Comparative Efficacy and Precision of Robot-Assisted vs. Conventional Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design and Literature Search
2.2. Selection Strategy
- Population: patients with knee osteoarthritis.
- Intervention: RA-TKA
- Comparison: C-TKA.
- Outcome: efficacy (clinical and radiographic) and safety endpoints. A full list is provided below.
- Study Design: only randomized controlled trials (RCTs).
- Non-original research.
- Abstract-only publications.
- Non-randomized studies.
- Duplicated records or studies with overlapping datasets.
- Non-comparative studies or comparisons with non-TKA modalities.
2.3. Data Collection and Outcomes
2.4. Risk of Bias Assessment
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
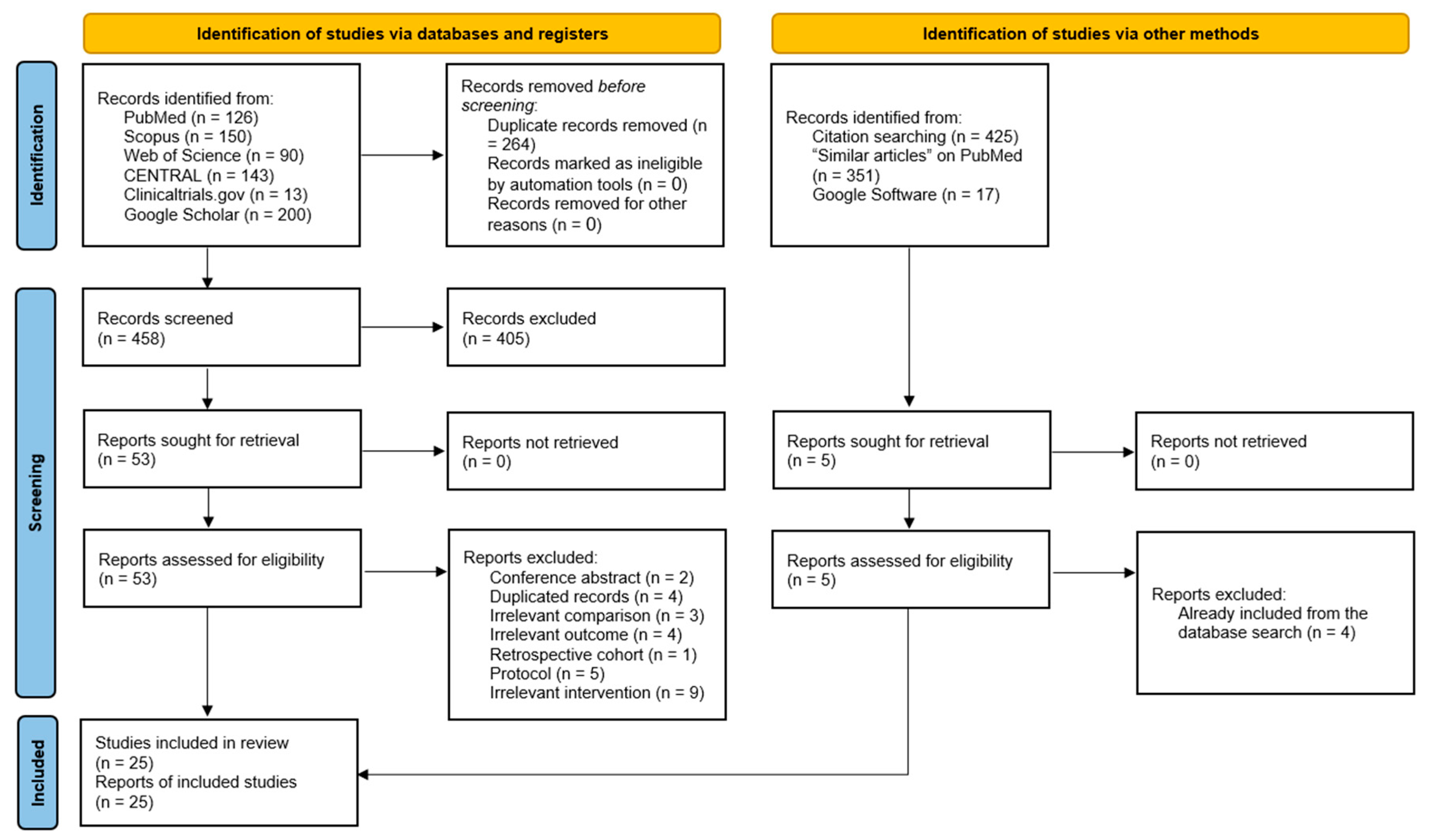
3.1. Literature Search Results
3.2. Baseline Characteristics of the Included Studies
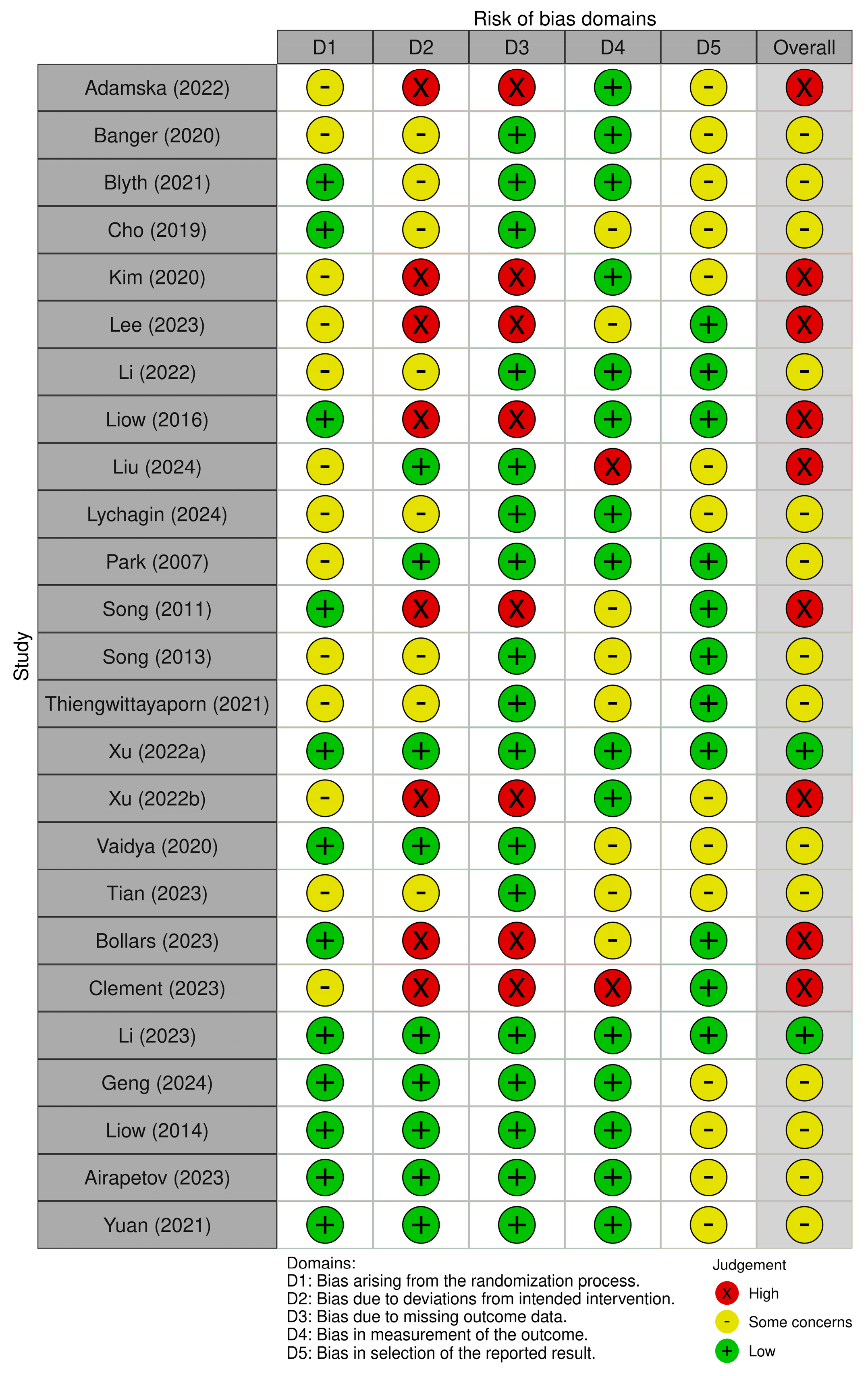
3.3. Risk of Bias Summary
3.4. Clinical Outcomes
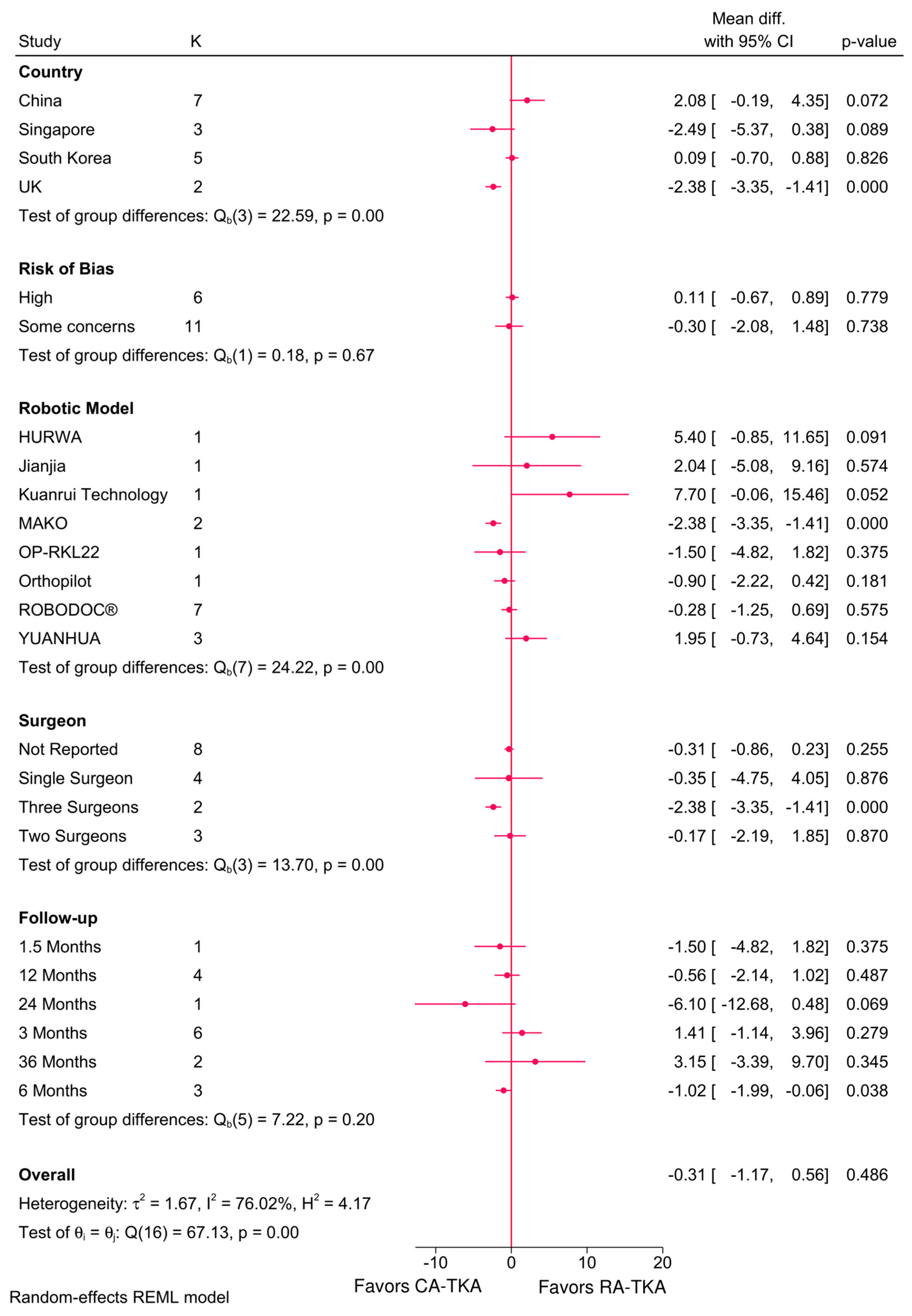
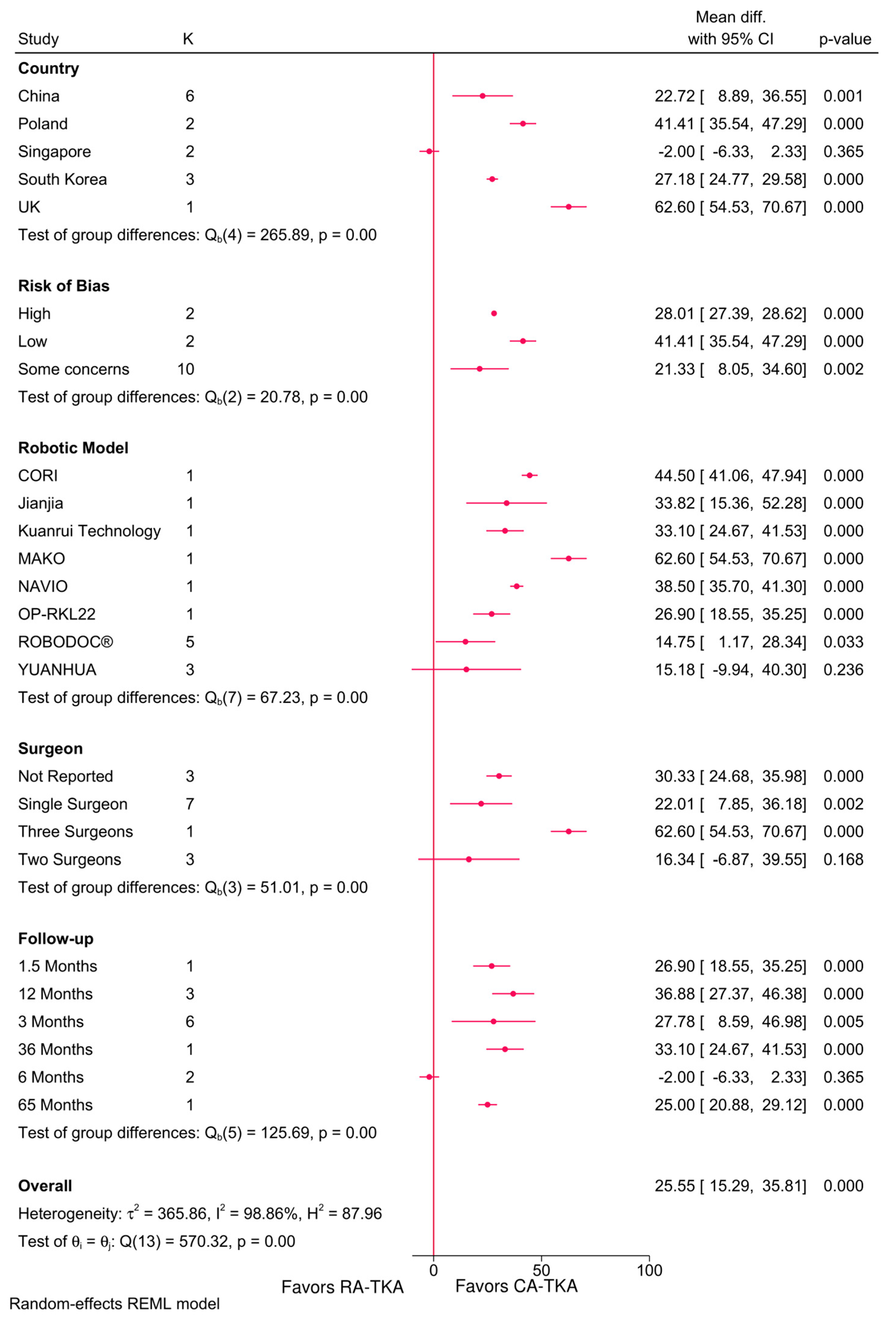
3.4.1. KSS Total and Functional Score
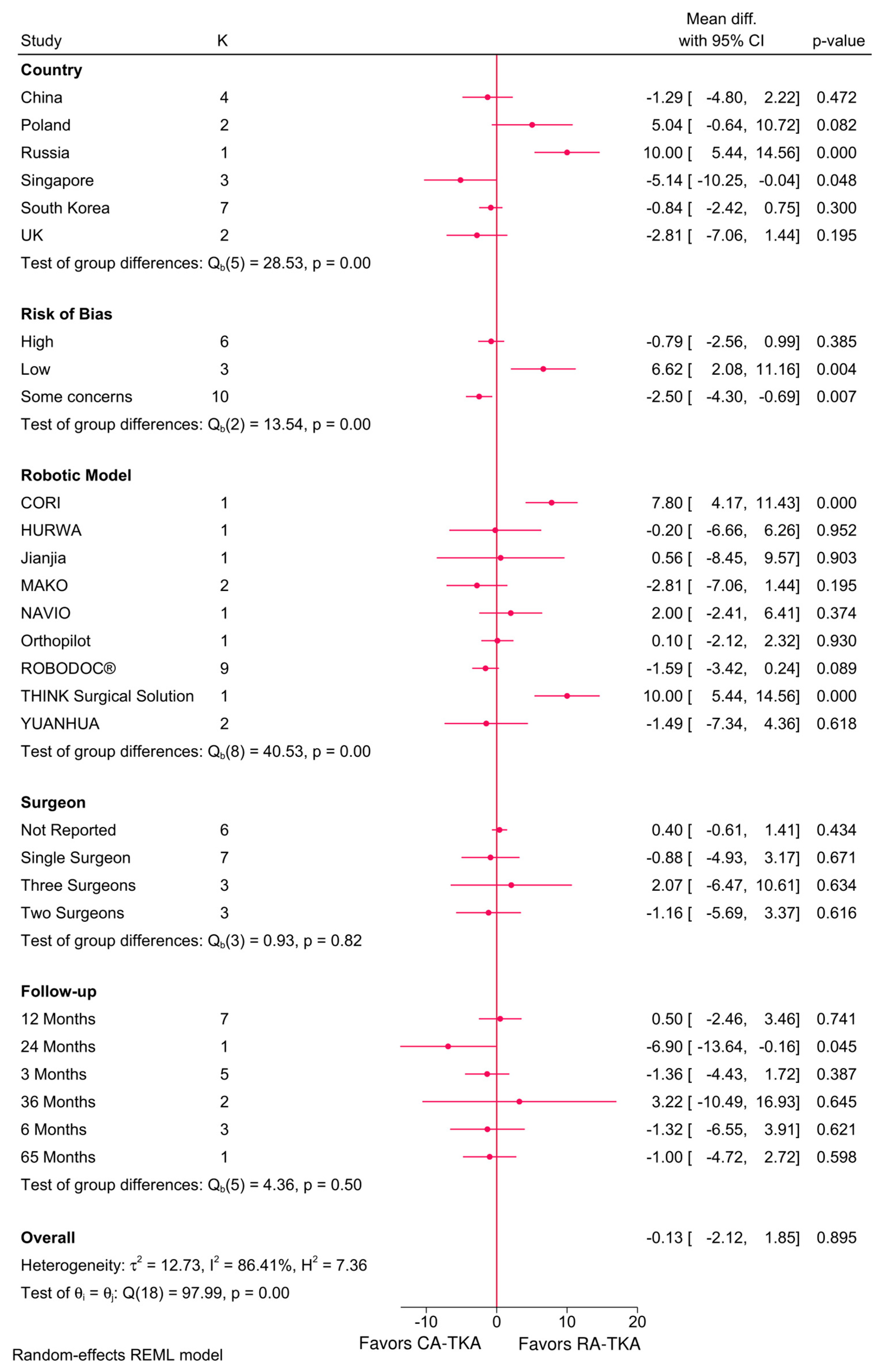
3.4.2. OKS Score
3.4.3. Pain Score
3.4.4. ROM—Flexion and Extension
3.4.5. HSS and WOMAC Scores
3.4.6. Operative Time
3.4.7. Intraoperative Blood Loss
3.4.8. Satisfaction Rate
3.4.9. Complication Rate
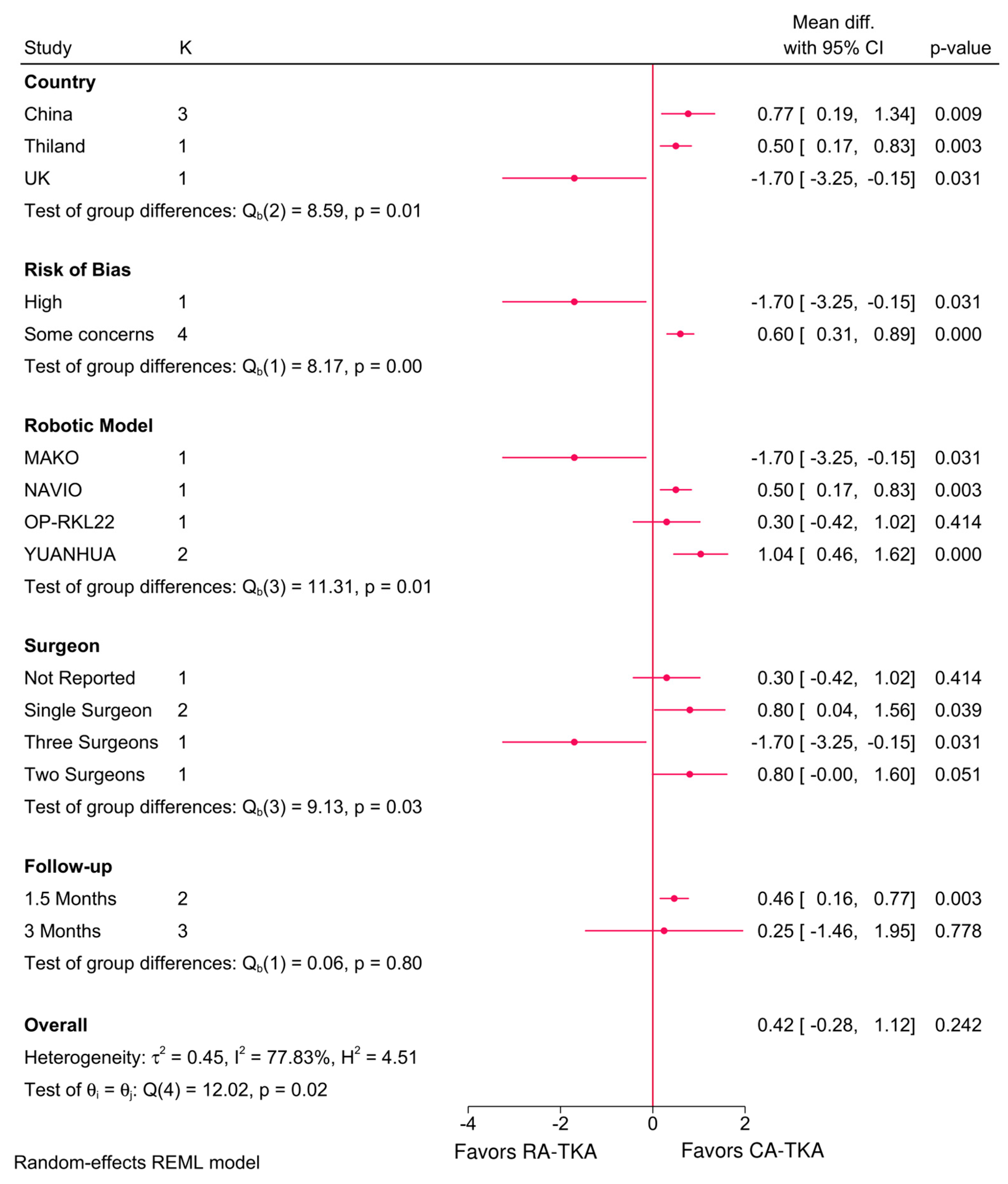
3.5. Radiographic Outcomes
4. Discussion
4.1. Clinical Outcomes
4.2. Radiographic Outcomes
4.3. Safety and Complications
4.4. Comparison with Other Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses
4.5. Limitations and Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AMSTAR | Assessing the Methodological Quality of Systematic Reviews |
| C-TKA | Conventional Total Knee Arthroplasty |
| CI | Confidence Interval |
| FCIA | Femoral Coronal Inclination Angle |
| FSIA | Femoral Sagittal Inclination Angle |
| HKA | Hip–Knee–Ankle |
| HSS | Hospital for Special Surgery |
| KSS | Knee Society Score |
| MD | Mean Difference |
| NAVIO | Name of a robotic system used in TKA |
| OKS | Oxford Knee Score |
| OR | Odds Ratio |
| PRISMA | Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses |
| RA-TKA | Robot-Assisted Total Knee Arthroplasty |
| RCT | Randomized Controlled Trial |
| REM | Restricted Maximum Likelihood |
| ROB-2 | Revised Cochrane Risk of Bias Tool |
| ROM | Range of Motion |
| TCIA | Tibial Coronal Inclination Angle |
| TSIA | Tibial Sagittal Inclination Angle |
| TFA | Transverse Femoral Angle |
| TKA | Total Knee Arthroplasty |
| VAS | Visual Analogue Scale |
| YUANHUA | Name of a robotic system used in TKA |
References
- Kane, R.L.; Saleh, K.J.; Wilt, T.J.; Bershadsky, B. The functional outcomes of total knee arthroplasty. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2005, 87, 1719–1724. [Google Scholar]
- Steinhaus, M.E.; Christ, A.B.; Cross, M.B. Total knee arthroplasty for knee osteoarthritis: Support for a foregone conclusion? HSS J. 2017, 13, 207–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, J.A.; Yu, S.; Chen, L.; Cleveland, J.D. Rates of total joint replacement in the United States: Future projections to 2020–2040 using the national inpatient sample. J. Rheumatol. 2019, 46, 1134–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oussedik, S.; Abdel, M.P.; Victor, J.; Pagnano, M.W.; Haddad, F.S. Alignment in total knee arthroplasty: What’s in a name? Bone Jt. journal 2020, 102, 276–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, F.M.; Insall, J.N.; Scuderi, G.R. Accuracy of soft tissue balancing in total knee arthroplasty. J. Arthroplast. 