Beyond Size: Advanced MRI Breakthroughs in Predicting Intracranial Aneurysm Rupture Risk
Abstract
1. Introduction
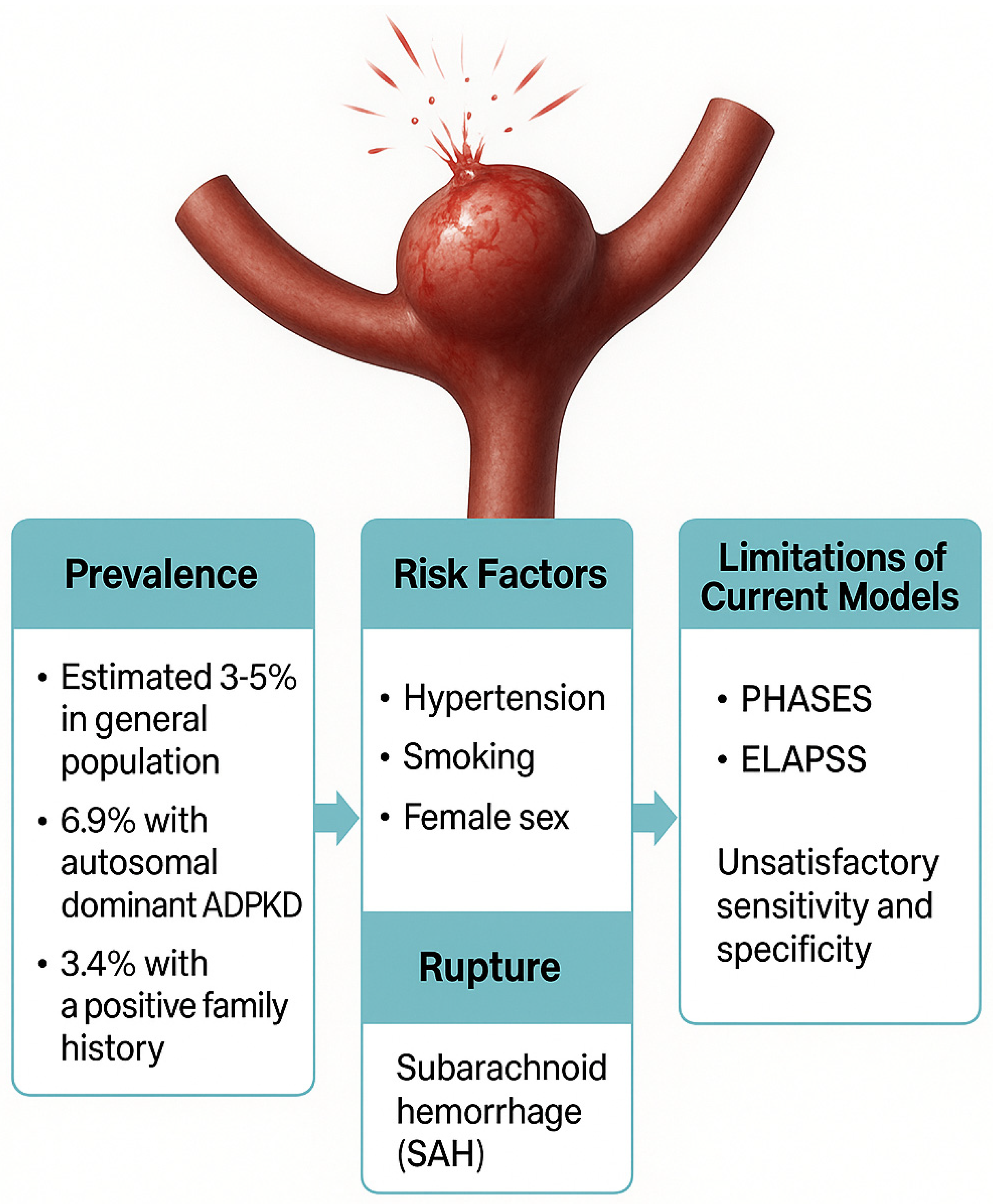
2. Current Challenges in Intracranial Aneurysm Rupture Risk Prediction
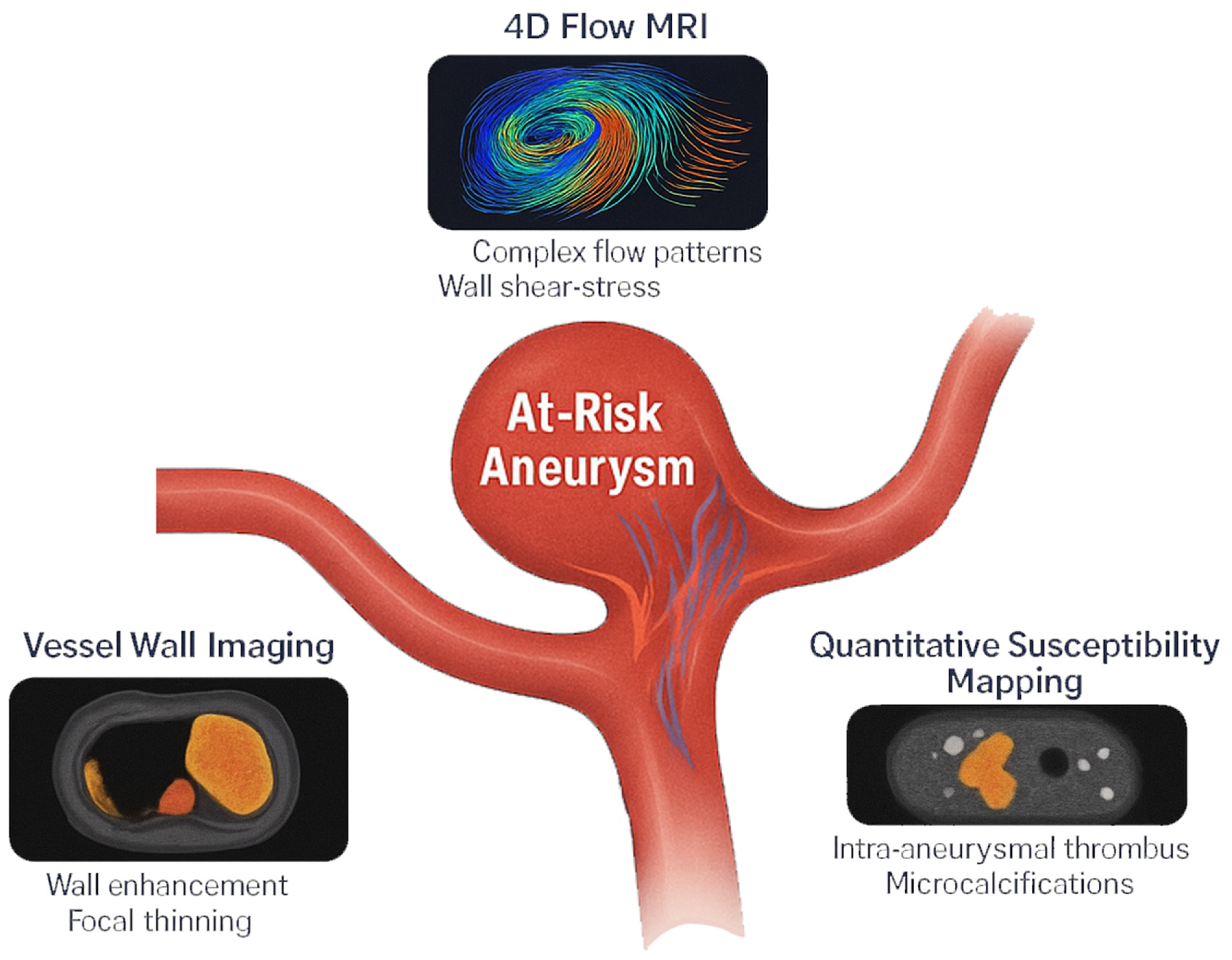
3. Advanced MRI Techniques for Rupture Risk Assessment
3.1. High-Resolution Vessel Wall Imaging (VWI)
3.2. Four-Dimensional Flow MRI for Hemodynamic Assessment
3.3. Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping (QSM)
4. Integration of Artificial Intelligence with MRI for IAs
5. Future Directions and Limitations
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AUC | Area Under the Curve |
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| AWE | Aneurysmal Wall Enhancement |
| CNN | Convolutional Neural Network |
| CFD | Computational Fluid Dynamics |
| ELAPSS | Earlier SAH, Location, Age, Population, Size, and Shape (risk score) |
| IA | Intracranial Aneurysm |
| ISUIA | International Study of Unruptured Intracranial Aneurysms |
| KE | Kinetic Energy |
| ML | Machine Learning |
| MPO | Myeloperoxidase |
| MRI | Magnetic Resonance Imaging |
| OSI | Oscillatory Shear Index |
| PHASES | Population, Hypertension, Age, Size of aneurysm, Earlier SAH, Site (risk score) |
| PWV | Pulse Wave Velocity |
| QSM | Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping |
| RT | Residence Time |
| SI | Signal Intensity |
| T1-VISTA | T1-weighted Volumetric Isotropic Turbo spin echo Acquisition |
| TOF-MRA | Time-of-Flight Magnetic Resonance Angiography |
| TSE | Turbo Spin Echo |
| VWI | Vessel Wall Imaging |
| WEI | Wall Enhancement Index |
| WSS | Wall Shear Stress |
References
- Vlak, M.H.; Algra, A.; Brandenburg, R.; Rinkel, G.J. Prevalence of Unruptured Intracranial Aneurysms, with Emphasis on Sex, Age, Comorbidity, Country, and Time Period: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Lancet Neurol. 2011, 10, 626–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hishikawa, T.; Date, I. Unruptured Cerebral Aneurysms in Elderly Patients. Neurol. Med. Chir. 2017, 57, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Etminan, N.; Rinkel, G.J. Unruptured Intracranial Aneurysms: Development, Rupture and Preventive Management. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2016, 12, 699–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seule, M.; Oswald, D.; Muroi, C.; Brandi, G.; Keller, E. Outcome, Return to Work and Health-Related Costs After Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. Neurocritical Care 2020, 33, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, B.G.; Brown, R.D.; Amin-Hanjani, S.; Broderick, J.P.; Cockroft, K.M.; Connolly, E.S.; Duckwiler, G.R.; Harris, C.C.; Howard, V.J.; Johnston, S.C.; et al. Guidelines for the Management of Patients With Unruptured Intracranial Aneurysms: A Guideline for Healthcare Professionals From the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 2015, 46, 2368–2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greving, J.P.; Wermer, M.J.H.; Brown, R.D.; Morita, A.; Juvela, S.; Yonekura, M.; Ishibashi, T.; Torner, J.C.; Nakayama, T.; Rinkel, G.J.E.; et al. Development of the PHASES Score for Prediction of Risk of Rupture of Intracranial Aneurysms: A Pooled Analysis of Six Prospective Cohort Studies. Lancet Neurol. 