Clinical Application of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicle-Based Therapeutics for Inflammatory Lung Diseases
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Classes, Biogenesis and Cargos of Extracellular Vesicles
3. Isolation and Characterization of Extracellular Vesicles
4. Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Their Characteristics
5. Functions of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles
6. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicle-Based Therapeutics for Inflammatory Lung Diseases
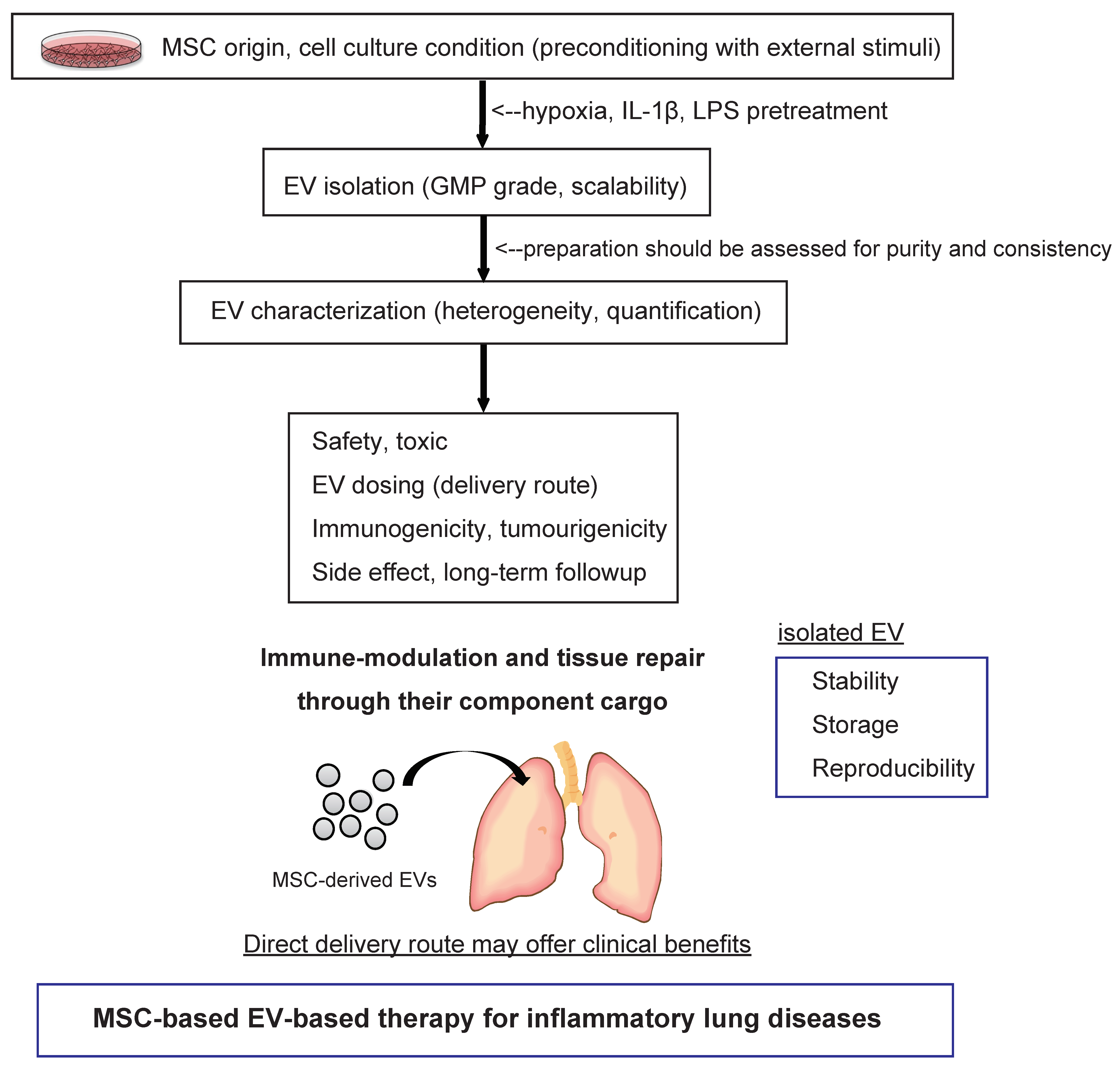
7. Pharmaceutical Development of Extracellular Vesicle-Based Therapeutics for Inflammatory Lung Diseases
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Raposo, G.; Stoorvogel, W. Extracellular vesicles: Exosomes, microvesicles and friends. J. Cell Biol. 2013, 200, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gould, S.J.; Raposo, G. As we wait: Coping with an imperfect nomenclature for extracellular vesicles. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2013, 2, 20389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witwer, K.W.; Buzas, E.I.; Bemis, L.T.; Bora, A.; Lasser, C.; Lotvall, J.; Nolte-’t Hoen, E.N.; Piper, M.G.; Sivaraman, S.; Skog, J.; et al. Standardization of sample collection, isolation and analysis methods in extracellular vesicle research. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2013, 2, 20360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanez-Mo, M.; Siljander, P.R.; Andreu, Z.; Zavec, A.B.; Borras, F.E.; Buzas, E.I.; Buzas, K.; Casal, E.; Cappello, F.; Carvalho, J.; et al. Biological properties of extracellular vesicles and their physiological functions. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2015, 4, 27066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raposo, G.; Nijman, H.W.; Stoorvogel, W.; Liejendekker, R.; Harding, C.V.; Melief, C.J.; Geuze, H.J. B lymphocytes secrete antigen-presenting vesicles. J. Exp Med. 1996, 183, 1161–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faure, J.; Lachenal, G.; Court, M.; Hirrlinger, J.; Chatellard-Causse, C.; Blot, B.; Grange, J.; Schoehn, G.; Goldberg, Y.; Boyer, V.; et al. Exosomes are released by cultured cortical neurones. Mol. Cell Neurosci. 2006, 31, 642–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujita, Y.; Yoshioka, Y.; Ochiya, T. Extracellular vesicle transfer of cancer pathogenic components. Cancer Sci. 2016, 107, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geiger, S.; Hirsch, D.; Hermann, F.G. Cell therapy for lung disease. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2017, 26, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lassance, R.M.; Prota, L.F.; Maron-Gutierrez, T.; Garcia, C.S.; Abreu, S.C.; Passaro, C.P.; Xisto, D.G.; Castiglione, R.C.; Carreira, H., Jr.; Ornellas, D.S.; et al. Intratracheal instillation of bone marrow-derived cell in an experimental model of silicosis. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2009, 169, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes-Pacheco, M.; Xisto, D.G.; Ornellas, F.M.; Antunes, M.A.; Abreu, S.C.; Rocco, P.R.; Takiya, C.M.; Morales, M.M.; et al. Repeated administration of bone marrow-derived cells prevents disease progression in experimental silicosis. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2013, 32, 1681–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gnecchi, M.; He, H.; Liang, O.D.; Melo, L.G.; Morello, F.; Mu, H.; Noiseux, N.; Zhang, L.; Pratt, R.E.; Ingwall, J.S.; et al. Paracrine action accounts for marked protection of ischemic heart by Akt-modified mesenchymal stem cells. Nat. Med. 2005, 11, 367–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gnecchi, M.; Danieli, P.; Malpasso, G.; Ciuffreda, M.C. Paracrine Mechanisms of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Tissue Repair. Methods Mol. Biol. 2016, 1416, 123–146. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Abreu, S.C.; Weiss, D.J.; Rocco, P.R. Extracellular vesicles derived from mesenchymal stromal cells: A therapeutic option in respiratory diseases? Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2016, 7, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz, F.F.; Rocco, P.R.M. Stem-cell extracellular vesicles and lung repair. Stem. Cell Investig. 2017, 4, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colombo, M.; Raposo, G.; Thery, C. Biogenesis, secretion and intercellular interactions of exosomes and other extracellular vesicles. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2014, 30, 255–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshioka, Y.; Konishi, Y.; Kosaka, N.; Katsuda, T.; Kato, T.; Ochiya, T. Comparative marker analysis of extracellular vesicles in different human cancer types. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2013, 2, 20424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cocucci, E.; Meldolesi, J. Ectosomes and exosomes: Shedding the confusion between extracellular vesicles. Trends. Cell Biol. 2015, 25, 364–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valadi, H.; Ekstrom, K.; Bossios, A.; Sjostrand, M.; Lee, J.J.; Lotvall, J.O. Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2007, 9, 654–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skog, J.; Wurdinger, T.; van Rijn, S.; Meijer, D.H.; Gainche, L.; Sena-Esteves, M.; Curry, W.T., Jr.; Carter, B.S.; Krichevsky, A.M.; Breakefield, X.O. Glioblastoma microvesicles transport RNA and proteins that promote tumour growth and provide diagnostic biomarkers. Nat. Cell Biol. 2008, 10, 1470–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratajczak, J.; Miekus, K.; Kucia, M.; Zhang, J.; Reca, R.; Dvorak, P.; Ratajczak, M.Z. Embryonic stem cell-derived microvesicles reprogram hematopoietic progenitors: Evidence for horizontal transfer of mRNA and protein delivery. Leukemia 2006, 20, 847–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kucharzewska, P.; Belting, M. Emerging roles of extracellular vesicles in the adaptive response of tumour cells to microenvironmental stress. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2013, 2, 20304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beninson, L.A.; Fleshner, M. Exosomes: An emerging factor in stress-induced immunomodulation. Semin. Immunol. 2014, 26, 394–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujita, Y.; Kosaka, N.; Araya, J.; Kuwano, K.; Ochiya, T. Extracellular vesicles in lung microenvironment and pathogenesis. Trends Mol. Med. 2015, 21, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujita, Y.; Kadota, T.; Araya, J.; Ochiya, T.; Kuwano, K. Extracellular Vesicles: New Players in Lung Immunity. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2018, 58, 560–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, R.; Greening, D.W.; Zhu, H.J.; Takahashi, N.; Simpson, R.J. Extracellular vesicle isolation and characterization: Toward clinical application. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 1152–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Deun, J.; Mestdagh, P.; Sormunen, R.; Cocquyt, V.; Vermaelen, K.; Vandesompele, J.; Bracke, M.; De Wever, O.; Hendrix, A. The impact of disparate isolation methods for extracellular vesicles on downstream RNA profiling. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2014, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linares, R.; Tan, S.; Gounou, C.; Arraud, N.; Brisson, A.R. High-speed centrifugation induces aggregation of extracellular vesicles. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2015, 4, 29509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thind, A.; Wilson, C. Exosomal miRNAs as cancer biomarkers and therapeutic targets. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2016, 5, 31292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Kaslan, M.; Lee, S.H.; Yao, J.; Gao, Z. Progress in Exosome Isolation Techniques. Theranostics 2017, 7, 789–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willis, G.R.; Kourembanas, S.; Mitsialis, S.A. Toward Exosome-Based Therapeutics: Isolation, Heterogeneity and Fit-for-Purpose Potency. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2017, 4, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinclair, K.; Yerkovich, S.T.; Chambers, D.C. Mesenchymal stem cells and the lung. Respirology 2013, 18, 397–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kern, S.; Eichler, H.; Stoeve, J.; Kluter, H.; Bieback, K. Comparative analysis of mesenchymal stem cells from bone marrow, umbilical cord blood, or adipose tissue. Stem Cells 2006, 24, 1294–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, L.; Jia, Z.; Yin, X.