Multifidus Fat Infiltration in Patients with Persistent Spinal Pain Syndrome Type II Treated with Spinal Cord Stimulation: A Preliminary Report
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Protocol
2.2. Participants
2.3. Segmentation Composition Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographics
3.2. Prevalence of Fat Infiltration
3.3. Reliability Analysis
3.4. Fat Infiltration over Lumbar Levels
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lavand’homme, P. ‘Why me?’ The problem of chronic pain after surgery. Br. J. Pain. 2017, 11, 162–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanguay-Sabourin, C.; Fillingim, M.; Guglietti, G.V.; Zare, A.; Parisien, M.; Norman, J.; Sweatman, H.; Da-ano, R.; Heikkala, E.; Breitner, J.C.S.; et al. A prognostic risk score for development and spread of chronic pain. Nat. Med. 2023, 29, 1821–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabel, C.P.; Mokhtarinia, H.R.; Melloh, M. The Politics of Chronic LBP: Can We Rely on a Proxy-Vote? Linking Multifidus Intra-Myo-Cellular Lipid (IMCL) Fatty Infiltration with Arthrogenic Muscle Inhibition (AMI)-induced Chronic Nonspecific Low Back Pain. Spine 2021, 46, 129–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacDonald, D.; Moseley, L.G.; Hodges, P.W. Why do some patients keep hurting their back? Evidence of ongoing back muscle dysfunction during remission from recurrent back pain. Pain. 2009, 142, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodges, P.W.; Danneels, L. Changes in Structure and Function of the Back Muscles in Low Back Pain: Different Time Points, Observations, and Mechanisms. J. Orthop. Sport. Phys. 2019, 49, 464–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, S.R.; Kim, C.W.; Eng, C.M.; Gottschalk, L.J.I.V.; Tomiya, A.; Garfin, S.R.; Lieber, R.L. Architectural Analysis and Intraoperative Measurements Demonstrate the Unique Design of the Multifidus Muscle for Lumbar Spine Stability. JBJS 2009, 91, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danneels, L.A.; Vanderstraeten, G.G.; Cambier, D.C.; Witvrouw, E.E.; De Cuyper, H.J. CT imaging of trunk muscles in chronic low back pain patients and healthy control subjects. Eur. Spine J. 2000, 9, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.-B.; Wang, L.-S.; Li, M.