Fractional Excretion of Phosphate (FeP) Is Associated with End-Stage Renal Disease Patients with CKD 3b and 5
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Data Collection
2.2. Outcome Assessment
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bellasi, A.; Mandreoli, M.; Baldrati, L.; Corradini, M.; Di Nicolo, P.; Malmusi, G.; Santoro, A. Chronic Kidney Disease Progression and Outcome According to Serum Phosphorus in Mild-to-Moderate Kidney Dysfunction. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 6, 883–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, S.C.; Hayen, A.; Macaskill, P.; Pellegrini, F.; Craig, J.C.; Elder, G.J.; Strippoli, G.F. Serum levels of phosphorus, parathyroid hormone, and calcium and risks of death and cardiovascular disease in individuals with chronic kidney disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA 2011, 305, 1119–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoccali, C.; Ruggenenti, P.; Perna, A.; Leonardis, D.; Tripepi, R.; Tripepi, G.; Mallamaci, F.; Remuzzi, G. Phosphate may promote CKD progression and attenuate renoprotective effect of ACE inhibition. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 22, 1923–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dominguez, J.R.; Shlipak, M.G.; Whooley, M.A.; Ix, J.H. Fractional Excretion of Phosphorus Modifies the Association between Fibroblast Growth Factor-23 and Outcomes. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2013, 24, 647–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isakova, T.; Wahl, P.; Vargas, G.S.; Gutiérrez, O.M.; Scialla, J.; Xie, H.; Appleby, D.; Nessel, L.; Bellovich, K.; Chen, J.; et al. Fibroblast growth factor 23 is elevated before parathyroid hormone and phosphate in chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2011, 79, 1370–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellasi, A. Pro: Should phosphate binders be used in chronic kidney disease stage 3–4? Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2016, 31, 184–188. [Google Scholar]
- Vervloet, M.G.; Sezer, S.; Massy, Z.A.; Johansson, L.; Cozzolino, M.; Fouque, D. The role of phosphate in kidney disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2017, 13, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellasi, A.; Di Lullo, L.; Raggi, P. Cardiovascular calcification: The emerging role of micronutrients. Atherosclerosis 2018, 273, 119–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henaut, L.; Chillon, J.M.; Kamel, S.; Massy, Z.A. Updates on the Mechanisms and the Care of Cardiovascular Calcification in Chronic Kidney Disease. Semin. Nephrol. 