Combined Albumin-Bilirubin Grade and Skeletal Muscle Mass as a Predictor in Liver Cirrhosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Patients and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. ALBI Score and ALBI Grade
2.3. Skeletal Muscle Mass and ALBI-SMM Grade
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
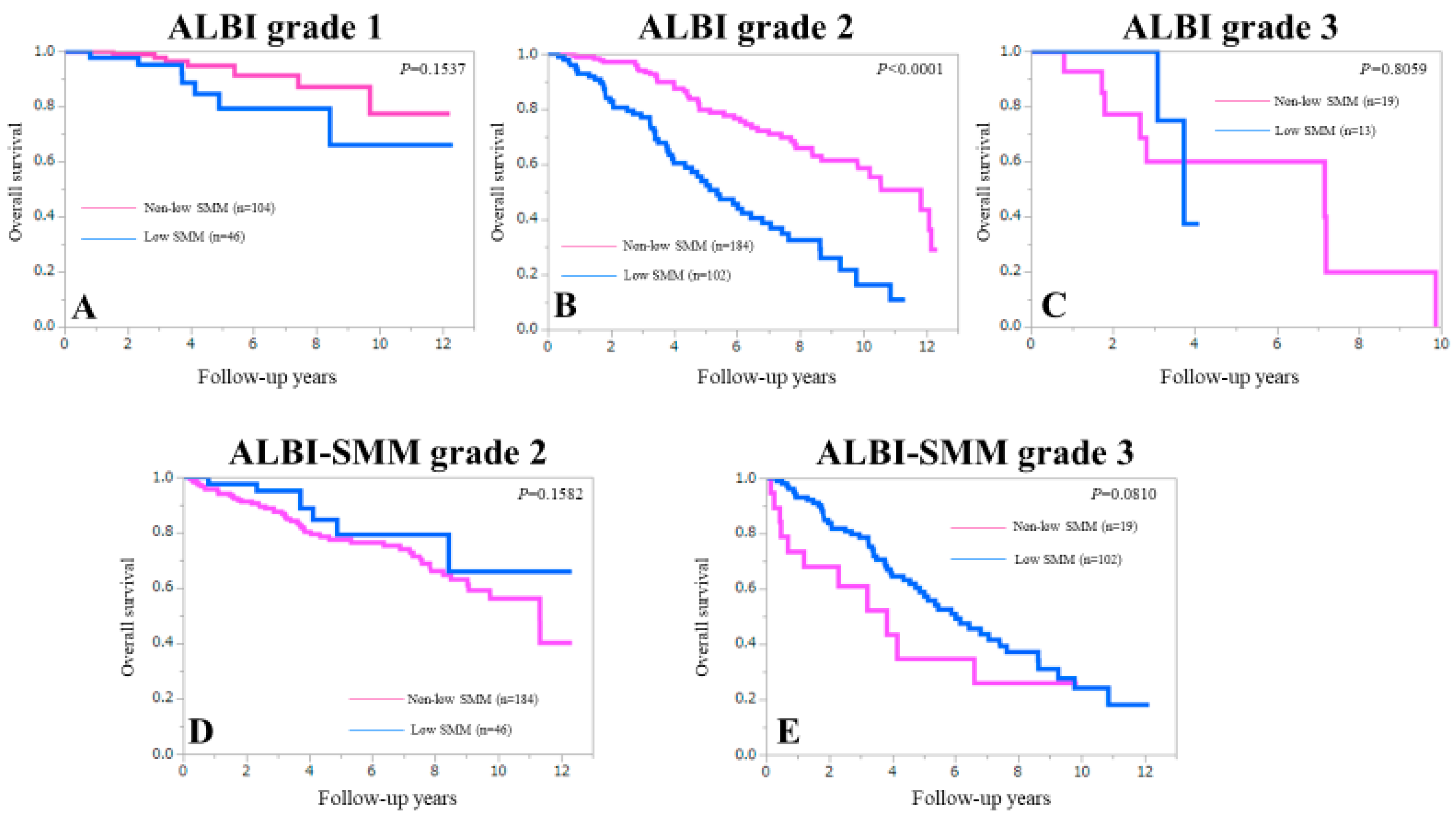
3.2. Cumulative Overall Survival Rates According to the Presence of Low SMM
3.3. Causes of Death in the Low SMM Group and the Non-Low SMM Group
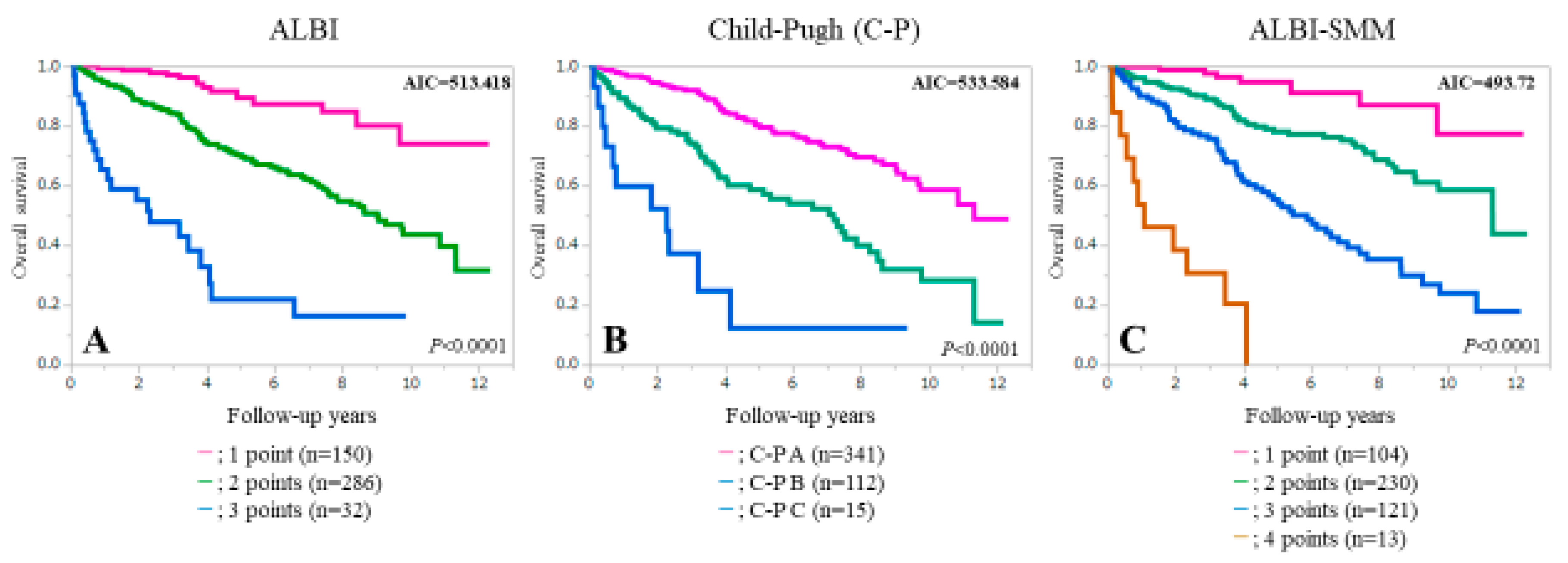
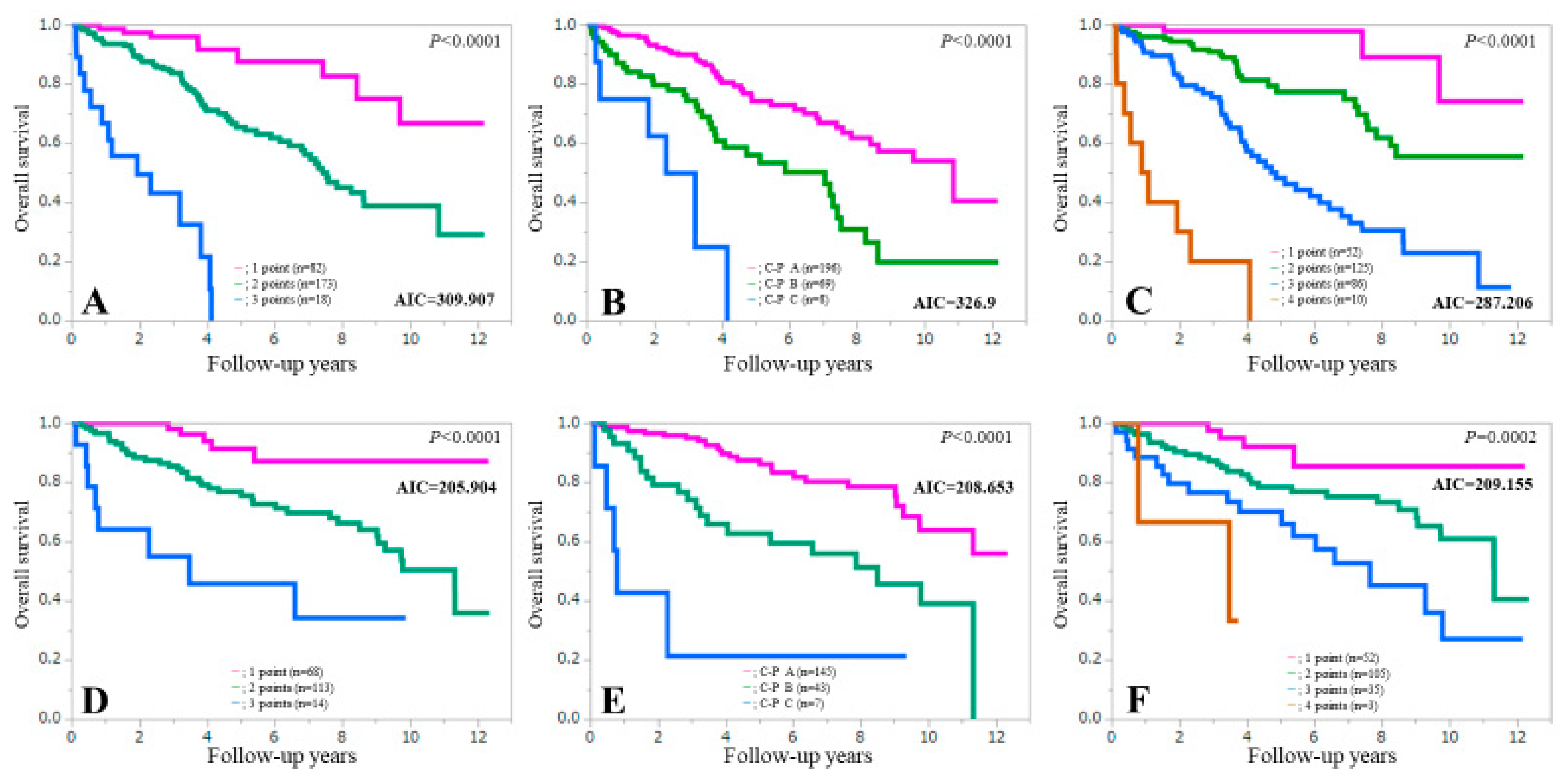
3.4. Comparison of Prognostic Accuracy among Three Assessment Methods for All Cases
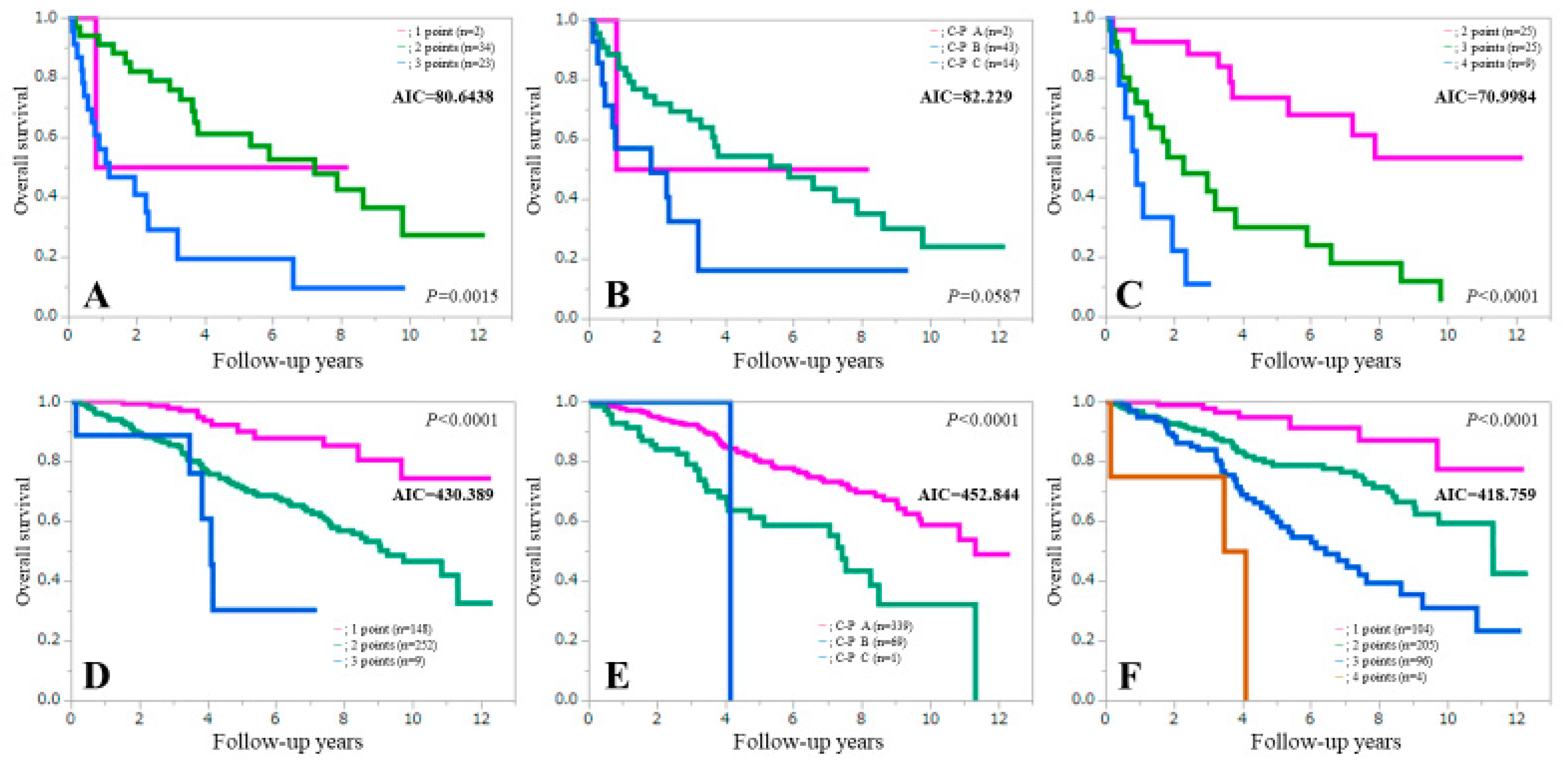
3.5. Comparison of Prognostic Accuracy among Three Assessment Methods Stratified by Gender
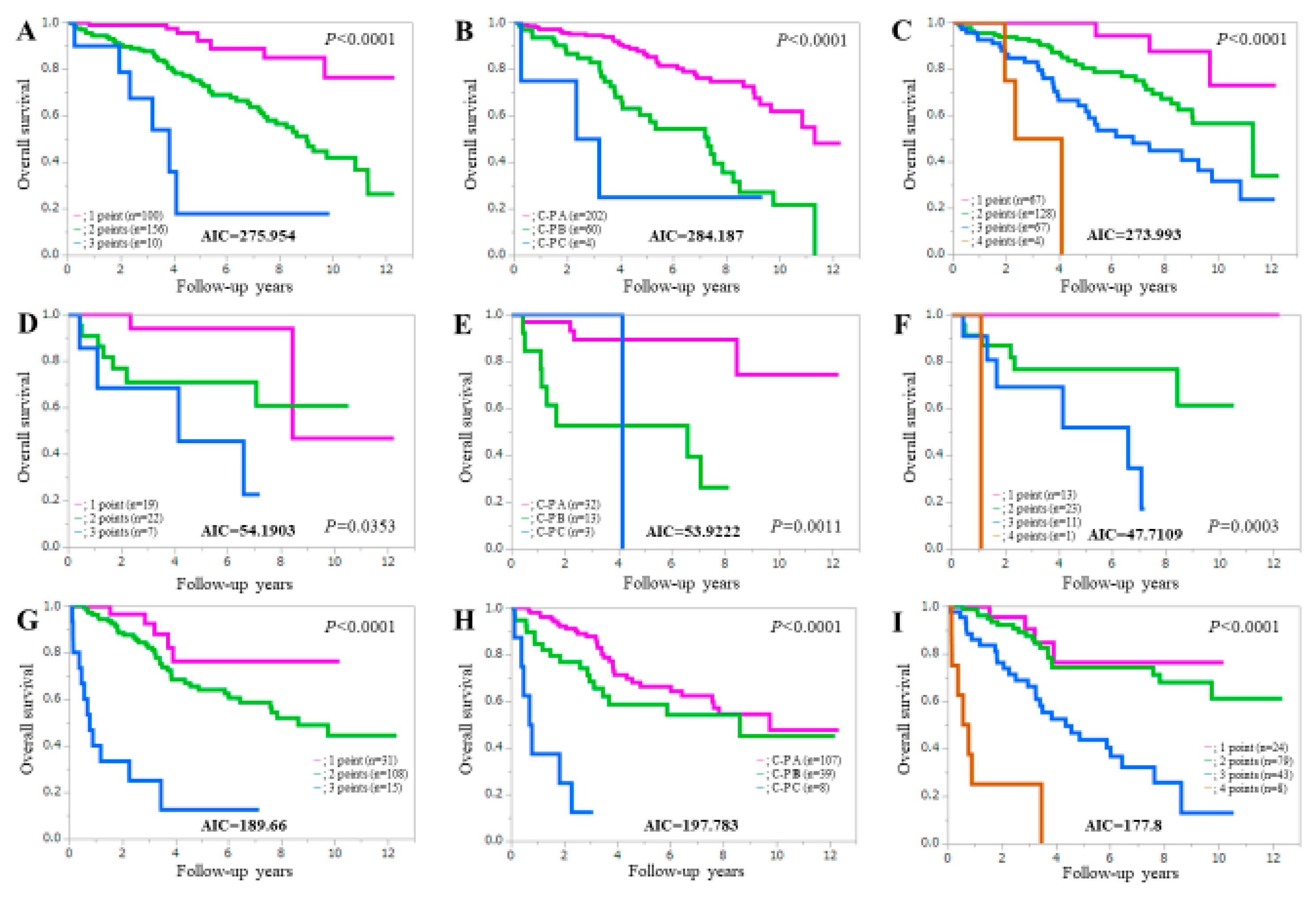
3.6. Comparison of Prognostic Accuracy among Three Assessment Methods in Patients with or without Ascites
3.7. Comparison of Prognostic Accuracy among Three Assessment Methods Stratified by Liver Disease Etiologies
3.8. Comparison of Prognostic Accuracy among Three Assessment Methods According to Age
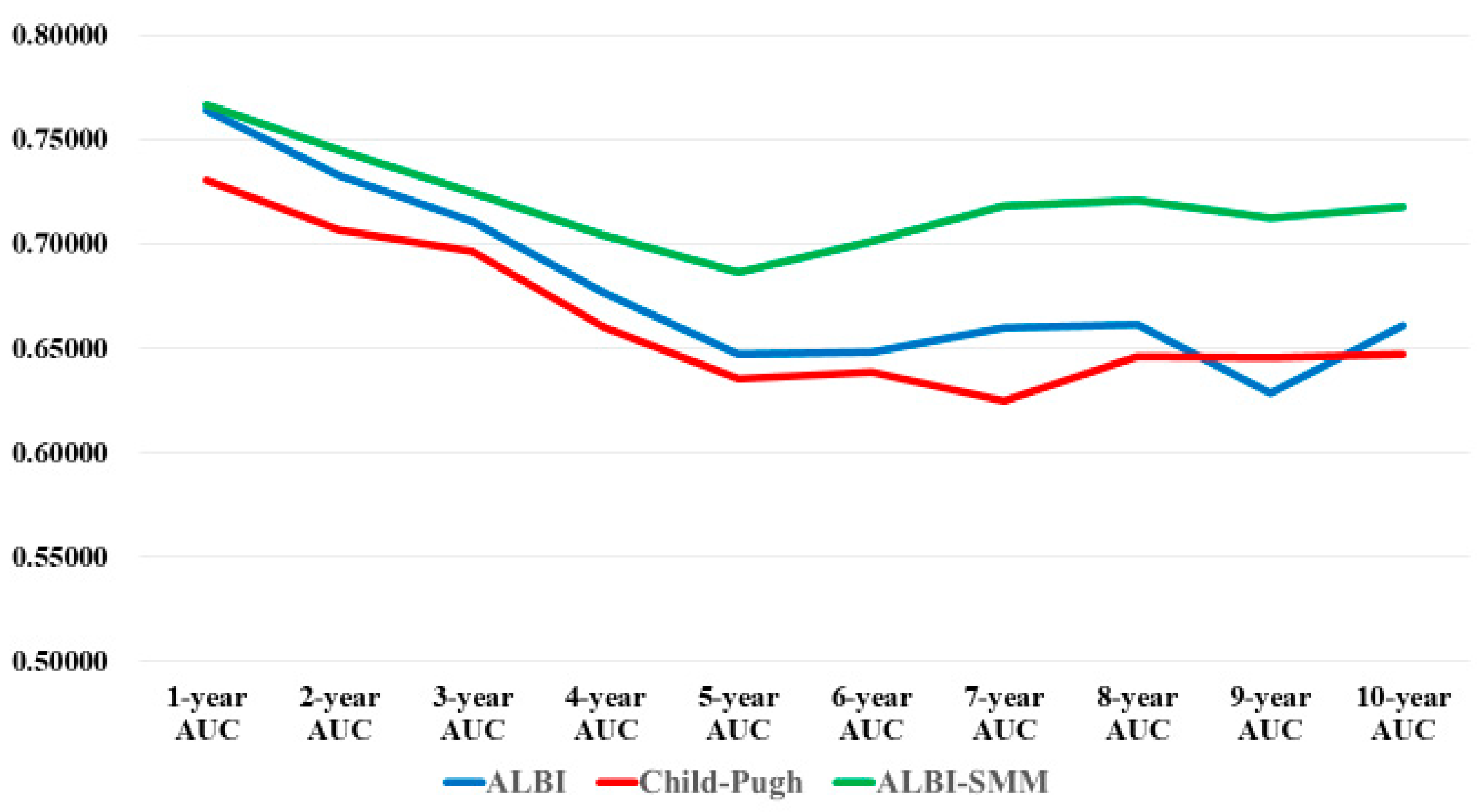
3.9. Comparison of Prognostic Accuracy among Three Assessment Methods Using Time-Dependent ROC Analysis
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Tsochatzis, E.A.; Bosch, J.; Burroughs, A.K. Liver cirrhosis. Lancet 2014, 383, 1749–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thandassery, R.B.; Montano-Loza, A.J. Role of Nutrition and Muscle in Cirrhosis. Curr. Treat Options Gastroenterol. 2016, 14, 257–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunsar, F.; Raimondo, M.L.; Jones, S.; Terreni, N.; Wong, C.; Patch, D.; Sabin, C.; Burroughs, A.K. Nutritional status and prognosis in cirrhotic patients. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2006, 24, 563–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pugh, R.N.; Murray-Lyon, I.M.; Dawson, J.L.; Pietroni, M.C.; Williams, R. Transection of the oesophagus for bleeding oesophageal varices. Br. J. Surg. 1973, 60, 646–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, P.J.; Berhane, S.; Kagebayashi, C.; Satomura, S.; Teng, M.; Reeves, H.L.; O’Beirne, J.; Fox, R.; Skowronska, A.; Palmer, D.; et al. Assessment of liver function in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: A new evidence-based approach-the ALBI grade. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 550–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.Y.; Zhong, J.H.; Su, Z.Y.; Huang, J.F.; Lu, S.D.; Xiang, B.D.; Ma, L.; Qi, L.N.; Ou, B.N.; Li, L.Q. Albumin-bilirubin versus Child-Pugh score as a predictor of outcome after liver resection for hepatocellular carcinoma. Br. J. Surg. 2016, 103, 725–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toyoda, H.; Lai, P.B.; O’Beirne, J.; Chong, C.C.; Berhane, S.; Reeves, H.; Manas, D.; Fox, R.P.; Yeo, W.; Mo, F.; et al. Long-term impact of liver function on curative therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: Application of the ALBI grade. Br. J. Cancer. 2016, 114, 744–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiraoka, A.; Kumada, T.; Michitaka, K.; Toyoda, H.; Tada, T.; Ueki, H.; Kaneto, M.; Aibiki, T.; Okudaira, T.; Kawakami, T.; et al. Usefulness of albumin-bilirubin grade for evaluation of prognosis of 2584 Japanese patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 31, 1031–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edeline, J.; Blanc, J.F.; Johnson, P.; Campillo-Gimenez, B.; Ross, P.; Ma, Y.T.; King, J.; Hubner, R.A.; Sumpter, K.; Darby, S.; et al. A multicentre comparison between Child Pugh and Albumin-Bilirubin scores in patients treated with sorafenib for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Liver Int. 2016, 36, 1821–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujita, K.; Oura, K.; Yoneyama, H.; Ting, T.S.; Takuma, K.; Nakahara, M.; Tadokoro, T.; Nomura, T.; Morishita, A.; Tsutsui, K.; et al. Albumin-bilirubin score indicates liver fibrosis staging and prognosis in chronic hepatitis C patients. Hepatol. Res. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Yan, X.; Li, M.; Xia, J.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Jia, B.; Zhu, L.; Zhu, C.; et al. Albumin-Bilirubin (ALBI) as an accurate and simple prognostic score for chronic hepatitis B-related liver cirrhosis. Dig. Liver Dis. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, Y.C.; Lee, K.C.; Wang, Y.W.; Yang, Y.Y.; Hou, M.C.; Huo, T.I.; Lin, H.C. Correlation and prognostic accuracy between noninvasive liver fibrosismarkers and portal pressure in cirrhosis: Role of ALBI score. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0208903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiraoka, A.; Michitaka, K.; Kumada, T.; Izumi, N.; Kadoya, M.; Kokudo, N.; Kubo, S.; Matsuyama, Y.; Nakashima, O.; Sakamoto, M.; et al. Validation and Potential of Albumin-Bilirubin Grade and Prognostication in a Nationwide Survey of 46,681 Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients in Japan: The Need for a More Detailed Evaluation of Hepatic Function. Liver Cancer 2017, 6, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guha, I.N.; Harris, R.; Berhane, S.; Dillon, A.; Coffey, L.; James, M.W.; Cucchetti, A.; Harman, D.J.; Aithal, G.P.; Elshaarawy, O.; et al. Validation of a Model for Identification of Patients with Compensated Cirrhosis at High Risk of Decompensation. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.H.; Hsu, C.Y.; Hsia, C.Y.; Lee, Y.H.; Chiou, Y.Y.; Huang, Y.H.; Lee, F.Y.; Lin, H.C.; Hou, M.C.; Huo, T.I. ALBI and PALBI grade predict survival for HCC across treatment modalities and BCLC stages in the MELD Era. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 32, 879–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chedid, M.F.; Picon, R.V.; Chedid, A.D. ALBI and PALBI: Novel Scores for Outcome Prediction of Cirrhotic Outpatients Awaiting Liver Transplantation. Ann. Hepatol. 2018, 17, 906–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Landi, F.; Schneider, S.M.; Zúñiga, C.; Arai, H.; Boirie, Y.; Chen, L.K.; Fielding, R.A.; Martin, F.C.; Michel, J.P.; et al. Prevalence of and interventions for sarcopenia in ageing adults: A systematic review. Report of the International Sarcopenia Initiative (EWGSOP and IWGS). Age Ageing 2014, 43, 748–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santilli, V.; Bernetti, A.; Mangone, M.; Paoloni, M. Clinical definition of sarcopenia. Clin. Cases Min. Bone Metab. 2014, 11, 177–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.K.; Liu, L.K.; Woo, J.; Assantachai, P.; Auyeung, T.W.; Bahyah, K.S.; Chou, M.Y.; Chen, L.Y.; Hsu, P.S.; Krairit, O.; et al. Sarcopenia in Asia: Consensus Report of the Asian Working Group for Sarcopenia. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2014, 15, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berzigotti, A.; Saran, U.; Dufour, J.F. Physical activity and liver diseases. Hepatology 2016, 63, 1026–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinclair, M.; Gow, P.J.; Grossmann, M.; Angus, P.W. Review article: Sarcopenia in cirrhosis-aetiology, implications and potential therapeutic interventions. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 43, 765–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stangl, M.K.; Böcker, W.; Chubanov, V.; Ferrari, U.; Fischereder, M.; Gudermann, T.; Hesse, E.; Meinke, P.; Reincke, M.; Reisch, N.; et al. Sarcopenia-Endocrinological and Neurological Aspects. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2019, 127, 8–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishikawa, H.; Shiraki, M.; Hiramatsu, A.; Moriya, K.; Hino, K.; Nishiguchi, S. JSH guidelines for sarcopenia in liver disease (first edition): Recommendation from the working group for creation of sarcopenia assessment criteria in the JSH. Hepatol. Res. 2016, 46, 951–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nardelli, S.; Lattanzi, B.; Torrisi, S.; Greco, F.; Farcomeni, A.; Gioia, S.; Merli, M.; Riggio, O. Sarcopenia is Risk Factor for Development of Hepatic Encephalopathy After Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosysthemic Shunt Placement. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 15, 934–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dasarathy, S.; Merli, M. Sarcopenia from mechanism to diagnosis and treatment in liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2016, 65, 1232–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalafateli, M.; Mantzoukis, K.; Choi, Y.Y.; Mohammad, A.O.; Arora, S.; Rodrigues, S.; de Vos, M.; Papadimitriou, K.; Thorburn, D.; O’Beirne, J.; et al. Malnutrition and sarcopenia predict post-liver transplantation outcomes independently of the Model for End-stage Liver Disease score. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2017, 8, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, S.J.; Mozer, M. Differentiating Sarcopenia and Cachexia Among Patients with Cancer. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2017, 32, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dos Santos, L.; Cyrino, E.S.; Antunes, M.; Santos, D.A.; Sardinha, L.B. Sarcopenia and physical independence in older adults: The independent and synergic role of muscle mass and muscle function. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2016, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalyani, R.R.; Corriere, M.; Ferrucci, L. Age-related and disease-related muscle loss: The effect of diabetes, obesity, and other diseases. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2014, 2, 819–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasarathy, S. Consilience in sarcopenia of cirrhosis. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2012, 3, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montano-Loza, A.J. Clinical relevance of sarcopenia in patients with cirrhosis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 8061–8071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lattanzi, B.; D’Ambrosio, D.; Merli, M. Hepatic Encephalopathy and Sarcopenia: Two Faces of the Same Metabolic Alteration. J. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2019, 9, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, L.G.; Santos, L.F.; Anastácio, L.R.; Lima, A.S.; Correia, M.I. Resting energy expenditure, body composition, and dietary intake: A longitudinal study before and after liver transplantation. Transplantation 2013, 96, 579–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Vugt, J.L.; Levolger, S.; de Bruin, R.W.; van Rosmalen, J.; Metselaar, H.J.; IJzermans, J.N. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Impact of Computed Tomography-Assessed Skeletal Muscle Mass on Outcome in Patients Awaiting or Undergoing Liver Transplantation. Am. J. Transpl. 2016, 16, 2277–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudo, M.; Zheng, R.Q.; Kim, S.R.; Okabe, Y.; Osaki, Y.; Iijima, H.; Itani, T.; Kasugai, H.; Kanematsu, M.; Ito, K.; et al. Diagnostic accuracy of imaging for liver cirrhosis compared to histologically proven liver cirrhosis. A multicenter collaborative study. Intervirology 2008, 51 (Suppl. 1), 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarski, J.P.; Sturm, N.; Guechot, J.; Paris, A.; Zafrani, E.S.; Asselah, T.; Boisson, R.C.; Bosson, J.L.; Guyader, D.; Renversez, J.C.; et al. ANRS HCEP 23 Fibrostar Group. Comparison of nine blood tests and transient elastography for liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis C: The ANRS HCEP-23 study. J. Hepatol. 