Is the Superparamagnetic Approach Equal to Radioisotopes in Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy? The Over-Collecting Node Issue in Breast Cancer Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Group
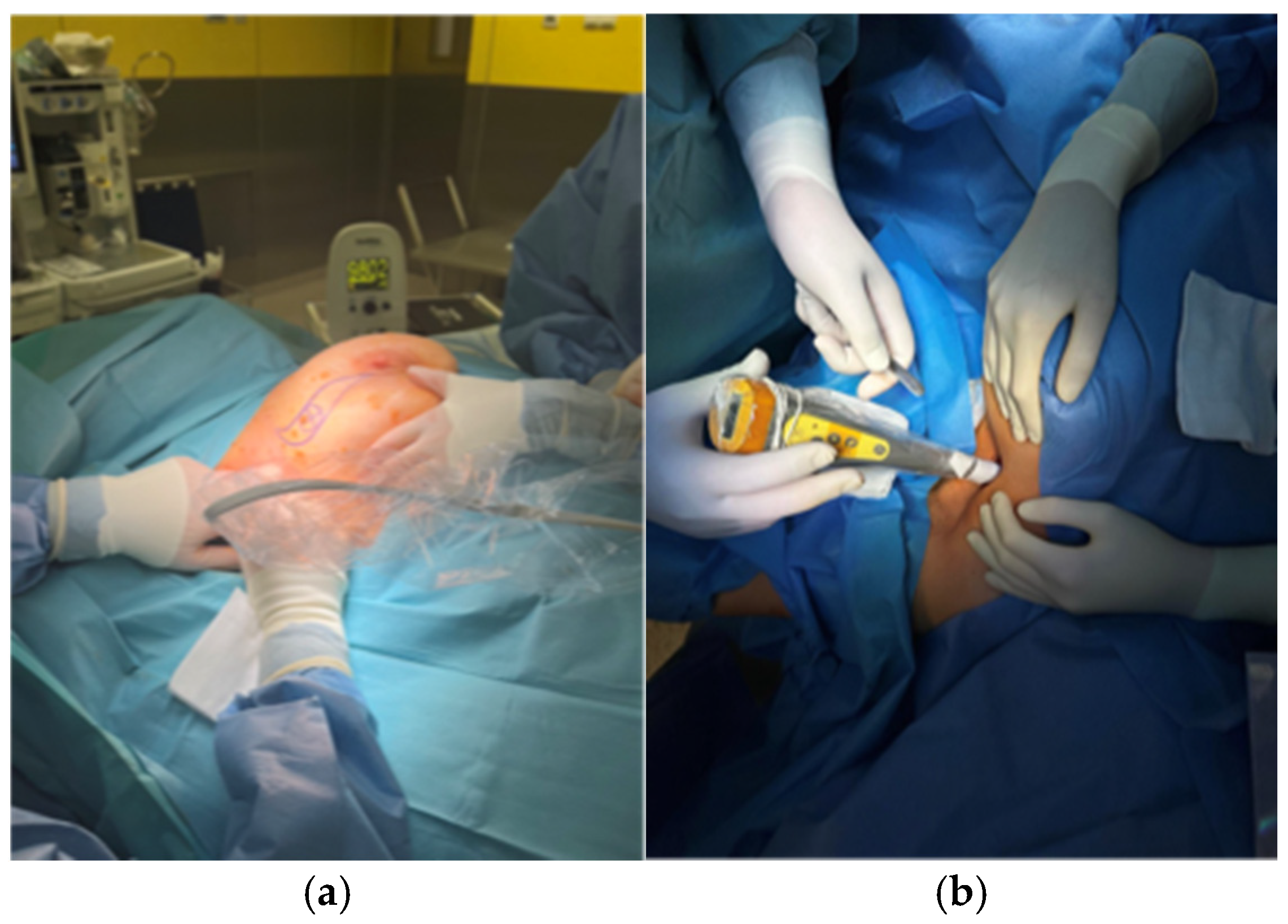
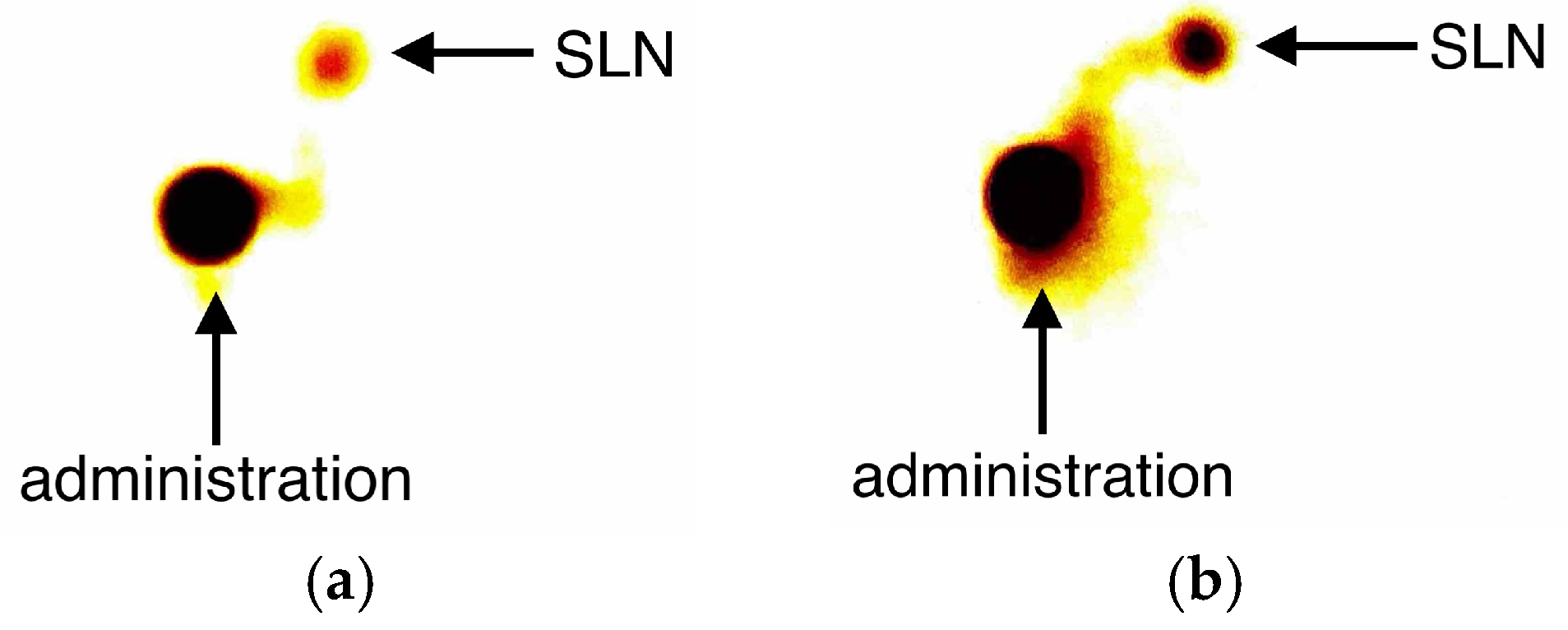
2.2. Description of the Technique
2.3. Pathological Evaluation
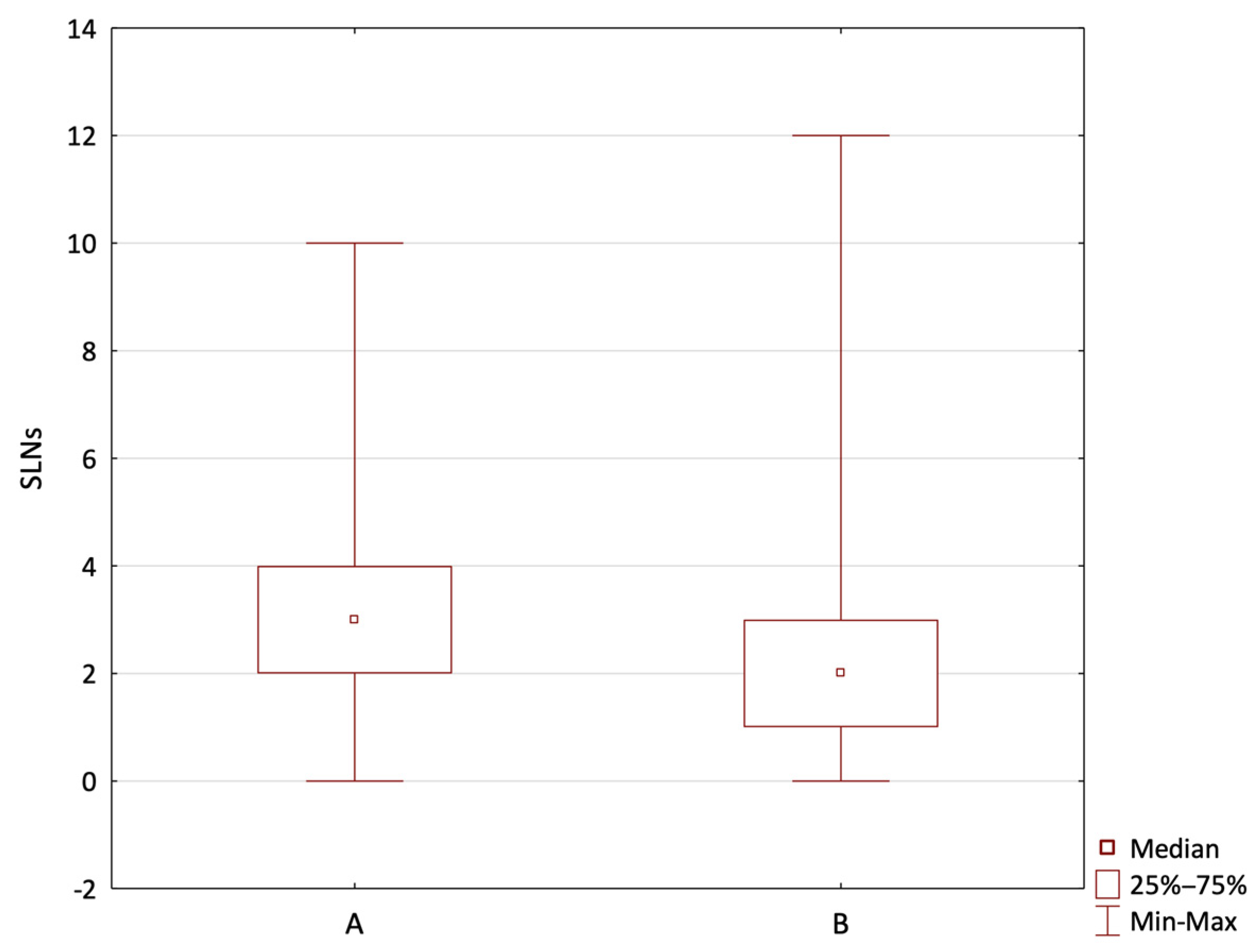
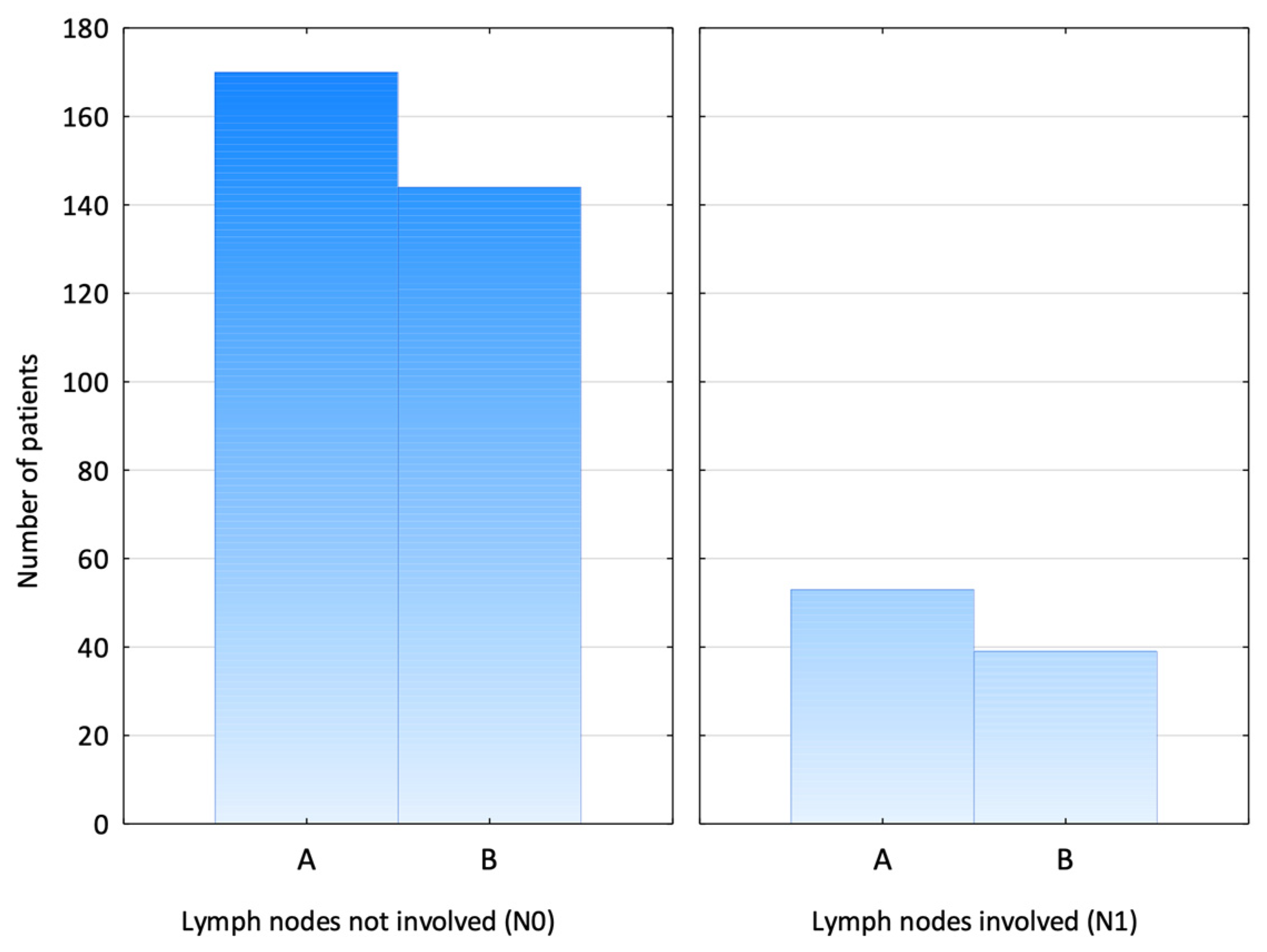
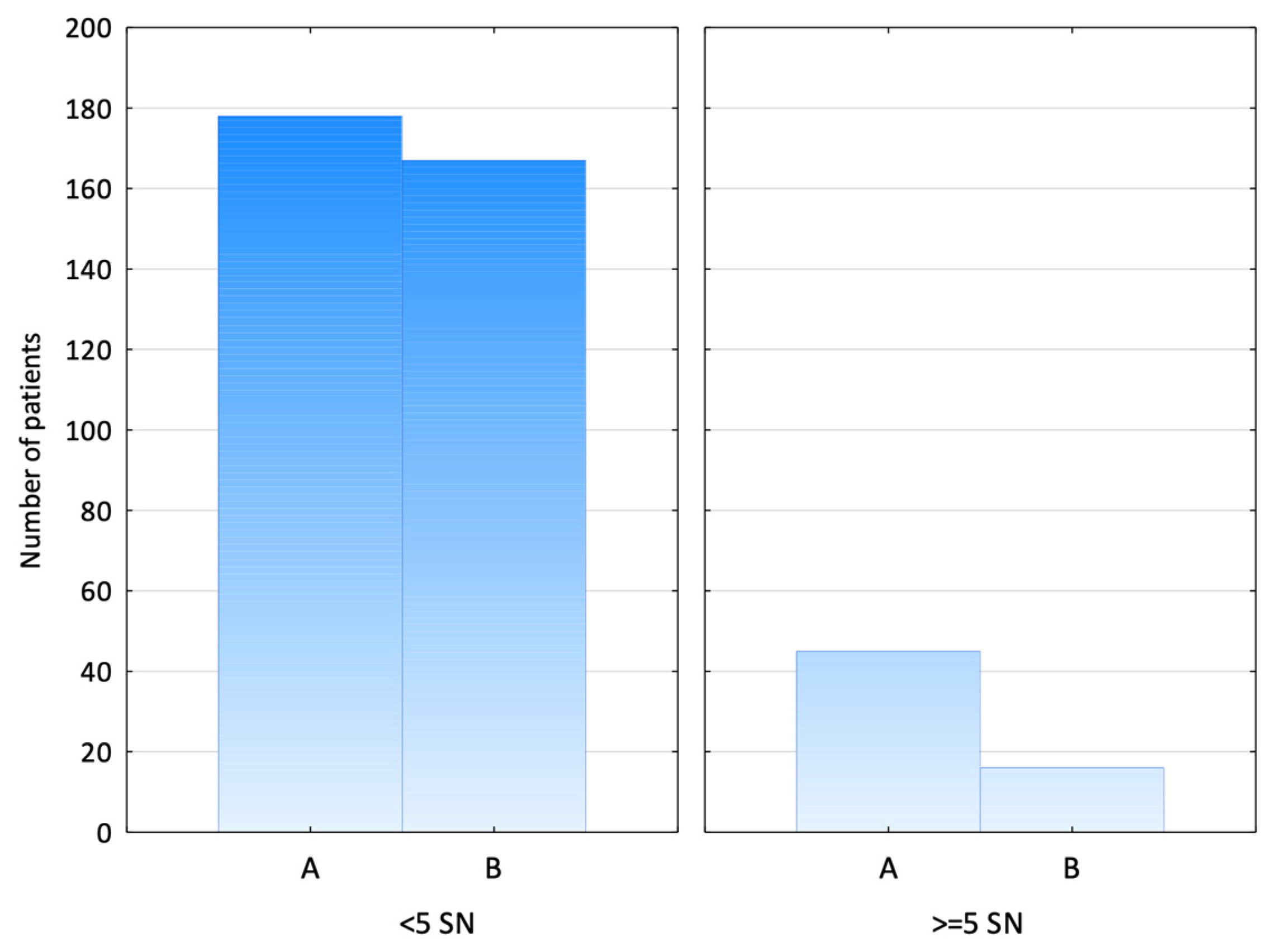
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SLNB | Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy |
| SPIO | Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide |
| RI | Radioisotope |
| ALND | Axillary Lymph Node Dissection |
| SLN | Sentinel Lymph Node |
| BCT | Breast-Conserving Therapy |
| IBR | Immediate Breast Reconstruction |
| DCIS | Ductal Cancer In Situ |
| IDC | Invasive Ductal Cancer |
| NAC | Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy |
References
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanis, J.P.; Nieweg, E.O.; Olmos, V.A.R.; Rutgers, T.J.E.; Kroon, B.B. History of sentinel node and validation of the technique. Breast Cancer Res. 2001, 3, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banys-Paluchowski, M.; Gasparri, M.L.; de Boniface, J.; Gentilini, O.; Stickeler, E.; Hartmann, S.; Thill, M.; Rubio, I.T.; Di Micco, R.; Bonci, E.A.; et al. Surgical Management of the Axilla in Clinically Node-Positive Breast Cancer Patients Converting to Clinical Node Negativity through Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy: Current Status, Knowledge Gaps, and Rationale for the EUBREAST-03 AXSANA Study. Cancers 2021, 13, 1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giammarile, F.; Vidal-Sicart, S.; Paez, D.; Pellet, O.; Enrique, E.L.; Mikhail-Lette, M.; Morozova, O.; Maria Camila, N.M.; Diana Ivonne, R.S.; Delgado Bolton, R.C.; et al. Sentinel Lymph Node Methods in Breast Cancer. Semin. Nucl. Med. 2022, 52, 551–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuliano, A.E.; McCall, L.; Beitsch, P.; Whitworth, P.W.; Blumencranz, P.; Leitch, A.M.; Saha, S.; Hunt, K.K.; Morrow, M.; Ballman, K. Locoregional recurrence after sentinel lymph node dissection with or without axillary