Predictors of Assessment of Spondyloarthritis International Society (ASAS) Health Index in Axial Spondyloarthritis and Comparison of ASAS Health Index between Ankylosing Spondylitis and Nonradiographic Axial Spondyloarthritis: Data from the Catholic Axial Spondyloarthritis COhort (CASCO)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Patients and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Study Design
2.3. Collected Data
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics of Patients with Axial Spodyloarthritis (axSpA) and Comparison between Those with Ankylosing Spondylitis (AS) and Nonradiographic (nr) axSpA
3.2. Correlation between ASAS HI and PROs
3.3. Predictors of ASAS HI in axSpA, AS, and nr-axSpA
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kiltz, U.; van der Heijde, D.; Boonen, A.; Cieza, A.; Stucki, G.; Khan, M.A.; Maksymowych, W.P.; Marzo-Ortega, H.; Reveille, J.; Stebbings, S.; et al. Development of a health index in patients with ankylosing spondylitis (ASAS HI): Final result of a global initiative based on the ICF guided by ASAS. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 74, 830–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boonen, A.; Braun, J.; van der Horst Bruinsma, I.E.; Huang, F.; Maksymowych, W.; Kostanjsek, N.; Cieza, A.; Stucki, G.; van der Heijde, D. ASAS/WHO ICF Core Sets for ankylosing spondylitis (AS): How to classify the impact of AS on functioning and health. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2010, 69, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.H.; Kim, T.J.; Shin, K.; Choi, C.B.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, N.I.; Ahn, M.J.; Jung, H.J.; Lee, K.E.; et al. The reliability and validity of a Korean translation of the ASAS Health Index and Environmental Factors in Korean patients with axial spondyloarthritis. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2014, 29, 334–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiltz, U.; van der Heijde, D.; Boonen, A.; Akkoc, N.; Bautista-Molano, W.; Burgos-Vargas, R.; Wei, J.C.; Chiowchanwisawakit, P.; Dougados, M.; Duruoz, M.T.; et al. Measurement properties of the ASAS Health Index: Results of a global study in patients with axial and peripheral spondyloarthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2018, 77, 1311–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Gabriel, S.E.; Ward, M.M. Progression of Nonradiographic Axial Spondyloarthritis to Ankylosing Spondylitis: A Population-Based Cohort Study. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016, 68, 1415–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Linden, S.; Valkenburg, H.A.; Cats, A. Evaluation of diagnostic criteria for ankylosing spondylitis. A proposal for modification of the New York criteria. Arthritis Rheum. 