Tarsal Tunnel Mechanosensitivity Is Increased in Patients with Asthma: A Case-Control Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Ethical Statement
2.3. Sample Size Calculation
2.4. Sample
2.5. Socio-Demographic and Descriptive Data
2.6. Primary Outcome Measurements
2.7. Secondary Outcome Measurements
2.8. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Socio-Demographic and Descriptive Data
3.2. Primary Outcome Measurements
3.3. Secondary Outcome Measurements
3.4. Multivariate Predictive Analysis of Tarsal Tunnel PPT
4. Discussion
4.1. Tarsal Tunnel Mechanosensitivity in Asthma Patients
4.2. Lung Function
4.3. Clinical Implications and Future Studies
4.4. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Masoli, M.; Fabian, D.; Holt, S.; Beasley, R. Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA) Program The global burden of asthma: Executive summary of the GINA Dissemination Committee report. Allergy 2004, 59, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banjari, M.; Kano, Y.; Almadani, S.; Basakran, A.; Al-Hindi, M.; Alahmadi, T. The Relation between Asthma Control and Quality of Life in Children. Int. J. Pediatr. 2018, 2018, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coban, H.; Aydemir, Y. The relationship between allergy and asthma control, quality of life, and emotional status in patients with asthma: A cross-sectional study. Allergy Asthma Clin. Immunol. 2014, 10, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Khateeb, A.J.; Al Khateeb, J.M. Research on psychosocial aspects of asthma in the Arab world: A literature review. Multidiscip. Respir. Med. 2015, 10, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, D.M.; Jurdi, R.; Roberts, C.A.; Hernandez, M.; Horne, R.; Chan, A. A Review of Portable Electronic Spirometers: Implications for Asthma Self-Management. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2018, 18, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharan, R.V.; Abeyratne, U.R.; Swarnkar, V.R.; Claxton, S.; Hukins, C.; Porter, P. Predicting spirometry readings using cough sound features and regression. Physiol. Meas. 2018, 39, 095001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunardi, A.C.; Marques da Silva, C.C.B.; Rodrigues Mendes, F.A.; Marques, A.P.; Stelmach, R.; Fernandes Carvalho, C.R. Musculoskeletal Dysfunction and Pain in Adults with Asthma. J. Asthma 2011, 48, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaves, T.C.; Grossi, D.B.; de Oliveira, A.S.; Bertolli, F.; Holtz, A.; Costa, D. Correlation between signs of temporomandibular (TMD) and cervical spine (CSD) disorders in asthmatic children. J. Clin. Pediatr. Dent. 2005, 29, 287–292. [Google Scholar]
- Mazzone, S.B.; Canning, B.J. Central nervous system control of the airways: Pharmacological implications. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2002, 2, 220–228. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Velden, V.H.J.; Hulsmann, A.R. Autonomic Innervation of Human Airways: Structure, Function, and Pathophysiology in Asthma. Neuroimmunomodulation 1999, 6, 145–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyasaka, T.; Dobashi-Okuyama, K.; Takahashi, T.; Takayanagi, M.; Ohno, I. The interplay between neuroendocrine activity and psychological stress-induced exacerbation of allergic asthma. Allergol. Int. 2018, 67, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terada, M.; Kosik, K.B.; McCann, R.S.; Gribble, P.A. Diaphragm Contractility in Individuals with Chronic Ankle Instability. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2016, 48, 2040–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palacios-Ceña, M.; Lima Florencio, L.; Natália Ferracini, G.; Barón, J.; Guerrero, Á.L.; Ordás-Bandera, C.; Arendt-Nielsen, L.; Fernández-de-las-Peñas, C. Women with Chronic and Episodic Migraine Exhibit Similar Widespread Pressure Pain Sensitivity. Pain Med. 2016, 17, 2127–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Corrêa, J.B.; Costa, L.O.P.; de Oliveira, N.T.B.; Sluka, K.A.; Liebano, R.E. Central sensitization and changes in conditioned pain modulation in people with chronic nonspecific low back pain: A case–control study. Exp. Brain Res. 2015, 233, 2391–2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Røsland, T.; Gregersen, L.; Eskehave, T.; Kersting, U.; Arendt-Nielsen, L. Pain sensitization and degenerative changes are associated with aberrant plantar loading in patients with painful knee osteoarthritis. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 2015, 44, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilder-Smith, C.H.; Robert-Yap, J. Abnormal endogenous pain modulation and somatic and visceral hypersensitivity in female patients with irritable bowel syndrome. World J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 13, 3699–3704. [Google Scholar]
- Plaza-Manzano, G.; Vergara-Vila, M.; Val-Otero, S.; Rivera-Prieto, C.; Pecos-Martin, D.; Gallego-Izquierdo, T.; Ferragut-Garcías, A.; Romero-Franco, N. Manual therapy in joint and nerve structures combined with exercises in the treatment of recurrent ankle sprains: A randomized, controlled trial. Man. Ther. 2016, 26, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dellon, A.; Muse, V.; Scott, N.; Akre, T.; Anderson, S.R.; Barret, S.L.; Biddinger, K.R.; Bregman, P.J.; Bullard, B.P.; Dauphinee, D.M.; et al. A Positive Tinel Sign as Predictor of Pain Relief or Sensory Recovery after Decompression of Chronic Tibial Nerve Compression in Patients with Diabetic Neuropathy. J. Reconstr. Microsurg. 2012, 28, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fingleton, C.P.; Dempsey, L.; Smart, K.; Doody, C.M. Intraexaminer and Interexaminer Reliability of Manual Palpation and Pressure Algometry of the Lower Limb Nerves in Asymptomatic Subjects. J. Manip. Physiol. Ther. 2014, 37, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saggini, R.; Bellomo, R.G.; Affaitati, G.; Lapenna, D.; Giamberardino, M.A. Sensory and Biomechanical Characterization of Two Painful Syndromes in the Heel. J. Pain 2007, 8, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaza-Manzano, G.; Ríos-León, M.; Martín-Casas, P.; Arendt-Nielsen, L.; Fernández-de-las-Peñas, C.; Ortega-Santiago, R. Widespread Pressure Pain Hypersensitivity in Musculoskeletal and Nerve Trunk Areas as a Sign of Altered Nociceptive Processing in Unilateral Plantar Heel Pain. J. Pain 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trepman, E.; Kadel, N.J.; Chisholm, K.; Razzano, L. Effect of Foot and Ankle Position on Tarsal Tunnel Compartment Pressure. Foot Ankle Int. 1999, 20, 721–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aweid, O.; Gallie, R.; Morrissey, D.; Crisp, T.; Maffulli, N.; Malliaras, P.; Padhiar, N. Medial tibial pain pressure threshold algometry in runners. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2014, 22, 1549–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenbroucke, J.P.; von Elm, E.; Altman, D.G.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Pocock, S.J.; Poole, C.; Schlesselman, J.J.; Egger, M. STROBE Initiative Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE): Explanation and elaboration. Int. J. Surg. 2014, 12, 1500–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holt, G.R. Declaration of Helsinki-the world’s document of conscience and responsibility. South. Med. J. 2014, 107, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Medical Association. World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki Ethical principles for medical research involving human subjects. J. Am. Coll. Dent. 2014, 81, 14–18. [Google Scholar]
- Löwhagen, O. Diagnosis of asthma—New theories. J. Asthma 2015, 52, 538–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrow, J.S. Quetelet index as indicator of obesity. Lancet 1986, 1, 1219. [Google Scholar]
- Gauthier, A.P.; Lariviere, M.; Young, N. Psychometric properties of the IPAQ: A validation study in a sample of northern Franco-Ontarians. J. Phys. Act. Health 2009, 6 (Suppl. 1), S54–S60. [Google Scholar]
- Koo, T.K.; Guo, J.; Brown, C.M. Test-retest reliability, repeatability, and sensitivity of an automated deformation-controlled indentation on pressure pain threshold measurement. J. Manip. Physiol. Ther. 2013, 36, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debouche, S.; Pitance, L.; Robert, A.; Liistro, G.; Reychler, G. Reliability and Reproducibility of Chest Wall Expansion Measurement in Young Healthy Adults. J. Manip. Physiol. Ther. 2016, 39, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Irwig, L.; Groeneveld, H.; Becklake, M. Relationship of lung function loss to level of initial function: Correcting for measurement error using the reliability coefficient. J. Epidemiol. Community Health 1988, 42, 383–389. [Google Scholar]
- Manske, M.C.; McKeon, K.E.; McCormick, J.J.; Johnson, J.E.; Klein, S.E. Arterial Anatomy of the Posterior Tibial Nerve in the Tarsal Tunnel. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 2016, 98, 499–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nijs, J.; Malfliet, A.; Ickmans, K.; Baert, I.; Meeus, M. Treatment of central sensitization in patients with ‘unexplained’ chronic pain: An update. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2014, 15, 1671–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Listernick, R. A 15-Year-Old Male with Pain and Numbness in His Right Foot. Pediatr. Ann. 2014, 43, 430–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mehta, A.K.; Langford, C.A.; Taylor, D.O.; Bolen, M.; Reddy, A.J. A 39-Year-Old Postpartum Woman With Foot Drop and Shortness of Breath. Chest 2016, 149, e61–e64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- François, A.; Low, S.A.; Sypek, E.I.; Christensen, A.J.; Sotoudeh, C.; Beier, K.T.; Ramakrishnan, C.; Ritola, K.D.; Sharif-Naeini, R.; Deisseroth, K.; et al. A Brainstem-Spinal Cord Inhibitory Circuit for Mechanical Pain Modulation by GABA and Enkephalins. Neuron 2017, 93, 822–839.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, L.R. Chronic Pain and the Opioid Conundrum. Anesthesiol. Clin. 2016, 34, 341–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panczyk, K.; Golda, S.; Waszkielewicz, A.; Zelaszczyk, D.; Gunia-Krzyzak, A.; Marona, H. Serotonergic system and its role in epilepsy and neuropathic pain treatment: A review based on receptor ligands. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2015, 21, 1723–1740. [Google Scholar]