2018, 38, 233–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeney, K.L.; Siscovick, D.S.; Ix, J.H.; Seliger, S.L.; Shlipak, M.G.; Jenny, N.S.; Kestenbaum, B.R. Association of serum phosphate with vascular and valvular calcification in moderate CKD. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 20, 381–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chue, C.D.; Edwards, N.C.; Davis, L.J.; Steeds, R.P.; Townend, J.N.; Ferro, C.J. Serum phosphate but not pulse wave velocity predicts decline in renal function in patients with early chronic kidney disease. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2011, 26, 2576–2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ix, J.H.; De Boer, I.H.; Peralta, C.A.; Adeney, K.L.; Duprez, D.A.; Jenny, N.S.; Siscovick, D.S.; Kestenbaum, B.R. Serum phosphorus concentrations and arterial stiffness among individuals with normal kidney function to moderate kidney disease in MESA. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 4, 609–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Iorio, B.R.; Bellizzi, V.; Bellasi, A.; Torraca, S.; D’Arrigo, G.; Tripepi, G.; Zoccali, C. Phosphate attenuates the anti-proteinuric effect of very low-protein diet in CKD patients. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2013, 28, 632–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Nicola, L.; Provenzano, M.; Chiodini, P.; Borrelli, S.; Russo, L.; Bellasi, A.; Santoro, D.; Conte, G.; Minutolo, R. Epidemiology of low-proteinuric chronic kidney disease in renal clinics. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0172241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cirillo, M.; Ciacci, C.; De Santo, N.G. Age, renal tubular phosphate reabsorption, and serum phosphate levels in adults. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 864–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, K.M.; Martin, B.R.; Wastney, M.E.; McCabe, G.P.; Moe, S.M.; Weaver, C.M.; Peacock, M. Oral calcium carbonate affects calcium but not phosphorus balance in stage 3-4 chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2013, 83, 959–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selamet, U.; Tighiouart, H.; Sarnak, M.J.; Beck, G.; Levey, A.S.; Block, G.; Ix, J.H. Relationship of dietary phosphate intake with risk of end-stage renal disease and mortality in chronic kidney disease stages 3–5: The Modification of Diet in Renal Disease Study. Kidney Int. 2016, 89, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuro-o, M. Klotho, phosphate and FGF-23 in ageing and disturbed mineral metabolism. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2013, 9, 650–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levey, A.S.; Stevens, L.A.; Schmid, C.H.; Zhang, Y.L.; Castro, A.F.; Feldman, H.I.; Kusek, J.W.; Eggers, P.; Van Lente, F.; Greene, T.; et al. A new equation to estimate glomerular filtration rate. Ann. Intern. Med. 2009, 150, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shlipak, M.G.; Katz, R.; Kestenbaum, B.; Siscovick, D.; Fried, L.; Newman, A.; Rifkin, D.; Sarnak, M.J. Rapid decline of kidney function increases cardiovascular risk in the elderly. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 20, 2625–2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.R. Crystal-induced inflammation of the kidneys: Results from human studies, animal models, and tissue-culture studies. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2004, 8, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuro, O.M. Klotho and endocrine fibroblast growth factors: Markers of chronic kidney disease progression and cardiovascular complications? Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2019, 34, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruggiero, B.; Trillini, M.; Tartaglione, L.; Rotondi, S.; Perticucci, E.; Tripepi, R.; Aparicio, C.; Lecchi, V.; Perna, A.; Peraro, F.; et al. Effects of Sevelamer Carbonate in Patients With CKD and Proteinuria: The ANSWER Randomized Trial. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chue, C.D.; Townend, J.N.; Moody, W.E.; Zehnder, D.; Wall, N.A.; Harper, L.; Edwards, N.C.; Steeds, R.P.; Ferro, C.J. Cardiovascular Effects of Sevelamer in Stage 3 CKD. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2013, 24, 842–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Block, G.A.; Wheeler, D.C.; Persky, M.S.; Kestenbaum, B.; Ketteler, M.; Spiegel, D.M.; Allison, M.A.; Asplin, J.; Smits, G.; Hoofnagle, A.N.; et al. Effects of phosphate binders in moderate CKD. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2012, 23, 1407–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moranne, O.; Froissart, M.; Rossert, J.; Gauci, C.; Boffa, J.J.; Haymann, J.P.; M’rad, M.B.; Jacquot, C.; Houillier, P.; Stengel, B.; et al. Timing of onset of CKD-related metabolic complications. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 20, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ix, J.H.; Anderson, C.A.; Smits, G.; Persky, M.S.; Block, G.A. Effect of dietary phosphate intake on the circadian rhythm of serum phosphate concentrations in chronic kidney disease: A crossover study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 100, 1392–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakobsuk, S.; Sirilak, S.; Vipattawat, K.; Taweesedt, P.T.; Sumethkul, V.; Kantachuvesiri, S.; Disthabanchong, S. Hyperparathyroidism and increased fractional excretion of phosphate predict allograft loss in long-term kidney transplant recipients. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2017, 21, 926–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, T.; Maeda, Y.; Matsuki, H.; Matsumoto, Y.; Akazawa, M.; Kuyama, T. Urinary phosphorus excretion per creatinine clearance as a prognostic marker for progression of chronic kidney disease: A retrospective cohort study. BMC Nephrol. 2015, 16, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santamaria, R.; Diaz-Tocados, J.M.; de Mier, P.R.M.V.; Robles, A.; Salmerón-Rodríguez, M.D.; Ruiz, E.; Vergara, N.; Aguilera-Tejero, E.; Raya, A.; Ortega, R.; et al. Increased Phosphaturia Accelerates The Decline in Renal Function: A Search for Mechanisms. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
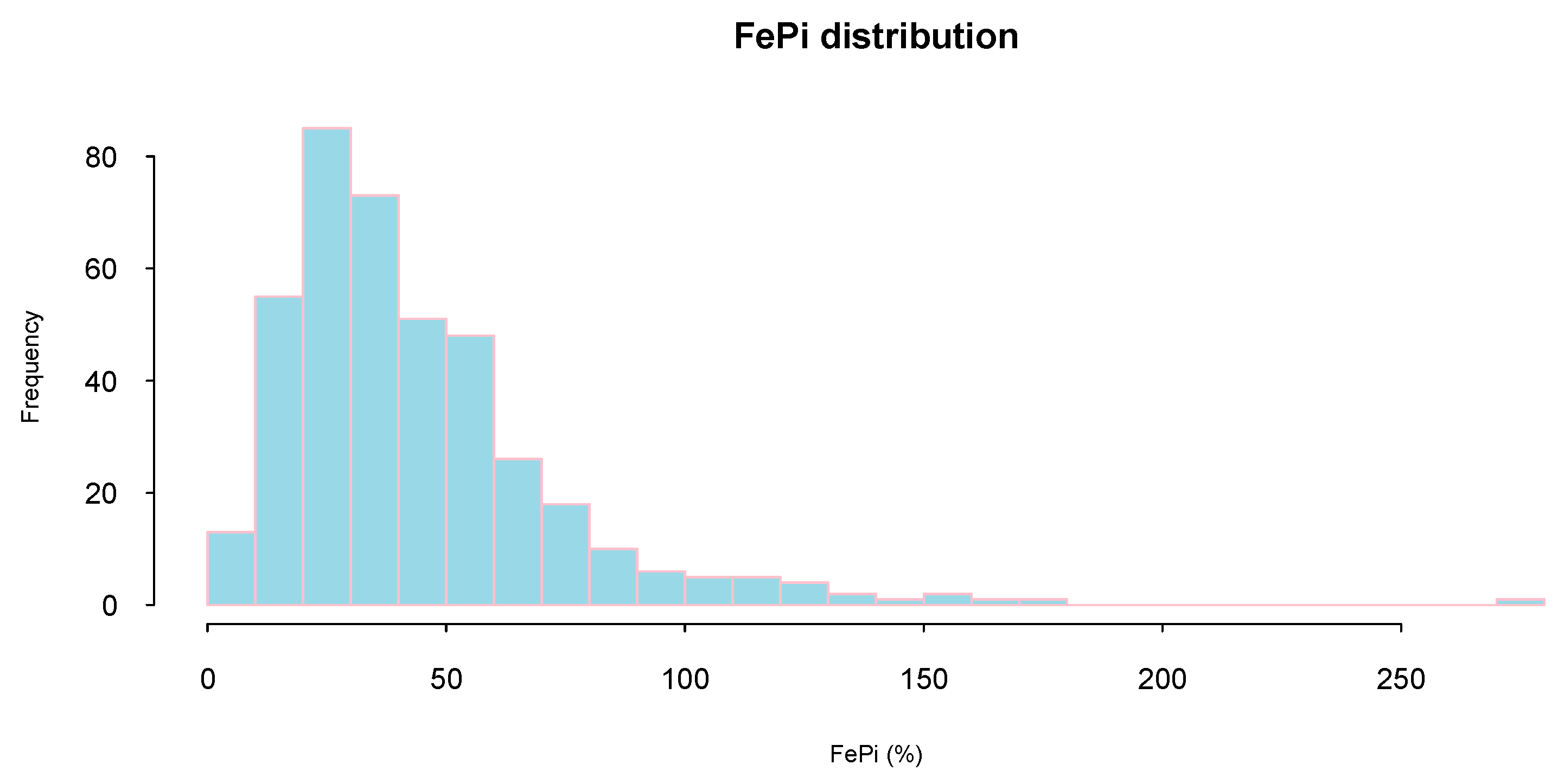
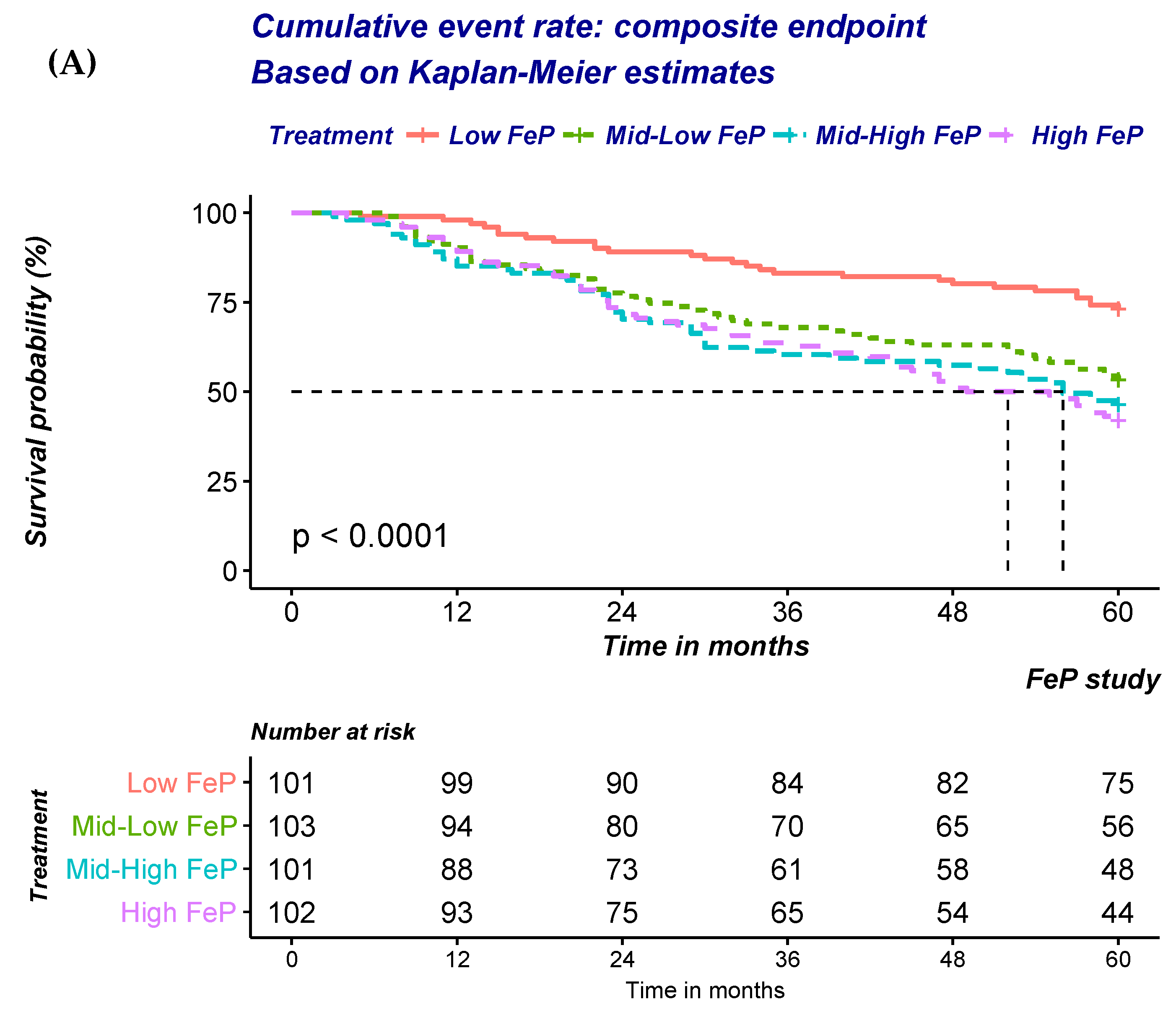
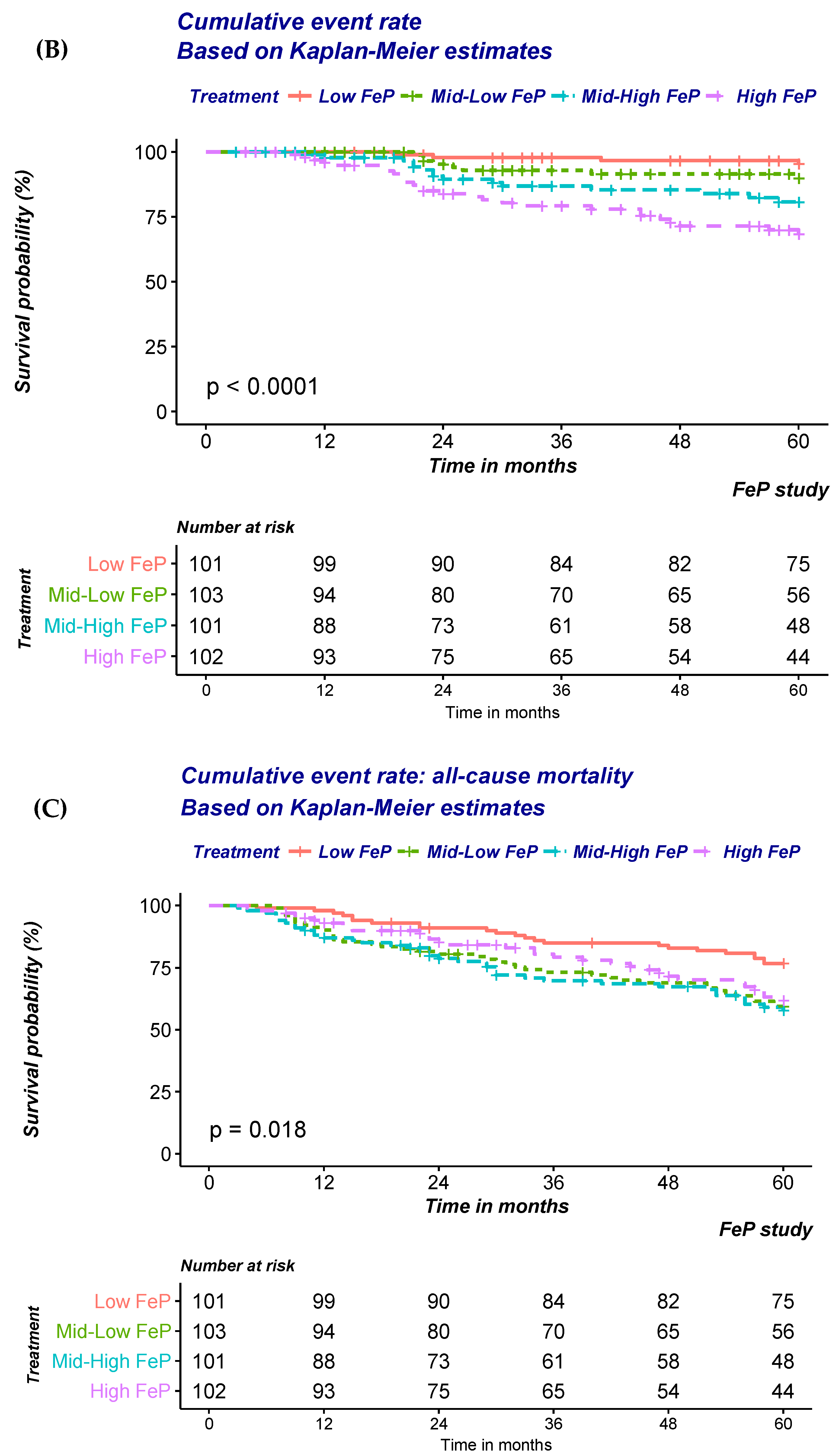
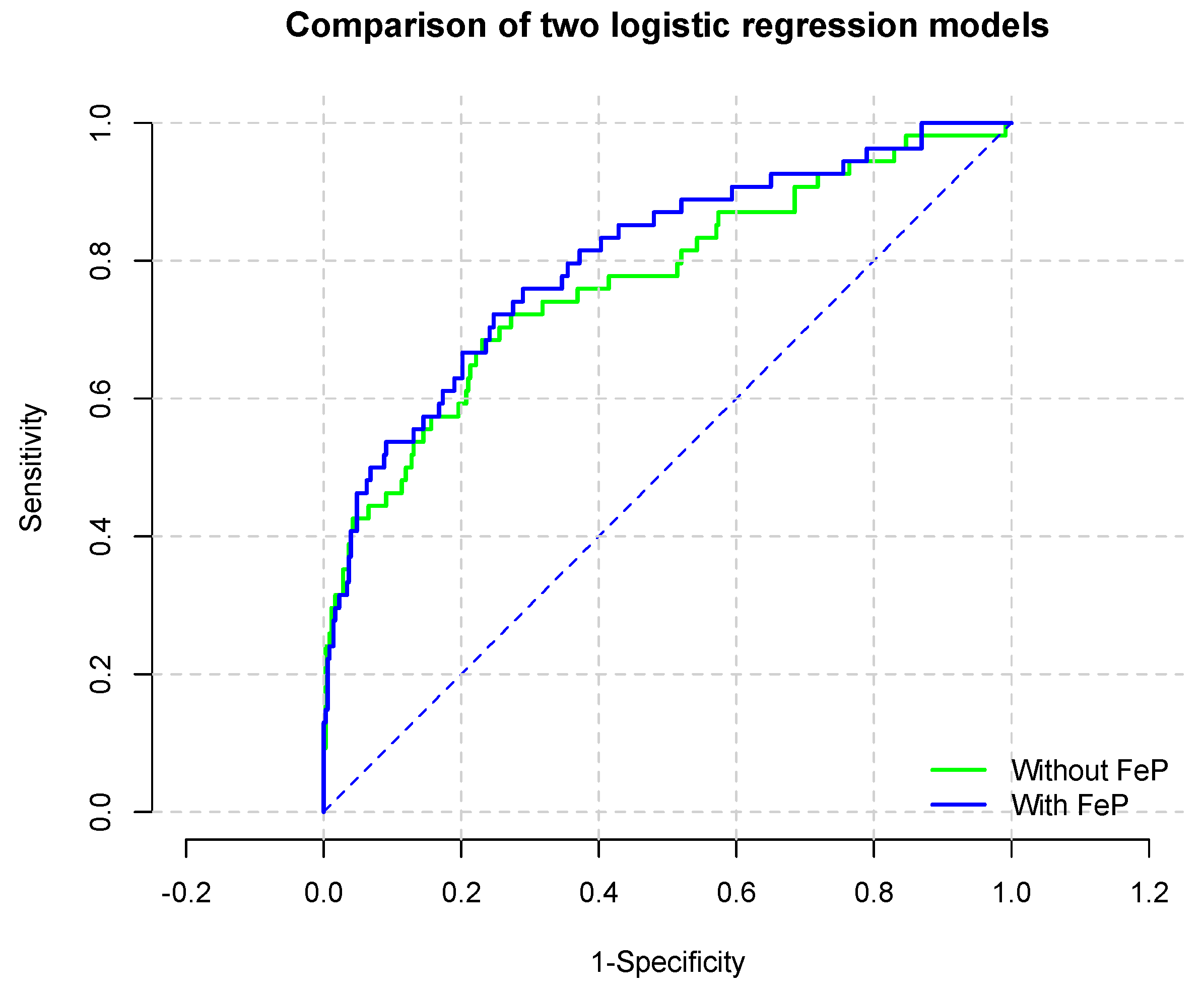
| Total (n = 407) | Low Quartile (n = 102) | Mid–Low Quartile (n = 102) | Mid–High Quartile (n = 101) | High Quartile (n = 102) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | Mean (SD) (n) | Mean (SD) (n) | Mean (SD) (n) | Mean (SD) (n) | Mean (SD) (n) | p-Value |
| Age (years) | 66 (12.31) (407) | 68.24 (11.23) (102) | 66.99 (10.42) (102) | 66.61 (12.09) (101) | 62.16 (14.44) (102) | 0.009 |
| Female (%) | 43.73% (178) | 50.98% (52) | 39.22% (40) | 37.62% (38) | 47.06% (48) | 0.171 |
| CKD etiology % (n) | 0.426 | |||||
| Unknown cause | 18.23% (406) | 15.62% (15) | 20.39% (21) | 20% (21) | 16.67(17) | |
| Diabetes mellitus | 37.68% (153) | 37.5% (36) | 38.83% (40) | 32.38% (34) | 42.16% (43) | |
| APKD | 1.72% (7) | 3.12% (3) | 0% (0) | 2.86% (3) | 0.98% (1) | |
| Cardiorenal syndrome | 7.88% (32) | 5.21% (5) | 10.68% (11) | 6.67% (7) | 8.82% (9) | |
| Hypertension | 23.4% (95) | 30.21% (29) | 20.39% (21) | 20% (21) | 23.53% (24) | |
| Glomerulonephritis | 7.88% (32) | 6.25% (6) | 7.77% (8) | 12.38% (13) | 4.9% (5) | |
| Other etiology | 3.2% (13) | 2.08% (2) | 1.94% (2) | 5.71% (6) | 2.94% (3) | |
| Protein intake (g/Kg/day) | 0.74 (0.24) (407) | 0.71 (0.28) (102) | 0.7 (0.21) (102) | 0.76 (0.23) (101) | 0.79 (0.23) (102) | 0.03 |
| BMI (m2/kg) | 28.24 (5.48) (407) | 27.93 (6.08) (102) | 28.9 (4.96) (102) | 28.22 (5.19) (101) | 27.9 (5.63) (102) | 0.495 |
| Systolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 124.88 (17.39) (407) | 125.23 (16.48) (102) | 123.02 (17.72) (102) | 125.74 (18.49) (101) | 125.55 (16.93) (102) | 0.674 |
| Diastolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 74.02 (9.09) (407) | 73.24 (8.42) (102) | 72.88 (11.01) (102) | 74.19 (8.51) (101) | 75.79 (7.94) (102) | 0.079 |
| Cardiovascular disease (%) | 18.18% (74) | 18.63% (19) | 19.61% (20) | 16.83% (17) | 17.65% (18) | 0.961 |
| Diabetes mellitus (%) | 37.59% (153) | 37.25% (38) | 34.31% (35) | 38.61% (39) | 40.2% (41) | 0.847 |
| Hypertension (%) | 37.1% (151) | 41.18% (42) | 41.18% (42) | 34.65% (35) | 31.37% (32) | 0.37 |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 12.11 (1.54) (407) | 11.99 (1.53) (102) | 11.85 (1.43) (102) | 12.5 (1.59) (101) | 12.09 (1.57) (102) | 0.021 |
| Glucose (mg/dL) | 123.27 (69.08) (407) | 121.58 (37.96) (102) | 114.62 (41.98) (102) | 132.3 (115.6) (101) | 124.69 (50.84) (102) | 0.286 |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 3.83 (0.39) (407) | 3.72 (0.41) (102) | 3.83 (0.33) (102) | 3.86 (0.37) (101) | 3.89 (0.42) (102) | 0.027 |
| Azotemia (mg/dL) | 92.44 (37.15) (407) | 103.56 (35.82) (102) | 95.27 (36.7) (102) | 82.06 (34.15) (101) | 88.75 (38.83) (102) | 0.0002 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 2.35 (0.91) (407) | 2.69 (1.01) (102) | 2.48 (0.97) (102) | 2.07 (0.81) (101) | 2.14 (0.71) (102) | <0.0001 |
| Creatinine Clearance (mL/min) | 32.07 (13.31) (407) | 26.96 (12.91) (102) | 30.6 (11.67) (102) | 35.09 (12.05) (101) | 35.64 (14.65) (102) | <0.0001 |
| Phosphate (mg/dL) | 3.88 (0.86) (407) | 3.42 (0.68) (102) | 3.82 (0.6) (102) | 3.86 (0.73) (101) | 4.42 (1.05) (102) | <0.0001 |
| Calcium (mg/dL) | 9.13 (0.6) (407) | 9.05 (0.67) (102) | 9.11 (0.64) (102) | 9.16 (0.53) (101) | 9.19 (0.53) (102) | 0.392 |
| PTH (pg/mL) | 153.63 (124.71) (407) | 166.31 (123.2) (102) | 166.26 (128.84) (102) | 122.37 (81.33) (101) | 159.26 (151.17) (102) | 0.003 |
| Potassium (mEq/L) | 4.9 (0.69) (407) | 4.82 (0.7) (102) | 4.96 (0.61) (102) | 4.82 (0.67) (101) | 4.98 (0.75) (102) | 0.171 |
| Sodium (mEq/L) | 139.57 (3.16) (407) | 139.54 (3.21) (102) | 139.96 (3.01) (102) | 139.33 (3.09) (101) | 139.47 (3.33) (102) | 0.49 |
| Bicarbonate (mEq/L) | 23.64 (3.06) (407) | 23.59 (3.25) (102) | 23.57 (3.22) (102) | 23.91 (3.01) (101) | 23.5 (2.79) (102) | 0.766 |
| Uric Acid (mg/dL) | 5 (1.69) (407) | 5.1 (1.76) (102) | 5.04 (1.68) (102) | 4.9 (1.54) (101) | 4.97 (1.79) (102) | 0.833 |
