Genomic Variations in Susceptibility to Intracranial Aneurysm in the Korean Population
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Genotyping and Sample Quality Control
2.3. Statistical Analysis
2.4. Gene Functional Enrichment, Pathway, and Network Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Characteristics of the Enrolled Patients
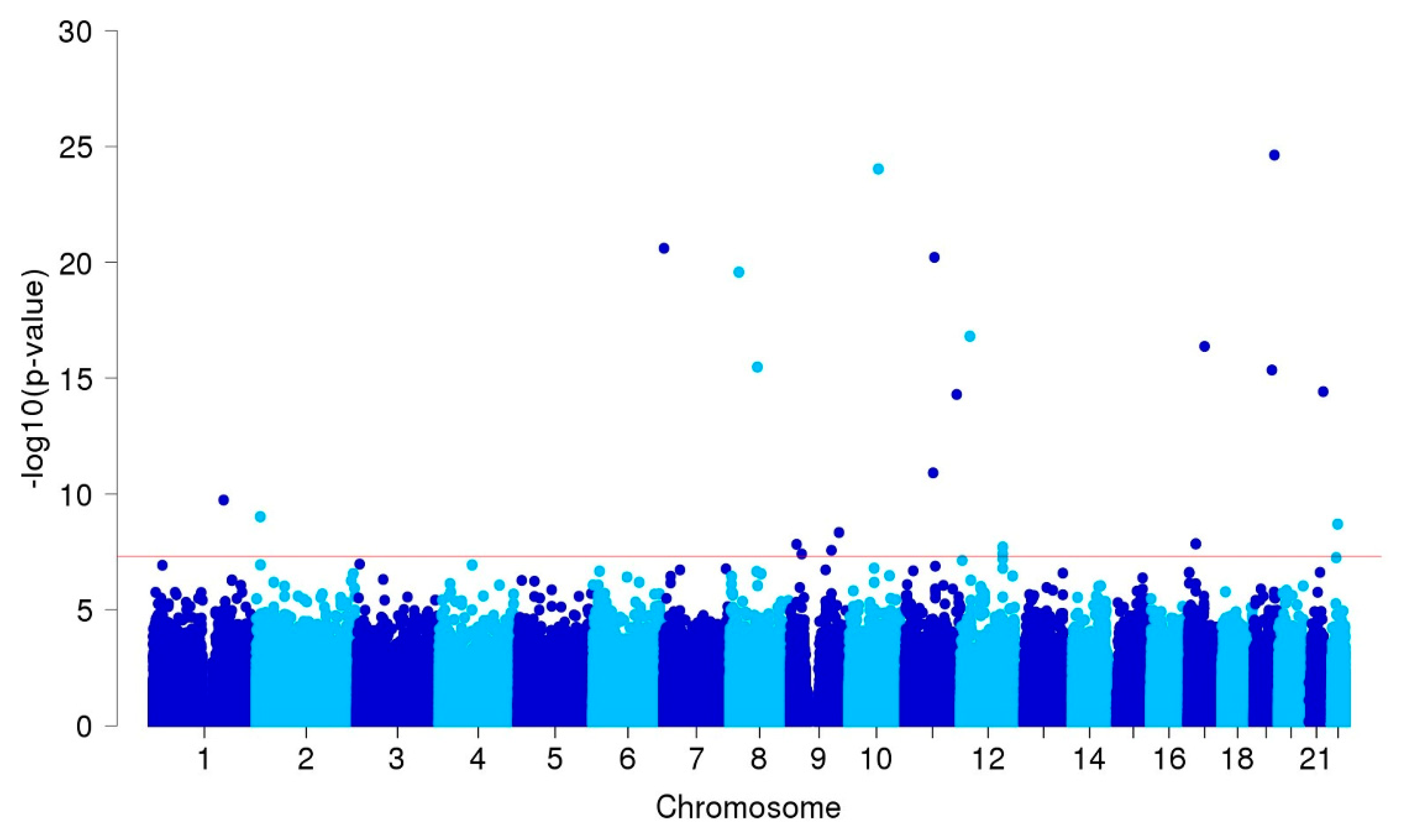
3.2. GWAS and Single-cell eQTL Analysis
3.3. Gene Function and Network Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vlak, M.H.; Algra, A.; Brandenburg, R.; Rinkel, G.J. Prevalence of unruptured intracranial aneurysms, with emphasis on sex, age, comorbidity, country, and time period: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Neurol. 2011, 10, 626–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katati, M.J.; Santiago-Ramajo, S.; Perez-Garcia, M.; Meersmans-Sanchez Jofre, M.; Vilar-Lopez, R.; Coin-Mejias, M.A.; Caracuel-Romero, A.; Arjona-Moron, V. Description of quality of life and its predictors in patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2007, 24, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nahed, B.V.; Bydon, M.; Ozturk, A.K.; Bilguvar, K.; Bayrakli, F.; Gunel, M. Genetics of intracranial aneurysms. Neurosurgery 2007, 60, 213–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caranci, F.; Briganti, F.; Cirillo, L.; Leonardi, M.; Muto, M. Epidemiology and genetics of intracranial aneurysms. Eur. J. Radiol. 2013, 82, 1598–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onda, H.; Kasuya, H.; Yoneyama, T.; Takakura, K.; Hori, T.; Takeda, J.; Nakajima, T.; Inoue, I. Genomewide-linkage and haplotype-association studies map intracranial aneurysm to chromosome 7q11. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2001, 69, 804–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olson, J.M.; Vongpunsawad, S.; Kuivaniemi, H.; Ronkainen, A.; Hernesniemi, J.; Ryynanen, M.; Kim, L.L.; Tromp, G. Search for intracranial aneurysm susceptibility gene(s) using Finnish families. BMC Med. Genet. 2002, 3, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahed, B.V.; Seker, A.; Guclu, B.; Ozturk, A.K.; Finberg, K.; Hawkins, A.A.; DiLuna, M.L.; State, M.; Lifton, R.P.; Gunel, M. Mapping a Mendelian form of intracranial aneurysm to 1p34.3-p36.13. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2005, 76, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, S.; Utsunomiya, M.; Inoue, K.; Nozaki, K.; Inoue, S.; Takenaka, K.; Hashimoto, N.; Koizumi, A. Genome-wide scan for Japanese familial intracranial aneurysms: linkage to several chromosomal regions. Circulation 2004, 110, 3727–3733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilguvar, K.; Yasuno, K.; Niemela, M.; Ruigrok, Y.M.; von Und, Z.; Fraunberg, M.; van Duijn, C.M.; Tajima, A.; Laakso, A.; Hata, A.; et al. Susceptibility loci for intracranial aneurysm in European and Japanese populations. Nat. Genet. 