Large-Fiber Neuropathy in Parkinson’s Disease: Clinical, Biological, and Electroneurographic Assessment of a Romanian Cohort
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Method
2.1. Clinical Features
2.2. Biological Features
2.3. Nerve Conduction Studies
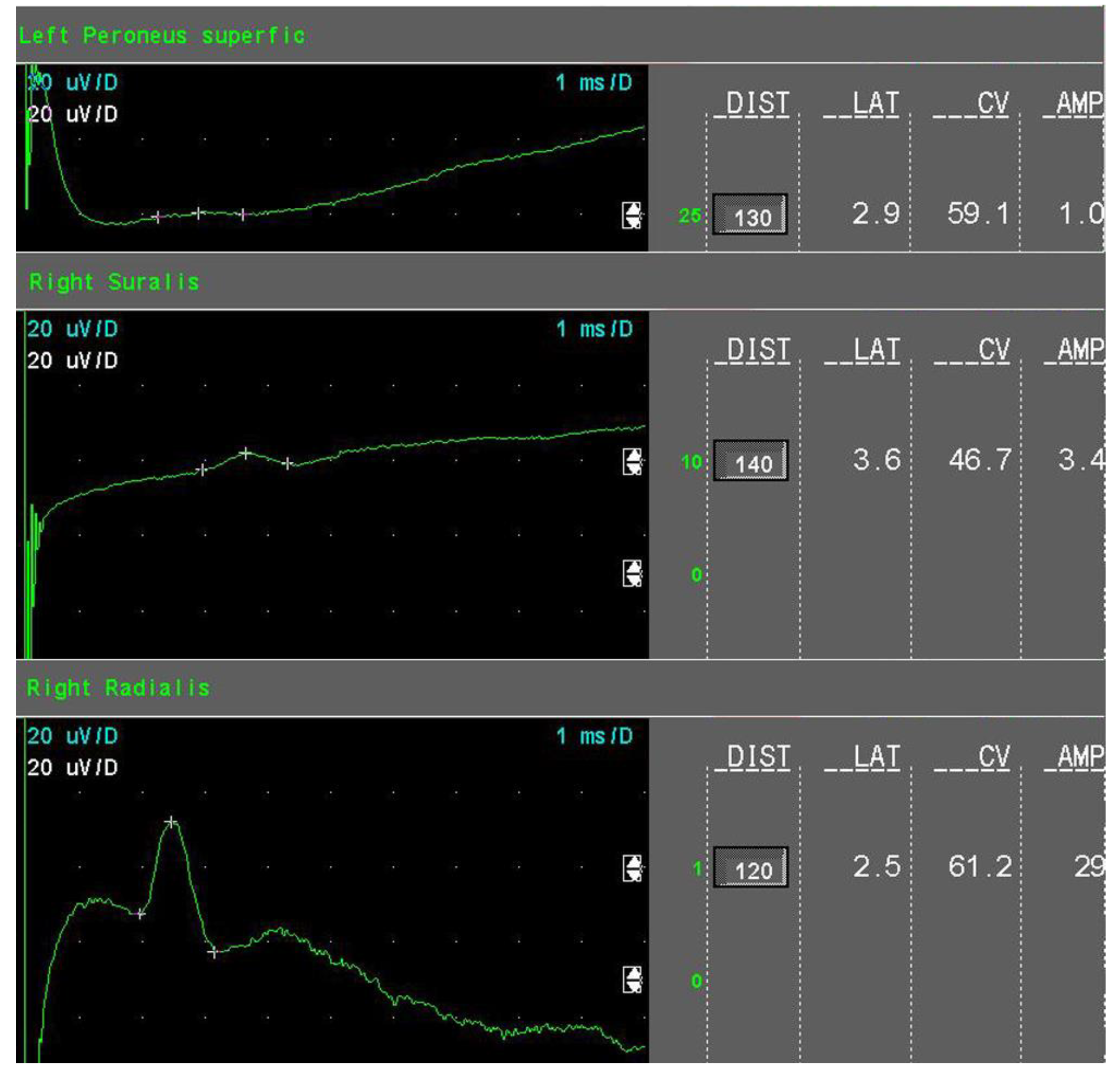
- Mild sensory axonal loss: a reduction of the SNAP amplitude of more than 15% but no more than 50% of LNL for the sural and superficial peroneal nerves. LNL values for the sural and superficial peroneal nerves were considered to be 6 µV and 20 µV for the radial nerve, respectively (Figure 1).