dissection in patients with sentinel lymph node metastases: The American College of Surgeons Oncology Group Z0011 randomized trial. Ann. Surg. 2010, 252, 426–432; discussion 432–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuehn, T.; Bauerfeind, I.; Fehm, T.; Fleige, B.; Hausschild, M.; Helms, G.; Lebeau, A.; Liedtke, C.; Minckwitz, G.v.; Nekljudova, V.; et al. Sentinel-lymph-node biopsy in patients with breast cancer before and after neoadjuvant chemotherapy (SENTINA): A prospective, multicentre cohort study. Lancet Oncol. 2013, 14, 609–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zurrida, S.; Veronesi, U. Milestones in breast cancer treatment. Breast J. 2015, 21, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niebling, M.G.; Pleijhuis, R.G.; Bastiaannet, E.; Brouwers, A.H.; van Dam, G.M.; Hoekstra, H.J. A systematic review and meta-analyses of sentinel lymph node identification in breast cancer and melanoma, a plea for tracer mapping. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. (EJSO) 2016, 42, 466–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidya, R.; Khosla, M.; Laws, S.; Harvey, J.; Kaushik, M.; Mullapudi, N.A.; Macmillan, D. Axillary sentinel lymph node identification using superparamagnetic iron oxide versus radioisotope in early stage breast cancer: The UK SentiMag trial (SMART study). Surgeon 2023, 21, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abidi, H.; Bold, R.J. Assessing the Sentimag system for guiding sentinel node biopsies in patients with breast cancer. Expert. Rev. Med. Devices 2024, 21, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarado, M.D.; Mittendorf, E.A.; Teshome, M.; Thompson, A.M.; Bold, R.J.; Gittleman, M.A.; Beitsch, P.D.; Blair, S.L.; Kivilaid, K.; Harmer, Q.J.; et al. SentimagIC: A Non-inferiority Trial Comparing Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Versus Technetium-99m and Blue Dye in the Detection of Axillary Sentinel Nodes in Patients with Early-Stage Breast Cancer. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2019, 26, 3510–3516, Correction in: Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2020, 27, 979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gentilini, O.; Cremonesi, M.; Trifirò, G.; Ferrari, M.; Baio, S.M.; Caracciolo, M.; Rossi, A.; Smeets, A.; Galimberti, V.; Luini, A.; et al. Safety of sentinel node biopsy in pregnant patients with breast cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2004, 15, 1348–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersi, A.F.; Pistiolis, L.; Dussan Luberth, C.; Vikhe-Patil, E.; Nilsson, F.; Mohammed, I.; Olofsson Bagge, R.; Wärnberg, F.; Eriksson, S.; Karakatsanis, A. Optimizing Dose and Timing in Magnetic Tracer Techniques for Sentinel Lymph Node Detection in Early Breast Cancers: The Prospective Multicenter SentiDose Trial. Cancers 2021, 13, 693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, B.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, J.; Jung, J.H.; Kim, W.W.; Chu, G.; Chae, Y.; Lee, S.J.; Lee, I.H.; Yang, J.D.; et al. Comparative Study Between Radioisotope Uptake and Fluorescence Intensity of Indocyanine Green for Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy in Breast Cancer. J. Breast Cancer 2022, 25, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, V.; Suen, D.; Kwong, A. Use of Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide (SPIO) Versus Conventional Technique in Sentinel Lymph Node Detection for Breast Cancer: A Randomised Controlled Trial. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2023, 30, 3237–3244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mok, C.W.; Tan, S.M.; Zheng, Q.; Shi, L. Network meta-analysis of novel and conventional sentinel lymph node biopsy techniques in breast cancer. BJS Open 2019, 3, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pantiora, E.; Eriksson, S.; Wärnberg, F.; Karakatsanis, A. Magnetically guided surgery after primary systemic therapy for breast cancer: Implications for enhanced axillary mapping. Br. J. Surg. 2024, 111, znae008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez, D.I.C.; Sánchez, P.V.; Soliveres, S.E.; Baldó, C.J.M.; Vilanova, C.A.; Cazalla, R.L.; Kosny, P.; Rodenas, M.Á.M. Match detection analysis on SentiMag® system and standard technique in SLNB of breast cancer. Cirugía Española 2024, 103, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gropper, A.B.; Calvillo, K.Z.; Dominici, L.; Troyan, S.; Rhei, E.; Economy, K.E.; Tung, N.M.; Schapira, L.; Meisel, J.L.; Partridge, A.H.; et al. Sentinel lymph node biopsy in pregnant women with breast cancer. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2014, 21, 2506–2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakatsanis, A.; Eriksson, S.; Pistiolis, L.; Olofsson Bagge, R.; Nagy, G.; Man, V.; Kwong, A.; Wärnberg, F.; Group, S.T. Delayed Sentinel Lymph Node Dissection in Patients with a Preoperative Diagnosis of Ductal Cancer In Situ by Preoperative Injection with Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide (SPIO) Nanoparticles: The SentiNot Study. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2023, 30, 4064–4072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jazrawi, A.; Wärnberg, M.; Hersi, A.F.; Obondo, C.; Pistioli, L.; Eriksson, S.; Karakatsanis, A.; Wärnberg, F. A Comparison of Skin Staining after Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy in Women Undergoing Breast Cancer Surgery Using Blue Dye and Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticle (SPIO) Tracers. Cancers 2022, 14, 6017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karakatsanis, A.; Christiansen, P.M.; Fischer, L.; Hedin, C.; Pistioli, L.; Sund, M.; Rasmussen, N.R.; Jørnsgård, H.; Tegnelius, D.; Eriksson, S.; et al. The Nordic SentiMag trial: A comparison of super paramagnetic iron oxide (SPIO) nanoparticles versus Tc(99) and patent blue in the detection of sentinel node (SN) in patients with breast cancer and a meta-analysis of earlier studies. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2016, 157, 281–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thill, M.; Kurylcio, A.; Welter, R.; van Haasteren, V.; Grosse, B.; Berclaz, G.; Polkowski, W.; Hauser, N. The Central-European SentiMag study: Sentinel lymph node biopsy with superparamagnetic iron oxide (SPIO) vs. radioisotope. Breast 2014, 23, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio, I.T.; Diaz-Botero, S.; Esgueva, A.; Rodriguez, R.; Cortadellas, T.; Cordoba, O.; Espinosa-Bravo, M. The superparamagnetic iron oxide is equivalent to the Tc99 radiotracer method for identifying the sentinel lymph node in breast cancer. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2015, 41, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douek, M.; Klaase, J.; Monypenny, I.; Kothari, A.; Zechmeister, K.; Brown, D.; Wyld, L.; Drew, P.; Garmo, H.; Agbaje, O.; et al. Sentinel node biopsy using a magnetic tracer versus standard technique: The SentiMAG Multicentre Trial. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2014, 21, 1237–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ban, E.J.; Lee, J.S.; Koo, J.S.; Park, S.; Kim, S.I.; Park, B.W. How many sentinel lymph nodes are enough for accurate axillary staging in t1-2 breast cancer? J. Breast Cancer 2011, 14, 296–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chagpar, A.B.; Scoggins, C.R.; Martin, R.C.; Carlson, D.J.; Laidley, A.L.; El-Eid, S.E.; McGlothin, T.Q.; McMasters, K.M.; University of Louisville Breast Sentinel Lymph Node Study Investigators. Investigators. Are 3 sentinel nodes sufficient? Arch. Surg. 2007, 142, 456–459; discussion 459–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isik, A.; Soran, A.; Grasi, A.; Barry, N.; Sezgin, E. Lymphedema After Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy: Who Is at Risk? Lymphat. Res. Biol. 2022, 20, 160–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, M.; Meric-Bernstam, F.; Ross, M.I.; Akins, J.S.; Hwang, R.F.; Lucci, A.; Kuerer, H.M.; Babiera, G.V.; Gilcrease, M.Z.; Hunt, K.K. How many sentinel lymph nodes are enough during sentinel lymph node dissection for breast cancer? Cancer 2008, 113, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cipolla, C.; Galvano, A.; Vieni, S.; Saputo, F.; Lupo, S.; Latteri, M.; Graceffa, G.; Valerio, M.R. Effects of the number of removed lymph nodes on survival outcome in patients with sentinel node-negative breast cancer. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2021, 19, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Shurbasi, N.; Hirst, N.A.; Kohlhardt, S. Sentinel Node Biopsy in Ductal Carcinoma in Situ: Is it Justifiable? Cureus 2021, 13, e13062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, Y.D.; Lee, H.M.; Choi, Y.J. Necessity of sentinel lymph node biopsy in ductal carcinoma in situ patients: A retrospective analysis. BMC Surg. 2021, 21, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makita, M.; Manabe, E.; Sato, M.; Hiroyuki, T. The