Outcome of Cerebral Venous Thrombosis Requiring Mechanical Ventilation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Inclusion Criteria
2.2. Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Clinical Evaluation
2.4. Investigations
2.5. Risk Factor Evaluation
2.6. MRI and MR Venography
2.7. Mechanical Ventilation
2.8. Treatment
2.9. Outcomes
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Clinical and Risk Factors
3.2. MRI and MRV Findings
3.3. Comparison of MV and Non-MV Patients
3.4. Comparison of MV and Non-MV ICU Patients
3.4.1. Comparison of Clinical Parameters
3.4.2. Comparison of MRV and MRI Findings
3.4.3. Comparison of Risk Factors
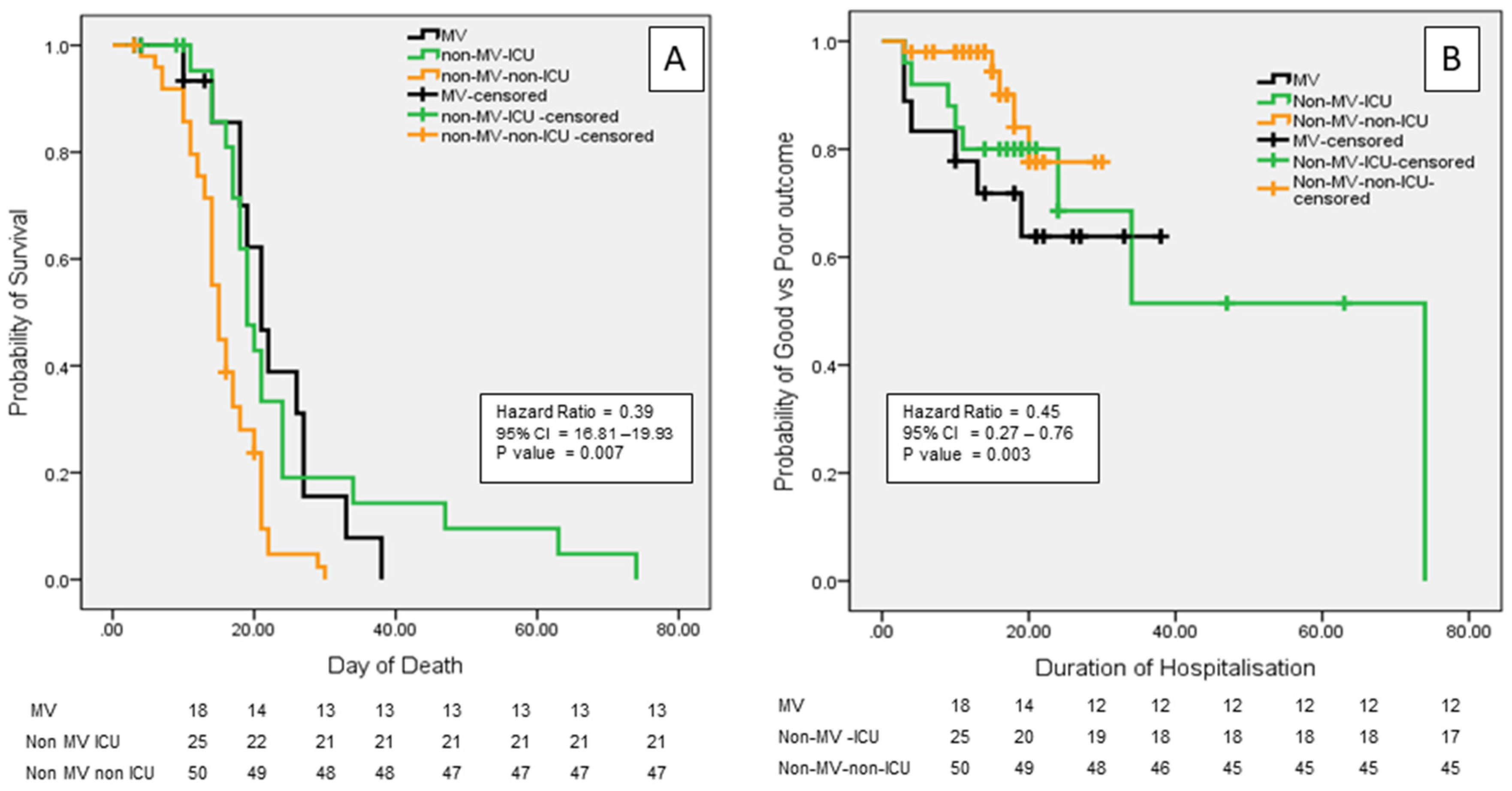
3.5. Outcomes
3.6. Complications
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- GBD 2021 Causes of Death Collaborators. Global burden of 288 causes of death and life expectancy decomposition in 204 countries and territories and 811 subnational locations, 1990–2021: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet 2024, 403, 2100–2132, Erratum in Lancet 2024, 403, 1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- de Montmollin, E.; Terzi, N.; Dupuis, C.; Garrouste-Orgeas, M.; da Silva, D.; Darmon, M.; Laurent, V.; Thiéry, G.; Oziel, J.; Marcotte, G.; et al. One-year survival in acute stroke patients requiring mechanical ventilation: A multicenter cohort study. Ann. Intensive Care 2020, 10, 53. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lahiri, S.; Mayer, S.A.; Fink, M.E.; Lord, A.S.; Rosengart, A.; Mangat, H.S.; Segal, A.Z.; Claassen, J.; Kamel, H. Mechanical Ventilation for Acute Stroke: A Multi-state Population-Based Study. Neurocrit. Care 2015, 23, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Young, P.; Beasley, R.; Bailey, M.; Bellomo, R.; Eastwood, G.M.; Nichol, A.; Pilcher, D.V.; Yunos, N.M.; Egi, M.; Hart, G.K.; et al. The association between early arterial oxygenation and mortality in ventilated patients with acute ischaemic stroke. Crit. Care Resusc. 2012, 14, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Popat, C.; Ruthirago, D.; Shehabeldin, M.; Yang, S.; Nugent, K. Outcomes in Patients With Acute Stroke Requiring Mechanical Ventilation: Predictors of Mortality and Successful Extubation. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2018, 356, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schielke, E.; Busch, M.A.; Hildenhagen, T.; Holtkamp, M.; Küchler, I.; Harms, L.; Masuhr, F. Functional, cognitive and emotional long-term outcome of patients with ischemic stroke requiring mechanical ventilation. J. Neurol. 2005, 252, 648–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steiner, T.; Mendoza, G.; De Georgia, M.; Schellinger, P.; Holle, R.; Hacke, W. Prognosis of stroke patients requiring mechanical ventilation in a neurological critical care unit. Stroke 1997, 28, 711–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santoli, F.; De Jonghe, B.; Hayon, J.; Tran, B.; Piperaud, M.; Merrer, J.; Outin, H. Mechanical ventilation in patients with acute ischemic stroke: Survival and outcome at one year. Intensive Care Med. 2001, 27, 1141–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milhaud, D.; Popp, J.; Thouvenot, E.; Heroum, C.; Bonafé, A. Mechanical ventilation in ischemic stroke. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2004, 13, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burtin, P.; Bollaert, P.E.; Feldmann, L.; Nace, L.; Lelarge, P.; Bauer, P.; Larcan, A. Prognosis of stroke patients undergoing mechanical ventilation. Intensive Care Med. 1994, 20, 32–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonneville, R.; Mazighi, M.; Collet, M.; Gayat, E.; Degos, V.; Duranteau, J.; Grégoire, C.; Sharshar, T.; Naim, G.; Cortier, D.; et al. One-Year Outcomes in Patients With Acute Stroke Requiring Mechanical Ventilation. Stroke 2023, 54, 2328–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saposnik, G.; Barinagarrementeria, F.; Brown, R.D., Jr.; Bushnell, C.D.; Cucchiara, B.; Cushman, M.; deVeber, G.; Ferro, J.M.; Tsai, F.Y. on behalf of the American Heart Association Stroke Council and the Council on Epidemiology and Prevention. Diagnosis and management of cerebral venous thrombosis: A statement for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 2011, 42, 1158–1192. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sadik, J.C.; Jianu, D.C.; Sadik, R.; Purcell, Y.; Novaes, N.; Saragoussi, E.; Obadia, M.; Lecler, A.; Savatovsky, J. Imaging of Cerebral Venous Thrombosis. Life 2022, 12, 1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.W.; Gao, W.L.; Feng, L.M. Clinical characteristics and prognosis of cerebral venous thrombosis in Chinese women during pregnancy and puerperium. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasay, M.; Kaul, S.; Menon, B.; Dai, A.I.; Saadatnia, M.; Malik, A.; Khalifa, A.; Borhani-Haghighi, A.; Mehndiratta, M.; Khan, M.; et al. Asian Study of Cerebral Venous Thrombosis. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2019, 28, 104247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qureshi, A.I. A Classification Scheme for Assessing Recanalization and Collateral Formation following Cerebral Venous Thrombosis. J. Vasc. Interv. Neurol. 2010, 3, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Ferro, J.M.; Canhão, P.; Stam, J.; Bousser, M.G.; Barinagarrementeria, F.; ISCVT Investigators. Prognosis of cerebral vein and dural sinus thrombosis: Results of the International Study on Cerebral Vein and Dural Sinus Thrombosis (ISCVT). Stroke 2004, 35, 664–670. [Google Scholar]
- Kalita, J.; Misra, U.K.; Singh, R.K. Do the Risk Factors Determine the Severity and Outcome of Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis? Transl. Stroke Res. 2018, 9, 575–581. [Google Scholar]