- Moderate sensory axonal loss: a reduction of the SNAP amplitude of more than 50% of LNL for the sural and superficial peroneal nerves and a decrease of the SNAP amplitude of more than 15% but no more than 50% of LNL for the radial nerve (Figure 2).
- Severe sensory axonal loss: a reduction of the SNAP amplitude of more than 50% of LNL for sural, superficial peroneal nerve, and radial nerves (Figure 3).
- Motor axonal loss: a reduction of the CMAP amplitude of more than 25% of LNL for the tibial nerve (LNL = 4 mV) or/and the peroneal nerve (LNL = 2 mV), or/and the median nerve (LNL = 4 mV).
- Mild axonal sensory polyneuropathy—the presence of mild sensory axonal loss, absence of motor axonal loss, and demyelinating features;
- Moderate axonal sensory PNP—the presence of moderate sensory axonal loss, absence of motor axonal loss, and demyelinating features;
- Severe axonal sensory with motor features—the presence of severe sensory axonal loss and motor axonal loss with or without demyelinating features.
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. L-Dopa Group Versus Non-L-Dopa Group
3.2. Differences Between the L-Dopa-PNP Group, the L-Dopa-Non-PNP Group Versus the Non-L-Dopa-Non-PNP Group
- Subgroup 1—L-Dopa-PNP—included 35 patients undergoing L-dopa treatment with polyneuropathy;
- Subgroup 2—L-Dopa-non-PNP—included 17 patients undergoing L-dopa treatment without polyneuropathy;
- Subgroup 3—non-L-Dopa-non-PNP—included 20 patients without L-dopa treatment and polyneuropathy.
3.3. The Severity of Axonal Loss in the L-Dopa-PNP Group
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Braak, H.; Tredici, K.D.; Rüb, U.; de Vos, R.A.I.; Jansen Steur, E.N.H.; Braak, E. Staging of brain pathology related to sporadic Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2003, 24, 197–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braak, H.; Rüb, U.; Gai, W.P.; Del Tredici, K. Idiopathic Parkinson’s disease: Possible routes by which vulnerable neuronal types may be subject to neuroinvasion by an unknown pathogen. J. Neural Transm. 2003, 110, 517–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andréasson, M.; Brodin, L.; Laffita-Mesa, J.M.; Svenningsson, P. Correlations Between Methionine Cycle Metabolism, COMT Genotype, and Polyneuropathy in L-Dopa Treated Parkinson’s Disease: A Preliminary Cross-Sectional Study. JPD 2017, 7, 619–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grambalová, Z.; Kaiserová, M.; Vaštík, M.; Menšíková, K.; Otruba, P.; Zapletalová, J.; Dufek, J.; Kaňovský, P. Peripheral neuropathy in Parkinson’s disease. Neuroendocrinol. Lett. 2015, 36, 363–367. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jugel, C.; Ehlen, F.; Taskin, B.; Marzinzik, F.; Müller, T.; Klostermann, F. Neuropathy in Parkinson’s disease patients with intestinal levodopa infusion versus oral drugs. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e66639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loens, S.; Chorbadzhieva, E.; Kleimann, A.; Dressler, D.; Schrader, C. Effects of levodopa/carbidopa intestinal gel versus oral levodopa/carbidopa on B vitamin levels and neuropathy. Brain Behav. 2017, 7, e00698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancini, F.; Comi, C.; Oggioni, G.D.; Pacchetti, C.; Calandrella, D.; Coletti Moja, M.; Riboldazzi, G.; Tunesi, S.; Dal Fante, M.; Manfredi, L.; et al. Prevalence and features of peripheral neuropathy in Parkinson’s disease patients under different therapeutic regimens. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2014, 20, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-S.; Park, D.; Ko, P.