PRF and PRP in Dentistry: An Umbrella Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
- -
- Release of numerous growth factors important for tissue regeneration/healing, lasting up to 14 days;
- -
- Promotion of angiogenesis;
- -
- Provision of antibacterial properties;
- -
- Increased graft stability when mixed with a bone substitute;
- -
- Support for soft tissue healing.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Protocol
2.2. Search Strategy
2.3. Eligibility Criteria
2.4. Study Resarch
2.5. Data Extraction and Collection
- First author, year, journal, funding, and quality of the study;
- Number and design of the studies included in each systematic review;
- Characteristics of oral intervention with PRF or PRP;
- Outcomes;
- Conclusions.
2.6. Data Synthesis
2.7. Quality Assessment
3. Results
3.1. Study Selection
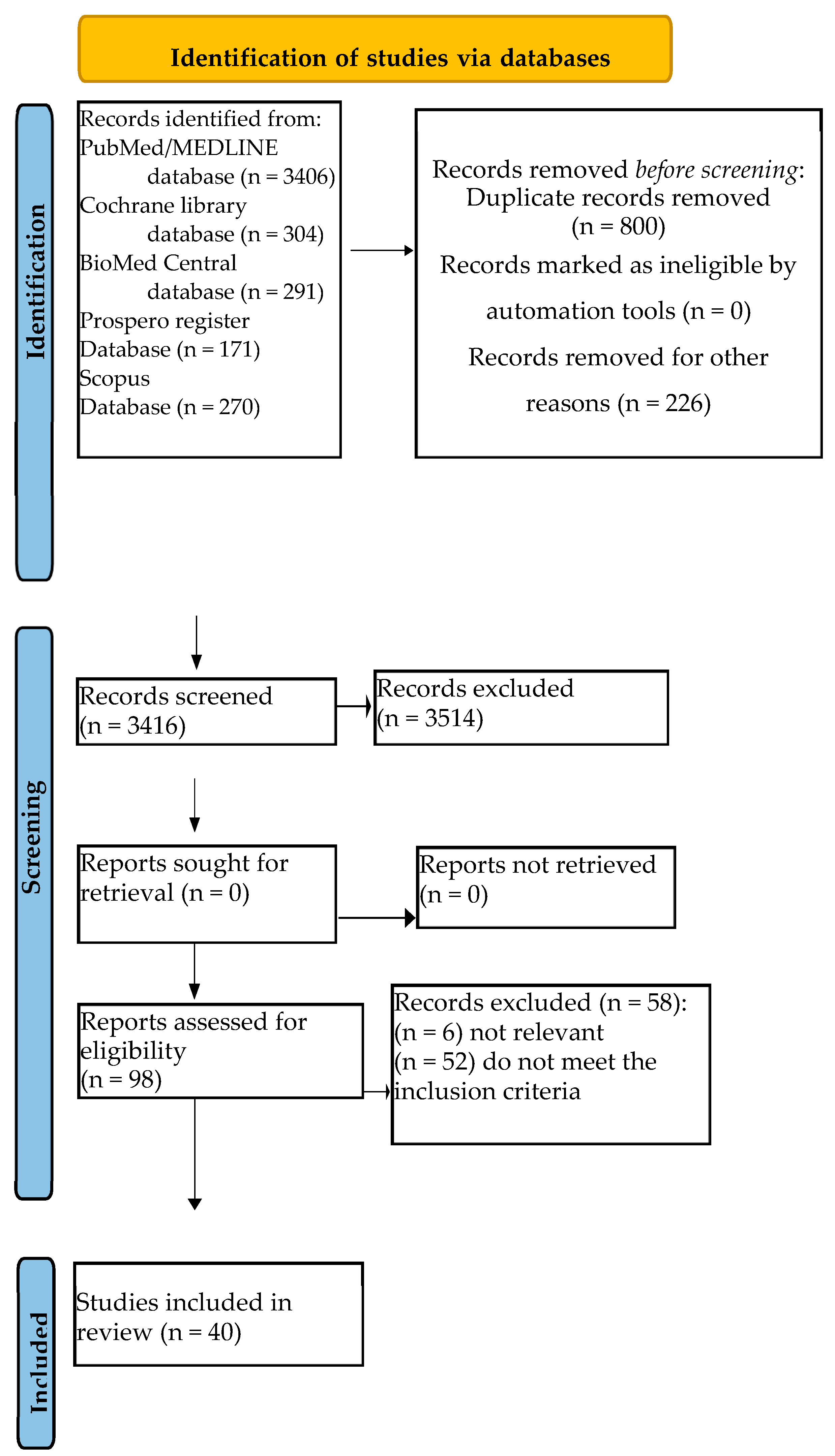
3.2. Quality and Risk of Bias Assessment of Included Systematic Review
4. Discussion
4.1. Oral Surgery
4.2. Implantology
4.3. Periodontology
4.4. ONJ
4.5. Regenerative
4.6. Endodontics
4.7. Orthodontics
4.8. Oral Lesion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Waller, C. Platelet-rich plasma. Ann. Fr. Anesth. Reanim. 1995, 14, 536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croisé, B.; Paré, A.; Joly, A.; Louisy, A.; Laure, B.; Goga, D. Optimized Centrifugation Preparation of the Platelet Rich Plasma: Literature Review. J. Stomatol. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2020, 121, 150–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calciolari, E.; Dourou, M.; Akcali, A.; Donos, N. Differences between First- and Second-Generation Autologous Platelet Concentrates. Periodontology 2000 2025, 97, 52–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Perez, K.; Dym, H. Clinical Uses of Platelet-Rich Fibrin in Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery. Dent. Clin. N. Am. 2020, 64, 291–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quirynen, M.; Siawasch, S.A.M.; Yu, J.; Miron, R.J. Essential Principles for Blood Centrifugation. Periodontology 2000 2025, 97, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choukroun, J.; Adda, F.; Schoeffler, C.; Vervelle, A. Une Opportunité En Paro-Implantologie: Le PRF. Implantodontie 2001, 42, e62. [Google Scholar]
- Miron, R.J.; Dham, A.; Dham, U.; Zhang, Y.; Pikos, M.A.; Sculean, A. The Effect of Age, Gender, and Time between Blood Draw and Start of Centrifugation on the Size Outcomes of Platelet-Rich Fibrin (PRF) Membranes. Clin. Oral Investig. 2019, 23, 2179–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, A.B.; Andrade, C.; Li, X.; Pinto, N.; Teughels, W.; Quirynen, M. Impact of g Force and Timing on the Characteristics of Platelet-Rich Fibrin Matrices. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 6038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miron, R.J.; Gruber, R.; Farshidfar, N.; Sculean, A.; Zhang, Y. Ten Years of Injectable Platelet-Rich Fibrin. Periodontology 2000 2024, 94, 92–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 Statement: An Updated Guideline for Reporting Systematic Reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booth, A.; Clarke, M.; Dooley, G.; Ghersi, D.; Moher, D.; Petticrew, M.; Stewart, L. The Nuts and Bolts of PROSPERO: An International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews. Syst. Rev. 2012, 1, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shea, B.J.; Reeves, B.C.; Wells, G.; Thuku, M.; Hamel, C.; Moran, J.; Moher, D.; Tugwell, P.; Welch, V.; Kristjansson, E.; et al. AMSTAR 2: A Critical Appraisal Tool for Systematic Reviews That Include Randomised or Non-Randomised Studies of Healthcare Interventions, or Both. BMJ 2017, 358, j4008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, N.; Cairns, M. Autologous Platelet Concentrates to Improve Post Extraction Outcomes. Evid. Based Dent. 2018, 19, 118–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, B.J.; Sharif, M.O.; Jones, K.; Worthington, H.V.; Beattie, A. Local Interventions for the Management of Alveolar Osteitis (Dry Socket). Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2022, 9, CD006968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garola, F.; Gilligan, G.; Panico, R.; Leonardi, N.; Piemonte, E. Clinical Management of Alveolar Osteitis. A Systematic Review. Med. Oral Patol Oral Cir. Bucal 2021, 26, e691–e702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attar-Attar, L.; Bernabeu-Mira, J.-C.; Cervera-Ballester, J.; Peñarrocha-Diago, M.; Peñarrocha-Diago, M. Systematic Review of Surgical Regenerative Treatment for Apicomarginal Lesions in Periapical Surgery. Med. Oral Patol Oral Cir. Bucal 2024, 29, e416–e422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salas, G.A.; Lai, S.A.; Verdugo-Paiva, F.; Requena, R.A. Platelet-Rich Fibrin in Third Molar Surgery: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Protocol. Craniomaxillofacial Trauma Reconstr. 2022, 15, 164–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canellas, J.V.D.S.; Medeiros, P.J.D.; Figueredo, C.M.D.S.; Fischer, R.G.; Ritto, F.G. Platelet-Rich Fibrin in Oral Surgical Procedures: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2019, 48, 395–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Rosa, G.R.M.; Marcianò, A.; Priolo, C.Y.; Peditto, M.; Pedullà, E.; Bianchi, A. Effectiveness of the Platelet-Rich Fibrin in the Control of Pain Associated with Alveolar Osteitis: A Scoping Review. Clin. Oral Investig. 2023, 27, 3321–3330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canellas, J.V.D.S.; Fraga, S.R.G.; Santoro, M.F.; Netto, J.D.N.S.; Tinoco, E.M.B. Intrasocket Interventions to Prevent Alveolar Osteitis after Mandibular Third Molar Surgery: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. J. Cranio-Maxillofac. Surg. 2020, 48, 902–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Ambrosio, F.; Caggiano, M.; Acerra, A.; Pisano, M.; Giordano, F. Is Ozone a Valid Adjuvant Therapy for Periodontitis and Peri-Implantitis? A Systematic Review. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ferreira, L.H., Jr.; Mendonça, K.D., Jr.; Chaves de Souza, J.; Soares Dos Reis, D.C.; do Carmo Faleiros Veloso Guedes, C.; de Souza Castro Filice, L.; Bruzadelli Macedo, S.; Soares Rocha, F. Bisphosphonate-Associated Osteonecrosis of the Jaw. Minerva Dent. Oral Sci. 2021, 70, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beth-Tasdogan, N.H.; Mayer, B.; Hussein, H.; Zolk, O.; Peter, J.-U. Interventions for Managing Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2022, 7, CD012432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rollason, V.; Laverrière, A.; MacDonald, L.C.I.; Walsh, T.; Tramèr, M.R.; Vogt-Ferrier, N.B. Interventions for Treating Bisphosphonate-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw (BRONJ). Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2016, 2, CD008455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quah, B.; Yong, C.W.; Lai, C.W.M.; Islam, I. Efficacy of Adjunctive Modalities during Tooth Extraction for the Prevention of Osteoradionecrosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Oral Dis. 2024, 30, 3732–3744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motta, C.; Cavagnetto, D.; Amoroso, F.; Baldi, I.; Mussano, F. Bioactive Glass for Periodontal Regeneration: A Systematic Review. BMC Oral Health 2023, 23, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavelli, L.; Chen, C.