Role of Respiratory Viruses in Severe Acute Respiratory Failure
Abstract
1. Introduction
Literature Search Strategy
2. Impact of Molecular Testing in Discovering Viruses in Lower Respiratory Tract Infections
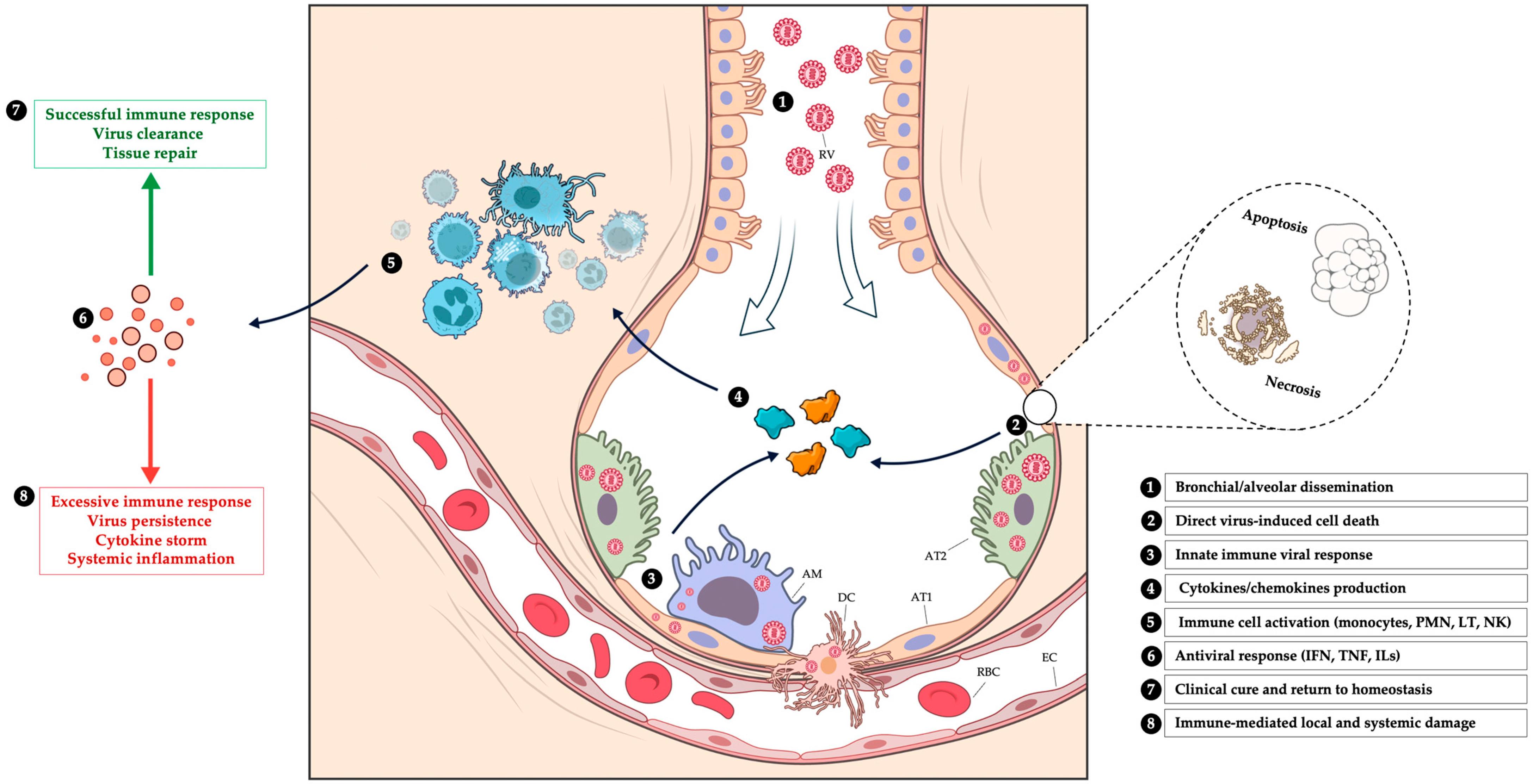
3. Physiopathology of Respiratory Viral Infections
3.1. Epithelial Tropism and Viral-Induced Cell Death
3.2. Immune Dysregulation and Inflammation-Mediated Injury
3.3. Histopathological Evidence from Human Studies
4. Clinical Consequences of Respiratory Virus in Severe Acute Respiratory Failure in ICU
5. Outcomes
Population at Risk of Severe Outcome
6. Treatment of Severe Respiratory Viral Infections
6.1. Noninvasive Respiratory Support in Viral Pneumonia
6.2. Antiviral Therapy
6.3. Immunomodulation
7. Vaccination as a Key Strategy Against Severe Respiratory Viral Infections
8. Future Risks
8.1. Post-Pandemic Effects
8.2. Emerging Threats
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ARDS | acute respiratory distress syndrome |
| ARF | acute respiratory failure |
| CAP | community-acquired pneumonia |
| CDC | Centers for Disease Control and Prevention |
| CI | confidence interval |
| COPD | chronic obstructive pulmonary disease |
| COVID-19 | Coronavirus Disease 2019 |
| FA-PP | Film-Array Pneumonia Panel |
| HFNC | high-flow nasal cannula |
| hMPV | human metapneumovirus |
| ICU | intensive care unit |
| IFN | Interferon |
| IRR | incidence rate ratio |
| LRTI | lower respiratory tract infection |
| MERS | Middle East Respiratory Syndrome |
| mPCR | multiplex PCR |
| NAI | neuraminidase inhibitor |
| NPI | non-pharmaceutical intervention |
| OR | odds ratio |
| PCR | Polymerase Chain Reaction |
| RSV | respiratory syncytial virus |
| RVI | respiratory viral infection |
| SARI | severe acute respiratory infection |
| SARS | Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome |
| SARS-CoV-2 | Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 |
| SOC | standard of care |
| TNF | tumor necrosis factor |
References
- Leber, A.L.; Lisby, J.G.; Hansen, G.; Relich, R.F.; Schneider, U.V.; Granato, P.; Young, S.; Pareja, J.; Hannet, I. Multicenter Evaluation of the QIAstat-Dx Respiratory Panel for Detection of Viruses and Bacteria in Nasopharyngeal Swab Specimens. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2020, 58, e00155-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visseaux, B.; Le Hingrat, Q.; Collin, G.; Bouzid, D.; Lebourgeois, S.; Le Pluart, D.; Deconinck, L.; Lescure, F.-X.; Lucet, J.-C.; Bouadma, L.; et al. Evaluation of the QIAstat-Dx Respiratory SARS-CoV-2 Panel, the First Rapid Multiplex PCR Commercial Assay for SARS-CoV-2 Detection. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2020, 58, e00630-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Someren Gréve, F.; Juffermans, N.P.; Bos, L.D.J.; Binnekade, J.M.; Braber, A.; Cremer, O.L.; de Jonge, E.; Molenkamp, R.; Ong, D.S.Y.; Rebers, S.P.H.; et al. Respiratory Viruses in Invasively Ventilated Critically Ill Patients-A Prospective Multcenter Observational Study. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 46, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byington, C.L.; Ampofo, K.; Stockmann, C.; Adler, F.R.; Herbener, A.; Miller, T.; Sheng, X.; Blaschke, A.J.; Crisp, R.; Pavia, A.T. Community Surveillance of Respiratory Viruses Among Families in the Utah Better Identification of Germs-Longitudinal Viral Epidemiology (BIG-LoVE) Study. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2015, 61, 1217–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voiriot, G.; Visseaux, B.; Cohen, J.; Nguyen, L.B.L.; Neuville, M.; Morbieu, C.; Burdet, C.; Radjou, A.; Lescure, F.-X.; Smonig, R.; et al. Viral-Bacterial Coinfection Affects the Presentation and Alters the Prognosis of Severe Community-Acquired Pneumonia. Crit. Care 2016, 20, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loubet, P.; Voiriot, G.; Houhou-Fidouh, N.; Neuville, M.; Bouadma, L.; Lescure, F.-X.; Descamps, D.; Timsit, J.-F.; Yazdanpanah, Y.; Visseaux, B. Impact of Respiratory Viruses in Hospital-Acquired Pneumonia in the Intensive Care Unit: A Single-Center Retrospective Study. J. Clin. Virol. 2017, 91, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin-Loeches, I.; Schultz, M.J.; Vincent, J.-L.; Alvarez-Lerma, F.; Bos, L.D.; Solé-Violán, J.; Torres, A.; Rodriguez, A. Increased Incidence of Co-Infection in Critically Ill Patients with Influenza. Intensive Care Med. 2017, 43, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zilberbeg, M.D.; Khan, I.; Shorr, A.F. Respiratory Viruses in Nosocomial Pneumonia: An Evolving Paradigm. Viruses 2023, 15, 1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jitmuang, A.; Puttinad, S.; Hemvimol, S.; Pansasiri, S.; Horthongkham, N. A Multiplex Pneumonia Panel for Diagnosis of Hospital-Acquired and Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia in the Era of Emerging Antimicrobial Resistance. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 977320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosai, K.; Akamatsu, N.; Ota, K.; Mitsumoto-Kaseida, F.; Sakamoto, K.; Hasegawa, H.; Izumikawa, K.; Mukae, H.; Yanagihara, K. BioFire FilmArray Pneumonia Panel Enhances Detection of Pathogens and Antimicrobial Resistance in Lower Respiratory Tract Specimens. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2022, 21, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, F.J.; Botero, L.E.; Isaza, J.P.; Cano, L.E.; López, L.; Tamayo, L.; Torres, A. Diagnostic Concordance between BioFire® FilmArray® Pneumonia Panel and Culture in Patients with COVID-19 Pneumonia Admitted to Intensive Care Units: The Experience of the Third Wave in Eight Hospitals in Colombia. Crit. Care 2022, 26, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, R.; Babushkin, F.; Finn, T.; Geller, K.; Alexander, H.; Datnow, C.; Uda, M.; Shapiro, M.; Paikin, S.; Lellouche, J. High Rates of Bacterial Pulmonary Co-Infections and Superinfections Identified by Multiplex PCR among Critically Ill COVID-19 Patients. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gastli, N.; Loubinoux, J.; Daragon, M.; Lavigne, J.-P.; Saint-Sardos, P.; Pailhoriès, H.; Lemarié, C.; Benmansour, H.; d’Humières, C.; Broutin, L.; et al. Multicentric Evaluation of BioFire FilmArray Pneumonia Panel for Rapid Bacteriological Documentation of Pneumonia. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2021, 27, 1308–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Ruan, S.-Y.; Pan, S.-C.; Lee, T.-F.; Chien, J.