- Delvalle, N.M.; Dharshika, C.; Morales-Soto, W.; Fried, D.E.; Gaudette, L.; Gulbransen, B.D. Communication Between Enteric Neurons, Glia, and Nociceptors Underlies the Effects of Tachykinins on Neuroinflammation. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 6, 321–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzitelli, M.; Palazzo, E.; Maione, S.; Neugebauer, V. Group II Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors: Role in Pain Mechanisms and Pain Modulation. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2018, 11, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, C.-K.; MacDermott, A.B. Both Ca2+-permeable and -impermeable AMPA receptors contribute to primary synaptic drive onto rat dorsal horn neurons. J. Physiol. 2006, 575, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arendt-Nielsen, L. Central sensitization in humans: Assessment and pharmacology. In Pain Control. Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology; Schaible, H.G., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; Volume 227, pp. 79–102. [Google Scholar]
- Lobo, C.C.; Morales, C.R.; Sanz, D.R.; Corbalán, I.S.; Romero, E.A.S.; Carnero, J.F.; López, D.L. Comparison of hand grip strength and upper limb pressure pain threshold between older adults with or without non-specific shoulder pain. PeerJ 2017, 5, e2995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Almeida, Y.; King, C.D.; Goodin, B.R.; Sibille, K.T.; Glover, T.L.; Riley, J.L.; Sotolongo, A.; Herbert, M.S.; Schmidt, J.; Fessler, B.J.; et al. Psychological Profiles and Pain Characteristics of Older Adults with Knee Osteoarthritis. Arthritis Care Res. (Hoboken) 2013, 65, 1786–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Quantitative Data | Total Group | Asthma | Control | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (n = 100) | (n = 50) | (n = 50) | ||
| Age (years) | 39.35 ± 12.25 | 37.22 ± 11.94 | 41.48 ± 12.31 | 0.082 * |
| (19–65) | (20–65) | (19–65) | ||
| Weight (kg) | 70.64 ± 14.33 | 70.90 ± 15.84 | 70.38 ± 12.80 | 0.857 * |
| (47–120) | (48–120) | (47–96) | ||
| Height (m) | 1.64 ± 0.15 | 1.66 ± 0.15 | 1.64 ± 0.13 | 0.305 † |
| (1.50–1.97) | (1.53–1.97) | (1.50–1.87) | ||
| BMI (kg/m2) | 24.81 ± 5.61 | 24.43 ± 6.03 | 24.81 ± 7.00 | 0.398 † |
| (17.30–39.18) | (18.41–39.18) | (17.30–34.72) | ||
| IPAQ (METS/min/week) | 2119.50 ± 3620.25 | 1524.00 ± 3391.13 | 2772.00 ± 3365.25 | 0.128 † |
| (0–15,918) | (0–15,918) | (0–15,243) |
| Categorical Data | Total Group | Asthma | Control | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (n = 100) | (n = 50) | (n = 50) | |||
| Professional activity | student | 15 (15%) | 8 (16%) | 7 (14%) | 0.440 ‡ |
| freeland | 12 (12%) | 7 (14%) | 5 (10%) | ||
| employed | 58 (58%) | 28 (56%) | 30 (60%) | ||
| unemployed | 8 (8%) | 2 (4%) | 6 (12%) | ||
| retired | 7 (7%) | 5 (10%) | 2 (4%) | ||
| Civil status | single | 27 (27%) | 12 (24%) | 15 (30%) | 0.894 ‡ |
| divorced | 4 (4%) | 2 (4%) | 2 (4%) | ||
| widowed | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | ||
| couple | 16 (16%) | 9 (18%) | 7 (14%) | ||