-Y.J.; Barootchi, S.; Kim, D.M. Efficacy of Biologics for the Treatment of Periodontal Infrabony Defects: An American Academy of Periodontology Best Evidence Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. J. Periodontol. 2022, 93, 1803–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Sun, C.; Huang, S.; Wu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Pan, C.; Wang, H.; Liu, J.; Li, Q.; Kou, Y. Efficacy of Adjunctive Bioactive Materials in the Treatment of Periodontal Intrabony Defects: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Biomed. Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 8670832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambrone, L.; Barootchi, S.; Avila-Ortiz, G. Efficacy of Biologics in Root Coverage and Gingival Augmentation Therapy: An American Academy of Periodontology Best Evidence Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. J. Periodontol. 2022, 93, 1771–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amine, K.; El Amrani, Y.; Chemlali, S.; Kissa, J. Alternatives to Connective Tissue Graft in the Treatment of Localized Gingival Recessions: A Systematic Review. J. Stomatol. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2018, 119, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suárez-López Del Amo, F.; Monje, A. Efficacy of Biologics for Alveolar Ridge Preservation/Reconstruction and Implant Site Development: An American Academy of Periodontology Best Evidence Systematic Review. J. Periodontol. 2022, 93, 1827–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farshidfar, N.; Jafarpour, D.; Firoozi, P.; Sahmeddini, S.; Hamedani, S.; de Souza, R.F.; Tayebi, L. The Application of Injectable Platelet-Rich Fibrin in Regenerative Dentistry: A Systematic Scoping Review of In Vitro and In Vivo Studies. JPN Dent. Sci. Rev. 2022, 58, 89–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malcangi, G.; Patano, A.; Palmieri, G.; Di Pede, C.; Latini, G.; Inchingolo, A.D.; Hazballa, D.; de Ruvo, E.; Garofoli, G.; Inchingolo, F.; et al. Maxillary Sinus Augmentation Using Autologous Platelet Concentrates (Platelet-Rich Plasma, Platelet-Rich Fibrin, and Concentrated Growth Factor) Combined with Bone Graft: A Systematic Review. Cells 2023, 12, 1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Du, R.; Yang, B.; Tao, J.; Jing, W. Efficacy of Autologous Platelet Concentrate Products for Alveolar Preservation: A Meta-Analysis. Oral Dis. 2024, 30, 3658–3670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, M.; Felice, P.; Worthington, H.V. Interventions for Replacing Missing Teeth: Augmentation Procedures of the Maxillary Sinus. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2014, 2014, CD008397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdalla, R.I.B.; Alqutaibi, A.Y.; Kaddah, A. Does the Adjunctive Use of Platelet-Rich Plasma to Bone Graft during Sinus Augmentation Reduce Implant Failure and Complication? Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Quintessence Int. 2018, 49, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos Pereira, V.B.; da Silva Barbirato, D.; do Lago, C.A.P.; do Egito Vasconcelos, B.C. The Effect of Advanced Platelet-Rich Fibrin in Tissue Regeneration in Reconstructive and Graft Surgery: Systematic Review. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2023, 34, 1217–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pocaterra, A.; Caruso, S.; Bernardi, S.; Scagnoli, L.; Continenza, M.A.; Gatto, R. Effectiveness of Platelet-Rich Plasma as an Adjunctive Material to Bone Graft: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Clinical Trials. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2016, 45, 1027–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balli, G.; Ioannou, A.; Powell, C.A.; Angelov, N.; Romanos, G.E.; Soldatos, N. Ridge Preservation Procedures after Tooth Extractions: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Dent. 2018, 2018, 8546568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alrayyes, Y.; Al-Jasser, R. Regenerative Potential of Platelet Rich Fibrin (PRF) in Socket Preservation in Comparison with Conventional Treatment Modalities: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2022, 19, 463–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stumbras, A.; Kuliesius, P.; Januzis, G.; Juodzbalys, G. Alveolar Ridge Preservation after Tooth Extraction Using Different Bone Graft Materials and Autologous Platelet Concentrates: A Systematic Review. J. Oral Maxillofac. Res. 2019, 10, e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Fabbro, M.; Panda, S.; Taschieri, S. Adjunctive Use of Plasma Rich in Growth Factors for Improving Alveolar Socket Healing: A Systematic Review. J. Evid. Based Dent. Pract. 2019, 19, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemos, C.A.A.; Mello, C.C.; dos Santos, D.M.; Verri, F.R.; Goiato, M.C.; Pellizzer, E.P. Effects of Platelet-Rich Plasma in Association with Bone Grafts in Maxillary Sinus Augmentation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2016, 45, 517–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anitua, E.; Allende, M.; Eguia, A.; Alkhraisat, M.H. Bone-Regenerative Ability of Platelet-Rich Plasma Following Sinus Augmentation with Anorganic Bovine Bone: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Yan, M.; Chen, S.; Huang, W.; Wu, D.; Chen, J. Effectiveness of Platelet-Rich Fibrin as an Adjunctive Material to Bone Graft in Maxillary Sinus Augmentation: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trails. Biomed. Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 7267062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, V.B.S.; Lago, C.A.P.; Almeida, R.d.A.C.; da S. Barbirato, D.; do E. Vasconcelos, B.C. Biological and Cellular Properties of Advanced Platelet-Rich Fibrin (A-PRF) Compared to Other Platelet Concentrates: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 25, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, E.D.; de Santana, I.H.G.; Viana, M.R.M.; Júnior, E.S.H.; Dias, J.C.P.; Ferreira-Júnior, O.; Sant’Ana, E. The Efficacy of Platelet and Leukocyte Rich Fibrin (L-PRF) in the Healing Process and Bone Repair in Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeries: A Systematic Review. Clin. Oral Investig. 2024, 28, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schliephake, H. Clinical Efficacy of Growth Factors to Enhance Tissue Repair in Oral and Maxillofacial Reconstruction: A Systematic Review. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2015, 17, 247–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strauss, F.J.; Stähli, A.; Gruber, R. The Use of Platelet-Rich Fibrin to Enhance the Outcomes of Implant Therapy: A Systematic Review. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2018, 29 (Suppl. 18), 6–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, C.; Luo, F.; Hong, G.; Wan, Q. Effects of Platelet Concentrates on Implant Stability and Marginal Bone Loss: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. BMC Oral Health 2021, 21, 579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabri, H.; Manouchehri, N.; Mandil, O.; Alrmali, A.; AlHachache, S.; Rodriguez, J.C.; Wang, H.-L. Efficacy of Autogenous Platelet Concentrates in Immediate Implant Therapy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Prospective Controlled Clinical Trials. Int. J. Oral Implantol. 2024, 17, 137–161. [Google Scholar]
