The Extended Postoperative Care-Score (EXPO-Score)—An Objective Tool for Early Identification of Indication for Extended Postoperative Care
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Primary Outcome: Indication for ICU
2.3. Choice of Included Risk Factors
2.4. Study Design
- Pilot period; staff training (data excluded).
- Extended Postoperative Care-Score (EXPO)-Score generation period (Period 1); data collection for 16 weeks.
- EXPO-Score validation period (Period 2); data collection for eight weeks.
2.5. Sample Size Rationale
2.6. Statistical Analysis
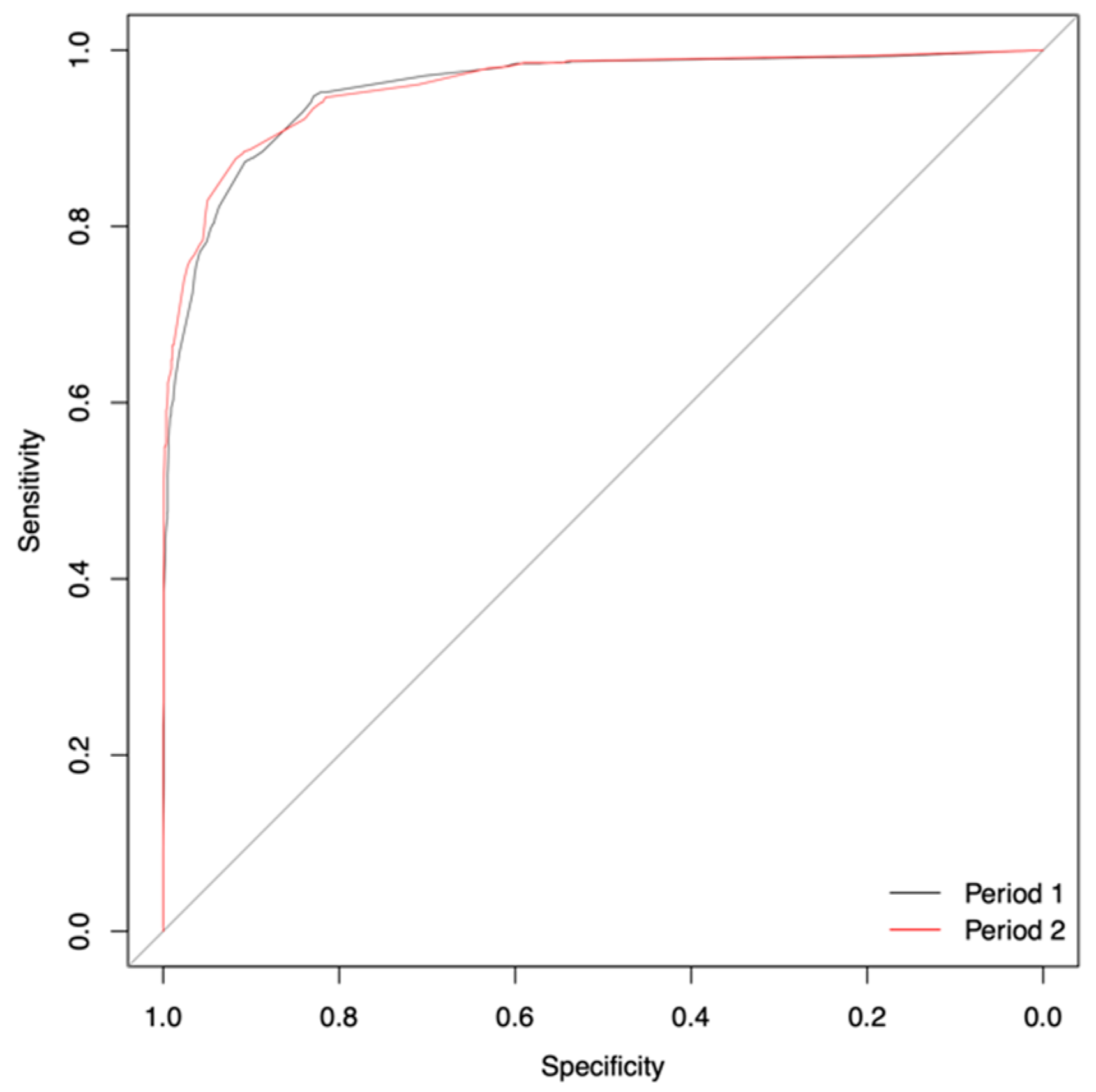
3. Results
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gillies, M.A.; Sander, M.; Shaw, A.; Wijeysundera, D.N.; Myburgh, J.; Aldecoa, C.; Jammer, I.; Lobo, S.M.; Pritchard, N.; Grocott, M.P.W.; et al. Current research priorities in perioperative intensive care medicine. Intensive Care Med. 2017, 43, 1173–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ESICM. Available online: https://www.Esicm.Org/research/surveys/completed-surveys/ (accessed on 8 April 2018).
