Gallbladder Stone Disease Is Associated with an Increased Risk of Migraines
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Data Source
2.2. Sample Participants
2.3. Outcome and Comorbidities
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GSD | Gallbladder Stone Disease |
| NHIRD | National Health Insurance Research Database |
| CAD | Coronary Artery Disease |
| aHR | Adjusted Hazard Ratio |
| CI | Confidence Interval |
| CCK | Cholecystokinin |
| CGRP | Calcitonin Gene Related Peptide |
| NHI | National Health Insurance |
| LHID2000 | Longitudinal Health Insurance Database |
| ICD-9-CM | International Codes of Disease Ninth Edition Clinical Modification |
| COPD | Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease |
| CAD | Coronary Artery Disease |
| LDL-C | Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol |
| CVD | Cardiovascular Disorder |
| IGF-1 | Insulin-Like Growth Factor-1 |
| HDL-C | Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol |
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
References
- Goadsby, P.J. Recent advances in the diagnosis and management of migraine. BMJ 2006, 332, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goadsby, P.J.; Lipton, R.B.; Ferrari, M.D. Migraine-Current understanding and treatment. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 346, 257–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scher, A.I.; Stewart, W.F.; Lipton, R.B. Migraine and headache: A meta-analytic approach. Epidemiol. Pain 1999, 1, 159–170. [Google Scholar]
- Diener, H.C.; Dodick, D.W.; Goadsby, P.J.; Lipton, R.B.; Olesen, J.; Silberstein, S.D. Chronic migraine-classification, characteristics and treatment. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2012, 8, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.H.; Huang, M.H.; Yang, J.C.; Nien, C.K.; Etheredge, G.D.; Yang, C.C.; Yeh, Y.H.; Wu, H.S.; Chou, D.A.; Yueh, S.K. Prevalence and risk factors of gallstone disease in an adult population of Taiwan: An epidemiologic survey. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2006, 21, 1737–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gracie, W.A.; Ransohoff, D.F. The natural history of silent gallstone: The innocent gallstone is not a myth. N. Engl. J. Med. 1982, 307, 798–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acalovschi, M. Cholesterol gallstones: From epidemiology to prevention. Postgrad. Med. J. 2001, 77, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, I.C.; Yang, Y.W.; Wu, M.F.; Yeh, Y.H.; Liou, J.C.; Lin, Y.L.; Chiang, C.H. The association of metabolic syndrome and its factors with gallstone disease. BMC Family Practice 2014, 15, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nilsson, S.; Edvinsson, L.; Malmberg, B.; Johansson, B.; Linde, M. A relationship between migraine and biliary tract disorders: Findings in two Swedish samples of elderly twins. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2010, 122, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Erpecum, K.J.; Venneman, N.G.; Portincasa, P.; Vanberge-Henegouwen, G.P. Review article: Agents affecting gall-bladder motility-role in treatment and prevention of gallstones. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2000, 14 (Suppl. 2), 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Han, T.Q.; Chen, S.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, S.D. Gallbladder motor function, plasma cholecystokinin and cholecystokinin receptor of gallbladder in cholesterol stone patients. World J. Gastroenterol. 2005, 11, 1685–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcus, D.A. Serotonin and its role in headache pathogenesis and treatment. Clin. J. Pain 1993, 9, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubovsky, S.L. Beyond the serotonin reuptake inhibitors: Rationales for the development of new serotoninergic agents. J. Clin. Psychiatry 1994, 55, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Grundy, S.M.; Brewer, B.; Cleeman, J.I.; Smith, S.C., Jr.; Lenfant, C.; American Heart Association; National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Definition of metabolic syndrome: Report of the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute/American Heart Association Conference on Scientific Issues Related to Definition. Circulation 2004, 109, 433–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Portincasa, P.; Di Ciaula, A.; Wang, H.H.; Palasciano, G.; van Erpecum, K.J.; Moschetta, A.; Wang, D.Q. Coordinate regulation of gallbladder motor function in the gut-liver axis. Hepatology 2008, 47, 2112–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fioroni, L.; Martignoni, E.; Facchinetti, F. Changes of neuroendocrine axes in patients with menstrual migraine. Cephalalgia 1995, 15, 297–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frediani, F.; Villani, V. Migraine and depression. Neurol. Sci. 2007, 28, S161–S165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Gayo, M.; Gonzalez, M.; Fernandez-Alfonso, S. Vasodilatory effects of cholecystokinin: New role for an old peptide? Regul. Pept. 2006, 137, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Database NHIR. Available online: http://nhird.nhri.org.tw/en/index.html (accessed on 21 September 2018).