-Q.; Chen, X. The association between changes in multifidus muscle morphology and back pain scores following discectomy surgery for lumbar disc herniation: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. Spine J. 2022, 31, 1784–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofste, A.; Soer, R.; Groen, G.J.; van der Palen, J.; Geerdink, F.J.B.; Oosterveld, F.G.J.; Kiers, H.; Wolff, A.P.; Hermens, H. Functional and morphological lumbar multifidus characteristics in subgroups with low back pain in primary care. Musculoskelet. Sci. Pract. 2021, 55, 102429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasetyo, M.; Nindita, N.; Murdana, I.N.; Prihartono, J.; Setiawan, S.I. Computed tomography evaluation of fat infiltration ratio of the multifidus muscle in chronic low back pain patients. Eur. J. Radiol. Open 2020, 7, 100293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballatori, A.M.; Shahrestani, S.; Nyayapati, P.; Agarwal, V.; Krug, R.; Han, M.; Fields, A.J.; O’Neill, C.; Demir-Deviren, S.; Lotz, J.C.; et al. Influence of patient-specific factors when comparing multifidus fat infiltration between chronic low back pain patients and asymptomatic controls. JOR SPINE 2022, 5, e1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarafadeen, R.; Ganiyu, S.O.; Ibrahim, A.A.; Ismail, A.; Akindele, M.O.; Kaka, B.; Awotidebe, A.W. Effectiveness of lumbar stabilization exercise with real-time ultrasound imaging biofeedback on lumbar multifidus muscle cross-sectional area in individuals with non-specific chronic low back pain: A study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials 2022, 23, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balasch-Bernat, M.; Willems, T.; Danneels, L.; Meeus, M.; Goubert, D. Differences in myoelectric activity of the lumbar muscles between recurrent and chronic low back pain: A cross-sectional study. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2021, 22, 756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranger, T.A.; Cicuttini, F.M.; Jensen, T.S.; Peiris, W.L.; Hussain, S.M.; Fairley, J.; Urquhart, D.M. Are the size and composition of the paraspinal muscles associated with low back pain? A systematic review. Spine J. 2017, 17, 1729–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jermy, J.E.; Copley, P.C.; Poon, M.T.C.; Demetriades, A.K. Does pre-operative multifidus morphology on MRI predict clinical outcomes in adults following surgical treatment for degenerative lumbar spine disease? A systematic review. Eur. Spine J. 2020, 29, 1318–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Han, S.; Hu, X.; Ye, L.; Li, Y.; Gao, J. Advances in research on fat infiltration and lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 1067373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goutallier, D.; Postel, J.M.; Bernageau, J.; Lavau, L.; Voisin, M.C. Fatty muscle degeneration in cuff ruptures. Pre- and postoperative evaluation by CT scan. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1994, 304, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, F.A.; Del Grande, F.; Rizzo, S.; Guglielmi, G.; Guggenberger, R. MRI in the assessment of adipose tissues and muscle composition: How to use it. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2020, 10, 1636–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Chen, J.; Huang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Qian, X.; Li, Y.; Li, M.; Yang, L.; Kui, X.; Wu, J.; et al. Deep learning-based segmentation and quantitative analysis of lumbar paraspinal muscles and fat infiltration in multicenter T2-weighted MRI data. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. Rep. 2025, 2, 100020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, S.M.; Boghra, S.B.; Macedo, L.G.; Zheng, Y.-P.; Pang, M.Y.C.; Cheung, J.P.Y.; Karppinen, J.; Samartzis, D.; Wong, A.Y.L. Does Motor Control Exercise Restore Normal Morphology of Lumbar Multifidus Muscle in People with Low Back Pain?—A Systematic Review. J. Pain Res. 2021, 14, 2543–2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, M.; Deckers, K.; Eldabe, S.; Kiesel, K.; Gilligan, C.; Vieceli, J.; Crosby, P. Muscle Control and Non-specific Chronic Low Back Pain. Neuromodulation 2018, 21, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorio, M.; Lewandrowski, K.U.; Coric, D.; Phillips, F.; Shaffrey, C.I. International Society for the Advancement of Spine Surgery Statement: Restorative Neurostimulation for Chronic Mechanical Low Back Pain Resulting from Neuromuscular Instability. Int. J. Spine Surg. 2023, 17, 728–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckermann, J.M.; Pilitsis, J.G.; Vannaboutathong, C.; Wagner, B.J.; Province-Azalde, R.; Bendel, M.A. Systematic Literature Review of Spinal Cord Stimulation in Patients with Chronic Back Pain Without Prior Spine Surgery. Neuromodulation Technol. Neural Interface 2022, 25, 648–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rigoard, P.; Basu, S.; Desai, M.; Taylor, R.; Annemans, L.; Tan, Y.; Johnson, M.J.; Van den