- Barona-Dorado, C.; González-Regueiro, I.; Martín-Ares, M.; Arias-Irimia, O.; Martínez-González, J.-M. Efficacy of Platelet-Rich Plasma Applied to Post-Extraction Retained Lower Third Molar Alveoli. A Systematic Review. Med. Oral Patol. Oral Cir. Bucal. 2014, 19, e142–e148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stähli, A.; Strauss, F.J.; Gruber, R. The Use of Platelet-Rich Plasma to Enhance the Outcomes of Implant Therapy: A Systematic Review. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2018, 29 (Suppl. 18), 20–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, X.; Yuan, J.; Aisaiti, A.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, J. The Effect of Platelet-Rich Plasma on Clinical Outcomes of the Surgical Treatment of Periodontal Intrabony Defects: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. BMC Oral Health 2016, 16, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pullishery, F.; Hussein Alattas, M.; Roshdy Abdelrasoul, M.; Fouad Hassan, A.; Abdelhamid Ahmed Derbala, D.; Hashir, S. Effectiveness of I-PRF in Periodontal Regeneration—A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Saudi Dent. J. 2024, 36, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roselló-Camps, À.; Monje, A.; Lin, G.-H.; Khoshkam, V.; Chávez-Gatty, M.; Wang, H.-L.; Gargallo-Albiol, J.; Hernandez-Alfaro, F. Platelet-Rich Plasma for Periodontal Regeneration in the Treatment of Intrabony Defects: A Meta-Analysis on Prospective Clinical Trials. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2015, 120, 562–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, F.F.V.E.; Chauca-Bajaña, L.; Caponio, V.C.A.; Cueva, K.A.S.; Velasquez-Ron, B.; Padín-Iruegas, M.E.; Almeida, L.L.; Lorenzo-Pouso, A.I.; Suárez-Peñaranda, J.M.; Pérez-Sayáns, M. Regeneration of Periodontal Intrabony Defects Using Platelet-Rich Fibrin (PRF): A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Odontology 2024, 112, 1047–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, S.; Doraiswamy, J.; Malaiappan, S.; Varghese, S.S.; Del Fabbro, M. Additive Effect of Autologous Platelet Concentrates in Treatment of Intrabony Defects: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Investig. Clin. Dent. 2016, 7, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Jornet, P.; Sanchez Perez, A.; Amaral Mendes, R.; Tobias, A. Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw: Is Autologous Platelet Concentrate Application Effective for Prevention and Treatment? A Systematic Review. J. Craniomaxillofac. Surg. 2016, 44, 1067–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, S.M.; Sacco, R.; Mitchell, F.L.; Patel, V.; Gurzawska-Comis, K. The Effectiveness of Autologous Platelet Concentrates in Prevention and Treatment of Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaws: A Systematic Review. J. Craniomaxillofac. Surg. 2024, 52, 671–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, R.V.; Gomes, T.P.; da Silva, F.M.; Chambrone, L.; Marques, M.M.; Palma, L.F. Autologous Platelet Concentrates in Extraction Sockets for the Prevention of Osteoradionecrosis: A Systematic Review of Controlled Clinical Trials. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2022, 26, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miron, R.J.; Fujioka-Kobayashi, M.; Moraschini, V.; Zhang, Y.; Gruber, R.; Wang, H.-L. Efficacy of Platelet-Rich Fibrin on Bone Formation, Part 1: Alveolar Ridge Preservation. Int. J. Oral Implantol. 2021, 14, 181–194. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Badran, A.; Bierbaum, S.; Wolf-Brandstetter, C. Does the Choice of Preparation Protocol for Platelet-Rich Fibrin Have Consequences for Healing and Alveolar Ridge Preservation After Tooth Extraction? A Meta-Analysis. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2023, 81, 602–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damsaz, M.; Castagnoli, C.Z.; Eshghpour, M.; Alamdari, D.H.; Alamdari, A.H.; Noujeim, Z.E.F.; Haidar, Z.S. Evidence-Based Clinical Efficacy of Leukocyte and Platelet-Rich Fibrin in Maxillary Sinus Floor Lift, Graft and Surgical Augmentation Procedures. Front. Surg. 2020, 7, 537138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega-Mejia, H.; Estrugo-Devesa, A.; Saka-Herrán, C.; Ayuso-Montero, R.; López-López, J.; Velasco-Ortega, E. Platelet-Rich Plasma in Maxillary Sinus Augmentation: Systematic Review. Materials 2020, 13, 622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragonas, P.; Schiavo, J.H.; Avila-Ortiz, G.; Palaiologou, A.; Katsaros, T. Plasma Rich in Growth Factors (PRGF) in Intraoral Bone Grafting Procedures: A Systematic Review. J. Craniomaxillofac. Surg. 2019, 47, 443–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, A.B.; Meschi, N.; Temmerman, A.; Pinto, N.; Lambrechts, P.; Teughels, W.; Quirynen, M. Regenerative Potential of Leucocyte- and Platelet-Rich Fibrin. Part B: Sinus Floor Elevation, Alveolar Ridge Preservation and Implant Therapy. A Systematic Review. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2017, 44, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivakumar, I.; Arunachalam, S.; Mahmoud Buzayan, M.; Sharan, J. Does the Use of Platelet-Rich Plasma in Sinus Augmentation Improve the Survival of Dental Implants? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Oral Biol. Craniofac. Res. 2023, 13, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.; Bakry, S.A.; Abd-Elhakam, H. Platelet-Rich Fibrin in Maxillary Sinus Augmentation: A Systematic Review. J. Oral Implantol. 2015, 41, 746–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasparro, R.; Di Lauro, A.E.; Campana, M.D.; Rosiello, N.; Mariniello, M.; Sammartino, G.; Marenzi, G. Effectiveness of Autologous Platelet Concentrates in the Sinus Lift Surgery: Findings from Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses. Dent. J. 2024, 12, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filho, E.L.C.; Franco, J.M.P.L.; Ribeiro, T.R.; de Barros Silva, P.G.; Costa, F.W.G. Does Platelet-Rich Fibrin Prevent Hemorrhagic Complications After Dental Extractions in Patients Using Oral Anticoagulant Therapy? J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2021, 79, 2215–2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, M.-Z.; Liu, W.; Yu, S.-R.; Men, Y.; Han, B.; Li, C.-J. Application of Platelet-Rich Fibrin on Mandibular Third Molar Extraction: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Hua Xi Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi 2021, 39, 605–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franchini, M.; Cruciani, M.; Mengoli, C.; Masiello, F.; Marano, G.; D’Aloja, E.; Dell’Aringa, C.; Pati, I.; Veropalumbo, E.; Pupella, S.; et al. The Use of Platelet-Rich Plasma in Oral Surgery: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Blood Transfus. 2019, 17, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hamed, F. Efficacy of Platelet-Rich Fibrin After Mandibular Third Molar Extraction: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2017, 75, 1124–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salgado-Peralvo, A.-O.; Mateos-Moreno, M.-V.; Uribarri, A.; Kewalramani, N.; Peña-Cardelles, J.-F.; Velasco-Ortega, E. Treatment of Oroantral Communication with Platelet-Rich Fibrin: A Systematic Review. J. Stomatol. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2022, 123, e367–e375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Chen, J.; Huang, Y.; Pan, Q.; Nie, M. Local Application of Platelet-Rich Fibrin During Lower Third Molar Extraction Improves Treatment Outcomes. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2017, 75, 2497–2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitenson, J.; Starch-Jensen, T.; Bruun, N.H.; Larsen, M.K. The Use of Advanced Platelet-Rich Fibrin after Surgical Removal of Mandibular Third Molars: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2022, 51, 962–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, M.; Du, G.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, P.; Cao, Y.; Li, C. Application of Platelet-Rich Fibrin Derivatives for Mandibular Third Molar Extraction Related Post-Operative Sequelae: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2021, 79, 2421–2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, E.U.; Bizelli, V.F.; Pereira Baggio, A.M.; Ferriolli, S.C.; Silva Prado, G.A.; Farnezi Bassi, A.P. Do the New Protocols of Platelet-Rich Fibrin Centrifugation Allow Better Control of Postoperative Complications and Healing After Surgery of Impacted Lower Third Molar? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2022, 80, 1238–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, X.; Shi, P.; Zhang, P.; Shen, J.; Kang, J. Impact of Platelet-Rich Fibrin on Mandibular Third Molar Surgery Recovery: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. BMC Oral Health 2019, 19, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canellas, J.V.D.S.; Ritto, F.G.; Medeiros, P.J.D. Evaluation of Postoperative Complications after Mandibular Third Molar Surgery with the Use of Platelet-Rich Fibrin: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2017, 46, 1138–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campana, M.D.; Aliberti, A.; Acerra, A.; Sammartino, P.; Dolce, P.; Sammartino, G.; Gasparro, R. The Effectiveness and Safety of Autologous Platelet Concentrates as Hemostatic Agents after Tooth Extraction in Patients on Anticoagulant Therapy: A Systematic Review of Randomized, Controlled Trials. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 5342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Zhang, S.; Yuan, X.; He, T.; Liu, H.; Wang, J.; Xu, B. Effect of Platelet-Rich Fibrin on the Control of Alveolar Osteitis, Pain, Trismus, Soft Tissue Healing, and Swelling Following Mandibular Third Molar Surgery: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2021, 50, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, E.D.; de Santana, I.H.G.; Viana, M.R.M.; Freire, J.C.P.; Ferreira-Júnior, O.; Sant’Ana, E. Use of Platelet- and Leukocyte-Rich Fibrin (L-PRF) as a Healing Agent in the Postoperative Period of Third Molar Removal Surgeries: A Systematic Review. Clin. Oral Investig. 2024, 28, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyris, V.; Millen, C.; Besi, E.; Pace-Balzan, A. Effect of Leukocyte and Platelet Rich Fibrin (L-PRF) on Stability of Dental Implants. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2021, 59, 1130–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, S.; Xiao, T.; Bai, J.; Ning, C.; Zhang, X.; Yang, L.; Li, X. Clinical Application of Platelet-Rich Fibrin to Enhance Dental Implant Stability: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Heliyon 2023, 9, e13196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miron, R.J.; Moraschini, V.; Del Fabbro, M.; Piattelli, A.; Fujioka-Kobayashi, M.; Zhang, Y.; Saulacic, N.; Schaller, B.; Kawase, T.; Cosgarea, R.; et al. Use of Platelet-Rich Fibrin for the Treatment of Gingival Recessions: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. Oral Investig. 2020, 24, 2543–2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gusman, D.-J.-R.; Matheus, H.-R.; Alves, B.-E.-S.; de Oliveira, A.-M.-P.; Britto, A.-C.-D.S.; Novaes, V.-C.-N.; Nagata, M.-J.-H.; Batista, V.-E.S.; de Almeida, J.-M. Platelet-Rich Fibrin for Wound Healing of Palatal Donor Sites of Free Gingival Grafts: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Exp. Dent. 2021, 13, e190–e200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skurska, A.; Chwiedosik, M.; Ślebioda, Z. Adjunctive Use of Platelet-Rich Fibrin in Surgical Treatment of Furcation Defects: A Systematic Review. Adv. Med. Sci. 2023, 68, 366–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, A.B.; Meschi, N.; Temmerman, A.; Pinto, N.; Lambrechts, P.; Teughels, W.; Quirynen, M. Regenerative Potential of Leucocyte- and Platelet-Rich Fibrin. Part A: Intra-Bony Defects, Furcation Defects and Periodontal Plastic Surgery. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2017, 44, 67–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meza-Mauricio, J.; Furquim, C.P.; Geldres, A.; Mendoza-Azpur, G.; Retamal-Valdes, B.; Moraschini, V.; Faveri, M. Is the Use of Platelet-Rich Fibrin Effective in the Healing, Control of Pain, and Postoperative Bleeding in the Palatal Area after Free Gingival Graft Harvesting? A Systematic Review of Randomized Clinical Studies. Clin. Oral Investig. 2021, 25, 4239–4249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panda, S.; Satpathy, A.; Chandra Das, A.; Kumar, M.; Mishra, L.; Gupta, S.; Srivastava, G.; Lukomska-Szymanska, M.; Taschieri, S.; Del Fabbro, M. Additive Effect of Platelet Rich Fibrin with Coronally Advanced Flap Procedure in Root Coverage of Miller’s Class I and II Recession Defects-A PRISMA Compliant Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Materials 2020, 13, 4314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rusilas, H.; Balčiūnaitė, A.; Žilinskas, J. Autologous Platelet Concentrates in Treatment of Medication Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw. Stomatologija 2020, 22, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Niu, W.; Wang, P.; Ge, S.; Ji, P. Effects of Platelet Concentrates Used in Alveolar Ridge Preservation: A Systematic Review. Implant. Dent. 2018, 27, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miron, R.J.; Zucchelli, G.; Pikos, M.A.; Salama, M.; Lee, S.; Guillemette, V.; Fujioka-Kobayashi, M.; Bishara, M.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.-L.; et al. Use of Platelet-Rich Fibrin in Regenerative Dentistry: A Systematic Review. Clin. Oral Investig. 2017, 21, 1913–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miron, R.J.; Moraschini, V.; Fujioka-Kobayashi, M.; Zhang, Y.; Kawase, T.; Cosgarea, R.; Jepsen, S.; Bishara, M.; Canullo, L.; Shirakata, Y.; et al. Use of Platelet-Rich Fibrin for the Treatment of Periodontal Intrabony Defects: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. Oral Investig. 2021, 25, 2461–2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Maawi, S.; Becker, K.; Schwarz, F.; Sader, R.; Ghanaati, S. Efficacy of Platelet-Rich Fibrin in Promoting the Healing of Extraction Sockets: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Implant. Dent. 2021, 7, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraschini, V.; Barboza, E.S.P. Effect of Autologous Platelet Concentrates for Alveolar Socket Preservation: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2015, 44, 632–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Fabbro, M.; Ceresoli, V. The Fate of Marginal Bone around Axial vs. Tilted Implants: A Systematic Review. Eur. J. Oral Implantol. 2014, 7 (Suppl. 2), S171–S189. [Google Scholar]