- Wang, D.Q.H. Aging per se is an independent risk factor for cholesterol gallstone formation in gallstone susceptible mice. J. Lipid Res. 2002, 43, 1950–1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovacs, P.; Kurtz, U.; Wittenburg, H. Hepatic insulin resistance ties cholesterol gallstone formation and the metabolic syndrome. Ann. Hepatol. 2008, 7, 262–264. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liew, P.L.; Wang, W.; Lee, Y.C.; Huang, M.T.; Lin, Y.C.; Lee, W.J. Gallbladder disease among obese patients in Taiwan. Obes. Surg. 2007, 17, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smelt, A.H. Triglycerides and gallstone formation. Clin. Chim. Acta 2010, 411, 1625–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olaiya, M.T.; Chiou, H.Y.; Jeng, J.S.; Lien, L.M.; Hsieh, F.I. Significantly increased risk of cardiovascular disease among patients with gallstone disease: A population-based cohort study. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, E76448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, C.B. Pathophysiology and biochemistry of cardiovascular disease. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2004, 14, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marschall, H.U.; Einarsson, C. Gallstone disease. J. Intern. Med. 2007, 261, 529–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moschetta, A.; Twickler, T.B.; Rehfeld, J.F.; van Ooteghem, N.A.; Cabezas, M.C.; Portincasa, P.; van Berge-Henegouwen, G.P.; van Erpecum, K.J. Effects of growth hormone deficiency and recombinant growth hormone therapy on postprandial gallbladder motility and cholecystokinin release. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2004, 49, 529–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Twickler, M.T.; Cramer, M.J.; van Erpecum, K.J. Insulin-like growth factor-1: A common metabolic pathway in the origin of both gallstones and coronary artery disease. Am. J. Gastroeneterol. 2005, 100, 2363–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geetha, A. Evidence for oxidative stress in the gall bladder mucosa of gall stone patients. J. Biochem. Mol. Biol. Biophys. 2002, 6, 428–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otani, H. Oxidative stress as pathogenesis of cardiovascular risk associated with metabolic syndrome. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2011, 15, 1911–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Portincasa, P.; Di Giaula, A.; Baldassarre, G.; Palmieri, V.; Gentile, A.; Cimmino, A.; Palasciano, G. Gallbladder motor function in gallstone patients: Sonographic and in vitro studies on the role of gallstones, smooth muscle function and gallbladder wall inflammation. J. Hepatol. 