2000, 15, 970–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howell, S.M.; Shelton, T.J.; Hull, M.L. Implant survival and function ten years after kinematically aligned total knee arthroplasty. J. Arthroplast. 2018, 33, 3678–3684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadi, M.; Barlow, T.; Ahmed, I.; Dunbar, M.; McCulloch, P.; Griffin, D. Does malalignment affect revision rate in total knee replacements: A systematic review of the literature. Springerplus 2015, 4, 835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellemans, J.; Vandenneucker, H.; Vanlauwe, J. Robot-assisted total knee arthroplasty. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2007, 464, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermue, H.; Tack, P.; Gryson, T.; Victor, J. Can robot-assisted total knee arthroplasty be a cost-effective procedure? A Markov decision analysis. Knee 2021, 29, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancino, F.; Cacciola, G.; Malahias, M.-A.; De Filippis, R.; De Marco, D.; Di Matteo, V.; Gu, A.; Sculco, P.K.; Maccauro, G.; De Martino, I. What are the benefits of robotic-assisted total knee arthroplasty over conventional manual total knee arthroplasty? A systematic review of comparative studies. Orthop. Rev. 2020, 12, 8657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, J.-I.; Oh, M.-K.; Lee, S.-U.; Lee, C.H. Robot-assisted rehabilitation for total knee or hip replacement surgery patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine 2022, 101, e30852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mellema, P.; Deutmeyer, B.; Wasielewski, P. Non-arteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy secondary to tadalafil use. Spartan Med. Res. J. 2024, 9, 122862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leelasestaporn, C.; Tarnpichprasert, T.; Arirachakaran, A.; Kongtharvonskul, J. Comparison of 1-year outcomes between MAKO versus NAVIO robot-assisted medial UKA: Nonrandomized, prospective, comparative study. Knee Surg. Relat. Res. 2020, 32, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liow, M.H.L.; Chin, P.L.; Tay, K.J.D.; Chia, S.L.; Lo, N.N.; Yeo, S.J. Early experiences with robot-assisted total knee arthroplasty using the DigiMatch™ ROBODOC® surgical system. Singap. Med. J. 2014, 55, 529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fozo, Z.A.; Ghazal, A.H.; Gamal, M.H.; Matar, S.G.; Kamal, I.; Ragab, K.M. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Conventional Versus Robotic-Assisted Total Knee Arthroplasty. Cureus 2023, 15, e46845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaudiani, M.A.; Samuel, L.T.; Kamath, A.F.; Courtney, P.M.; Lee, G.-C. Robotic-assisted versus manual unicompartmental knee arthroplasty: Contemporary systematic review and meta-analysis of early functional outcomes. J. Knee Surg. 2021, 34, 1048–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoeffel, D.; Goldstein, L.; Intwala, D.; Kaindl, L.; Dineen, A.; Patel, L.; Mayle, R. Systematic review and meta-analysis of economic and healthcare resource utilization outcomes for robotic versus manual total knee arthroplasty. J. Robot. Surg. 2023, 17, 2899–2910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruangsomboon, P.; Ruangsomboon, O.; Pornrattanamaneewong, C.; Narkbunnam, R.; Chareancholvanich, K. Clinical and radiological outcomes of robotic-assisted versus conventional total knee arthroplasty: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Acta Orthop. 2023, 94, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alrajeb, R.; Zarti, M.; Shuia, Z.; Alzobi, O.; Ahmed, G.; Elmhiregh, A. Robotic-assisted versus conventional total knee arthroplasty: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Eur. J. Orthop. Surg. Traumatol. 