Activation of the Alternate Renin-Angiotensin System Correlates with the Clinical Status in Human Cirrhosis and Corrects Post Liver Transplantation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Study Subjects
2.2. Blood Sampling
2.3. Measurement of ACE and ACE2 Activity and Angiotensin Peptide Levels
2.4. Hemodynamic Parameters
2.5. Data and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
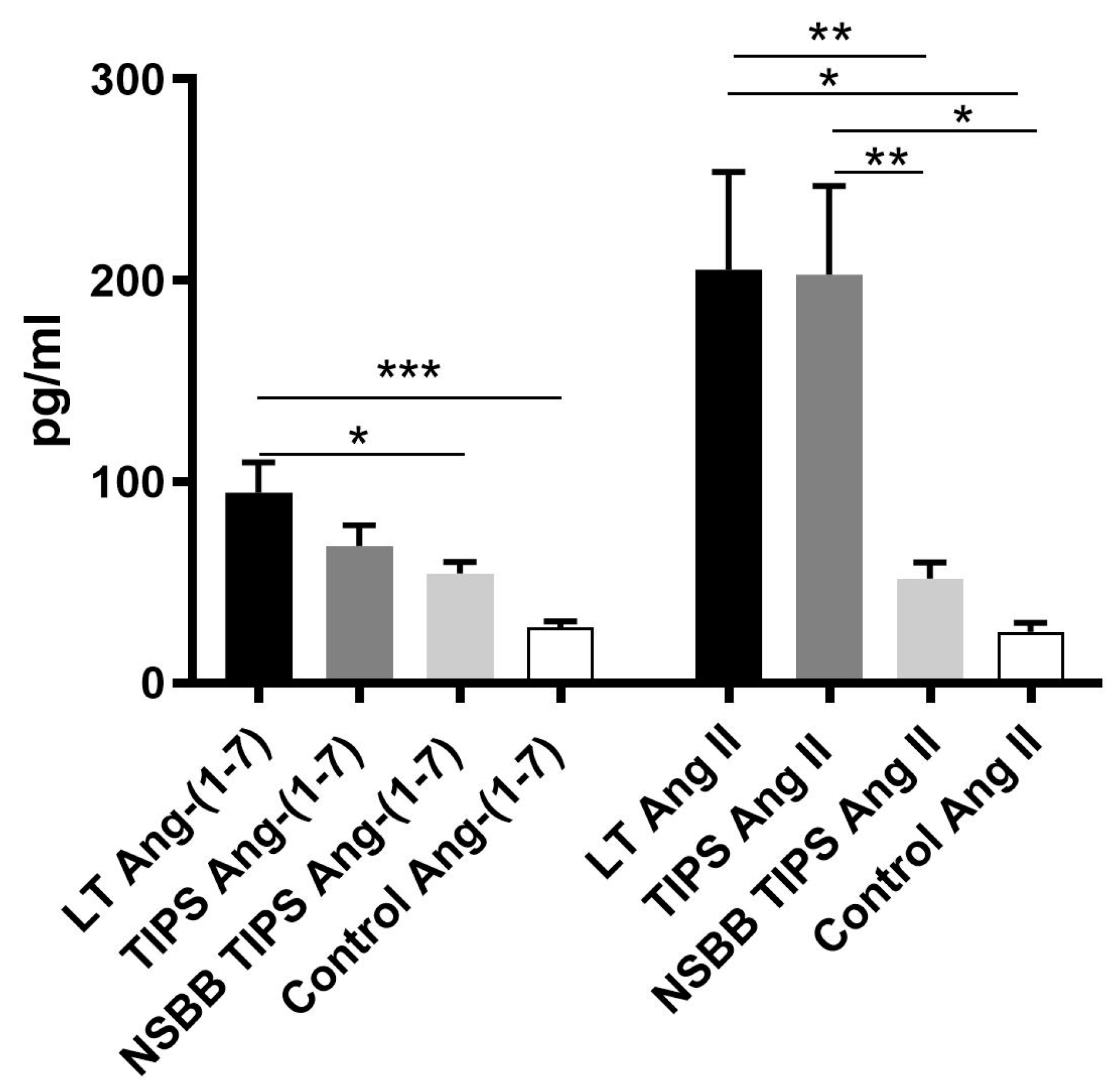
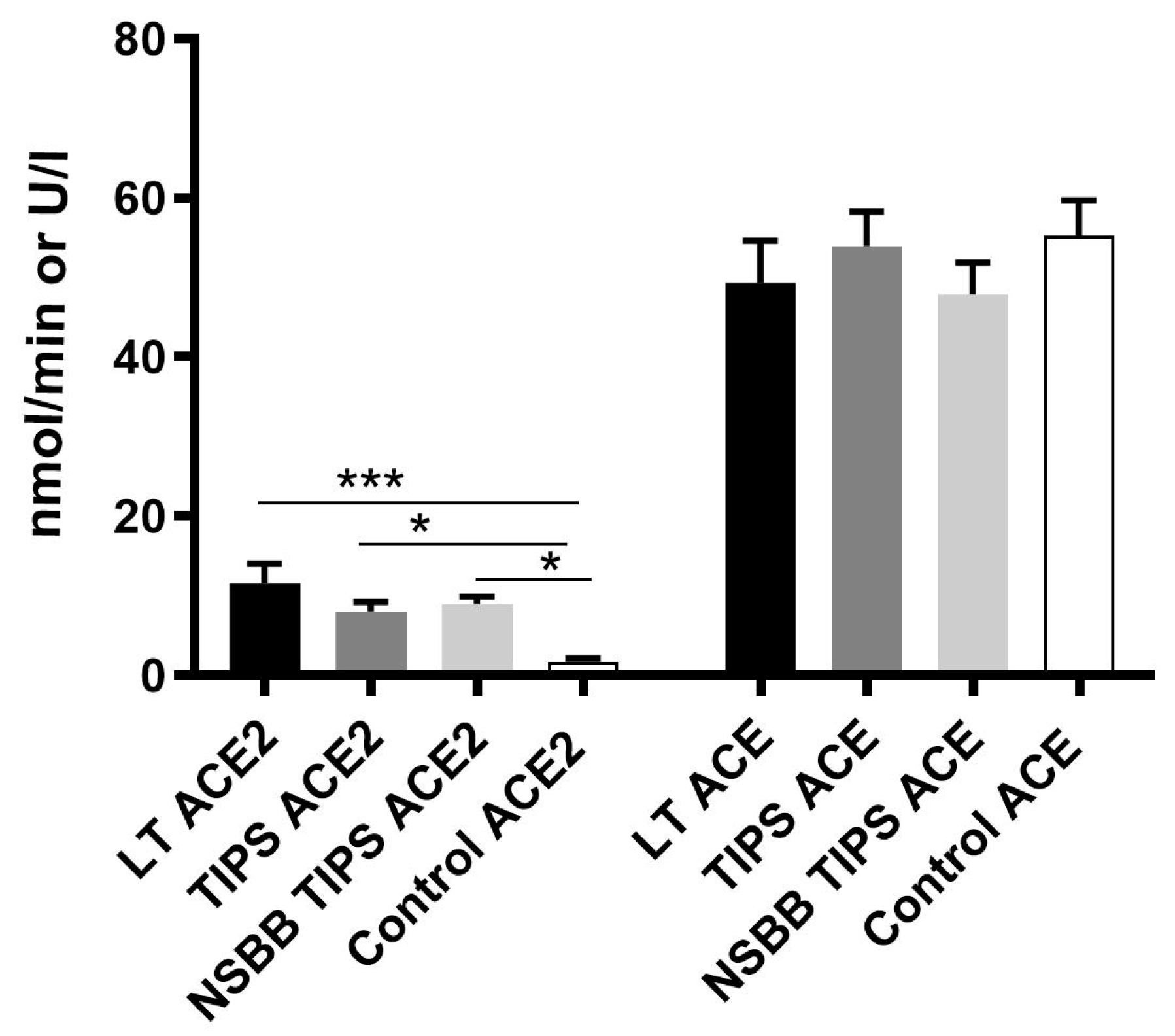
3.2. Peripheral Ang-(1–7), Ang II and ACE2 Levels are Elevated in Human Cirrhosis
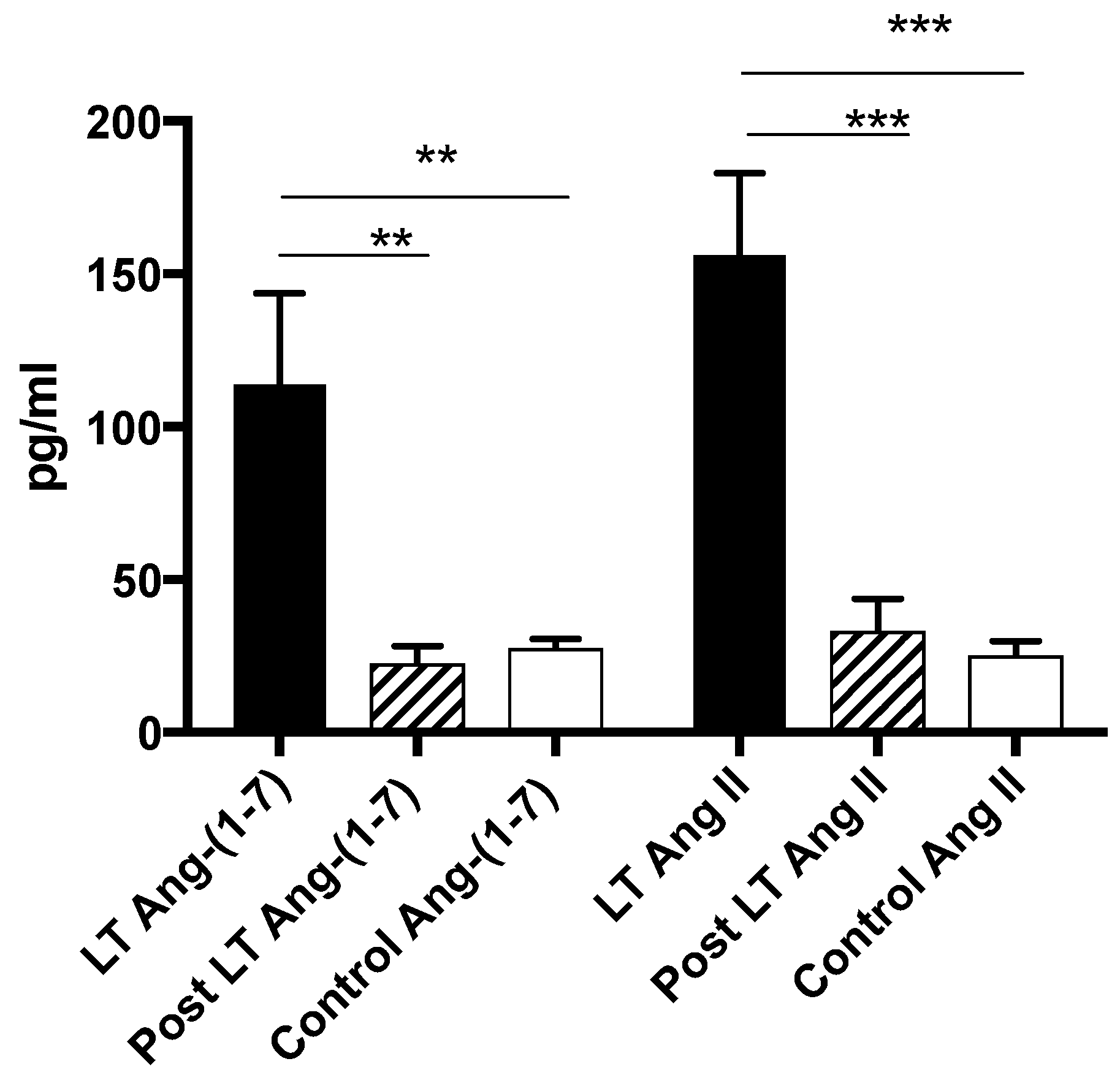
3.3. Ang-(1–7), Ang II and ACE2 Levels Return to Normal Post Liver Transplantation
3.4. Comparison of Peptide and ACE2 Enzyme Activity Levels in Different Vascular Beds
3.5. The Relative RAS Enzyme Activity (ACE2:ACE) is Highly Predictive of Local Peptide Production
3.6. Ang-(1–7) is Increased in Cirrhotic Patients with Advanced Liver Disease and Clinical Features of a Hyperdynamic Circulation
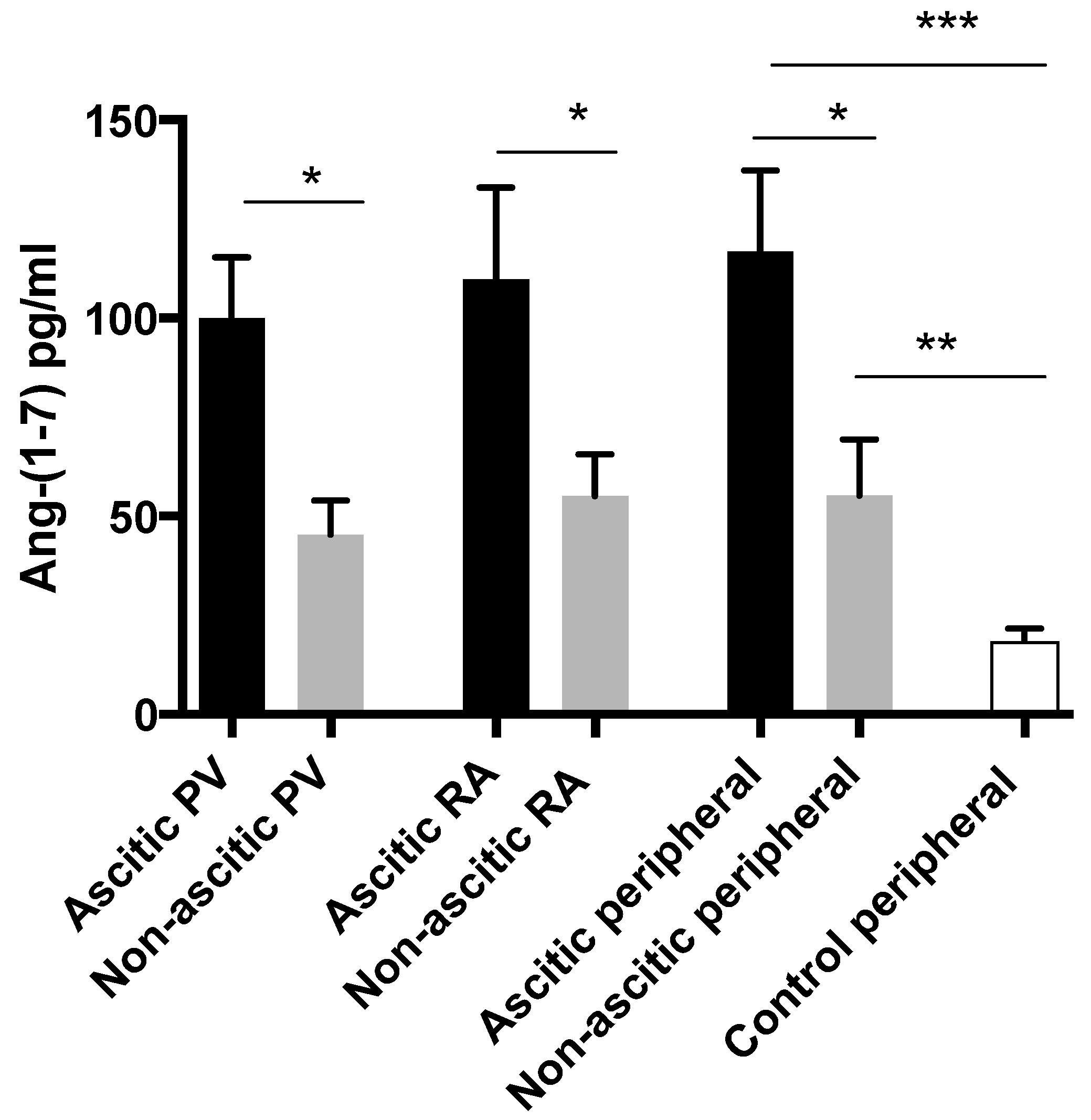
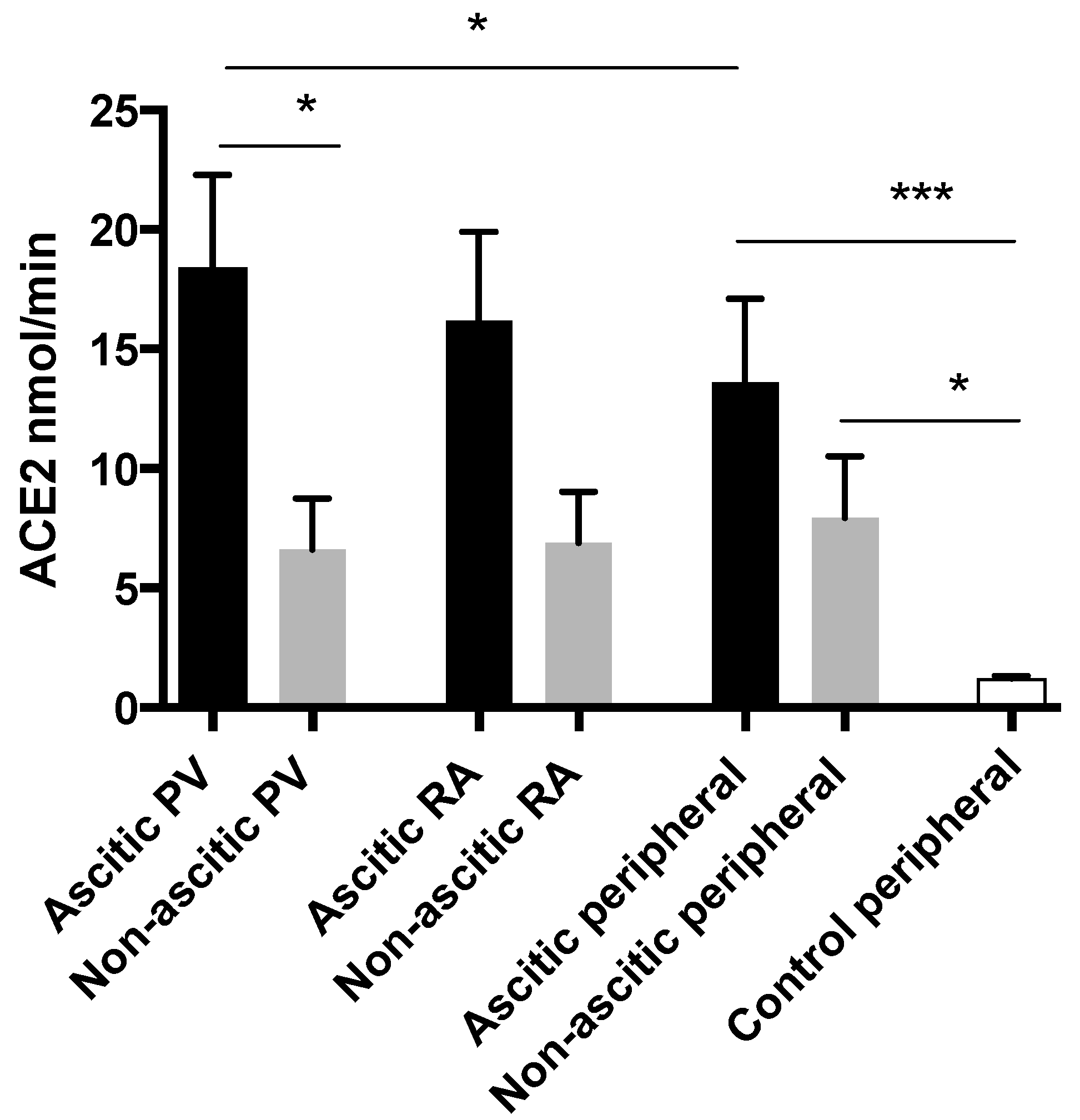
3.7. Alternate RAS Upregulation is Greatest in Patients with Ascites
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Iwakiri, Y. Endothelial dysfunction in the regulation of cirrhosis and portal hypertension. Liver Int. Off. J. Int. Assoc. Study Liver 2012, 32, 199–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abraldes, J.G.; Iwakiri, Y.; Loureiro-Silva, M.; Haq, O.; Sessa, W.C.; Groszmann, R.J. Mild increases in portal pressure upregulate vascular endothelial growth factor and endothelial nitric oxide synthase in the intestinal microcirculatory bed, leading to a hyperdynamic state. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2006, 290, G980–G987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiest, R.; Shah, V.; Sessa, W.C.; Groszmann, R.J. NO overproduction by eNOS precedes hyperdynamic splanchnic circulation in portal hypertensive rats. Am. J. Physiol. 