- Del Fabbro, M.; Bucchi, C.; Lolato, A.; Corbella, S.; Testori, T.; Taschieri, S. Healing of Postextraction Sockets Preserved With Autologous Platelet Concentrates. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2017, 75, 1601–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miron, R.J.; Fujioka-Kobayashi, M.; Bishara, M.; Zhang, Y.; Hernandez, M.; Choukroun, J. Platelet-Rich Fibrin and Soft Tissue Wound Healing: A Systematic Review. Tissue Eng. Part B Rev. 2017, 23, 83–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dragonas, P.; Katsaros, T.; Avila-Ortiz, G.; Chambrone, L.; Schiavo, J.H.; Palaiologou, A. Effects of Leukocyte-Platelet-Rich Fibrin (L-PRF) in Different Intraoral Bone Grafting Procedures: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2019, 48, 250–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anitua, E.; Allende, M.; Alkhraisat, M.H. Unravelling Alveolar Bone Regeneration Ability of Platelet-Rich Plasma: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Xu, Q.; Hou, J.; Wu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, R.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, D. Effect of Platelet-Rich Fibrin on Alveolar Ridge Preservation: A Systematic Review. J. Am. Dent. Assoc. 2019, 150, 766–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-Y.; Chen, Z.; Pan, W.-L.; Wang, H.-L. Effect of Platelet-Rich Fibrin on Ridge Preservation in Perspective of Bone Healing: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 2019, 34, 845–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caponio, V.C.A.; Baca-González, L.; González-Serrano, J.; Torres, J.; López-Pintor, R.M. Effect of the Use of Platelet Concentrates on New Bone Formation in Alveolar Ridge Preservation: A Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis, and Trial Sequential Analysis. Clin. Oral Investig. 2023, 27, 4131–4146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meschi, N.; Castro, A.B.; Vandamme, K.; Quirynen, M.; Lambrechts, P. The Impact of Autologous Platelet Concentrates on Endodontic Healing: A Systematic Review. Platelets 2016, 27, 613–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farshidfar, N.; Amiri, M.A.; Firoozi, P.; Hamedani, S.; Ajami, S.; Tayebi, L. The Adjunctive Effect of Autologous Platelet Concentrates on Orthodontic Tooth Movement: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Current Randomized Controlled Trials. Int. Orthod. 2022, 20, 100596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddheshiya, N.; Srivastava, A.; Rastogi, V.; Shekhar, A.; Sah, N.; Kumar, A. Platelet-Rich Plasma Protein as a Therapeutic Regimen for Oral Lichen Planus: An Evidence-Based Systematic Review. Natl. J. Maxillofac. Surg. 2023, 14, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, N.; Bhargava, A.; Saigal, S.; Sharma, S.; Patel, M.; Prakash, O. Effectiveness of Injectable Platelet-Rich Fibrin in the Treatment of Oral Lichen Planus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cureus 2024, 16, e51626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemczyk, W.; Janik, K.; Żurek, J.; Skaba, D.; Wiench, R. Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) and Injectable Platelet-Rich Fibrin (i-PRF) in the Non-Surgical Treatment of Periodontitis-A Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 6319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghanaati, S.; Booms, P.; Orlowska, A.; Kubesch, A.; Lorenz, J.; Rutkowski, J.; Landes, C.; Sader, R.; Kirkpatrick, C.; Choukroun, J. Advanced Platelet-Rich Fibrin: A New Concept for Cell-Based Tissue Engineering by Means of Inflammatory Cells. J. Oral Implantol. 2014, 40, 679–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niemczyk, W.; Żurek, J.; Niemczyk, S.; Kępa, M.; Zięba, N.; Misiołek, M.; Wiench, R. Antibiotic-Loaded Platelet-Rich Fibrin (AL-PRF) as a New Carrier for Antimicrobials: A Systematic Review of In Vitro Studies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pantaleo, G.; Acerra, A.; Giordano, F.; D’Ambrosio, F.; Langone, M.; Caggiano, M. Immediate Loading of Fixed Prostheses in Fully Edentulous Jaws: A 7-Year Follow-Up from a Single-Cohort Retrospective Study. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 12427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pistilli, R.; Simion, M.; Barausse, C.; Gasparro, R.; Pistilli, V.; Bellini, P.; Felice, P. Guided Bone Regeneration with Nonresorbable Membranes in the Rehabilitation of Partially Edentulous Atrophic Arches: A Retrospective Study on 122 Implants with a 3- to 7-Year Follow-Up. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 2020, 40, 685–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caggiano, M.; D’Ambrosio, F.; Giordano, F.; Acerra, A.; Sammartino, P.; Iandolo, A. The “Sling” Technique for Horizontal Guided Bone Regeneration: A Retrospective Case Series. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 5889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- di Lauro, A.E.; Valletta, A.; Aliberti, A.; Cangiano, M.; Dolce, P.; Sammartino, G.; Gasparro, R. The Effectiveness of Autologous Platelet Concentrates in the Clinical and Radiographic Healing after Endodontic Surgery: A Systematic Review. Materials 2023, 16, 7187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasparro, R.; Bucci, R.; De Rosa, F.; Sammartino, G.; Bucci, P.; D’Antò, V.; Marenzi, G. Effectiveness of Surgical Procedures in the Acceleration of Orthodontic Tooth Movement: Findings from Systematic Reviews and Meta-analyses. JPN Dent. Sci. Rev. 2022, 58, 137–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caggiano, M.; Di Spirito, F.; Acerra, A.; Galdi, M.; Sisalli, L. Multiple-Drugs-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw in a Patient Affected by Multiple Myeloma: A Case Report. Dent. J. 2023, 11, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Inclusion Criteria | Exclusion Criteria |
|---|---|
| Systematic review about only human subjects who have undergone oral surgery or a dental procedure with only autologous platelet concentrates (PRF * or PRP *) | Not a systematic review with or without meta-analysis |
| Systematic review with or without meta-analysis | Not an English language article |
| Only English articles | Not an in vitro or animal systematic review |
| Only reviews published in the last ten years | Does not meet the inclusion criteria |
| Not relevant (missing data) | |
| Reviews published more than ten years ago |
| Reference | Reasons for Exclusion |
|---|---|
| [14] | did not meet the inclusion criteria |
| [15] | did not meet the inclusion criteria |
| [16] | did not meet the inclusion criteria |
| [17] | did not meet the inclusion criteria |
| [18] | not relevant (missing data) |
| [19] | did not meet the inclusion criteria |
| [20] | did not meet the inclusion criteria |
| [21] | did not meet the inclusion criteria |
| [22] | did not meet the inclusion criteria |
| [23] | did not meet the inclusion criteria |
| [24] | did not meet the inclusion criteria |
| [25] | did not meet the inclusion criteria |
| [26] | did not meet the inclusion criteria |
| [27] | did not meet the inclusion criteria |
| [28] | did not meet the inclusion criteria |
| [29] | did not meet the inclusion criteria |
| [30] | did not meet the inclusion criteria |
| [31] | did not meet the inclusion criteria |
| [32] | did not meet the inclusion criteria |
| [33] | did not meet the inclusion criteria |
| [34] | did not meet the inclusion criteria |
