Stronger Correlations between Neurophysiological and Peripheral Disease Biomarkers Predict Better Prognosis in Two Severe Diseases
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
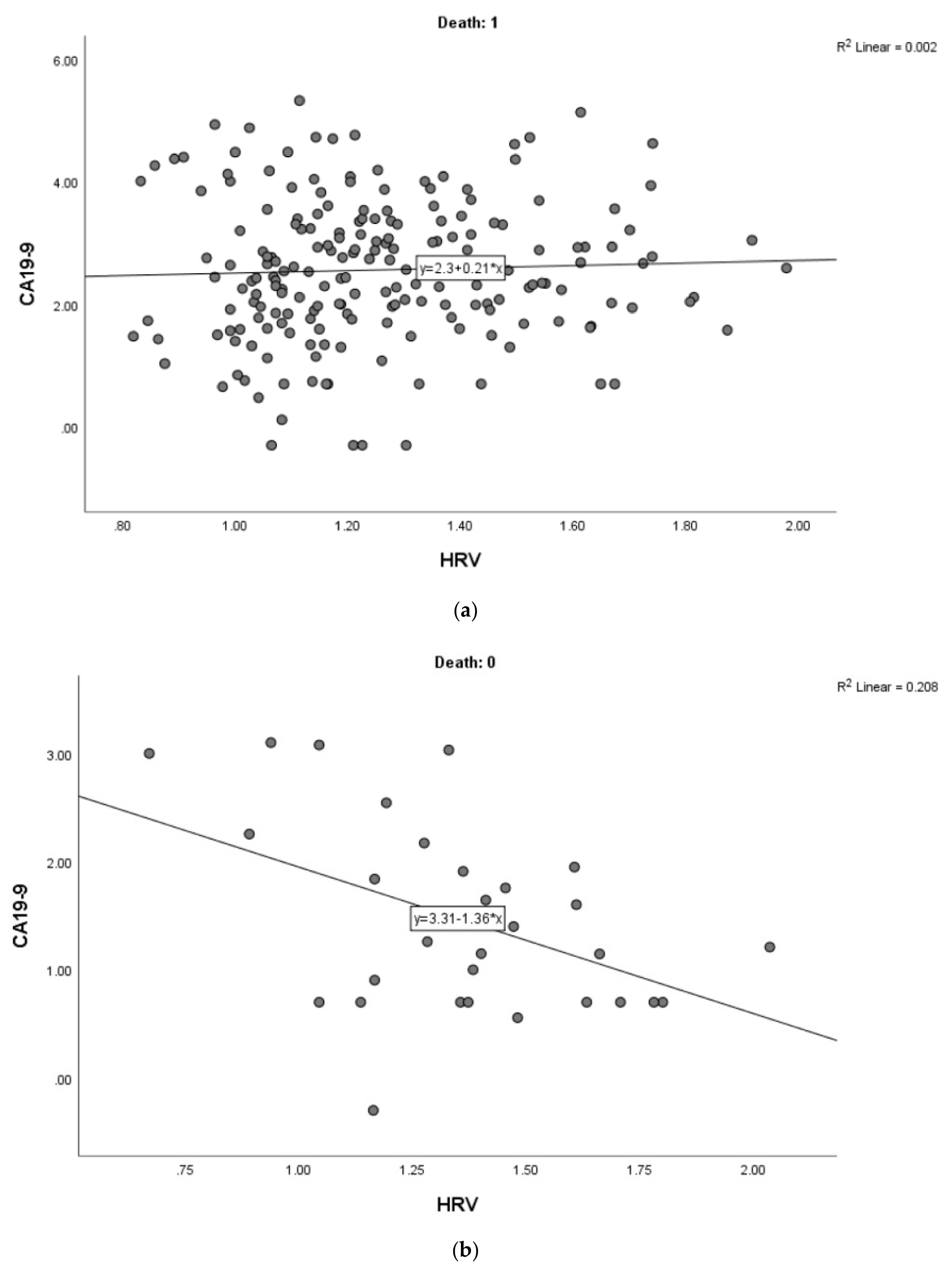
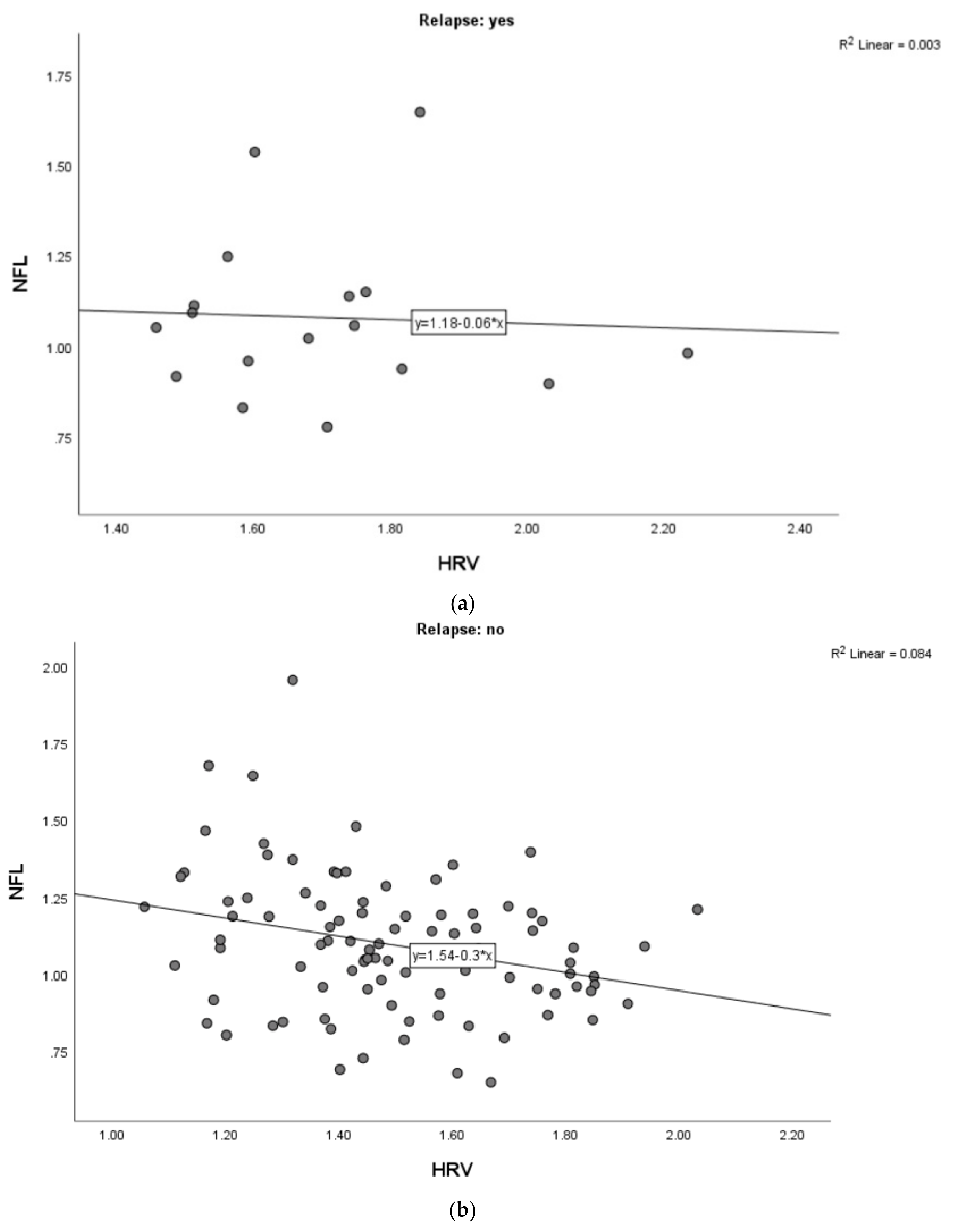
3. Result
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Suvak, M.K.; Barrett, L.F. Considering PTSD from the perspective of brain processes: A psychological construction approach. J. Trauma Stress 2011, 24, 3–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, S.; Janicki-Deverts, D.; Doyle, W.J.; Miller, G.E.; Frank, E.; Rabin, B.S.; Turner, R.B. Chronic stress, glucocorticoid receptor resistance, inflammation, and disease risk. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 5995–5999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nathan, C.; Ding, A. Nonresolving inflammation. Cell 2010, 140, 871–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tracey, K.J. Reflex control of immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunolgy 2009, 9, 418–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, T.B.J.; Lai, C.J.; Huang, Y.-T.; Yang, C.C.H. Regression Analysis between Heart Rate Variability and Baroreflex-Related Vagus Nerve Activity in Rats. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2005, 16, 864–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aeschbacher, S.; Bossard, M.; Ruperti Repilado, F.J.; Good, N.; Schoen, T.; Zimny, M.; Probst-Hensch, N.M.; Schmidt-Trucksäss, A.; Risch, M.; Risch, L.; et al. Healthy lifestyle and heart rate variability in young adults. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2016, 23, 1037–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thayer, J.F.; Ahs, F.; Fredrikson, M.; Sollers, J.J., 3rd; Wager, T.D. A meta-analysis of heart rate variability and neuroimaging studies: Implications for heart rate variability as a marker of stress and health. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2012, 36, 747–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buccelletti, E.; Gilardi, E.; Scaini, E.; Galiuto, L.; Persiani, R.; Biondi, A.; Basile, F.; Silveri, N.G. Heart rate variability and myocardial infarction: Systematic literature review and metanalysis. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2009, 13, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Ma, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, S.; Wang, J.; Wang, B.; Fu, W. Heart rate variability in the prediction of survival in patients with cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Psychosom. Res. 2016, 89, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gidron, Y.; Deschepper, R.; De Couck, M.; Thayer, J.F.; Velkeniers, B. The Vagus Nerve Can Predict and Possibly Modulate Non-Communicable Chronic Diseases: Introducing a Neuroimmunological Paradigm to Public Health. J. Clin. Med. 2018, 7, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohira, H.; Matsunaga, M.; Osumi, T.; Fukuyama, S.; Shinoda, J.; Yamada, J.; Gidron, Y. Vagal nerve activity as a moderator of brain–immune relationships. J. Neuroimmunol. 2013, 260, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glazer Baron, K.; Reid, K.J. Circadian misalignment and health. Int. Rev. Psychiatry 2014, 26, 139–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamilton, R.M.; McKechnie, P.S.; Macfarlane, P.W. Can cardiac vagal tone be estimated from the 10-second ECG? Int. J. Cardiol. 