| Cholesterol (mg/dL) | 159.02 (35.57) (407) | 158.75 (31.51) (102) | 156.67 (32.8) (102) | 154.37 (35.18) (101) | 166.26 (41.36) (102) | 0.156 |
| LDL cholesterol (mg/dL) | 91.65 (28.39) (407) | 90.45 (22.22) (102) | 89.04 (28.79) (102) | 91.57 (29.93) (101) | 95.52 (31.74) (102) | 0.464 |
| Triglicerides (mg/dL) | 142.74 (60.57) (406) | 146.36 (80.15) (102) | 131.37 (48.65) (102) | 138.11 (49.14) (101) | 155.21 (56.92) (101) | 0.013 |
| C-reactive protein | 5.93 (7.57) (406) | 6.39 (8.34) (102) | 5.78 (5.81) (102) | 5.84 (8.24) (101) | 5.69 (7.72) (101) | 0.924 |
| Homocystein | 42.27 (48) (404) | 43.15 (41.61) (101) | 30.66 (24.26) (102) | 38.31 (44.25) (100) | 57.05 (68.17) (101) | 0.001 |
| 24-h phosphaturia (mg/day) | 518.67 (237.99) (407) | 533.12 (249.77) (102) | 501.85 (221.58) (102) | 525.44 (226.65) (101) | 514.35 (254.49) (102) | 0.792 |
| FePi (%) | 44.19 (30.09) (407) | 82.07 (34.03) (102) | 45.68 (8.72) (102) | 30.8 (6.7) (101) | 18.08 (6.55) (102) | <0.0001 |
| 24 h sodiuria (mEq/day) | 137.2 (53.95) (407) | 132.4 (53.27) (102) | 132.31 (47.5) (102) | 144.25 (59.71) (101) | 139.92 (54.52) (102) | 0.326 |
| 24-h potassiuria (mEq/day) | 43.49 (18.01) (407) | 39.05 (15.21) (102) | 43.94 (17.72) (102) | 45.49 (17.49) (101) | 45.51 (20.68) (102) | 0.015 |
| 24-h proteinuria (mg/day) | 484.14 (725.41) (407) | 466.78 (784.05) (102) | 488.08 (673.73) (102) | 370.96 (485.15) (101) | 609.64 (885.77) (102) | 0.1 |
| Estimate | Std. Error | t Value | Pr(>|t|) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Intercept) | 5.040 | 0.454 | 11.108 | <2 × 10−16 | *** |
| Creatinine Clearance (mL/min) | −0.015 | 0.003 | −5.574 | 0.000 | *** |
| age (years) | 0.004 | 0.002 | 1.886 | 0.060 | . |
| Protein Intake (g/Kg/day) | −0.170 | 0.128 | −1.324 | 0.186 | |
| Azotemia (mg/dL) | 0.003 | 0.001 | 3.960 | 0.000 | *** |
| Diastolic Blood Pressure (mmHg) | −0.006 | 0.003 | −2.001 | 0.046 | * |
| Albumin (g/dL) | −0.047 | 0.074 | −0.636 | 0.525 | |
| Serum Phosphate (mg/dL) | −0.221 | 0.034 | −6.479 | 0.000 | *** |
| Parathyroid hormone (pg/mL) | 0.000 | 0.000 | 1.176 | 0.240 | |
| Triglicerides (mg/dL) | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.685 | 0.494 | |
| 24-h potassiuria (mEq/day) | −0.001 | 0.002 | −0.552 | 0.581 |
| OR | LCI | UCI | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Creatinine Clearance (mL/min) | 0.995 | 0.992 | 0.998 | ** |
| age (years) | 1.003 | 1 | 1.006 | |
| Protein Intake (g/Kg/day) | 0.919 | 0.781 | 1.082 | |
| Azotemia (mg/dL) | 1 | 0.999 | 1.001 | |
| Diastolic Blood Pressure (mmHg) | 0.995 | 0.992 | 0.999 | * |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 0.933 | 0.849 | 1.026 | |
