Determinants of Early Response to Low-Intensity Extracorporeal Shockwaves for the Treatment of Vasculogenic Erectile Dysfunction: An Open-Label, Prospective Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
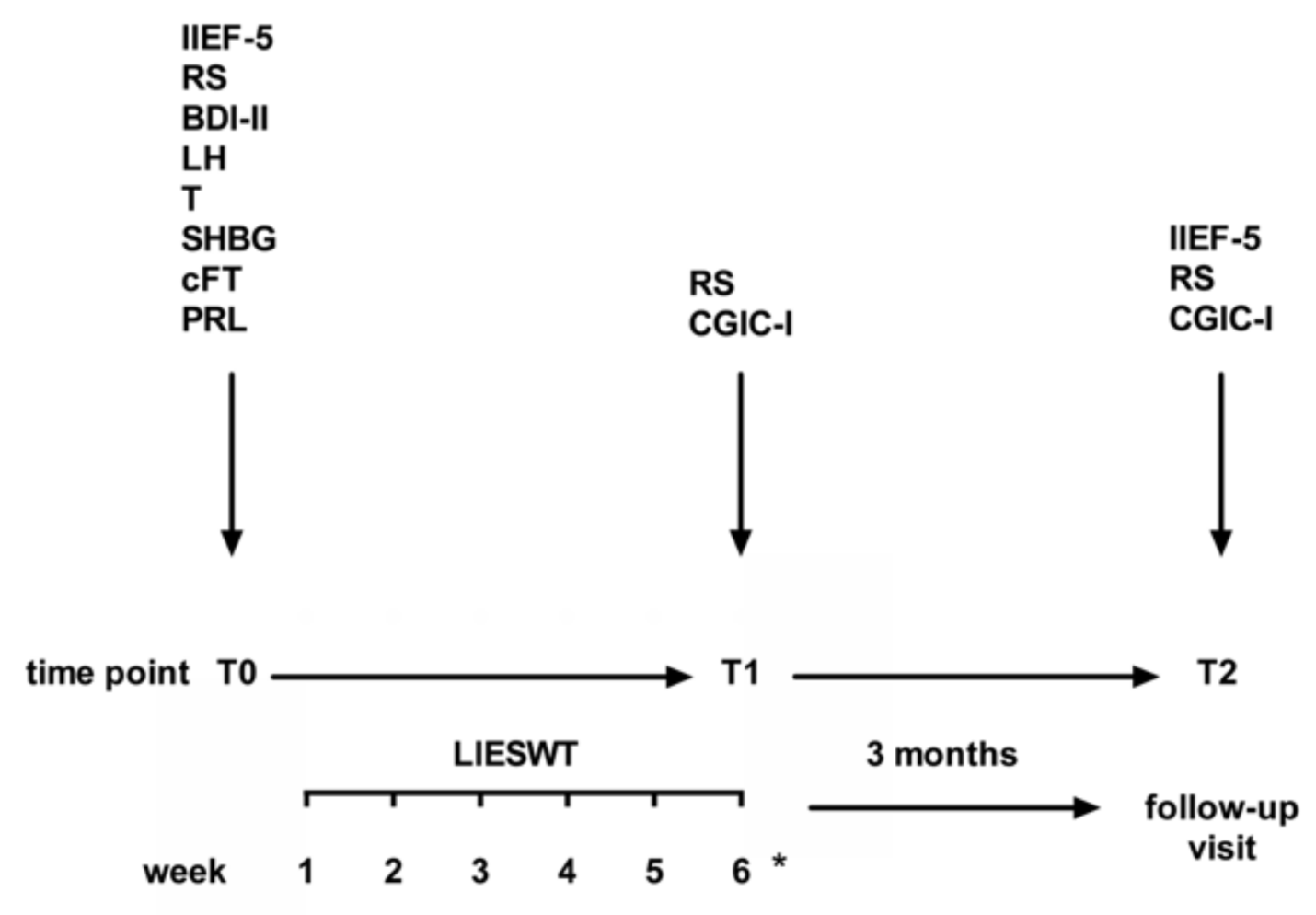
2. Materials and Methods
Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Groups Analysis
3.2. Follow-Up
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shamloul, R.; Ghanem, H. Erectile dysfunction. Lancet 2013, 381, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.Y.; Zhang, Y.H.; Qin, L.Q. Erectile dysfunction and risk of cardiovascular disease: Meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2011, 58, 1378–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponholzer, A.; Gutjahr, G.; Temml, C.; Madersbacher, S. Is erectile dysfunction a predictor of cardiovascular events or stroke? A prospective study using a validated questionnaire. Int. J. Impot. Res. 2010, 22, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, S.D.; Chen, Y.K.; Lin, H.C.; Lin, H.C. Increased risk of stroke among men with erectile dysfunction: A nationwide population-based study. J. Sex. Med. 2011, 8, 240–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nehra, A.; Jackson, G.; Miner, M.; Billups, K.L.; Burnett, A.L.; Buvat, J.; Carson, C.C.; Cunningham, G.R.; Ganz, P.; Goldstein, I.; et al. The Princeton III Consensus recommendations for the management of erectile dysfunction and cardiovascular disease. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2012, 87, 766–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alberti, L.; Torlasco, C.; Lauretta, L.; Loffi, M.; Maranta, F.; Salonia, A.; Margonato, A.; Montorsi, F.; Fragasso, G. Erectile dysfunction in heart failure patients: A critical reappraisal. Andrology 2013, 1, 177–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djordjevic, D.; Vukovic, I.; Milenkovic Petronic, D.; Radovanovic, G.; Seferovic, J.; Micic, S.; Kisic Tepavcevic, D. Erectile dysfunction as a predictor of advanced vascular age. Andrology 2015, 3, 1125–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Condorelli, R.A.; Calogero, A.E.; Favilla, V.; Morgia, G.; Johnson, E.O.; Castiglione, R.; Salemi, M.; Mongioi, L.; Nicoletti, C.; Duca, Y.; et al. Arterial erectile dysfunction: Different severities of endothelial apoptosis between diabetic patients “responders” and “non responders” to sildenafil. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2013, 24, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porst, H.; Burnett, A.; Brock, G.; Ghanem, H.; Giuliano, F.; Glina, S.; Hellstrom, W.; Martin-Morales, A.; Salonia, A.; Sharlip, I.; et al. SOP conservative (medical and mechanical) treatment of erectile dysfunction. J. Sex. Med. 2013, 10, 130–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardi, Y.; Appel, B.; Kilchevsky, A.; Gruenwald, I. Does low intensity extracorporeal shock wave therapy have a physiological effect on erectile function? Short-term results of a randomized, double-blind, sham controlled study. J. Urol. 2012, 187, 1769–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young Academic Urologists Men’s Health Group; Fode, M.; Hatzichristodoulou, G.; Serefoglu, E.C.; Verze, P.; Albersen, M. Low-intensity shockwave therapy for erectile dysfunction: Is the evidence strong enough? Nat. Rev. Urol. 2017, 14, 