1999, 276 Pt 1, G1043–G1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albornoz, L.; Motta, A.; Alvarez, D.; Estevez, A.; Bandi, J.C.; McCormack, L.; Matera, J.; Bonofiglio, C.; Ciardullo, M.; De Santibanes, E.; et al. Nitric oxide synthase activity in the splanchnic vasculature of patients with cirrhosis: Relationship with hemodynamic disturbances. J. Hepatol. 2001, 35, 452–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwakiri, Y.; Shah, V.; Rockey, D.C. Vascular pathobiology in chronic liver disease and cirrhosis - current status and future directions. J. Hepatol. 2014, 61, 912–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gracia-Sancho, J.; Maeso-Diaz, R.; Fernández-Iglesias, A.; Navarro-Zornoza, M.; Bosch, J. New cellular and molecular targets for the treatment of portal hypertension. Hepatol. Int. 2015, 9, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helmy, A.; Jalan, R.; Newby, D.E.; Hayes, P.C.; Webb, D.J. Role of angiotensin ii in regulation of basal and sympathetically stimulated vascular tone in early and advanced cirrhosis. Gastroenterology 2000, 118, 565–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paizis, G.; Cooper, M.E.; Schembri, J.M.; Tikellis, C.; Burrell, L.M.; Angus, P.W. Up-regulation of components of the renin-angiotensin system in the bile duct-ligated rat liver. Gastroenterology 2002, 123, 1667–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrier, R.W.; Arroyo, V.; Bernardi, M.; Epstein, M.; Henriksen, J.H.; Rodes, J. Peripheral arterial vasodilation hypothesis: A proposal for the initiation of renal sodium and water retention in cirrhosis. Hepatology 1988, 8, 1151–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grace, J.A.; Herath, C.B.; Mak, K.Y.; Burrell, L.M.; Angus, P.W. Update on new aspects of the renin-angiotensin system in liver disease: Clinical implications and new therapeutic options. Clin. Sci. (Lond.) 2012, 123, 