| Serum Phosphate (mg/dL) | 0.939 | 0.899 | 0.981 | ** |
| Parathyroid hormone (pg/mL) | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| Triglicerides (mg/dL) | 1 | 0.999 | 1.001 | |
| 24-h potassiuria (mEq/day) | 1 | 0.998 | 1.002 |
| (A) Risk of ESRD or all-cause mortality according to quartile of FePi. | ||||
| Unadjusted | exp(coef) | lower. 95 u | upper. 95 | Pr (>|z|) |
| Low FePi | Ref | Ref | Ref | Ref |
| Mid-low FePi | 2.06 | 1.29 | 3.30 | 0.003 |
| Mid-High FePi | 2.54 | 1.60 | 4.04 | 0.000 |
| High FePi | 2.75 | 1.74 | 4.34 | 0.000 |
| Case-Mix adjusetd | exp(coef) | lower. 95 u | upper. 95 | Pr (>|z|) |
| Low FePi | Ref | Ref | Ref | Ref |
| Mid-low FePi | 1.80 | 1.12 | 2.90 | 0.015 |
| Mid-High FePi | 2.20 | 1.38 | 3.51 | 0.001 |
| High FePi | 2.42 | 1.50 | 3.91 | 0.000 |
| Fully adjusetd | exp(coef) | lower. 95 u | upper. 95 | Pr (>|z|) |
| Low FePi | Ref | Ref | Ref | Ref |
| Mid-low FePi | 2.02 | 1.23 | 3.31 | 0.006 |
| Mid-High FePi | 2.29 | 1.42 | 3.71 | 0.001 |
| High FePi | 2.40 | 1.44 | 3.99 | 0.001 |
| (B) Risk of ESRD according to quartile of FePi | ||||
| Unadjusted | exp(coef) | lower. 95 u | upper. 95 | Pr (>|z|) |
| Low FePi | Ref | Ref | Ref | Ref |
| Mid-low FePi | 2.32 | 0.70 | 7.70 | 0.170 |
| Mid-High FePi | 4.73 | 1.57 | 14.25 | 0.006 |
| High FePi | 8.46 | 2.96 | 24.20 | 0.000 |
| Case-Mix adjusetd | exp(coef) | lower. 95 u | upper. 95 | Pr (>|z|) |
| Low FePi | Ref | Ref | Ref | Ref |
| Mid-low FePi | 2.31 | 0.69 | 7.71 | 0.174 |
| Mid-High FePi | 4.49 | 1.47 | 13.68 | 0.008 |
| High FePi | 6.47 | 2.16 | 19.41 | 0.001 |
| Fully adjusetd | exp(coef) | lower. 95 u | upper. 95 | Pr (>|z|) |
| Low FePi | Ref | Ref | Ref | Ref |
| Mid-low FePi | 3.29 | 0.88 | 12.33 | 0.078 |
| Mid-High FePi | 7.34 | 2.14 | 25.16 | 0.002 |
| High FePi | 12.34 | 3.65 | 41.73 | 0.000 |
| (C) Risk of All-cause mortality according to quartile of FePi | ||||
| Unadjusted | exp(coef) | lower. 95 u | upper. 95 | Pr (>|z|) |
| Low FePi | Ref | Ref | Ref | Ref |
| Mid-low FePi | 2.01 | 1.21 | 3.36 | 0.008 |
| Mid-High FePi | 2.16 | 1.29 | 3.61 | 0.004 |
| High FePi | 1.75 | 1.02 | 2.99 | 0.041 |
| Case-Mix adjusetd | exp(coef) | lower. 95 u | upper.95 | Pr (>|z|) |
| Low FePi | Ref | Ref | Ref | Ref |
| Mid-low FePi | 1.43 | 0.85 | 2.41 | 0.175 |
| Mid-High FePi | 1.79 | 1.06 | 3.01 | 0.030 |
| High FePi | 1.45 | 0.83 | 2.56 | 0.193 |
| Fully adjusetd | exp(coef) | lower. 95 u | upper. 95 | Pr (>|z|) |
| Low FePi | Ref | Ref | Ref | Ref |
| Mid-low FePi | 1.44 | 0.84 | 2.49 | 0.187 |
| Mid-High FePi | 1.68 | 0.98 | 2.88 | 0.058 |
| High FePi | 1.33 | 0.72 | 2.46 | 0.359 |