2008, 40, 1472–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Akiyama, K.; Narita, A.; Nakaoka, H.; Cui, T.; Takahashi, T.; Yasuno, K.; Tajima, A.; Krischek, B.; Yamamoto, K.; Kasuya, H.; et al. Genome-wide association study to identify genetic variants present in Japanese patients harboring intracranial aneurysms. J. Hum. Genet. 2010, 55, 656–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yasuno, K.; Bilguvar, K.; Bijlenga, P.; Low, S.K.; Krischek, B.; Auburger, G.; Simon, M.; Krex, D.; Arlier, Z.; Nayak, N.; et al. Genome-wide association study of intracranial aneurysm identifies three new risk loci. Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 420–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Low, S.K.; Takahashi, A.; Cha, P.C.; Zembutsu, H.; Kamatani, N.; Kubo, M.; Nakamura, Y. Genome-wide association study for intracranial aneurysm in the Japanese population identifies three candidate susceptible loci and a functional genetic variant at EDNRA. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2012, 21, 2102–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alg, V.S.; Sofat, R.; Houlden, H.; Werring, D.J. Genetic risk factors for intracranial aneurysms: A meta-analysis in more than 116,000 individuals. Neurology 2013, 80, 2154–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, T.; Shu, Y.; Cai, Y.D. Genetic differences among ethnic groups. BMC Genomics 2015, 16, 1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.Y.; Kim, T.H.; Yang, P.S.; Lim, H.E.; Choi, E.K.; Shim, J.; Shin, E.; Uhm, J.S.; Kim, J.S.; Joung, B.; et al. Korean atrial fibrillation network genome-wide association study for early-onset atrial fibrillation identifies novel susceptibility loci. Eur. Heart J. 2017, 38, 2586–2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, C.H.; Jeon, J.P.; Kim, S.E.; Choi, H.J.; Cho, Y.J. Endovascular Treatment with Intravenous Thrombolysis versus Endovascular Treatment Alone for Acute Anterior Circulation Stroke: A Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies. J. Korean Neurosurg. Soc. 2018, 61, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, E.P.; Jeon, J.P.; Kim, S.E.; Yang, J.S.; Choi, H.J.; Kang, S.H.; Cho, Y.J. A Novel Association between Lysyl Oxidase Gene Polymorphism and Intracranial Aneurysm in Koreans. Yonsei Med. J. 2017, 58, 1006–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, E.P.; Kim, B.J.; Kim, C.; Choi, H.J.; Jeon, J.P. Association of SOX17 Gene Polymorphisms and Intracranial Aneurysm: A Case-Control Study and Meta-Analysis. World Neurosurg. 