593–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vardi, Y.; Appel, B.; Jacob, G.; Massarwi, O.; Gruenwald, I. Can low-intensity extracorporeal shockwave therapy improve erectile function? A 6-month follow-up pilot study in patients with organic erectile dysfunction. Eur. Urol. 2010, 58, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitrey, N.D.; Gruenwald, I.; Appel, B.; Shechter, A.; Massarwa, O.; Vardi, Y. Penile Low Intensity Shock Wave Treatment is Able to Shift PDE5i Nonresponders to Responders: A Double-Blind, Sham Controlled Study. J. Urol. 2016, 195, 1550–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fojecki, G.L.; Tiessen, S.; Osther, P.J. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy (ESWT) in urology: A systematic review of outcome in Peyronie’s disease, erectile dysfunction and chronic pelvic pain. World J. Urol. 2017, 35, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Z.; Lin, G.; Reed-Maldonado, A.; Wang, C.; Lee, Y.C.; Lue, T.F. Low-intensity Extracorporeal Shock Wave Treatment Improves Erectile Function: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Eur. Urol. 2017, 71, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clavijo, R.I.; Kohn, T.P.; Kohn, J.R.; Ramasamy, R. Effects of Low-Intensity Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy on Erectile Dysfunction: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Sex. Med. 2017, 14, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizk, P.J.; Krieger, J.R.; Kohn, T.P.; Pastuszak, A.W. Low-Intensity Shockwave Therapy for Erectile Dysfunction. Sex. Med. Rev. 2018, 6, 624–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behr-Roussel, D.; Giuliano, F. Low-energy shock wave therapy ameliorates erectile dysfunction in a pelvic neurovascular injuries rat model. Transl. Androl. Urol. 2016, 5, 977–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Wang, Y.L.; Gong, D.X.; Zhang, Z.X.; Yu, X.T.; Ma, Y.W. Radial Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy as a Novel Agent for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Refractory to Current Medical Therapy. Am. J. Men’s Health 2019, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Császár, N.B.; Angstman, N.B.; Milz, S.; Sprecher, C.M.; Kobel, P.; Farhat, M.; Furia, J.P.; Schmitz, C. Radial Shock Wave Devices Generate Cavitation. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0140541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hisasue, S.; China, T.; Horiuchi, A.; Kimura, M.; Saito, K.; Isotani, S.; Ide, H.; Muto, S.; Yamaguchi, R.; Horie, S. Impact of aging and comorbidity on the efficacy of low-intensity shock wave therapy for erectile dysfunction. Int. J. Urol. 2016, 23, 80–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bechara, A.; Casabe, A.; De Bonis, W.; Ciciclia, P.G. Twelve-Month Efficacy and Safety of Low-Intensity Shockwave Therapy for Erectile Dysfunction in Patients Who Do Not Respond to Phosphodiesterase Type 5 Inhibitors. Sex. Med. 2016, 4, e225–e232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, C.C.; Wang, C.J.; Lee, Y.C.; Kuo, Y.T.; Lin, H.H.; Li, C.C.; Wu, W.J.; Liu, C.C. Low-Intensity Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy Can Improve Erectile Function in Patients Who Failed to Respond to Phosphodiesterase Type 5 Inhibitors. Am. J. Men’s Health 2017, 11, 