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Y.; Chen, P.; Ma, K.; Zhou, C. Comparative analysis of mesenchymal stem cells from bone marrow, cartilage and adipose tissue. Stem Cells Dev. 2008, 17, 761–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mouiseddine, M.; Francois, S.; Semont, A.; Sache, A.; Allenet, B.; Mathieu, N.; Frick, J.; Thierry, D.; Chapel, A. Human mesenchymal stem cells home specifically to radiation-injured tissues in a non-obese diabetes/severe combined immunodeficiency mouse model. Br. J. Radiol. 2007, 80, S49–S55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fong, E.L.; Chan, C.K.; Goodman, S.B. Stem cell homing in musculoskeletal injury. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 395–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salem, H.K.; Thiemermann, C. Mesenchymal stromal cells: Current understanding and clinical status. Stem Cells 2010, 28, 585–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsuda, T.; Kosaka, N.; Takeshita, F.; Ochiya, T. The therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles. Proteomics 2013, 13, 1637–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernardo, M.E.; Fibbe, W.E. Mesenchymal stromal cells: Sensors and switchers of inflammation. Cell Stem Cell 2013, 13, 392–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, W.; Song, L.; Li, X.M.; Wang, D.; Guo, X.J.; Xu, W.G. Mesenchymal stem cells alleviate airway inflammation and emphysema in COPD through down-regulation of cyclooxygenase-2 via p38 and ERK MAPK pathways. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antunes, M.A.; Lapa, E.S.J.R.; Rocco, P.R. Mesenchymal stromal cell therapy in COPD: From bench to bedside. Int. J. Chron. Obstruct. Pulmon. Dis. 2017, 12, 3017–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dominici, M.; Le Blanc, K.; Mueller, I.; Slaper-Cortenbach, I.; Marini, F.; Krause, D.; Deans, R.; Keating, A.; Prockop, D.J.; Horwitz, E. Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy 2006, 8, 315–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lalu, M.M.; McIntyre, L.; Pugliese, C.; Fergusson, D.; Winston, B.W.; Marshall, J.C.; Granton, J.; Stewart, D.J.; Canadian Critical Care Trials Group. Safety of cell therapy with mesenchymal stromal cells (SafeCell): A systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simones, A.A.; Beisang, D.J.; Panoskaltsis-Mortari, A.; Roberts, K.D. Mesenchymal stem cells in the pathogenesis and treatment of bronchopulmonary dysplasia: A clinical review. Pediatr. Res. 2018, 83, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, D.J.; Casaburi, R.; Flannery, R.; LeRoux-Williams, M.; Tashkin, D.P. A placebo-controlled, randomized trial of mesenchymal stem cells in COPD. Chest 2013, 143, 1590–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stolk, J.; Broekman, W.; Mauad, T.; Zwaginga, J.J.; Roelofs, H.; Fibbe, W.E.; Oostendorp, J.; Bajema, I.; Versteegh, M.I.; Taube, C.; et al. A phase I study for intravenous autologous mesenchymal stromal cell administration to patients with severe emphysema. QJM 2016, 109, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, G.; Huang, L.; Tong, H.; Shu, Q.; Hu, Y.; Ge, M.; Deng, K.; Zhang, L.; Zou, B.; Cheng, B.; et al. Treatment of acute respiratory distress syndrome with allogeneic adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells: A randomized, placebo-controlled pilot study. Respir. Res. 2014, 15, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, J.G.; Liu, K.D.; Zhuo, H.; Caballero, L.; McMillan, M.; Fang, X.; Cosgrove, K.; Vojnik, R.; Calfee, C.S.; Lee, J.W.; et al. Mesenchymal stem (stromal) cells for treatment of ARDS: A phase 1 clinical trial. Lancet. Respir. Med. 2015, 3, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzouvelekis, A.; Paspaliaris, V.; Koliakos, G.; Ntolios, P.; Bouros, E.; Oikonomou, A.; Zissimopoulos, A.; Boussios, N.; Dardzinski, B.; Gritzalis, D.; et al. A prospective, non-randomized, no placebo-controlled, phase Ib clinical trial to study the safety of the adipose derived stromal cells-stromal vascular fraction in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. J. Transl. Med. 2013, 11, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chambers, D.C.; Enever, D.; Ilic, N.; Sparks, L.; Whitelaw, K.; Ayres, J.; Yerkovich, S.T.; Khalil, D.; Atkinson, K.M.; Hopkins, P.M. A phase 1b study of placenta-derived mesenchymal stromal cells in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Respirology 2014, 19, 1013–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Dennis, J.E.; Muzic, R.F.; Lundberg, M.; Caplan, A.I. The dynamic in vivo distribution of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells after infusion. Cells Tissues Organs 2001, 169, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iso, Y.; Spees, J.L.; Serrano, C.; Bakondi, B.; Pochampally, R.; Song, Y.H.; Sobel, B.E.; Delafontaine, P.; Prockop, D.J. Multipotent human stromal cells improve cardiac function after myocardial infarction in mice without long-term engraftment. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 354, 700–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, R.H.; Pulin, A.A.; Seo, M.J.; Kota, D.J.; Ylostalo, J.; Larson, B.L.; Semprun-Prieto, L.; Delafontaine, P.; Prockop, D.J. Intravenous hMSCs improve myocardial infarction in mice because cells embolized in lung are activated to secrete the anti-inflammatory protein TSG-6. Cell Stem Cell 2009, 5, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eggenhofer, E.; Benseler, V.; Kroemer, A.; Popp, F.C.; Geissler, E.K.; Schlitt, H.J.; Dahlke, M.H.; Hoogduijn, M.J. Mesenchymal stem cells are short-lived and do not migrate beyond the lungs after intravenous infusion. Front. Immunol. 2012, 3, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.S.; Lee, H.J.; Doo, S.H.; Lee, S.J.; Lim, I.; Chang, K.T.; Kim, S.U. Mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) inhibit collagen deposit and improve bladder function in rat model of bladder outlet obstruction. Cell Transplant. 2012, 21, 1641–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maguire, G. Stem cell therapy without the cells. Commun. Integr. Biol. 2013, 6, e26631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vizoso, F.J.; Eiro, N.; Cid, S.; Schneider, J.; Perez-Fernandez, R. Mesenchymal Stem Cell Secretome: Toward Cell-Free Therapeutic Strategies in Regenerative Medicine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gazdic, M.; Volarevic, V.; Arsenijevic, N.; Stojkovic, M. Mesenchymal stem cells: A friend or foe in immune-mediated diseases. Stem. Cell Rev. 2015, 11, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gnecchi, M.; He, H.; Noiseux, N.; Liang, O.D.; Zhang, L.; Morello, F.; Mu, H.; Melo, L.G.; Pratt, R.E.; Ingwall, J.S.; et al. Evidence supporting paracrine hypothesis for Akt-modified mesenchymal stem cell-mediated cardiac protection and functional improvement. FASEB J. 2006, 20, 661–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, R.C.; Arslan, F.; Lee, M.M.; Sze, N.S.; Choo, A.; Chen, T.S.; Salto-Tellez, M.; Timmers, L.; Lee, C.N.; El Oakley, R.M.; et al. Exosome secreted by MSC reduces myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. Stem. Cell Res. 2010, 4, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, G.; Chen, Z.; Zheng, M.; Liu, Y. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes as a new therapeutic strategy for liver diseases. Exp. Mol. Med. 2017, 49, e346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos., T.L.; Sanchez-Abarca, L.I.; Muntion, S.; Preciado, S.; Puig, N.; Lopez-Ruano, G.; Hernández-Hernández, Á.; Redondo, A.; Ortega, R.; Rodríguez, C.; et al. MSC surface markers (CD44, CD73 and CD90) can identify human MSC-derived extracellular vesicles by conventional flow cytometry. Cell Commun. Signal. 2016, 14, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.S.; Choi, D.Y.; Yun, S.J.; Choi, S.M.; Kang, J.W.; Jung, J.W.; Hwang, D.; Kim, K.P.; Kim, D.W. Proteomic analysis of microvesicles derived from human mesenchymal stem cells. J. Proteome. Res. 2012, 11, 839–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomasoni, S.; Longaretti, L.; Rota, C.; Morigi, M.; Conti, S.; Gotti, E.; Capelli, C.; Introna, M.; Remuzzi, G.; Benigni, A. Transfer of growth factor receptor mRNA via exosomes unravels the regenerative effect of mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2013, 22, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.S.; Lai, R.C.; Lee, M.M.; Choo, A.B.; Lee, C.N.; Lim, S.K. Mesenchymal stem cell secretes microparticles enriched in pre-microRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, R.C.; Tan, S.S.; The, B.J.; Sze, S.K.; Arslan, F.; de Kleijn, D.P.; Choo, A.; Lim, S.K. Proteolytic Potential of the MSC Exosome Proteome: Implications for an Exosome-Mediated Delivery of Therapeutic Proteasome. Int. J. Proteomics 2012, 2012, 971907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baglio, S.R.; Pegtel, D.M.; Baldini, N. Mesenchymal stem cell secreted vesicles provide novel opportunities in (stem) cell-free therapy. Front. Physiol. 