2018, 110, e823–e829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.C.; Chow, C.C.; Tellier, L.C.; Vattikuti, S.; Purcell, S.M.; Lee, J.J. Second-generation PLINK: Rising to the challenge of larger and richer datasets. Gigascience 2015, 4, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GTEx Consortium. Human genomics. The Genotype-Tissue Expression (GTEx) pilot analysis: Multitissue gene regulation in humans. Science 2015, 348, 648–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pruim, R.J.; Welch, R.P.; Sanna, S.; Teslovich, T.M.; Chines, P.S.; Gliedt, T.P.; Boehnke, M.; Abecasis, G.R.; Willer, C.J. LocusZoom: Regional visualization of genome-wide association scan results. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2336–22337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dennis, G., Jr.; Sherman, B.T.; Hosack, D.A.; Yang, J.; Gao, W.; Lane, H.C.; Lempicki, R.A. DAVID: Database for Annotation, Visualization, and Integrated Discovery. Genome Biol. 2003, 4, P3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Franceschini, A.; Wyder, S.; Forslund, K.; Heller, D.; Huerta-Cepas, J.; Simonovic, M.; Roth, A.; Santos, A.; Tsafou, K.P.; et al. STRING v10: Protein-protein interaction networks, integrated over the tree of life. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 4, D447–D452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loirand, G.; Pacaud, P. Involvement of Rho GTPases and their regulators in the pathogenesis of hypertension. Small GTPases 2014, 5, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, X.; Lenhart, K.C.; Bird, K.E.; Suen, A.A.; Rojas, M.; Kakoki, M.; Li, F.; Smithies, O.; Mack, C.P.; Taylor, J.M. The smooth muscle-selective RhoGAP GRAF3 is a critical regulator of vascular tone and hypertension. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Inci, S.; Spetzler, R.F. Intracranial aneurysms and arterial hypertension: A review and hypothesis. Surg. Neurol. 2000, 53, 530–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malek, N.; Weil, R.S.; Bresner, C.; Lawton, M.A.; Grosset, K.A.; Tan, M.; Bajaj, N.; Barker, R.A.; Burn, D.J.; Foltynie, T.; et al. Features of GBA-associated Parkinson’s disease at presentation in the UK Tracking Parkinson’s study. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2018, 89, 702–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan-Or, Z.; Amshalom, I.; Kilarski, L.L.; Bar-Shira, A.; Gana-Weisz, M.; Mirelman, A.; arder, K.; Bressman, S.; Giladi, N.; Orr-Urtreger, A. Differential effects of severe vs mild GBA mutations on Parkinson disease. Neurology 2015, 84, 880–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, E.J.; Yang, N.Y.; Lee, C.