | 12 (12.8) | 51 (12.1) | 0.478 |
| NYHA class III/IV, n (%) | 442 (86.0) | 79 (84.0) | 363 (86.4) | 0.908 |
| Renal impairment eGFR < 60 mL/min/1.73 m², n (%) | 87 (16.9) | 16 (17.0) | 71 (16.9) | 0.891 |
| eGFR mL/min/1.73 m², mean (±SD) | 54.2 (25.6) | 58.4 (25.6) | 58.4 (26.7) | 0.478 |
| Creatinine mg/dL, median (IQR) | 1.1 (0.6) | 1.0 (0.4) | 1.1 (0.6) | 0.143 |
| Creatinine clearance mL/min, mean (±SD) | 48.7 (19.9) | 52 (18.3) | 51.5 (22.2) | 0.841 |
| Hematocrit %, median (IQR) | 36.0 (6.7) | 35.2 (6.0) | 36.2 (6.9) | 0.298 |
| Dialysis, n (%) | 1 (0.2) | 0 (0) | 1 (0.2) | 0.820 |
| Permanent pacemaker, n (%) | 83 (16.1) | 18 (19.1) | 65 (15.5) | 0.233 |
| Prior myocardial infarction, n (%) | 73 (14.2) | 13 (13.8) | 60 (14.3) | 0.558 |
| Prior PCI, n (%) | 139 (27.0) | 28 (29.8) | 111 (26.4) | 0.256 |
| Previous CABG, n (%) | 78 (15.2) | 14 (14.9) | 64 (15.2) | 0.569 |
| Previous valve surgery, n (%) | 44 (8.6) | 5 (5.3) | 39 (9.3) | 0.161 |
| Preoperative Echocardiographic Data | ||||
| LVEF %, median (IQR) | 55 (15) | 55 (12.5) | 55 (20) | 0.565 |
| Aortic valve area, mean (±SD) | 0.7 (0.3) | 0.8 (0.6) | 0.7 (0.2) | 0.368 |
| Mean pressure gradient, mean (±SD) | 46.7 (16.2) | 49.8 (18.4) | 46.3 (15.8) | 0.154 |
| Peak velocity m/sec, median (IQR) | 4.2 (0.8) | 4.2 (0.95) | 4.19 (0.86) | 0.875 |
| sPAP, mean (±SD) | 41.1 (20.7) | 39 (23.1) | 42.1 (20.1) | 0.361 |
| Overall n = 514 | AKI n = 94 | Non-AKI n = 420 | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Contrast Medium Dose and AKI Risk Ratio Models | ||||
| CM dose ml, median (IQR) | 174.5 (131.3) | 171 (136.3) | 157 (127) | 0.968 |
| CM × SCr, median (IQR) | 197.2 (163.2) | 198.7 (155.3) | 186.3 (166.5) | 0.271 |
| CM × SCr/BW ratio, median (IQR) | 2.3 (2.7) | 2.6 (2.7) | 2.7 (2.3) | 0.543 |
| CM × SCr/BW ratio > 5, n (%) | 63 (12.3) | 6 (6.4) | 57 (13.6) | 0.030 |
| CM × SCr/BMI ratio, median (IQR) | 6.2 (7.8) | 6.9 (6.8) | 7.3 (6.8) | 0.422 |
| Risk Stratification Score Model, median (IQR) | 12 (7) | 12 (8) | 12 (8) | 0.918 |
| Risk Stratification Score Model > 10, n (%) | 337 (65.6) | 63 (67) | 274 (65.2) | 0.370 |
| Procedural Variables | ||||
| Transapical access, n (%) | 256 (49.8) | 42 (44.7) | 214 (51) | 0.174 |
| Balloon expanding valve, n (%) | 255 (49.6) | 38 (40.4) | 217 (51.7) | 0.035 |
| Predillatation necessary, n (%) | 325 (63.2) | 68 (72.3) | 257 (61.2) | 0.042 |
| Postdillatation necessary, n (%) | 59 (11.5) | 8 (8.5) | 51 (12.1) | 0.188 |
| Max. creatinine within 72 h mg/dL, median (IQR) | 1.1 (0.6) | 2.5 (4.8) | 0.97 (0.3) | <0.001 |
| Total hours in ICU, median (IQR) | 21 (45) | 55.5 (141.5) | 21 (24) | <0.001 |
| Total hours ventilated, median (IQR) | 4 (7) | 6 (17) | 6 (4) | 0.112 |
| RBC units used, mean (±SD) | 1.2 (2.7) | 2.3 (4.3) | 0.9 (2.4) | 0.004 |
| Any paravalvular leak, n (%) | 229 (44.6) | 38 (40.4) | 191 (45.5) | 0.149 |
| Mean gradient post-implant, median (IQR) | 9 (7) | 4.5 (9.8) | 6 (11) | 0.244 |
| Max. gradient post-implant, median (IQR) | 17 (15) | 8 (16) | 16 (18.5) | 0.956 |
| Max. flow post-implant, mean (±SD) | 2.1 (1) | 2 (0) | 2.1 (1) | 0.347 |
| Overall n = 514 | AKI n = 94 | Non-AKI n = 420 | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Myocardial infarction, n (%) | 2(0.4) | 1 (1.1) | 1 (0.2) | 0.321 |
| Neurological adverse event, n (%) | 12 (2.3) | 2 (2.1) | 10 (2.4) | 0.619 |
| Major vascular complication, n (%) | 9 (1.8) | 2 (2.1) | 7 (1.7) | 0.722 |
| Major bleeding complication, n (%) | 44 (8.6) | 13 (13.8) | 31 (7.4) | 0.027 |
| New AV-block, n (%) | 59 (11.5) | 6 (6.4) | 53 (12.6) | 0.121 |
| New bundle branch block, n (%) | 78 (15.2) | 16 (17.0) | 62 (14.8) | 0.372 |
| New atrial fibrillation, n (%) | 53 (10.3) | 8 (8.5) | 45 (10.7) | 0.388 |
