Modern Biomarkers in IgA Nephropathy and Their Potential in Paediatric Research
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Pathogenesis and Biomarkers
3. Gd-IgA1
4. Anti Gd-IgA1
5. IgA/C3
6. Complement C4
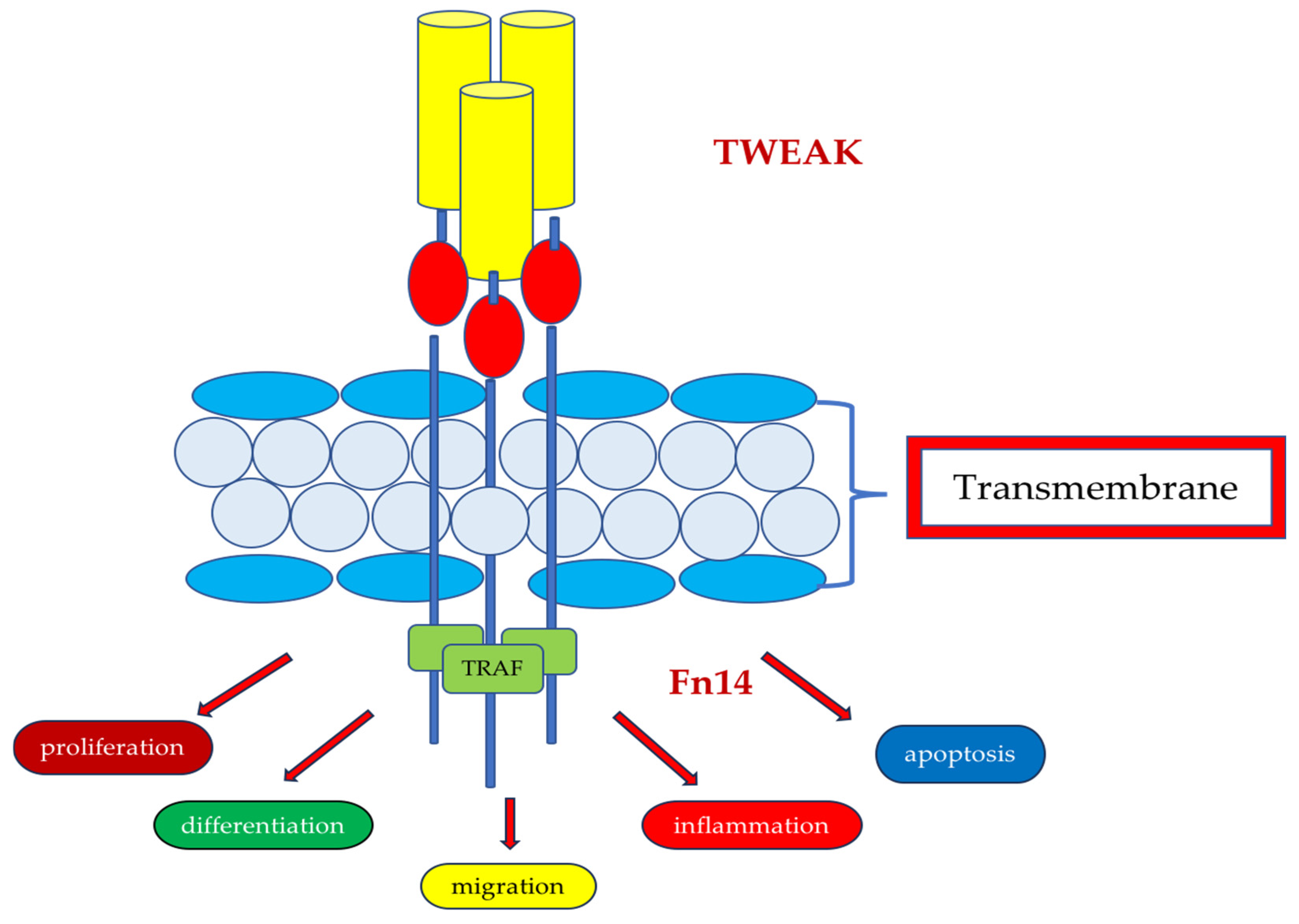
7. TWEAK
8. APRIL
9. CD147
10. Angiostatin
11. Phosphatidylethanolamine Binding Protein-4 (PEBP4)
12. Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Berger, J.; Hinglais, N. Intercapillary deposits of IgA-IgG. J. D’urologie Nephrol. 1968, 74, 694. [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues, J.C.; Haas, M.; Reich, H.N. IgA Nephropathy. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 12, 677–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Amico, G.; Imbasciati, E.; Barbiano Di Belgioioso, G.; Bertoli, S.; Fogazzi, G.; Ferrario, F.; Fellin, G.; Ragni, A.; Colasanti, G.; Minetti, L.; et al. Idiopathic IgA mesangial nephropathy. Clinical and histological study of 374 patients. Medicine 1985, 64, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizik, D.V.; Maillard, N.; Julian, B.A.; Knoppova, B.; Green, T.J.; Novak, J.; Wyatt, R.J. The Emerging Role of Complement Proteins as a Target for Therapy of IgA Nephropathy. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Zhang, H. The Genetics of IgA Nephropathy: An Overview from China. Kidney Dis. 2015, 1, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willey, C.J.; Coppo, R.; Schaefer, F.; Mizerska-Wasiak, M.; Mathur, M.; Schultz, M.J. The incidence and prevalence of IgA nephropathy in Europe. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2023, 10, 2340–2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppo, R. Clinical and histological risk factors for progression of IgA nephropathy: An update in children, young and adult patients. J. Nephrol. 2017, 30, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamei, K.; Harada, R.; Hamada, R.; Sakai, T.; Hamasaki, Y.; Hataya, H.; Ito, S.; Ishikura, K.; Honda, M. Proteinuria during follow-up period and long-term renal survival of childhood IgA nephropathy. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0150885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schena, F.P.; Rossini, M.; Abbrescia, D.I.; Zaza, G. The molecular mechanisms of inflammation and scarring in the kidneys of immunoglobulin A nephropathy. Semin. Immunopathol. 2021, 43, 691–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trimarchi, H.; Barratt, J.; Cattran, D.C. Oxford Classification of IgA nephropathy 2016:an update from the IgA Nephropathy Classification Working Group. Kidney Int. 2017, 91, 1014–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glassock, R.J. The phatogenesis of igA nephropathy. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2011, 20, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, K.N. Pathogenesis of IgA nephropathy. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2012, 20, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gharavi, A.G.; Moldoveanu, Z.; Wyatt, R.J.; Barker, C.V.; Woodford, S.Y.; Lifton, R.P.; Mestecky, J.; Novak, J.; Julian, B.A. Aberrant IgA1 glycosylation is inherited in familial and sporadic IgA nephropathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2008, 19, 1008–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gale, D.P.; Molyneux, K.; Wimbury, D.; Higgins, P.; Levine, A.P.; Caplin, B.; Ferlin, A.; Yin, P.; Nelson, C.P.; Stanescu, H.; et al. Galactosylation of IgA1 is associated with common variation in C1GALT1. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 28, 2158–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moura, I.C.; Arcos-Fajardo, M.; Sadaka, C.; Leroy, V.; Benhamou, M.; Novak, J.; Vrtovsnik, F.; Haddaad, E.; Chinatalacharuvu, K.R.; Monteiro, R.C. Glycosylation and size of IgA1 are essential for interaction with mesangial transferrin receptor in IgA nephropathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2004, 15, 622–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maillard, N.; Wyatt, R.J.; Julian, B.A.; Kiryluk, K.; Gharavi, A.; Fermeaux-Bacchi, V.; Novak, J. Current understanding of the role of complement in IgA nephropathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 26, 1503–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daha, M.R.; van Kotten, C. Role of complement in IgA nephropathy. J. Nephrol. 2016, 29, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, H.; Fan, R.; Zhang, Z.; Brown, R.; Hall, S.; Julian, B.A.; Winn Chatham, W.; Suzuki, Y.; Wyatt, R.J.; Molodoveanu, Z.; et al. Aberrantly glycosylated IgA1 in IgA nephropathy patients is recognized by IgG antibodies with restricted heterogeneity. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 1668–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, Y.; Matsuzaki, K.; Suzuki, H.; Okazaki, K.; Yanagawa, H.; Ieiri, N.; Sato, M.; Sato, T.; Taguma, J.; Matusoka, J.; et al. Serum levels of galactose-deficient immunoglobulin (Ig) A1 and related immune complex are associated with disease activity of IgA nephropathy. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2014, 18, 770–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiryluk, K.; Moldoveanu, Z.; Sanders, J.T.; Eison, T.M.; Suzuki, H.; Julian, B.A.; Novak, J.; Gharavu, A.G.; Wyatt, R.J. Aberrant glycosylation of IgA1 is inherited in both pediatric IgA nephropathy and Henoch-Schönlein purpura nephritis. Kidney Int. 2011, 80, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizerska-Wasiak, M.; Gajewski, Ł.; Cichoń-Kawa, K.; Małdyk, J.; Dziedzic-Jankowska, K.; Leszczyńska, B.; Rybi-Szumińska, A.; Wasilewska, A.; Pukajło-Marczyk, A.; Zwolińska, D.; et al. Serum GDIgA1 levels in children with IgA nephropathy and Henoch-Schonlein nephritis. Cent. Eur. J. Immunol. 2018, 43, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Placzek, W.J.; Yanagawa, H.; Makita, Y.; Renfrow, M.B.; Julian, B.A.; Rizik, D.V.; Suzuki, Y.; Novak, J.; Suzuki, H. Deficient-IgA1 and IgG autoantibodies correlate in patients with IgA nephropathy. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0190967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berthoux, F.; Suzuki, H.; Thibaudin, L.; Yanagawa, H.; Maillard, N.; Mariat, C.; Tomino, Y.; Julian, B.A.; Novak, J. Autoantibodies targeting galactose-deficient IgA1 associate with progression of IgA nephropathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2012, 23, 1579–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellur, S.S.; Troyanov, S.; Cook, H.T.; Roberts, I.S.D. Immunostaining findings in IgA nephropathy: Correlation with histology and clinical outcome in the Oxford classification patient cohort. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2011, 26, 2533–2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, C.; Tang, Y.; Peng, H.; Ye, Z.C.; Li, C.C.; Lou, T.Q. Serum immunoglobulin A/C3 ratio predicts progression of immunoglobulin A nephropathy. Nephrology 2013, 18, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komatsu, H.; Fujimoto, S.; Hara, S.; Sato, Y.; Yamada, K.; Eto, T. Relationship between serum IgA/C3 ratio and progression of IgA nephropathy. Intern. Med. 2004, 43, 1023–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, W.Y.; Liu, M.; Lou, D.; Liu, F.N.; Yin, L.H.; Li, Y.Q.; Zhang, J.; Peng, H. High serum IgA/C3 ratio better predicts a diagnosis of IgA nephropathy among primary glomerular nephropathy patients with proteinuria ≤ 1 g/d: An observational cross-sectional study. BMC Nephrol. 2019, 20, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizerska-Wasiak, M.; Małdyk, J.; Turczyn, A.; Cichoń-Kawa, K.; Rybi-Szumińska, A.; Wasilewska, A.; Bieniaś, B.; Zajączkowska, M.; Miklaszewska, M.; Pietrzyk, J.; et al. Predictors of Progression in IgA Nephropathy in Childhood. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2017, 955, 65–73. [Google Scholar]