-W.; Kang, K.; Lee, H.-W. Serum methylmalonic acid correlates with neuropathic pain in idiopathic Parkinson’s disease. Neurol. Sci. 2017, 38, 1799–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajabally, Y.A.; Martey, J. Levodopa, vitamins, ageing and the neuropathy of Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurol. 2013, 260, 2844–2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajabally, Y.A.; Martey, J. Neuropathy in Parkinson disease: Prevalence and determinants. Neurology 2011, 77, 1947–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahrizaila, N.; Mahamad, U.A.; Yap, A.-C.; Choo, Y.-M.; Marras, C.; Lim, S.-Y. Is chronic levodopa therapy associated with distal symmetric polyneuropathy in Parkinson’s disease? Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2013, 19, 391–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toth, C.; Breithaupt, K.; Ge, S.; Duan, Y.; Terris, J.M.; Thiessen, A.; Wiebe, S.; Zochodne, D.W.; Suchowersky, O. Levodopa, methylmalonic acid, and neuropathy in idiopathic Parkinson disease. Ann. Neurol. 2010, 68, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szadejko, K.; Dziewiatowski, K.; Szabat, K.; Robowski, P.; Schinwelski, M.; Sitek, E.; Sławek, J. Polyneuropathy in levodopa-treated Parkinson’s patients. J. Neurol. Sci. 2016, 371, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toth, C.; Brown, M.S.; Furtado, S.; Suchowersky, O.; Zochodne, D. Neuropathy as a potential complication of levodopa use in Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2008, 23, 1850–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceravolo, R.; Cossu, G.; Bandettini di Poggio, M.; Santoro, L.; Barone, P.; Zibetti, M.; Frosini, D.; Nicoletti, V.; Manganelli, F.; Iodice, R.; et al. Neuropathy and levodopa in Parkinson’s disease: Evidence from a multicenter study: Levodopa and Peripheral Neuropathy. Mov. Disord. 2013, 28, 1391–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merola, A.; Zibetti, M.; Rizzone, M.G.; Troiano, M.; Artusi, C.A.; Angrisano, S.; Cocito, D.; Lopiano, L. Prospective assessment of peripheral neuropathy in Duodopa-treated parkinsonian patients. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2014, 129, e1–e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devigili, G.; Rinaldo, S.; Lettieri, C.; Eleopra, R. Levodopa/carbidopa intestinal gel therapy for advanced Parkinson Disease: AN early toxic effect for small nerve fibers?: SFN and L-Dopa Gel Therapy. Muscle Nerve 2016, 54, 970–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doppler, K.; Ebert, S.; Üçeyler, N.; Trenkwalder, C.; Ebentheuer, J.; Volkmann, J.; Sommer, C. Cutaneous neuropathy in Parkinson’s disease: A window into brain pathology. Acta Neuropathol. 2014, 128, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kass-Iliyya, L.; Javed, S.; Gosal, D.; Kobylecki, C.; Marshall, A.; Petropoulos, I.N.; Ponirakis, G.; Tavakoli, M.; Ferdousi, M.; Chaudhuri, K.R.; et al. Small fiber neuropathy in Parkinson’s disease: A clinical, pathological and corneal confocal microscopy study. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2015, 21, 1454–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolano, M.; Provitera, V.; Estraneo, A.; Selim, M.M.; Caporaso, G.; Stancanelli, A.; Saltalamacchia, A.M.; Lanzillo, B.; Santoro, L. Sensory deficit in Parkinson’s disease: Evidence of a cutaneous denervation. Brain 2008, 131, 1903–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolano, M.; Provitera, V.; Manganelli, F.; Iodice, R.; Stancanelli, A.; Caporaso, G.; Saltalamacchia, A.; Califano, F.; Lanzillo, B.; Picillo, M.; et al. Loss of cutaneous large and small fibers in naive and l-dopa–treated PD patients. Neurology 2017, 89, 776–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romagnolo, A.; Merola, A.; Artusi, C.A.; Rizzone, M.G.; Zibetti, M.; Lopiano, L. Levodopa-Induced Neuropathy: A Systematic Review. Mov. Disord. Clin. Pract. 