Abeele, C.; North, R.; Group, P.S. Multicolumn spinal cord stimulation for predominant back pain in failed back surgery syndrome patients: A multicenter randomized controlled trial. Pain 2019, 160, 1410–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyerson, B.A.; Herregodts, P.; Linderoth, B.; Ren, B. An experimental animal model of spinal cord stimulation for pain. Stereotact. Funct. Neurosurg. 1994, 62, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melzack, R.; Wall, P.D. Pain mechanisms: A new theory. Science 1965, 150, 971–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goudman, L.; De Groote, S.; Linderoth, B.; De Smedt, A.; Eldabe, S.; Duarte, R.V.; Moens, M. Exploration of the Supraspinal Hypotheses about Spinal Cord Stimulation and Dorsal Root Ganglion Stimulation: A Systematic Review. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkley, J.E.; Vucetic, H.; Leone, D.; Mehta, B.; Rebold, M.; Kobak, M.; Carnes, A.; Farnell, G. Increased Physical Activity and Reduced Pain with Spinal Cord Stimulation: A 12-Month Study. Int. J. Exerc. Sci. 2020, 13, 1583–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welch, N.; Moran, K.; Antony, J.; Richter, C.; Marshall, B.; Coyle, J.; Falvey, E.; Franklyn-Miller, A. The effects of a free-weight-based resistance training intervention on pain, squat biomechanics and MRI-defined lumbar fat infiltration and functional cross-sectional area in those with chronic low back. BMJ Open Sport Exerc. Med. 2015, 1, e000050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebert, J.J.; Le Cara, C.E.; Koppenhaver, S.L.; Hoffman, M.D.; Marcus, R.L.; Dempsey, A.R.; Albert, W.J. Predictors of clinical success with stabilization exercise are associated with lower levels of lumbar multifidus intramuscular adipose tissue in patients with low back pain. Disabil. Rehabil. 2020, 42, 679–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubino, S.; Adepoju, A.; Kumar, V.; Prusik, J.; Murphy, N.; Owusu-Sarpong, S.; Pilitsis, J.G. MRI Conditionality in Patients with Spinal Cord Stimulation Devices. Stereotact. Funct. Neurosurg. 2016, 94, 254–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goudman, L.; Russo, M.; Pilitsis, J.G.; Eldabe, S.; Duarte, R.V.; Billot, M.; Roulaud, M.; Rigoard, P.; Moens, M. Treatment modalities for patients with Persistent Spinal Pain Syndrome Type II: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Commun. Med. 2025, 5, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crawford, R.J.; Cornwall, J.; Abbott, R.; Elliott, J.M. Manually defining regions of interest when quantifying paravertebral muscles fatty infiltration from axial magnetic resonance imaging: A proposed method for the lumbar spine with anatomical cross-reference. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2017, 18, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urrutia, J.; Besa, P.; Lobos, D.; Andia, M.; Arrieta, C.; Uribe, S. Is a single-level measurement of paraspinal muscle fat infiltration and cross-sectional area representative of the entire lumbar spine? Skelet. Radiol. 2018, 47, 939–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazici, A.; Yerlikaya, T.; Oniz, A. An evaluation of the efficacy of a four-grade fat infiltration classification method, presented for the first time in literature. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2022, 23, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayed, D.; Chakravarthy, K.; Amirdelfan, K.; Kalia, H.; Meacham, K.; Shirvalkar, P.; Falowski, S.; Petersen, E.; Hagedorn, J.M.; Pope, J.; et al. A Comprehensive Practice Guideline for Magnetic Resonance Imaging Compatibility in Implanted Neuromodulation Devices. Neuromodulation 2020, 23, 893–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, M.J.; Hargens, L.M.; Breitenfeldt, M.D.; Doth, A.H.; Ryan, M.P.; Gunnarsson, C.; Safriel, Y. The rate of magnetic resonance imaging in patients with spinal cord stimulation. Spine 2015, 40, E531–E537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, C.; Komoroski, C.; Roy, L. Evaluation of an innovative spinal cord stimulator platform for the treatment of chronic pain. Pain Manag. 2018, 8, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavrogeni, S.I.; Poulos, G.; Kolovou, G.; Theodorakis, G. Magnetic resonance imaging-conditional devices: Luxury or real clinical need? Hell. J. Cardiol. 2017, 58, 256–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jotwani, R.; Abd-Elsayed, A.; Villegas, K.; Shakil, A.; Gulati, A.; Sayed, D.; Lam, C.; Mehta, N. Failure of SCS MR-Conditional Modes Due to High Impedance: A Review of Literature and Case Series. Pain Ther. 2021, 10, 729–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goudman, L.; Rigoard, P.; Billot, M.; Duarte, R.V.; Eldabe, S.; Moens, M. Patient Selection for Spinal Cord Stimulation in Treatment of Pain: Sequential Decision-Making Model—A