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, S.; Sardi, S.P.; Lee, S.J. Loss of glucocerebrosidase 1 activity causes lysosomal dysfunction and alpha-synuclein aggregation. Exp. Mol. Med. 2015, 47, e153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Z.; Sun, Y.; Liu, K.; Wang, F.; Zhang, T.; Li, Q.; Shen, L.; Zhou, L.; Dong, L.; Shi, N.; et al. The role of autophagic and lysosomal pathways in ischemic brain injury. Neural Regen. Res. 2013, 23, 2117–2125. [Google Scholar]
- Tu, C.; Ortega-Cava, C.F.; Chen, G.; Fernandes, N.D.; Cavallo-Medved, D.; Sloane, B.F.; Band, V.; Band, H. Lysosomal cathepsin B participates in the podosome-mediated extracellular matrix degradation and invasion via secreted lysosomes in v-Src fibroblasts. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 9147–9156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, M.; Luo, D.; Yu, S.; Liu, P.; Zhou, Q.; Hu, M.; Liu, Y.; Wang, S.; Huang, Q.; Niu, Y.; et al. Misshapen/NIK-related kinase (MINK1) is involved in platelet function, hemostasis, and thrombus formation. Blood 2016, 127, 927–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, K.B.; Arzani, A.; Shadden, S.C. Mechanical platelet activation potential in abdominal aortic aneurysms. J. Biomech. Eng. 2015, 137, 041005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biasetti, J.; Spazzini, P.G.; Hedin, U.; Gasser, T.C. Synergy between shear-induced migration and secondary flows on red blood cells transport in arteries: considerations on oxygen transport. J. R. Soc. Interface. 2014, 11, 20140403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ungvari, Z.; Valcarcel-Ares, M.N.; Tarantini, S.; Yabluchanskiy, A.; Fulop, G.A.; Kiss, T.; Csiszar, A. Connective tissue growth factor (CTGF) in age-related vascular pathologies. Geroscience 2017, 39, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Santiago-Sim, T.; Mathew-Joseph, S.; Pannu, H.; Milewicz, D.M.; Seidman, C.E.; Seidman, J.G.; Kim, D.H. Sequencing of TGF-beta pathway genes in familial cases of intracranial aneurysm. Stroke 2009, 40, 1604–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anholt, R.R. Olfactomedin proteins: Central players in development and disease. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2014, 2, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furutani, Y.; Manabe, R.; Tsutsui, K.; Yamada, T.; Sugimoto, N.; Fukuda, S.; Kawai, J.; Sugiura, N.; Kimata, K.; Hayashizaki, Y.; et al. Identification and characterization of photomedins: Novel olfactomedin-domain-containing proteins with chondroitin sulphate-E-binding activity. Biochem. J. 2005, 389, 675–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomarev, S.I.; Nakaya, N. Olfactomedin domain-containing proteins: Possible mechanisms of action and functions in normal development and pathology. Mol. Neurobiol. 