- Triquenot Bagan, A.; Crassard, I.; Drouet, L.; Barbieux-Guillot, M.; Marlu, R.; Robinet-Borgomino, E.; Morange, P.E.; Wolff, V.; Grunebaum, L.; Klapczynski, F.; et al. Cerebral Venous Thrombosis: Clinical, Radiological, Biological, and Etiological Characteristics of a French Prospective Cohort (FPCCVT)-Comparison With ISCVT Cohort. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 753110. [Google Scholar]
- Soyer, B.; Rusca, M.; Lukaszewicz, A.C.; Crassard, I.; Guichard, J.P.; Bresson, D.; Mateo, J.; Payen, D. Outcome of a cohort of severe cerebral venous thrombosis in intensive care. Ann. Intensive Care 2016, 6, 29. [Google Scholar]
- Wall, J.; Enblad, P. Neurointensive care of patients with cerebral venous sinus thrombosis and intracerebral haemorrhage. J. Clin. Neurosci. Off. J. Neurosurg. Soc. Australas. 2018, 58, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behrouzi, R.; Punter, M. Diagnosis and management of cerebral venous thrombosis. Clin. Med. 2018, 18, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proaño, J.S.; Martinez, P.A.; Sendi, P.; Totapally, B.R. Characteristics and Outcomes of Children with Cerebral Sinus Venous Thrombosis. Neurocrit. Care 2023, 39, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Dandu, C.; Guo, Y.; Gao, M.; Lan, D.; Pan, L.; Zhou, D.; Ding, Y.; Ji, X.; Meng, R. A novel score to estimate thrombus burden and predict intracranial hypertension in cerebral venous sinus thrombosis. J. Headache Pain 2023, 24, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalita, J.; Singh, V.K.; Jain, N.; Misra, U.K.; Kumar, S. Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis Score and its Correlation with Clinical and MRI Findings. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. Off. J. Natl. Stroke Assoc. 2019, 28, 104324. [Google Scholar]
- Kalita, J.; Misra, U.K.; Singh, V.K.; Dubey, D. Predictors and outcome of status epilepticus in cerebral venous thrombosis. J. Neurol. 2019, 266, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalita, J.; Ranjan, A.; Misra, U.K. Outcome of Guillain-Barre syndrome patients with respiratory paralysis. QJM Mon. J. Assoc. Physicians 2016, 109, 319–323. [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Sandoval, J.L.; Chiquete, E.; Bañuelos-Becerra, L.J.; Torres-Anguiano, C.; González-Padilla, C.; Arauz, A.; León-Jiménez, C.; Murillo-Bonilla, L.M.; Villarreal-Careaga, J.; Barinagarrementería, F.; et al. Cerebral venous thrombosis in a Mexican multicenter registry of acute cerebrovascular disease: The RENAMEVASC study. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. Off. J. Natl. Stroke Assoc. 2012, 21, 395–400. [Google Scholar]
- Abdo, R.; Abboud, H.; Salameh, P.; El Hajj, T.; Hosseini, H. Mortality and Predictors of Death Poststroke: Data from a Multicenter Prospective Cohort of Lebanese Stroke Patients. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. Off. J. Natl. Stroke Assoc. 2019, 28, 859–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hénon, H.; Godefroy, O.; Leys, D.; Mounier-Vehier, F.; Lucas, C.; Rondepierre, P.; Duhamel, A.; Pruvo, J.P. Early predictors of death and disability after acute cerebral ischemic event. Stroke 1995, 26, 392–398. [Google Scholar]