-Y.; Hsueh, P.-R. Performance of a Multiplex PCR Pneumonia Panel for the Identification of Respiratory Pathogens and the Main Determinants of Resistance from the Lower Respiratory Tract Specimens of Adult Patients in Intensive Care Units. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2019, 52, 920–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, J.; Yang, J.; Liu, L.; Chen, X.; Yang, G.; He, Y.; Sun, R. Evaluation and Clinical Practice of Pathogens and Antimicrobial Resistance Genes of BioFire FilmArray Pneumonia Panel in Lower Respiratory Tract Infections. Infection 2024, 52, 545–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verroken, A.; Favresse, J.; Anantharajah, A.; Rodriguez-Villalobos, H.; Wittebole, X.; Laterre, P.-F. Optimized Antibiotic Management of Critically Ill Patients with Severe Pneumonia Following Multiplex Polymerase Chain Reaction Testing: A Prospective Clinical Exploratory Trial. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Søgaard, K.K.; Hinic, V.; Goldenberger, D.; Gensch, A.; Schweitzer, M.; Bättig, V.; Siegemund, M.; Bassetti, S.; Bingisser, R.; Tamm, M.; et al. Evaluation of the Clinical Relevance of the Biofire© FilmArray Pneumonia Panel among Hospitalized Patients. Infection 2024, 52, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falsey, A.R.; Branche, A.R.; Croft, D.P.; Formica, M.A.; Peasley, M.R.; Walsh, E.E. Real-Life Assessment of BioFire FilmArray Pneumonia Panel in Adults Hospitalized with Respiratory Illness. J. Infect. Dis. 2024, 229, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Feng, B.; Shi, W.; Cheng, W.; Zhang, T. Concomitant Viral and Bacterial Pneumonia among Patients in ICU with Mechanical Respiratory Support. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2022, 16, 1482–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamel, N.A.; Alshahrani, M.Y.; Aboshanab, K.M.; El Borhamy, M.I. Evaluation of the BioFire FilmArray Pneumonia Panel Plus to the Conventional Diagnostic Methods in Determining the Microbiological Etiology of Hospital-Acquired Pneumonia. Biology 2022, 11, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enne, V.I.; Aydin, A.; Baldan, R.; Owen, D.R.; Richardson, H.; Ricciardi, F.; Russell, C.; Nomamiukor-Ikeji, B.O.; Swart, A.-M.; High, J.; et al. Multicentre Evaluation of Two Multiplex PCR Platforms for the Rapid Microbiological Investigation of Nosocomial Pneumonia in UK ICUs: The INHALE WP1 Study. Thorax 2022, 77, 1220–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchan, B.W.; Windham, S.; Balada-Llasat, J.-M.; Leber, A.; Harrington, A.; Relich, R.; Murphy, C.; Dien Bard, J.; Naccache, S.; Ronen, S.; et al. Practical Comparison of the BioFire FilmArray Pneumonia Panel to Routine Diagnostic Methods and Potential Impact on Antimicrobial Stewardship in Adult Hospitalized Patients with Lower Respiratory Tract Infections. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2020, 58, e00135-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matrosovich, M.N.; Matrosovich, T.Y.; Gray, T.; Roberts, N.A.; Klenk, H.-D. Human and Avian Influenza Viruses Target Different Cell Types in Cultures of Human Airway Epithelium. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 4620–4624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiege, J.K.; Langlois, R.A. Investigating Influenza A Virus Infection: Tools to Track Infection and Limit Tropism. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 6167–6170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumlin, U.; Olofsson, S.; Dimock, K.; Arnberg, N. Sialic Acid Tissue Distribution and Influenza Virus Tropism. Influenza Other Respir. Viruses 2008, 2, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinya, K.; Ebina, M.; Yamada, S.; Ono, M.; Kasai, N.; Kawaoka, Y. Influenza Virus Receptors in the Human Airway. Nature 2006, 440, 435–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolas de Lamballerie, C.; Pizzorno, A.; Dubois, J.; Julien, T.; Padey, B.; Bouveret, M.; Traversier, A.; Legras-Lachuer, C.; Lina, B.; Boivin, G.; et al. Characterization of Cellular Transcriptomic Signatures Induced by Different Respiratory Viruses in Human Reconstituted Airway Epithelia. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 11493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rameix-Welti, M.-A.; Le Goffic, R.; Hervé, P.-L.; Sourimant, J.; Rémot, A.; Riffault, S.; Yu, Q.; Galloux, M.; Gault, E.; Eléouët, J.-F. Visualizing the Replication of Respiratory Syncytial Virus in Cells and in Living Mice. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajon, A.E.; Lu, X.; Erdman, D.D.; Louie, J.; Schnurr, D.; George, K.S.; Koopmans, M.P.; Allibhai, T.; Metzgar, D. Molecular Epidemiology and Brief History of Emerging Adenovirus 14-Associated Respiratory Disease in the United States. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 202, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudding, B.A.; Wagner, S.C.; Zeller, J.A.; Gmelich, J.T.; French, G.R.; Top, F.H. Fatal Pneumonia Associated with Adenovirus Type 7 in Three Military Trainees. N. Engl. J. Med. 1972, 286, 1289–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arndt, U.; Wennemuth, G.; Barth, P.; Nain, M.; Al-Abed, Y.; Meinhardt, A.; Gemsa, D.; Bacher, M. Release of Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor and CXCL8/Interleukin-8 from Lung Epithelial Cells Rendered Necrotic by Influenza A Virus Infection. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 9298–9306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, W.Y.; Tang, J.W.; Yeung, A.C.M.; Chiu, L.C.M.; Sung, J.J.Y.; Chan, P.K.S. Avian Influenza Virus A/HK/483/97(H5N1) NS1 Protein Induces Apoptosis in Human Airway Epithelial Cells. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 2741–2751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atkin-Smith, G.K.; Duan, M.; Chen, W.; Poon, I.K.H. The Induction and Consequences of Influenza A Virus-Induced Cell Death. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, M.; Schulze, K.E.; Ghildyal, R.; Henstridge, D.C.; Kolanowski, J.L.; New, E.J.; Hong, Y.; Hsu, A.C.; Hansbro, P.M.; Wark, P.A.; et al. Respiratory Syncytial Virus Co-Opts Host Mitochondrial Function to Favour Infectious Virus Production. eLife 2019, 8, e42448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, C.H.T.; Chan, R.W.Y.; Ng, M.M.T.; Cheung, M.-C.; Ng, K.