- Mizerska-Wasiak, M.; Małdyk, J.; Rybi-Szumińska, A.; Wasilewska, A.; Miklaszewska, M.; Pietrzyk, J.; Firszt-Adamczyk, A.; Stankiewicz, R.; Bieniaś, B.; Zajączkowska, M.; et al. Relationship between serum IgA/C3 ratio and severity of histological lesions using the Oxford classification in children with IgA nephropathy. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2015, 30, 1113–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, T.D.; Zheng, J.N.; Zhang, J.X.; Yang, L.S.; Liu, N.; Yao, L.; Liu, L.L. Serum complement C4 is an important prognosticc factor for IgA nephropathy: A retrospective study. BMC Nephrol. 2019, 20, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Tang, X.; Yang, Y.; Li, X.; Li, L.; Huang, K.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Fu, P. Glomerular C4 deposition and glomerulosclerosis predict worse renal outcomes in Chinese patients with IgA nephropathy. Ren. Fail. 2020, 42, 629–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winkles, J.A. The TWEAK-Fn14 cytokine-receptor axis: Discovery, biology and therapeutic targeting. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2008, 7, 411–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanz, A.B.; Sanchez-Nino, M.D.; Ortiz, A. TWEAK, a multifunctional cytokine in kidney injury. Kidney Int. 2011, 80, 708–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.S.; Jeong, K.H. Clinical significance of urinary tumor necrosis factor-like weak inducer of apoptosis (TWEAK) in immunoglobulin A nephropathy. Clin. Nephrol. 2020, 93, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, N.; Rubinstein, T.; Burkly, L.C.; Collins, C.E.; Blanco, I.; Su, L.; Hojaili, B.; Mackay, M.; Aranow, C.; Stohl, W.; et al. Urinary TWEAK as a biomarker of lupus nephritis: A multicenter cohort study. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2009, 11, R143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, Y.; Shimizu, Y.; Suzuki, Y.; Horikoshi, S.; Tomino, Y. TWEAK/Fn14 system and crescent formation in IgA nephropathy. BMC Nephrol. 2015, 16, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, P.; MacKay, F.; Steiner, V.; Hoffman, K.; Bodmer, J.L.; Holler, N.; Ambrose, C.; Lawton, P.; Bixler, S.; Acha-Orbea, H.; et al. BAFF, a novel ligand of the tumor necrosis factor family, stimulates B cell growth. J. Exp. Med. 1999, 189, 1747–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiryluk, K.; Li, Y.; Scolari, F.; Sanna-Cherchi, S.; Choi, M.; Verbitsky, M.; Fasel, D.; Lata, S.; Prakash, S.; Shapiro, S.; et al. Discovery of new risk loci for IgA nephropathy implicates genes involved in immunity against intestinal pathogens. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 1187–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makita, Y.; Suzuki, H.; Kano, T.; Takahata, A.; Julian, B.A.; Novak, J.; Suzuki, Y. TLR9 activation induces aberrant IgA glycosylation via APRIL- and IL-6-mediated pathways in IgA nephropathy. Kidney Int. 2020, 97, 340–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.G.; Alvarez, M.; Suzuki, H.; Hirose, S.; Izui, S.; Tomino, Y.; Huard, B.; Suzuki, Y. Pathogenic Role of a Proliferation-Inducing Ligand (APRIL) in Murine IgA Nephropathy. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0137044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myette, J.R.; Kano, T.; Suzuki, H.; Sloan, S.E.; Szretter, K.J.; Ramakrishan, B.; Adari, H.; Deotale, K.D.; Engler, F.; Shriver, Z.; et al. A Proliferation Inducing Ligand (APRIL) targeted antibody is a safe and effective treatment of murine IgA nephropathy. Kidney Int. 2019, 96, 104–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muramatsu, T.; Miyauchi, T. Basigin (CD147): A multifunctional transmembrane protein involved in reproduction, neural function, inflammation and tumor invasion. Histol. Histopathol. 2003, 18, 981–987. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kosugi, T.; Maeda, K.; Sato, W.; Maruyama, S.; Kadomatsu, K. CD147 (EMMPRIN/Basigin) in kidney diseases: From an inflammation and immune system viewpoint. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2015, 30, 1097–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeda-Hori, M.; Kosugi, T.; Kojima, H.; Sato, W.; Inaba, S.; Maeda, K.; Nagaya, H.; Sato, Y.; Ishimoto, T.; Ozaki, T.; et al. Plasma CD147 reflects histological features in patients with lupus nephritis. Lupus 2014, 23, 342–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, Y.; Masuda, T.; Kosugi, T.; Yoshioka, T.; Hori, M.; Nagaya, H.; Maeda, K.; Sato, Y.; Kojima, H.; Kato, N.; et al. The clinical relevance of plasma CD147/basigin in biopsy-proven kidney diseases. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2018, 22, 815–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaya, H.; Kosugi, T.; Maeda-Hori, M.; Maeda, K.; Sato, Y.; Kojima, H.; Hayashi, H.; Kato, N.; Ishimoto, T.; Sato, W.; et al. CD147/basigin reflects renal dysfunction in patients with acute kidney injury. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2014, 18, 746–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Reilly, M.S.; Holmgren, L.; Shing, Y.; Chen, C.; Roshental, R.A.; Moses, M.; Lane, W.S.; Cao, Y.; Sage, E.H.; Folkman, J. Angiostatin: A novel angiogenesis inhibitor that mediates the suppression of metastases by a Lewis lung carcinoma. Cell 1994, 79, 315–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.X.; Wang, J.J.; Lu, K.; Mott, R.; Longeras, R.; Ma, J.X. Therapeutic potential of angiostatin in diabetic nephropathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2006, 17, 475–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aulakh, G.K.; Balachandran, Y.; Liu, L.; Singh, B. Angiostatin inhibits activation and migration of neutrophils. Cell Tissue Res. 2014, 355, 375–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Nangaku, M. Angiogenesis and hypoxia in the kidney. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2013, 9, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satoh, M.; Kidokoro, K.; Ozeki, M.; Nagasu, H.; Nishi, Y.; Ihoriya, C.; Fujimoto, S.; Sasaki, T.; Kashihara, N. Angiostatin production increases in response to decreased nitric oxide in aging rat kidney. Lab. Investig. 2013, 93, 334–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, T.; Du, Y.; Han, J.; Singh, S.; Xie, C.; Guo, Y.; Zhou, X.J.; Ahn, C.; Saxena, R.; Mohan, C. Urinary angiostatin—A novel putative marker of renal pathology chronicity in lupus nephritis. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2013, 12, 1170–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mok, C.C.; Soliman, S.; Ho, L.Y.; Mohamed, F.A.; Mohamed, F.I.; Mohan, C. Urinary angiostatin, CXCL4 and VCAM-1 as biomarkers of lupus nephritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2018, 20, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Y.; Bu, R.; Cai, G.Y.; Zhan, X.G.; Duan, S.W.; Wu, J.; Wu, D.; Chen, X.M. Urinary angiostatin: A novel biomarker of kidney disease associated with disease severity and progression. BMC Nephrol. 