2019, 6, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajabally, Y.A.; Martey, J. No association between neuropathy and restless legs in Parkinson’s disease. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2013, 127, 216–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merola, A.; Rosso, M.; Romagnolo, A.; Comi, C.; Fasano, A.; Zibetti, M.; Lopez-Castellanos, J.R.; Cocito, D.; Lopiano, L.; Espay, A.J. Peripheral neuropathy as marker of severe Parkinson’s disease phenotype: PNP and Disease Severity in PD. Mov. Disord. 2017, 32, 1256–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cossu, G.; Melis, M. The peripheral nerve involvement in Parkinson Disease: A multifaceted phenomenon. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2016, 25, 17–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos-García, D.; de la Fuente-Fernández, R.; Valldeoriola, F.; Palasí, A.; Carrillo, F.; Grande, M.; Mir, P.; De Fabregues, O.; Casanova, J. Polyneuropathy while on duodenal levodopa infusion in Parkinson’s disease patients: We must be alert. J. Neurol. 2012, 259, 1668–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uncini, A.; Eleopra, R.; Onofrj, M. Polyneuropathy associated with duodenal infusion of levodopa in Parkinson’s disease: Features, pathogenesis and management. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2015, 86, 490–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merola, A.; Romagnolo, A.; Zibetti, M.; Bernardini, A.; Cocito, D.; Lopiano, L. Peripheral neuropathy associated with levodopa–carbidopa intestinal infusion: A long-term prospective assessment. Eur. J. Neurol. 2016, 23, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocer, B.; Guven, H.; Comoglu, S.S. Homocysteine Levels in Parkinson’s Disease: Is Entacapone Effective? BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 7563705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.-W.; Sohn, Y.H. Hyperhomocysteinemia in Patients with Parkinson’s Disease and Relationship to Vitamin B Level. JMD 2009, 2, 33–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamberti, P.; Zoccolella, S.; Iliceto, G.; Armenise, E.; Fraddosio, A.; de Mari, M.; Livrea, P. Effects of levodopa and COMT inhibitors on plasma homocysteine in Parkinson’s disease patients. Mov. Disord. 2005, 20, 69–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valkovic, P.; Benetin, J.; Blazícek, P.; Valkovicová, L.u.; Gmitterová, K.; Kukumberg, P. Reduced plasma homocysteine levels in levodopa/entacapone treated Parkinson patients. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2005, 11, 253–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoccolella, S.; Lamberti, P.; Iliceto, G.; Dell’Aquila, C.; Diroma, C.; Fraddosio, A.; Lamberti, S.V.; Armenise, E.; Defazio, G.; de Mari, M.; et al. Elevated plasma homocysteine levels in L-dopa-treated Parkinson’s disease patients with dyskinesias. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2006, 44, 863–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cossu, G.; Ceravolo, R.; Zibetti, M.; Arca, R.; Ricchi, V.; Paribello, A.; Murgia, D.; Merola, A.; Romagnolo, A.; Nicoletti, V.; et al. Levodopa and neuropathy risk in patients with Parkinson disease: Effect of COMT inhibition. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2016, 27, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, T.; Renger, K.; Kuhn, W. Levodopa-Associated Increase of Homocysteine Levels and Sural Axonal Neurodegeneration. Arch. Neurol. 2004, 61, 657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimber, T.; Blumbergs, P.; Thompson, P. Severe ataxic polyneuropathy associated with chronic levodopa use in Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2013, 19, 847–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zis, P.; Grünewald, R.A.; Chaudhuri, R.K.; Hadjivassiliou, M. Peripheral neuropathy in idiopathic Parkinson’s disease: A systematic review. J. Neurol. Sci. 2017, 378, 204–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manca, D.; Cossu, G.; Murgia, D.; Molari, A.; Ferrigno, P.; Marcia, E.; Melis, M. Reversible encephalopathy and axonal neuropathy in Parkinson’s disease during duodopa therapy. Mov. Disord. 2009, 24, 2293–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galazky, I.; Schoof, J.; Stallforth, S.; Kupsch, A.; Heinze, H.-J.; Kluge, C. Guillain–Barre/CIDP-like neuropathy in two parkinsonian patients following intestinal levodopa/carbidopa treatment. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2014, 20, 125–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klostermann, F.; Jugel, C.; Müller, T.; Marzinzik, F. Malnutritional neuropathy under intestinal levodopa infusion. J. Neural. Transm. 2012, 119, 369–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urban, P.P.; Wellach, I.; Faiss, S.; Layer, P.; Rosenkranz, T.; Knop, K.; Weis, J. Subacute axonal neuropathy in Parkinson’s disease with cobalamin and vitamin B6 deficiency under duodopa therapy. Mov. Disord. 2010, 25, 1748–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos-García, D.; Macías, M.; Llaneza, M.; Grande, M.; de la Fuente-Fernández, R. Serum vitamin B12 and folate levels in Parkinson’s disease patients treated with duodenal levodopa infusion. Mov. Disord. 2011, 26, 558–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adewusi, J.K.; Hadjivassiliou, M.; Vinagre-Aragón, A.; O’Connor, K.R.; Khan, A.; Grünewald, R.A.; Zis, P. Sensory neuropathic symptoms in idiopathic Parkinson’s disease: Prevalence and impact on quality of life. Acta Neurol. Belg. 2018, 118, 445–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, T.; Laar, T.v.; Cornblath, D.R.; Odin, P.; Klostermann, F.; Grandas, F.J.; Ebersbach, G.; Urban, P.P.; Valldeoriola, F.; Antonini, A. Peripheral neuropathy in Parkinson’s disease: Levodopa exposure and implications for duodenal delivery. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2013, 19, 501–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, A.J.; Daniel, S.E.; Kilford, L.; Lees, A.J. Accuracy of clinical diagnosis of idiopathic Parkinson’s disease: A clinico-pathological study of 100 cases. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1992, 55, 181–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Postuma, R.B.; Berg, D.; Stern, M.; Poewe, W.; Olanow, C.W.; Oertel, W.; Obeso, J.; Marek, K.; Litvan, I.; Lang, A.E.; et al. MDS clinical diagnostic criteria for Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2015, 30, 1591–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bril, V.; Perkins, B.A. Validation of the Toronto Clinical Scoring System for Diabetic Polyneuropathy. Diabetes Care 2002, 25, 2048–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preston, D.C.; Shapiro, B.E. Electromyography and Neuromuscular Disorders: Clinical-Electrophysiologic Correlations, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2005; p. 685. [Google Scholar]