- Weiser, T.G.; Haynes, A.B.; Molina, G.; Lipsitz, S.R.; Esquivel, M.M.; Uribe-Leitz, T.; Fu, R.; Azad, T.; Chao, T.E.; Berry, W.R.; et al. Estimate of the global volume of surgery in 2012: An assessment supporting improved health outcomes. Lancet 2015, 385 (Suppl. 2), S11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearse, R.M.; Harrison, D.A.; James, P.; Watson, D.; Hinds, C.; Rhodes, A.; Grounds, R.M.; Bennett, E.D. Identification and characterisation of the high-risk surgical population in the United Kingdom. Crit. Care 2006, 10, R81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jhanji, S.; Thomas, B.; Ely, A.; Watson, D.; Hinds, C.J.; Pearse, R.M. Mortality and utilisation of critical care resources amongst high-risk surgical patients in a large nhs trust. Anaesthesia 2008, 63, 695–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearse, R.M.; Moreno, R.P.; Bauer, P.; Pelosi, P.; Metnitz, P.; Spies, C.; Vallet, B.; Vincent, J.L.; Hoeft, A.; Rhodes, A.; et al. Mortality after surgery in europe: A 7 day cohort study. Lancet 2012, 380, 1059–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothschild, J.M.; Landrigan, C.P.; Cronin, J.W.; Kaushal, R.; Lockley, S.W.; Burdick, E.; Stone, P.H.; Lilly, C.M.; Katz, J.T.; Czeisler, C.A.; et al. The critical care safety study: The incidence and nature of adverse events and serious medical errors in intensive care. Crit. Care Med. 2005, 33, 1694–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, M.C.; Spieth, P.M.; Quinn, K.; Parotto, M.; Zhang, H.; Slutsky, A.S. Circadian rhythms: From basic mechanisms to the intensive care unit. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 40, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuire, B.E.; Basten, C.J.; Ryan, C.J.; Gallagher, J. Intensive care unit syndrome: A dangerous misnomer. Arch. Intern. Med. 2000, 160, 906–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobol, J.B.; Wunsch, H. Triage of high-risk surgical patients for intensive care. Crit. Care 2011, 15, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jette, M.; Sidney, K.; Blumchen, G. Metabolic equivalents (mets) in exercise testing, exercise prescription, and evaluation of functional capacity. Clin. Cardiol. 1990, 13, 555–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleisher, L.A.; Fleischmann, K.E.; Auerbach, A.D.; Barnason, S.A.; Beckman, J.A.; Bozkurt, B.; Davila-Roman, V.G.; Gerhard-Herman, M.D.; Holly, T.A.; Kane, G.C.; et al. 2014 acc/aha guideline on perioperative cardiovascular evaluation and management of patients undergoing noncardiac surgery: Executive summary: A report of the american college of cardiology/american heart association task force on practice guidelines. Circulation 2014, 130, 2215–2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinstein, A.S.; Sigurdsson, M.I.; Bader, A.M. Comparison of preoperative assessment of patient’s metabolic equivalents (mets) estimated from history versus measured by exercise cardiac stress testing. Anesthesiol. Res. Pract. 2018, 2018, 5912726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steyerberg, E.W. Clinical Prediction Models; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria; Available online: https://www.R-project.Org/ (accessed on 1 January 2017).
- Venables, W.N.; Ripley, B.D. Modern Applied Statistics with S, 4th ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Hastie, T. Gam: Generalized Additive Models. R Package Version 1.14. 2016. Available online: Http://cran.Rproject.Org/package=gam (accessed on 1 January 2017).
