Rituximab and Fibrillary Glomerulonephritis: Interest of B Cell Reconstitution Monitoring
Abstract
1. Introduction
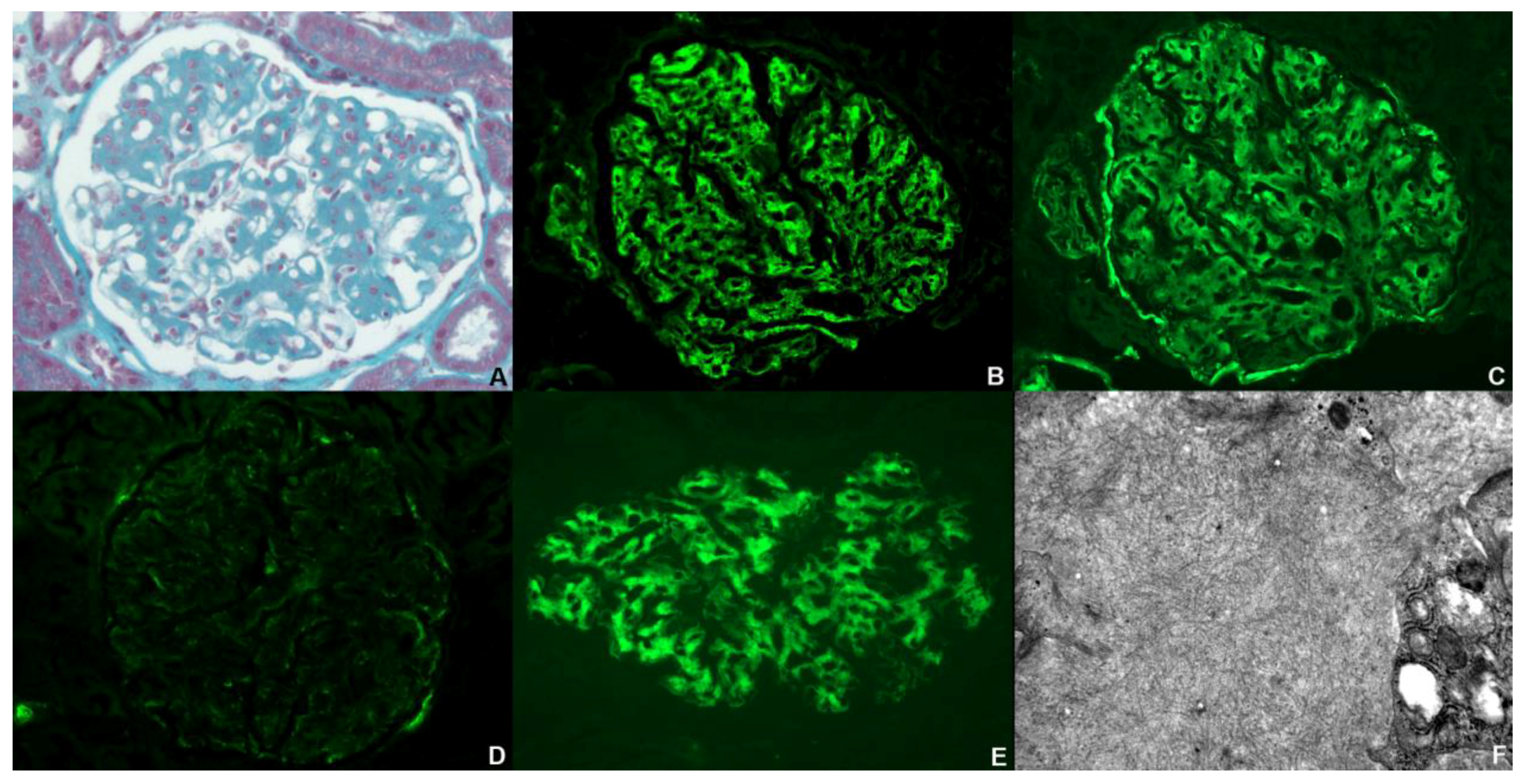
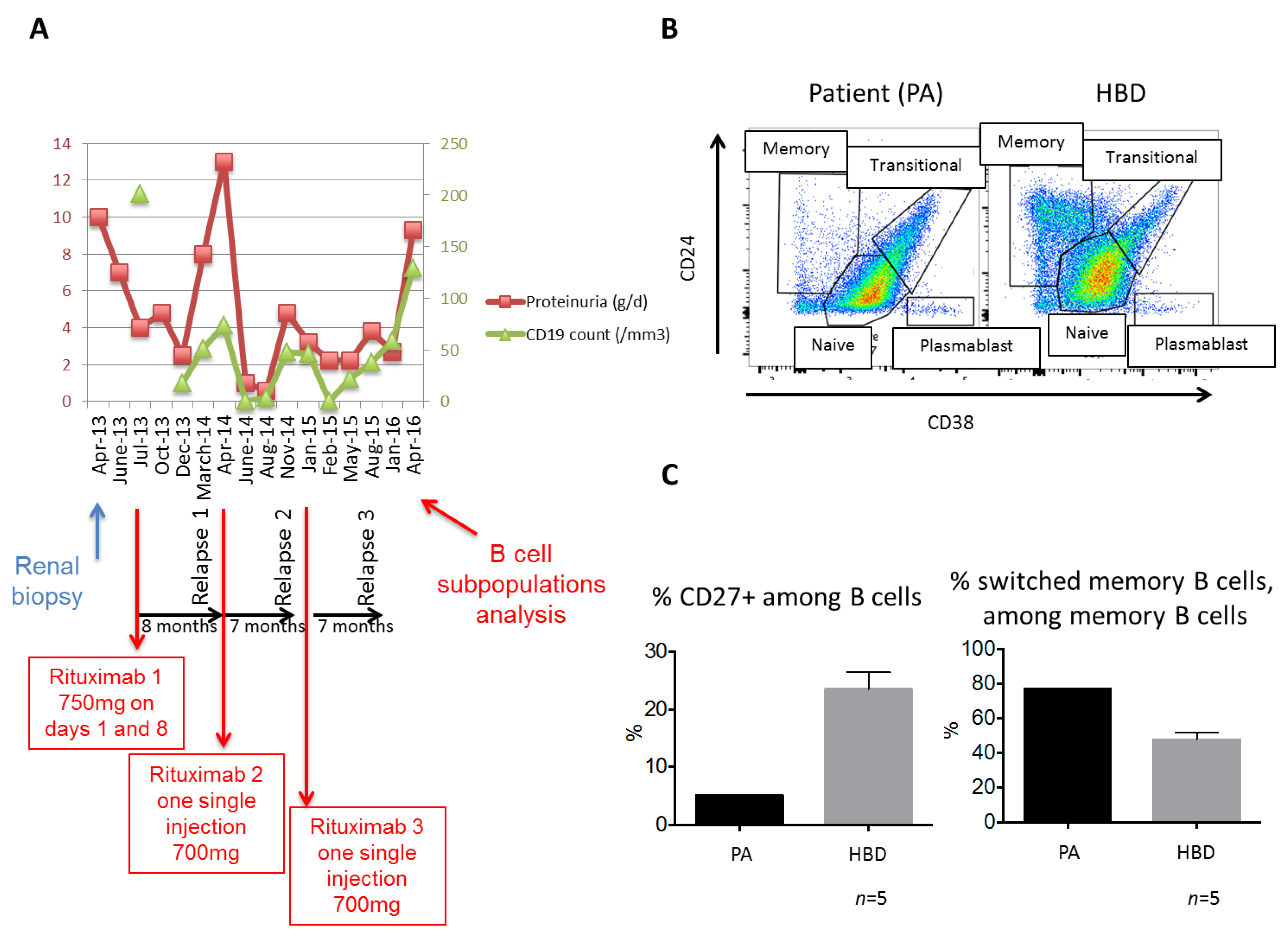
2. Case Presentation
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Detailed Methods
Appendix A1. Analysis of Renal Biopsy Specimen
Appendix A2. B Cell Subset Analysis by Flow Cytometry
| Circulating B Cell Subpopulations | Markers |
|---|---|
| Transitional (Immature) | CD19+CD24hiCD38hi |
| Antigen independent maturation | |
| Mature naïve | CD19+CD24intCD38int |
| Antigen dependent maturation in lymphoid follicles: TFH-B cells cooperation | |
| Memory | CD19+CD27+ or CD19+CD24hiCD38− |
| Switched memory | CD19+CD27+IgD− |
| Unswitched memory | CD19+CD27+IgD+ |
| Plasma cells | CD19+CD24−CD38hi |
References
- Lusco, M.A.; Fogo, A.B.; Najafian, B.; Alpers, C.E. AJKD Atlas of Renal Pathology: Fibrillary Glomerulonephritis. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2015, 66, e27–e28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bridoux, F.; Hugue, V.; Coldefy, O.; Goujon, J.M.; Baumens, M.; Sechet, A.; Preud’Homme, J.L.; Touchard, G. Fibrillary glomerulonephritis and immunotactoid (microtubular) glomerulopathy are associated with distinct immunologic features. Kidney Int. 2002, 62, 1764–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alpers, C.E.; Kowalewska, J. Fibrillary Glomerulonephritis and Immunotactoid Glomerulopathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2008, 19, 34–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasr, S.H.; Valeri, A.M.; Cornell, L.D.; Fidler, M.E.; Sethi, S.; Leung, N.; Fervenza, F.C. Fibrillary glomerulonephritis: A report of 66 cases from a single institution. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 6, 775–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasr, S.H.; Vrana, J.A.; Dasari, S.; Bridoux, F.; Fidler, M.E.; Kaaki, S.; Quellard, N.; Rinsant, A.; Goujon, J.M.; Sethi, S.; et al. DNAJB9 Is a Specific Immunohistochemical Marker for Fibrillary Glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int. Rep. 2017, 3, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andeen, N.K.; Yang, H.Y.; Dai, D.F.; MacCoss, M.J.; Smith, K.D. DnaJ Homolog Subfamily B Member 9 Is a Putative Autoantigen in Fibrillary GN. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2018, 29, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dasari, S.; Alexander, M.P.; Vrana, J.A.; Theis, J.D.; Mills, J.R.; Negron, V.; Sethi, S.; Dispenzieri, A.; Highsmith, W.E., Jr.; Nasr, S.H.; et al. DnaJ Heat Shock Protein Family B Member 9 Is a Novel Biomarker for Fibrillary GN. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2018, 29, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javaugue, V.; Karras, A.; Glowacki, F.; McGregor, B.; Lacombe, C.; Goujon, J.M.; Ragot, S.; Aucouturier, P.; Touchard, G.; Bridoux, F. Long-term Kidney Disease Outcomes in Fibrillary Glomerulonephritis: A Case Series of 27 Patients. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2013, 62, 679–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hogan, J.; Restivo, M.; Canetta, P.A.; Herlitz, L.C.; Radhakrishnan, J.; Appel, G.B.; Bomback, A.S. Rituximab treatment for fibrillary glomerulonephritis. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2014, 29, 1925–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, M.; Navaneethan, S.D.; Chung, M.; Sloand, J.; Goldman, B.; Appel, G.; Rovin, B.H. Rituximab treatment of fibrillary glomerulonephritis. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2008, 52, 1158–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Payan Schober, F.; Jobson, M.A.; Poulton, C.J.; Singh, H.K.; Nickeleit, V.; Falk, R.J.; Jennette, J.C.; Nachman, P.H.; Pendergraft Iii, W.F. Clinical features and outcomes of a racially diverse population with fibrillary glomerulonephritis. Am. J. Nephrol. 