Number of Sentinel Lymph Nodes Could be Optimized by Adjusting the Injection Dose. Arch. Breast Cancer 2021, 8, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, J.M.; Grewar, J.; Twelves, D.; Graham, A.; Martinez-Perez, C.; Turnbull, A. Factors affecting the number of sentinel lymph nodes removed in patients having surgery for breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2020, 184, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boileau, J.F.; Poirier, B.; Basik, M.; Holloway, C.M.; Gaboury, L.; Sideris, L.; Meterissian, S.; Arnaout, A.; Brackstone, M.; McCready, D.R.; et al. Sentinel node biopsy after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in biopsy-proven node-positive breast cancer: The SN FNAC study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boughey, J.C.; Suman, V.J.; Mittendorf, E.A.; Ahrendt, G.M.; Wilke, L.G.; Taback, B.; Leitch, A.M.; Kuerer, H.M.; Bowling, M.; Flippo-Morton, T.S.; et al. Sentinel lymph node surgery after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in patients with node-positive breast cancer: The ACOSOG Z1071 (Alliance) clinical trial. JAMA 2013, 310, 1455–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caudle, A.S.; Yang, W.T.; Krishnamurthy, S.; Mittendorf, E.A.; Black, D.M.; Gilcrease, M.Z.; Bedrosian, I.; Hobbs, B.P.; DeSnyder, S.M.; Hwang, R.F.; et al. Improved Axillary Evaluation Following Neoadjuvant Therapy for Patients with Node-Positive Breast Cancer Using Selective Evaluation of Clipped Nodes: Implementation of Targeted Axillary Dissection. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 1072–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalcante, F.P.; Millen, E.C.; Novita, G.G.; Zerwes, F.P.; Mattar, A.; Machado, R.H.S.; Frasson, A.L. Sentinel lymph node biopsy following neoadjuvant chemotherapy: An evidence-based review and recommendations for current practice. Chin. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 12, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shirzadi, A.; Mahmoodzadeh, H.; Qorbani, M. Assessment of sentinel lymph node biopsy after neoadjuvant chemotherapy for breast cancer in two subgroups: Initially node negative and node positive converted to node negative—A systemic review and