| [35] | did not meet the inclusion criteria |
| [36] | did not meet the inclusion criteria |
| [37] | did not meet the inclusion criteria |
| [38] | did not meet the inclusion criteria |
| [39] | did not meet the inclusion criteria |
| [40] | did not meet the inclusion criteria |
| [41] | did not meet the inclusion criteria |
| [42] | did not meet the inclusion criteria |
| [43] | did not meet the inclusion criteria |
| [44] | did not meet the inclusion criteria |
| [45] | did not meet the inclusion criteria |
| [46] | did not meet the inclusion criteria |
| [47] | did not meet the inclusion criteria |
| [48] | did not meet the inclusion criteria |
| [49] | did not meet the inclusion criteria |
| [50] | did not meet the inclusion criteria |
| [51] | did not meet the inclusion criteria |
| [52] | not relevant (missing data) |
| [53] | did not meet the inclusion criteria |
| [54] | did not meet the inclusion criteria |
| [55] | not relevant |
| [56] | not relevant |
| [57] | did not meet the inclusion criteria |
| [58] | did not meet the inclusion criteria |
| [59] | did not meet the inclusion criteria |
| [60] | did not meet the inclusion criteria |
| [61] | not relevant |
| [62] | did not meet the inclusion criteria |
| [63] | did not meet the inclusion criteria |
| [64] | did not meet the inclusion criteria |
| [65] | did not meet the inclusion criteria |
| [66] | did not meet the inclusion criteria |
| [67] | did not meet the inclusion criteria |
| [68] | not relevant |
| [69] | did not meet the inclusion criteria |
| [70] | did not meet the inclusion criteria |
| Authors, Year Reference Journal Study Design | PRF or PRP and Oral Surgery Application | Evaluation | Conclusions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Filho et al., 2021 [71] J. of Oral and Maxillofacial surgery Systematic review and meta-analysis | PRF and PRP after tooth extraction in patients using oral anticoagulant therapy | Bleeding after extraction Pain Alveolitis after extraction | The use of PRF did not improve the risk of bleeding, pain score, and alveolitis after extraction. |
| Bao et al., 2021 [72] West China Journal of Stomatology Systematic review and meta-analysis | PRF after mandibular third molar extraction | Pain Swelling Soft tissue healing Trismus Alveolar osteitis Bone healing | PRF effectively reduced pain after extraction, attenuated post-extraction swelling, and promoted soft tissue healing. PRF significantly reduced trismus and alveolar osteitis. No positive effect was reported on bone healing vs. control group. |
| Franchini et al., 2019 [73] Blood transfusion Systematic review and meta-analysis | PRP in periodontal bone defects | PD CAL Gingival recession Bony defect | PRP was slightly more effective compared to control groups in all the outcomes described. |
| Al-Hamed et al., 2017 [74] J. of Oral and Maxillofacial surgery Systematic review and meta-analysis | PRF after mandibular third molar extraction | Pain Trismus Swelling PD Soft tissue healing Incidence of localized osteitis Bone healing | Positive results were recorded for all the outcomes described, but no beneficial role was reported in bone healing. |
| Salgado-Peralvo et al., 2022 [75] J Stomatol Oral Maxillofac Surg Systematic review | PRF in oroantral communication | Pain Soft tissue healing Number of analgesic OAC closure | PRF group had significantly lower pain and number of analgesics than control group. There was OAC closure in 100% of cases using PRF alone when diameter was up to 5 mm. |
| He et al., 2017 [76] J. of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery Systematic review and meta-analysis | PRF during lower third molar extraction | Wound healing Osseous and soft tissue regeneration Pain Swelling Alveolar osteitis | Local application of PRF after lower third molar extraction is a valid method for relieving pain and 3-day postoperative swelling and reducing the incidence of alveolar osteitis. |
| Vitenson et al., 2022 [77] J. of Oral Maxillofacial Surgery Systematic review and meta-analysis | A-PRF after mandibular third molar extraction | Pain Facial swelling Trismus Soft tissue healing | A-PRF resulted in lower pain scores after 2, 3, and 7 days, had a negligible effect on facial swelling and trismus, and seems to have some beneficial effect on soft tissue healing. |
| Bao et al., 2021 [78] J. of Oral Maxillofacial Surgery Systematic review and meta-analysis | L-PRF and A-PRF in mandibular third molar extraction | Postoperative pain Soft tissue healing | Application of A-PRF after third molar extraction had the best effect in improving postoperative pain after 3 and 7 days, and L-PRF promoted the degree of soft tissue healing after 7 days. |
| Ramos et al., 2022 [79] J. of Oral and Maxillofacial surgery Systematic review and meta-analysis | PRF, A-PRF, and L-PRF in impacted lower third molar extraction | Pain Edema Trismus Soft tissue healing Periodontal regeneration adjacent to the second molar | The use of L-PRF and A-PRF allows for better control of pain and edema, but neither has an effect on trisumus. PRF and L-PRF protocols improve soft tissue healing and probing depth at the third month after third molar surgery. |
| Xiang et al., 2019 [80] BMC Oral Health Systematic review and meta-analysis | PRF in mandibular third molar surgery | Pain Swelling Trismus Osteoblastic activity Soft tissue healing Alveolar osteitis | PRF only reduces some of the postoperative complications; it significantly relieved the pain and swelling and reduced the incidence of alveolar osteitis after the extraction of an impacted lower third molar, but no significant differences were revealed between PRF and non-PRF groups in trismus, osteoblastic activity and soft tissue healing. |
| Canellas et al., 2017 [81] Int J. of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery Systematic review and meta-analysis | PRF in mandibular third molar surgery | Postoperative pain Alveolar osteitis Swelling Bone healing | PRF reduced postoperative pain and swelling and showed a decrease in prevalence of alveolar osteitis. Further investigation needs to be conducted to assess the real effect of the PRF on bone healing. |
| Campana et al., 2023 [82] Journal of clinical medicine Systematic review | APC (L-PRF, A-PRF) after tooth extraction in patients on anticoagulant therapy | Postoperative bleeding Pain Wound healing | Patients on anticoagulant therapy who received APCs without discontinuing their medication experienced decreased postoperative bleeding, a shorter hemostasis time, reduced pain, and accelerated wound healing. |
| Zhu et al., 2021 [83] Int J. of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery Systematic review and meta-analysis | PRF in mandibular third molar surgery | Alveolar osteitis Pain Trismus Soft tissue healing Swelling | The use of PRF reduced the incidence of alveolar osteitis and postoperative pain following third molar surgery. Furthermore, PRF may also improve postoperative soft tissue healing. |
| Riberio et al., 2024 [84] Clin Oral Investig. Systematic review | L-PRF in third molar surgery | Pain Edema Postoperative healing | L-PRF plays an important role in reducing postoperative pain, edema, and the incidence of alveolar osteitis and infections. |