| married | 53 (53%) | 27 (54%) | 26 (52%) | ||
| IPAQ category * | low | 25 (25%) | 16 (32%) | 9 (18%) | 0.264 ‡ |
| moderate | 43 (43%) | 19 (38%) | 24 (48%) | ||
| vigorous | 32 (32%) | 15 (30%) | 17 (34%) | ||
| Sex | Male | 36 (36%) | 18 (36%) | 18 (36%) | 1.000 † |
| Female | 64 (64%) | 32 (64%) | 32 (64%) | ||
| Plantar orthosis | Yes | 12 (12%) | 7 (14%) | 5 (10%) | 0.760 † |
| No | 88 (88%) | 43 (86%) | 45 (90%) | ||
| Outcome Measurements | Total Group | Asthma | Control | p-Value Asthma vs. Control |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (n = 100) | (n = 50) | (n = 50) | ||
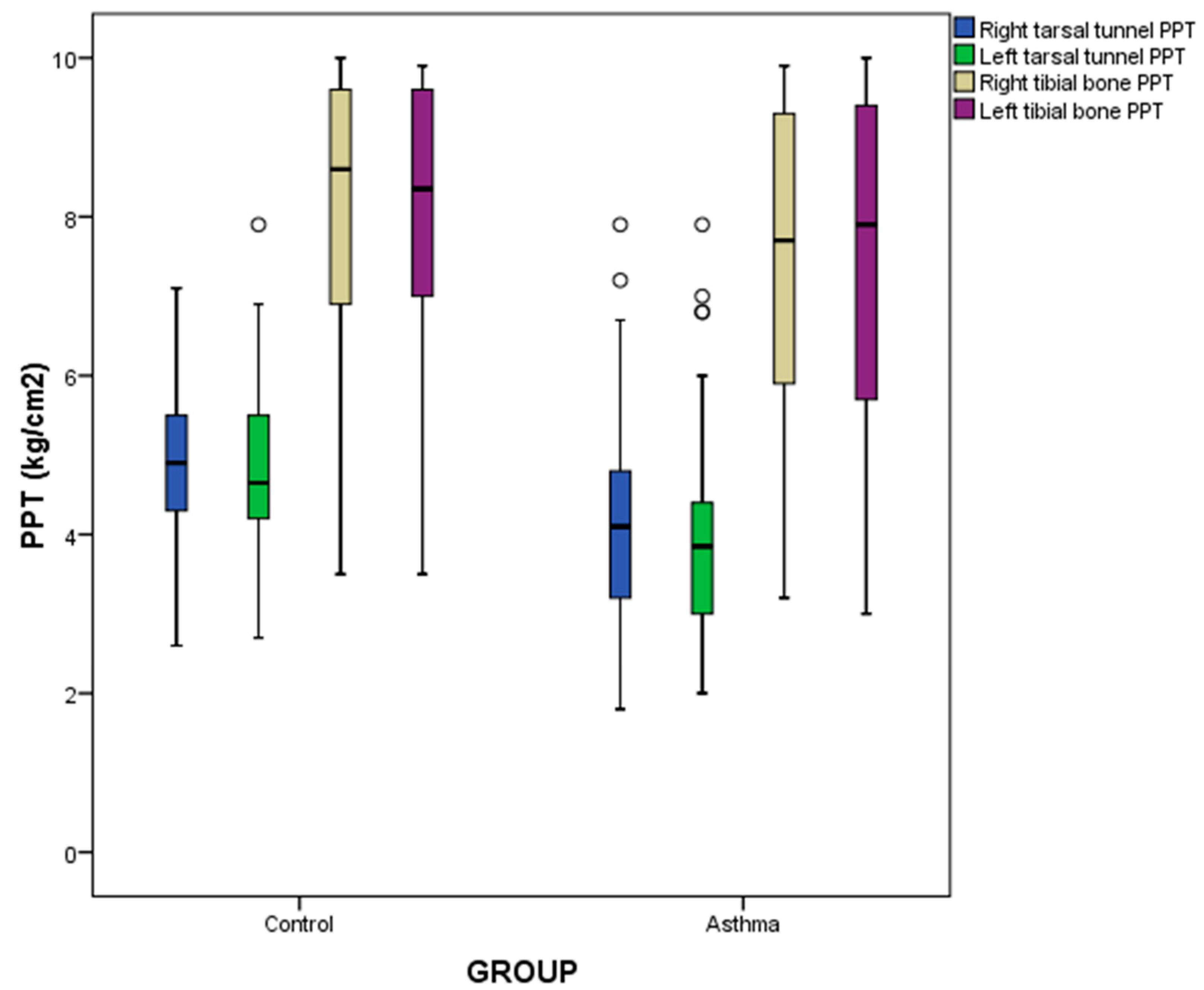
| Right tarsal tunnel PPT (kg/cm2) | 4.58 ± 1.21 | 4.24 ± 1.32 | 4.93 ± 0.99 | 0.004 * |
| (1.80–7.90) | (1.80–7.90) | (2.60–7.10) | ||
| Left tarsal tunnel PPT (kg/cm2) | 4.20 ± 1.50 | 3.85 ± 1.45 | 4.65 ± 1.33 | <0.001† |
| (2.00–7.90) | (2.00–7.90) | (2.70–7.90) | ||
| Right fibular bone PPT (kg/cm2) | 8.20 ± 3.12 | 7.70 ± 3.43 | 8.60 ± 2.72 | 0.097 † |
| (3.20–10.00) | (3.20–9.90) | (3.50–10.00) | ||
| Left fibular bone PPT (kg/cm2) | 8.20 ± 3.07 | 7.90 ± 3.73 | 8.35 ± 2.63 | 0.102 † |
| (3.00–10.00) | (3.00–10.00) | (3.50–9.90) | ||
| FVC (%) | 96.00 ± 13.00 | 95.50 ± 15.75 | 96.50 ± 12.25 | 0.907 † |
| (64–170) | (64–113) | (80–170) | ||
| FEV1 (%) | 100.13 ± 11.16 | 98.48 ± 12.21 | 101.78 ± 9.84 | 0.140 * |
| (61–141) | (61–121) | (84–141) | ||
| FEV1/FVC (%) | 103.00 ± 10.75 | 100.00 ± 11.00 | 105.50 ± 10.00 | 0.003† |
| (85–123) | (85–122) | (94–123) |
| Parameter | Model | R2 Change | Model R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Right tarsal tunnel PPT (kg/cm2) | 5.594 | 0.279 | |
| −0.809 * Sex | 0.145 ‡ | ||
| −0.613 * Group | 0.083 ‡ | ||
| +0.158 * Left tarsal tunnel PPT | 0.051 † | ||
| Left tarsal tunnel PPT (kg/cm2) | 3.748 | ||
| +0.266 * Left fibular bone PPT | 0.189 ‡ | ||
| −0.617 * Group | 0.060 ‡ | 0.249 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Calvo-Lobo, C.; Painceira-Villar, R.; López-López, D.; García-Paz, V.; Becerro-de-Bengoa-Vallejo, R.; Losa-Iglesias, M.E.; Palomo-López, P. Tarsal Tunnel Mechanosensitivity Is Increased in Patients with Asthma: A Case-Control Study. J. Clin. Med. 2018, 7, 541. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm7120541
Calvo-Lobo C, Painceira-Villar R, López-López D, García-Paz V, Becerro-de-Bengoa-Vallejo R, Losa-Iglesias ME, Palomo-López P. Tarsal Tunnel Mechanosensitivity Is Increased in Patients with Asthma: A Case-Control Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2018; 7(12):541. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm7120541
Chicago/Turabian StyleCalvo-Lobo, César, Roi Painceira-Villar, Daniel López-López, Vanesa García-Paz, Ricardo Becerro-de-Bengoa-Vallejo, Marta Elena Losa-Iglesias, and Patricia Palomo-López. 2018. "Tarsal Tunnel Mechanosensitivity Is Increased in Patients with Asthma: A Case-Control Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 7, no. 12: 541. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm7120541
APA StyleCalvo-Lobo, C., Painceira-Villar, R., López-López, D., García-Paz, V., Becerro-de-Bengoa-Vallejo, R., Losa-Iglesias, M. E., & Palomo-López, P. (2018). Tarsal Tunnel Mechanosensitivity Is Increased in Patients with Asthma: A Case-Control Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 7(12), 541. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm7120541