Narrative Review. J. Pain Res. 2022, 15, 1163–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Y.; Zhao, C.; Wang, L.; Su, Y.; Shang, D.; Li, F.; Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Li, J.; Wang, W. Target volumes comparison between postoperative simulation magnetic resonance imaging and preoperative diagnostic magnetic resonance imaging for prone breast radiotherapy after breast-conserving surgery. Cancer Med. 2024, 13, e6956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moens, M.; Goudman, L.; Van de Velde, D.; Godderis, L.; Putman, K.; Callens, J.; Lavreysen, O.; Ceulemans, D.; Leysen, L.; OPERA consortium; et al. Personalised rehabilitation to improve return to work in patients with persistent spinal pain syndrome type II after spinal cord stimulation implantation: A study protocol for a 12-month randomised controlled trial-the OPERA study. Trials 2022, 23, 974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tekmyster, G.; Jonely, H.; Lee, D.W.; Myerson, J.; Avery, M.; Moradian, M.; Desai, M.J. Physical Therapy Considerations and Recommendations for Patients Following Spinal Cord Stimulator Implant Surgery. Neuromodulation 2023, 26, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, S.; Williams, A.; Vajramani, G.; Sharma, M.; Love-Jones, S.; Chawla, R.; Eldabe, S. Restorative neurostimulation for chronic mechanical low back pain—Three year results from the United Kingdom post market clinical follow-up registry. Br. J. Pain 2023, 17, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilligan, C.; Volschenk, W.; Russo, M.; Green, M.; Gilmore, C.; Mehta, V.; Deckers, K.; De Smedt, K.; Latif, U.; Sayed, D.; et al. Three-Year Durability of Restorative Neurostimulation Effectiveness in Patients with Chronic Low Back Pain and Multifidus Muscle Dysfunction. Neuromodulation 2023, 26, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francio, V.T.; Westerhaus, B.D.; Carayannopoulos, A.G.; Sayed, D. Multifidus dysfunction and restorative neurostimulation: A scoping review. Pain Med. 2023, 24, 1341–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilligan, C.; Volschenk, W.; Russo, M.; Green, M.; Gilmore, C.; Mehta, V.; Deckers, K.; De Smedt, K.; Latif, U.; Sayed, D.; et al. Five-Year Longitudinal Follow-up of Restorative Neurostimulation Shows Durability of Effectiveness in Patients with Refractory Chronic Low Back Pain Associated with Multifidus Muscle Dysfunction. Neuromodulation 