225–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubel, J.S.; Herath, C.B.; Tchongue, J.; Grace, J.; Jia, Z.; Spencer, K.; Casley, D.; Crowley, P.; Sievert, W.; Burrell, L.M.; et al. Angiotensin-(1–7), an alternative metabolite of the renin-angiotensin system, is up-regulated in human liver disease and has antifibrotic activity in the bile-duct-ligated rat. Clin. Sci. 2009, 117, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donoghue, M.; Hsieh, F.; Baronas, E.; Godbout, K.; Gosselin, M.; Stagliano, N.; Donovan, M.; Woolf, B.; Robison, K.; Jeyaseelan, R.; et al. A novel angiotensin-converting enzyme-related carboxypeptidase (ace2) converts angiotensin i to angiotensin 1-9. Circ. Res. 2000, 87, E1–E9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herath, C.B.; Warner, F.J.; Lubel, J.S.; Dean, R.G.; Jia, Z.; Lew, R.A.; Smith, A.I.; Burrell, L.M.; Angus, P.W. Upregulation of hepatic angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) and angiotensin-(1–7) levels in experimental biliary fibrosis. J. Hepatol. 2007, 47, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mak, K.Y.; Chin, R.; Cunningham, S.C.; Habib, M.R.; Torresi, J.; Sharland, A.F.; Alexander, I.E.; Angus, P.W.; Herath, C.B. Ace2 therapy using adeno-associated viral vector inhibits liver fibrosis in mice. Mol. Ther. J. Am. Soc. Gene Ther. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grace, J.A.; Klein, S.; Herath, C.B.; Granzow, M.; Schierwagen, R.; Masing, N.; Walther, T.; Sauerbruch, T.; Burrell, L.M.; Angus, P.W.; et al. Activation of the mas receptor by angiotensin-(1–7) in the renin-angiotensin system mediates mesenteric vasodilation in cirrhosis. Gastroenterology 2013, 145, 878–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, R.A.; Simoes e Silva, A.C.; Maric, C.; Silva, D.M.; Machado, R.P.; de Buhr, I.; Heringer-Walther, S.; Pinheiro, S.V.; Lopes, M.T.; Bader, M.; et al. Angiotensin-(1–7) is an endogenous ligand for the g protein-coupled receptor mas. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. United States Am. 2003, 100, 8258–8263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chappell, M.C.; Pirro, N.T.; Sykes, A.; Ferrario, C.M. Metabolism of angiotensin-(1–7) by angiotensin-converting enzyme. Hypertension 1998, 31, 362–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grobe, J.L.; Mecca, A.P.; Mao, H.; Katovich, M.J. Chronic angiotensin-(1–7) prevents cardiac fibrosis in doca-salt model of hypertension. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2006, 290, H2417–H2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loot, A.E.; Roks, A.J.M.; Henning, R.H.; Tio, R.A.; Suurmeijer, A.J.H.; Boomsma, F.; van Gilst, W.H. Angiotensin-(1–7) attenuates the development of heart failure after myocardial infarction in rats. Circulation 2002, 105, 1548–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benter, I.F.; Yousif, M.H.; Dhaunsi, G.S.; Kaur, J.; Chappell, M.C.; Diz, D.I. Angiotensin-(1–7) prevents activation of nadph oxidase and renal vascular dysfunction in diabetic hypertensive rats. Am. J. Nephrol. 2008, 28, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paizis, G.; Tikellis, C.; Cooper, M.E.; Schembri, J.M.; Lew, R.A.; Smith, A.I.; Shaw, T.; Warner, F.J.; Zuilli, A.; Burrell, L.M.; et al. Chronic liver injury in rats and humans upregulates the novel enzyme angiotensin converting enzyme 2. Gut 2005, 54, 1790–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilas-Boas, W.W.; Ribeiro-Oliveira, A., Jr.; Pereira, R.M.; Ribeiro Rda, C.; Almeida, J.; Nadu, A.P.; Simoes e Silva, A.C.; dos Santos, R.A. Relationship between angiotensin-(1–7) and angiotensin ii correlates with hemodynamic changes in human liver cirrhosis. World J. Gastroenterol. WJG 2009, 15, 2512–2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilas-Boas, W.W.; Ribeiro-Oliveira, A., Jr.; Ribeiro Rda, C.; Vieira, R.L.; Almeida, J.; Nadu, A.P.; Simoes e Silva, A.C.; Santos, R.A. Effect of propranolol on