Hypertension Types and Associated Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Lithuanians Aged 50–54 Years
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Population
2.2. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. General Characteristics
3.2. Primary Arterial Hypertension
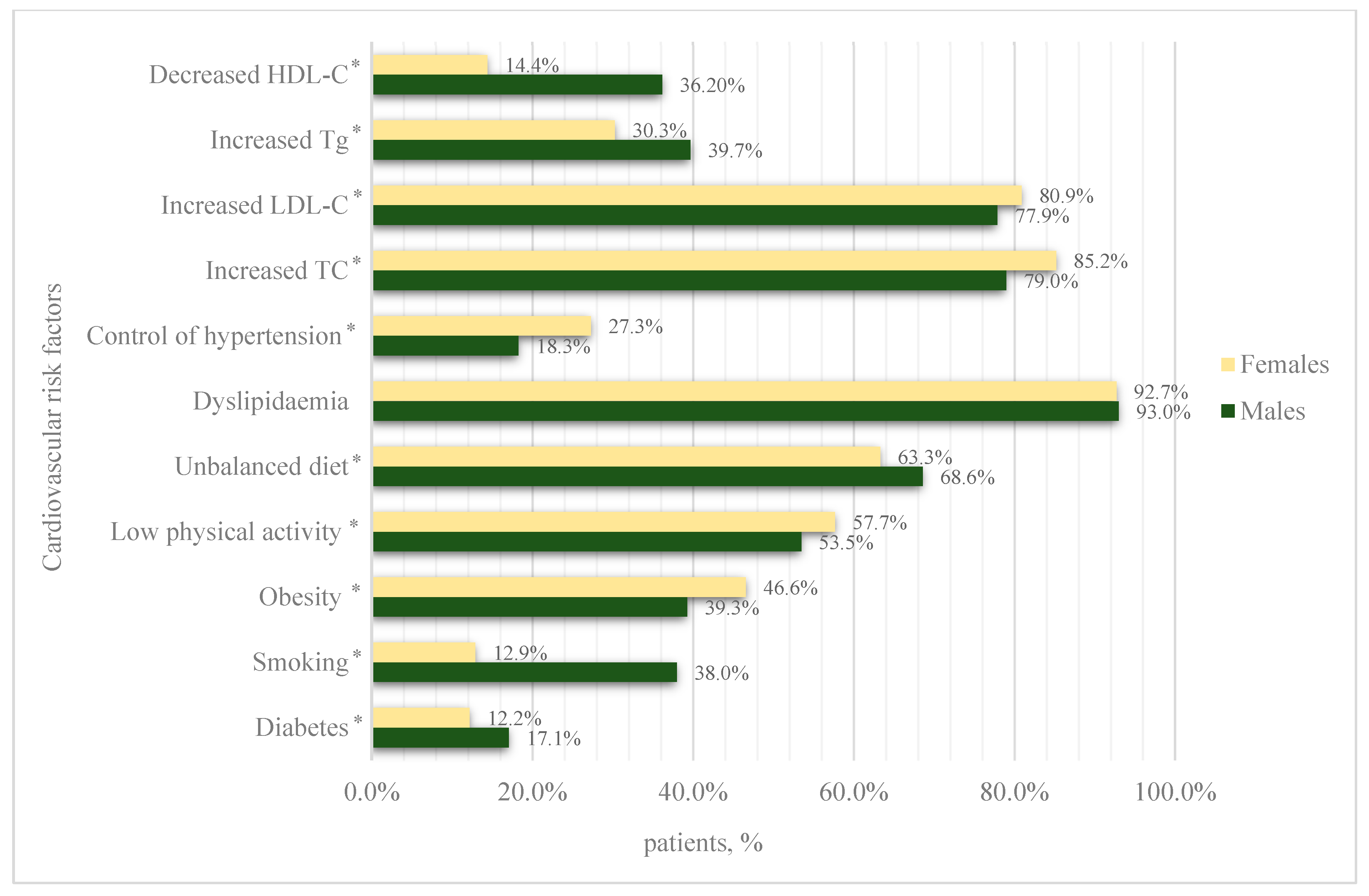
3.3. Non-Resistant Primary Arterial Hypertension