- Hothorn, T.; Bretz, F.; Westfall, P. Simultaneous inference in general parametric models. Biom. J. 2008, 50, 346–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robin, X.; Turck, N.; Hainard, A.; Tiberti, N.; Lisacek, F.; Sanchez, J.C.; Muller, M. Proc: An open-source package for r and s+ to analyze and compare roc curves. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sprung, C.L.; Danis, M.; Iapichino, G.; Artigas, A.; Kesecioglu, J.; Moreno, R.; Lippert, A.; Curtis, J.R.; Meale, P.; Cohen, S.L.; et al. Triage of intensive care patients: Identifying agreement and controversy. Intensive Care Med. 2013, 39, 1916–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, D.W.; Shapiro, M.F. Association between intensive care unit utilization during hospitalization and costs, use of invasive procedures, and mortality. JAMA Intern. Med. 2016, 176, 1492–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vacanti, C.J.; VanHouten, R.J.; Hill, R.C. A statistical analysis of the relationship of physical status to postoperative mortality in 68,388 cases. Anesth. Analg. 1970, 49, 564–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, T.J.; Raghunathan, K.; Barbeito, A.; Cooter, M.; Stafford-Smith, M.; Schroeder, R.; Grichnik, K.; Gilbert, R.; Aronson, S. Associations between asa physical status and postoperative mortality at 48 h: A contemporary dataset analysis compared to a historical cohort. Perioper. Med. 2016, 5, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boersma, E.; Kertai, M.D.; Schouten, O.; Bax, J.J.; Noordzij, P.; Steyerberg, E.W.; Schinkel, A.F.; van Santen, M.; Simoons, M.L.; Thomson, I.R.; et al. Perioperative cardiovascular mortality in noncardiac surgery: Validation of the lee cardiac risk index. Am. J. Med. 2005, 118, 1134–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.H.; Marcantonio, E.R.; Mangione, C.M.; Thomas, E.J.; Polanczyk, C.A.; Cook, E.F.; Sugarbaker, D.J.; Donaldson, M.C.; Poss, R.; Ho, K.K.; et al. Derivation and prospective validation of a simple index for prediction of cardiac risk of major noncardiac surgery. Circulation 1999, 100, 1043–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reilly, D.F.; McNeely, M.J.; Doerner, D.; Greenberg, D.L.; Staiger, T.O.; Geist, M.J.; Vedovatti, P.A.; Coffey, J.E.; Mora, M.W.; Johnson, T.R.; et al. Self-reported exercise tolerance and the risk of serious perioperative complications. Arch. Intern. Med. 1999, 159, 2185–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leskinen, T.; Stenholm, S.; Heinonen, O.J.; Pulakka, A.; Aalto, V.; Kivimaki, M.; Vahtera, J. Change in physical activity and accumulation of cardiometabolic risk factors. Prev. Med. 2018, 112, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meybohm, P.; Schmitz-Rixen, T.; Steinbicker, A.; Schwenk, W.; Zacharowski, K. The patient blood management concept: Joint recommendation of the german society of anaesthesiology and intensive care medicine and the german society of surgery. Chirurg 2017, 88, 867–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Guen, J.; Boumendil, A.; Guidet, B.; Corvol, A.; Saint-Jean, O.; Somme, D. Are elderly patients’ opinions sought before admission to an intensive care unit? Results of the ice-cub study. Age Ageing 2016, 45, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyland, D.K.; Ilan, R.; Jiang, X.; You, J.J.; Dodek, P. The prevalence of medical error related to end-of-life communication in canadian hospitals: Results of a multicentre observational study. BMJ Qual. Saf. 2016, 25, 671–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Indications for ICU Admission |