2014, 13, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bijlenga, P.; Gondar, R.; Schilling, S.; Morel, S.; Hirsch, S.; Cuony, J.; Corniola, M.-V.; Perren, F.; Rüfenacht, D.; Schaller, K. PHASES Score for the Management of Intracranial Aneurysm: A Cross-Sectional Population-Based Retrospective Study. Stroke 2017, 48, 2105–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backes, D.; Rinkel, G.J.E.; Greving, J.P.; Velthuis, B.K.; Murayama, Y.; Takao, H.; Ishibashi, T.; Igase, M.; terBrugge, K.G.; Agid, R.; et al. ELAPSS Score for Prediction of Risk of Growth of Unruptured Intracranial Aneurysms. Neurology 2017, 88, 1600–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backes, D.; Rinkel, G.J.E.; Laban, K.G.; Algra, A.; Vergouwen, M.D.I. Patient-and Aneurysm-Specific Risk Factors for Intracranial Aneurysm Growth: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Stroke 2016, 47, 951–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, J.; Natarajan, S.K.; Tremmel, M.; Ma, D.; Mocco, J.; Hopkins, L.N.; Siddiqui, A.H.; Levy, E.I.; Meng, H. Hemodynamic–Morphologic Discriminants for Intracranial Aneurysm Rupture. Stroke 2011, 42, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, N.; Flüh, C.; Saalfeld, S.; Voß, S.; Hille, G.; Trick, D.; Wodarg, F.; Synowitz, M.; Jansen, O.; Berg, P. Multimodal Validation of Focal Enhancement in Intracranial Aneurysms as a Surrogate Marker for Aneurysm Instability. Neuroradiology 2020, 62, 1627–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, F.; Xia, J.; Zhang, F.; Lu, S.; Wang, H.; Li, J.; Liu, X.; Zhong, Y.; Guo, J.; Duan, Y.; et al. Intracranial Aneurysm Instability Prediction Model Based on 4D-Flow MRI and HR-MRI. Neurotherapeutics 2025, 22, e00505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishii, D.; Nakagawa, D.; Zanaty, M.; Roa, J.A.; Al Kasab, S.; Shaban, A.; Hudson, J.S.; Osorno-Cruz, C.; Byer, S.; Allan, L.; et al. Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping and Vessel Wall Imaging as Screening Tools to Detect Microbleed in Sentinel Headache. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiebers, D.O. Unruptured Intracranial Aneurysms: Natural History, Clinical Outcome, and Risks of Surgical and Endovascular Treatment. Lancet 2003, 362, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korja, M.; Lehto, H.; Juvela, S. Lifelong Rupture Risk of Intracranial Aneurysms Depends on Risk Factors: A Prospective Finnish Cohort Study. Stroke 2014, 45, 1958–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kailaya-Vasan, A.; Frantzias, J.; Kailaya-Vasan, J.; Anderson, I.A.; Walsh, D.C. Current Decision Support Tools Fail to Agree or Predict Therapeutic Decisions in a Single Cohort of Unruptured Intracranial Aneurysms. Acta Neurochir. 