Disease and Treatment-Related Sequelae in Patients with Complex Jugulotympanic Paraganglioma
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Patients and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Clinical Evaluation
2.3. Radiologic Evaluation
2.4. Treatment Modalities
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Data
3.2. Treatment and Outcome
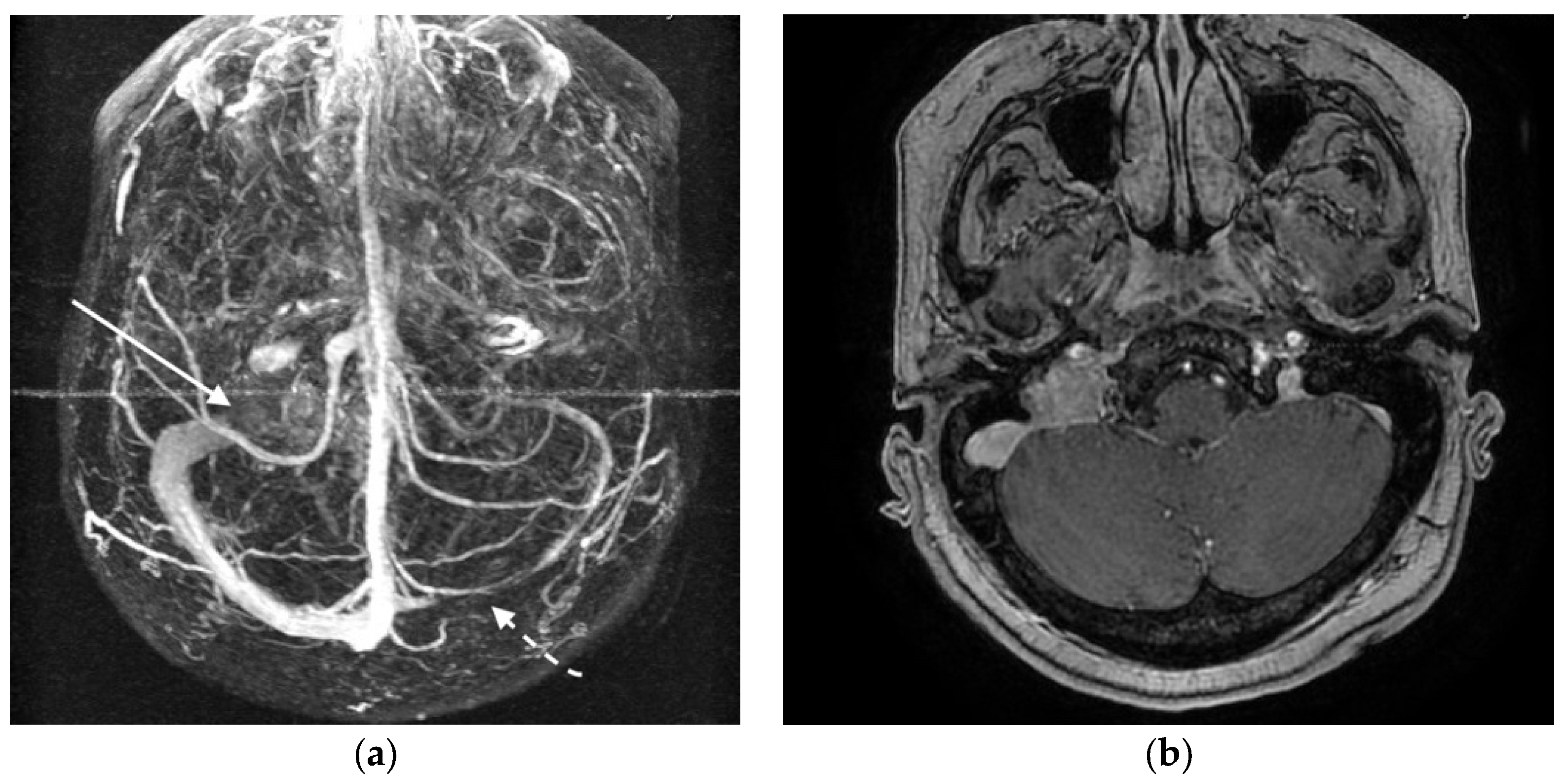
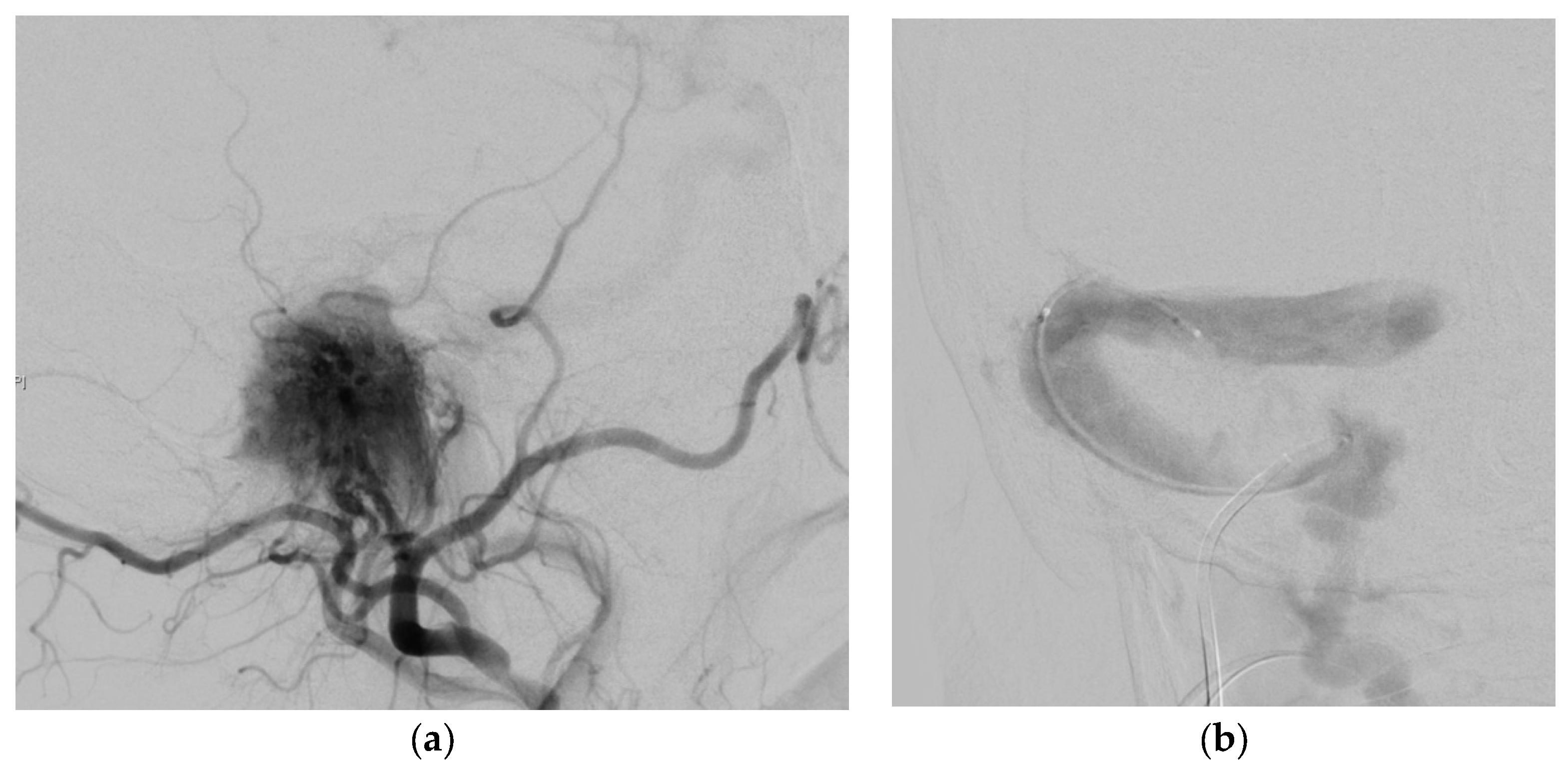
3.3. Illustrative Case Reports
3.3.1. Case 1
3.3.2. Case 2
4. Discussion
4.1. Hearing Impairment and Facial Nerve Affection
4.2. Lower Cranial Nerves Affection
4.3. Brainstem Compression
4.4. Cerebral Sinus Affection
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Harati, A.; Deitmer, T.; Rohde, S.; Ranft, A.; Weber, W.; Schultheiß, R. Microsurgical treatment of large and giant tympanojugular paragangliomas. Surg. Neurol. Int. 2014, 5, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Offergeld, C.; Brase, C.; Yaremchuk, S.; Mader, I.; Rischke, H.C.; Glasker, S.; Schmid, K.W.; Wiech, T.; Preuss, S.F.; Suárez, C.; et al. Head and neck paragangliomas: Clinical and molecular genetic classification. Clinics 2012, 67, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.K.; Sameshima, T.; Gottfried, O.N.; Couldwell, W.T.; Fukushima, T. The combined transmastoid retro- and infralabyrinthine transjugular transcondylar transtubercular high cervical approach for resection of glomus jugulare tumors. Neurosurgery 2006, 59, ons115–ons125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilbo, P.; Morris, C.G.; Amdur, R.J.; Werning, J.W.; Dziegielewski, P.T.; Kirwan, J.; Mendenhall, W.M. Radiotherapy for benign head and neck paragangliomas: A 45-year experience. Cancer 2014, 120, 3738–3743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boedeker, C.C.; Ridder, G.J.; Schipper, J. Paragangliomas of the head and neck: Diagnosis and treatment. Fam. Cancer 2005, 4, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makiese, O.; Chibbaro, S.; Marsella, M.; Tran Ba Huy, P.; GEORGE, B. Jugular foramen paragangliomas: Management, outcome and avoidance of complications in a series of 75 cases. Neurosurg. Rev. 2012, 35, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanna, M.; Shin, S.-H.; De Donato, G.; Sivalingam, S.; Lauda, L.; Vitullo, F.; Piazza, P. Management of complex tympanojugular paragangliomas including endovascular intervention. Laryngoscope 2011, 121, 1372–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanna, M.; Jain, Y.; De Donato, G.; Rohit; Lauda, L.; Taibah, A. Management of jugular paragangliomas: The gruppo otologico experience. Otol. Neurotol. 