2024, 34, 1333–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shea, B.J.; Hamel, C.; Wells, G.A.; Bouter, L.M.; Kristjansson, E.; Grimshaw, J.; Henry, D.A.; Boers, M. AMSTAR is a reliable and valid measurement tool to assess the methodological quality of systematic reviews. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2009, 62, 1013–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muka, T.; Glisic, M.; Milic, J.; Verhoog, S.; Bohlius, J.; Bramer, W.; Chowdhury, R.; Franco, O.H. A 24-step guide on how to design, conduct, and successfully publish a systematic review and meta-analysis in medical research. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2020, 35, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Airapetov, G.A.; Yablonskiy, P.K.; Serdobintsev, M.S.; Dziov, Z.V.; Naumov, D. Robot-assisted knee arthroplasty: First experience (a prospective randomized study). Genij Ortop. 2023, 29, 475–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Cao, L.; Sun, Y.; Ye, Y.; Xie, J.; Hu, Y.; Li, Z.; Tang, B. A multicenter randomized controlled trial of domestic robot-assisted and conventional total knee arthroplasty. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi = Zhongguo Xiufu Chongjian Waike Zazhi = Chin. J. Reparative Reconstr. Surg. 2023, 37, 1326–1334. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, M.; Shi, X.; Su, Q.; Wan, X.; Zhou, Z. A prospective randomized controlled trial on the short-term effectiveness of domestic robot-assisted total knee arthroplasty. Zhongguo Xiufu Chongjian Waike Zazhi = Chin. J. Reparative Reconstr. Surg. 2021, 35, 1251–1258. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelaal, A.; Eltaras, M.M.; Katamesh, B.E.; Serhan, H.A.; Farahat, R.A.; Badr, H.; Abdelazeem, B. The prevalence and presentation patterns of microcystic macular oedema: A systematic review and meta-analysis of 2128 glaucomatous eyes. Eye 2023, 37, 3322–3333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amir-Behghadami, M.; Janati, A. Population, Intervention, Comparison, Outcomes and Study (PICOS) design as a framework to formulate eligibility criteria in systematic reviews. Emerg. Med. J. 2020, 37, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrah, K.; Young, K.; Tunis, M.C.; Zhao, L. Risk of bias tools in systematic reviews of health interventions: An analysis of PROSPERO-registered protocols. Syst. Rev. 2019, 8, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daoud, J.I. Multicollinearity and regression analysis. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2017, 949, 012009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamska, O.; Modzelewski, K.; Szymczak, J.; Świderek, J.; Maciąg, B.; Czuchaj, P.; Poniatowska, M.; Wnuk, A. Robotic-assisted total knee arthroplasty utilizing NAVIO, CORI imageless systems and manual TKA accurately restore femoral rotational alignment and yield satisfactory clinical outcomes: A randomized controlled trial. Medicina 2023, 59, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banger, M.S.; Johnston, W.D.; Razii, N.; Doonan, J.; Rowe, P.J.; Jones, B.G.; MacLean, A.D.; Blyth, M.J. Robotic arm-assisted bi-unicompartmental knee arthroplasty maintains natural knee joint anatomy compared with total knee arthroplasty: A prospective randomized controlled trial. Bone Jt. J. 2020, 102, 1511–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blyth, M.J.; Banger, M.S.; Doonan, J.; Jones, B.G.; MacLean, A.D.; Rowe, P.J. Early outcomes after robotic arm-assisted bi-unicompartmental knee arthroplasty compared with total knee arthroplasty: A prospective, randomized controlled trial. Bone Jt. J. 2021, 103, 1561–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bollars, P.; Janssen, D.; De Weerdt, W.; Albelooshi, A.; Meshram, P.; Nguyen, T.D.; Lacour, M.T.; Schotanus, M.G. Improved accuracy of implant placement with an imageless handheld robotic system compared to conventional instrumentation in patients undergoing total knee arthroplasty: A prospective randomized controlled trial using CT-based assessment of radiological outcomes. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2023, 31, 5446–5452. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cho, K.-J.; Seon, J.-K.; Jang, W.-Y.; Park, C.-G.; Song, E.-K. Robotic versus conventional primary total knee arthroplasty: Clinical and radiological long-term results with a minimum follow-up of ten years. Int. Orthop. 2019, 43, 1345–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clement, N.D.; Galloway, S.; Baron, Y.J.; Smith, K.; Weir, D.J.; Deehan, D.J. Robotic Arm-assisted versus Manual (ROAM) total knee arthroplasty: A randomized controlled trial. Bone Jt. J. 2023, 105, 961–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, X.; Zheng, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhao, M.; Liu, Y.; Li, Z.; Cai, H.; Zhang, M.; Yan, X.; Sun, Z. Early Radiographic and Clinical Outcomes of Robotic-arm-assisted versus Conventional Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Multicenter Randomized Controlled Trial. Orthop. Surg. 2024, 16, 2732–2740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-H.; Yoon, S.-H.; Park, J.-W. Does robotic-assisted TKA result in better outcome scores or long-term survivorship than conventional TKA? A randomized, controlled trial. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2020, 478, 266–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.M.; Kim, G.W.; Lee, C.Y.; Song, E.-K.; Seon, J.-K. No difference in clinical outcomes and survivorship for robotic, navigational, and conventional primary total knee arthroplasty with a minimum follow-up of 10 years. Clin. Orthop. Surg. 2023, 15, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, W.; Zhang, X.; Wu, Y. Azacitidine and donor lymphocyte infusion for patients with relapsed acute myeloid leukemia and myelodysplastic syndromes after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: A meta-analysis. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 949534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liow, M.H.L.; Goh, G.S.H.; Wong, M.K.; Chin, P.L.; Tay, D.K.J.; Yeo, S.J. Robotic-assisted total knee arthroplasty may lead to improvement in quality-of-life measures: A 2-year follow-up of a prospective randomized trial. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2017, 25, 2942–2951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liow, M.H.L.; Xia, Z.; Wong, M.K.; Tay, K.J.; Yeo, S.J.; Chin, P.L. Robot-assisted total knee arthroplasty accurately restores the joint line and mechanical axis. A prospective randomised study. J. Arthroplast. 2014, 29, 2373–2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Liu, Q.; Tian, R.; Wang, K.; Yang, P. Associations of postoperative outcomes with geriatric nutritional risk index after conventional and robotic-assisted total knee arthroplasty: A randomized controlled trial. Int. J. Surg. 2024, 110, 2115–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lychagin, A.V.; Gritsyuk, A.A.; Elizarov, M.P.; Rukin, Y.A.; Gritsyuk, A.A.; Gavlovsky, M.Y.; Elizarov, P.M.; Berdiyev, M.; Kalinsky, E.B.; Vyazankin, I.A. Short-Term Outcomes of Total Knee Arthroplasty Using a Conventional, Computer-Assisted, and Robotic Technique: A Pilot Clinical Trial. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 3125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.E.; Lee, C.T. Comparison of robotic-assisted and conventional manual implantation of a primary total knee arthroplasty. J. Arthroplast. 2007, 22, 1054–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, E.K.; Seon, J.K.; Park, S.J.; Jung, W.B.; Park, H.W.; Lee, G.W. Simultaneous bilateral total knee arthroplasty with robotic and conventional techniques: A prospective, randomized study. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2011, 19, 1069–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, E.-K.; Seon, J.-K.; Yim, J.-H.; Netravali, N.A.; Bargar, W.L. Robotic-assisted TKA reduces postoperative alignment outliers and improves gap balance compared to conventional TKA. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2013, 471, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiengwittayaporn, S.; Uthaitas, P.; Senwiruch, C.; Hongku, N.; Tunyasuwanakul, R. Imageless robotic-assisted total knee arthroplasty accurately restores the radiological alignment with a short learning curve: A randomized controlled trial. Int. Orthop. 2021, 45, 2851–2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, R.; Duan, X.; Kong, N.; Li, X.; Wang, J.; Tian, H.; Shi, Z.; Yan, S.; Lyu, J.; Wang, K. Robotic-assisted total knee arthroplasty is more advantageous for knees with severe deformity: A randomized controlled trial study design. Int. J. Surg. 2023, 109, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaidya, N.V.; Deshpande, A.N.; Panjwani, T.; Patil, R.; Jaysingani, T.; Patil, P. Robotic-assisted TKA leads to a better prosthesis alignment and a better joint line restoration as compared to conventional TKA: A prospective randomized controlled trial. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2022, 30, 621–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Li, L.; Fu, J.; Xu, C.; Ni, M.; Chai, W.; Hao, L.; Zhang, G.; Chen, J. Early clinical and radiographic outcomes of robot-assisted versus conventional manual total knee arthroplasty: A randomized controlled study. Orthop. Surg. 2022, 14, 1972–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Li, H.; Liu, Z.; Li, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, M.; Zhang, Y. Robot-assisted surgery in total knee arthroplasty: Trauma maker or trauma savior? A prospective, randomized cohort study. Burn. Trauma 2022, 10, tkac034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinjens, R.N.; Senden, R.; Heyligers, I.C.; Grimm, B. Clinimetric quality of the new 2011 Knee Society score: High validity, low completion rate. Knee 2014, 21, 647–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sodhi, N.; Khlopas, A.; Piuzzi, N.S.; Sultan, A.A.; Marchand, R.C.; Malkani, A.L.; Mont, M.A. The learning curve associated with robotic total knee arthroplasty. J. Knee Surg. 2018, 31, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deckey, D.G.; Rosenow, C.S.; Verhey, J.T.; Brinkman, J.C.; Mayfield, C.K.; Clarke, H.D.; Bingham, J.S. Robotic-assisted total knee arthroplasty improves accuracy and precision compared to conventional techniques. Bone Jt. J. 2021, 103, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheehy, L.; Felson, D.; Zhang, Y.; Niu, J.; Lam, Y.-M.; Segal, N.; Lynch, J.; Cooke, T.D.V. Does measurement of the anatomic axis consistently predict hip-knee-ankle angle (HKA) for knee alignment studies in osteoarthritis? Analysis of long limb radiographs from the multicenter osteoarthritis (MOST) study. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2011, 19, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogalo, C.; Meena, A.; Abermann, E.; Fink, C. Complications and downsides of the robotic total knee arthroplasty: A systematic review. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2023, 31, 736–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, N.; To, K.; McDonnell, S.; Khan, W. Clinical and radiological outcomes in robotic-assisted total knee arthroplasty: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Arthroplast. 2020, 35, 3393–3409.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshahrani, A. Efficacy and safety of robotic-assisted knee reconstruction: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2024, 28, 2250–2262. [Google Scholar]


| Author (YOP) | Study Design | Registration Number | Country | YOI | Sample | Sample | Robot Type | Age; M (SD) | Gender (M/F) | Surgeon Expertise | Cost Analysis | FI (Month) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RA-TKA | C-TKA | RA-TKA | C-TKA | RA-TKA | C-TKA | RA-TKA | C-TKA | |||||||||
| Adamska (2022) [30] | RCT | NR | Poland | 2022 | 215 | 76 | 68 | NAVIO | 66 (7.5) | 65 (8.2) | 22/42 | 30/35 | An experienced arthroplasty surgeon | No | 12 | |
| 215 | 71 | CORI | 69 (6.8) | 34/35 | ||||||||||||
| Banger (2020) [31] | RCT | (ISRCTN 12151461) | UK | 2020 | 70 | 38 | 32 | MAKO | 68.7 (7.8) | 70.5 (7.1) | 15/17 | 18/20 | Three orthopedic surgeons with extensive experience in both TKA and robotic-assisted UKA | No | 3 | |
| Blyth (2021) [32] | RCT | (ISRCTN 12151461) | UK | 2021 | 76 | 34 | 42 | MAKO | 68.7 (7.7) | 70.4 (7.1) | 17/17 | 21/21 | Three surgeons with extensive experience in TKA, robotic-assisted, and computer-navigated knee surgery | No | 12 | |
| Cho (2019) [34] | RCT | NR | South Korea | 2007 | 390 | 160 | 230 | ROBODOC® | 68.2 (3.83) | 67.6 (4.17) | 14/141 | 33/163 | Not clarified | No | 10.8 (0.9) | 11.2 (1.1) |
| Kim (2020) [37] | RCT | NCT 03659318). | South Korea | 2008 | 1348 | 674 | 674 | ROBODOC® | 60 (7) | 61 (8) | 132/542 | 144/530 | The surgeon who performed the procedures in this report performed 30 robotic-assisted TKAs using the system | No | 13 (0.83) | 14 (0.83) |
| Lee (2023) [38] | RCT | NR | Korea | 2009 | 855 | 194 | 270 | ROBODOC® | 71.8 (8.2) | 71.0 (7) | 18/176 | 20/250 | Not clarified | No | 11.9 (1.5) | 11.8 (1.5) |
| 855 | 391 | Orthopilot | 71.6 (8.1) | 71.0 (7) | 26/365 | 12 (1.4) | 11.8 (1.5) | |||||||||
| Li (2022) [39] | RCT | NR | China | 2020 | 150 | 73 | 77 | HURWA | 68.0 (7.97) | 69.0 (6.00) | 13/60 | 15/62 | All operations were performed by experienced surgeons | No | 3 | |
| Liow (2017) [40] | RCT | NR | Singapore | 2012 | 60 | 31 | 29 | ROBODOC® | - | - | - | - | A single experienced surgeon | No | 24 | |
| Liu (2024) [42] | RCT | ChiCTR2200065786) | China | 2021 | 88 | 44 | 44 | - | 71.75 (2.067) | 72.25 (2.067) | 11/0 | 12/0 | Not clarified | No | 3 | |
| Lychagin (2024) [43] | RCT | NR | Russia | 2019 | 118 | 56 | 62 | THINK Surgical Solution | 67.7 (10.2) | 66.5 (8.7) | 12/44 | 15/47 | Three experienced surgeons performed the surgical procedures in all groups | No | 36 | |
| Park (2007) [44] | RCT | NR | South Korea | 2007 | 62 | 32 | 30 | ROBODOC® | 62.7 (6.51) | 67.8 (6.44) | - | - | Not clarified | No | 45.0 (0.69) | 49.3 (3.47) |
| Song (2011) [45] | RCT | NR | Korea | 2004 | 30 | 15 | 15 | ROBODOC® | - | - | 0/15 | 0/15 | Single surgeon who had experience of more than 150 cases of robot-assisted TKA | Yes | 16 (3.2) | |
| Song (2013) [46] | RCT | NR | Korea | 2004 | 100 | 50 | 50 | ROBODOC® | 66.1 (7.1) | 64.8 (5.3) | 4/46 | 5/45 | One surgeon experienced in both conventional TKA techniques and the ROBODOC system for TKA | No | 65 (4.25) | 65 (10) |