2024, 27, 930–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goudman, L.; Smet, I.; Marien, P.; De Jaeger, M.; De Groote, S.; Huysmans, E.; Putman, K.; Van Buyten, J.P.; Buyl, R.; Moens, M. Is the Self-Reporting of Failed Back Surgery Syndrome Patients Treated with Spinal Cord Stimulation in Line with Objective Measurements? Neuromodulation 2018, 21, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazeminasab, S.; Nejadghaderi, S.A.; Amiri, P.; Pourfathi, H.; Araj-Khodaei, M.; Sullman, M.J.M.; Kolahi, A.-A.; Safiri, S. Neck pain: Global epidemiology, trends and risk factors. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2022, 23, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranidharan, G.; Bretherton, B.; Montgomery, C.; Titterington, J.; Crowther, T.; Vannabouathong, C.; Inzana, J.A.; Rotte, A. Pain Relief and Safety Outcomes with Cervical 10 kHz Spinal Cord Stimulation: Systematic Literature Review and Meta-analysis. Pain. Ther. 2021, 10, 849–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Zoete, R.M.J. Exercise Therapy for Chronic Neck Pain: Tailoring Person-Centred Approaches within Contemporary Management. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 7108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
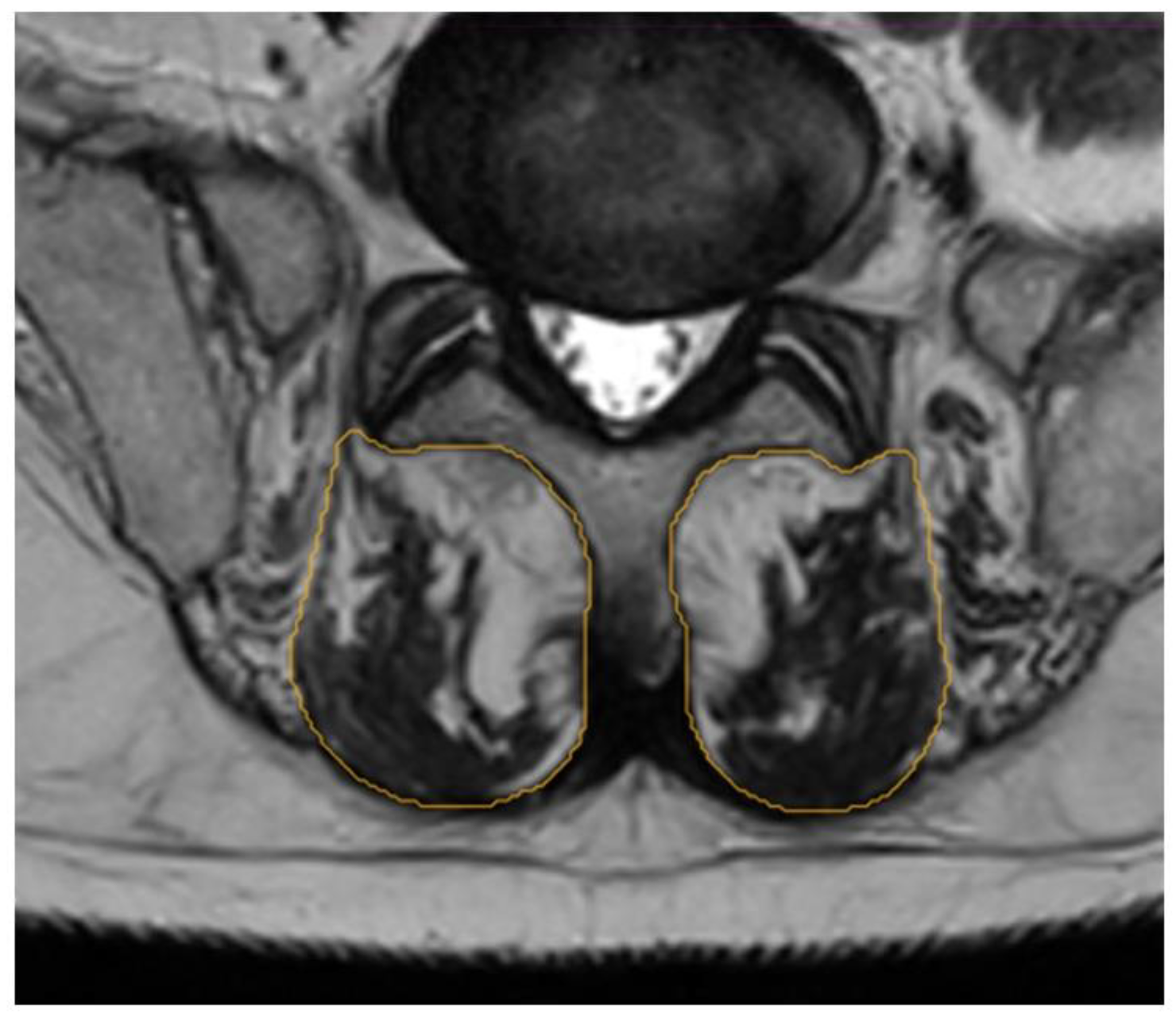
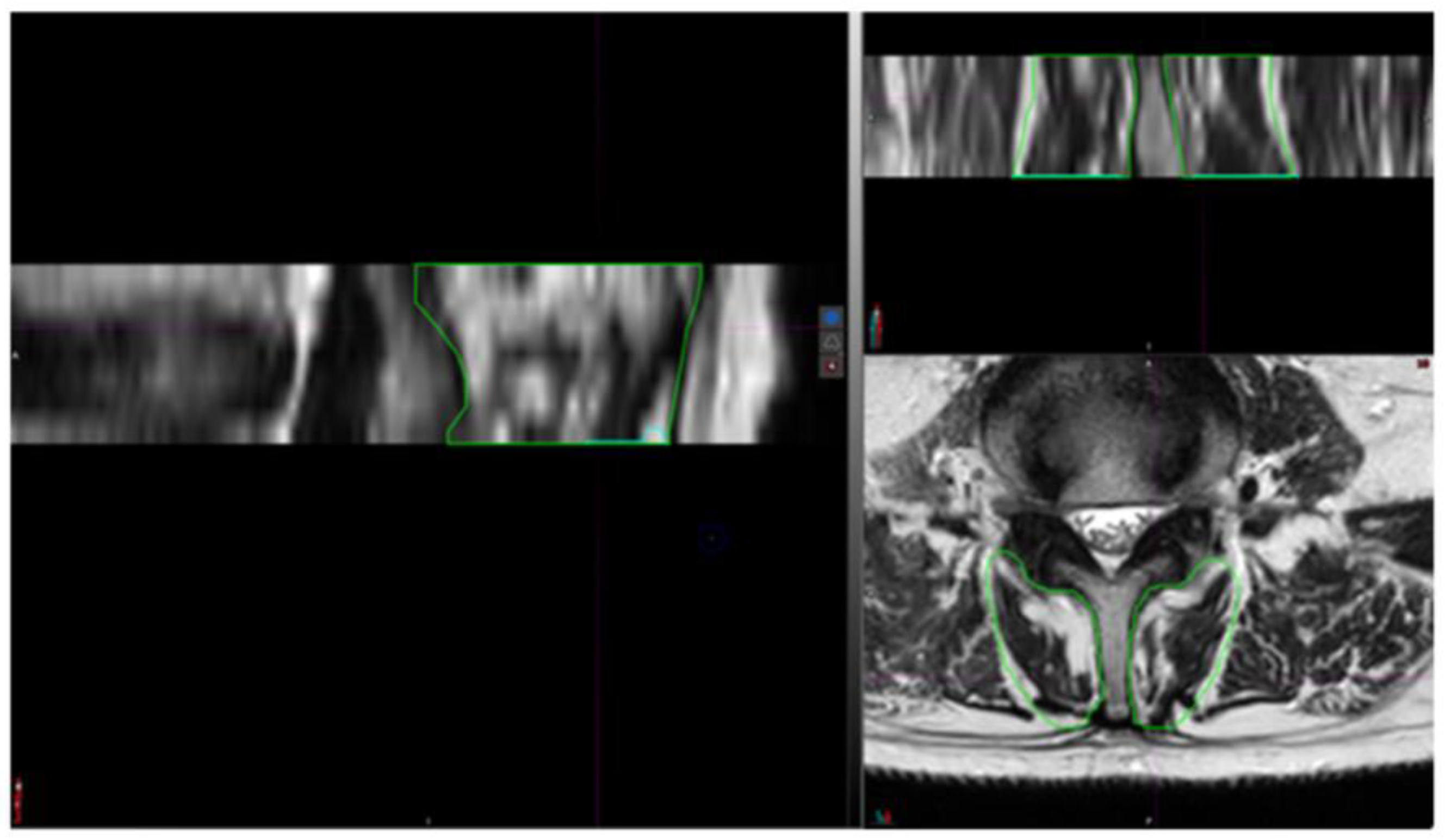
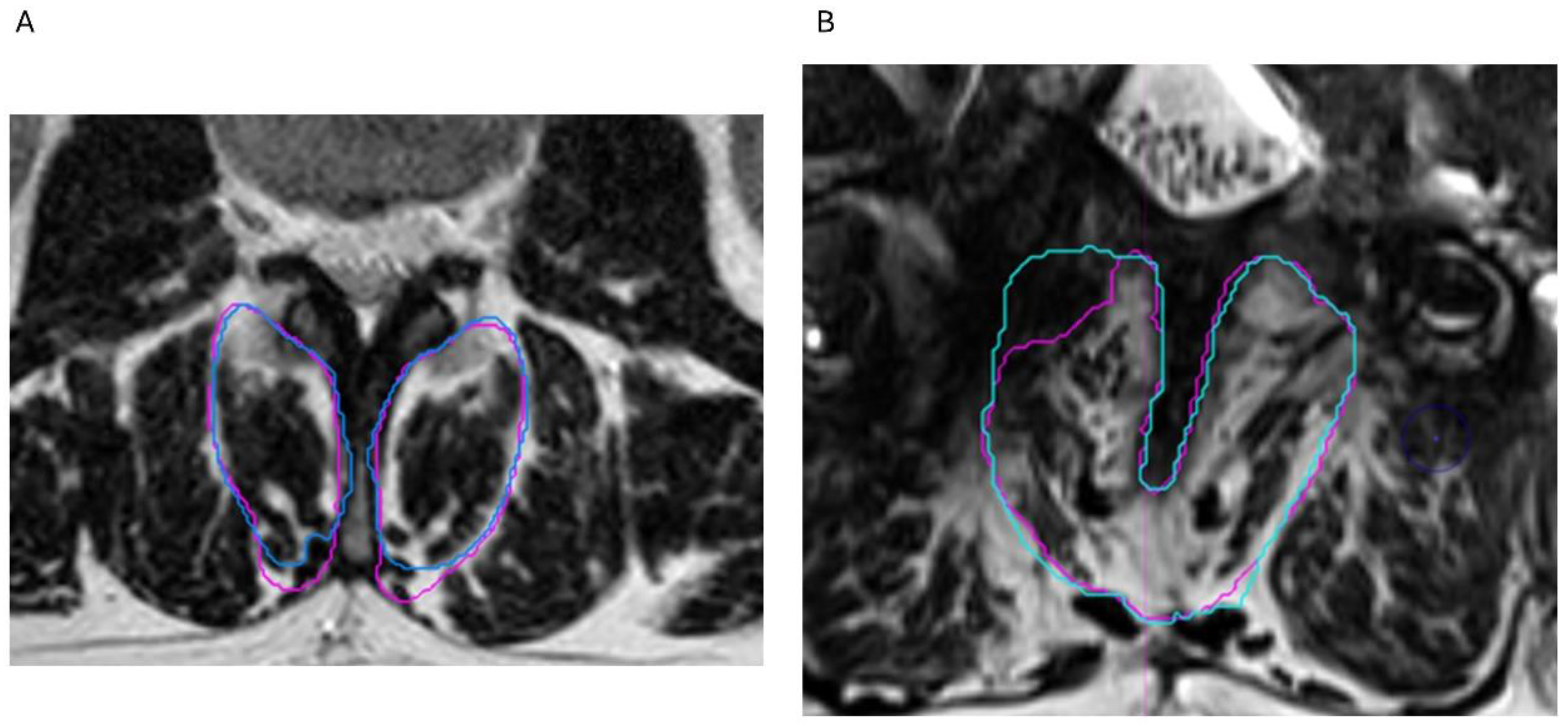


| Patient Profile | BMI (kg/m2) | Level of Surgery | IPG Implantation | Pain Medication | Pain Duration |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male, 61 y | 26.2 | L2–L3 | 2022 | Lyrica | 11 years, after herniectomy L2–L3 |
| Female, 47 y | 29.7 | L4–L5 | 2021 | Tramadol retard | 5 years, after lumbar fusion L4–L5 |
| Female, 45 y | 40.6 | L4–L5, L5–S1 | 2018 | Oxycodone, Lyrica, Diclofenac, Cymbalta | 18 years, after disc herniation L5–S1 and 6 years later L4–L5 |
| Female, 47 y | 27.2 | L4–L5 | 2018 | Oxycontin, Oxynorm, NSAIDs | 6 years, after L4–L5 ALIF |
| Level | Contingency Table | Intraclass Correlation Coefficient [95% CI] for Muscle Volume | Cohen’s Weighted Kappa [95% CI] for Visual Grading | Kendall’s tau Correlation for Segmentation Versus Visual Grading | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L2–L3 (n = 2) | Grade 2 (R2) | Grade 3 (R2) | 0.969 [0.248 to 1], p = 0.01 | NA | NA | ||
| Grade 2 (R1) | 0 | 1 | |||||
| Grade 3 (R1) | 0 | 1 | |||||
| L3–L4 (n = 4) | Grade 2 (R2) | Grade 3 (R2) | 1 [1 to 1], p < 0.001 | 0.5 [−0.235 to 1], p = 0.18 | r = 0, p = 1 | ||