-C.; Chan, M.P.K.; Chan, L.L.Y.; Fong, J.H.M.; Nicholls, J.M.; Peiris, J.S.M.; et al. Tropism of Influenza B Viruses in Human Respiratory Tract Explants and Airway Organoids. Eur. Respir. J. 2019, 54, 1900008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clementi, N.; Ghosh, S.; De Santis, M.; Castelli, M.; Criscuolo, E.; Zanoni, I.; Clementi, M.; Mancini, N. Viral Respiratory Pathogens and Lung Injury. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2021, 34, e00103-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, A.H.; Cardani, A.; Braciale, T.J. ƒcousse The Host Immune Response in Respiratory Virus Infection: Balancing Virus Clearance and Immunopathology. Semin. Immunopathol. 2016, 38, 471–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murawski, M.R.; Bowen, G.N.; Cerny, A.M.; Anderson, L.J.; Haynes, L.M.; Tripp, R.A.; Kurt-Jones, E.A.; Finberg, R.W. Respiratory Syncytial Virus Activates Innate Immunity through Toll-Like Receptor 2. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 1492–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Metzger, D.W. Inhibition of Pulmonary Antibacterial Defense by Interferon-γ during Recovery from Influenza Infection. Nat. Med. 2008, 14, 558–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stark, J.M.; Stark, M.A.; Colasurdo, G.N.; LeVine, A.M. Decreased Bacterial Clearance from the Lungs of Mice Following Primary Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection. J. Med. Virol. 2006, 78, 829–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iverson, A.R.; Boyd, K.L.; McAuley, J.L.; Plano, L.R.; Hart, M.E.; McCullers, J.A. Influenza Virus Primes Mice for Pneumonia From Staphylococcus Aureus. J. Infect. Dis. 2011, 203, 880–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taubenberger, J.K.; Morens, D.M. The Pathology of Influenza Virus Infections. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2008, 3, 499–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.E.; Gonzales, R.A.; Olson, S.J.; Wright, P.F.; Graham, B.S. The Histopathology of Fatal Untreated Human Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection. Mod. Pathol. 2007, 20, 108–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritt, B.S.; Aubry, M.C. Histopathology of Viral Infections of the Lung. Semin. Diagn. Pathol. 2017, 34, 510–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, S.O.; Kozakewich, H.P.W.; Perez-Atayde, A.R.; McAdam, A.J. Pathology of Human Metapneumovirus Infection: Insights into the Pathogenesis of a Newly Identified Respiratory Virus. Pediatr. Dev. Pathol. 2004, 7, 478–486; discussion 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mokrani, D.; Le Hingrat, Q.; Thy, M.; Choquet, C.; Joly, V.; Lariven, S.; Rioux, C.; Deconinck, L.; Loubet, P.; Papo, T.; et al. Clinical Characteristics and Outcomes of Respiratory Syncytial Virus-Associated ARF in Immunocompetent Patients: A Seven-Year Experience at a Tertiary Hospital in France. J. Infect. 2024, 89, 106180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodruff, R.C.; Melgar, M.; Pham, H.; Sperling, L.S.; Loustalot, F.; Kirley, P.D.; Austin, E.; Yousey-Hindes, K.; Openo, K.P.; Ryan, P.; et al. Acute Cardiac Events in Hospitalized Older Adults with Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection. JAMA Intern. Med. 2024, 184, 602–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren-Gash, C.; Blackburn, R.; Whitaker, H.; McMenamin, J.; Hayward, A.C. Laboratory-Confirmed Respiratory Infections as Triggers for Acute Myocardial Infarction and Stroke: A Self-Controlled Case Series Analysis of National Linked Datasets from Scotland. Eur. Respir. J. 2018, 51, 1701794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shorr, A.F.; Fisher, K.; Micek, S.T.; Kollef, M.H. The Burden of Viruses in Pneumonia Associated with Acute Respiratory Failure: An Underappreciated Issue. Chest 2018, 154, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.-H.; Hong, S.-B.; Ko, G.-B.; Lee, Y.; Park, H.J.; Park, S.-Y.; Moon, S.M.; Cho, O.-H.; Park, K.-H.; Chong, Y.P.; et al. Viral Infection in Patients with Severe Pneumonia Requiring Intensive Care Unit Admission. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 186, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burk, M.; El-Kersh, K.; Saad, M.; Wiemken, T.; Ramirez, J.; Cavallazzi, R. Viral Infection in Community-Acquired Pneumonia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2016, 25, 178–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jennings, L.C.; Anderson, T.P.; Beynon, K.A.; Chua, A.; Laing, R.T.R.; Werno, A.M.; Young, S.A.; Chambers, S.T.; Murdoch, D.R. Incidence and Characteristics of Viral Community-Acquired Pneumonia in Adults. Thorax 2008, 63, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieberman, D.; Shimoni, A.; Shemer-Avni, Y.; Keren-Naos, A.; Shtainberg, R.; Lieberman, D. Respiratory Viruses in Adults with Community-Acquired Pneumonia. Chest 2010, 138, 811–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montull, B.; Menéndez, R.; Torres, A.; Reyes, S.; Méndez, R.; Zalacaín, R.; Capelastegui, A.; Rajas, O.; Borderías, L.; Martin-Villasclaras, J.; et al. Predictors of Severe Sepsis among Patients Hospitalized for Community-Acquired Pneumonia. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0145929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krammer, F.; Smith, G.J.D.; Fouchier, R.A.M.; Peiris, M.; Kedzierska, K.; Doherty, P.C.; Palese, P.; Shaw, M.L.; Treanor, J.; Webster, R.G.; et al. Influenza. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2018, 4, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fartoukh, M.; Voiriot, G.; Guérin, L.; Ricard, J.D.; Combes, A.; Faure, M.; Benghanem, S.; de Montmollin, E.; Tandjaoui-Lambiotte, Y.; Vieillard-Baron, A.; et al. Seasonal Burden of Severe Influenza Virus Infection in the Critically Ill Patients, Using the Assistance Publique-Hôpitaux de Paris Clinical Data Warehouse: A Pilot Study. Ann. Intensive Care 2021, 11, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Prost, N.; Audureau, E.; Guillon, A.; Handala, L.; Préau, S.; Guigon, A.; Uhel, F.; Le Hingrat, Q.; Delamaire, F.; Grolhier, C.; et al. Clinical Phenotypes and Outcomes Associated with SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Sublineage JN.1 in Critically Ill COVID-19 Patients: A Prospective, Multicenter Cohort Study in France, November 2022 to January 2024. Ann. Intensive Care 2024, 14, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datadot [En Ligne]. COVID-19 Cases|WHO COVID-19 Dashboard. Available online: https://data.who.int/dashboards/covid19/cases (accessed on 21 March 2025).