2019, 20, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.K.; Chen, Q.F.; Qu, X.; Zhou, H.Y. The roles and signaling pathways of phosphatidylethanolamine-binding protein 4 in tumors. OncoTargets Ther. 2019, 12, 7685–7690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, P.; Zhou, C.; Shen, H. Diagnostic value of phosphatidylethanolamine binding protein 4 levels in patients receiving nursing interventions for advanced chronic kidney disease. J. Int. Med. Res. 2021, 49, 300060521996179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, S.; Pieri, K.; Nanni, P.; Tica, J.; Barratt, J.; Didangelos, A. Phopspatidylethanolaminine binding protein-4 (PEBP4) is increased in IgA nephropathy and is associated with IgA-positive B-cells in affected kidneys. J. Autoimmun. 2019, 105, 102309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Biomarker | Serum/Plasma | Urine | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| GdIgA1 | IgAN > healthy control | [25] | |
| IgAN > other kidney diseases | [20] | ||
| In IgAN associated with a risk of disease activity | [19] | ||
| Potential marker of IgAN progression in children | [21] | ||
| Anti-GdIgA1 | IgAN > healthy control | [22,23] | |
| IgAN > other kidney diseases | [22,23] | ||
| In IgAN related to severity of proteinuria | [18] | ||
| IgA/C3 | IgAN > other kidney diseases | [27] | |
| Unrelated to proteinuria and GFR | [27,28] | ||
| C4 complement | In IgAN related to severity of proteinuria and GFR | [30] | |
| Glomerular C4 deposition—risk factor for poor prognosis in IgAN | [31] | ||
| TWEAK | IgAN and other renal diseases > healthy control | [34,36] | |
| In SLE related to disease activity | [35] | ||
| In IgAN related to severity of proteinuria | [34,36] | ||
| APRIL | Administrated APRIL antibody related to lower GdIgA1 in mice | [40,41] | |
| CD147 | In IgAN and other inflammation-related renal diseases related to GFR | [45] | |
| Increased in ATN | Increased in ATN | [46] | |
| Angiostatin | In IgAN and SLE related to severity of proteinuria | [53,55] | |
| In SLE > healthy control? | [53] | ||
| Potential marker of chronic phase of inflammation in IgAN | [55] | ||
| PEBP4 | Elevated level in patients with CKD | [56] | |
| In IgAN related to GFR | [57] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Such-Gruchot, A.; Mizerska-Wasiak, M.; Płatos, E.; Pańczyk-Tomaszewska, M. Modern Biomarkers in IgA Nephropathy and Their Potential in Paediatric Research. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 3263. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14093263
Such-Gruchot A, Mizerska-Wasiak M, Płatos E, Pańczyk-Tomaszewska M. Modern Biomarkers in IgA Nephropathy and Their Potential in Paediatric Research. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(9):3263. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14093263
Chicago/Turabian StyleSuch-Gruchot, Agnieszka, Małgorzata Mizerska-Wasiak, Emilia Płatos, and Małgorzata Pańczyk-Tomaszewska. 2025. "Modern Biomarkers in IgA Nephropathy and Their Potential in Paediatric Research" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 9: 3263. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14093263
APA StyleSuch-Gruchot, A., Mizerska-Wasiak, M., Płatos, E., & Pańczyk-Tomaszewska, M. (2025). Modern Biomarkers in IgA Nephropathy and Their Potential in Paediatric Research. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(9), 3263. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14093263