2012, 56, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsochatzis, E.A.; Gurusamy, K.S.; Ntaoula, S.; Cholongitas, E.; Davidson, B.R.; Burroughs, A.K. Elastography for the diagnosis of severity of fibrosis in chronic liver disease: A meta-analysis of diagnostic accuracy. J. Hepatol. 2011, 54, 650–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumada, H.; Okanoue, T.; Onji, M.; Moriwaki, H.; Izumi, N.; Tanaka, E.; Chayama, K.; Sakisaka, S.; Takehara, T.; Oketani, M.; et al. Study Group for the Standardization of Treatment of Viral Hepatitis Including Cirrhosis, Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare of Japan. Guidelines for the treatment of chronic hepatitis and cirrhosis due to hepatitis C virus infection for the fiscal year 2008 in Japan. Hepatol. Res. 2010, 40, 8–13. [Google Scholar]
- Kappus, M.R.; Mendoza, M.S.; Nguyen, D.; Medici, V.; McClave, S.A. Sarcopenia in Patients with Chronic Liver Disease: Can It Be Altered by Diet and Exercise? Curr. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2016, 18, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokudo, N.; Hasegawa, K.; Akahane, M.; Igaki, H.; Izumi, N.; Ichida, T.; Uemoto, S.; Kaneko, S.; Kawasaki, S.; Ku, Y.; et al. Evidence-based Clinical Practice Guidelines for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: The Japan Society of Hepatology 2013 update (3rd JSH-HCC Guidelines). Hepatol. Res. 2015, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omata, M.; Cheng, A.L.; Kokudo, N.; Kudo, M.; Lee, J.M.; Jia, J.; Tateishi, R.; Han, K.H.; Chawla, Y.K.; Shiina, S.; et al. Asia-Pacific clinical practice guidelines on the management of hepatocellular carcinoma: A 2017 update. Hepatol. Int. 2017, 11, 317–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishikawa, H.; Nishijima, N.; Enomoto, H.; Sakamoto, A.; Nasu, A.; Komekado, H.; Nishimura, T.; Kita, R.; Kimura, T.; Iijima, H.; et al. Comparison of FIB-4 index and aspartate aminotransferase to platelet ratio index on carcinogenesis in chronic hepatitis B treated with entecavir. J. Cancer 2017, 8, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tada, T.; Kumada, T.; Toyoda, H.; Kiriyama, S.; Tanikawa, M.; Hisanaga, Y.; Kanamori, A.; Kitabatake, S.; Yama, T.; Tanaka, J. HBcrAg predicts hepatocellular carcinoma development: An analysis using time-dependent receiver operating characteristics. J. Hepatol. 