2022, 164, 771–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pettersson, S.D.; Skrzypkowska, P.; Pietrzak, K.; Och, A.; Siedlecki, K.; Czapla-Iskrzycka, A.; Klepinowski, T.; Fodor, T.; Filo, J.; Meyer-Szary, J.; et al. Evaluation of PHASES Score for Predicting Rupture of Intracranial Aneurysms: Significance of Aneurysm Size. World Neurosurg. 2024, 184, e178–e184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villablanca, J.P.; Duckwiler, G.R.; Jahan, R.; Tateshima, S.; Martin, N.A.; Frazee, J.; Gonzalez, N.R.; Sayre, J.; Vinuela, F.V. Natural History of Asymptomatic Unruptured Cerebral Aneurysms Evaluated at CT Angiography: Growth and Rupture Incidence and Correlation with Epidemiologic Risk Factors. Radiology 2013, 269, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsubara, S.; Hadeishi, H.; Suzuki, A.; Yasui, N.; Nishimura, H. Incidence and Risk Factors for the Growth of Unruptured Cerebral Aneurysms: Observation Using Serial Computerized Tomography Angiography. J. Neurosurg. 2004, 101, 908–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimura, S.; Yamanaka, Y.; Takao, H.; Ishibashi, T.; Otani, K.; Karagiozov, K.; Fukudome, K.; Yamamoto, M.; Murayama, Y. Hemodynamic and Morphological Differences in Cerebral Aneurysms between before and after Rupture. J. Neurosurg. 2024, 140, 774–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurence, D.W.; Homburg, H.; Yan, F.; Tang, Q.; Fung, K.-M.; Bohnstedt, B.N.; Holzapfel, G.A.; Lee, C.-H. A Pilot Study on Biaxial Mechanical, Collagen Microstructural, and Morphological Characterizations of a Resected Human Intracranial Aneurysm Tissue. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 3525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frösen, J.; Piippo, A.; Paetau, A.; Kangasniemi, M.; Niemelä, M.; Hernesniemi, J.; Jääskeläinen, J. Remodeling of Saccular Cerebral Artery Aneurysm Wall Is Associated With Rupture: Histological Analysis of 24 Unruptured and 42 Ruptured Cases. Stroke 2004, 35, 2287–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimonaga, K.; Matsushige, T.; Ishii, D.; Sakamoto, S.; Hosogai, M.; Kawasumi, T.; Kaneko, M.; Ono, C.; Kurisu, K. Clinicopathological Insights From Vessel Wall Imaging of Unruptured Intracranial Aneurysms. Stroke 2018, 49, 2516–2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Haraldsson, H.; Tian, B.; Meisel, K.; Ko, N.; Lawton, M.; Grinstead, J.; Ahn, S.; Laub, G.; Hess, C.; et al. High Resolution Imaging of the Intracranial Vessel Wall at 3 and 7 T Using 3D Fast Spin Echo MRI. Magn. Reson. Mater. Phys. Biol. Med. 2016, 29, 559–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vranic, J.E.; Hartman, J.B.; Mossa-Basha, M. High-Resolution Magnetic Resonance Vessel Wall Imaging for the Evaluation of Intracranial Vascular Pathology. Neuroimaging Clin. N. Am. 2021, 31, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edjlali, M.; Gentric, J.