2012, 3, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rani, S.; Ryan, A.E.; Griffin, M.D.; Ritter, T. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-derived Extracellular Vesicles: Toward Cell-free Therapeutic Applications. Mol. Ther. 2015, 23, 812–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phinney, D.G.; Pittenger, M.F. Concise Review: MSC-Derived Exosomes for Cell-Free Therapy. Stem Cells 2017, 35, 851–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bian, S.; Zhang, L.; Duan, L.; Wang, X.; Min, Y.; Yu, H. Extracellular vesicles derived from human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells promote angiogenesis in a rat myocardial infarction model. J. Mol. Med. (Berl.) 2014, 92, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doeppner, T.R.; Herz, J.; Gorgens, A.; Schlechter, J.; Ludwig, A.K.; Radtke, S.; de Miroschedji, K.; Horn, P.A.; Giebel, B.; Hermann, D.M. Extracellular Vesicles Improve Post-Stroke Neuroregeneration and Prevent Postischemic Immunosuppression. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2015, 4, 1131–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reis, L.A.; Borges, F.T.; Simoes, M.J.; Borges, A.A.; Sinigaglia-Coimbra, R.; Schor, N. Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells repaired but did not prevent gentamicin-induced acute kidney injury through paracrine effects in rats. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e44092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, M.; Ban, T.; Rhim, T. Therapeutic use of stem cell transplantation for cell replacement or cytoprotective effect of microvesicle released from mesenchymal stem cell. Mol. Cells 2014, 37, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, M.G.; Tung, L.; Sekar, R.B.; Chang, C.Y.; Cysyk, J.; Dong, P.; Marbán, E.; Abraham, M.R. Proarrhythmic potential of mesenchymal stem cell transplantation revealed in an in vitro coculture model. Circulation 2006, 113, 1832–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breitbach, M.; Bostani, T.; Roell, W.; Xia, Y.; Dewald, O.; Nygren, J.M.; Fries, J.W.; Tiemann, K.; Bohlen, H.; Hescheler, J.; et al. Potential risks of bone marrow cell transplantation into infarcted hearts. Blood 2007, 110, 1362–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellani, G.; Laffey, J.G.; Pham, T.; Fan, E.; Brochard, L.; Esteban, A.; Gattinoni, L.; van Haren, F.; Larsson, A.; McAuley, D.F.; et al. Epidemiology, Patterns of Care and Mortality for Patients With Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome in Intensive Care Units in 50 Countries. JAMA 2016, 315, 788–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.G.; Feng, X.M.; Abbott, J.; Fang, X.H.; Hao, Q.; Monsel, A.; Qu, J.M.; Matthay, M.A.; Lee, J.W. Human mesenchymal stem cell microvesicles for treatment of Escherichia coli endotoxin-induced acute lung injury in mice. Stem Cells 2014, 32, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrison, T.J.; Jackson, M.V.; Cunningham, E.K.; Kissenpfennig, A.; McAuley, D.F.; O’Kane, C.M.; Krasnodembskaya, A.D. Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Modulate Macrophages in Clinically Relevant Lung Injury Models by Extracellular Vesicle Mitochondrial Transfer. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2017, 196, 1275–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monsel, A.; Zhu, Y.G.; Gennai, S.; Hao, Q.; Hu, S.; Rouby, J.J.; Rosenzwajg, M.; Matthay, M.A.; Lee, J.W. Therapeutic Effects of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cell-derived Microvesicles in Severe Pneumonia in Mice. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2015, 192, 324–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glassberg, M.K.; Minkiewicz, J.; Toonkel, R.L.; Simonet, E.S.; Rubio, G.A.; DiFede, D.; Shafazand, S.; Khan, A.; Pujol, M.V.; LaRussa, V.F.; et al. Allogeneic Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Patients With Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis via Intravenous Delivery (AETHER): A Phase I Safety Clinical Trial. Chest 2017, 151, 971–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shentu, T.P.; Huang, T.S.; Cernelc-Kohan, M.; Chan, J.; Wong, S.S.; Espinoza, C.R.; Tan, C.; Gramaglia, I.; van der Heyde, H.; Chien, S.; et al. Thy-1 dependent uptake of mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles blocks myofibroblastic differentiation. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 18052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shentu, T.P.; Wong, S.; Espinoza, C.; Cernelc-Kohan, M.; Hagood, J. Extracellular vesicles isolated from human mesenchymal stem cells promote resolution of pulmonary fibrosis. Faseb J. 2016, 30, 160–162. [Google Scholar]
