The Impact of Non-Invasive Scores and Hemogram-Derived Ratios in Differentiating Chronic Liver Disease from Cirrhosis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Participants
2.2. Laboratory and Clinical Data
2.3. Hepatic Steatosis and Liver Fibrosis Scores
2.4. Hemogram-Derived Ratios and Biomarkers
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. General Characteristics
3.2. CLD and Cirrhosis Etiologies
3.3. Laboratory Tests
3.4. Clinical Features and Prognostic Scores
3.5. Non-Invasive Biomarkers and Scores in Chronic Liver Disease and Liver Cirrhosis
3.6. Hemogram-Derived Ratios
3.7. Predictive Accuracy of Several Biomarkers and Scores in Differentiating CLD from Cirrhosis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Younossi, Z.M.; Wong, G.; Anstee, Q.M.; Henry, L. The Global Burden of Liver Disease. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 21, 1978–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devarbhavi, H.; Asrani, S.K.; Arab, J.P.; Nartey, Y.A.; Pose, E.; Kamath, P.S. Global burden of liver disease: 2023 update. J. Hepatol. 2023, 79, 516–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, C.; Yuan, Y.; Shen, H.; Gao, J.; Kong, X.; Che, Z.; Guo, Y.; Wang, H.; Dong, E.; Xiao, J. Liver diseases: Epidemiology, causes, trends and predictions. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2025, 10, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Nagalli, S. Chronic Liver Disease. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK554597/ (accessed on 3 July 2023).
- Ismaiel, A.; Portincasa, P.; Dumitrascu, D.L. Natural History of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. In Essentials of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease; Trifan, A., Stanciu, C., Muzica, C., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amico, G.; Garcia-Tsao, G.; Pagliaro, L. Natural history and prognostic indicators of survival in cirrhosis: A systematic review of 118 studies. J. Hepatol. 2006, 44, 217–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Premkumar, M.; Anand, A.C. Overview of Complications in Cirrhosis. J. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2022, 12, 1150–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanapirom, K.; Suksawatamnuay, S.; Tanpowpong, N.; Chaopathomkul, B.; Sriphoosanaphan, S.; Thaimai, P.; Srisoonthorn, N.; Treeprasertsuk, S.; Komolmit, P. Non-invasive tests for liver fibrosis assessment in patients with chronic liver diseases: A prospective study. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 4913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismaiel, A.; Leucuta, D.C.; Popa, S.L.; Fagoonee, S.; Pellicano, R.; Abenavoli, L.; Dumitrascu, D.L. Noninvasive biomarkers in predicting nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and assessing liver fibrosis: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Panminerva Med. 2021, 63, 508–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarlata, G.G.M.; Ismaiel, A.; Gambardella, M.L.; Leucuta, D.C.; Luzza, F.; Dumitrascu, D.L.; Abenavoli, L. Use of Non-Invasive Biomarkers and Clinical Scores to Predict the Complications of Liver Cirrhosis: A Bicentric Experience. Medicina 2024, 60, 1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singal, A.K.; Kamath, P.S. Model for End-stage Liver Disease. J. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2013, 3, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Lee, H.W. Important predictor of mortality in patients with end-stage liver disease. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2013, 19, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterling, R.K.; Lissen, E.; Clumeck, N.; Sola, R.; Correa, M.C.; Montaner, J.; SSulkowski, M.; Torriani, F.J.; Dieterich, D.T.; Thomas, D.L.; et al. Development of a simple noninvasive index to predict significant fibrosis in patients with HIV/HCV coinfection. Hepatology 2006, 43, 1317–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angulo, P.; Hui, J.M.; Marchesini, G.; Bugianesi, E.; George, J.; Farrell, G.C.; Enders, F.; Saksena, S.; Burt, A.D.; Bida, J.P.; et al. The NAFLD fibrosis score: A noninvasive system that identifies liver fibrosis in patients with NAFLD. Hepatology 2007, 45, 846–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wai, C.T.; Greenson, J.K.; Fontana, R.J.; Kalbfleisch, J.D.; Marrero, J.A.; Conjeevaram, H.S.; Lok, A.S. A simple noninvasive index can predict both significant fibrosis and cirrhosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology 2003, 38, 518–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.F.; Huang, Y.T.; Huang, C.H.; Chang, S.H.; Lin, C.Y. Fibrosis index predicts variceal bleeding and reduces need for nonselective beta-blocker in compensated cirrhosis with initial small esophageal varices without red-color sign. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Tang, S.; Liu, C.; Ma, J.; Cao, X.; Yang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, K.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, C.; et al. Systemic immune-inflammatory biomarkers (SII, NLR, PLR and LMR) linked to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease risk. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1337241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsoris, A.; Marlar, C.A. Use Of The Child Pugh Score In Liver Disease. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK542308/ (accessed on 13 March 2023).