| Thiengwittayaporn (2021) [47] | RCT | NCT04307251 | Thiland | 2020 | 152 | 75 | 77 | NAVIO | 69.0 (8.3) | 69.1 (7.3) | 6/69 | 15/62 | One experienced surgeon who had experience in computer navigation and the conventional jig-based instruments | No | 1.5 | |
| Xu (2022) [51] | RCT | (ChiCTR2000031282) | China | 2022 | 32 | 16 | 16 | YUANHUA | 66.6 (3.7) | 67.3 (3.5) | 3/14 | 3/13 | All the surgeries were completed by the same senior surgeon | No | 3 | |
| Xu (2022) [50] | RCT | ChiCTR2100042323) | China | 2020 | 72 | 37 | 35 | YUANHUA | 64.5 (5.3) | 63.4 (7.2) | 11/26 | 7/28 | Two senior joint surgeons | No | 3 | |
| Vaidya (2020) [49] | RCT | NR | India | 2020 | 60 | 32 | 28 | NAVIO | 62.2 (10) | 59.9 (8) | 8/24 | 4/24 | Not clarified | No | 3 | |
| Tian (2023) [48] | RCT | ChiCTR2200065786 | China | 2021 | 123 | 62 | 61 | Jianjia | 68.17 (7.59) | 68.84 (7.12) | 13/49 | 15/46 | Not clarified | No | 3 | |
| Bollars (2023) [33] | RCT | NR | Belgium | 2021 | 52 | 26 | 26 | NAVIO | 64.4 (8.7) | 66.4 (7.2) | 11/15 | 9/17 | Not clarified | No | 1.5 | |
| Clement (2023) [35] | RCT | (ISRCTN 47889316) | UK | 2020 | 87 | 46 | 41 | MAKO | 66.8 (8.7) | 66.7 (9.6) | 26/24 | 21/29 | Two surgeons, both of whom had over 20 years’ experience as primary and revision knee arthroplasty surgeons | Yes | 6 | |
| Li (2023) [24] | RCT | NR | China | 2023 | 134 | 68 | 66 | Kuanrui Technology | 64.5 (6.3) | 65.0 (5.5) | 9/57 | 16/45 | Not clarified | No | 36 | |
| Geng (2024) [36] | RCT | NR | China | 2023 | 130 | 65 | 65 | OP-RKL22 | 68.1 (5) | 67.4 (5.5) | 16/49 | 21/44 | Not clarified | No | 1.5 | |
| Liow (2014) [41] | RCT | NR | Singapore | 2012 | 60 | 31 | 29 | ROBODOC® | 67.5 (8.6) | 68.3 (7.7) | - | - | Two surgeons performed all operations | No | 6 | |
| Airapetov (2023) [23] | RCT | NR | Russia | 2023 | 20 | 10 | 10 | - | 61.4 (14.7) | 63.4 (14.7) | 4/6 | 3/7 | Single surgeon performed all operations | No | 0.33 | |
| Yuan (2021) [25] | RCT | NR | China | 2020 | 60 | 28 | 32 | YUANHUA | 65.2 | 65.4 | 9/19 | 4/28 | Two surgeons performed all operations | No | 3 | |
| KSS | OKS | ROM—Flexion | ROM—Extension | HSS | WOMAC | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coefficient | p-Value | Coefficient | p-Value | Coefficient | p-Value | Coefficient | p-Value | Coefficient | p-Value | Coefficient | p-Value | |
| Robotic System [Reference Group: ROBODOC] | ||||||||||||
| NAVIO | - | - | - | - | −568.11 | 0.049 | −0.30 | 0.585 | - | - | - | - |
| MAKO | −279.33 | 0.402 | - | - | −31.23 | 0.305 | - | - | - | - | −475.99 | 0.475 |
| YUANHUA | −282.42 | 0.413 | - | - | −36.42 | 0.285 | - | - | −1.40 | 0.950 | −39.67 | 0.701 |
| CORI | - | - | - | - | −562.31 | 0.051 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| THINK Surgical Solution | - | - | - | - | −601.71 | 0.055 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Risk of Bias [Reference Group: Low Risk] | ||||||||||||
| Some concerns | - | - | - | - | −612.79 | 0.055 | - | - | - | - | −452.60 | 0.486 |
| Number of Surgeons [Reference Group: Single Surgeon] | ||||||||||||
| Two surgeons | 4.90 | 0.644 | 1.73 | 0.275 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 30.03 | 0.072 |
| Follow-up (month) | −0.07 | 0.506 | 0.32 | 0.009 | −0.31 | 0.561 | - | - | - | - | 0.10 | 0.949 |
| Sample size (per patient) | −0.22 | 0.408 | - | - | −0.51 | 0.047 | - | - | - | - | −0.36 | 0.487 |
| Constant | 293.95 | 0.405 | −2.31 | 0.031 | 682.60 | 0.047 | 0.30 | 0.244 | 1.00 | 0.941 | 480.83 | 0.489 |
| Operative Time | Intraoperative Blood Loss | Satisfaction Rate | Complications | HKA Angle | HKA Deviation | |||||||
| Coefficient | p-Value | Coefficient | p-Value | Coefficient | p-Value | Coefficient | p-Value | Coefficient | p-Value | Coefficient | p-Value | |