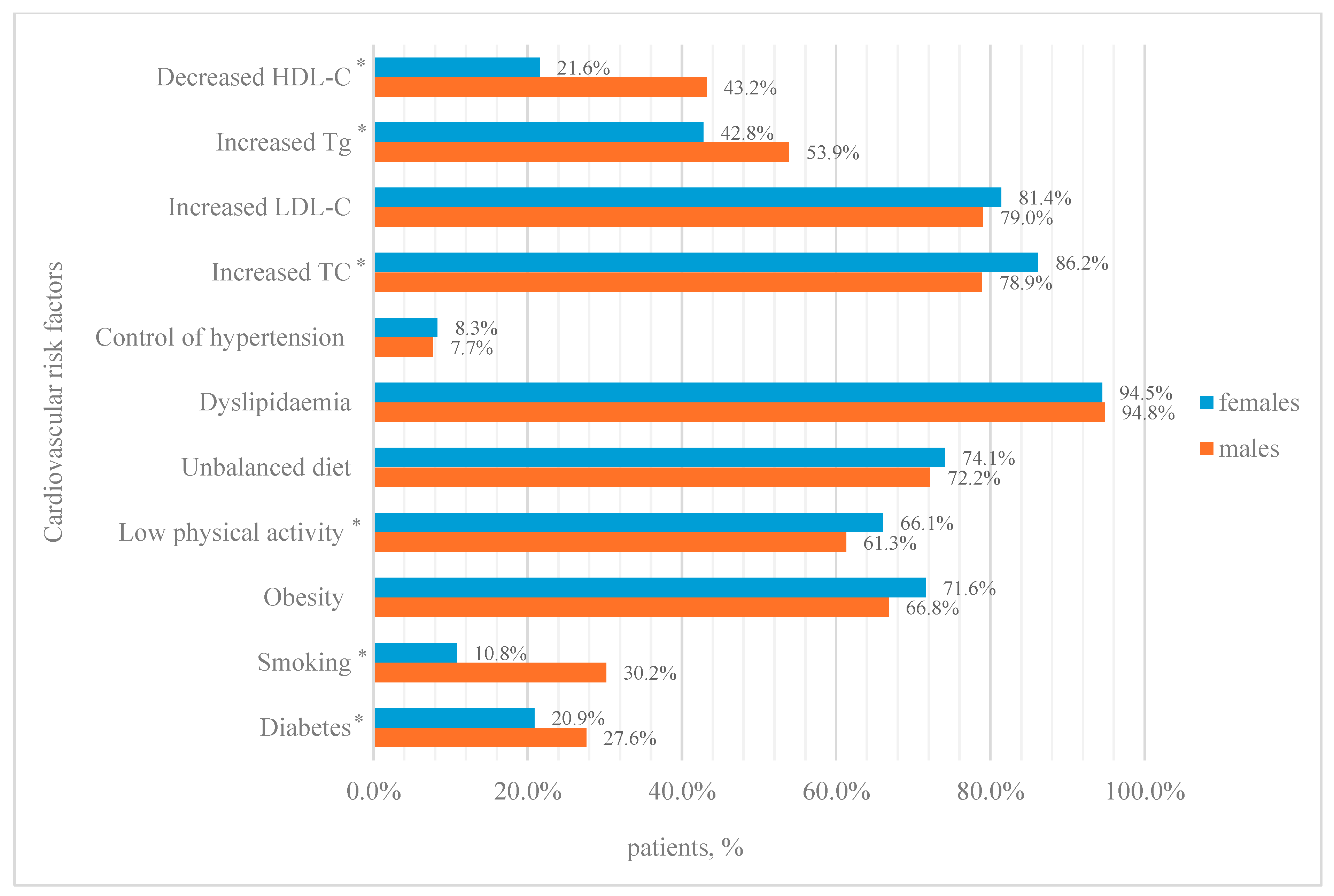
3.4. Resistant Hypertension
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- The prevalence of primary arterial hypertension in the Lithuanian population aged 50–54 years was 49.9%, but only 66.9% of patients with hypertension were receiving treatment.
- The prevalence of resistant primary arterial hypertension was 4.1%.