|---|
| Hemodynamic instability (e.g., vasopressor therapy) n = 372 |
| Respiratory instability (e.g., re-intubation) n = 72 |
| Massive intraoperative bleeding/transfusion n = 34 |
| New severe cardiac arrhythmia (e.g., ventricular tachycardia) n = 15 |
| Severe pre-existing disease (e.g., myasthenia, ejection fraction < 25%) n = 79 |
| Surgery-related risk factor (e.g., liver transplantation) n = 479 |
| Altered consciousness (e.g., delirium) n = 38 |
| Hypothermia (body core temperature <36° Celsius) n = 13 |
| High nursing care effort needed (e.g., immobility) n = 53 |
| Other n = 108 |
| Clinical Comorbidities |
|---|
| Cardiovascular (e.g., heart failure NYHA III-IV) |
| Pulmonary (e.g., COPD) |
| Liver cirrhosis/insufficiency (e.g., GOT/GPT > 2 × normal value) |
| Renal failure (e.g., creatinine > 200 µmol/L) |
| Neurologic disorders (e.g., stroke) |
| Sepsis/infection |
| Isolation/infection prevention (e.g., MRSA) |
| Endocrinopathy (e.g., complex diabetes mellitus) |
| Characteristics & Risk Factors | With Indication for ICU (n = 866) | No Indication for ICU (n = 3176) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | <0.001 | ||
| Men | 556 (26.8) | 1519 (73.2) | |
| Women | 310 (15.8) | 1657 (84.2) | |
| Age (years) | <0.001 | ||
| <50 | 94 (7.4) | 1179 (92.6) | |
| 50–59 | 124 (18.3) | 555 (81.7) | |
| 60–69 | 210 (26.4) | 584 (73.6) | |
| 70–79 | 298 (31.9) | 635 (68.1) | |
| 80–89 | 124 (37.3) | 208 (62.7) | |
| >90 | 16 (51.6) | 15 (48.4) | |
| BMI kg/m−2 (Median (IQR)) | 26 (23–30) | 26 (23–30) | 0.49 |
| ASA | <0.001 | ||
| I | 13 (1.9) | 662 (98.1) | |
| II | 90 (5.1) | 1660 (94.9) | |
| III | 592 (41.7) | 828 (58.3) | |
| IV | 171 (86.8) | 26 (13.2) | |
| Priority of Surgery | <0.001 | ||
| Elective | 659 (19.2) | 2769 (80.8) | |
| N0 | 51 (61.4) | 32 (38.6) | |
| N1 | 53 (47.3) | 59 (52.7) | |
| N2 | 63 (27.2) | 169 (72.8) | |
| N3 | 33 (20.4) | 129 (79.6) | |
| Preconditions | |||
| Cardiovascular | 514 (57.7) | 377 (46.3) | <0.001 |
| Pulmonary | 124 (34.8) | 232 (65.2) | <0.001 |
| Liver insufficiency | 24 (66.7) | 12 (33.3) | <0.001 |
| Renal insufficiency | 71 (51.4) | 67 (48.6) | <0.001 |
| Endocrinopathy | 64 (27.2) | 171 (71.8) | 0.033 |
| Neurologic | 112 (45.0) | 137 (55.0) | <0.001 |
| Infection/Sepsis | 32 (69.6) | 14 (30.4) | <0.001 |
| Isolation/Infection (e.g., MRSA) | 29 (70.7) | 12 (29.3) | <0.001 |
| Hemoglobin g/dl (Median [IQR]) | 13 (11–14) | 14 (12–15) | <0.001 |
| Physical Activity | <0.001 | ||
| ≥4 MET | 486 (14.6) | 2848 (83.4) | |
| <4 MET | 376 (53.7) | 324 (46.3) | |
| Planned Postoperative Unit | <0.001 | ||
| Post anesthetic care unit | 48 (1.6) | 2983 (98.4) | |
| Intermediate care unit | 27 (20.5) | 105 (79.5) | |
| Intensive care unit | 781 (91.8) | 70 (8.2) | |
| Planned surgery | <0.001 | ||
| Thoracic with OLV | 13 (36.1) | 23 (63.9) | |
| Upper abdomen | 25 (37.9) | 41 (62.1) | |
| Hip/knee arthroplasty | 22 (15.7) | 118 (84.3) | |
| Large ENT/maxillofacial tumor | 23 (50.0) | 23 (50.0) | |
| Urogenital | 20 (16.9) | 98 (83.1) | |
| Vascular | 38 (35.2) | 70 (64.8) | |
| Endovascular aortic repair | 30 (75.0) | 10 (25.0) | |
| Cardiac | 300 (99.0) | 3 (1.0) | |
| Non-cardiac with planned ICU | 94 (94.9) | 5 (5.1) | |
| Miscellaneous minor | 94 (4.0) | 2246 (96.0) | |
| Miscellaneous intermediate | 132 (20.5) | 513 (79.5) | |