- Marcellin, P.; Kutala, B.K. Liver diseases: A major, neglected global public health problem requiring urgent actions and large-scale screening. Liver Int. 2018, 38 (Suppl. S1), 2–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciornolutchii, V.; Ruta, V.M.; Man, A.M.; Motoc, N.S.; Popa, S.L.; Dumitrascu, D.L.; Ismaiel, A.; Leucuta, D.C. Exploring the Role of Hemogram-Derived Ratios and Liver Fibrosis Scores in Pulmonary Fibrosis. Medicina 2024, 60, 1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qamar, A.A.; Grace, N.D. Abnormal hematological indices in cirrhosis. Can. J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 23, 441–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadir, M.R.; Riahin, A.A.; Havaspour, A.; Nooranipour, M.; Habibinejad, A.A. The relationship between lipid profile and severity of liver damage in cirrhotic patients. Hepat. Mon. 2010, 10, 285–288. [Google Scholar]
- Liguori, A.; Zoncapè, M.; Casazza, G.; Easterbrook, P.; Tsochatzis, E.A. Staging liver fibrosis and cirrhosis using non-invasive tests in people with chronic hepatitis B to inform WHO 2024 guidelines: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2025, 10, 332–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, Y.; Wu, D.; Zhang, Q.; Yu, Z.; Yu, J.; Zhou, D. Elevated ALT/AST ratio as a marker for NAFLD risk and severity: Insights from a cross-sectional analysis in the United States. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1457598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chedid, M.F.; Picon, R.V.; Chedid, A.D. ALBI and PALBI: Novel Scores for Outcome Prediction of Cirrhotic Outpatients Awaiting Liver Transplantation. Ann. Hepatol. 2018, 17, 906–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsayed, A.; Ismaiel, A.; Procopio, A.C.; Luzza, F.; Abenavoli, L.; Dumitrascu, D.L. Noninvasive biochemical markers and surrogate scores in evaluating nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Minerva Med. 2022, 113, 864–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaaouani, A.; Al Srouji, N.; Popa, S.L.; Ismaiel, A. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Literature Review of Epidemiology, Pathophysiology, and Diagnostic Approaches. Glob. J. Med. Therap. 2024, 6, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priego-Parra, B.A.; Triana-Romero, A.; Bernal-Reyes, R.; Icaza-Chávez, M.E.; Martínez-Vázquez, S.E.; Amieva-Balmori, M.; Cano-Contreras, A.D.; Vivanco-Cid, H.; Remes-Troche, J.M. Comparative evaluation of APRI, FIB-4, HFS, and NFS: Scoring tools for liver fibrosis in a Mexican population with MASLD. Rev. Gastroenterol. Mex. (Engl. Ed.) 2024, 89, 498–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines on non-invasive tests for evaluation of liver disease severity and prognosis—2021 update. J. Hepatol. 