- England, J.D.; Gronseth, G.S.; Franklin, G.; Miller, R.G.; Asbury, A.K.; Carter, G.T.; Cohen, J.A.; Fisher, M.A.; Howard, J.F.; Kinsella, L.J.; et al. Distal symmetric polyneuropathy: A definition for clinical research: Report of the American Academy of Neurology, the American Association of Electrodiagnostic Medicine, and the American Academy of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation. Neurology 2005, 64, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gondim, F.d.A.A.; de Oliveira, G.R.; Peixoto, A.A.; Horta, W.G. A case series of peripheral neuropathy in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Ann. Neurol. 2010, 68, 973–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutkove, S.B.; Kothari, M.J.; Raynor, E.M.; Levy, M.L.; Fadic, R.; Nardin, R.A. Sural/radial amplitude ratio in the diagnosis of mild axonal polyneuropathy. Muscle Nerve 1997, 20, 1236–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Araújo, D.F.; de Melo Neto, A.P.; Oliveira, Í.S.C.; Brito, B.S.; de Araújo, I.T.; Barros, I.S.; Lima, J.W.O.; Horta, W.G.; Gondim, F.D.A.A. Small (autonomic) and large fiber neuropathy in Parkinson disease and parkinsonism. BMC Neurol. 2016, 16, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verschuur, C.V.M.; Suwijn, S.R.; Boel, J.A.; Post, B.; Bloem, B.R.; Hilten, J.J.V.; Laar, T.V.; Tissingh, G.; Munts, A.G.; Deuschl, G.; et al. Randomized Delayed-Start Trial of Levodopa in Parkinson’s Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| L-Dopa Group (n = 52) | Non-LDopa Group (n = 21) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 67.60 (8.58) | 60.10 (11.02) | 0.001 |
| Sex (F:M) | 26:26 | 10:11 | 0.853 |
| Hoehn and Yahr stage | 3.19 (0.72) | 2.05 (0.59) | 0.001 |
| PD Disease Duration(years) | 8.65 (5.17) | 2.31 (1.52) | 0.001 |
| UPDRS II | 15.38 (9.15) | 6.05 (3.46) | 0.001 |
| UPDRS III | 21.62 (10.06) | 10.62 (4.67) | 0.001 |
| TCSS | 8.46 (5.3) | 3.43 (3.28) | 0.001 |
| Cyanocobalmin (pg/mL) | 228.81 (109.60) | 306.38 (160.47) | 0.020 |
| Folic acid (ng/mL) | 8.1 (4.77) | 9.05 (3.46) | 0.413 |
| LDD (mg/day) | 891.98 (423.827) | - | - |
| LDDA (months) | 72.34 (49.68) | - | - |
| ENoG Parameters | L-Dopa Group (n = 52) | Non-L-Dopa Group (n = 21) | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| aSNAP Sural nerve (µV) | 5.32 (4.64) | 9.99 (3.91) | 0.001 |
| Sensory NCV Sural nerve (m/s) | 50.83 (9.64) | 52.75 (7.52) | 0.424 |
| aSNAP Superficial peroneal nerve (µV) | 2.88 (3.44) | 8.00 (3.69) | 0.001 |
| Sensory NCV Superficial peroneal nerve (m/s) | 47.58 (8.48) | 48.64 (7.84) | 0.656 |
| aSNAP Radial nerve (µV) | 16.72 (8.42) | 21.94 (4.99) | 0.004 |
| Sensory NCV Radial nerve (m/s) | 59.2 (10.74) | 66.47 (6.99) | 0.011 |
| aSNAP Median nerve (µV) | 13.08 (6.53) | 36.33 (13.2) | 0.001 |
| Sensory NCV Median nerve (m/s) | 55.21 (12.56) | 63.03 (10.09) | 0.324 |
| aCMAP Tibial nerve (mV) | 7.69 (3.44) | 8.89 (2.95) | 0.165 |
| aCMAP Median nerve (mV) | 6.04 (1.84) | 7.87 (1.82) | 0.031 |
| aCMAP Common peroneal nerve (mV) | 4.75 (2.79) | 6.66 (2.48) | 0.008 |
| Motor NCV Common peroneal nerve (m/s) | 49.29 (7.24) | 50.14 (4.23) | 0.541 |
| L-Dopa-PNP n = 35 | L-Dopa-non-PNP n = 17 | non-L-Dopa-non-PNP n = 20 | F | p | Post-hoc Scheffe | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 68.37 (8.05) | 66.00 (9.64) | 60.85 (10.73) | 4.23 | 0.018 | 1–3 |