1994, 21, 430–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandes, J.L. The influence of estrogen on migraine: A systematic review. JAMA 2006, 295, 1824–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Losel, R.M.; Falkenstein, E.; Feuring, M.; Schultz, A.; Tillmann, H.C.; Rossol-Haseroth, K.; Wehling, M. Nongenomic steroid action: Controversies, questions, and answers. Physiol. Rev. 2003, 83, 965–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puri, V.; Puri, S.; Svojanovsky, S.; Mathur, S.; Macgregor, R.R.; Klein, R.M.; Welch, K.M.; Berman, N.E. Effects of oestrogen on trigeminal ganglia in culture: Implications for hormonal effects on migraine. Cephalalgia 2006, 26, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Splett, C.L.; Scheffen, J.R.; Desotelle, J.A.; Plamann, V.; Bauer-Dantoin, A.C. Galanin enhancement of gonadotropin-releasing hormone-stimulated luteinizing hormone secretion in female rats is estrogen dependent. Endocrinology 2003, 144, 484–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benedetti, F.; Lanotte, M.; Lopiano, L.; Colloca, L. When words are painful: Unraveling the mechanisms of the nocebo effect. Neuroscience 2007, 147, 260–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurth, T.; Gaziano, J.M.; Cook, N.R.; Logroscino, G.; Diener, H.C.; Buring, J.E. Migraine and risk of cardiovascular disease in women. JAMA 2006, 296, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ransohoff, D.F.; Gracie, W.A.; Wolfenson, L.B.; Neuhauser, D. Prophylactic cholecystectomy or expectant management for silent gallstones. A decision analysis to assess survival. Ann. Intern. Med. 1983, 99, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipton, R.B.; Diamond, S.; Reed, M.; Diamond, M.L.; Stewart, W.F. Migraine diagnosis and treatment: Results from the American Migraine Study II. Headache 2001, 41, 638–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
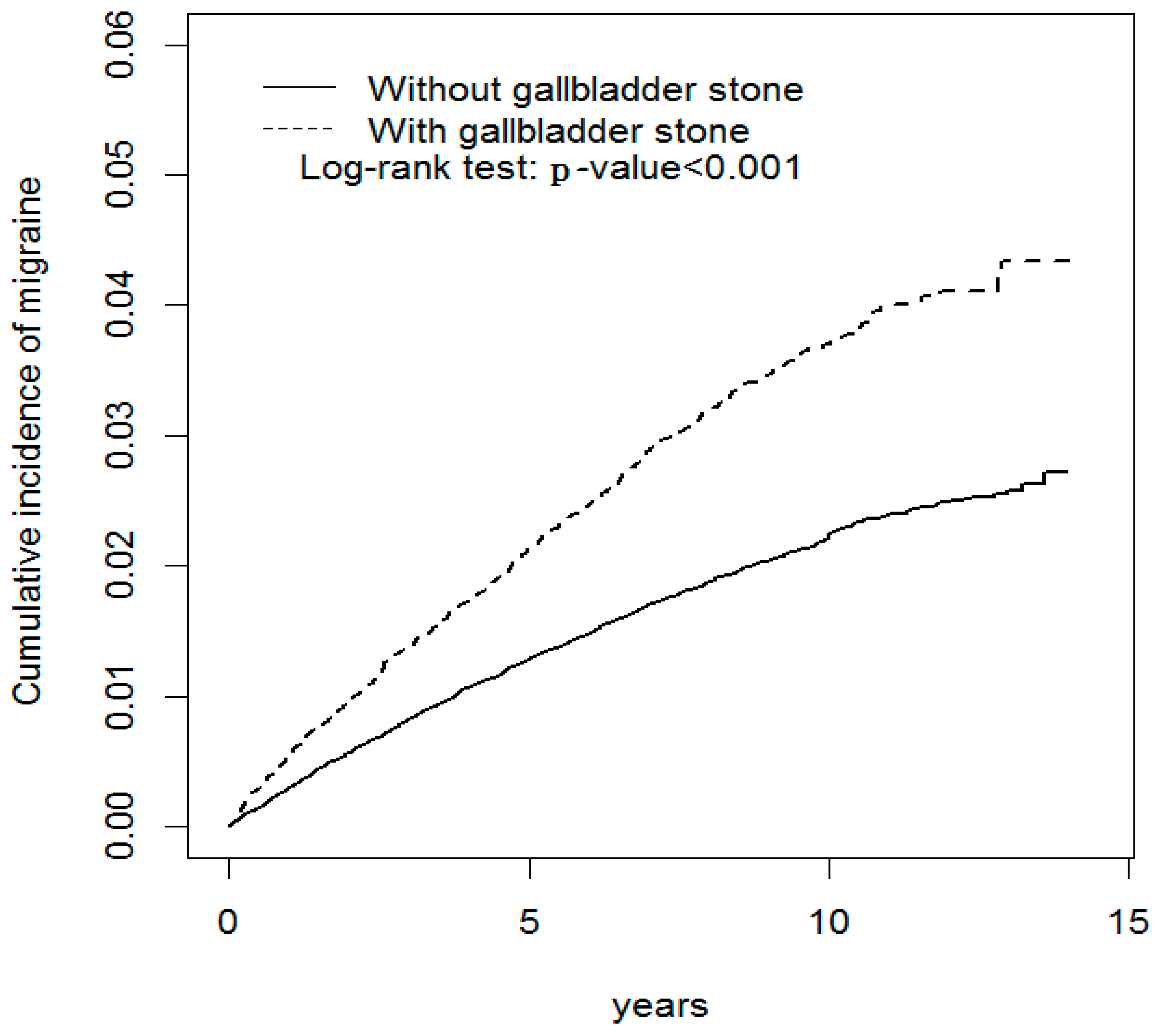
| Variable | Gallbladder Stone Disease | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| No | Yes | ||
| N = 81,706 | N = 20,427 | ||
| Age, year | 0.99 | ||
| ≤34 | 8576 (10.5) | 2144 (10.5) | |
| 35–49 | 22,188 (27.2) | 5547 (27.2) | |
| 50–64 | 25,436 (31.1) | 6359 (31.1) | |
| 65+ | 25,506 (31.2) | 6377 (31.2) | |
| Mean ± SD † | 55.2 (16.0) | 55.9 (15.7) | <0.001 |
| Sex | 0.99 | ||