| Grade 2 (R1) | 2 | 0 | |||||
| Grade 3 (R1) | 1 | 1 | |||||
| L4–L5 (n = 4) | Grade 2 (R2) | Grade 3 (R2) | 1 [1 to 1], p = 1 | 1 [1 to 1] | r = 1, p = 0.08 | ||
| Grade 2 (R1) | 1 | 0 | |||||
| Grade 3 (R1) | 0 | 3 | |||||
| L5–S1 (n = 4) | Grade 2 (R2) | Grade 3 (R2) | Grade 4 (R2) | 0.999 [0.994 to 1], p < 0.001 | 1 [1 to 1] | r = 0.77, p = 0.16 | |
| Grade 2 (R1) | 1 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| Grade 3 (R1) | 0 | 2 | 0 | ||||
| Grade 4 (R1) | 0 | 0 | 1 | ||||
| All levels (n = 14) | Grade 2 (R2) | Grade 3 (R2) | Grade 4 (R2) | 1 [0.999 to 1], p < 0.001 | 0.759 [0.430 to 1], p < 0.001 | r = 0.56, p = 0.04 | |
| Grade 2 (R1) | 4 | 1 | 0 | ||||
| Grade 3 (R1) | 1 | 7 | 0 | ||||
| Grade 4 (R1) | 0 | 0 | 1 | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moens, M.; Genot, L.V.; Van Gestel, F.; Pilitsis, J.G.; Billot, M.; Roulaud, M.; Rigoard, P.; Goudman, L. Multifidus Fat Infiltration in Patients with Persistent Spinal Pain Syndrome Type II Treated with Spinal Cord Stimulation: A Preliminary Report. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 3124. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14093124
Moens M, Genot LV, Van Gestel F, Pilitsis JG, Billot M, Roulaud M, Rigoard P, Goudman L. Multifidus Fat Infiltration in Patients with Persistent Spinal Pain Syndrome Type II Treated with Spinal Cord Stimulation: A Preliminary Report. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(9):3124. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14093124
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoens, Maarten, Laurène V. Genot, Frederick Van Gestel, Julie G. Pilitsis, Maxime Billot, Manuel Roulaud, Philippe Rigoard, and Lisa Goudman. 2025. "Multifidus Fat Infiltration in Patients with Persistent Spinal Pain Syndrome Type II Treated with Spinal Cord Stimulation: A Preliminary Report" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 9: 3124. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14093124
APA StyleMoens, M., Genot, L. V., Van Gestel, F., Pilitsis, J. G., Billot, M., Roulaud, M., Rigoard, P., & Goudman, L. (2025). Multifidus Fat Infiltration in Patients with Persistent Spinal Pain Syndrome Type II Treated with Spinal Cord Stimulation: A Preliminary Report. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(9), 3124. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14093124








