Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte, Monocyte-to-Lymphocyte and Platelet-to-Lymphocyte Ratios in Relation to Clinical Parameters and Smoking Status in Patients with Graves’ Orbitopathy—Novel Insight into Old Tests
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Statement of Ethics
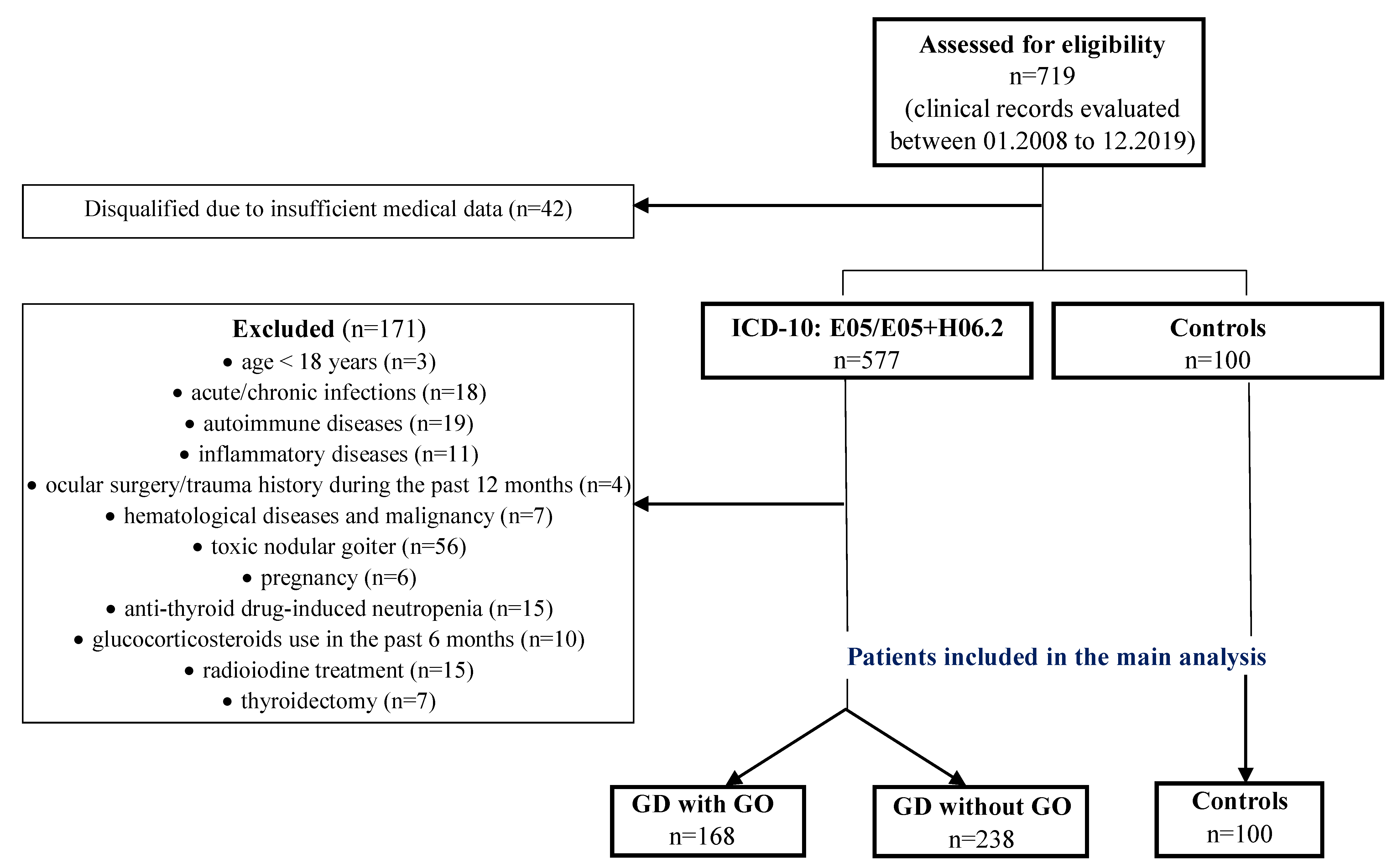
2.2. Study Design and Patients
2.3. Clinical and Laboratory Assessments
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics of Study and Control Group
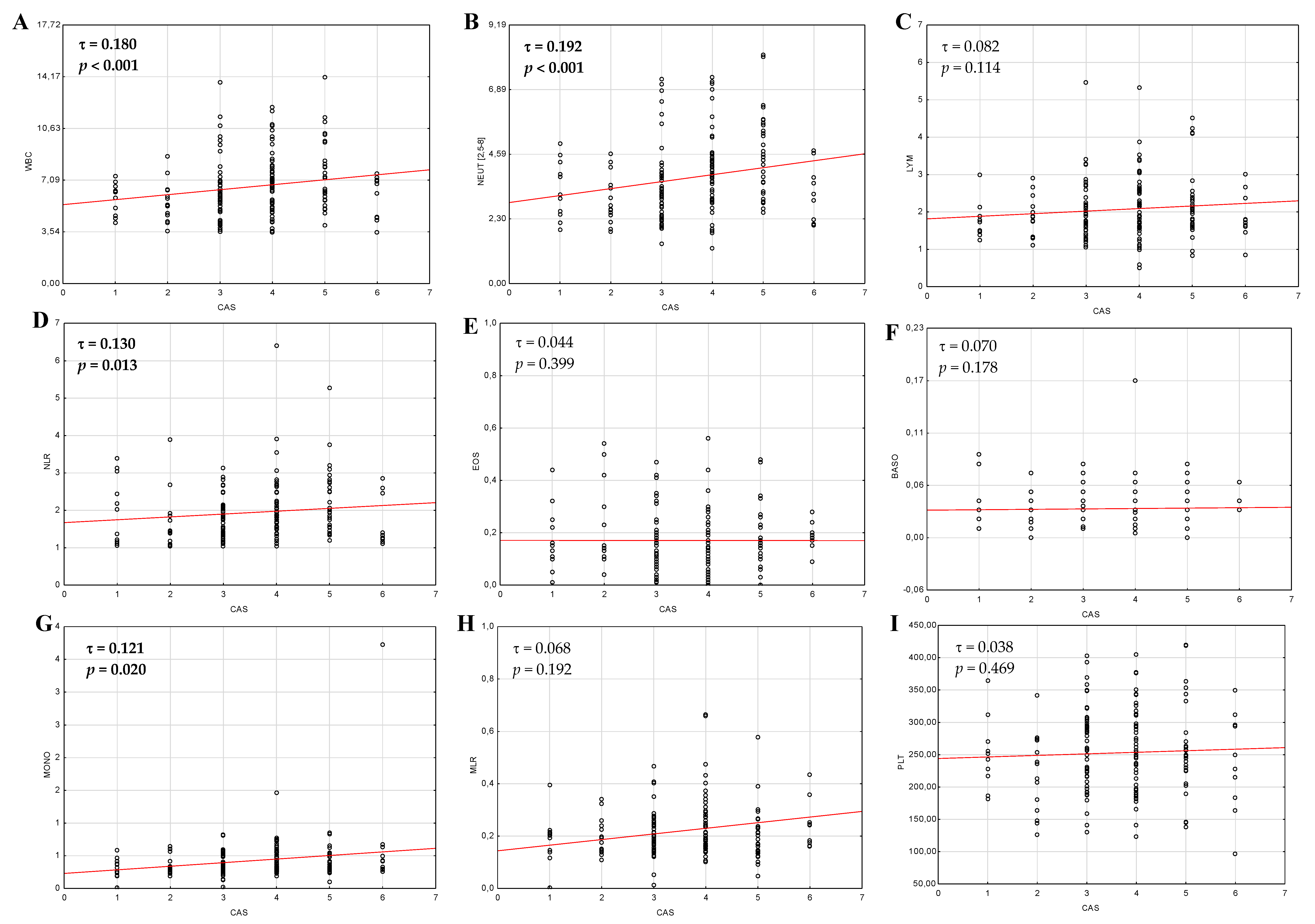
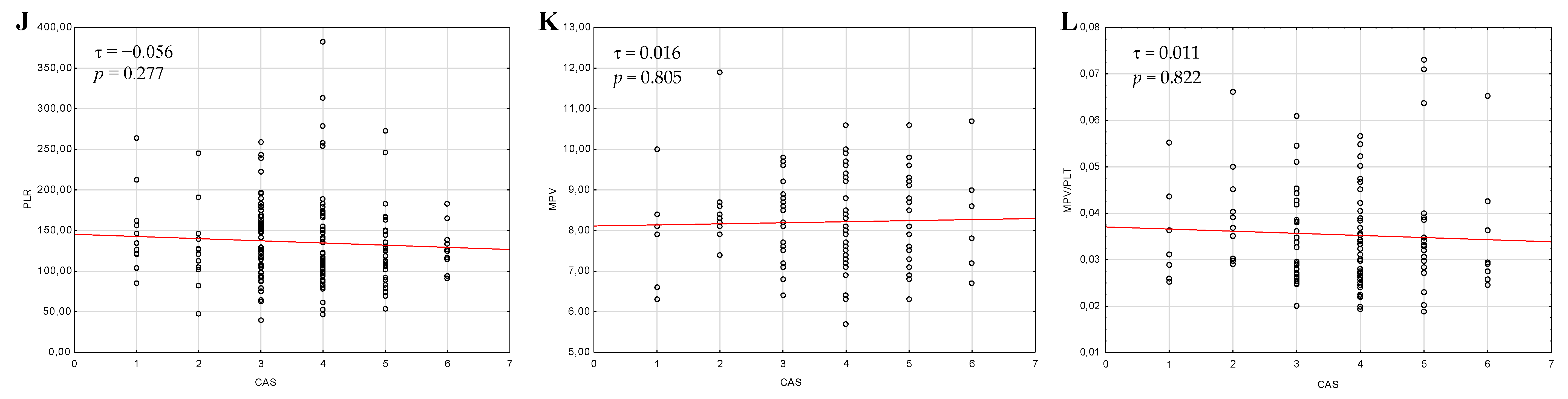
3.2. Differences in Hematological Indices between Active and Inactive Graves’ Orbitopathy
3.3. Differences in Hematological Parameters According to Thyroid Status
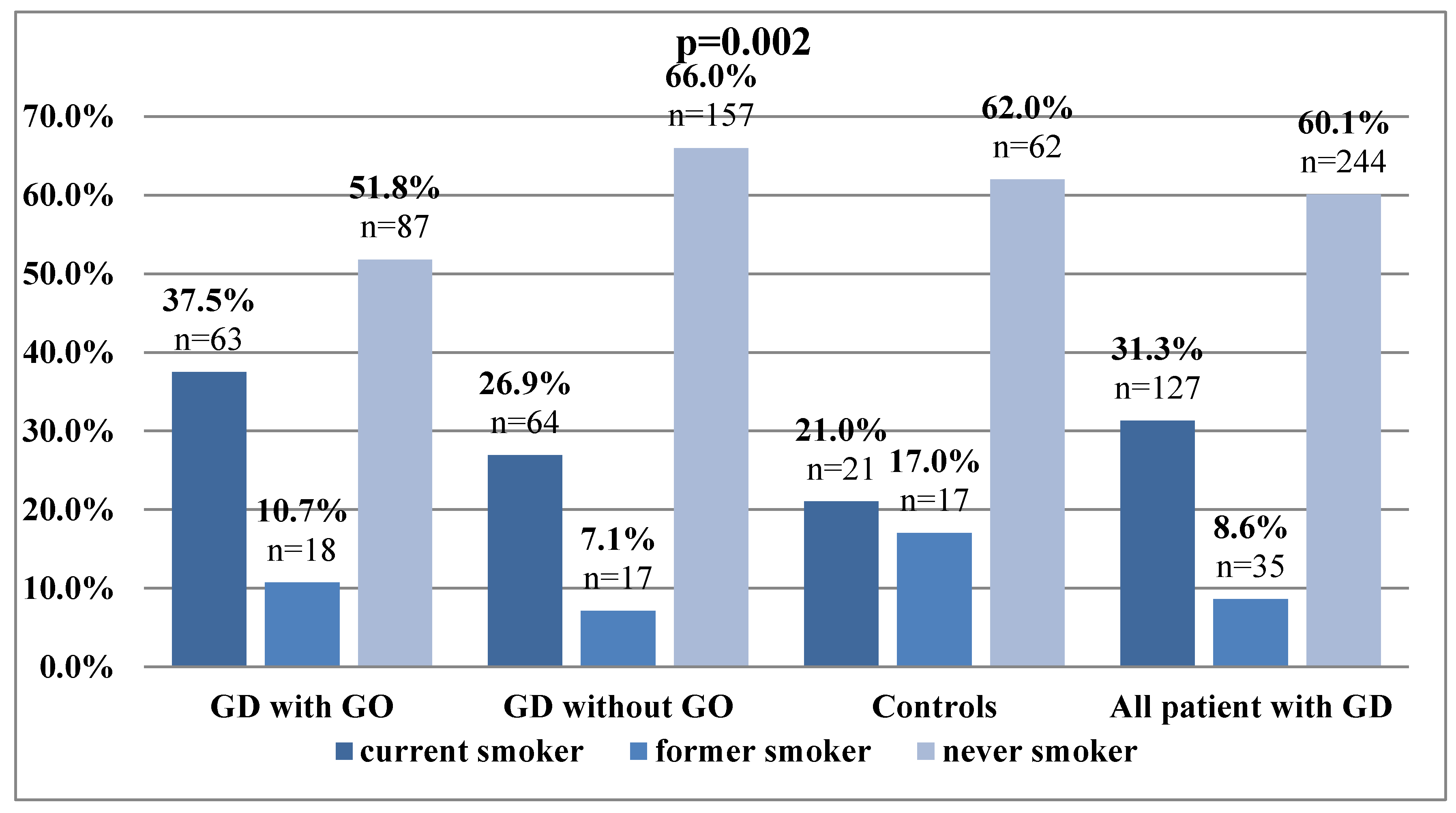
3.4. Differences in Hematological Parameters in the Study and Control Group According to Smoking Status
3.5. Factors Associated with Higher Risk of Graves’ Orbitopathy Development
4. Discussion
5. Limitations of the Study
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GD | Graves’ disease |
| GO | Graves’ orbitopathy |
| CAS | Clinical Activity Score |
| CBC | complete blood count |
| WBC | white blood cell |
| NEU | neutrophil |
| LYM | lymphocyte |
| EOS | eosinophil |
| BASO | basophil |
| MONO | monocyte |
| NLR | neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio |
| MLR | monocyte-to-neutrophil ratio |
| PLR | platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio |
| MPV | mean platelet value |
| MPV/PLT | mean platelet volume-to-platelet ratio |
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
| TRAb | anti-TSH receptor antibody |
| TSH | thyroid stimulating hormone |
| fT3 | free triodothyronine |
| fT4 | free thyroxine |
References
- Drui, D.; Du Pasquier-Fediaevsky, L.; Vignal-Clermont, C.; Daumerie, C. Graves’ orbitopathy: Diagnosis and treatment. Ann. Endocrinol. 2018, 79, 656–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrio-Barrio, J.; Sabater, A.L.; Bonet-Farriol, E.; Velázquez-Villoria, Á.; Galofré, J.C. Graves’ Ophthalmopathy: VISA versus EUGOGO Classification, Assessment, and Management. J. Ophthalmol. 2015, 2015, 249125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiersinga, W.M. Smoking and Prevention of Thyroid Eye Disease. In Thyroid Eye Disease; Douglas, R.S., McCoy, A.N., Gupta, S., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 39–51. ISBN 978-1-4939-1745-7. [Google Scholar]
- Bahn, R.S. Graves’ Ophthalmopathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 726–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rydzewska, M.; Jaromin, M.; Pasierowska, I.E.; Stożek, K.; Bossowski, A. Role of the T and B lymphocytes in pathogenesis of autoimmune thyroid diseases. Thyroid. Res. 2018, 11, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prummel, M.F.; Wiersinga, W.M. Smoking and risk of Graves’ disease. JAMA 1993, 269, 479–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfeilschifter, J.; Ziegler, R. Smoking and endocrine ophthalmopathy: Impact of smoking severity and current vs lifetime cigarette consumption. Clin. Endocrinol. 