-C.; Régent-Rodriguez, C.; Trystram, D.; Hassen, W.B.; Lion, S.; Nataf, F.; Raymond, J.; Wieben, O.; Turski, P.; et al. Does Aneurysmal Wall Enhancement on Vessel Wall MRI Help to Distinguish Stable From Unstable Intracranial Aneurysms? Stroke 2014, 45, 3704–3706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samaniego, E.A.; Roa, J.A.; Hasan, D. Vessel Wall Imaging in Intracranial Aneurysms. J. NeuroInterventional Surg. 2019, 11, 1105–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsen, N.; Von Der Brelie, C.; Trick, D.; Riedel, C.H.; Lindner, T.; Madjidyar, J.; Jansen, O.; Synowitz, M.; Flüh, C. Vessel Wall Enhancement in Unruptured Intracranial Aneurysms: An Indicator for Higher Risk of Rupture? High-Resolution MR Imaging and Correlated Histologic Findings. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2018, 39, 1617–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Texakalidis, P.; Hilditch, C.A.; Lehman, V.; Lanzino, G.; Pereira, V.M.; Brinjikji, W. Vessel Wall Imaging of Intracranial Aneurysms: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. World Neurosurg. 2018, 117, 453–458.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinloog, R.; Korkmaz, E.; Zwanenburg, J.J.M.; Kuijf, H.J.; Visser, F.; Blankena, R.; Post, J.A.; Ruigrok, Y.M.; Luijten, P.R.; Regli, L.; et al. Visualization of the Aneurysm Wall: A 7.0-Tesla Magnetic Resonance Imaging Study. Neurosurgery 2014, 75, 614–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blankena, R.; Kleinloog, R.; Verweij, B.H.; van Ooij, P.; Haken, B.T.; Luijten, P.R.; Rinkel, G.J.E.; Zwanenburg, J.J.M. Thinner Regions of Intracranial Aneurysm Wall Correlate with Regions of Higher Wall Shear Stress: A 7T MRI Study. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2016, 37, 1310–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omodaka, S.; Endo, H.; Niizuma, K.; Fujimura, M.; Inoue, T.; Sato, K.; Sugiyama, S.-I.; Tominaga, T. Quantitative Assessment of Circumferential Enhancement along the Wall of Cerebral Aneurysms Using MR Imaging. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2016, 37, 1262–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghuram, A.; Varon, A.; Roa, J.A.; Ishii, D.; Lu, Y.; Raghavan, M.L.; Wu, C.; Magnotta, V.A.; Hasan, D.M.; Koscik, T.R.; et al. Semiautomated 3D Mapping of Aneurysmal Wall Enhancement with 7T-MRI. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 18344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandell, D.M.; Mossa-Basha, M.; Qiao, Y.; Hess, C.P.; Hui, F.; Matouk, C.; Johnson, M.H.; Daemen, M.J.A.P.; Vossough, A.; Edjlali, M.; et al. Intracranial Vessel Wall MRI: Principles and Expert Consensus Recommendations of the American Society of Neuroradiology. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2017, 38, 218–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Jiang, Y.; You, W.; Liu, P.; Wang, Y.; et al. Comparison of 7 T and 3 T Vessel Wall MRI for the Evaluation of Intracranial Aneurysm Wall. Eur. Radiol. 