2021, 75, 659–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekin, N.; Ucmak, F.; Ebik, B.; Tugba Tuncel, E.; Kacmaz, H.; Arpa, M.; Engin Atay, A. GPR, King’s Score and S-Index are superior to other non-invasive fibrosis markers in predicting the liver fibrosis in chronic Hepatitis B patients. Acta Gastro-Enterol. Belg. 2022, 85, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, L.; Schuch, A.; Longo, L.; Valentini, B.B.; Galvão, G.S.; Luchese, E.; Pinzon, C.; Bartels, R.; Álvares-da-Silva, M.R. New FIB-4 and NFS cutoffs to guide sequential non-invasive assessment of liver fibrosis by magnetic resonance elastography in NAFLD. Ann. Hepatol. 2023, 28, 100774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahani, S.; Das, D. Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio (NLR) and its Correlation with Child Turcotte Pugh (CTP) Score in Prediciting Severity of Decompensated Liver Cirrhosis. J. Assoc. Physicians India 2022, 70, 11–12. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, C.; Zhang, W.; Xiao, Y.; Sun, Y.; Peng, X.; Cai, W. The predictive role of the platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio for the risk of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and cirrhosis: A nationwide cross-sectional study. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1376894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glisic, T.; Popovic, D.D.; Lolic, I.; Toplicanin, A.; Jankovic, K.; Dragasevic, S.; Aleksic, M.; Stjepanovic, M.; Oluic, B.; Matovic Zaric, V.; et al. Hematological Indices Are Useful in Predicting Complications of Liver Cirrhosis. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 4820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Score | Formula |
|---|---|
| Fibrosis-4 Index (FIB-4) | Age (years) × AST (U/L)/{platelet (×109/L) × [ALT (U/L)]1/2} |
| AST to Platelet Ratio Index (APRI) | [(AST/ULN AST)/platelet (×109/L)] × 100 |
| NAFLD Fibrosis Score (NFS) | −1.675 + (0.037 × Age) + (0.094 × BMI) + (1.13 × IFG/DM) + (0.99 × AST/ALT) − (0.013 × Platelets) − (0.66 × Albumin) |
| AST/ALT Ratio | AST/ALT |
| BARD Score | BMI ≥ 28 = 1 point, AST/ALT ≥ 0.8 = 2 points, Diabetes = 1 point |
| ABIC Score | (0.62 × Age) + (0.91 × Bilirubin) + (0.48 × INR) + (0.11 × Creatinine) |
| King’s Score | Age (years) × AST (U/L) × INR/Platelet (109/L) |
| LogOddsLok | (1.26 × AST/ALT) + (5.27 × INR) − [0.0089 × Platelet (×109/L)] − 5.56 |
| Lok Index | e(LogOddsLok)/(1 + e(LogOddsLok)) |
| Triglyceride–Glucose (TyG) Ratio | Fasting Triglycerides × Fasting Glucose/2 |
| Prognostic Nutritional Index (PNI) | (10 × Albumin [g/dL]) + (0.005 × Total Lymphocyte Count) |