1781–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosen, R.C.; Cappelleri, J.C.; Smith, M.D.; Lipsky, J.; Pena, B.M. Development and evaluation of an abridged, 5-item version of the International Index of Erectile Function (IIEF-5) as a diagnostic tool for erectile dysfunction. Int. J. Impot. Res. 1999, 11, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulhall, J.P.; Goldstein, I.; Bushmakin, A.G.; Cappelleri, J.C.; Hvidsten, K. Validation of the erection hardness score. J. Sex. Med. 2007, 4, 1626–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rush, J.A. (Ed.) Clinical Global Impressions (CGI) Scale, Modified. In Task Force for the Handbook of Psychiatric Measures; American Psychiatric Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Beck, A.T.; Steer, R.A.; Ball, R.; Ranieri, W. Comparison of Beck Depression Inventories -IA and -II in psychiatric outpatients. J. Personal. Assess. 1996, 67, 588–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalyvianakis, D.; Hatzichristou, D. Low-Intensity Shockwave Therapy Improves Hemodynamic Parameters in Patients with Vasculogenic Erectile Dysfunction: A Triplex Ultrasonography-Based Sham-Controlled Trial. J. Sex. Med. 2017, 14, 891–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitrey, N.D.; Vardi, Y.; Appel, B.; Shechter, A.; Massarwi, O.; Abu-Ghanem, Y.; Gruenwald, I. Low Intensity Shock Wave Treatment for Erectile Dysfunction-How Long Does the Effect Last? J. Urol. 2018, 200, 167–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fojecki, G.L.; Tiessen, S.; Osther, P.J.S. Effect of Linear Low-Intensity Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy for Erectile Dysfunction-12-Month Follow-Up of a Randomized, Double-Blinded, Sham-Controlled Study. Sex. Med. 2018, 6, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, A.B.; Persiani, M.; Boie, S.; Hanna, M.; Lund, L. Can low-intensity extracorporeal shockwave therapy improve erectile dysfunction? A prospective, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Scand. J. Urol. 2015, 49, 329–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srini, V.S.; Reddy, R.K.; Shultz, T.; Denes, B. Low intensity extracorporeal shockwave therapy for erectile dysfunction: A study in an Indian population. Can. J. Urol. 2015, 22, 7614–7622. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Qiu, X.; Lin, G.; Xin, Z.; Ferretti, L.; Zhang, H.; Lue, T.F.; Lin, C.S. Effects of low-energy shockwave therapy on the erectile function and tissue of a diabetic rat model. J. Sex. Med. 2013, 10, 738–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Matheu, M.P.; Sun, F.; Wang, L.; Sanford, M.T.; Ning, H.; Banie, L.; Lee, Y.C.; Xin, Z.; Guo, Y.; et al. Low-energy Shock Wave Therapy Ameliorates Erectile Dysfunction in a Pelvic Neurovascular Injuries Rat Model. J. Sex. Med. 2016, 13, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assaly-Kaddoum, R.; Giuliano, F.; Laurin, M.; Gorny, D.; Kergoat, M.; Bernabe, J.; Vardi, Y.; Alexandre, L.; Behr-Roussel, D. Low Intensity Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy Improves Erectile Function in a Model of Type II Diabetes Independently of NO/cGMP Pathway. J. Urol. 2016, 196, 950–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, G.; Reed-Maldonado, A.B.; Wang, B.; Lee, Y.C.; Zhou, J.; Lu, Z.; Wang, G.; Banie, L.; Lue, T.F. In Situ Activation of Penile Progenitor Cells with