the splanchnic and peripheral renin angiotensin system in cirrhotic patients. World J. Gastroenterol. WJG 2008, 14, 6824–6830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLean, A.S.; Needham, A.; Stewart, D.; Parkin, R. Estimation of cardiac output by noninvasive echocardiographic techniques in the critically ill subject. Anaesth. Intensive Care 1997, 25, 250–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mercado, P.; Maizel, J.; Beyls, C.; Titeca-Beauport, D.; Joris, M.; Kontar, L.; Riviere, A.; Bonef, O.; Soupison, T.; Tribouilloy, C.; et al. Transthoracic echocardiography: An accurate and precise method for estimating cardiac output in the critically ill patient. Crit. Care (Lond. Engl.) 2017, 21, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navasa, M.; Feu, F.; Garcia-Pagan, J.C.; Jimenez, W.; Llach, J.; Rimola, A.; Bosch, J.; Rodes, J. Hemodynamic and humoral changes after liver transplantation in patients with cirrhosis. Hepatology 1993, 17, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piscaglia, F.; Zironi, G.; Gaiani, S.; Mazziotti, A.; Cavallari, A.; Gramantieri, L.; Valgimigli, M.; Bolondi, L. Systemic and splanchnic hemodynamic changes after liver transplantation for cirrhosis: A long-term prospective study. Hepatology 1999, 30, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Studdy, P.R.; Lapworth, R.; Bird, R. Angiotensin-converting enzyme and its clinical significance—A review. J. Clin. Pathol. 1983, 36, 938–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumenfeld, J.D.; Sealey, J.E.; Mann, S.J.; Bragat, A.; Marion, R.; Pecker, M.S.; Sotelo, J.; August, P.; Pickering, T.G.; Laragh, J.H. Beta-adrenergic receptor blockade as a therapeutic approach for suppressing the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system in normotensive and hypertensive subjects. Am. J. Hypertens. 1999, 12, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Franchis, R.; Salerno, F. Pathogenesis of ascites and predictors of resistance to therapy. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2002, 17 (Suppl. 3), S242–S247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiese, S.; Hove, J.D.; Bendtsen, F.; Moller, S. Cirrhotic cardiomyopathy: Pathogenesis and clinical relevance. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 11, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolognesi, M.; Sacerdoti, D.; Bombonato, G.; Merkel, C.; Sartori, G.; Merenda, R.; Nava, V.; Angeli, P.; Feltracco, P.; Gatta, A. Change in portal flow after liver transplantation: Effect on hepatic arterial resistance indices and role of spleen size. Hepatology 2002, 35, 601–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angeli, P.; Fernandez-Varo, G.; Dalla Libera, V.; Fasolato, S.; Galioto, A.; Arroyo, V.; Sticca, A.; Guarda, S.; Gatta, A.; Jimenez, W. The role of nitric oxide in the pathogenesis of systemic and splanchnic vasodilation in cirrhotic rats before and after the onset of ascites. Liver Int. Off. J. Int. Assoc. Study Liver 2005, 25, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martell, M.; Coll, M.; Ezkurdia, N.; Raurell, I.; Genesca, J. Physiopathology of splanchnic vasodilation in portal hypertension. World J. Hepatol. 2010, 2, 208–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen Dinh Cat, A.; Touyz, R.M. A new look at the renin-angiotensin system--focusing on the vascular system. Peptides 2011, 32, 2141–2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| LT (n = 25) | TIPS (n = 35) | NSBB TIPS (n = 54) | Control (n = 15) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 53 (2) | 53 (2) | 61 (2) * | 50 (4) |
| Sex (M/F) | 20/5 | 26/9 | 31/23 | 7/8 |
| Child Pugh score | 10 (0.5) * | 7 (0.3) | 7 (0.2) | N/A |
| MELD | 21 (2) * | 12 (1) | 12 (1) | N/A |
| MAP | 84 (2) | 80 (2) | 80 (2) | 78 (2) |
| HR | 83 (3) | 83 (3) | 73 (2) # | 64 (2) ! |
| CO | 6.9 (0.4) * | 5.4 (0.4) ^ | 3.4 (0.3) | N/A |