| MELD score | 9.57 × loge (creatinine) + 3.78 × loge (total bilirubin) + 11.2 × loge (INR) + 6.43 |
| Platelet-Albumin-Bilirubin (PALBI) Score | 2.02 × log10[bilirubin (μmol/L)] − 0.37 × [log10(bilirubin)]2 − 0.04 × albumin (g/L) − 3.48 × log10[platelets (×109/L)] + 1.01 × log10(platelets) |
| Albumin-Bilirubin (ALBI) Score | [log10(bilirubin (μmol/L)] × 0.66 − [Albumin (g/L) × 0.085] |
| ALBI grade | ALBI grade 1 (≤−2.60) ALBI grade 2 (>−2.60 to ≤−1.39) ALBI grade 3 (>−1.39) |
| Fibrosis Index | 8 − 0.01 × platelets (109/L) − albumin (g/dL) |
| Variable | CLD (n = 113) | Cirrhosis (n = 137) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex (F), nr (%) | 82 (72.57) | 47 (34.31) | <0.001 |
| Age (years), median (IQR) | 63 (53–69) | 64 (59–70) | 0.052 |
| BMI (kg/m2), median (IQR) | 22.49 (21–32) | 21 (21–31.25) | 0.539 |
| Sex (F), nr (%) | 82 (72.57) | 47 (34.31) | <0.001 |
| Hypertension, n (%) | 70 (61.95) | 65 (47.45) | 0.022 |
| Diabetes, n (%) | 19 (16.81) | 43 (31.39) | 0.008 |
| Insulin use, n (%) | 11 (9.73) | 23 (16.79) | 0.105 |
| Dyslipidemia, n (%) | 43 (38.05) | 12 (8.76) | <0.001 |
| Statin use, n (%) | 43 (38.05) | 12 (8.76) | <0.001 |
| Metabolic syndrome, n (%) | 30 (26.55) | 24 (17.52) | 0.084 |
| Etiologies | CLD (n = 113) | Cirrhosis (n = 137) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hepatitis B, nr (%) | 42 (37.17) | 15 (10.95) | <0.001 |
| Hepatitis C, nr (%) | 39 (34.51) | 33 (24.09) | |
| Hepatitis B–C co-infection, nr (%) | 1 (0.88) | 3 (2.19) | |
| Hepatitis B–D co-infection, nr (%) | 1 (0.88) | 0 (0) | |
| Primary biliary cholangitis, nr (%) | 14 (12.39) | 1 (0.73) | |
| Autoimmune hepatitis, nr (%) | 16 (14.16) | 8 (5.84) | |
| Alcohol-related, nr (%) | 0 (0) | 64 (46.72) | |
| Overlap (autoimmune + PBC), nr (%) | 0 (0) | 4 (2.92) | |
| Other causes (Cryptogenic, Wilson’s disease, Drug induced), nr (%) | 0 (0) | 9 (6.57) |
| Variable | CLD (n = 113) | Cirrhosis (n = 137) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Complete blood count | |||
| Hemoglobin (g/dL), median (IQR) | 13.2 (12.4–14.5) | 11.8 (10–13.5) | <0.001 |
| Hematocrit (%), median (IQR) | 39.3 (37–42.4) | 34.5 (30.1–39.7) | <0.001 |
| Leukocytes/L, median (IQR) | 6.12 (5.02–8.09) | 6.48 (4.3–9.35) | 0.838 |
| Platelets/L, median (IQR) | 217 (177–265) | 122 (84–179) | <0.001 |
| Neutrophils × 109/L, median (IQR) | 3.8 (2.88–4.9) | 3.99 (2.62–6.28) | 0.582 |
| Lymphocytes × 109/L, median (IQR) | 1.68 (1.3–2.21) | 1.26 (0.74–1.63) | <0.001 |
| Leucocytes × 109/L, median (IQR) | 6.12 (5.02–8.09) | 6.48 (4.3–9.35) | 0.838 |
| Eosinophils × 109/L, median (IQR) | 0.12 (0.06–0.19) | 0.09 (0.05–0.17) | 0.224 |