Low-Intensity Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy. J. Sex. Med. 2017, 14, 493–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruffo, A.; Capece, M.; Prezioso, D.; Romeo, G.; Illiano, E.; Romis, L.; Di Lauro, G.; Iacono, F. Safety and efficacy of low intensity shockwave (LISW) treatment in patients with erectile dysfunction. Int. Braz. J. Urol. 2015, 41, 967–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, E.; Cartmill, R. Evaluation of clinical efficacy, safety and patient satisfaction rate after low-intensity extracorporeal shockwave therapy for the treatment of male erectile dysfunction: An Australian first open-label single-arm prospective clinical trial. BJU Int. 2015, 115 (Suppl. 5), 46–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fojecki, G.L.; Tiessen, S.; Osther, P.J. Effect of Low-Energy Linear Shockwave Therapy on Erectile Dysfunction-A Double-Blinded, Sham-Controlled, Randomized Clinical Trial. J. Sex. Med. 2017, 14, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Vignera, S.; Condorelli, R.A.; Vicari, E.; Calogero, A.E. Statins and erectile dysfunction: A critical summary of current evidence. J. Androl. 2012, 33, 552–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalka, D.; Gebala, J.; Smolinski, R.; Rusiecki, L.; Pilecki, W.; Zdrojowy, R. Low-energy Shock Wave Therapy-A Novel Treatment Option for Erectile Dysfunction in Men with Cardiovascular Disease. Urology 2017, 109, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Vignera, S.; Calogero, A.E.; Condorelli, R.; Lanzafame, F.; Giammusso, B.; Vicari, E. Andrological characterization of the patient with diabetes mellitus. Minerva Endocrinol. 2009, 34, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Malavige, L.S.; Levy, J.C. Erectile dysfunction in diabetes mellitus. J. Sex. Med. 2009, 6, 1232–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Zhou, F.; Li, G.Y.; Wang, L.; Li, H.X.; Bai, G.Y.; Guan, R.L.; Xu, Y.D.; Gao, Z.Z.; Tian, W.J.; et al. Evaluation of the effect of different doses of low energy shock wave therapy on the erectile function of streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetic rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 10661–10673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, H.; Xin, H.; Guan, R.; Xu, Y.; Li, H.; Tian, W.; Wang, L.; Gao, Z.; Guo, Y.; Lue, T.F.; et al. Low-intensity Pulsed Ultrasound Improves Erectile Function in Streptozotocin-induced Type I Diabetic Rats. Urology 2015, 86, e1211–e1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reisman, Y.; Hind, A.; Varaneckas, A.; Motil, I. Initial experience with linear focused shockwave treatment for erectile dysfunction: A 6-month follow-up pilot study. Int. J. Impot. Res. 2015, 27, 108–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sambuceti, G.; Morbelli, S.; Vanella, L.; Kusmic, C.; Marini, C.; Massollo, M.; Augeri, C.; Corselli, M.; Ghersi, C.; Chiavarina, B.; et al. Diabetes impairs the vascular recruitment of normal stem cells by oxidant damage, reversed by increases in pAMPK, heme oxygenase-1, and adiponectin. Stem Cells 2009, 27, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatzimouratidis, K.E.I.; Giuliano, F.; Moncada, I.; Salonia, A. Guidelines on Male Sexual Dysfunction: Erectile Dysfunction and Premature Ejaculation. Available online: http://uroweb.org/guideline/male-sexual-dysfunction/ (accessed on 1 June 2019).