- Kaku, Y.; Uriu, K.; Okumura, K.; Genotype to Phenotype Japan (G2P-Japan) Consortium; Ito, J.; Sato, K. Virological Characteristics of the SARS-CoV-2 KP.3.1.1 Variant. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2024, 24, e609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaillet, A.; Layese, R.; Fourati, S.; Celante, H.; Pham, T.; Benghanem, S.; Mekontso Dessap, A.; de Montmollin, E.; Pirault, J.; Vieillard-Baron, A.; et al. Clinical Phenotypes and Outcomes Associated with Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection in Critically Ill Patients: A Retrospective Multicentre Cohort Study in Great Paris Area Hospitals, 2017–2023. J. Infect. Dis. 2025, jiaf129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philippot, Q.; Rammaert, B.; Dauriat, G.; Daubin, C.; Schlemmer, F.; Costantini, A.; Tandjaoui-Lambiotte, Y.; Neuville, M.; Desrochettes, E.; Ferré, A.; et al. Human Metapneumovirus Infection Is Associated with a Substantial Morbidity and Mortality Burden in Adult Inpatients. Heliyon 2024, 10, e33231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.; Zhou, Q.; Li, W.; Xiao, W.; Li, S.; Liu, B.; Li, H.; Cui, Y.; Lu, R.; Li, Y.; et al. A Prediction Model for Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome in Immunocompetent Adults with Adenovirus-Associated Pneumonia: A Multicenter Retrospective Analysis. BMC Pulm. Med. 2023, 23, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, S.; Reinhart, K.; Couture, A.; Kniss, K.; Davis, C.T.; Kirby, M.K.; Murray, E.L.; Zhu, S.; Kraushaar, V.; Wadford, D.A.; et al. Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza A(H5N1) Virus Infections in Humans. N. Engl. J. Med. 2025, 392, 843–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajema, K.L.; Bui, D.P.; Yan, L.; Li, Y.; Rajeevan, N.; Vergun, R.; Berry, K.; Huang, Y.; Lin, H.-M.; Aslan, M.; et al. Severity and Long-Term Mortality of COVID-19, Influenza, and Respiratory Syncytial Virus. JAMA Intern. Med. 2025, 185, 324–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grangier, B.; Vacheron, C.-H.; De Marignan, D.; Casalegno, J.-S.; Couray-Targe, S.; Bestion, A.; Ader, F.; Richard, J.-C.; Frobert, E.; Argaud, L.; et al. Comparison of Mortality and Outcomes of Four Respiratory Viruses in the Intensive Care Unit: A Multicenter Retrospective Study. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 6690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cillóniz, C.; Ewig, S.; Ferrer, M.; Polverino, E.; Gabarrús, A.; Puig de la Bellacasa, J.; Mensa, J.; Torres, A. Community-Acquired Polymicrobial Pneumonia in the Intensive Care Unit: Aetiology and Prognosis. Crit. Care 2011, 15, R209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coussement, J.; Zuber, B.; Garrigues, E.; Gros, A.; Vandueren, C.; Epaillard, N.; Voiriot, G.; Tandjaoui-Lambiotte, Y.; Lascarrou, J.-B.; Boissier, F.; et al. Characteristics and Outcomes of Patients in the ICU with Respiratory Syncytial Virus Compared with Those with Influenza Infection: A Multicenter Matched Cohort Study. Chest 2022, 161, 1475–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.-H.; Hong, S.-B.; Huh, J.W.; Jung, J.; Kim, M.J.; Chong, Y.P.; Kim, S.-H.; Sung, H.; Koo, H.J.; Do, K.-H.; et al. Outcomes of Severe Human Metapneumovirus-Associated Community-Acquired Pneumonia in Adults. J. Clin. Virol. 2019, 117, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasvold, J.; Sjoding, M.; Pohl, K.; Cooke, C.; Hyzy, R.C. The Role of Human Metapneumovirus in the Critically Ill Adult Patient. J. Crit. Care 2016, 31, 233–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vento, T.J.; Prakash, V.; Murray, C.K.; Brosch, L.C.; Tchandja, J.B.; Cogburn, C.; Yun, H.C. Pneumonia in Military Trainees: A Comparison Study Based on Adenovirus Serotype 14 Infection. J. Infect. Dis. 2011, 203, 1388–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiemken, T.; Peyrani, P.; Bryant, K.; Kelley, R.R.; Summersgill, J.; Arnold, F.; Carrico, R.; McKinney, W.P.; Jonsson, C.; Carrico, K.; et al. Incidence of Respiratory Viruses in Patients with Community-Acquired Pneumonia Admitted to the Intensive Care Unit: Results from the Severe Influenza Pneumonia Surveillance (SIPS) Project. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2013, 32, 705–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Gu, L.; Zhang, X.; Pu, Z.; Yang, G.; Liu, B.; Nie, Q.; et al. Disease Severity and Clinical Outcomes of Community-Acquired Pneumonia Caused by Non-Influenza Respiratory Viruses in Adults: A Multicentre Prospective Registry Study from the CAP-China Network. Eur. Respir. J. 2019, 54, 1802406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, E.; Yang, A.; Tardrew, S.; Ison, M.G. Parainfluenza Virus in Hospitalized Adults: A 7-Year Retrospective Study. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2019, 68, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karhu, J.; Ala-Kokko, T.I.; Vuorinen, T.; Ohtonen, P.; Syrjälä, H. Lower Respiratory Tract Virus Findings in Mechanically Ventilated Patients with Severe Community-Acquired Pneumonia. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2014, 59, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.-H.; Huh, J.W.; Hong, S.-B.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, S.-H.; Sung, H.; Do, K.-H.; Lee, S.-O.; Kim, M.-N.; Jeong, J.-Y.; et al. Clinical Characteristics and Outcomes of Severe Rhinovirus-Associated Pneumonia Identified by Bronchoscopic Bronchoalveolar Lavage in Adults: Comparison with Severe Influenza Virus-Associated Pneumonia. J. Clin. Virol. 2015, 62, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaunt, E.R.; Hardie, A.; Claas, E.C.J.; Simmonds, P.; Templeton, K.E. Epidemiology and Clinical Presentations of the Four Human Coronaviruses 229E, HKU1, NL63, and OC43 Detected over 3 Years Using a Novel Multiplex Real-Time PCR Method. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2010, 48, 2940–2947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, H.; Hong, S.-B.; Huh, J.W.; Sung, H.; Do, K.-H.; Lee, S.-O.; Lim, C.-M.; Koh, Y.; Choi, S.-H. Clinical Features and Outcomes of Severe Pneumonia Caused by Endemic Human Coronavirus in Adults. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2022, 205, 1116–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.-H.; Huh, J.W.; Hong, S.-B.; Jung, J.; Kim, M.J.; Chong, Y.P.; Kim, S.-H.; Sung, H.; Chae, E.J.; Do, K.-H.; et al. Severe Human Bocavirus-Associated Pneumonia in Adults at a Referral Hospital, Seoul, South Korea. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2021, 27, 226–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishiguro, T.; Hirota, S.; Kobayashi, Y.; Takano, K.; Kobayashi, Y.; Shimizu, Y.; Takayanagi, N. Fatal Primary Human Bocavirus Pneumonia in an Immunocompetent Adult. Intern. Med. 2020, 59, 421–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, N.; Lui, G.C.Y.; Wong, K.T.; Li, T.C.M.; Tse, E.C.M.; Chan, J.Y.C.; Yu, J.; Wong, S.S.M.; Choi, K.W.; Wong, R.Y.K.; et al. High Morbidity and Mortality in Adults Hospitalized for Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infections. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2013, 57, 1069–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celante, H.; Oubaya, N.; Fourati, S.; Beaune, S.; Khellaf, M.; Casalino, E.; Ricard, J.-D.; Vieillard-Baron, A.; Heming, N.; Mekontso Dessap, A.; et al. Prognosis of Hospitalised Adult Patients with Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection: A Multicentre Retrospective Cohort Study. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2023, 29, 943.e1–943.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ling, L.; Wong, S.H.; Wang, M.H.; Fitzgerald, J.R.; Zou, X.; Fang, S.; Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Hu, W.; et al. Outcomes of Respiratory Viral-Bacterial Co-Infection in Adult Hospitalized Patients. eClinicalMedicine 2021, 37, 100955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loubet, P.; Fernandes, J.; de Pouvourville, G.; Sosnowiez, K.; Elong, A.; Guilmet, C.; Omichessan, H.; Bureau, I.; Fagnani, F.; Emery, C.; et al. Respiratory Syncytial Virus-Related Hospital Stays in Adults in France from 2012 to 2021: A National Hospital Database Study. J. Clin. Virol. 2024, 171, 105635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackerson, B.; Tseng, H.F.; Sy, L.S.; Solano, Z.; Slezak, J.; Luo, Y.; Fischetti, C.A.; Shinde, V. Severe Morbidity and Mortality Associated with Respiratory Syncytial Virus Versus Influenza Infection in Hospitalized Older Adults. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2019, 69, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beumer, M.C.; Koch, R.M.; van Beuningen, D.; OudeLashof, A.M.; van de Veerdonk, F.L.; Kolwijck, E.; van der Hoeven, J.G.; Bergmans, D.C.; Hoedemaekers, C.W.E. Influenza Virus and Factors That Are Associated with ICU Admission, Pulmonary Co-Infections and ICU Mortality. J. Crit. Care 2019, 50, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdier, V.; Lilienthal, F.; Desvergez, A.; Gazaille, V.; Winer, A.; Paganin, F. Severe Forms of Influenza Infections Admitted in Intensive Care Units: Analysis of Mortality Factors. Influenza Other Respir. Viruses 2023, 17, e13168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonmarin, I.; Belchior, E.; Bergounioux, J.; Brun-Buisson, C.; Mégarbane, B.; Chappert, J.L.; Hubert, B.; Strat, Y.L.; Lévy-Bruhl, D. Intensive Care Unit Surveillance of Influenza Infection in France: The 2009/10 Pandemic and the Three Subsequent Seasons. Eurosurveillance 2015, 20, 30066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouzid, D.; Hadad, O.; Bertine, M.; Houhou-Fidouh, N.; Mirand, A.; Duval, X.; Bunel, V.; Borie, R.; Lucet, J.C.; Descamps, D.; et al. Rhinoviruses: Molecular Diversity and Clinical Characteristics. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2022, 118, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boon, H.; Meinders, A.-J.; van Hannen, E.J.; Tersmette, M.; Schaftenaar, E. Comparative Analysis of Mortality in Patients Admitted with an Infection with Influenza A/B Virus, Respiratory Syncytial Virus, Rhinovirus, Metapneumovirus or SARS-CoV-2. Influenza Other Respir. Viruses 2024, 18, e13237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Nava, G.; Egoryan, G.; Dong, T.; Zhang, Q.; Hyser, E.; Poudel, B.; Yanez-Bello, M.A.; Trelles-Garcia, D.P.; Chung, C.W.; Pyakuryal, B.; et al. Comparison of Clinical Characteristics and Outcomes of Hospitalized Patients with Seasonal Coronavirus Infection and COVID-19: A Retrospective Cohort Study. BMC Infect. Dis. 2022, 22, 618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, N.; Smith, S.; Zelyas, N.; Klarenbach, S.; Zapernick, L.; Bekking, C.; So, H.; Yip, L.; Tipples, G.; Taylor, G.; et al. Burden of Noninfluenza Respiratory Viral Infections in Adults Admitted to Hospital: Analysis of a Multiyear Canadian Surveillance Cohort from 2 Centres. CMAJ 2021, 193, E439–E446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savic, M.; Penders, Y.; Shi, T.; Branche, A.; Pirçon, J.-Y. Respiratory Syncytial Virus Disease Burden in Adults Aged 60 Years and Older in High-Income Countries: A Systematic Literature Review and Meta-Analysis. Influenza Other Respir. Viruses 2023, 17, e13031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maleki, F.; Welch, V.; Lopez, S.M.C.; Cane, A.; Langer, J.; Enstone, A.; Markus, K.; Wright, O.; Hewitt, N.; Whittle, I. Understanding the Global Burden of Influenza in Adults Aged 18–64 Years: A Systematic Literature Review from 2012 to 2022. Adv. Ther. 2023, 40, 4166–4188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Branche, A.R.; Saiman, L.; Walsh, E.E.; Falsey, A.R.; Sieling, W.D.; Greendyke, W.; Peterson, D.R.; Vargas, C.Y.; Phillips, M.; Finelli, L. Incidence of Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection Among Hospitalized Adults, 2017-2020. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2022, 74, 1004–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Branche, A.R.; Saiman, L.; Walsh, E.E.; Falsey, A.R.; Jia, H.; Barrett, A.; Alba, L.; Phillips, M.; Finelli, L. Change in Functional Status Associated with Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection in Hospitalized Older Adults. Influenza Other Respir. Viruses 2022, 16, 1151–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajema, K.L.; Yan, L.; Li, Y.; Argraves, S.; Rajeevan, N.; Fox, A.; Vergun, R.; Berry, K.; Bui, D.; Huang, Y.; et al. Respiratory Syncytial Virus Vaccine Effectiveness among US Veterans, September, 2023 to March, 2024: A Target Trial Emulation Study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, M.; Demoule, A.; Hajage, D.; Pham, T.; Combes, A.; Dres, M.; Lebbah, S.; Kimmoun, A.; Mercat, A.; Beduneau, G.; et al. Benefits and Risks of Noninvasive Oxygenation Strategy in COVID-19: A Multicenter, Prospective Cohort Study (COVID-ICU) in 137 Hospitals. Crit. Care 2021, 25, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouadma, L.; Mekontso-Dessap, A.; Burdet, C.; Merdji, H.; Poissy, J.; Dupuis, C.; Guitton, C.; Schwebel, C.; Cohen, Y.; Bruel, C.; et al. High-Dose Dexamethasone and Oxygen Support Strategies in Intensive Care Unit Patients with Severe COVID-19 Acute Hypoxemic Respiratory Failure: The COVIDICUS Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Intern. Med. 2022, 182, 906–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Guyatt, G.; Uyeki, T.M.; Liu, M.