meta-analysis. J. Res. Med. Sci. 2019, 24, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tee, S.R.; Devane, L.A.; Evoy, D.; Rothwell, J.; Geraghty, J.; Prichard, R.S.; McDermott, E.W. Meta-analysis of sentinel lymph node biopsy after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in patients with initial biopsy-proven node-positive breast cancer. Br. J. Surg. 2018, 105, 1541–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Association of Breast Surgery at Baso. Surgical guidelines for the management of breast cancer. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. (EJSO) 2009, 35, S1–S22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ersoy, Y.E.; Kadioglu, H. Review of Novel Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy Techniques in Breast Cancer Patients Treated with Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy. Clin. Breast Cancer 2018, 18, e555–e559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, P.S.; Li, F.; Li, G.H.; Guo, C.; Chen, T.J. The combination of blue dye and radioisotope versus radioisotope alone during sentinel lymph node biopsy for breast cancer: A systematic review. BMC Cancer 2016, 16, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micha, A.; Parvaiz, M.A.; O’Riordan, L.; MacNeill, F.; Rusby, J.E. Isotope-Only Localization for Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy—Medium-Term Oncological Outcomes. Clin. Breast Cancer 2022, 22, e636–e640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harper, N.J.N.; Cook, T.M.; Garcez, T.; Farmer, L.; Floss, K.; Marinho, S.; Torevell, H.; Warner, A.; Ferguson, K.; Hitchman, J.; et al. Anaesthesia, surgery, and life-threatening allergic reactions: Epidemiology and clinical features of perioperative anaphylaxis in the 6th National Audit Project (NAP6). Br. J. Anaesth. 2018, 121, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurylcio, A.; Pelc, Z.; Skórzewska, M.; Rawicz-Pruszyński, K.; Mlak, R.; Gęca, K.; Sędłak, K.; Kurylcio, P.; Małecka-Massalska, T.; Polkowski, W. Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide for Identifying Sentinel Lymph Node in Breast Cancer after Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy: Feasibility Study. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Group A—SPIO | Group B—RI | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patients | 223 | 183 | 406 |