| Robotic System [Reference Group: ROBODOC] | ||||||||||||
| NAVIO | 2446.45 | <0.0001 | - | - | - | - | 0.59 | 0.780 | −0.80 | 0.084 | - | - |
| MAKO | 89.20 | <0.0001 | - | - | 2.85 | 0.566 | −2.44 | 0.237 | −3.00 | 0.001 | - | - |
| YUANHUA | 115.70 | 0.004 | 4691.57 | 0.693 | - | - | −0.21 | 0.869 | - | - | 0.97 | 0.009 |
| CORI | 2452.45 | <0.0001 | - | - | - | - | 0.65 | 0.756 | - | - | - | - |
| THINK Surgical Solution | - | - | - | - | - | - | −3.31 | 0.275 | - | - | - | - |
| Number of Surgeons [Reference Group: Single Surgeon] | ||||||||||||
| Two surgeons | −41.40 | 0.030 | −55.63 | 0.830 | 2.16 | 0.018 | 0.36 | 0.678 | −0.50 | 0.400 | - | - |
| Three surgeons | - | - | - | - | - | - | 2.73 | 0.134 | - | - | - | - |
| Risk of Bias [Reference Group: Low Risk] | ||||||||||||
| Some concerns | 2680.20 | <0.0001 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Follow-up (month) | - | - | - | - | 0.09 | 0.311 | −0.04 | 0.693 | - | - | - | - |
| Sample size (per patient) | 2.15 | <0.0001 | 3.58 | 0.691 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Constant | −2870.20 | <0.0001 | −4824.33 | 0.692 | −3.51 | 0.525 | −0.25 | 0.843 | 1.30 | 0.003 | −1.87 | <0.0001 |
| FCIA | TCIA | FSIA | TSIA | TTA | ||||||||
| Coefficient | p-Value | Coefficient | p-Value | Coefficient | p-Value | Coefficient | p-Value | Coefficient | p-Value | |||
| Robotic System [Reference Group: ROBODOC] | ||||||||||||
| NAVIO | 1.50 | 0.492 | 3.37 | 0.080 | −3.93 | 0.312 | −1.67 | <0.0001 | - | - | ||
| MAKO | −63.40 | 0.232 | −57.25 | 0.218 | 10.55 | 0.912 | 3.80 | <0.0001 | −6.90 | <0.0001 | ||
| YUANHUA | −6.00 | 0.041 | −1.03 | 0.683 | −0.27 | 0.918 | - | - | - | - | ||
| CORI | - | - | - | - | - | - | −1.82 | <0.0001 | - | - | ||
| Number of Surgeons [Reference Group: Single Surgeon] | ||||||||||||
| Two surgeons | 2.70 | 0.082 | 0.37 | 0.768 | - | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| Risk of Bias [Reference Group: Low Risk] | ||||||||||||
| Some concerns | −61.90 | 0.232 | −53.60 | 0.238 | 9.40 | 0.919 | - | - | - | - | ||
| Sample size (per patient) | −0.05 | 0.229 | −0.04 | 0.252 | 0.01 | 0.911 | - | - | - | - | ||
| Constant | 68.40 | 0.222 | 57.17 | 0.244 | −10.23 | 0.919 | 0.001 | 1.000 | 0.001 | 1.000 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mert, Ü.; Khasawneh, M.Y.; Ghandour, M.; Al Zuabi, A.; Horst, K.; Hildebrand, F.; Bouillon, B.; Mahmoud, M.A.; Kabir, K. Comparative Efficacy and Precision of Robot-Assisted vs. Conventional Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 3249. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14093249
Mert Ü, Khasawneh MY, Ghandour M, Al Zuabi A, Horst K, Hildebrand F, Bouillon B, Mahmoud MA, Kabir K. Comparative Efficacy and Precision of Robot-Assisted vs. Conventional Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(9):3249. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14093249
Chicago/Turabian StyleMert, Ümit, Moh’d Yazan Khasawneh, Maher Ghandour, Ahmad Al Zuabi, Klemens Horst, Frank Hildebrand, Bertil Bouillon, Mohamad Agha Mahmoud, and Koroush Kabir. 2025. "Comparative Efficacy and Precision of Robot-Assisted vs. Conventional Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 9: 3249. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14093249
APA StyleMert, Ü., Khasawneh, M. Y., Ghandour, M., Al Zuabi, A., Horst, K., Hildebrand, F., Bouillon, B., Mahmoud, M. A., & Kabir, K. (2025). Comparative Efficacy and Precision of Robot-Assisted vs. Conventional Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(9), 3249. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14093249