1984, 27, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sieper, J.; Rudwaleit, M.; Baraliakos, X.; Brandt, J.; Braun, J.; Burgos-Vargas, R.; Dougados, M.; Hermann, K.G.; Landewe, R.; Maksymowych, W.; van der Heijde, D. The Assessment of SpondyloArthritis international Society (ASAS) handbook: A guide to assess spondyloarthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2009, 68 (Suppl. 2), ii1–ii44. [Google Scholar]
- Garrett, S.; Jenkinson, T.; Kennedy, L.G.; Whitelock, H.; Gaisford, P.; Calin, A. A new approach to defining disease status in ankylosing spondylitis: The Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index. J. Rheumatol. 1994, 21, 2286–2291. [Google Scholar]
- Calin, A.; Garrett, S.; Whitelock, H.; Kennedy, L.G.; O’Hea, J.; Mallorie, P.; Jenkinson, T. A new approach to defining functional ability in ankylosing spondylitis: The development of the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Functional Index. J. Rheumatol. 1994, 21, 2281–2285. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- EuroQol Group. EuroQol—A new facility for the measurement of health-related quality of life. Health Policy 1990, 16, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukas, C.; Landewe, R.; Sieper, J.; Dougados, M.; Davis, J.; Braun, J.; van der Linden, S.; van der Heijde, D. Development of an ASAS-endorsed disease activity score (ASDAS) in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2009, 68, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.K.; Nam, H.S.; Chuang, L.H.; Kim, K.Y.; Yang, H.K.; Kwon, I.S.; Kind, P.; Kweon, S.S.; Kim, Y.T. South Korean time trade-off values for EQ-5D health states: Modeling with observed values for 101 health states. Value Health 2009, 12, 1187–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.K.; Lee, W.Y.; Kang, J.H.; Kang, J.H.; Kim, B.T.; Kim, S.M.; Kim, E.M.; Suh, S.H.; Shin, H.J.; Lee, K.R.; et al. 2014 Clinical practice guidelines for overweight and obesity in Korea. Endocrinol. Metab. (Seoul) 2014, 29, 405–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dougados, M.; Simon, P.; Braun, J.; Burgos-Vargas, R.; Maksymowych, W.P.; Sieper, J.; van der Heijde, D. ASAS recommendations for collecting, analysing and reporting NSAID intake in clinical trials/epidemiological studies in axial spondyloarthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2011, 70, 249–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poddubnyy, D.; Rudwaleit, M.; Haibel, H.; Listing, J.; Marker-Hermann, E.; Zeidler, H.; Braun, J.; Sieper, J. Effect of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs on radiographic spinal progression in patients with axial spondyloarthritis: Results from the German Spondyloarthritis Inception Cohort. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2012, 71, 1616–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Law, L.; Beckman Rehnman, J.; Deminger, A.; Klingberg, E.; Jacobsson, L.T.H.; Forsblad-d’Elia, H. Factors related to health-related quality of life in ankylosing spondylitis, overall and stratified by sex. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2018, 20, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molnar, C.; Scherer, A.; Baraliakos, X.; de Hooge, M.; Micheroli, R.; Exer, P.; Kissling, R.O.; Tamborrini, G.; Wildi, L.M.; Nissen, M.J.; et al. TNF blockers inhibit spinal radiographic progression in ankylosing spondylitis by reducing disease activity: Results from the Swiss Clinical Quality Management cohort. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2018, 77, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Carlo, M.; Lato, V.; Carotti, M.; Salaffi, F. Clinimetric properties of the ASAS health index in a cohort of Italian patients with axial spondyloarthritis. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 2016, 14, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Roussou, E.; Kennedy, L.G.; Garrett, S.; Calin, A. Socioeconomic status in ankylosing spondylitis: Relationship between occupation and disease activity. J. Rheumatol. 1997, 24, 908–911. [Google Scholar]
- Chorus, A.M.; Miedema, H.S.; Boonen, A.; Van Der Linden, S. Quality of life and work in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis of working age. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2003, 62, 1178–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Thong, D.; Duffield, S.J.; Hughes, D.; Goodson, N.J. Alcohol and disease activity in axial spondyloarthritis: A cross-sectional study. Rheumatol. Int. 2018, 38, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Li, Y.; Xu, X.; Feng, X.; Yang, D.; Lin, G. Effect of cigarette smoking and alcohol consumption on disease activity and physical functioning in ankylosing spondylitis: A cross-sectional study. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 13919–13927. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Baskan, B.M.; Sivas, F.; Inal, E.E.; Duran, S.; Elverici, E.; Ozoran, K.; Bodur, H. Comparison of the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Radiology Index and the modified Stoke Ankylosing Spondylitis Spine Score in Turkish patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2010, 29, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landewe, R.; Dougados, M.; Mielants, H.; van der Tempel, H.; van der Heijde, D. Physical function in ankylosing spondylitis is independently determined by both disease activity and radiographic damage of the spine. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2009, 68, 863–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, P.; Landewe, R.; Braun, J.; Hermann, K.G.; Baker, D.; van der Heijde, D. Both structural damage and inflammation of the spine contribute to impairment of spinal mobility in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2010, 69, 1465–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Heijde, D.; Ramiro, S.; Landewe, R.; Baraliakos, X.; Van den Bosch, F.; Sepriano, A.; Regel, A.; Ciurea, A.; Dagfinrud, H.; Dougados, M.; et al. 2016 Update of the ASAS-EULAR management recommendations for axial spondyloarthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 978–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arevalo, M.; Gratacos Masmitja, J.; Moreno, M.; Calvet, J.; Orellana, C.; Ruiz, D.; Castro, C.; Carreto, P.; Larrosa, M.; Collantes, E.; Font, P. Influence of HLA-B27 on the Ankylosing Spondylitis phenotype: Results from the REGISPONSER database. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2018, 20, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
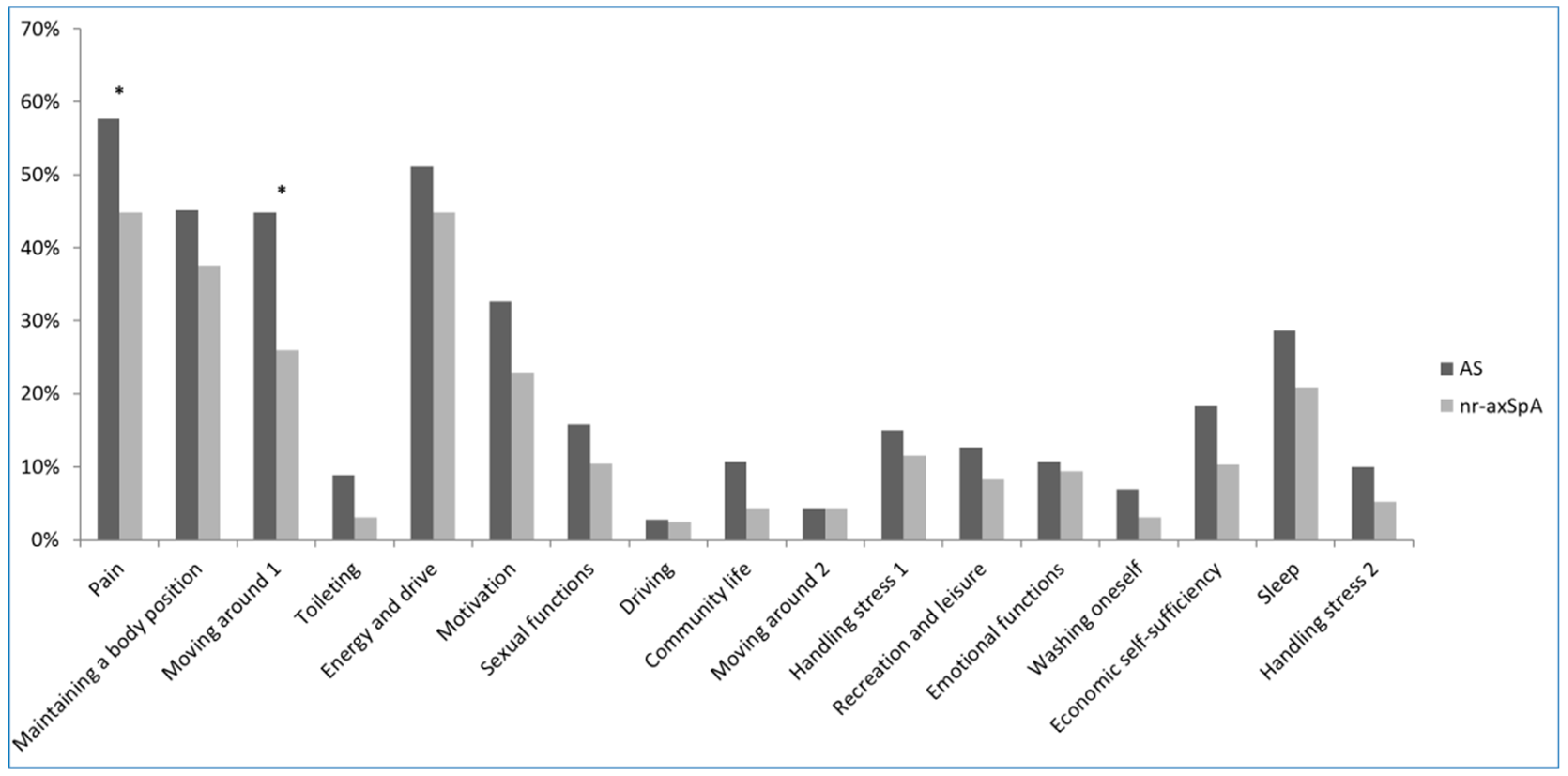
| Characteristics | Total axSpA (N = 357) | Nr-axSpA (N = 96) | AS (N = 261) | p† |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 38.7 ± 11.2 | 34.8 ± 10.7 | 40.1 ± 11.1 | <0.001 |
| Diagnosed age (years) | 31.0 ± 11.5 | 29.3 ± 10.9 | 31.6 ± 11.6 | 0.083 |
| Disease duration (years) | 7.6 ± 6.6 | 5.3 ± 3.8 | 8.4 ± 7.2 | <0.001 |
| Male gender (N, %) | 273 (76.5%) | 66 (68.8%) | 207 (79.3%) | 0.052 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 24.0 ± 3.3 | 23.3 ± 3.2 | 24.3 ± 3.2 | 0.008 |
| Education | 0.864 | |||
| Below high school | 102 (29.8%) | 26 (28.6%) | 76 (30.3%) | |
| College or postgraduate | 240 (70.2%) | 65 (71.4%) | 175 (69.7%) | |
| Salary | 0.026 | |||
| <50,000 US dollar/year | 244 (71.8%) | 74 (81.3%) | 170 (68.3%) | |
| ≥50,000 US dollar/year | 96 (28.2%) | 17 (18.7%) | 79 (31.7%) | |
| Marriage | 0.001 | |||
| Single/divorced/bereaved | 151 (42.4%) | 55 (57.3%) | 96 (36.9%) | |
| Married | 205 (57.6%) | 41 (42.7%) | 164 (63.1%) | |
| Current smoker | 99 (28.0%) | 17 (17.9%) | 82 (31.8%) | 0.015 |
| Current alcohol drinker | 244 (69.1%) | 68 (70.8%) | 176 (68.5%) | 0.767 |
| Uveitis | 161 (45.5%) | 33 (34.4%) | 128 (49.6%) | 0.015 |
| IBD | 6 (1.7%) | 1 (1.0%) | 5 (1.9%) | 0.903 |
| Dactylitis | 28 (7.9%) | 10 (10.4%) | 18 (7.0%) | 0.398 |
| Psoriasis | 17 (4.8%) | 3 (3.1%) | 14 (5.4%) | 0.535 |
| Variables | Total axSpA (N = 357) | Nr-axSpA (N = 96) | AS (N = 261) | p† |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CRP elevation (>0.5 mg/dL) | 67 (18.8%) | 8 (8.3%) | 59 (22.7%) | 0.003 |
| HLA-B27 positive | 310 (93.1%) | 82 (87.2%) | 228 (95.4%) | 0.016 |
| High NSAID intake (ASAS NSAID index ≥ 50) | 195 (54.6%) | 43 (44.8%) | 152 (58.2%) | 0.032 |
| Sulfasalazine | 122 (34.3%) | 32 (33.3%) | 90 (34.6%) | 0.920 |