| Miscellaneous major | 73 (74.5) | 25 (25.5) |
| Statistical Measure | Period 1 | Period 2 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Variables | |||||||||
| 9 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | Grey Zone | 3 | |
| Specificity | 0.91 | 0.90 | 0.91 | 0.87 | 0.89 | 0.91 | 0.88 | 0.91 | 0.92 |
| Sensitivity | 0.90 | 0.91 | 0.89 | 0.93 | 0.90 | 0.87 | 0.89 | 0.82 | 0.88 |
| AUC | 0.96 | 0.96 | 0.96 | 0.96 | 0.96 | 0.96 | 0.95 | 0.92 | 0.96 |
| (95% CI) | (0.96–0.97) | (0.96–0.97) | (0.96–0.97) | (0.95–0.97) | (0.95–0.97) | (0.95–0.96) | (0.94–0.96) | (0.91–0.94) | (0.95–0.97) |
| Accuracy | 0.91 | 0.90 | 0.91 | 0.88 | 0.89 | 0.90 | 0.88 | 0.83 | 0.91 |
| Threshold | 0.21 | 0.18 | 0.21 | 0.16 | 0.20 | 0.23 | 0.26 | 0.23 | 0.23 |
| Variable | Regression Coefficient | Standard Error | Odds Ratio | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ASA status | ||||
| ASA I | Reference | |||
| ASA II | 0.40 | 0.37 | 1.49 | 0.27 |
| ASA III | 2.32 | 0.36 | 10.18 | <0.001 |
| ASA IV | 4.56 | 0.43 | 95.58 | <0.001 |
| Physical exercise status | ||||
| ≥4 MET | Reference | |||
| <4 MET | 1.26 | 0.15 | 3.53 | <0.001 |
| Conducted surgery | ||||
| Miscellaneous minor | Reference | |||
| Miscellaneous intermediate | 1.78 | 0.18 | 5.93 | <0.001 |
| Miscellaneous major | 4.37 | 0.31 | 79.04 | <0.001 |
| Vascular | 1.20 | 0.27 | 3.32 | <0.001 |
| Hip/knee arthroplasty | 1.27 | 0.30 | 3.56 | <0.001 |
| Urogenital | 1.61 | 0.31 | 5.00 | <0.001 |
| Thoracic with OLV | 2.32 | 0.41 | 10.18 | <0.001 |
| Upper abdomen | 2.95 | 0.33 | 19.11 | <0.001 |
| Endovascular aortic repair | 3.51 | 0.43 | 33.45 | <0.001 |
| Large ENT/maxillofacial tumor | 3.83 | 0.37 | 46.06 | <0.001 |
| Non-cardiac with planned ICU | 6.79 | 0.50 | 888.91 | <0.001 |
| Cardiac | 7.11 | 0.60 | 1224.15 | <0.001 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Iden, T.; Caliebe, A.; Renner, J.; Hertz, M.-B.; Höcker, J.; Suvanto-Scholz, P.; Steinfath, M.; Weiler, N.; Gruenewald, M. The Extended Postoperative Care-Score (EXPO-Score)—An Objective Tool for Early Identification of Indication for Extended Postoperative Care. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1666. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8101666
Iden T, Caliebe A, Renner J, Hertz M-B, Höcker J, Suvanto-Scholz P, Steinfath M, Weiler N, Gruenewald M. The Extended Postoperative Care-Score (EXPO-Score)—An Objective Tool for Early Identification of Indication for Extended Postoperative Care. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2019; 8(10):1666. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8101666
Chicago/Turabian StyleIden, Timo, Amke Caliebe, Jochen Renner, Maj-Britt Hertz, Jan Höcker, Päivi Suvanto-Scholz, Markus Steinfath, Norbert Weiler, and Matthias Gruenewald. 2019. "The Extended Postoperative Care-Score (EXPO-Score)—An Objective Tool for Early Identification of Indication for Extended Postoperative Care" Journal of Clinical Medicine 8, no. 10: 1666. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8101666
APA StyleIden, T., Caliebe, A., Renner, J., Hertz, M.-B., Höcker, J., Suvanto-Scholz, P., Steinfath, M., Weiler, N., & Gruenewald, M. (2019). The Extended Postoperative Care-Score (EXPO-Score)—An Objective Tool for Early Identification of Indication for Extended Postoperative Care. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 8(10), 1666. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8101666