| Authors, Year Reference Journal Study Design | Application | Evaluation | Conclusions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lyris et al., 2021 [85] J Stomatol Oral Maxillofac Surg Systematic review and meta-analysis | * L-PRF in implant bed prior to implant placement | Implant stability quotient (ISQ) * | L-PRF had a positive effect on secondary implant stability. |
| Guan et al., 2023 [86] Heliyon Systematic review and meta-analysis | Application of PRF * on implant stability | Implant stability Bone healing and formation | PRF can increase implant stability and may accelerate bone healing and promote new bone formation at the implant site. |
| Authors, Year Reference Journal Study Design | Application | Evaluation | Conclusions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Miron et al., 2020 [87] Clinical oral investigations Systematic review and meta-analysis | PRF for the treatment of gingival recession | Root coverage CAL Keratinized mucosa width (KMW) PD | PRF used with coronally advanced flap improved CAL and root coverage vs. CAF alone but did not improve KMW or PD. |
| Gusman et al., 2021 [88] Journal of clinical and experimental dentistry Systematic review and meta-analysis | PRF in palatal wounds following free gingival graft harvesting | Palatal wound Epthelialization Postoperative pain | PRF may decrease postoperative pain and induce earlier complete wound epithelialization. |
| Skurska et al., 2023 [89] Adv Med Sci Systematic review | PRF in class II furcation defects | Wound healing | The adjunctive use of platelet-rich fibrin in surgical treatment of furcation defects |
| Castro et al., 2017 [90] J Clin Periodontol. Systematic review and meta-analysis | L-PRF in periodontal surgery | PD CAL Bone fill Keratinized tissue width (KTW) Recession reduction Root coverage (%) | Significant PD reduction, CAL gain, and bone fill were found when comparing L-PRF to open flap debridement. For furcation defects, significant PD reduction, CAL gain, and bone fill were reported when comparing L-PRF to OFD. When L-PRF was compared to a connective tissue graft, similar outcomes were recorded for PD reduction, CAL gain, KTW, and recession reduction. |
| Meza-Mauricio et al., 2021 [91] Clin Oral Investig Systematic review | PRF after free gingival graft harvesting | Healing Control of pain Postoperative bleeding in palatal area after free gingival graft harvesting | The use of a PRF membrane for the protection of the palatal donor site following free gingival graft harvesting procedures improves wound healing and patients’ quality of life. |
| Panda et al., 2020 [92] Materials Systematic review and meta-analysis | L-PRF on coronally advanced flap (CAF) procedure in recession defects (Miller’s class I and II) | Gingival thickness (GT) Width of keratinized gingiva (WKG) Root coverage (%) CAL Recession depth (RD) | A significant improvement in GT, CAL, and RD was found when treated with CAF + L-PRF. L-PRF use in addition to CAF showed favorable results for the treatment of class I and II gingival recession defects. |
| Authors, Year Reference Journal Study Design | Application | Evaluation | Conclusions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rusilas et al., 2020 [93] Stomatologija Systematic review | APC (PRF or PRP) in MRONJ | Mucosal integrity Absence of residual infection Presence of cutaneous fistulas Re-intervention necessary to healing Reduction in pain-VAS score evaluation | Faster wound closure (after 1 month) and decreased risk of infection in surgical site were observed in PRF group vs. control. Lower necessity of re-intervention was observed in PRF group as well as a lower VAS score was observed in PRF group after surgery. |
| Authors, Year Reference Journal Study Design | Application | Evaluation | Conclusions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Niu et al., 2018 [94] Implant dentistry Systematic review | PRP and L-PRP, PRF and L-PRF in alveolar ridge preservation | Alveolar width Alveolar height | Leukocyte- and platelet-rich fibrin might have a more positive effect on alveolar width and height preservation than PRP. |
| Miron et al., 2017 [95] Clinical oral investigations Systematic review | PRF in regenerative dentistry | PPD and CAL gain for intrabony defects Soft tissue generation Root coverage (%) for gingival recession CAL gain for furcation defects Dimensional change/density of hard tissue for bone regeneration | PRF leads to statistically superior periodontal repair (PPD and CAL gain) of intrabony defects when compared to OFD alone. The use of PRF led to a significant improvement in CAL when compared to controls (OFD alone), but the process can solely be defined as tissue “repair.” The use of PRF favors a slight gain in root coverage when compared to CAF alone, but further studies are needed to validate the potential advantages of the use of PRF for bone regeneration. |
| Miron et al., 2021 [96] Clinical oral investigations Systematic review and meta-analysis | PRF in periodontal intrabony defects | PD CAL gain Radiographic bone fill | The use of PRF in conjunction with open flap debridement statistically significantly reduced PD and improved CAL and RBF values. |
| Al-Maawi et al., 2021 [97] International journal of implant dentistry Systematic review | PRF in post-extraction sockets | Postoperative pain Wound healing Soft tissue regeneration Bone regeneration Bone loss | PRF significantly reduces postoperative pain (66.6% studies) and is most effective in the early healing period of 2–3 months after tooth extraction. Dimensional bone loss was lower in PRF group vs. spontaneous healing after 8–15 weeks. Socket fill was in 85% of cases and was higher in PRF group compared to spontaneous wound healing. |
| Moraschini et al., 2015 [98] International journal of oral and maxillofacial surgery Systematic review | APC in alveolar socket preservation | Healing Soft tissue epithelialization Postoperative pain and discomfort Hard tissue regeneration | The use of plasma concentrates seems to accelerate healing and soft tissue epithelialization in extraction sockets and reduce postoperative pain and discomfort. The use of PRF improved gain of keratinized gingiva after soft tissue surgery. Plasma concentrates reduce pain and inflammation and, therefore, provide more comfort postoperatively, but there is no evidence to date for their effect on bone regeneration. |
| Del Fabbro et al., 2014 [99] European journal of oral Systematic review and meta-analysis | APC in post-extraction socket healing | Hard and soft tissue healing Tissue regeneration Socket healing Postoperative complications Patient satisfaction Pain Swelling | There was a positive effect of platelet concentrates on soft tissue healing and the patient’s reported postoperative symptoms, like pain and swelling. Positive effects were also highlighted for bone formation, but the results need to be cautiously interpreted. |
| Del Fabbro et al., 2017 [100] Journal of oral and maxillofacial surgery Systematic review and meta-analysis | APC in post-extraction sockets | Soft tissue healing Swelling Trismus Incidence of alveolar osteitis Bone healing and remodeling | APCs should be used in post-extraction sites to improve clinical and radiographic outcomes, such as bone density and soft tissue healing, and postoperative symptoms (swelling, trismus), but their benefit is still not quantifiable in pain reduction. |
| Miron et al., 2017 [101] Tissue engineering Systematic review | PRF in soft tissue wound healing | Wound healing Soft tissue regeneration | PRF has positive effects on wound healing after regenerative therapy in various soft tissue defects. |