| New pacemaker implanted, n (%) | 70 (13.6) | 16 (17.0) | 54 (12.9) | 0.129 |
| Reoperation for valvular dysfunction, n (%) | 4 (0.8) | 1 (1.1) | 3 (0.7) | 0.540 |
| Reoperation for bleeding/tamponade, n (%) | 14 (2.7) | 4 (4.3) | 10 (2.4) | 0.181 |
| Reoperation for other cardiac problems, n (%) | 45 (8.8) | 13 (13.8) | 32 (7.6) | 0.035 |
| Reoperation for non-cardiac problems, n (%) | 40 (7.8) | 13 (13.8) | 27 (6.4) | 0.013 |
| Conversion to open surgery, n (%) | 4 (0.8) | 1 (1.1) | 3 (0.7) | 0.535 |
| Unplanned valve-in-valve implantation, n (%) | 8 (1.6) | 2 (2.1) | 6 (1.4) | 0.418 |
| Length of stay after TAVR in days, median (IQR) | 10 (8) | 15.5 (14.5) | 12 (8) | 0.150 |
| Procedural success, n (%) | 454 (88.3) | 73 (77.7) | 381 (90.7) | 0.006 |
| 30-day combined safety endpoint, n (%) | 424 (82.5) | 53 (56.4) | 371 (88.3) | <0.001 |
| 30-day all-cause mortality, n (%) | 14 (2.7) | 8 (8.5) | 6 (1.4) | 0.001 |
| 1-year all-cause mortality, n (%) | 77 (15.0) | 22 (23.4) | 55 (13.1) | 0.007 |
| Univariate Analysis | Multivariate Analysis | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR | 95% CI | p Value | OR | 95% CI | p Value | |
| Peripheral Vascular Disease | 0.04 | 0.004–0.437 | 0.008 | 0.01 | −0.096–0.099 | 0.995 |
| Coronary Vascular Disease | 5.51 | 1.020–29.753 | 0.047 | 0.64 | −0.033–0.161 | 0.172 |
| Prior PCI | 0.12 | 0.019–0.734 | 0.022 | −0.79 | −0.169–0.011 | 0.100 |
| LVEF % | 1.09 | 1.010–1.184 | 0.027 | 0.00 | −0.003–0.004 | 0.983 |
| sPAP | 0.97 | 0.934–0.996 | 0.030 | 0.00 | −0.002–0.002 | 0.643 |
| CM x SCr | 0.97 | 0.953–0.991 | 0.004 | 0.00 | 0.000–0.001 | 0.134 |
| CM × SCr/BW ratio | 0.77 | 0.349–1.707 | 0.523 | |||
| CM × SCr/BMI ratio | 1.50 | 0.922–2.454 | 0.102 | |||
| Risk Stratification Score Model | 1.10 | 0.990–1.216 | 0.077 | |||
| CM × SCr/BW ratio > 5 | 0.78 | 0.200–3.059 | 0.724 | |||
| Risk Stratification Score Model > 10 | 1.03 | 0.438–2.436 | 0.940 | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mach, M.; Hasan, W.; Andreas, M.; Winkler, B.; Weiss, G.; Adlbrecht, C.; Delle-Karth, G.; Grabenwöger, M. Evaluating the Association between Contrast Medium Dosage and Acute Kidney Injury in Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement Using Different Predictive Models. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3476. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9113476
Mach M, Hasan W, Andreas M, Winkler B, Weiss G, Adlbrecht C, Delle-Karth G, Grabenwöger M. Evaluating the Association between Contrast Medium Dosage and Acute Kidney Injury in Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement Using Different Predictive Models. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2020; 9(11):3476. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9113476
Chicago/Turabian StyleMach, Markus, Waseem Hasan, Martin Andreas, Bernhard Winkler, Gabriel Weiss, Christopher Adlbrecht, Georg Delle-Karth, and Martin Grabenwöger. 2020. "Evaluating the Association between Contrast Medium Dosage and Acute Kidney Injury in Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement Using Different Predictive Models" Journal of Clinical Medicine 9, no. 11: 3476. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9113476
APA StyleMach, M., Hasan, W., Andreas, M., Winkler, B., Weiss, G., Adlbrecht, C., Delle-Karth, G., & Grabenwöger, M. (2020). Evaluating the Association between Contrast Medium Dosage and Acute Kidney Injury in Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement Using Different Predictive Models. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(11), 3476. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9113476