2009, 40, 122–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.H.; Li, P.G.; Huang, Q.L.; Ling, J. Endothelial injury preceding intracranial aneurysm formation in rabbits. West Indian Med. J. 2014, 63, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ramirez-Ortiz, Z.G.; Pendergraft, W.F., 3rd; Prasad, A.; Byrne, M.H.; Iram, T.; Blanchette, C.J.; Luster, A.D.; Hacohen, N.; El Khoury, J.; Means, T.K. The scavenger receptor SCARF1 mediates the clearance of apoptotic cells and prevents autoimmunity. Nat. Immunol. 2013, 14, 917–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Patten, D.A. SCARF1: A multifaceted, yet largely understudied, scavenger receptor. Inflamm. Res. 2018, 67, 627–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- HUGO Pan-Asian SNP Consortium; Abdulla, M.A.; Ahmed, I.; Assawamakin, A.; Bhak, J.; Brahmachari, S.K.; Calacal, G.C.; Chaurasia, A.; Chen, C.H.; Chen, J.; et al. Indian Genome Variation Consortium. Mapping human genetic diversity in Asia. Science 2009, 326, 1541–1545. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Wang, T.; You, C.; Liu, W.; Zhao, K.; Sun, H.; Mao, B.; Li, X.; Xiao, A.; Mao, X.; et al. Association of polymorphisms in the elastin gene with sporadic ruptured intracranial aneurysms and unruptured intracranial aneurysms in Chinese patients. Int. J. Neurosci. 2013, 123, 454–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.C.; Pickard, J.D.; Davenport, A.P. Endothelin ETA receptor expression in human cerebrovascular smooth muscle cells. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1995, 116, 2441–2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fassbender, K.; Hodapp, B.; Rossol, S.; Bertsch, T.; Schmeck, J.; Schutt, S.; Fritzinger, M.; Horn, P.; Vajkoczy, P.; Wendel-Wellner, M.; et al. Endothelin-1 in subarachnoid hemorrhage: An acute-phase reactant produced by cerebrospinal fluid leukocytes. Stroke 2000, 31, 2971–2975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wheeler, M.T.; Zarnegar, S.; McNally, E.M. Zeta-sarcoglycan, a novel component of the sarcoglycan complex, is reduced in muscular dystrophy. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2002, 11, 2147–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herold, C.; Hooli, B.V.; Mullin, K.; Liu, T.; Roehr, J.T.; Mattheisen, M.; Parrado, A.R.; Bertram, L.; Lange, C.; Tanzi, R.E. Family-based association analyses of imputed genotypes reveal genome-wide significant association of Alzheimer’s disease with OSBPL6, PTPRG, and PDCL3. Mol. Psychiatry 2016, 21, 1608–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asaithambi, G.; Adil, M.M.; Chaudhry, S.A.; Qureshi, A.I. Incidences of unruptured intracranial aneurysms and subarachnoid hemorrhage: Results of a statewide study. J. Vasc. Interv. Neurol. 