- Lobb, R.J.; Becker, M.; Wen, S.W.; Wong, C.S.; Wiegmans, A.P.; Leimgruber, A.; Möller, A. Optimized exosome isolation protocol for cell culture supernatant and human plasma. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2015, 4, 27031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phinney, D.G.; Di Giuseppe, M.; Njah, J.; Sala, E.; Shiva, S.; St Croix, C.M.; Watkins, S.C.; Di, Y.P.; Leikauf, G.D.; Kolls, J.; et al. Mesenchymal stem cells use extracellular vesicles to outsource mitophagy and shuttle microRNAs. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bandeira, E.; Oliveira, H.; Silva, J.D.; Menna-Barreto, R.F.S.; Takyia, C.M.; Suk, J.S.; Witwer, K.W.; Paulaitis, M.E.; Hanes, J.; Rocco, P.R.M.; et al. Therapeutic effects of adipose-tissue-derived mesenchymal stromal cells and their extracellular vesicles in experimental silicosis. Respir. Res. 2018, 19, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broekman, W.; Khedoe, P.; Schepers, K.; Roelofs, H.; Stolk, J.; Hiemstra, P.S. Mesenchymal stromal cells: A novel therapy for the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease? Thorax 2018, 73, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.S.; Kim, J.Y.; Cho, R.; Shin, D.M.; Lee, S.W.; Oh, Y.M. Adipose stem cell-derived nanovesicles inhibit emphysema primarily via an FGF2-dependent pathway. Exp. Mol. Med. 2017, 49, e284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holgate, S.T.; Wenzel, S.; Postma, D.S.; Weiss, S.T.; Renz, H.; Sly, P.D. Asthma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers. 2015, 1, 15025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz, F.F.; Borg, Z.D.; Goodwin, M.; Sokocevic, D.; Wagner, D.E.; Coffey, A.; Antunes, M.; Robinson, K.L.; Mitsialis, S.A.; Kourembanas, S.; et al. Systemic Administration of Human Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Extracellular Vesicles Ameliorates Aspergillus Hyphal Extract-Induced Allergic Airway Inflammation in Immunocompetent Mice. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2015, 4, 1302–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Castro, L.L.; Xisto, D.G.; Kitoko, J.Z.; Cruz, F.F.; Olsen, P.C.; Redondo, P.A.G.; Weiss, D.J.; Martins, M.A.; Morales, M.M.; Rocco, P.R.M. Human adipose tissue mesenchymal stromal cells and their extracellular vesicles act differentially on lung mechanics and inflammation in experimental allergic asthma. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2017, 8, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.; Mitsialis, S.A.; Aslam, M.; Vitali, S.H.; Vergadi, E.; Konstantinou, G.; Sdrimas, K.; Fernandez-Gonzalez, A.; Kourembanas, S. Exosomes mediate the cytoprotective action of mesenchymal stromal cells on hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension. Circulation 2012, 126, 2601–2611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.Y.; An, R.; Liu, Z.J.; Wang, J.J.; Chen, S.Z.; Hong, M.M.; Liu, J.H.; Xiao, M.Y.; Chen, Y.F. Therapeutic effects of mesenchymal stem cell-derived microvesicles on pulmonary arterial hypertension in rats. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2014, 35, 1121–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aliotta, J.M.; Pereira, M.; Wen, S.; Dooner, M.S.; Del Tatto, M.; Papa, E.; Goldberg, L.R.; Baird, G.L.; Ventetuolo, C.E.; Quesenberry, P.J.; et al. Exosomes induce and reverse monocrotaline-induced pulmonary hypertension in mice. Cardiovasc. Res. 2016, 110, 319–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Haaften, T.; Byrne, R.; Bonnet, S.; Rochefort, G.Y.; Akabutu, J.; Bouchentouf, M.; Rey-Parra, G.J.; Galipeau, J.; Haromy, A.; Eaton, F.; et al. Airway delivery of mesenchymal stem cells prevents arrested alveolar growth in neonatal lung injury in rats. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2009, 180, 1131–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aslam, M.; Baveja, R.; Liang, O.D.; Fernandez-Gonzalez, A.; Lee, C.; Mitsialis, S.A.; Kourembanas, S. Bone marrow stromal cells attenuate lung injury in a murine model of neonatal chronic lung disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2009, 180, 1122–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willis, G.R.; Fernandez-Gonzalez, A.; Anastas, J.; Vitali, S.H.; Liu, X.; Ericsson, M.; Kwong, A.; Mitsialis, S.A.; Kourembanas, S. Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Exosomes Ameliorate Experimental Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia and Restore Lung Function through Macrophage Immunomodulation. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 197, 104–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaubey, S.; Thueson, S.; Ponnalagu, D.; Alam, M.A.; Gheorghe, C.P.; Aghai, Z.; Singh, H.; Bhandari, V. Early gestational mesenchymal stem cell secretome attenuates experimental bronchopulmonary dysplasia in part via exosome-associated factor TSG-6. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2018, 9, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Dou, H.; Li, X.; Zhao, X.; Li, Y.; Liu, D.; Ji, J.; Liu, F.; Ding, L.; Ni, Y.; et al. Exosomal miR-146a Contributes to the Enhanced Therapeutic Efficacy of Interleukin-1beta-Primed Mesenchymal Stem Cells Against Sepsis. Stem Cells 2017, 35, 1208–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basu, J.; Ludlow, J.W. Exosomes for repair, regeneration and rejuvenation. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2016, 16, 489–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kordelas, L.; Rebmann, V.; Ludwig, A.K.; Radtke, S.; Ruesing, J.; Doeppner, T.R.; Epple, M.; Horn, P.A.; Beelen, D.W.; Giebel, B. MSC-derived exosomes: A novel tool to treat therapy-refractory graft-versus-host disease. Leukemia 2014, 28, 970–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lener, T.; Gimona, M.; Aigner, L.; Borger, V.; Buzas, E.; Camussi, G.; Chaput, N.; Chatterjee, D.; Court, F.A.; Del Portillo, H.A.; et al. Applying extracellular vesicles based therapeutics in clinical trials—An ISEV position paper. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2015, 4, 30087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madrigal, M.; Rao, K.S.; Riordan, N.H. A review of therapeutic effects of mesenchymal stem cell secretions and induction of secretory modification by different culture methods. J. Transl. Med. 2014, 12, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ti, D.; Hao, H.; Tong, C.; Liu, J.; Dong, L.; Zheng, J.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, H.; Fu, X.; Han, W. LPS-preconditioned mesenchymal stromal cells modify macrophage polarization for resolution of chronic inflammation via exosome-shuttled let-7b. J. Transl. Med. 2015, 13, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lotvall, J.; Hill, A.F.; Hochberg, F.; Buzas, E.I.; Di Vizio, D.; Gardiner, C.; Gho, Y.S.; Kurochkin, I.V.; Mathivanan, S.; Quesenberry, P.; et al. Minimal experimental requirements for definition of extracellular vesicles and their functions: A position statement from the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2014, 3, 26913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koritzinsky, E.H.; Street, J.M.; Star, R.A.; Yuen, P.S. Quantification of Exosomes. J. Cell Physiol. 2017, 232, 1587–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navabi, H.; Croston, D.; Hobot, J.; Clayton, A.; Zitvogel, L.; Jasani, B.; Bailey-Wood, R.; Wilson, K.; Tabi, Z.; Mason, M.D.; et al. Preparation of human ovarian cancer ascites-derived exosomes for a clinical trial. Blood Cells Mol. Dis. 2005, 35, 149–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pachler, K.; Lener, T.; Streif, D.; Dunai, Z.A.; Desgeorges, A.; Feichtner, M.; Öller, M.; Schallmoser, K.; Rohde, E.; Gimona, M. A Good Manufacturing Practice-grade standard protocol for exclusively human mesenchymal stromal cell-derived extracellular vesicles. Cytotherapy 2017, 19, 458–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, D.C.; Bayik, D.; Srivatsan, A.; Bergamaschi, C.; Valentin, A.; Niu, G.; Bear, J.; Monninger, M.; Sun, M.; Morales-Kastresana, A.; et al. Efficient production and enhanced tumor delivery of engineered extracellular vesicles. Biomaterials 2016, 105, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorincz, A.M.; Timar, C.I.; Marosvari, K.A.; Veres, D.S.; Otrokocsi, L.; Kittel, A.; Ligeti, E. Effect of storage on physical and functional properties of extracellular vesicles derived from neutrophilic granulocytes. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2014, 3, 25465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, C.P.; Mardini, O.; Ericsson, M.; Prabhakar, S.; Maguire, C.; Chen, J.W.; Tannous, B.A.; Breakefield, X.O. Dynamic biodistribution of extracellular vesicles in vivo using a multimodal imaging reporter. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 483–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujita, Y.; Takeshita, F.; Kuwano, K.; Ochiya, T. RNAi Therapeutic Platforms for Lung Diseases. Pharmaceuticals 2013, 6, 223–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