2004, 25, 797–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, Q.; Yang, J.; Wu, H. Surgical management of extensive jugular paragangliomas: 10-year-experience with a large cohort of patients in China. Int. J. Surg. 2013, 11, 853–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, J.B.; Link, M.J.; Cloft, H.J. Endovascular embolization of paragangliomas: A safe adjuvant to treatment. J. Vascular. Interv. Neurol. 2008, 1, 37–41. [Google Scholar]
- Künzel, J.; Iro, H.; Hornung, J.; Koch, M.; Brase, C.; Klautke, G.; Zenk, J. Function-preserving therapy for jugulotympanic paragangliomas: A retrospective analysis from 2000 to 2010. Laryngoscope 2012, 122, 1545–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonetti, J.P.; Anderson, D.E.; Marzo, S.J.; Origitano, T.C.; Vandevender, D.; Quinonez, R. Facial paralysis associated with glomus jugulare tumors. Otol. Neurotol. 2007, 28, 104–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borba, L.A.B.; Araújo, J.C.; de Oliveira, J.G.; Filho, M.G.; Moro, M.S.; Tirapelli, L.F.; Colli, B.O. Surgical management of glomus jugulare tumors: A proposal for approach selection based on tumor relationships with the facial nerve. J. Neurosurg. 2010, 112, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nonaka, Y.; Fukushima, T.; Watanabe, K.; Friedman, A.H.; Sampson, J.H.; McElveen, J.T.; Cunningham, C.D.; Zomorodi, A.R. Contemporary surgical management of vestibular schwannomas: Analysis of complications and lessons learned over the past decade. Neurosurgery 2013, 72, ons103–ons115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borba, L.A.B.; Ale-Bark, S.; London, C. Surgical treatment of glomus jugulare tumors without rerouting of the facial nerve: An infralabyrinthine approach. Neurosurg. Focus 2004, 17, E8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Shazly, M.A.; Mokbel, M.A.; Elbadry, A.A.; Badran, H.S. Management of the facial nerve in lateral skull base surgery analytic retrospective study. Clin. Med. Insights Ear Nose Throat 2011, 4, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boedeker, C.C.; Neumann, H.P.H.; Maier, W.; Bausch, B.; Schipper, J.; Ridder, G.J. Malignant head and neck paragangliomas in SDHB mutation carriers. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2007, 137, 126–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sen, C.; Hague, K.; Kacchara, R.; Jenkins, A.; Das, S.; Catalano, P. Jugular foramen: Microscopic anatomic features and implications for neural preservation with reference to glomus tumors involving the temporal bone. Neurosurgery 2001, 48, 838–847. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Carlson, M.L.; Driscoll, C.L.W.; Garcia, J.J.; Janus, J.R.; Link, M.J. Surgical management of giant transdural glomus jugulare tumors with cerebellar and brainstem compression. J. Neurol. Surg. Part B Skull Base 2012, 73, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Mefty, O.; Teixeira, A. Complex tumors of the glomus jugulare: Criteria, treatment, and outcome. J. Neurosurg. 2002, 97, 1356–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lertakyamanee, P.; Srinivasan, A.; De Lott, L.B.; Trobe, J.D. Papilledema and vision loss caused by jugular paragangliomas. J. Neuroophthalmol. 2015, 35, 364–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, V.M.; Prabhu, V. A rare case of glomus jugulare tumor presenting as papilledema. J. Neuroophthalmol. 2016, 36, 110–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, D.; Meng, R.; Zhang, X.; Guo, L.; Li, S.; Wu, W.; Duan, J.; Song, H.; Ding, Y.; Ji, X. Intracranial hypertension induced by internal jugular vein stenosis can be resolved by stenting. Eur. J. Neurol. 2018, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asif, H.; Craven, C.L.; Siddiqui, A.H.; Shah, S.N.; Matloob, S.A.; Thorne, L.; Robertson, F.; Watkins, L.D.; Toma, A.K. Idiopathic intracranial hypertension: 120-day clinical, radiological, and manometric outcomes after stent insertion into the dural venous sinus. J. Neurosurg. 2017, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Classification | Tumor Extension |
|---|---|
| Class A | Tumor limited to the middle ear cleft |
| Class B | Tumor limited to the tympanomastoid area with no infralabyrinthine compartment involvement |
| Class C | Tumor involving the infralabyrinthine compartment of the temporal bone and extending into the petrous apex |
| Subclass C1 | Involvement of the vertical portion of the carotid canal |
| Subclass C2 | Invasion of the vertical portion of the carotid canal |
| Subclass C3 | invasion of the horizontal portion of the carotid canal |
| Subclass C4 | invasion of the foramen lacerum and the cavernous sinus |
| Class D | Tumor with an intracranial extension |
| Subclass D1 | Less than 2 cm in diameter |
| Subclass D2 | Greater than 2 cm in diameter |
| Clinical Characteristics | All | Observation | Radiotherapy (Alone) | Embolization | Embolization and Surgery |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of patients | 22 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 17 |