| Portal Vein | Right Atrium | Radial Artery | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ang-(1–7) pg/mL | 81(12) | 90 (17) | 95 (16) |
| Ang II pg/mL | 138 (24) ** | 163 (30) | 206 (52) |
| Ang-(1–7):Ang II | 1.022 (0.18) * | 1.194 (0.34) | 0.828 (0.18) |
| ACE2 nmol/L | 14.1 (2.8) | 13.6 (2.9) | 12.1 (2.7) |
| TIPS | Portal Vein | Peripheral Vein | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ang-(1–7) pg/mL | 64 (11) | 68 (10) | NS |
| Ang II pg/mL | 119 (27) | 175 (46) | NS |
| Ang-(1–7):Ang II | 0.65 (0.1) | 0.74 (0.1) | NS |
| ACE2 nmol/L | 6.5 (1) | 8 (1) | NS |
| NSBB TIPS | Portal Vein | Peripheral Vein | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ang-(1–7) pg/mL | 65 (7) | 55 (6) | 0.0148 |
| Ang II pg/mL | 53 (9) | 50 (8) | NS |
| Ang-(1–7):Ang II | 1.59 (0.2) | 1.32 (0.2) | 0.068 |
| ACE2 nmol/L | 10 (1) | 9 (1) | NS |
| Local Ang-(1–7) | Local Ang II | Local 1–7:II | |
|---|---|---|---|
| PV ACE2 | 0.004 0.590 | 0.433 | 0.003 0.611 |
| PV ACE | 0.41 | 0.64 | 0.345 |
| PV ACE2:ACE | 0.007 0.56 | 0.195 | <0.0001 0.7 |
| RA ACE2 | 0.004 0.557 | 0.869 | 0.008 0.515 |
| RA ACE | 0.657 | 0.17 | 0.471 |
| RA ACE2:ACE | 0.006 0.536 | 0.27 | 0.00024 0.671 |
| Rad art ACE2 | 0.044 0.406 | 0.092 (0.344) | <0.0001 0.711 |
| Rad art ACE | 0.759 | 0.183 | 0.341 |
| Rad art ACE2:ACE | 0.031 0.432 | 0.035 (0.423) | <0.0001 0.8 |
| MELD | Child-Pugh | CO | MAP | HR | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PV Ang-(1–7) | 0.042 0.428 | 0.057 0.403 | 0.004 0.648 | NS | NS |
| RA Ang-(1–7) | 0.108 | NS | 0.003 0.635 | NS | NS |
| Rad art Ang-(1–7) | NS | NS | 0.015 0.537 | NS | NS |
| MELD | Child-Pugh | CO | MAP | HR | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PV Ang-(1–7) | 0.059 0.338 | NS | 0.002 0.632 | NS | 0.032 0.379 |
| Periph Ang-(1–7) | 0.032 0.399 | NS | 0.07 0.232 | NS | 0.075 0.336 |
| Ascitic (n = 16) | Non-Ascitic (n = 9) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 52 (2) | 55 (3) | NS |