2014, 7, 14–17. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Etminan, N.; Dreier, R.; Buchholz, B.A.; Bruckner, P.; Steiger, H.J.; Hanggi, D.; Macdonald, R.L. Exploring the age of intracranial aneurysms using carbon birth dating: Preliminary results. Stroke 2013, 44, 799–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dattani, N.; Sayers, R.D.; Bown, M.J. Diabetes mellitus and abdominal aortic aneurysms: A review of the mechanisms underlying the negative relationship. Diab. Vasc. Dis. Res. 2018, 15, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, E.P.; Park, J.W. Sample size and statistical power calculation in genetic association studies. Genomics Inform. 2012, 10, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variables a | Case (n = 250) | Control (n = 296) | Pb |
|---|---|---|---|
| Female, N (%) | 146 (58.4) | 154 (52.0) | 0.74 |
| Age, years | 59.3 ± 0.8 | 52.1 ± 1.0 | <0.001 |
| Hypertension, N (%) | 93 (37.2) | 88 (29.7) | 0.865 |
| Diabetes mellitus, N (%) | 17 (6.8) | 37 (12.5) | 0.001 |
| Hyperlipidemia, N (%) | 29 (11.6) | 27 (9.1) | 0.476 |
| Cigarette smoking, N (%) | 26 (10.4) | 37 (12.5) | 0.615 |
| Principal components, mean c | |||
| Principal component 1 | 0.0014 | −0.0012 | 0.169 |
| Principal component 2 | −0.0002 | 0.0001 | 0.656 |
| Principal component 3 | −0.0010 | 0.0008 | 0.039 |
| Principal component 4 | −0.0011 | 0.0009 | 0.031 |
| Rupture status, N (%) | |||
| UIA | 99 (39.6) | - | - |
| SAH | 151 (60.4) | - | - |
| Gene | Chr. | SNP | Class | M/m a | MAF b | OR c | L95 c | U95 c | Pc | Power d |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PRDM2 | 1p36.21 | rs61775135 | intron | C/A | 0.16/0.41 | 0.32 | 0.23 | 0.43 | 3.6E-13 | 0.42 |
| GBA | 1q22 | rs75822236 | R535H | C/T | 0.33/0.01 | 161.40 | 53.86 | 483.60 | 1.1E-19 | 1.00 |
| FMO4 | 1q24.3 | rs3737926 | F281F | C/T | 0.16/0.37 | 0.36 | 0.27 | 0.50 | 1.8E-10 | 0.32 |
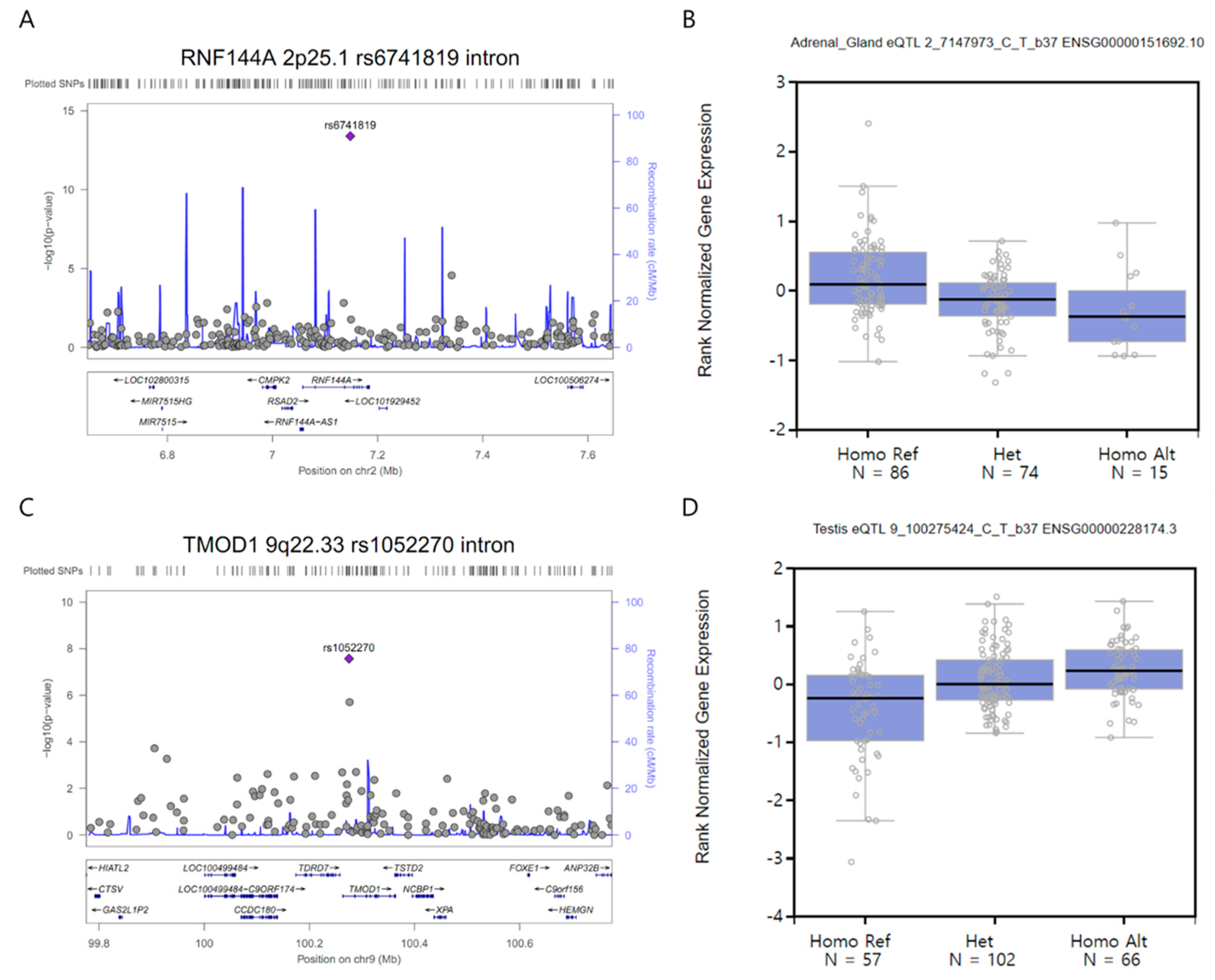
| RNF144A | 2p25.1 | rs6741819 | intron | C/T | 0.13/0.37 | 0.25 | 0.18 | 0.36 | 4.0E-14 | 0.72 |
| FLJ45964 | 2q37.3 | rs59626274 | stop-gained | C/T | 0.13/0.36 | 0.26 | 0.18 | 0.37 | 5.8E-14 | 0.71 |
| LINC01237 | 2q37.3 | rs78458145 | intron | G/A | 0.17/0.4 | 0.24 | 0.17 | 0.35 | 3.1E-15 | 0.68 |
| SPCS3 | 4q34.2 | rs17688188 | intergenic | G/A | 0.11/0.33 | 0.27 | 0.19 | 0.38 | 6.0E-13 | 0.73 |