1996, 45, 477–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Träisk, F.; Tallstedt, L.; Abraham-Nordling, M.; Andersson, T.; Berg, G.; Calissendorff, J.; Hallengren, B.; Hedner, P.; Lantz, M.; Nyström, E.; et al. Thyroid-associated ophthalmopathy after treatment for Graves’ hyperthyroidism with antithyroid drugs or iodine-131. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 94, 3700–3707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piantanida, E.; Tanda, M.L.; Lai, A.; Sassi, L.; Bartalena, L. Prevalence and natural history of Graves’ orbitopathy in the XXI century. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2013, 444–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnson, Y.; Shoenfeld, Y.; Amital, H. Effects of tobacco smoke on immunity, inflammation and autoimmunity. J. Autoimmun. 2010, 34, J258–J265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lymperaki, E.; Makedou, K.; Iliadis, S.; Vagdatli, E. Effects of acute cigarette smoking on total blood count and markers of oxidative stress in active and passive smokers. Hippokratia 2015, 19, 293–297. [Google Scholar]
- Kolaczkowska, E.; Kubes, P. Neutrophil recruitment and function in health and inflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 159–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mertoglu, C.; Gunay, M. Neutrophil-Lymphocyte ratio and Platelet-Lymphocyte ratio as useful predictive markers of prediabetes and diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 2017, 11, S127–S131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angkananard, T.; Anothaisintawee, T.; McEvoy, M.; Attia, J.; Thakkinstian, A. Neutrophil Lymphocyte Ratio and Cardiovascular Disease Risk: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Biomed. Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 2703518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilen, M.A.; Martini, D.J.; Liu, Y.; Lewis, C.; Collins, H.H.; Shabto, J.M.; Akce, M.; Kissick, H.T.; Carthon, B.C.; Shaib, W.L.; et al. The Prognostic and Predictive Impact of Inflammatory Biomarkers in Patients Who Have Advanced-Stage Cancer Treated With Immunotherapy. Cancer 2019, 125, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korniluk, A.; Koper-Lenkiewicz, O.M.; Kamińska, J.; Kemona, H.; Dymicka-Piekarska, V. Mean platelet volume (MPV): New perspectives for an old marker in the course and prognosis of inflammatory conditions. Mediat. Inflamm. 2019, 2019, 9213074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sit, M.; Aktas, G.; Erkol, H.; Yaman, S.; Keyif, F.; Savli, H. Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio is Useful in Differentiation of Malign and Benign Thyroid Nodules. P. R. Health Sci. J. 2019, 38, 60–63. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, F.; Yang, P.S.; Chien, M.N.; Lee, J.J.; Leung, C.H.; Cheng, S.P. An Increased Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio Predicts Incomplete Response to Therapy in Differentiated Thyroid Cancer. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2018, 15, 1757–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Wang, Y.; Shan, G.; Gao, L. Clinical and prognostic value of neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio for patients with thyroid cancer: A meta-analysis. Medicine 2020, 99, e19686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Wei, T.; Li, Z.; Gong, R.; Lei, J.; Zhu, J.; Huang, T. Association of the Preoperative Inflammation-Based Scores with TNM Stage and Recurrence in Patients with Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma: A Retrospective, Multicenter Analysis. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 1809–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keskin, H.; Kaya, Y.; Cadirci, K.; Kucur, C.; Ziypak, E.; Simsek, E.; Gozcu, H.; Arikan, S.; Carlioglu, A. Elevated neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio in patients with euthyroid chronic autoimmune thyreotidis. Endocr. Regul. 2016, 50, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aktas, G.; Sit, M.; Dikbas, O.; Erkol, H.; Altinordu, R.; Erkus, E.; Savli, H. Elevated neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in the diagnosis of Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. Rev. Assoc. Med. Bras. 2017, 63, 1065–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arpaci, D.; Gürol, G.; Ergenc, H.; Yazar, H.; Tocoglu, A.G.; Ciftci, I.H.; Tamer, A. A controversial new approach to address hematological parameters in Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. Clin. Lab. 2016, 62, 1225–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilge, M.; Yesilova, A.; Adas, M.; Helvaci, A. Neutrophil- and Platelet- to Lymphocyte Ratio in Patients with Euthyroid Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2019, 127, 545–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onalan, E.; Dönder, E. Neutrophil and platelet to lymphocyte ratio in patients with hypothyroid Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. Acta Biomed. 2020, 91, 310–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dasgupta, R.; Atri, A.; Jebasingh, F.; Hepzhibah, J.; Christudoss, P.; Asha, H.S.; Paul, T.V.; Thomas, N. Platelet-Lymphocyte Ratio (PLR) as a Novel Surrogate Marker to Differentiate Thyrotoxic Patients with Graves’ Disease (GD) from Sub-Acute Thyroiditis (SAT): A Cross-Sectional Study from South India. Endocr. Pract. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taşkaldiran, I.; Omma, T.; Önder, Ç.E.; Firat, S.N.; Koç, G.; Kiliç, M.K.; Kuşkonmaz, Ş.M.; Çulha, C. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, monocyte-to-lymphocyte ratio, and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio in different etiological causes of thyrotoxicosis. Turk. J. Med. Sci. 2019, 49, 1687–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celik, T. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in thyroid ophthalmopathy. Bratisl. Lek. Listy. 2017, 118, 495–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atılgan, C.Ü.; Şendül, S.Y.; Kösekahya, P.; Çağlayan, M.; Alkan, A.; Güven, D.; Yılmazbaş, P. Evaluation of Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio and Mean Platelet Volume in Patients with Active and Inactive Thyroid Orbitopathy. Sisli. Etfal. Hastan. Tip. Bul. 2018, 52, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartalena, L.; Baldeschi, L.; Dickinson, A.; Eckstein, A.; Kendall-Taylor, P.; Marcocci, C.; Moourits, M.; Perros, P.; Boboridis, K.; Boschi, A.; et al. Consensus statement of the European Group on Graves’ orbitopathy (EUGOGO) on management of GO. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2008, 15, 273–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente, N.; Cardoso, L.; Barros, L.; Carrrilho, F. Antithyroid Drug-Induced Agranulocytosis: State of the Art on Diagnosis and Management. Drugs R D 2017, 17, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheaton, A.G.; Liu, Y.; Croft, J.B.; VanFrank, B.; Croxton, T.L.; Punturieri, A.; Postow, L.; Greenlund, K.J. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease and Smoking Status—United States, 2017. MMWR Morb. Mortal Wkly. Rep. 2019, 68, 533–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karim, H.M.R. Smoked for Years but Stopped a Few Months Back: Dilemma Regarding the American Society of Anesthesiologists Physical Status. Turk. J. Anaesthesiol. Reanim. 2019, 47, 515–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bain, B.J.; Rothwell, M.; Feher, M.D.; Robinson, R.; Brown, J.; Sever, P.S. Acute changes in haematological parameters on cessation of smoking. J. R. Soc. Med. 1992, 85, 80–82. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bartalena, L.; Baldeschi, L.; Boboridis, K.; Eckstein, A.; Kahaly, G.J.; Marcocci, C.; Perros, P.; Salvi, M.; Wiersinga, W.M. The 2016 European Thyroid Association/European Group on Graves’ Orbitopathy Guidelines for the Management of Graves’ Orbitopathy. Eur. Thyroid. J. 2016, 5, 9–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Du, J.; Li, T.; Liao, H. Platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio and neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio associated with disease activity in patients with Takayasu’s arteritis: A case-control study. BMJ Open 2017, 7, e014451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, B.H.; Ng, C.P.; Au, K.B.; Wong, P.K.; Wong, K.K.C.; Wan, K.Y. Does Preoperative Neutrophil Lymphocyte Ratio Predict Risk of Recurrence and Occult Central Nodal Metastasis in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma? World J. Surg. 2014, 38, 2605–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozmen, S.; Timur, O.; Calik, I.; Altinkaynak, K.; Simsek, E.; Gozcu, H.; Arslan, A.; Carlioglu, A. Neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and platelet-lymphocyte ratio (PLR) may be superior to C-reactive protein (CRP) for predicting the occurrence of differentiated thyroid cancer. Endocr. Regul. 