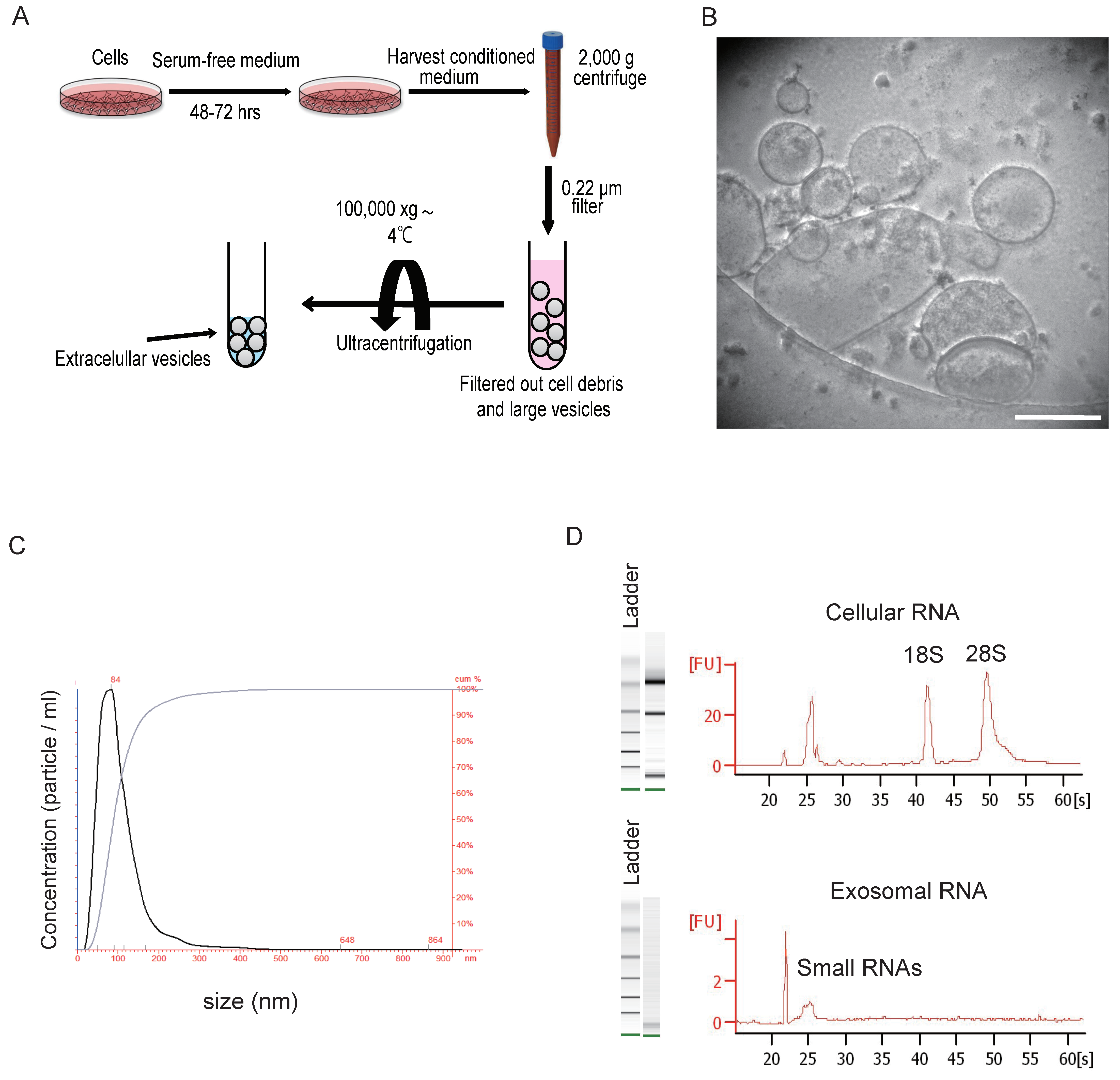
| Experimental Model | EV Source | EV Delivery | Mechanisms/Target Cells | EV Dose | EV Isolation | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ARDS (E. coli endotoxin) | Human BM-MSCs | IT/IV | KGF-expressing EV transfer | EVs released by 3 × 106 MSCs over 48 h | UCF | [76] |
| ARDS (E. coli endotoxin) | Human BM-MSCs | ex vivo | EV-mediated mitochondrial transfer | EVs released by 15 × 106 MSCs over 48 h | UCF | [77] |
| ARDS (caecal ligation and puncture) | Human UC-MSCs | IV | Exosomal miR-146a transfer to macrophages | 30 μg protein | UCF | [97] |
| Pneumonia/ALI (E. coli pneumonia) | Human BM-MSCs | IT/IV | KGF-expressing EV transfer | IT; 3–6 × 106 MSCs over 48 h/IV; 9 × 106 MSCs over 48 h | UCF | [78] |
| IPF (bleomycin) | Human BM-MSCs | IV | Thy-1-expressing EV transfer to fibroblasts | 50 μg protein | UCF | [81] |
| Silicosis | Human BM-MSCs | IV | not reported | 10 μg protein | ExoQuick | [72] |
| Silicosis | Mouse or human BM-MSCs | IV | EVs to outsource mitophagy and shuttle miRNAs | 40 μg protein (−3 × 1011 EVs) | UCF | [83] |
| Silicosis | Mouse AD-MSCs | IT | not reported | EVs released by 1 × 106 MSCs over 24 h | UCF | [84] |
| COPD (elastase) | Human AD-MSCs | IT | EV transfer to epithelium (FGF2 signaling) | EVs released by 1 × 105 MSCs | UCF | [86] |
| Asthma (Aspergillus extract hyphae) | Mouse or human BM-MSCs | IV | not reported | EVs released by 3 × 106 MSCs | UCF | [88] |
| Asthma (ovalbumin) | Human AD-MSCs | IV | not reported | 37 μg protein | UCF | [89] |
| PAH (hypoxia) | Mouse BM-MSCs human UC-MSCs | IV | EV transfer to endothelial cells suppress STAT3 signaling | 10 μg protein | UCF | [90] |
| Rat PAH (monocrotaline) | Rat BM-MSCs | IV | not reported | 30 μg protein | UCF | [91] |
| PAH | Mouse or human BM-MSCs | IV | EV miRNA transfer | 25 μg protein | UCF | [92] |
| BPD (hyperoxia) | Human UC- or BM-MSCs | IV | EVs modulate the macrophage phenotype | 0.9–3 μg protein | UCF (OptiPrep) | [95] |
| BPD (hyperoxia) | Human UC-MSCs | IP | TSG-6-expressing EV transfer | 2.4–2.8 μg protein | UCF | [96] |
| Disease (Number) | Clinical Trial Phase | EV Source | EV Delivery | EV Dose | EV Isolation | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type 1 diabetes (n = 20) | Clinical trial Phase 1, open label | UC-MSCs (allogeneic) | IV | EVs released from (1.22–1.51) × 106 cells/kg, day0 and day7 | not reported | NCT02138331 |
| Macular holes (n = 44) | Clinical trial early Phase 1 | UC-MSCs | dripped into vitreous cavity | 50 or 20 μg/10 μL PBS | UCF | NCT03437759 |
| Acute ischemic stroke (n = 5) | Clinical trial Phase 1,2, open label | MSCs (allogeneic) | stereotaxic injection | 200 μg protein, one month after attack | not reported | NCT03384433 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fujita, Y.; Kadota, T.; Araya, J.; Ochiya, T.; Kuwano, K. Clinical Application of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicle-Based Therapeutics for Inflammatory Lung Diseases. J. Clin. Med. 2018, 7, 355. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm7100355
Fujita Y, Kadota T, Araya J, Ochiya T, Kuwano K. Clinical Application of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicle-Based Therapeutics for Inflammatory Lung Diseases. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2018; 7(10):355. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm7100355
Chicago/Turabian StyleFujita, Yu, Tsukasa Kadota, Jun Araya, Takahiro Ochiya, and Kazuyoshi Kuwano. 2018. "Clinical Application of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicle-Based Therapeutics for Inflammatory Lung Diseases" Journal of Clinical Medicine 7, no. 10: 355. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm7100355
APA StyleFujita, Y., Kadota, T., Araya, J., Ochiya, T., & Kuwano, K. (2018). Clinical Application of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicle-Based Therapeutics for Inflammatory Lung Diseases. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 7(10), 355. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm7100355