| Parameter | |
|---|---|
| Age (m ± SD) | 58.5 ± 10.3 years |
| Diabetes (number of patients (%), duration (m ± SD), HbA1c (m ± SD)) | 8 (40%), 13.9 ± 9.7 years, 8.2 ± 2.0% |
| Hypertension (number of patients (%), duration (m ± SD)) | 9 (45%), 5.7 ± 6.1 years |
| History of MI (number of patients (%)) | 4 (20%) |
| Hypercholesterolemia (number of patients (%), duration (m ± SD)) | 9 (45%), 8.4 ± 6.1 years |
| ED duration (m ± SD) | 8.2 ± 6.7 years |
| Number of PDE5i to which patients failed to respond (m ± SD) PDE5i (number of patients) | 1.9 ± 0.9 avanafil (3), sildenafil (12), tadalafil (19), vardenafil (5) |
| i.c. Alprostadil (number of patients (%)) | 2 (10%) |
| LH (mU/mL) (m ± SD) | 3.8 ± 1.3 |
| Total testosterone (nmol/L) (m ± SD) ^ | 15.9 ± 6.2 |
| SHBG (nmol/L) | 38.2 ± 11.2 |
| Calculated free testosterone (pmol/L) (m ± SD) | 330.7 ± 95.0 |
| Prolactin (μU/mL) (m ± SD) | 191.5 ± 85.1 |
| Rigidity Score (m ± SD) Erection hardness # | 1.4 ± 0.7 0:2 (10%) 1:8 (40%) 2:10 (50%) 3:0 4:0 |
| IIEF-5 (m ± SD) ED severity* (number of patients (%)) | 11.6 ± 3.6 severe: 4 (20%) moderate: 3 (15%) mild to moderate: 13 (65%) mild: 0 |
| IIEF-5 EFD (m ± SD) | 5.9 ± 3.0 |
| IIEF-5 ISD (m ± SD) | 5.7 ± 1.3 |
| BDI-II Depression severity ** (number of patients (%)) | 5.8 ± 4.7 minimal: 19 (95%) mild: 1 (5%) moderate: 0 severe: 0 |
| N | T0 | T1 | T2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RS ≥ 3 | RS ≥3 | CGIC-I ≥ 1 | RS ≥ 3 | CGIC-I ≥ 1 | ||
| All | 20 | 0 ***,**** | 12 (60%) **** | 16 (80%) | 11 (55%) *** | 13 (65%) |
| Diabetes, yes | 8 | 0 * | 5 (62.5%) * | 5 (62.5%) | 5 (62.5%) * | 3 (37.5%) |
| Diabetes, no | 12 | 0 *, ** | 7 (58.3%) ** | 11 (91.7%) | 6 (50%) * | 10 (83.3%) |
| Hypertension, yes | 9 | 0 *, ** | 6 (66.7%) ** | 8 (88.9%) | 5 (55.5%) * | 6 (66.7%) |
| Hypertension, no | 11 | 0 * | 6 (54.5%) * | 8 (72.7%) | 6 (54.5%) * | 7 (63.6%) |
| Myocardial infarction, yes | 4 | 0 | 2 (50%) | 3 (75%) | 2 (50%) | 2 (50%) |
| Myocardial infarction, no | 16 | 0 *** | 10 (62.5%) *** | 13 (81.2%) | 9 (56.2%) *** | 11 (68.7%) |
| Hypercholesterolemia, yes | 9 | 0 | 3 (33.3%) ^ | 7 (77.8%) | 3 (33.3%) | 6 (66.7%) |
| Hypercholesterolemia, no | 11 | 0 **,*** | 9 (81.8%) ***^ | 9 (81.8%) | 8 (72.7%) ** | 7 (63.6%) |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vita, R.; Benvenga, S.; Giammusso, B.; La Vignera, S. Determinants of Early Response to Low-Intensity Extracorporeal Shockwaves for the Treatment of Vasculogenic Erectile Dysfunction: An Open-Label, Prospective Study. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1017. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8071017
Vita R, Benvenga S, Giammusso B, La Vignera S. Determinants of Early Response to Low-Intensity Extracorporeal Shockwaves for the Treatment of Vasculogenic Erectile Dysfunction: An Open-Label, Prospective Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2019; 8(7):1017. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8071017
Chicago/Turabian StyleVita, Roberto, Salvatore Benvenga, Bruno Giammusso, and Sandro La Vignera. 2019. "Determinants of Early Response to Low-Intensity Extracorporeal Shockwaves for the Treatment of Vasculogenic Erectile Dysfunction: An Open-Label, Prospective Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 8, no. 7: 1017. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8071017
APA StyleVita, R., Benvenga, S., Giammusso, B., & La Vignera, S. (2019). Determinants of Early Response to Low-Intensity Extracorporeal Shockwaves for the Treatment of Vasculogenic Erectile Dysfunction: An Open-Label, Prospective Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 8(7), 1017. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8071017