2017, 51, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Kim, B.H.; Jang, M.H.; Kim, J.M.; Kim, E.H.; Jeon, Y.K.; Kim, S.S.; Kim, I.J. High neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio is associated with relapse in Graves’ disease after antithyroid drug therapy. Endocrine 2020, 67, 406–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonelli, A.; Ferrari, S.M.; Ragusa, F.; Elia, G.; Paparo, S.R.; Ruffilli, I.; Patrizio, A.; Giusti, C.; Gonnella, D.; Cristaudo, A.; et al. Graves’ disease: Epidemiology, genetic and environmental risk factors and viruses. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 34, 101387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wémeau, J.L.; Klein, M.; Sadoul, J.L.; Briet, C.; Vélayoudom-Céphise, F.L. Graves’ disease: Introduction, epidemiology, endogenous and environmental pathogenic factors. Ann. Endocrinol. 2018, 79, 599–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, S.M.; Fallahi, P.; Vita, R.; Antonelli, A.; Benvenga, S. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ in thyroid autoimmunity. PPAR Res. 2015, 2015, 232818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fallahi, P.; Ferrari, S.M.; Elia, G.; Nasini, F.; Colaci, M.; Giuggioli, D.; Vita, R.; Benvenga, S.; Ferri, C.; Antonelli, A. Novel Therapies for Thyroid Autoimmune Diseases. Expert Rev. Clin. Pharmacol. 2016, 9, 853–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turan, E. Evaluation of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and hematologic parameters in patients with Graves’ disease. Bratisl. Lek. Listy. 2019, 120, 476–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daǧdeviren, M.; Akkan, T.; Yapar, D.; Karakaya, S.; Daǧdeviren, T.; Ertuǧrul, D.; Altay, M. Can Neutrophil/Lymphocyte Ratio Be Used as an Indicator of Inflammation in Patients with Hyperthyroidism? J. Med. Biochem. 2019, 39, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Fang, S.; Li, D.; Zhou, H.; Li, B.; Fan, X. The involvement of T cell pathogenesis in thyroid-associated ophthalmopathy. Eye 2019, 33, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panzer, S.; Haubenstock, A.; Minar, E. Platelets in hyperthyroidism: Studies on platelet counts, mean platelet volume, 111-indium-labeled platelet kinetics, and platelet-associated immunoglobulins G and M. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1990, 70, 491–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Zhou, D.; Chen, J.; Shan, P. Eosinophil/Monocyte Ratio Combined With Serum Thyroid Hormone for Distinguishing Graves’ Disease and Subacute Thyroiditis. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouveris, H.T.; Al-Homsi, J.; Gosepath, J.; Mann, W.J. Histological and radiological signs indicative for chronic sinus mucosal inflammation in Graves’ ophthalmopathy. Rhinology 2009, 47, 144–147. [Google Scholar]