| TNF-α inhibitor | 170 (47.8%) | 41 (42.7%) | 129 (49.6%) | 0.299 |
| Sum of sacroiliitis grade (0–8) | 5.0 ± 2.1 | 2.1 ± 0.9 | 6.0 ± 1.4 | <0.001 |
| mSASSS (0–72) | 12.2 ± 18.7 | 3.0 ± 5.1 | 15.6 ± 20.6 | <0.001 |
| Presence of syndesmophyte | 210 (58.8%) | 36 (37.5%) | 174 (66.7%) | <0.001 |
| BASDAI (0–10) | 3.1 ± 1.9 | 2.7 ± 1.7 | 3.2 ± 2.0 | 0.023 |
| ASDAS-CRP (0–10) | 1.9 ± 0.9 | 1.6 ± 0.7 | 2.0 ± 0.9 | <0.001 |
| ASDAS-ESR (0–10) | 2.0 ± 0.9 | 1.7 ± 0.7 | 2.1 ± 1.0 | <0.001 |
| BASFI (0–10) | 1.0 ± 1.4 | 0.5 ± 0.8 | 1.1 ± 1.5 | <0.001 |
| PGA (0–10) | 3.2 ± 2.2 | 2.6 ± 1.9 | 3.4 ± 2.3 | 0.001 |
| Spinal pain VAS (0–10) | 2.8 ± 2.4 | 2.2 ± 2.0 | 3.1 ± 2.5 | 0.001 |
| Nocturnal spinal pain VAS (0–10) | 2.3 ± 2.3 | 1.7 ± 2.1 | 2.5 ± 2.3 | 0.003 |
| PhyGA (0–10) | 2.4 ± 1.6 | 2.1 ± 1.6 | 2.4 ± 1.6 | 0.131 |
| EQ-5D-TTO (0–1) | 0.79 ± 0.10 | 0.82 ± 0.08 | 0.78 ± 0.10 | 0.001 |
| EQ-VAS (0–100) | 72.0 ± 18.1 | 72.9 ± 18.5 | 71.7 ± 17.9 | 0.577 |
| ASAS health index (0–17) | 3.5 ± 3.4 | 2.7 ± 2.8 | 3.8 ± 3.5 | 0.003 |
| Health index | 0.053 * | |||
| Poor (≥12) | 13 (3.6%) | 1 (1.0%) | 12 (4.6%) | |
| Moderate (5–12) | 73 (20.4%) | 14 (14.6%) | 59 (22.6%) | |
| Good (≤5) | 271 (75.9%) | 81 (84.4%) | 190 (72.8%) | |
| Environmental factor related to ASAS health index (0–9) | 2.1 ± 1.6 | 1.8 ± 1.2 | 2.2 ± 1.7 | 0.009 |
| Rho | p | |
|---|---|---|
| BASDAI | 0.58 | <0.001 |
| ASDAS-CRP | 0.56 | <0.001 |
| ASDAS-ESR | 0.52 | <0.001 |
| BASFI | 0.65 | <0.001 |
| EQ-5D-TTO | −0.71 | <0.001 |
| EQ-VAS | −0.54 | <0.001 |
| PGA | 0.53 | <0.001 |
| PhyGA | 0.49 | <0.001 |
| Variables | Total axSpA | AS | Nr-axSpA | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Univariable | Multivariable | Univariable | Multivariable | Univariable | |||||||||||
| β | SE | p | β | SE | p | β | SE | p | β | SE | p | β | SE | p | |
| Age (year) | 0.076 | 0.015 | <0.001 | 0.035 | 0.020 | 0.079 | 0.094 | 0.019 | <0.001 | 0.046 | 0.024 | 0.057 | 0.001 | 0.026 | 0.974 |
| Male gender | −0.699 | 0.417 | 0.095 | −0.822 | 0.437 | 0.061 | −1.083 | 0.533 | 0.043 | −1.065 | 0.554 | 0.056 | −0.318 | 0.609 | 0.603 |
| Obesity (BMI ≥ 25 kg/m2) | 0.064 | 0.372 | 0.863 | −0.059 | 0.448 | 0.896 | −0.008 | 0.636 | 0.989 | ||||||
| Higher education level (college or postgraduate) | −1.192 | 0.397 | 0.003 | −1.394 | 0.481 | 0.004 | −0.555 | 0.650 | 0.396 | ||||||
| Higher economic status (≥50,000 US dollar/year) | −0.892 | 0.407 | 0.029 | −1.045 | 0.423 | 0.014 | −1.148 | 0.480 | 0.018 | −1.205 | 0.487 | 0.014 | −0.617 | 0.753 | 0.415 |
| Married | −0.180 | 0.360 | 0.617 | −0.495 | 0.451 | 0.274 | −0.050 | 0.571 | 0.931 | ||||||
| Current smoker | 0.141 | 0.398 | 0.723 | 0.119 | 0.470 | 0.800 | −0.480 | 0.743 | 0.518 | ||||||