| Female | 44,248 (54.2) | 11,062 (54.2) | |
| Male | 37,458 (45.8) | 9365 (45.8) | |
| Comorbidity | |||
| Diabetes | 6854 (8.39) | 2642 (12.9) | <0.001 |
| Hypertension | 26,745 (32.7) | 8448 (41.4) | <0.001 |
| Hyperlipidemia | 14,765 (18.1) | 5622 (27.5) | <0.001 |
| Stroke | 3245 (3.97) | 995 (4.87) | <0.001 |
| Chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases | 8211 (10.1) | 2909 (14.2) | <0.001 |
| Coronary artery disease | 12,495 (15.3) | 4862 (23.8) | <0.001 |
| Depression | 2803 (3.43) | 1227 (6.01) | <0.001 |
| Anxiety | 4165 (5.10) | 1783 (8.73) | <0.001 |
| Gallbladder Stone Disease | Gallbladder Stone Disease to Non-Gallbladder Stone Disease | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No | Yes | |||||||
| Variables | Event | Person-Years | Rate # | Event | Person-Years | Rate # | Crude HR ※ (95% CI) | Adjusted HR † (95% CI) |
| All | 1286 | 558,325 | 2.30 | 536 | 137,776 | 3.89 | 1.69 (1.52, 1.86) *** | 1.56 (1.41, 1.73) *** |
| Stratify age | ||||||||
| ≤34 | 115 | 57,278 | 2.01 | 50 | 14,645 | 3.41 | 1.70 (1.22, 2.37) ** | 1.59 (1.14, 2.24) ** |
| 35–49 | 414 | 165,593 | 2.05 | 190 | 40,652 | 4.67 | 1.86 (1.57, 2.21) *** | 1.66 (1.39, 1.98) *** |
| 50–64 | 455 | 183,146 | 2.48 | 184 | 44,704 | 4.12 | 1.65 (1.39, 1.96) *** | 1.50 (1.26, 1.78) *** |
| 65+ | 302 | 152,307 | 1.98 | 112 | 37,775 | 2.96 | 1.49 (1.20, 1.85) *** | 1.41 (1.13, 1.75) ** |
| Sex | ||||||||
| Female | 961 | 311,909 | 3.08 | 382 | 76,969 | 4.96 | 1.61 (1.43, 1.81) *** | 1.49 (1.32, 1.68) *** |
| Male | 325 | 246,416 | 1.32 | 154 | 60,806 | 2.53 | 1.92 (1.58, 2.32) *** | 1.77 (1.46, 2.15) *** |
| Comorbidity ‡ | ||||||||
| No | 614 | 324,976 | 1.89 | 209 | 58,059 | 3.60 | 1.90 (1.63, 2.23) *** | 1.87 (1.60, 2.19) *** |
| Yes | 672 | 233,349 | 2.88 | 327 | 79,716 | 4.10 | 1.43 (1.26, 1.64) *** | 1.38 (1.21, 1.58) *** |
| Crude HR ※ | Adjusted HR † | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | HR | (95% CI) | HR | (95% CI) |
| Gallbladder stone disease | 1.69 | (1.52, 1.86) *** | 1.56 | (1.41, 1.73) *** |
| Age, years | 0.99 | (0.992, 0.998) ** | 0.99 | (0.98, 0.99) *** |
| Sex (Female vs. male) | 2.24 | (2.02, 2.49) *** | 2.16 | (1.95, 2.40) *** |
| Baseline comorbidities (yes vs. no) | ||||
| Diabetes | 0.84 | (0.70, 1.02) | - | - |
| Hypertension | 1.15 | (1.05, 1.27) ** | 1.10 | (0.97, 1.24) |
| Hyperlipidemia | 1.18 | (1.06, 1.32) ** | 0.98 | (0.87, 1.11) |
| Stroke | 0.79 | (0.59, 1.07) | - | - |
| Chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases | 1.12 | (0.96, 1.30) | - | - |