- Izumi, Y.; Hidaka, Y.; Tada, H.; Takano, T.; Kashiwai, T.; Tatsumi, K.; Ichihara, K.; Amino, N. Simple and practical parameters for differentiation between destruction-induced thyrotoxicosis and Graves’ thyrotoxicosis. Clin. Endocrinol. 2002, 57, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, M.J. Role of neutrophils in systemic autoimmune diseases. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2013, 15, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klecha, A.J.; Barreiro Arcos, M.L.; Frick, L.; Genaro, A.M.; Cremaschi, G. Immune-endocrine interactions in autoimmune thyroid diseases. Neuroimmunomodulation 2008, 15, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tulgar, Y.K.; Cakar, S.; Tulgar, S.; Dalkilic, O.; Cakiroglu, B.; Uyanik, B.S. The effect of smoking on neutrophil/lymphocyte and platelet/lymphocyte ratio and platelet indices: A retrospective study. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2016, 20, 3112–3118. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gumus, F.; Solak, I.; Eryilmaz, M.A. The effects of smoking on neutrophil/lymphocyte, platelet//lymphocyte ratios. Bratisl. Lek. Listy. 2018, 119, 116–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Çekici, Y.; Yılmaz, M.; Seçen, Ö. New inflammatory indicators: Association of high eosinophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and low lymphocyte-to-monocyte ratio with smoking. J. Int. Med. Res. 2019, 47, 4292–4303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elkhalifa, A.M. Effects of cigarette smoking on coagulation screening tests and platelet counts in a Sudanese male adults population. Saudi Med. J. 2018, 39, 897–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
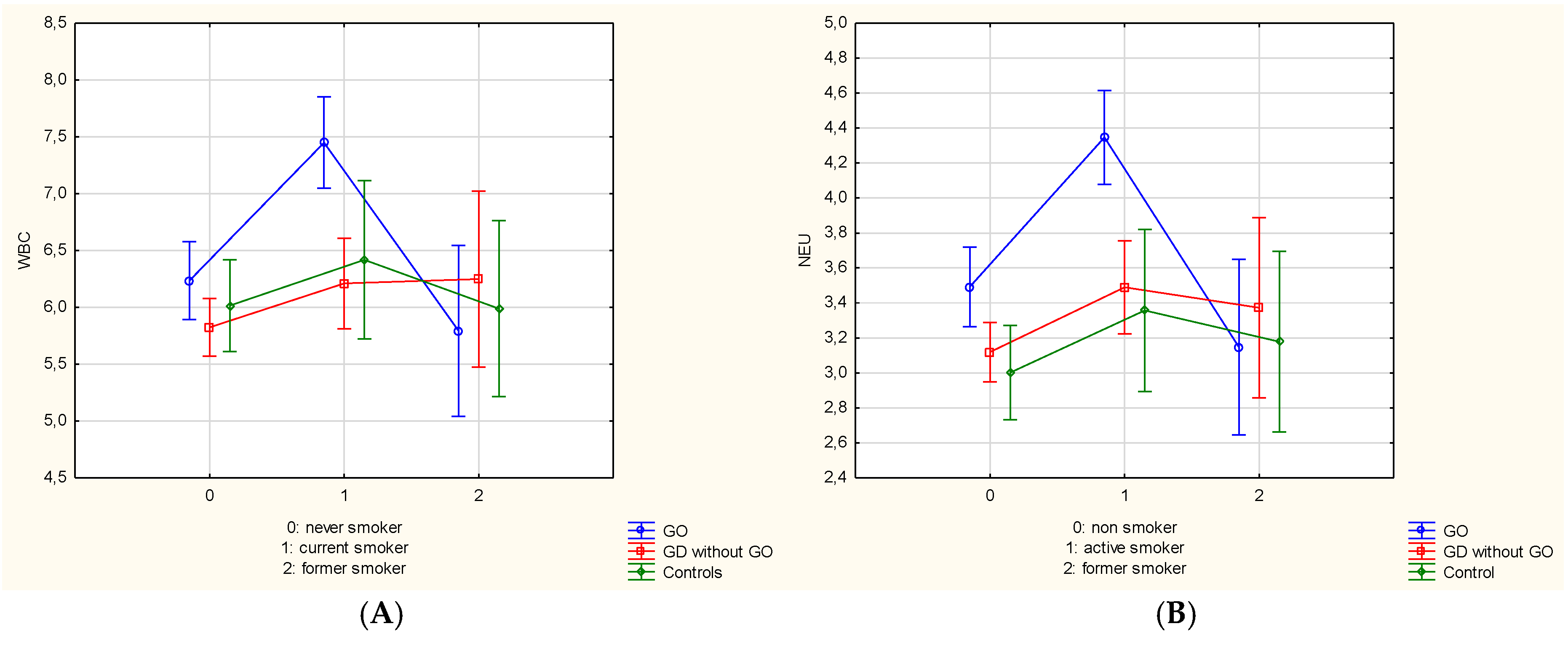
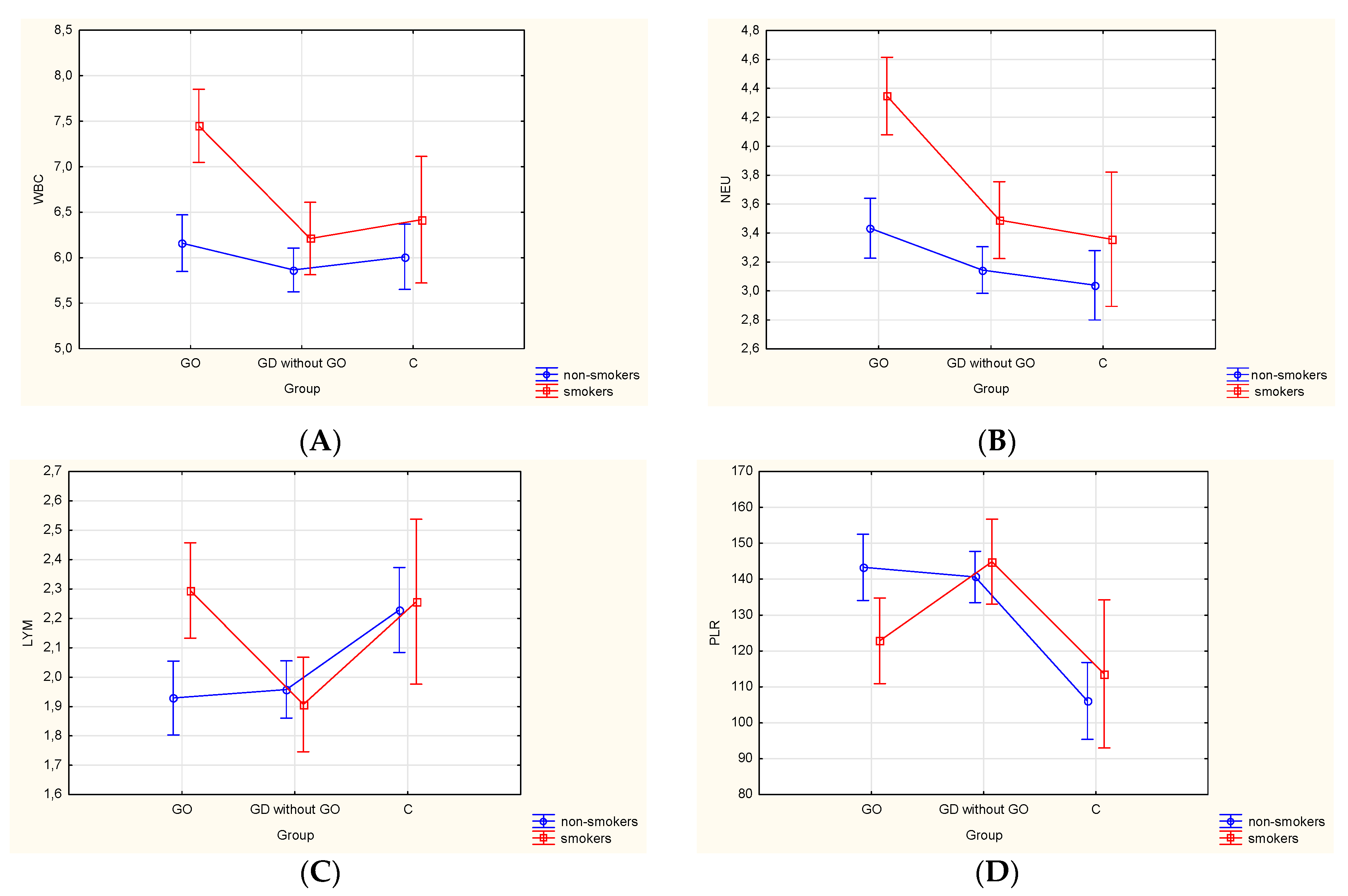
| Variables | GD with GO | GD without GO | Controls | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (n = 168) | (n = 238) | (n = 100) | ||
| Age [years] | 50.4 ± 12.9 | 46.7 ± 16.5 | 42.5 ± 17.3 | <0.001 * 1 |
| Female, n (%) | 138 (82) | 193 (81) | 65 (65) | 0.002 * 2 |
| Male, n (%) | 30 (18) | 45 (19) | 35 (35) | |
| BMI [kg/m2] | 26.1 ± 5.4 | 25.3 ± 4.8 | 25.5 ± 4.1 | 0.280 1 |
| Duration of GD [months] | 52.3 ± 74.4 | 34.9 ± 66.3 | - | 0.013 * 3 |
| Duration of GO [months] | 20.7 ± 47.6 | - | - | - |
| Variables | Group 1 GD with GO | Group 2 GD without GO | Group 3 Controls | p-Value | p (Groups 1&2) | p (Groups 1&3) | p (Groups 2&3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (n = 168) | (n = 238) | (n = 100) | |||||
| WBC [109/L] | 6.64 ± 2.09 | 5.96 ± 1.56 | 6.10 ± 0.90 | 0.014 * | 0.022 * | NS | NS |
| NEU [109/L] | 3.78 ± 1.42 | 3.24 ± 1.06 | 3.11 ± 0.46 | <0.001 * | <0.001 * | <0.001 * | NS |
| LYM [109/L] | 2.07 ± 0.79 | 1.94 ± 0.64 | 2.23 ± 0.43 | 0.008 * | NS | NS | 0.005 * |
| NLR | 1.95 ± 0.77 | 1.76 ± 0.62 | 1.41 ± 0.21 | <0.001 * | 0.018 * | <0.001 * | <0.001 * |
| EOS [109/L] | 0.17 ± 0.12 | 0.18 ± 0.20 | 0.18 ± 0.11 | 0.663 | NS | NS | NS |
| BASO [109/L] | 0.03 ± 0.02 | 0.03 ± 0.05 | 0.03 ± 0.02 | 0.881 | NS | NS | NS |