| Current alcohol drinker | −1.437 | 0.381 | <0.001 | −1.045 | 0.396 | 0.009 | −1.421 | 0.466 | 0.003 | −1.052 | 0.474 | 0.028 | −1.395 | 0.605 | 0.023 |
| High NSAID intake | 1.169 | 0.351 | 0.001 | 1.034 | 0.357 | 0.004 | 1.483 | 0.431 | 0.001 | 1.419 | 0.433 | 0.001 | −0.038 | 0.568 | 0.947 |
| TNF-α blocker user | 0.435 | 0.356 | 0.223 | 0.450 | 0.436 | 0.303 | 0.177 | 0.571 | 0.758 | ||||||
| HLA-B27 positive | −1.201 | 0.707 | 0.090 | −1.140 | 0.720 | 0.115 | −2.694 | 1.047 | 0.011 | −2.113 | 1.008 | 0.037 | −0.228 | 0.861 | 0.792 |
| Sum of sacroiliitis grade | 0.255 | 0.082 | 0.002 | 0.247 | 0.155 | 0.113 | −0.040 | 0.302 | 0.895 | ||||||
| Existence of syndesmophyte | 1.273 | 0.355 | <0.001 | 1.261 | 0.455 | 0.006 | 0.651 | 0.580 | 0.264 | ||||||
| mSASSS | 0.052 | 0.009 | <0.001 | 0.035 | 0.013 | 0.006 | 0.048 | 0.010 | <0.001 | 0.032 | 0.014 | 0.021 | 0.039 | 0.056 | 0.485 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Min, H.K.; Lee, J.; Ju, J.H.; Park, S.-H.; Kwok, S.-K. Predictors of Assessment of Spondyloarthritis International Society (ASAS) Health Index in Axial Spondyloarthritis and Comparison of ASAS Health Index between Ankylosing Spondylitis and Nonradiographic Axial Spondyloarthritis: Data from the Catholic Axial Spondyloarthritis COhort (CASCO). J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 467. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8040467
Min HK, Lee J, Ju JH, Park S-H, Kwok S-K. Predictors of Assessment of Spondyloarthritis International Society (ASAS) Health Index in Axial Spondyloarthritis and Comparison of ASAS Health Index between Ankylosing Spondylitis and Nonradiographic Axial Spondyloarthritis: Data from the Catholic Axial Spondyloarthritis COhort (CASCO). Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2019; 8(4):467. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8040467
Chicago/Turabian StyleMin, Hong Ki, Jennifer Lee, Ji Hyeon Ju, Sung-Hwan Park, and Seung-Ki Kwok. 2019. "Predictors of Assessment of Spondyloarthritis International Society (ASAS) Health Index in Axial Spondyloarthritis and Comparison of ASAS Health Index between Ankylosing Spondylitis and Nonradiographic Axial Spondyloarthritis: Data from the Catholic Axial Spondyloarthritis COhort (CASCO)" Journal of Clinical Medicine 8, no. 4: 467. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8040467
APA StyleMin, H. K., Lee, J., Ju, J. H., Park, S.-H., & Kwok, S.-K. (2019). Predictors of Assessment of Spondyloarthritis International Society (ASAS) Health Index in Axial Spondyloarthritis and Comparison of ASAS Health Index between Ankylosing Spondylitis and Nonradiographic Axial Spondyloarthritis: Data from the Catholic Axial Spondyloarthritis COhort (CASCO). Journal of Clinical Medicine, 8(4), 467. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8040467