2017, 45, 248–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahan, K.; Debiec, H.; Plaisier, E.; Cachanado, M.; Rousseau, A.; Wakselman, L.; Michel, P.A.; Mihout, F.; Dussol, B.; Matignon, M.; et al. Rituximab for Severe Membranous Nephropathy: A 6-Month Trial with Extended Follow-Up. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 28, 348–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munyentwali, H.; Bouachi, K.; Audard, V.; Remy, P.; Lang, P.; Mojaat, R.; Deschênes, G.; Ronco, P.M.; Plaisier, E.M.; Dahan, K.Y. Rituximab is an efficient and safe treatment in adults with steroid-dependent minimal change disease. Kidney Int. 2013, 83, 511–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anolik, J.H.; Barnard, J.; Owen, T.; Zheng, B.; Kemshetti, S.; Looney, R.J.; Sanz, I. Delayed memory B cell recovery in peripheral blood and lymphoid tissue in systemic lupus erythematosus after B cell depletion therapy. Arthritis Rheum. 2007, 56, 3044–3056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venhoff, N.; Niessen, L.; Kreuzaler, M.; Rolink, A.G.; Hässler, F.; Rizzi, M.; Voll, R.E.; Thiel, J. Reconstitution of the peripheral B lymphocyte compartment in patients with ANCA-associated vasculitides treated with rituximab for relapsing or refractory disease. Autoimmunity 2014, 47, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adlowitz, D.G.; Barnard, J.; Biear, J.N.; Cistrone, C.; Owen, T.; Wang, W.; Palanichamy, A.; Ezealah, E.; Campbell, D.; Wei, C.; et al. Expansion of Activated Peripheral Blood Memory B Cells in Rheumatoid Arthritis, Impact of B Cell Depletion Therapy, and Biomarkers of Response. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0128269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colucci, M.; Carsetti, R.; Cascioli, S.; Casiraghi, F.; Perna, A.; Ravà, L.; Ruggiero, B.; Emma, F.; Vivarelli, M. B Cell Reconstitution after Rituximab Treatment in Idiopathic Nephrotic Syndrome. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2016, 27, 1811–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheson, B.D.; Leonard, J.P. Monoclonal antibody therapy for B-cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 613–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Leibler, C.; Moktefi, A.; Matignon, M.; Debiais-Delpech, C.; Oniszczuk, J.; Sahali, D.; Cohen, J.L.; Grimbert, P.; Audard, V. Rituximab and Fibrillary Glomerulonephritis: Interest of B Cell Reconstitution Monitoring. J. Clin. Med. 2018, 7, 430. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm7110430
Leibler C, Moktefi A, Matignon M, Debiais-Delpech C, Oniszczuk J, Sahali D, Cohen JL, Grimbert P, Audard V. Rituximab and Fibrillary Glomerulonephritis: Interest of B Cell Reconstitution Monitoring. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2018; 7(11):430. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm7110430
Chicago/Turabian StyleLeibler, Claire, Anissa Moktefi, Marie Matignon, Céline Debiais-Delpech, Julie Oniszczuk, Dil Sahali, José L. Cohen, Philippe Grimbert, and Vincent Audard. 2018. "Rituximab and Fibrillary Glomerulonephritis: Interest of B Cell Reconstitution Monitoring" Journal of Clinical Medicine 7, no. 11: 430. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm7110430
APA StyleLeibler, C., Moktefi, A., Matignon, M., Debiais-Delpech, C., Oniszczuk, J., Sahali, D., Cohen, J. L., Grimbert, P., & Audard, V. (2018). Rituximab and Fibrillary Glomerulonephritis: Interest of B Cell Reconstitution Monitoring. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 7(11), 430. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm7110430