| MONO [109/L] | 0.43 ± 0.31 | 0.46 ± 0.28 | 0.41 ± 0.13 | 0.156 | NS | NS | NS |
| MLR | 0.22 ± 0.14 | 0.25 ± 0.23 | 0.19 ± 0.06 | 0.010 * | NS | NS | 0.033 * |
| PLT [109/L] | 252.88 ± 65.07 | 257.57 ± 70.42 | 248.57 ± 64.36 | 0.997 | NS | NS | NS |
| PLR | 135.63 ± 53.04 | 141.77 ± 48.05 | 113.64 ± 31.56 | <0.001 * | NS | 0.003 * | <0.001 * |
| MPV [fL] | 8.21 ± 1.13 | 8.11 ± 1.04 | 7.87 ± 0.89 | 0.054 | NS | NS | NS |
| MPV/PLT | 0.04 ± 0.01 | 0.04 ± 0.01 | 0.03 ± 0.01 | 0.567 | NS | NS | NS |
| CBC Parameters and Ratios | CAS Scale | Subjective Symptoms of GO | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spontaneous Retrobulbar Pain | Ocular Pain on Attempted Upward or Downward Gaze | Redness of the Eyelids | Redness of the Conjunctiva | Swelling of the Eyelids | Chemosis of the Conjunctiva | Inflammation of Caruncule and/or Plica ** | Excessive Tearing or Dry Eyes | Diplopia | Photophobia | |
| WBC [109/L] | 6.80 ± 2.14 0.295 | 6.19 ± 1.87 0.050 * | 6.82 ± 2.09 0.531 | 6.84 ± 2.17 0.012 * | 6.66 ± 2.10 0.930 | 6.70 ± 2.11 0.483 | ** | 6.66 ± 2.13 0.890 | 7.00 ± 2.07 0.022 * | 7.14 ± 1.50 0.222 |
| NEU [109/L] | 3.93 ± 1.45 0.115 | 3.60 ± 1.33 0.260 | 4.02 ± 1.53 0.188 | 3.92 ± 1.46 0.005 * | 3.80 ± 1.38 0.804 | 3.81 ± 1.48 0.568 | ** | 3.81 ± 1.41 0.636 | 3.94 ± 1.33 0.131 | 4.21 ± 1.08 0.115 |
| LYM [109/L] | 2.08 ± 0.79 0.811 | 1.85 ± 0.68 0.013 * | 1.99 ± 0.86 0.490 | 2.10 ± 0.83 0.220 | 2.06 ± 0.83 0.886 | 2.07 ± 0.77 0.860 | ** | 2.04 ± 0.83 0.484 | 2.21 ± 0.80 0.017 * | 2.13 ± 0.62 0.670 |
| NLR | 2.03 ± 0.83 0.144 | 2.12 ± 0.99 0.050 * | 2.17 ± 0.84 0.031 * | 2.00 ± 0.80 0.050 * | 1.99 ± 0.83 0.400 | 1.96 ± 0.81 0.769 | ** | 2.00 ± 0.80 0.119 | 1.93 ± 0.84 0.713 | 2.13 ± 0.88 0.224 |
| EOS [109/L] | 0.18 ± 0.11 0.195 | 0.14 ± 0.11 0.029 * | 0.16 ± 0.10 0.553 | 0.16 ± 0.11 0.012 * | 0.17 ± 0.11 0.956 | 0.17 ± 0.11 0.391 | ** | 0.16 ± 0.11 0.257 | 0.18 ± 0.12 0.234 | 0.17 ± 0.12 0.970 |
| BASO [109/L] | 0.03 ± 0.02 0.950 | 0.03 ± 0.02 0.636 | 0.03 ± 0.02 0.978 | 0.03 ± 0.02 0.021 * | 0.03 ± 0.02 0.228 | 0.03 ± 0.02 0.151 | ** | 0.03 ± 0.02 0.466 | 0.04 ± 0.02 0.043 * | 0.03 ± 0.01 0.965 |
| MONO [109/L] | 0.47 ± 0.39 0.102 | 0.40 ± 0.20 0.403 | 0.50 ± 0.55 0.067 | 0.45 ± 0.34 0.144 | 0.45 ± 0.39 0.373 | 0.44 ± 0.33 0.500 | ** | 0.44 ± 0.35 0.334 | 0.47 ± 0.40 0.060 | 0.46 ± 0.26 0.619 |
| MLR | 0.24 ± 0.18 0.088 | 0.23 ± 0.11 0.488 | 0.27 ± 0.24 0.009 * | 0.23 ± 0.15 0.346 | 0.23 ± 0.17 0.371 | 0.23 ± 0.16 0.394 | ** | 0.23 ± 0.16 0.132 | 0.23 ± 0.18 0.702 | 0.23 ± 0.15 0.646 |
| PLT [109/L] | 254.23 ± 65.56 0.770 | 246.60 ± 68.41 0.385 | 254.79 ± 70.27 0.824 | 252.17 ± 67.13 0.768 | 256.75 ± 68.64 0.391 | 250.26 ± 65.47 0.337 | ** | 247.29 ± 67.74 0.058 | 256.94 ± 62.26 0.408 | 263.39 ± 64.50 0.406 |
| PLR | 135.05 ± 52.49 0.878 | 148.66 ± 63.84 0.026 * | 142.21 ± 55.31 0.347 | 133.84 ± 54.25 0.360 | 138.55 ± 55.02 0.429 | 134.26 ± 54.91 0.538 | ** | 135.03 ± 54.33 0.801 | 129.43 ± 53.63 0.121 | 133.95 ± 51.02 0.871 |