| Hoehn and Yahr stage | 3.31 (0.64) | 2.94 (0.83) | 2.05 (0.60) | 22.08 | 0.001 | 1–3, 2–3 |
| Cyanocobalmin (pg/mL) | 198.37 (100.24) | 291.47 (103.63) | 307.45 (164.56) | 6.32 | 0.003 | 1–2, 1–3 |
| Folic acid (ng/mL) | 6.81 (3.91) | 10.77 (5.36) | 8.85 (3.42) | 5.39 | 0.007 | 1–2 |
| PD Disease Duration (years) | 9.27 (5.09) | 7.38 (5.24) | 2.13 (1.3) | 16.74 | 0.001 | 1–3, 2–3 |
| LDD (mg/day) | 984.23 (441.94) | 702.06 (317.15) | - | 5.52 | 0.023 | 1–2 |
| LDDA (months) | 80.57 (54.22) | 55.41 (34.17) | - | 3.05 | 0.087 | 1–2 |
| UPDRS II | 16.2 (8.53) | 13.17 (10.4) | 6.25 (3.42) | 9.95 | 0.001 | 1–3, 2–3 |
| UPDRS III | 22.2 (9.24) | 20.41 (11.77) | 11.05 (4.35) | 10.37 | 0.001 | 1–3, 2–3 |
| TCSS | 10.31 (4.93) | 4.65 (3.87) | 3.1 (2.99) | 21.82 | 0.001 | 1–2, 1–3 |
| ENoG Parameters | Mild Axonal Sensory PNP n = 10 | Moderate Sensory Axonal PNP n = 10 | Severe Sensory Axonal PNP with Axonal Motor Loss n = 15 |
|---|---|---|---|
| aSNAP Sural nerve (µV) (N.V.1 > 6) (unobtained in 8 subjects) | 4.43 (0.73) | 2.14 (1.805) | 1.66 (1.731) |
| Sensory NCV Sural nerve (m/s) (N.V. > 40) | 54.64 (9.691) | 51.21 (14.449) | 46.23 (9.884) |
| aSNAP Superficial peroneal nerve (µV) (N.V. > 6) (unobtained in 24 subjects) | 1.76 (1.985) | 0.28 (0.533) | 0.29 (0.605) |
| Sensory NCV Superficial peroneal nerve (m/s) (N.V. > 40) | 42.38 (3.757) | 51.1 (7.882) | 43.1 (21.140) |
| aSNAP Radial nerve (µV) (N.V. > 20) | 21.53 (7.627) | 18.27 (3.959) | 8.82(5.944) |
| Sensory NCV Radial nerve (m/s) (N.V. > 50) | 60.54 (5.135) | 62.19 (10.385) | 55.49 (13.689) |
| aSNAP Median nerve (µV) (N.V. > 10) | 18.15 (5.502) | 20.5 (0.707) | 7.21(3.061) |
| Sensory NCV Median nerve (m/s) (N.V. > 50) | 55.05 (8.878) | 69.00 (18.385) | 49.89 (14.189) |
| aCMAP Tibial nerve (mV) (N.V. > 4) | 9.36 (3.162) | 8.78 (3.063) | 5.01 (3.574) |
| Motor NCV Tibial nerve (m/s) (N.V. > 40) | 46.74 (4.599) | 51.43 (7.501) | 49.71 (9.193) |
| aCMAP Median nerve (mV) (N.V. > 4) | 6.52 (1.825) | 4.30 (0.00) | 5.54 (2.148) |
| Motor NCV Median (m/s) (N.V. > 50) | 53.87 (3.629) | 65.60 (0.00) | 53.93 (6.823) |
| aCMAP Common peroneal nerve (mV) (N.V. > 2) | 4.69 (1.92) | 6.14 (2.348) | 2.67 (2.603) |
| Motor NCV Common peroneal nerve (m/s) (N.V. > 40) | 50.07 (8.94) | 46.41 (4.309) | 49.11 (6.562) |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vanta, O.M.; Tohanean, N.; Pintea, S.; Perju-Dumbrava, L. Large-Fiber Neuropathy in Parkinson’s Disease: Clinical, Biological, and Electroneurographic Assessment of a Romanian Cohort. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1533. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8101533
Vanta OM, Tohanean N, Pintea S, Perju-Dumbrava L. Large-Fiber Neuropathy in Parkinson’s Disease: Clinical, Biological, and Electroneurographic Assessment of a Romanian Cohort. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2019; 8(10):1533. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8101533
Chicago/Turabian StyleVanta, Oana Maria, Nicoleta Tohanean, Sebastian Pintea, and Lacramioara Perju-Dumbrava. 2019. "Large-Fiber Neuropathy in Parkinson’s Disease: Clinical, Biological, and Electroneurographic Assessment of a Romanian Cohort" Journal of Clinical Medicine 8, no. 10: 1533. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8101533
APA StyleVanta, O. M., Tohanean, N., Pintea, S., & Perju-Dumbrava, L. (2019). Large-Fiber Neuropathy in Parkinson’s Disease: Clinical, Biological, and Electroneurographic Assessment of a Romanian Cohort. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 8(10), 1533. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8101533