2016, 65, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamarudin, A.N.; Cox, T.; Kolamunnage-Dona, R. Time-dependent ROC curve analysis in medical research: Current methods and applications. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2017, 17, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioannou, G.N.; Feld, J.J. What Are the Benefits of a Sustained Virologic Response to Direct-Acting Antiviral Therapy for Hepatitis C Virus Infection? Gastroenterology 2019, 156, 446–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pradat, P.; Virlogeux, V.; Trépo, E. Epidemiology and Elimination of HCV-Related Liver Disease. Viruses 2018, 10, 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoh, K.; Nishikawa, H.; Enomoto, H.; Ishii, A.; Iwata, Y.; Miyamoto, Y.; Ishii, N.; Yuri, Y.; Hasegawa, K.; Nakano, C.; et al. Predictors Associated with Increase in Skeletal Muscle Mass after Sustained Virological Response in Chronic Hepatitis C Treated with Direct Acting Antivirals. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Points | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALBI grade | 1 | 2 | 3 | |
| Skeletal muscle mass (SMM) | 0 | 1 | ||
| ALBI-SMM grade | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| Variables | Number or Median (Interquartile Range) |
|---|---|
| Age (years) | 66 (60, 73) |
| Gender, male/female | 254/214 |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 23.1 (20.5, 25.8) |
| Skeletal muscle mass index (cm2/m2), male | 7.4 (6.9, 8.16) |
| Skeletal muscle mass index (cm2/m2), female | 6.0 (5.55, 6.41) |
| Causes of liver disease | 48/266/154 |
| Hepatitis B/Hepatitis C/others | |
| Child-Pugh classification, A/B/C | 341/112/15 |
| ALBI grade, 1/2/3 | 150/286/32 |
| Total bilirubin (mg/dL) | 1.0 (0.7, 1.4) |
| Serum albumin (g/dL) | 3.7 (3.2, 4.1) |
| Prothrombin time (PT, %) | 77.3 (66.65, 86.95) |
| PT-international normalized ratio (INR) | 1.16 (1.08, 1.26) |
| Platelets (×104/mm3) | 9.9 (7.1, 14.2) |
| Serum creatinine (mg/dL) | 0.67 (0.57, 0.79) |
| Serum sodium (mmol/L) | 140 (138, 141) |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | 152 (130, 177) |
| Triglyceride (mg/dL) | 83 (62, 111) |