| Monocytes × 109/L, median (IQR) | 0.43 (0.31–0.51) | 0.45 (0.32–0.66) | 0.104 |
| Basophils × 109/L, median (IQR) | 0.03 (0.02–0.04) | 0.03 (0.01–0.04) | 0.105 |
| RDW-CV (%), median (IQR) | 13.45 (12.9–14.33) | 14.6 (13.6–16.4) | <0.001 |
| PDW (fL), median (IQR) | 16.2 (15.95–16.45) | 16.3 (16.1–16.65) | 0.009 |
| Metabolic blood tests | |||
| Glycemia, median (IQR) | 101 (92–117) | 110 (95–137) | 0.011 |
| Triglycerides, median (IQR) | 103.5 (85.75–139.75) | 88.5 (72.75–125.75) | 0.007 |
| LDL, median (IQR) | 110.5 (87.5–134) | 71 (49–94) | <0.001 |
| HDL, median (IQR) | 49 (40–59) | 40 (28–54) | <0.001 |
| Liver function tests | |||
| Albumin (g/dL), median (IQR) | 4.2 (3.9–4.5) | 3.37 (2.8–4) | <0.001 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL), median (IQR) | 0.75 (0.66–0.98) | 0.85 (0.66–1.2) | 0.055 |
| ASAT (U/L), median (IQR) | 28 (22–40) | 45 (29–71) | <0.001 |
| ALAT (U/L), median (IQR) | 25 (16–39) | 26 (17–38) | 0.516 |
| GGT (U/L), median (IQR) | 31 (18–77) | 85 (34.25–168) | <0.001 |
| Alkaline Phosphatase, median (IQR) | 72 (57–97) | 96 (72.5–143) | <0.001 |
| Total Bilirubin mg/dL), median (IQR) | 0.65 (0.5–0.93) | 1.39 (0.84–2.54) | <0.001 |
| Coagulation profile | |||
| INR (sec), median (IQR) | 1.01 (0.96–1.09) | 1.28 (1.12–1.62) | <0.001 |
| Variable | CLD (n = 113) | Cirrhosis (n = 137) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Encephalopathy, n (%) | absent: 113 (100) | absent: 104 (75.91) | <0.001 |
| moderate: 0 (0) | moderate: 25 (18.25) | ||
| severe: 0 (0) | severe: 8 (5.84) | ||
| Ascites, n (%) | absent: 110 (97.35) | absent: 77 (56.2) | <0.001 |
| moderate: 3 (2.65) | moderate: 37 (27.01) | ||
| severe: 0 (0) | severe: 23 (16.79) | ||
| Child–Pugh Class, n (%) | A: 113 (100) | A: 52 (41.6) | <0.001 |
| B: 0 (0) | B: 48 (38.4) | ||
| C: 0 (0) | C: 25 (20) | ||
| ALBI grade, n (%) | A1: 7 (6.42) | A1: 2 (1.5) | <0.001 |
| A2: 90 (82.57) | A2: 44 (33.08) | ||
| A3: 12 (11.01) | A3: 87 (65.41) | ||
| ALBI score, median (IQR) | −1.91 (−2.3–−1.63) | −0.87 (−1.64–−0.27) | <0.001 |
| MELD, median (IQR) | 2.51 (0.46–5.94) | 9.34 (5.02–14.74) | <0.001 |
| Mortality risk %, median (IQR) | 1.9 (1.9–1.9) | 6 (1.9–6) | <0.001 |
| Variable | CLD (n = 113) | Cirrhosis (n = 137) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| APRI, median (IQR) | 0.37 (0.27–0.55) | 1.1 (0.57–2.27) | <0.001 |
| FIB4, median (IQR) | 1.68 (1.15–2.28) | 4.89 (2.79–9.31) | <0.001 |
| NFS, median (IQR) | −1.31 (−2.24–−0.05) | 1.14 (0–2.21) | <0.001 |
| Triglyceride–glucose index, median (IQR) | 3.76 (3.61–3.91) | 3.71 (3.58–3.88) | 0.426 |
| Prognostic nutritional index, median (IQR) | 42.82 (39.46–45.81) | 34.43 (29.1–40.71) | <0.001 |
| AST/ALT ratio, median (IQR) | 1.14 (0.91–1.5) | 1.77 (1.33–2.29) | <0.001 |