| TCF24 | 8q13.1 | rs112859779 | G141S | C/T | 0.1/0.33 | 0.19 | 0.12 | 0.28 | 3.3E-16 | 0.94 |
| C9orf92 | 9p22.3 | rs12350582 | intergenic | A/G | 0.33/0.18 | 2.43 | 1.79 | 3.31 | 1.5E-08 | 0.20 |
| LINGO2 | 9p21.1 | rs56942085 | intron | G/A | 0.1/0.03 | 6.11 | 3.20 | 11.64 | 3.9E-08 | 0.78 |
| TMOD1 | 9q22.33 | rs1052270 | intron | C/T | 0.27/0.42 | 0.41 | 0.30 | 0.56 | 2.7E-08 | 0.15 |
| SUSD1 | 9q31.3 | rs79461840 | intron | T/C | 0.13/0.02 | 6.92 | 3.55 | 13.49 | 1.4E-08 | 0.65 |
| LINC00474 | 9q33.1 | rs4979583 | intergenic | C/T | 0.41/0.24 | 2.45 | 1.82 | 3.31 | 4.6E-09 | 0.24 |
| OLFML2A | 9q33.3 | rs79134766 | A208T | G/A | 0.07/0.37 | 0.14 | 0.09 | 0.21 | 1.7E-19 | 0.96 |
| MYEOV | 11q13.3 | rs76855873 | intron | C/T | 0.16/0.37 | 0.33 | 0.24 | 0.46 | 1.2E-11 | 0.43 |
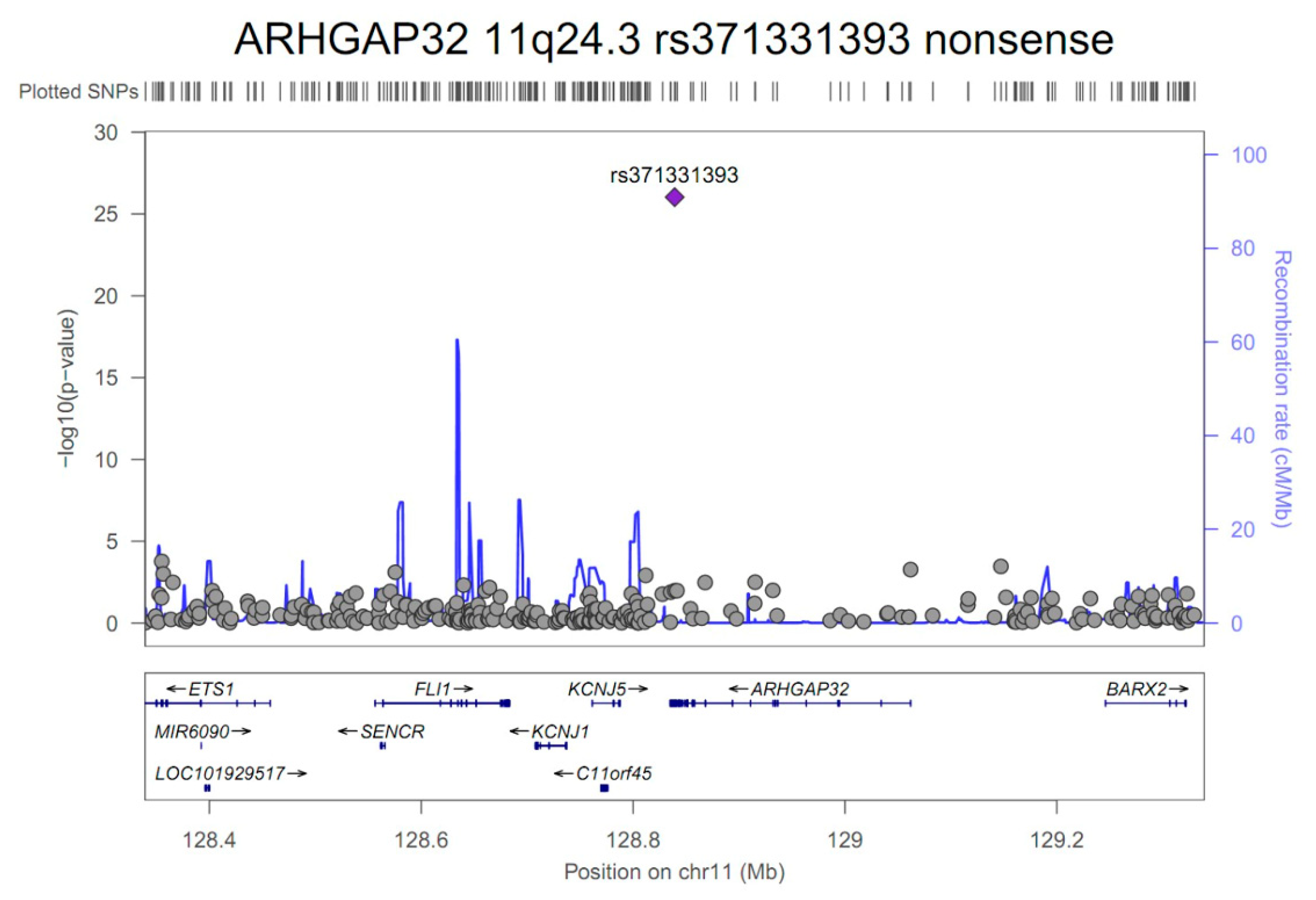
| ARHGAP32 | 11q24.3 | rs371331393 | stop-gained | G/A | 0.32/0.02 | 43.57 | 21.84 | 86.95 | 9.3E-27 | 1.00 |
| CD163L1 | 12p13.31 | rs138525217 | splice-site | C/T | 0.31/0.01 | 75.98 | 32.13 | 179.70 | 6.2E-23 | 1.00 |
| SLC2A14 | 12p13.31 | rs118107419 | intron | C/A | 0.14/0.39 | 0.25 | 0.17 | 0.35 | 1.4E-14 | 0.67 |
| DRAM1 | 12q23.2 | rs7964241 e | intergenic | A/G | 0.35/0.21 | 2.49 | 1.81 | 3.42 | 2.0E-08 | 0.25 |
| CUL4A | 13q34 | rs74115822 | intergenic | G/A | 0.19/0.03 | 6.25 | 3.58 | 10.90 | 1.1E-10 | 0.80 |
| LINC02130 | 16p13.12 | rs11646803 | intron | C/T | 0.28/0.48 | 0.45 | 0.35 | 0.58 | 4.8E-10 | 0.06 |
| LOC102724084 | 16q23.2 | rs75861150 | intron | T/C | 0.02/0.16 | 0.14 | 0.07 | 0.28 | 1.3E-08 | 1.00 |
| SCARF1 | 17p13.3 | rs3744644 | E639D | G/C | 0.18/0.35 | 0.39 | 0.28 | 0.54 | 6.0E-09 | 0.26 |
| MINK1 | 17p13.2 | rs72835045 | intron | G/A | 0.11/0.33 | 0.25 | 0.17 | 0.37 | 1.7E-12 | 0.79 |
| SLC47A1 | 17p11.2 | rs2440154 e | intron | G/A | 0.28/0.13 | 2.67 | 1.90 | 3.75 | 1.4E-08 | 0.26 |
| NAPA-AS1 | 19q13.32 | rs55800589 | intron | G/C | 0.32/0.4 | 0.38 | 0.29 | 0.49 | 3.4E-13 | 0.23 |
| DSCAM | 21q22.2 | rs727333 | intron | C/A | 0.14/0.38 | 0.26 | 0.18 | 0.36 | 3.7E-14 | 0.69 |
| LRRC3 | 21q22.3 | rs116969723 | P63P | G/A | 0.11/0.35 | 0.24 | 0.16 | 0.34 | 3.8E-15 | 0.81 |
| SLC5A4-AS1 | 22q12.3 | rs117398778 | intron | T/C | 0.21/0.07 | 3.74 | 2.43 | 5.75 | 2.0E-09 | 0.56 |
| Biological Function a | Pb | FDR, % b | Gene, N | Gene Set |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Biological process in ontology | ||||
| GO: 0030154~cell differentiation | 0.0117 | 16.8 | 10 | EDNRA, LINGO2, CUL4A, SLC2A14, MINK1, SCARF1, BOLL, DSCAM, TMOD1, GBA |
| GO: 0031175~neuron projection development | 0.0120 | 17.2 | 5 | LINGO2, MINK1, SCARF1, DSCAM, GBA |
| GO: 0048468~cell development | 0.0181 | 24.8 | 7 | EDNRA, LINGO2, MINK1, SCARF1, DSCAM, TMOD1, GBA |