| Dragonas et al., 2019 [102] Int J. of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery Systematic review | L-PRF in different intra-oral bone grafting procedures | Bone regeneration Soft tissue healing Postoperative complications | The use of L-PRF in extraction sockets was associated with a modest beneficial effect by decreasing alveolar ridge remodeling and postoperative pain when compared to natural healing. The use of L-PRF in maxillary sinus augmentation was not associated with more favorable outcomes. |
| Anitua et al., 2022 [103] Bioengineering Systematic review and meta-analysis | PRP (L-PRP and P-PRP) in post-extractive alveolar bone regeneration | New bone formation Bone density | A statistically significant difference was also observed in the P-PRP group for bone density outcome. The L-PRP treated sockets also showed higher bone density (SMD, 0.88; 95% CI, 0.31 to 1.45) in comparison to control sockets. |
| Pan et al., 2019 [104] J Am Dent Assoc. Systematic review and meta-analysis | PRF in alveolar ridge preservation | Postoperative pain Soft tissue healing Bone density Horizontal and vertical ridge dimension Alveolar osteitis Bone height Bone fill | PRF may play a positive role in reducing postoperative pain during the first week and ridge dimension changes after tooth extraction (6-month follow-up). PRF may be associated with smaller mesial bone height changes and more bone fill after tooth extraction, but further clinical studies are needed. |
| Lin et al., 2019 [105] Int J of oral and maxillofacial implants Systematic review and meta-analysis | PRF in ridge preservation | Bone healing Ridge height and width Osteoblastic activity Bone volume and density | PRF alone in ridge preservation does not provide significant additional benefits when compared to natural healing sockets with regard to bone volume, bone density, and osteoblastic activity. |
| Caponio et al., 2023 [106] Clin Oral Investig. Systematic review and meta-analysis | L-PRF and P-PRP in alveolar ridge preservation | Post-extraction socket healing Bone formation | In alveolar ridge preservation, the use of L-PRF and P-PRP is beneficial because any PC increases new bone formation compared to spontaneous healing. |
| Authors, Year Reference Journal Study Design | Application | Evaluation | Conclusions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Meschi et al., 2016 [107] Platelets Systematic review | APC in endodontic healing | Bone healing Soft tissue healing Postoperative quality of life Root development Pulp vitality | APCs in endodontic treatments seem to contribute to the healing of soft and hard tissues, improve the patients’ quality of life in the early postoperative period, aid further root development, and support maintenance or regaining of pulp vitality. |
| Authors, Year Reference Journal Study Design | Application | Evaluation | Conclusions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Farshidfar et al., 2022 [108] International orthodontics Systematic review and meta-analysis | APC (I-PRF) in orthodontic tooth movement | Orthodontic canine movement | I-PRF seems to be efficient in accelerating the orthodontic tooth movement of the canines, especially in the 2nd month. |
| Authors, Year Reference Journal Study Design | Application | Evaluation | Conclusions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Maddheshiya et al., 2023 [109] National journal of maxillofacial surgery Systematic review | PRP for oral lichen planus | Pain Lesion appearance | PRP can be considered a potential alternative therapy in treating non-responsive oral lichen planus, alleviating clinical signs and symptoms associated with oral lichen planus. |
| Gupta et al., 2024 [110] Cureus Systematic review and meta-analysis | i-PRF for oral lichen planus | Pain Surface area of lesions Patient satisfaction | i-PRF can be a potential treatment for oral lichen planus. The use of i-PRF resulted in pain reduction, lesion size improvement, and increased patient satisfaction. |
| Gupta et al., 2024 [110] | ✓ | |||
| Maddheshiya et al., 2023 [109] | ✓ | |||
| Farshidfar et al., 2022 [108] | ✓ | |||
| Meschi et al., 2016 [107] | ✓ | |||
| Caponio et al., 2023 [106] | ✓ | |||
| Lin et al., 2019 [105] | ✓ | |||
| Pan et al., 2019 [104] | ✓ | |||
| Anitua et al., 2022 [103] | ✓ | |||
| Dragonas et al., 2019 [102] | ✓ | |||
| Miron et al., 2017 [101] | ✓ | |||
| Del Fabbro et al., 2017 [100] | ✓ | |||
| Del Fabbro et al., 2014 [99] | ✓ | |||
| Moraschini et al., 2015 [98] | ✓ | |||
| Al-Maawi et al., 2021 [97] | ✓ | |||
| Miron et al., 2021 [96] | ✓ | |||
| Miron et al., 2017 [95] | ✓ | |||
| Niu et al., 2018 [94] | ✓ | |||
| Rusilas et al., 2020 [93] | ✓ | |||
| Panda et al., 2020 [92] | ✓ | |||
| Meza-Mauricio et al., 2021 [91] | ✓ | |||
| Castro et al., 2017 [90] | ✓ | |||
| Skurska et al., 2023 [89] | ✓ | |||
| Gusman et al., 2021 [88] | ✓ | |||
| Miron et al., 2020 [87] | ✓ | |||
| Guan et al., 2023 [86] | ✓ | |||
| Lyris et al., 2021 [85] | ✓ | |||
| Riberio et al. 2024 [84] | ✓ | |||
| Zhu et al., 2021 [83] | ✓ | |||
| Campana et al., 2023 [82] | ✓ | |||
| Canellas et al., 2017 [81] | ✓ | |||
| Xiang et al., 2019 [80] | ✓ | |||
| Ramos et al., 2022 [79] | ✓ | |||
| Bao et al., 2021 [78] | ✓ | |||
| Vitenson et al., 2022 [77] | ✓ | |||
| He et al., 2017 [76] | ✓ | |||
| Salgado-Peralvo et al., 2022 [75] | ✓ | |||
| Al-Hamed et al., 2017 [74] | ✓ | |||
| Franchini et al., 2019 [73] | ✓ | |||
| Bao et al., 2021 [72] | ✓ | |||
| Filho et al., 2021 [71] | ✓ | |||
| No or one non-critical weakness: the systematic review provides an accurate and comprehensive summary of the results of the available studies that address the question of interest. | Weakness: the systematic review has more than one weakness but no critical flaws. It may provide an accurate summary of the results of the available studies that were included in the review. | Without non-critical weaknesses: the review has a critical flaw and may not provide an accurate and comprehensive summary of the available studies that address the question of interest. | More than one critical flaw with or without non-critical weaknesses: the review has more than one critical flaw and should not be relied on to provide an accurate and comprehensive summary of the available studies. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Acerra, A.; Caggiano, M.; Chiacchio, A.; Scognamiglio, B.; D’Ambrosio, F. PRF and PRP in Dentistry: An Umbrella Review. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 3224. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14093224
Acerra A, Caggiano M, Chiacchio A, Scognamiglio B, D’Ambrosio F. PRF and PRP in Dentistry: An Umbrella Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(9):3224. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14093224
Chicago/Turabian StyleAcerra, Alfonso, Mario Caggiano, Andrea Chiacchio, Bruno Scognamiglio, and Francesco D’Ambrosio. 2025. "PRF and PRP in Dentistry: An Umbrella Review" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 9: 3224. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14093224
APA StyleAcerra, A., Caggiano, M., Chiacchio, A., Scognamiglio, B., & D’Ambrosio, F. (2025). PRF and PRP in Dentistry: An Umbrella Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(9), 3224. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14093224