| Age | 51.3 | 36 | 78.0 | 74.5 | 49.2 |
| Fisch type | |||||
| C2 | 8 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 3 |
| C3 | 12 | - | - | - | 13 |
| C4 | 1 | - | - | - | 1 |
| D 1&2 (%) | 88.4 | 0 | 100 | 100 | 87.7 |
| Multiple PGL | 1 | - | - | - | 2 |
| Malignant PGL | 1 | - | - | - | 1 |
| Follow-up time (months) | 81.7 | 24 | 90 | 80 | 81.3 |
| Karnofsky at latest Follow-up | 97.1 | 100 | 100 | 80 | 96.7 |
| Symptoms | Before Treatment | After Treatment | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Improved | Same | Worsened | New | ||
| Headache | 6 | 3 | 3 | - | - |
| Vertigo | 3 | 1 | 2 | - | - |
| Palpable cervical mass | 5 | 5 | - | - | |
| CN VII | |||||
| HB Grade 1 | 1 | - | - | - | - |
| HB Grade 2 | 2 | 1 | - | - | - |
| HB Grade 3 | - | - | - | - | 2 |
| HB Grade 4–6 | 3 | - | 3 | - | |
| CN VIII | |||||
| Otalgia | 4 | 4 | - | - | - |
| Pulsatile Tinnitus | 6 | 5 | 1 | - | - |
| Hearing deficit | 9 * | 3 | 3 | - | - |
| Hearing loss | 3 | - | 3 | - | 3 * |
| CN IX-X | |||||
| Hoarseness | 4 | - | 3 | 1 | 3 |
| Dysphagia | 4 | - | 3 | 1 | 3 |
| CN IX-Palsy | 3 | - | 3 | 1 | 3 |
| CN X-Palsy | 3 | - | 3 | 1 | 3 |
| CN XI-Palsy | 1 | - | 1 | - | 1 |
| CN XII-Palsy | 3 | - | 3 | - | 1 |
| Papilledema | 1 | 1 | - | - | - |
| Ataxia | 2 | 2 | - | - | - |
| Pathologic catecholeamine exprimation | 1 | 1 | - | - | - |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Harati, A.; Schultheiß, R.; Rohde, S.; Deitmer, T. Disease and Treatment-Related Sequelae in Patients with Complex Jugulotympanic Paraganglioma. J. Clin. Med. 2018, 7, 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm7030051
Harati A, Schultheiß R, Rohde S, Deitmer T. Disease and Treatment-Related Sequelae in Patients with Complex Jugulotympanic Paraganglioma. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2018; 7(3):51. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm7030051
Chicago/Turabian StyleHarati, Ali, Rolf Schultheiß, Stefan Rohde, and Thomas Deitmer. 2018. "Disease and Treatment-Related Sequelae in Patients with Complex Jugulotympanic Paraganglioma" Journal of Clinical Medicine 7, no. 3: 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm7030051
APA StyleHarati, A., Schultheiß, R., Rohde, S., & Deitmer, T. (2018). Disease and Treatment-Related Sequelae in Patients with Complex Jugulotympanic Paraganglioma. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 7(3), 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm7030051