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Shen, Y.; Xu, J.; Zheng, Q.; Li, Z.; et al. Antivirals for Treatment of Severe Influenza: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis of Randomised Controlled Trials. Lancet 2024, 404, 753–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, G.; Carbonell, R.; Díaz, E.; Martín-Loeches, I.; Restrepo, M.I.; Reyes, L.F.; Solé-Violán, J.; Bodí, M.; Canadell, L.; Guardiola, J.; et al. Effectiveness of Prolonged versus Standard-Course of Oseltamivir in Critically Ill Patients with Severe Influenza Infection: A Multicentre Cohort Study. J. Med. Virol. 2023, 95, e29010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duval, X.; van der Werf, S.; Blanchon, T.; Mosnier, A.; Bouscambert-Duchamp, M.; Tibi, A.; Enouf, V.; Charlois-Ou, C.; Vincent, C.; Andreoletti, L.; et al. Efficacy of Oseltamivir-Zanamivir Combination Compared to Each Monotherapy for Seasonal Influenza: A Randomized Placebo-Controlled Trial. PLoS Med. 2010, 7, e1000362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.; Ison, M.G.; Mira, J.-P.; Welte, T.; Hwan Ha, J.; Hui, D.S.; Zhong, N.; Saito, T.; Katugampola, L.; Collinson, N.; et al. Combining Baloxavir Marboxil with Standard-of-Care Neuraminidase Inhibitor in Patients Hospitalised with Severe Influenza (FLAGSTONE): A Randomised, Parallel-Group, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Superiority Trial. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2022, 22, 718–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejada, S.; Martinez-Reviejo, R.; Karakoc, H.N.; Peña-López, Y.; Manuel, O.; Rello, J. Ribavirin for Treatment of Subjects with Respiratory Syncytial Virus-Related Infection: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Adv. Ther. 2022, 39, 4037–4051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanula, R.; Bortolussi-Courval, É.; Mendel, A.; Ward, B.J.; Lee, T.C.; McDonald, E.G. Evaluation of Oseltamivir Used to Prevent Hospitalization in Outpatients with Influenza: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. JAMA Intern. Med. 2024, 184, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gubareva, L.V.; Besselaar, T.G.; Daniels, R.S.; Fry, A.; Gregory, V.; Huang, W.; Hurt, A.C.; Jorquera, P.A.; Lackenby, A.; Leang, S.-K.; et al. Global Update on the Susceptibility of Human Influenza Viruses to Neuraminidase Inhibitors, 2015–2016. Antivir. Res. 2017, 146, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lina, B.; Boucher, C.; Osterhaus, A.; Monto, A.S.; Schutten, M.; Whitley, R.J.; Nguyen-Van-Tam, J.S. Five Years of Monitoring for the Emergence of Oseltamivir Resistance in Patients with Influenza A Infections in the Influenza Resistance Information Study. Influenza Other Respir. Viruses 2018, 12, 267–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohno, S.; Yen, M.-Y.; Cheong, H.-J.; Hirotsu, N.; Ishida, T.; Kadota, J.; Mizuguchi, M.; Kida, H.; Shimada, J. S-021812 Clinical Study Group Phase III Randomized, Double-Blind Study Comparing Single-Dose Intravenous Peramivir with Oral Oseltamivir in Patients with Seasonal Influenza Virus Infection. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 5267–5276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.-D.; Wang, X.; Yu, S.-L.; Ding, Y.-H.; Wang, M.-L.; Wang, J.-N. Clinical Effectiveness of Intravenous Peramivir Compared with Oseltamivir in Patients with Severe Influenza A with Primary Viral Pneumonia: A Randomized Controlled Study. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2021, 8, ofaa562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marty, F.M.; Vidal-Puigserver, J.; Clark, C.; Gupta, S.K.; Merino, E.; Garot, D.; Chapman, M.J.; Jacobs, F.; Rodriguez-Noriega, E.; Husa, P.; et al. Intravenous Zanamivir or Oral Oseltamivir for Hospitalised Patients with Influenza: An International, Randomised, Double-Blind, Double-Dummy, Phase 3 Trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2017, 5, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayden, F.G.; Sugaya, N.; Hirotsu, N.; Lee, N.; de Jong, M.D.; Hurt, A.C.; Ishida, T.; Sekino, H.; Yamada, K.; Portsmouth, S.; et al. Baloxavir Marboxil for Uncomplicated Influenza in Adults and Adolescents. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 913–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ison, M.G.; Portsmouth, S.; Yoshida, Y.; Shishido, T.; Mitchener, M.; Tsuchiya, K.; Uehara, T.; Hayden, F.G. Early Treatment with Baloxavir Marboxil in High-Risk Adolescent and Adult Outpatients with Uncomplicated Influenza (CAPSTONE-2): A Randomised, Placebo-Controlled, Phase 3 Trial. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 1204–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manothummetha, K.; Mongkolkaew, T.; Tovichayathamrong, P.; Boonyawairote, R.; Meejun, T.; Srisurapanont, K.; Phongkhun, K.; Sanguankeo, A.; Torvorapanit, P.; Moonla, C.; et al. Ribavirin Treatment for Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection in Patients with Haematologic Malignancy and Haematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant Recipients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2023, 29, 1272–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindemans, C.A.; Leen, A.M.; Boelens, J.J. How I Treat Adenovirus in Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant Recipients. Blood 2010, 116, 5476–5485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dequin, P.-F.; Meziani, F.; Quenot, J.-P.; Kamel, T.; Ricard, J.-D.; Badie, J.; Reignier, J.; Heming, N.; Plantefève, G.; Souweine, B.; et al. Hydrocortisone in Severe Community-Acquired Pneumonia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 1931–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lansbury, L.E.; Rodrigo, C.; Leonardi-Bee, J.; Nguyen-Van-Tam, J.; Shen Lim, W. Corticosteroids as Adjunctive Therapy in the Treatment of Influenza: An Updated Cochrane Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 48, e98–e106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smit, J.M.; Van Der Zee, P.A.; Stoof, S.C.M.; Van Genderen, M.E.; Snijders, D.; Boersma, W.G.; Confalonieri, P.; Salton, F.; Confalonieri, M.; Shih, M.-C.; et al. Predicting Benefit from Adjuvant Therapy with Corticosteroids in Community-Acquired Pneumonia: A Data-Driven Analysis of Randomised Trials. Lancet Respir. Med. 2025, 13, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanner, A.R.; Dorey, R.B.; Brendish, N.J.; Clark, T.W. Influenza Vaccination: Protecting the Most Vulnerable. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2021, 30, 200258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demicheli, V.; Jefferson, T.; Di Pietrantonj, C.; Ferroni, E.; Thorning, S.; Thomas, R.E.; Rivetti, A. Vaccines for Preventing Influenza in the Elderly. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018, 2, CD004876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newall, A.T.; Nazareno, A.L.; Muscatello, D.J.; Boettiger, D.; Viboud, C.; Simonsen, L.; Turner, R.M. The Association between Influenza Vaccination Uptake and Influenza and Pneumonia-Associated Deaths in the United States. Vaccine 2024, 42, 2044–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonmarin, I.; Belchior, E.; Lévy-Bruhl, D. Impact of Influenza Vaccination on Mortality in the French Elderly Population during the 2000–2009 Period. Vaccine 2015, 33, 1099–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payne, A.B.; Watts, J.A.; Mitchell, P.K.; Dascomb, K.; Irving, S.A.; Klein, N.P.; Grannis, S.J.; Ong, T.C.; Ball, S.W.; DeSilva, M.B.; et al. Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Vaccine Effectiveness against RSV-Associated Hospitalisations and Emergency Department Encounters among Adults Aged 60 Years and Older in the USA, October, 2023, to March, 2024: A Test-Negative Design Analysis. Lancet 2024, 404, 1547–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyer, O. Measles: Texas Outbreak Spreads to New Mexico. BMJ 2025, 388, r357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuppalli, K.; Perl, T.M. Measles in Texas: Waning Vaccination and a Stark Warning for Public Health. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2025, 25, 485–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hübschen, J.M.; Gouandjika-Vasilache, I.; Dina, J. Measles. Lancet 2022, 399, 678–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lombardo, D.; Ciampi, G.; Spicuzza, L. Severe and Fatal Measles-Associated Pneumonia during an Outbreak in Italy: Data from the Heart of the Epidemic. Adv. Respir. Med. 2020, 88, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafat, C.; Klouche, K.; Ricard, J.-D.; Messika, J.; Roch, A.; Machado, S.; Sonneville, R.; Guisset, O.; Pujol, W.; Guérin, C.; et al. Severe Measles Infection: The Spectrum of Disease in 36 Critically Ill Adult Patients. Medicine 2013, 92, 257–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Tsui, J.L.-H.; Gutierrez, B.; Busch Moreno, S.; du Plessis, L.; Deng, X.; Cai, J.; Bajaj, S.; Suchard, M.A.; Pybus, O.G.; et al. COVID-19 Pandemic Interventions Reshaped the Global Dispersal of Seasonal Influenza Viruses. Science 2024, 386, eadq3003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, E.J.; Uyeki, T.M.; Chu, H.Y. The Effects of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Community Respiratory Virus Activity. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2023, 21, 195–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Walker, G.; Kim, K.W.; Stelzer-Braid, S.; Scotch, M.; Rawlinson, W.D. The Resurgence of Influenza A/H3N2 Virus in Australia after the Relaxation of COVID-19 Restrictions during the 2022 Season. J. Med. Virol. 2024, 96, e29922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perofsky, A.C.; Huddleston, J.; Hansen, C.L.; Barnes, J.R.; Rowe, T.; Xu, X.; Kondor, R.; Wentworth, D.E.; Lewis, N.; Whittaker, L.; et al. Antigenic Drift and Subtype Interference Shape A(H3N2) Epidemic Dynamics in the United States. Elife 2024, 13, RP91849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabaan, A.A.; Alenazy, M.F.; Alshehri, A.A.; Alshahrani, M.A.; Al-Subaie, M.F.; Alrasheed, H.A.; Al Kaabi, N.A.; Thakur, N.; Bouafia, N.A.; Alissa, M.; et al. An Updated Review on Pathogenic Coronaviruses (CoVs) amid the Emergence of SARS-CoV-2 Variants: A Look into the Repercussions and Possible Solutions. J. Infect. Public Health 2023, 16, 1870–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Wit, E.; van Doremalen, N.; Falzarano, D.; Munster, V.J. SARS and MERS: Recent Insights into Emerging Coronaviruses. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 14, 523–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girard, M.P.; Tam, J.S.; Assossou, O.M.; Kieny, M.P. The 2009 A (H1N1) Influenza Virus Pandemic: A Review. Vaccine 2010, 28, 4895–4902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, S.; Qin, Y.; Cowling, B.J.; Ren, X.; Wardrop, N.A.; Gilbert, M.; Tsang, T.K.; Wu, P.; Feng, L.; Jiang, H.; et al. Global Epidemiology of Avian Influenza A H5N1 Virus Infection in Humans, 1997-2015: A Systematic Review of Individual Case Data. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, e108–e118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zatta, M.; Brichler, S.; Vindrios, W.; Melica, G.; Gallien, S. Autochthonous Dengue Outbreak, Paris Region, France, September–October 2023. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2023, 29, 2538–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, R. Chikungunya Fever Is Transmitted Locally in Europe for First Time. BMJ 2007, 335, 532–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenhalgh, T.; MacIntyre, C.R.; Baker, M.G.; Bhattacharjee, S.; Chughtai, A.A.; Fisman, D.; Kunasekaran, M.; Kvalsvig, A.; Lupton, D.; Oliver, M.; et al. Masks and Respirators for Prevention of Respiratory Infections: A State of the Science Review. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2024, 37, e0012423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Xtag Respiratory Viral Panel FastV2 | Respifinder Smart 22 Fast | Allplex Respiratory Panel Assays | Filmarray Respiratory Plus 2,1 Panel | ePlex Respiratory Pathogen 2 Panel | QIAstatDx Respiratory Panel 2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Luminex | Pathofinder | Seegene | Biofire | GenMark Dx | Qiagen | |
| PCR | Semi quantitative | Final | Real time | Final | Final | Real time |
| Turn-around time | 4 h | 6 h | 4 h 30 min | 45 min | 70 min | 70 min |
| Targets | ||||||
| Influenzae A and B | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Respiratory syncytial virus | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Rhinovirus/enterovirus | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Human metapneumovirus | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Human coronaviruses | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Parainfluenza virus | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Adenovirus | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Bocavirus | X | X | X | X | X | |
| Mers-Cov | X | X | ||||
| SARS-CoV-2 | X | X | X |
| Virus | Clinical Vignettes/Specific Data | Precautions/Prevention |
|---|---|---|
| Common respiratory viruses | ||
| Influenza A and influenza B [55,56] | Short incubation (mean 2 days); viral shedding from 2 days prior to symptoms and peaks within 2–3 days afterwards. The most common cause of ICU admission either with pneumonia or with acute exacerbation of chronic or respiratory diseases. May be associated with acute myocardial infarction, myocarditis, rhabdomyolysis, acute renal failure, encephalopathy/encephalitis, and other non-pulmonary complications. | Droplet /Yearly vaccine |