- The most common concomitant cardiovascular risk factor in both resistant and non-resistant arterial hypertension was dyslipidaemia, with a prevalence of over 90%.
6. Strengths and Limitations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TC | Total cholesterol |
| LDL-C | Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol |
| HDL-C | High-density lipoprotein cholesterol |
| Tgs | Triglycerides |
| LitHir | Lithuanian High Cardiovascular Risk Primary Prevention Programme |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| ANOVA | One-way analysis of variance |
References
- Rafieian-Kopaei, M.; Setorki, M.; Doudi, M.; Baradaran, A.; Nasri, H. Atherosclerosis: Process, Indicators, Risk Factors and New Hopes. Int. J. Prev. Med. 2014, 5, 927–946. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hong, X.; Ye, Q.; He, J.; Wang, Z.; Yang, H.; Qi, S.; Chen, X.; Wang, C.; Zhou, H.; Li, C.; et al. Prevalence and clustering of cardiovascular risk factors: A cross-sectional survey among Nanjing adults in China. BMJ Open 2018, 8, e020530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, B.; Carrillo-Larco, R.M.; Danaei, G.; Riley, L.M.; Paciorek, C.J.; Stevens, G.A.; Gregg, E.W.; Bennett, J.E.; Solomon, B.; Singleton, R.K.; et al. Worldwide trends in hypertension prevalence and progress in treatment and control from 1990 to 2019: A pooled analysis of 1201 population-representative studies with 104 million participants. Lancet 2021, 398, 957–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noubiap, J.J.; Nansseu, J.R.; Nyaga, U.F.; Sime, P.S.; Francis, I.; Bigna, J.J. Global prevalence of resistant hypertension: A meta-analysis of data from 3.2 million patients. Heart 2019, 105, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maas, A.H.; Appelman, Y.E. Gender differences in coronary heart disease. Neth. Heart J. 2010, 18, 598–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laucevičius, A.; Kasiulevičius, V.; Jatužis, D.; Petrulionienė, Ž.; Ryliškytė, L.; Rinkūnienė, E.; Badarienė, J.; Gustienė, O.; Šlapikas, R. Lithuanian High Cardiovascular Risk (LitHiR) primary prevention programme—Rationale and design. Semin. Cardiovasc. Med. 2012, 18, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McEvoy, J.W.; McCarthy, C.P.; Bruno, R.M.; Brouwers, S.; Canavan, M.D.; Ceconi, C.; Christodorescu, R.M.; Daskalopoulou, S.S.; Ferro, C.J.; Gerdts, E.; et al. 2024 ESC Guidelines for the management of elevated blood pressure and hypertension: Developed by the task force on the management of elevated blood pressure and hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and endorsed by the European Society of Endocrinology (ESE) and the European Stroke Organisation (ESO). Eur. Heart J. 2024, 45, 3912–4018. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lu, W.; Pikhart, H.; Tamosiunas, A.; Kubinova, R.; Capkova, N.; Malyutina, S.; Pająk, A.; Bobak, M. Prevalence, awareness, treatment and control of hypertension, diabetes and hypercholesterolemia, and associated risk factors in the Czech Republic, Russia, Poland and Lithuania: A cross-sectional study. BMC Public Health 2022, 22, 883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laucevičius, A.; Rinkūnienė, E.; Petrulionienė, Ž.; Ryliškytė, L.; Jucevičienė, A.; Puronaitė, R.; Badarienė, J.; Navickas, R.; Mikolaitytė, J.; Gargalskaitė, U.; et al. Trends in cardiovascular risk factor prevalence among Lithuanian middle-aged adults between 2009 and 2018. Atherosclerosis 2020, 299, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connelly, P.J.; Currie, G.; Delles, C. Sex Differences in the Prevalence, Outcomes and Management of Hypertension. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2022, 24, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dąbrowska, E.; Narkiewicz, K. Hypertension and Dyslipidemia: The Two Partners in Endothelium-Related Crime. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2023, 25, 605–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohseni, P.; Khalili, D.; Djalalinia, S.; Mohseni, H.; Farzadfar, F.; Shafiee, A.; Izadi, N. The synergistic effect of obesity and dyslipidemia on hypertension: Results from the STEPS survey. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2024, 16, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ciobanu, D.M.; Kilfiger, H.; Apan, B.; Roman, G.; Veresiu, I.A. Resistant Hypertension in Type 2 Diabetes: Prevalence and Patient Characteristics. Med. Pharm. Rep. 2015, 88, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glasser, N.J.; Jameson, J.C.; Huang, E.S.; Kronish, I.M.; Lindau, S.T.; Peek, M.E.; Tung, E.L.; Pollack, H.A. Male Gender Expressivity and Diagnosis and Treatment of Cardiovascular Disease Risks in Men. JAMA Netw. Open 2024, 7, e2441281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, I.X.; Chen, J.; Ali, K.; Chen, Q. Relationship Between Hypertension, Antihypertensive Drugs and Sexual Dysfunction in Men and Women: A Literature Review. Vasc. Health Risk Manag. 2023, 19, 691–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kario, K.; Hoshide, S.; Narita, K.; Okawara, Y.; Kanegae, H. Cardiovascular Prognosis in Drug-Resistant Hypertension Stratified by 24-Hour Ambulatory Blood Pressure: The JAMP Study. Hypertension 2021, 78, 1781–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahapatra, R.; Kaliyappan, A.; Chinnakali, P.; Hanumanthappa, N.; Govindarajalou, R.; Bammigatti, C. Prevalence and Risk Factors for Resistant Hypertension: Cross-Sectional Study from a Tertiary Care Referral Hospital in South India. Cureus. Available online: https://www.cureus.com/articles/67785-prevalence-and-risk-factors-for-resistant-hypertension-cross-sectional-study-from-a-tertiary-care-referral-hospital-in-south-india (accessed on 14 October 2024).
- Chan, K.K.; Chiang, L.; Choi, C.C.; Li, Y.; Chen, C.X. Prevalence and associated risk factors of resistant hypertension among Chinese hypertensive patients in primary care setting. BMC Prim. Care 2024, 25, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Total (N = 49,155) | Females (N = 32,018) | Males (N = 17,137) | p Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 95% CI | 95% CI | |||||
| Age (mean, years) | 51.6 (±1.46) | [51.6; 51.6] | 51.9 (±1.42) | [51.9; 51.9] | <0.005 | |
| Diabetes (N, %) | 4940 | 2716 (8.48%) | [8.18%; 8.79%] | 2224 (13.0%) | [12.5%; 13.5%] | <0.001 |
| Obesity (N, %) | 15,727 | 10,697 (33.4%) | [32.9%; 33.9%] | 5030 (29.4%) | [28.7%; 30.0%] | <0.001 |
| Smoking (N, %) | 10,768 | 4060 (12.7%) | [12.3%; 13.0%] | 6708 (39.1%) | [38.4%; 39.9%] | <0.001 |
| Low physical activity levels (N, %) | 24,551 | 16,314 (51.0%) | [50.4%; 51.5%] | 8237 (48.1%) | [47.3%; 48.8%] | <0.001 |
| Unbalanced diet (N, %) | 29,310 | 18,237 (57.0%) | [56.4%; 57.5%] | 11,073 (64.6%) | [63.9%; 65.3%] | <0.001 |
| Dyslipidaemia (N, %) | 44,643 | 29,043 (90.7%) | [90.4%; 91.0%] | 15,600 (91.0%) | [90.6%; 91.5%] | 0.244 |
| Increased LDL-C (N, %) | 38,469 | 25,391 (79.3%) | [78.9%; 79.7%] | 13,078 (76.3%) | [75.7%; 76.9%] | <0.001 |
| Females | Males | p-Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total (N) | 15,327 | 95% CI | 9222 | 95% CI | - | |