| Sex (M/F) | 13/3 | 7/2 | NS |
| MELD | 24 (2) | 16 (3) | <0.05 |
| Child Pugh score | 11 (0.5) | 8 (1) | <0.05 |
| MAP | 84 (3) | 84 (4) | NS |
| HR | 85 (3) | 81 (5) | NS |
| CO | 7.4 (0.5) | 5.9 (0.4) | 0.0612 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Casey, S.; Schierwagen, R.; Mak, K.Y.; Klein, S.; Uschner, F.; Jansen, C.; Praktiknjo, M.; Meyer, C.; Thomas, D.; Herath, C.; et al. Activation of the Alternate Renin-Angiotensin System Correlates with the Clinical Status in Human Cirrhosis and Corrects Post Liver Transplantation. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 419. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8040419
Casey S, Schierwagen R, Mak KY, Klein S, Uschner F, Jansen C, Praktiknjo M, Meyer C, Thomas D, Herath C, et al. Activation of the Alternate Renin-Angiotensin System Correlates with the Clinical Status in Human Cirrhosis and Corrects Post Liver Transplantation. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2019; 8(4):419. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8040419
Chicago/Turabian StyleCasey, Stephen, Robert Schierwagen, Kai Yan Mak, Sabine Klein, Frank Uschner, Christian Jansen, Michael Praktiknjo, Carsten Meyer, Daniel Thomas, Chandana Herath, and et al. 2019. "Activation of the Alternate Renin-Angiotensin System Correlates with the Clinical Status in Human Cirrhosis and Corrects Post Liver Transplantation" Journal of Clinical Medicine 8, no. 4: 419. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8040419
APA StyleCasey, S., Schierwagen, R., Mak, K. Y., Klein, S., Uschner, F., Jansen, C., Praktiknjo, M., Meyer, C., Thomas, D., Herath, C., Jones, R., Trebicka, J., & Angus, P. (2019). Activation of the Alternate Renin-Angiotensin System Correlates with the Clinical Status in Human Cirrhosis and Corrects Post Liver Transplantation. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 8(4), 419. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8040419