| SARS-CoV-2 [57,58,59] | New variants are associated with high transmissibility, milder diseases, and immune escape (JN.1 is the most common sublineage; KP 3.1.1 is rapidly growing). Case fatality rate is 1.9% higher in the elderly and low- and middle-income countries. Severe forms are observed in immunocompetent patients with comorbid conditions (chronic diseases, obesity, and elderly). Compared to historical variants, higher rate of cases in vaccinated people (but delay since the last dose) and shorter delay from first symptom to ICU admission (5 days). | Droplet + Airborne /Vaccine |
| Respiratory syncytial virus [46,60] | Winter season. Elderly patients with chronic respiratory or cardiac diseases. Immunodepression in one-third of the cases of poor prognosis. Commonly associated with exacerbation of chronic respiratory or cardiac insufficiency. Bronchospasm is common. New vaccines offer about 90% protection to adults over 65. | Contact /Vaccine |
| Human metapneumovirus [61] | Elderly patients with chronic respiratory or cardiac diseases. Hospital admission after a median delay of 3 days of symptoms. Half of patients present with pneumonia (interstitial). Immunodepression in one-third of the ICU cases. | Contact |
| Adenoviruses [62] | Usually mild symptoms, keratoconjunctivitis, and gastro-intestinal symptoms. Severe forms are rare but observed in young and middle-aged adults (median age 40 yo). ARDS is common. Some cases are associated with hepatitis. Rare cases of myocarditis, cardiomyopathy, pancreatitis, encephalitis, meningitis, and mononucleosis-like syndromes. | Droplet + contact |
| Picornaviruses (rhinovirus and enterovirus) | Frequently detected in critically ill patients with severe acute respiratory infection. Excretion > 2 months are common. Questionable impact on respiratory insufficiency and prognosis in immunocompetent adults. | Droplet |
| Human coronaviruses (229E, NL63, OC43, and HKU1) Parainfluenza (1–4) | Year-long transmissibility. May cause severe illness in the elderly, persons with comorbidities including immunosuppression. Parainfluenza: usually mild upper respiratory diseases, cases of laryngotracheobronchitis (croup) and bronchiolitis. | Contact |
| Uncommon and emerging viruses | ||
| Avian influenza A/H5N1, A/H5N6, A/H7N9, and other subtypes [63] | Residence in or travel to Southeast and East Asia. Exposure to poultry or visits to poultry markets. Severe ARDS. | Airborne + contact |
| MERS-CoV | Severe pneumonia, gastro-intestinal symptoms. Residence in or travel to the Arabian Peninsula. Exposure to dromedary camel (in endemic areas). Nosocomial transmission risk to other patients and to healthcare workers. | Airborne + contact |
| Measles | Incomplete vaccination. Characteristic cutaneous rash. Progressive giant cell pneumonia. | Airborne /Vaccine |
| Hantaviruses (e.g., Sin Nombre and Andes) | Residence in or travel to affected areas of North, Central, or South America. Exposure to rodent excretions. | Standard |
| ICU Admission in Hospitalized Patients (%) | During ICU Stay | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mechanical Ventilation (%) | Bacterial Co-Infection (%) | ARDS (%) | Mortality (%) | ||
| Seasonal influenza [56,84,85,86,87] | 15–20 | 30–65 | 35 | 25–50 | 15–25 |
| Respiratory syncytial virus [46,60,67,81] | 15–20 | 30–35 | 25–35 | 15–20 | 10–15 |
| Human metapneumovirus [61,68,69] | 5–10 | 40–50 | 20 | 10–25 | 20 |
| Rhinovirus [75,88,89] | 15–20 | 50 | 30 | ? | 30 |
| Parainfluenza viruses * [73] | 25 | ? | 30 | ? | 20–25 |
| Adenovirus * [70] | 5 | 40–50 | ? | 10–20 | 0–5 |
| Seasonal coronoaviruses * [90,91] | 15–30 | 0–7 | 20–30 | 0–3 | ? |
| Bocavirus [78] * | ? | Case reports | Case reports | Case reports | Case reports |
| Treatment | Outcome | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| Influenza | ||
| Oseltamivir [99,104,105,106] (oral) | Outpatient population No reduction in hospitalization risk in the general population (RR, 0.79; 95% CI, 0.48–1.29) No reduction in hospitalization risk in high-risk patients (RR, 0.65; 0.33–1.28) No reduction in hospitalization risk in patients >65 years (RR, 1.01; 95% CI, 0.21–4.90) Hospitalized population Modest reduction in hospital stay duration (mean difference −1.63 days, 95% CI −2.81 to −0.45) No impact on ICU admission No impact on mortality | No specific serious adverse events Reported resistance: ~1% of strains globally |
| Peramivir [99,107,108] (IV) | Outpatient population (compared to oseltamivir) No difference in time to alleviation of influenza symptoms Hospitalized population (compared to oseltamivir) No difference in hospital stay duration No impact on ICU admission No impact on mortality | No specific serious adverse events Rare resistance Second-line therapy: For oseltamivir resistance or when oral administration is not possible |
| Zanamivir [109] (inhaled, IV) | Hospitalized population (compared to oseltamivir) No difference in time to alleviation of influenza symptoms No impact on ICU admission No impact on mortality | No specific serious adverse events Rare resistance Second-line therapy: For oseltamivir resistance or when oral administration is not possible |
| Baloxavir [102,110,111] (oral) | Outpatient population (compared to oseltamivir) No difference in time to alleviation of influenza symptoms Hospitalized population: baloxavir + oseltamivir compared to oseltamivir alone No clinical benefit from adding baloxavir | Second-line therapy: For oseltamivir resistance (no cross-resistance with neuraminidase inhibitors)? |
| Respiratory syncytial virus | ||
| Ribavirin [112] (oral, inhaled, IV) | Reduced mortality in LRTIs in patients with hematologic malignancies or hematopoietic stem cell transplants (aOR 0.19 [0.07, 0.51]) No indication for immunocompetent patients | Adverse events: nephrotoxicity, anemia, and rash |
| Adenovirus | ||
| Cidofovir [113] (IV). | Weak evidence (mainly case reports in pediatric patients) suggesting potential effect on adenovirus clearance in immunocompromised patients | Adverse events: nephrotoxicity and leukopenia |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mokrani, D.; Timsit, J.-F. Role of Respiratory Viruses in Severe Acute Respiratory Failure. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 3175. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14093175
Mokrani D, Timsit J-F. Role of Respiratory Viruses in Severe Acute Respiratory Failure. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(9):3175. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14093175
Chicago/Turabian StyleMokrani, David, and Jean-François Timsit. 2025. "Role of Respiratory Viruses in Severe Acute Respiratory Failure" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 9: 3175. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14093175
APA StyleMokrani, D., & Timsit, J.-F. (2025). Role of Respiratory Viruses in Severe Acute Respiratory Failure. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(9), 3175. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14093175