| Age, mean (±SD) (years) | 51.7 (±1.47) | [51.7; 51.7] | 52.0 (±1.42) | [51.9; 52.0] | <0.001 | |
| BMI, mean (±SD) | 30.5 (±6.11) | [30.4; 30.6] | 29.5 (±5.01) | [29.4; 29.6] | <0.001 | |
| Waist, mean (±SD) (cm) | 94.7 (±14.2) | [94.5; 95.0] | 101 (±12.7) | [101; 102] | <0.001 | |
| Systolic pressure, mean (±SD) (mmHg) | 142 (±15.2) | [141; 142] | 144 (±15.3) | [144; 144] | <0.001 | |
| Diastolic pressure, mean (±SD) (mmHg) | 86.9 (±9.17) | [86.7; 87.0] | 88.8 (±9.47) | [88.6; 89.0] | <0.001 | |
| Glucose, mean (±SD) (mmol/L) | 5.54 (±1.24) | [5.52; 5.56] | 5.84 (±1.62) | [5.81; 5.88] | <0.001 | |
| TC, mean (±SD) (mmol/L) | 6.16 (±1.18) | [6.14; 6.18] | 5.94 (±1.21) | [5.91; 5.96] | <0.001 | |
| LDL-C, mean (±SD) (mmol/L) | 3.87 (±1.04) | [3.86; 3.89] | 3.79 (±1.06) | [3.76; 3.81] | <0.001 | |
| HDL-C, mean (±SD) (mmol/L) | 1.61 (±0.44) | [1.60; 1.62] | 1.39 (±0.45) | [1.38; 1.39] | <0.001 | |
| Total (N = 49,155) | Females (N = 32,018) | Males (N = 17,137) | p Value | |||
| 95%CI | 95% CI | |||||
| Age (mean, years) | 51.6 (±1.46) | [51.6; 51.6] | 51.9 (±1.42) | [51.9; 51.9] | <0.005 | |
| Diabetes (N, %) | 4940 | 2716 (8.48%) | [8.18%; 8.79%] | 2224 (13.0%) | [12.5%; 13.5%] | <0.001 |
| Obesity (N, %) | 15,727 | 10,697 (33.4%) | [32.9%; 33.9%] | 5030 (29.4%) | [28.7%; 30.0%] | <0.001 |
| Smoking (N, %) | 10,768 | 4060 (12.7%) | [12.3%; 13.0%] | 6708 (39.1%) | [38.4%; 39.9%] | <0.001 |
| Low physical activity levels (N, %) | 24,551 | 16,314 (51.0%) | [50.4%; 51.5%] | 8237 (48.1%) | [47.3%; 48.8%] | <0.001 |
| Unbalanced diet (N, %) | 29,310 | 18,237 (57.0%) | [56.4%; 57.5%] | 11,073 (64.6%) | [63.9%; 65.3%] | <0.001 |
| Dyslipidaemia (N, %) | 44,643 | 29,043 (90.7%) | [90.4%; 91.0%] | 15,600 (91.0%) | [90.6%; 91.5%] | 0.244 |
| Increased LDL-C (N, %) | 38,469 | 25,391 (79.3%) | [78.9%; 79.7%] | 13,078 (76.3%) | [75.7%; 76.9%] | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Šileikienė, V.; Dženkevičiūtė, V.; Čypienė, A.; Smailytė, U.; Puronaitė, R.; Badarienė, J.; Laucevičius, A.; Butkevičiūtė, E.; Navickas, P.; Rinkūnienė, E. Hypertension Types and Associated Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Lithuanians Aged 50–54 Years. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 3177. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14093177
Šileikienė V, Dženkevičiūtė V, Čypienė A, Smailytė U, Puronaitė R, Badarienė J, Laucevičius A, Butkevičiūtė E, Navickas P, Rinkūnienė E. Hypertension Types and Associated Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Lithuanians Aged 50–54 Years. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(9):3177. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14093177
Chicago/Turabian StyleŠileikienė, Vaida, Vilma Dženkevičiūtė, Alma Čypienė, Urtė Smailytė, Roma Puronaitė, Jolita Badarienė, Aleksandras Laucevičius, Eglė Butkevičiūtė, Petras Navickas, and Egidija Rinkūnienė. 2025. "Hypertension Types and Associated Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Lithuanians Aged 50–54 Years" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 9: 3177. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14093177
APA StyleŠileikienė, V., Dženkevičiūtė, V., Čypienė, A., Smailytė, U., Puronaitė, R., Badarienė, J., Laucevičius, A., Butkevičiūtė, E., Navickas, P., & Rinkūnienė, E. (2025). Hypertension Types and Associated Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Lithuanians Aged 50–54 Years. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(9), 3177. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14093177