| AST to platelet ratio index (APRI), median (IQR) | 0.37 (0.27–0.55) | 1.1 (0.57–2.27) | <0.001 |
| Platelet–albumin–bilirubin (PALBI) score, median (IQR) | −3.86 (−3.97–−3.68) | −3.86 (−3.97–−3.76) | 0.44 |
| ABIC, median (IQR) | 7.31 (6.4–8.05) | 8.05 (7.52–8.83) | <0.001 |
| Fibrosis index, median (IQR) | 1.65 (1.02–2.34) | 3.44 (2.49–3.95) | <0.001 |
| King score, median (IQR) | 7.39 (5.16–13.04) | 36.67 (15.67–74.59) | <0.001 |
| Lok index, median (IQR) | 0.34 (0.24–0.57) | 0.92 (0.78–0.99) | <0.001 |
| Variable | CLD (n = 113) | Cirrhosis (n = 137) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| NLR, median (IQR) | 2.18 (1.7–3.3) | 3.2 (2.2–5.65) | <0.001 |
| dNLR, median (IQR) | 1.6 (1.21–2.24) | 1.68 (1.06–2.49) | 0.634 |
| PLR, median (IQR) | 129.32 (92.06–173.14) | 104.46 (59.61–157.68) | 0.002 |
| LMR, median (IQR) | 4.06 (3.3–5.42) | 2.74 (1.65–3.94) | <0.001 |
| PNR, median (IQR) | 55.64 (39.32–68.83) | 29.36 (20.37–45.21) | <0.001 |
| SII, median (IQR) | 439.46 (328.98–701.47) | 393.19 (213.5–763.19) | 0.109 |
| AISI, median (IQR) | 191.2 (113.2–313.71) | 189.14 (73.02–465.46) | 0.735 |
| ELR, median (IQR) | 0.07 (0.04–0.11) | 0.09 (0.05–0.15) | 0.098 |
| BLR, median (IQR) | 0.02 (0.01–0.03) | 0.02 (0.01–0.03) | 0.486 |
| Neutrophil–lymphocyte–albumin ratio, median (IQR) | 0.51 (0.4–0.77) | 0.98 (0.55–2.03) | <0.001 |
| Variable | AUC (95% CI) | Se | Sp | Cut-Off |
|---|---|---|---|---|
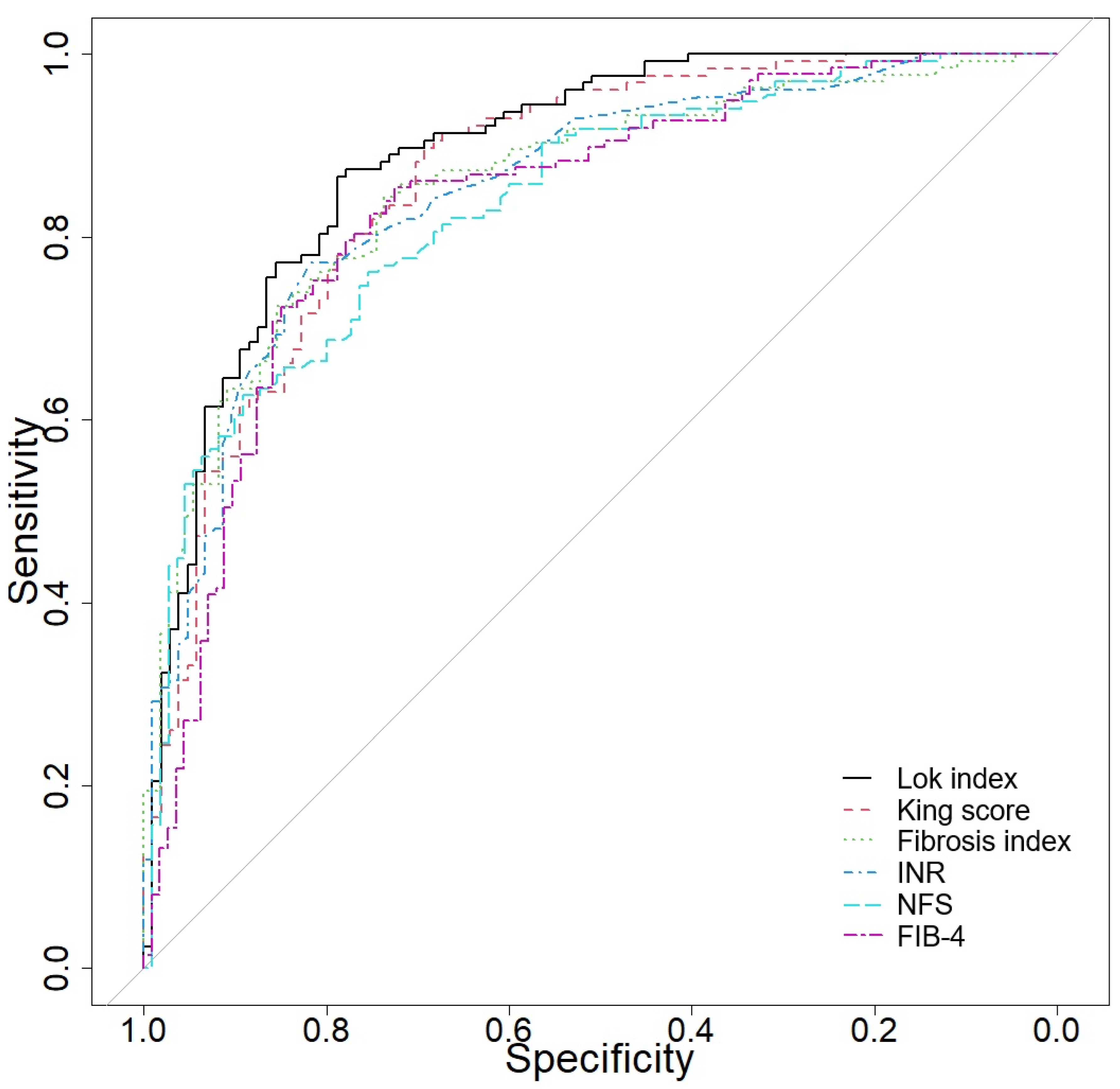
| Lok index | 0.89 (0.848–0.93) | 86.61 | 78.85 | 0.633044469 |
| King score | 0.864 (0.812–0.91) | 89.76 | 69.23 | 11.40065789 |
| Fibrosis index | 0.856 (0.807–0.902) | 84.33 | 73.64 | 2.19 |
| INR (sec) | 0.851 (0.8–0.899) | 77.17 | 81.73 | 1.11 |
| NFS | 0.836 (0.785–0.881) | 62.69 | 89.09 | 0.53 |
| FIB-4-index | 0.834 (0.782–0.885) | 85.4 | 72.57 | 2.186795399 |
| Score 5 | 0.83 (0.787–0.875) | 72 | 87 | 5 |
| RDW-to-platelet ratio | 0.826 (0.77–0.876) | 82.96 | 73.21 | 0.07 |
| ALBI score | 0.823 (0.773–0.872) | 71.43 | 85.32 | −1.508713864 |
| APRI | 0.805 (0.749–0.859) | 70.07 | 83.19 | 0.638297872 |
| MELD | 0.802 (0.743–0.855) | 79.37 | 67.65 | 4.51 |
| Platelets × 109/L | 0.795 (0.737–0.848) | 79.65 | 72.26 | 169 |
| Prognostic nutritional index | 0.776 (0.718–0.833) | 89.91 | 59.09 | 35.64 |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 0.775 (0.711–0.83) | 90 | 58.96 | 3.52 |
| PNR | 0.767 (0.707–0.825) | 64.29 | 81.48 | 48.46 |
| AST/ALT ratio | 0.748 (0.684–0.806) | 70.8 | 73.45 | 1.428571429 |
| LMR | 0.72 (0.654–0.778) | 74.11 | 66.67 | 3.37 |
| Neutrophil–lymphocyte–albumin ratio | 0.708 (0.641–0.773) | 60.61 | 76.15 | 0.79 |
| ABIC | 0.707 (0.638–0.773) | 73.81 | 61.76 | 7.5362 |