| GO: 0016358~dendrite development | 0.0192 | 26.1 | 3 | MINK1, SCARF1, DSCAM |
| GO: 0048869~cellular developmental process | 0.0209 | 28.1 | 10 | EDNRA, LINGO2, CUL4A, SLC2A14, MINK1, SCARF1, BOLL, DSCAM, TMOD1, GBA |
| GO: 0048666~neuron development | 0.0210 | 28.3 | 5 | LINGO2, MINK1, SCARF1, DSCAM, GBA |
| GO: 0007275~multicellular organism development | 0.0260 | 33.8 | 11 | EDNRA, LINGO2, CUL4A, SLC2A14, MINK1, PRDM2, SCARF1, BOLL, DSCAM, TMOD1, GBA |
| GO: 0051130~positive regulation of cellular component organization | 0.0406 | 47.7 | 5 | LINGO2, CUL4A, SCARF1, DSCAM, GBA |
| GO: 0030182~neuron differentiation | 0.0454 | 51.6 | 5 | LINGO2, MINK1, SCARF1, DSCAM, GBA |
| Cellular component in ontology | ||||
| GO:0044425~membrane part | 0.0088 | 9.7 | 15 | FMO4, RNF144A, LINGO2, EDNRA, LRRC3, ARHGAP32, CD163L1, SLC2A14, SUSD1, SPCS3, MINK1, SLC47A1, DRAM1, SCARF1, DSCAM |
| GO:0016021~integral component of membrane | 0.0160 | 16.9 | 13 | FMO4, RNF144A, LINGO2, EDNRA, LRRC3, CD163L1, SLC2A14, SUSD1, SPCS3, SLC47A1, DRAM1, SCARF1, DSCAM |
| GO:0031224~intrinsic component of membrane | 0.0186 | 19.4 | 13 | FMO4, RNF144A, LINGO2, EDNRA, LRRC3, CD163L1, SLC2A14, SUSD1, SPCS3, SLC47A1, DRAM1, SCARF1, DSCAM |
| GO:0016020~membrane | 0.0205 | 21.1 | 17 | RNF144A, LRRC3, SUSD1, SLC2A14, MINK1, SLC47A1, SCARF1, FMO4, EDNRA, LINGO2, ARHGAP32, CD163L1, SPCS3, DRAM1, DSCAM, TMOD1, GBA |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hong, E.P.; Kim, B.J.; Cho, S.S.; Yang, J.S.; Choi, H.J.; Kang, S.H.; Jeon, J.P. Genomic Variations in Susceptibility to Intracranial Aneurysm in the Korean Population. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 275. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8020275
Hong EP, Kim BJ, Cho SS, Yang JS, Choi HJ, Kang SH, Jeon JP. Genomic Variations in Susceptibility to Intracranial Aneurysm in the Korean Population. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2019; 8(2):275. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8020275
Chicago/Turabian StyleHong, Eun Pyo, Bong Jun Kim, Steve S. Cho, Jin Seo Yang, Hyuk Jai Choi, Suk Hyung Kang, and Jin Pyeong Jeon. 2019. "Genomic Variations in Susceptibility to Intracranial Aneurysm in the Korean Population" Journal of Clinical Medicine 8, no. 2: 275. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8020275
APA StyleHong, E. P., Kim, B. J., Cho, S. S., Yang, J. S., Choi, H. J., Kang, S. H., & Jeon, J. P. (2019). Genomic Variations in Susceptibility to Intracranial Aneurysm in the Korean Population. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 8(2), 275. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8020275