| Coronary artery disease | 1.49 | (1.33, 1.67) *** | 1.44 | (1.26, 1.64) *** |
| Depression | 2.41 | (2.01, 2.87) *** | 1.75 | (1.45, 2.11) *** |
| Anxiety | 2.25 | (1.92, 2.63) *** | 1.60 | (1.35, 1.89) *** |
| Variables | N | Event | Adjusted HR † (95% CI) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gallbladder stone disease | Coronary artery disease | |||
| No | No | 69,211 | 1037 | 1 (Reference) |
| No | Yes | 12,495 | 249 | 1.56 (1.33, 1.82) *** |
| Yes | No | 15,565 | 394 | 1.65 (1.47, 1.85) *** |
| Yes | Yes | 4862 | 142 | 2.05 (1.69, 2.48) *** |
| Gallbladder stone disease | Depression | |||
| No | No | 78,903 | 1215 | 1 (Reference) |
| No | Yes | 2803 | 71 | 1.67 (1.30, 2.13) *** |
| Yes | No | 19,200 | 475 | 1.54 (1.39, 1.72) *** |
| Yes | Yes | 1227 | 61 | 2.89 (2.21, 3.77) *** |
| Gallbladder stone disease | Anxiety | |||
| No | No | 77,541 | 1176 | 1 (Reference) |
| No | Yes | 4165 | 110 | 1.84 (1.50, 2.26) *** |
| Yes | No | 18,644 | 475 | 1.62 (1.46, 1.81) *** |
| Yes | Yes | 1783 | 61 | 2.07 (1.58, 2.70) *** |
| Variables | N | Event | PY | Rate # | Adjusted HR † (95% CI) | Adjusted HR † (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gallbladder stone disease (No) | 81,706 | 1286 | 558,325 | 2.30 | 1 (Reference) | |
| Gallbladder stone disease (Yes) Cholecystectomy (No) | 12,675 | 354 | 84,399 | 4.19 | 1.67 (1.48, 1.88) *** | 1 (Reference) |
| Cholecystectomy (Yes) | 7752 | 182 | 53,377 | 3.41 | 1.39 (1.19, 1.63) *** | 0.83 (0.69, 0.99) ** |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, C.-H.; Lin, C.-L.; Kao, C.-H. Gallbladder Stone Disease Is Associated with an Increased Risk of Migraines. J. Clin. Med. 2018, 7, 455. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm7110455
Chen C-H, Lin C-L, Kao C-H. Gallbladder Stone Disease Is Associated with an Increased Risk of Migraines. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2018; 7(11):455. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm7110455
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Chien-Hua, Cheng-Li Lin, and Chia-Hung Kao. 2018. "Gallbladder Stone Disease Is Associated with an Increased Risk of Migraines" Journal of Clinical Medicine 7, no. 11: 455. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm7110455
APA StyleChen, C.-H., Lin, C.-L., & Kao, C.-H. (2018). Gallbladder Stone Disease Is Associated with an Increased Risk of Migraines. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 7(11), 455. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm7110455