| AST (IU/L) | 38 (27, 58) |
| ALT (IU/L) | 30 (20, 49) |
| Fasting blood glucose (mg/dL) | 102 (93, 119) |
| Branched-chain amino acid to tyrosine ratio | 4.17 (3.265–5.445) |
| Ascites, yes/no | 59/409 |
| 1-Year AUC | 2-Year AUC | 3-Year AUC | 4-Year AUC | 5-Year AUC | |
| ALBI grade | 0.76386 | 0.73252 | 0.71098 | 0.67643 | 0.64719 |
| Child-Pugh classification | 0.73065 | 0.70642 | 0.69663 | 0.66004 | 0.63568 |
| ALBI-SMM grade | 0.76641 | 0.74486 | 0.72440 | 0.70407 | 0.68639 |
| 6-Year AUC | 7-Year AUC | 8-Year AUC | 9-Year AUC | 10-Year AUC | |
| ALBI grade | 0.64814 | 0.65992 | 0.66159 | 0.62852 | 0.66108 |
| Child-Pugh classification | 0.63889 | 0.62503 | 0.64606 | 0.64540 | 0.64710 |
| ALBI-SMM grade | 0.70133 | 0.71813 | 0.72086 | 0.71265 | 0.71749 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nishikawa, H.; Enomoto, H.; Yoh, K.; Iwata, Y.; Sakai, Y.; Kishino, K.; Ikeda, N.; Takashima, T.; Aizawa, N.; Takata, R.; et al. Combined Albumin-Bilirubin Grade and Skeletal Muscle Mass as a Predictor in Liver Cirrhosis. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 782. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8060782
Nishikawa H, Enomoto H, Yoh K, Iwata Y, Sakai Y, Kishino K, Ikeda N, Takashima T, Aizawa N, Takata R, et al. Combined Albumin-Bilirubin Grade and Skeletal Muscle Mass as a Predictor in Liver Cirrhosis. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2019; 8(6):782. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8060782
Chicago/Turabian StyleNishikawa, Hiroki, Hirayuki Enomoto, Kazunori Yoh, Yoshinori Iwata, Yoshiyuki Sakai, Kyohei Kishino, Naoto Ikeda, Tomoyuki Takashima, Nobuhiro Aizawa, Ryo Takata, and et al. 2019. "Combined Albumin-Bilirubin Grade and Skeletal Muscle Mass as a Predictor in Liver Cirrhosis" Journal of Clinical Medicine 8, no. 6: 782. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8060782
APA StyleNishikawa, H., Enomoto, H., Yoh, K., Iwata, Y., Sakai, Y., Kishino, K., Ikeda, N., Takashima, T., Aizawa, N., Takata, R., Hasegawa, K., Ishii, N., Yuri, Y., Nishimura, T., Iijima, H., & Nishiguchi, S. (2019). Combined Albumin-Bilirubin Grade and Skeletal Muscle Mass as a Predictor in Liver Cirrhosis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 8(6), 782. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8060782