| Estimate | Std. Error | z Value | Pr (>|z|) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Intercept) | 0.58 | 1.99 | 0.29 | 0.771 | |
| High FeP % (>75th percentile of study cohort distribution) | 1.42 | 0.37 | 3.79 | 0.000 | *** |
| Age (years) | −0.04 | 0.01 | −3.18 | 0.001 | ** |
| History of diabetes (yes vs. no) | 0.66 | 0.34 | 1.94 | 0.052 | . |
| Diastolic blood pressure (mmHg) | −0.03 | 0.02 | −1.86 | 0.063 | . |
| Azotemia (mg/dL) | 0.01 | 0.00 | 2.46 | 0.014 | * |
| Serum Phsophate (mg/dL) | 0.48 | 0.19 | 2.48 | 0.013 | * |
| 24-urine potassium | 0.02 | 0.01 | 2.13 | 0.033 | * |
| Protein Intake (g/Kg/day) | −1.17 | 0.36 | −3.25 | 0.001 | ** |
| Model | Estimate |
|---|---|
| Most parsimonious model without high-Fep | |
| C-statistic (95% CI) | 0.770 (95% CI: 0.695–0.846) |
| Most parsimonious model with high-Fep | |
| C-statistic (95% CI) | 0.802 (95% CI: 0.734–0.869) |
| Comparison of models | |
| Chi-square (p value) | 10.9 (0.0009) |
| IDI (95% CI) (p value) | 0.027 (−0.004−0.0544) (0.053) |
| Continuous NRI (95% CI) (p value) | 0.46(0.18−0.74) (0.001) |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bellasi, A.; Di Micco, L.; Russo, D.; De Simone, E.; Di Iorio, M.; Vigilante, R.; Di Lullo, L.; Di Iorio, B.R. Fractional Excretion of Phosphate (FeP) Is Associated with End-Stage Renal Disease Patients with CKD 3b and 5. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1026. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8071026
Bellasi A, Di Micco L, Russo D, De Simone E, Di Iorio M, Vigilante R, Di Lullo L, Di Iorio BR. Fractional Excretion of Phosphate (FeP) Is Associated with End-Stage Renal Disease Patients with CKD 3b and 5. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2019; 8(7):1026. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8071026
Chicago/Turabian StyleBellasi, Antonio, Lucia Di Micco, Domenico Russo, Emanuele De Simone, Mattia Di Iorio, Raffaella Vigilante, Luca Di Lullo, and Biagio Raffaele Di Iorio. 2019. "Fractional Excretion of Phosphate (FeP) Is Associated with End-Stage Renal Disease Patients with CKD 3b and 5" Journal of Clinical Medicine 8, no. 7: 1026. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8071026
APA StyleBellasi, A., Di Micco, L., Russo, D., De Simone, E., Di Iorio, M., Vigilante, R., Di Lullo, L., & Di Iorio, B. R. (2019). Fractional Excretion of Phosphate (FeP) Is Associated with End-Stage Renal Disease Patients with CKD 3b and 5. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 8(7), 1026. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8071026