2022, 32, 2384–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnell, S.; Ansari, S.A.; Vakil, P.; Wasielewski, M.; Carr, M.L.; Hurley, M.C.; Bendok, B.R.; Batjer, H.; Carroll, T.J.; Carr, J.; et al. Three-Dimensional Hemodynamics in Intracranial Aneurysms: Influence of Size and Morphology. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2014, 39, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnell, S.; Wu, C.; Ansari, S.A. 4D MRI Flow Examinations in Cerebral and Extracerebral Vessels. Ready for Clinical Routine? Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2016, 29, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cebral, J.R.; Castro, M.A.; Burgess, J.E.; Pergolizzi, R.S.; Sheridan, M.J.; Putman, C.M. Characterization of Cerebral Aneurysms for Assessing Risk of Rupture by Using Patient-Specific Computational Hemodynamics Models. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2005, 26, 2550–2559. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang, B.; Sirajuddin, A.; Zhao, S.; Lu, M. The Role of 4D Flow MRI for Clinical Applications in Cardiovascular Disease: Current Status and Future Perspectives. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2021, 11, 4193–4210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Tuijl, R.J.; den Hertog, C.S.; Timmins, K.M.; Velthuis, B.K.; van Ooij, P.; Zwanenburg, J.J.M.; Ruigrok, Y.M.; Schaaf, I.C. van der Intra-Aneurysmal High-Resolution 4D MR Flow Imaging for Hemodynamic Imaging Markers in Intracranial Aneurysm Instability. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2024, 45, 1678–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Janiga, G.; Berg, P.; Hosseini, S.A. On Flow Fluctuations in Ruptured and Unruptured Intracranial Aneurysms: Resolved Numerical Study. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 19658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottwald, L.M.; Töger, J.; Markenroth Bloch, K.; Peper, E.S.; Coolen, B.F.; Strijkers, G.J.; van Ooij, P.; Nederveen, A.J. High Spatiotemporal Resolution 4D Flow MRI of Intracranial Aneurysms at 7T in 10 Minutes. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2020, 41, 1201–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Amili, O.; Moen, S.; Van de Moortele, P.-F.; Grande, A.; Jagadeesan, B.; Coletti, F. Flow Residence Time in Intracranial Aneurysms Evaluated by in Vitro 4D Flow MRI. J. Biomech. 2022, 141, 111211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiyama, S.; Niizuma, K.; Nakayama, T.; Shimizu, H.; Endo, H.; Inoue, T.; Fujimura, M.; Ohta, M.; Takahashi, A.; Tominaga, T. Relative Residence Time Prolongation in Intracranial Aneurysms: A Possible Association with Atherosclerosis. Neurosurgery 2013, 73, 767–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakhshinejad, A.; Baghaie, A.; Vali, A.; Saloner, D.; Rayz, V.L.; D’Souza, R.M. Merging Computational Fluid Dynamics and 4D Flow MRI Using Proper Orthogonal Decomposition and Ridge Regression. J. Biomech. 