| RDW-CV (%) | 0.706 (0.639–0.769) | 73.33 | 59.82 | 13.6 |
| Lymphocytes × 109/L | 0.685 (0.618–0.748) | 69.64 | 61.48 | 1.39 |
| NLR | 0.658 (0.586–0.726) | 73.33 | 54.46 | 2.23 |
| PLR | 0.615 (0.548–0.683) | 93.75 | 34.07 | 69.88 |
| PDW (fL) | 0.596 (0.528–0.666) | 59.26 | 56.76 | 16.2 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 0.571 (0.499–0.64) | 61.31 | 57.14 | 0.77 |
| ELR | 0.561 (0.489–0.631) | 48.15 | 66.07 | 0.09047619 |
| Monocytes × 109/L | 0.56 (0.486–0.631) | 34.07 | 84.82 | 0.56 |
| SII | 0.559 (0.487–0.634) | 91.96 | 27.41 | 230.53 |
| Eosinophils × 109/L | 0.545 (0.471–0.616) | 60.71 | 54.07 | 0.1 |
| Triglyceride–glucose index | 0.531 (0.457–0.607) | 45.71 | 66.67 | 3.791374811 |
| Platelet–albumin–bilirubin (PALBI) score | 0.529 (0.458–0.603) | 24.77 | 85.71 | −3.675684415 |
| BLR | 0.526 (0.455–0.596) | 25.19 | 88.39 | 0.032786885 |
| Neutrophils × 109/L | 0.52 (0.449–0.591) | 34.07 | 79.46 | 5.28 |
| dNLR | 0.518 (0.447–0.589) | 49.63 | 59.82 | 1.72 |
| AISI | 0.513 (0.438–0.586) | 95.54 | 24.44 | 64.95828571 |
| Leucocytes × 109/L | 0.508 (0.435–0.581) | 27.01 | 86.73 | 9.23 |
| Basophils × 109/L | 0.441 (0.371–0.513) | 61.61 | 48.89 | 0.02 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ismaiel, A.; Katell, E.; Leucuta, D.-C.; Popa, S.-L.; Catana, C.S.; Dumitrascu, D.L.; Surdea-Blaga, T. The Impact of Non-Invasive Scores and Hemogram-Derived Ratios in Differentiating Chronic Liver Disease from Cirrhosis. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 3072. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14093072
Ismaiel A, Katell E, Leucuta D-C, Popa S-L, Catana CS, Dumitrascu DL, Surdea-Blaga T. The Impact of Non-Invasive Scores and Hemogram-Derived Ratios in Differentiating Chronic Liver Disease from Cirrhosis. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(9):3072. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14093072
Chicago/Turabian StyleIsmaiel, Abdulrahman, Evrard Katell, Daniel-Corneliu Leucuta, Stefan-Lucian Popa, Cristina Sorina Catana, Dan L. Dumitrascu, and Teodora Surdea-Blaga. 2025. "The Impact of Non-Invasive Scores and Hemogram-Derived Ratios in Differentiating Chronic Liver Disease from Cirrhosis" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 9: 3072. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14093072
APA StyleIsmaiel, A., Katell, E., Leucuta, D.-C., Popa, S.-L., Catana, C. S., Dumitrascu, D. L., & Surdea-Blaga, T. (2025). The Impact of Non-Invasive Scores and Hemogram-Derived Ratios in Differentiating Chronic Liver Disease from Cirrhosis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(9), 3072. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14093072