| Age | |||
| mean | 57.7 | 63.6 | 60.4 |
| <50 years old | 74 (33.2) | 42 (23.0) | 116 |
| >50 years old | 149 (66.8) | 141 (77.0) | 290 |
| Tumour size | |||
| Tis | 17 (7.6) | 8 (4.4) | 25 |
| T1 | 103 (46.2) | 96 (52.4) | 199 |
| T2 | 92 (41.3) | 70 (38.3) | 162 |
| T3 | 7 (3.1) | 8 (4.4) | 15 |
| T4 | 4 (1.8) | 1 (0.5) | 5 |
| Type of surgery | |||
| BCT | 143 (64.1) | 136 (74.3) | 279 |
| mastectomy | 80 (35.9) | 47 (25.7) | 127 |
| with IBR | 40 | 0 | 40 |
| Neoadjuvant chemotherapy | 31 (13.9) | 9 (4.9) | 40 |
| Histological type | |||
| DCIS | 17 (7.6) | 8 (4.4) | 25 |
| IDC | 166 (74.4) | 135 (73.8) | 301 |
| Other | 40 (17.9) | 40 (21.8) | 80 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zalewska, K.; Skonieczna, M.; Nejc, D.; Pluta, P. Is the Superparamagnetic Approach Equal to Radioisotopes in Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy? The Over-Collecting Node Issue in Breast Cancer Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 3148. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14093148
Zalewska K, Skonieczna M, Nejc D, Pluta P. Is the Superparamagnetic Approach Equal to Radioisotopes in Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy? The Over-Collecting Node Issue in Breast Cancer Patients. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(9):3148. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14093148
Chicago/Turabian StyleZalewska, Karolina, Maria Skonieczna, Dariusz Nejc, and Piotr Pluta. 2025. "Is the Superparamagnetic Approach Equal to Radioisotopes in Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy? The Over-Collecting Node Issue in Breast Cancer Patients" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 9: 3148. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14093148
APA StyleZalewska, K., Skonieczna, M., Nejc, D., & Pluta, P. (2025). Is the Superparamagnetic Approach Equal to Radioisotopes in Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy? The Over-Collecting Node Issue in Breast Cancer Patients. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(9), 3148. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14093148