2004, 95, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lerman, I.; Hauger, R.; Sorkin, L.; Proudfoot, J.; Davis, B.; Huang, A.; Lam, K.; Simon, B.; Baker, D.G. Noninvasive Transcutaneous Vagus Nerve Stimulation Decreases Whole Blood Culture-Derived Cytokines and Chemokines: A Randomized, Blinded, Healthy Control Pilot Trial. Neuromodulation 2016, 19, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gidron, Y.; De Couck, M.; Reynders, T.; Marechal, R.; Engelborghs, S.; D’hooghe, M. Stronger Correlations between Neurophysiological and Peripheral Disease Biomarkers Predict Better Prognosis in Two Severe Diseases. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9010026
Gidron Y, De Couck M, Reynders T, Marechal R, Engelborghs S, D’hooghe M. Stronger Correlations between Neurophysiological and Peripheral Disease Biomarkers Predict Better Prognosis in Two Severe Diseases. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2020; 9(1):26. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9010026
Chicago/Turabian StyleGidron, Yori, Marijke De Couck, Tatjana Reynders, Raphael Marechal, Sebastiaan Engelborghs, and Marie D’hooghe. 2020. "Stronger Correlations between Neurophysiological and Peripheral Disease Biomarkers Predict Better Prognosis in Two Severe Diseases" Journal of Clinical Medicine 9, no. 1: 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9010026
APA StyleGidron, Y., De Couck, M., Reynders, T., Marechal, R., Engelborghs, S., & D’hooghe, M. (2020). Stronger Correlations between Neurophysiological and Peripheral Disease Biomarkers Predict Better Prognosis in Two Severe Diseases. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(1), 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9010026