2017, 58, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Ooij, P.; Guédon, A.; Poelma, C.; Schneiders, J.; Rutten, M.C.M.; Marquering, H.A.; Majoie, C.B.; VanBavel, E.; Nederveen, A.J. Complex Flow Patterns in a Real-Size Intracranial Aneurysm Phantom: Phase Contrast MRI Compared with Particle Image Velocimetry and Computational Fluid Dynamics. NMR Biomed. 2012, 25, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haacke, E.M.; Liu, S.; Buch, S.; Zheng, W.; Wu, D.; Ye, Y. Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping: Current Status and Future Directions. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2015, 33, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.I.; Kim, D.; Jung, S.C.; Nam, Y.; Alabdulwahhab, A.; Lee, J.; Choi, K.M. Feasibility and Intra-and Interobserver Reproducibility of Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping with Radiomic Features for Intracranial Dissecting Intramural Hematomas and Atherosclerotic Calcifications. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 3651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madden, D.J.; Merenstein, J.L. Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping of Brain Iron in Healthy Aging and Cognition. Neuroimage 2023, 282, 120401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Yang, A.; Huang, W.; Du, L.; Liu, B.; Lv, K.; Luan, J.; Hu, P.; Shmuel, A.; Shu, N.; et al. Associations of Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping with Cortical Atrophy and Brain Connectome in Alzheimer’s Disease: A Multi-Parametric Study. Neuroimage 2024, 290, 120555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aimo, A.; Huang, L.; Tyler, A.; Barison, A.; Martini, N.; Saccaro, L.F.; Roujol, S.; Masci, P.-G. Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping (QSM) of the Cardiovascular System: Challenges and Perspectives. J. Cardiovasc. Magn. Reson. 2022, 24, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakagawa, D.; Cushing, C.; Nagahama, Y.; Allan, L.; Hasan, D. Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping as a Possible Tool to Radiographically Diagnose Sentinel Headache Associated with Intracranial Aneurysm: Case Report. World Neurosurg. 2017, 103, 954.e1–954.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, D.; Kudo, K.; Awe, O.; Zanaty, M.; Nagahama, Y.; Cushing, C.; Magnotta, V.; Hayakawa, M.; Allan, L.; Greenlee, J.; et al. Detection of Microbleeds Associated with Sentinel Headache Using MRI Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping: Pilot Study. J. Neurosurg. 2019, 130, 1391–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, A.; Chute, C.; Rajpurkar, P.; Lou, J.; Ball, R.L.; Shpanskaya, K.; Jabarkheel, R.; Kim, L.H.; McKenna, E.; Tseng, J.; et al. Deep Learning-Assisted Diagnosis of Cerebral Aneurysms Using the HeadXNet Model. JAMA Netw. Open 2019, 2, e195600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sichtermann, T.; Faron, A.; Sijben, R.; Teichert, N.; Freiherr, J.; Wiesmann, M. Deep Learning-Based Detection of Intracranial Aneurysms in 3D TOF-MRA. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2019, 40, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Chen, Y.; Lan, L.; Lin, B.; Chen, W.; Wang, M.; Li, R.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, B.; Hu, Z.; et al. Prediction of Rupture Risk in Anterior Communicating Artery Aneurysms with a Feed-Forward Artificial Neural Network. Eur. Radiol. 2018, 28, 3268–3275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhong, Y.; Hu, Y.; Yang, C.; Peng, Y.; Zhan, X.; Zhou, P.; Zeng, Z. Advances in Research and Application of Artificial Intelligence and Radiomic Predictive Models Based on Intracranial Aneurysm Images. Front. Neurol. 2024, 15, 1391382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peper, E.S.; van Ooij, P.; Jung, B.; Huber, A.; Gräni, C.; Bastiaansen, J.A.M. Advances in Machine Learning Applications for Cardiovascular 4D Flow MRI. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 1052068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Feature | Vessel Wall Imaging (VWI) | 4D Flow MRI | Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping (QSM) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Application | Wall inflammation, neovascularization, structural integrity | Hemodynamic stress, flow patterns, wall shear stress dynamics | Thrombus iron content, microcalcifications, wall composition, sentinel bleeding |
| Key Biomarkers |
|
|
|
| Advantages |
|
|
|
| Limitations |
|
|
|
| Clinical Utility | Rupture risk prediction (AWE: 95% sensitivity, 63% specificity) | Identifies high-risk haemodynamics (AUC = 0.85 vs. PHASES AUC = 0.73) |
|
| Cost/Accessibility | High (7T systems rare; 3T requires expertise) | Moderate (requires specialised 4D flow software) | Low (postprocessing-dependent; no contrast needed) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Leon-Rojas, J.E. Beyond Size: Advanced MRI Breakthroughs in Predicting Intracranial Aneurysm Rupture Risk. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 3158. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14093158
Leon-Rojas JE. Beyond Size: Advanced MRI Breakthroughs in Predicting Intracranial Aneurysm Rupture Risk. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(9):3158. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14093158
Chicago/Turabian StyleLeon-Rojas, Jose E. 2025. "Beyond Size: Advanced MRI Breakthroughs in Predicting Intracranial Aneurysm Rupture Risk" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 9: 3158. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14093158
APA StyleLeon-Rojas, J. E. (2025). Beyond Size: Advanced MRI Breakthroughs in Predicting Intracranial Aneurysm Rupture Risk. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(9), 3158. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14093158