| MPV [fL] | 8.29 ± 1.10 0.351 | 8.02 ± 1.06 0.220 | 8.03 ± 1.10 0.278 | 8.21 ± 1.16 0.984 | 8.01 ± 1.02 0.021 * | 8.36 ± 1.19 0.035 * | ** | 8.22 ± 1.19 0.826 | 8.14 ± 1.01 0.450 | 7.93 ± 0.97 0.269 |
| MPV/PLT | 0.04 ± 0.01 0.853 | 0.04 ± 0.01 0.748 | 0.03 ± 0.01 0.246 | 0.04 ± 0.01 0.928 | 0.03 ± 0.01 0.179 | 0.04 ± 0.01 0.846 | ** | 0.04 ± 0.01 0.601 | 0.04 ± 0.01 0.568 | 0.03 ± 0.01 0.389 |
| Variable | Univariate | Multivariate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR (95% CI) | p-Value | OR (95% CI) | p-Value | |
| Female | 1.059 (0.635–1.766) | 0.825 | ||
| Smoking | 1.656 (1.084–2.531) | 0.020 * | ||
| WBC | 1.232 (1.101–1.380) | <0.001 * | 1.209 (1.078–1.355) | 0.001 * |
| NEU | 1.421 (1.203–1.680) | <0.001 * | ||
| LYM | 1.280 (0.967–1.693) | 0.084 | ||
| NLR | 1.468 (1.093–1.970) | 0.011 * | 1.348 (1.078–1.355) | 0.048 * |
| EOS | 0.613 (0.167–2.243) | 0.459 | ||
| BASO | 9.797 (0.046–2081.645) | 0.404 | ||
| MONO | 0.720 (0.336–1.542) | 0.398 | ||
| MLR | 0.285 (0.052–1.579) | 0.151 | ||
| PLT | 0.999 (0.996–1.002) | 0.531 | ||
| PLR | 0.998 (0.994–1.002) | 0.239 | ||
| MPV | 1.096 (0.868–1.385) | 0.441 | ||
| MPV/PLT | 0.021 (0.000–6175859.283) | 0.698 | ||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Szydełko, J.; Litwińczuk, M.; Szydełko, M.; Matyjaszek-Matuszek, B. Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte, Monocyte-to-Lymphocyte and Platelet-to-Lymphocyte Ratios in Relation to Clinical Parameters and Smoking Status in Patients with Graves’ Orbitopathy—Novel Insight into Old Tests. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3111. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9103111
Szydełko J, Litwińczuk M, Szydełko M, Matyjaszek-Matuszek B. Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte, Monocyte-to-Lymphocyte and Platelet-to-Lymphocyte Ratios in Relation to Clinical Parameters and Smoking Status in Patients with Graves’ Orbitopathy—Novel Insight into Old Tests. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2020; 9(10):3111. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9103111
Chicago/Turabian StyleSzydełko, Joanna, Michał Litwińczuk, Magdalena Szydełko, and Beata Matyjaszek-Matuszek. 2020. "Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte, Monocyte-to-Lymphocyte and Platelet-to-Lymphocyte Ratios in Relation to Clinical Parameters and Smoking Status in Patients with Graves’ Orbitopathy—Novel Insight into Old Tests" Journal of Clinical Medicine 9, no. 10: 3111. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9103111
APA StyleSzydełko, J., Litwińczuk, M., Szydełko, M., & Matyjaszek-Matuszek, B. (2020). Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte, Monocyte-to-Lymphocyte and Platelet-to-Lymphocyte Ratios in Relation to Clinical Parameters and Smoking Status in Patients with Graves’ Orbitopathy—Novel Insight into Old Tests. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(10), 3111. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9103111