- Canhão, P.; Ferro, J.M.; Lindgren, A.G.; Bousser, M.G.; Stam, J.; Barinagarrementeria, F.; ISCVT Investigators. Causes and predictors of death in cerebral venous thrombosis. Stroke 2005, 36, 1720–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hervella, P.; Sampedro-Viana, A.; Rodríguez-Yáñez, M.; López-Dequidt, I.; Pumar, J.M.; Mosqueira, A.J.; Fernández-Rodicio, S.; Bazarra-Barreiros, M.; Serena, J.; Silva-Blas, Y.; et al. Systemic biomarker associated with poor outcome after futile reperfusion. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2024, 54, e14181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalita, J.; Singh, V.K.; Misra, U.K. A study of hyperhomocysteinemia in cerebral venous sinus thrombosis. Indian J. Med. Res. 2020, 152, 584–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stolz, E.; Trittmacher, S.; Rahimi, A.; Gerriets, T.; Röttger, C.; Siekmann, R.; Kaps, M. Influence of recanalization on outcome in dural sinus thrombosis: A prospective study. Stroke 2004, 35, 544–547. [Google Scholar]
- Baumgartner, R.W.; Studer, A.; Arnold, M.; Georgiadis, D. Recanalisation of cerebral venous thrombosis. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2003, 74, 459–461. [Google Scholar]
- Meyfroidt, G.; Bollaert, P.E.; Marik, P.E. Acute ischemic stroke in the ICU: To admit or not to admit? Intensive Care Med. 2014, 40, 749–751. [Google Scholar]
- Aguiar de Sousa, D.; Lucas Neto, L.; Canhão, P.; Ferro, J.M. Recanalization in Cerebral Venous Thrombosis. Stroke 2018, 49, 1828–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golestanian, E.; Liou, J.-I.; Smith, M.A. Long-term survival in older critically ill patients with acute ischemic stroke. Crit. Care Med. 2009, 37, 3107–3113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi Omran, S.; Shu, L.; Chang, A.; Parikh, N.S.; Zubair, A.S.; Simpkins, A.N.; Heldner, M.R.; Hakim, A.; Kasab, S.A.; Nguyen, T.; et al. Timing and Predictors of Recanalization After Anticoagulation in Cerebral Venous Thrombosis. J. Stroke 2023, 25, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ranjan, R.; Ken-Dror, G.; Sharma, P. Pathophysiology, diagnosis and management of cerebral venous thrombosis: A comprehensive review. Medicine 2023, 102, e36366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Singh, V.K.; Jain, N.; Kalita, J.; Misra, U.K.; Kumar, S. Significance of recanalization of sinuses and resolution of parenchymal lesion in cerebral venous sinus thrombosis. J. Clin. Neurosci. Off. J. Neurosurg. Soc. Australas. 2020, 77, 175–180. [Google Scholar]
- Röttger, C.; Trittmacher, S.; Gerriets, T.; Blaes, F.; Kaps, M.; Stolz, E. Reversible MR imaging abnormalities following cerebral venous thrombosis. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2005, 26, 607–613. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Giraldo Sanchez, J.M.; Giraldo Arboleda, D.L.; Giraldo Arboleda, R.A. Patient with Massive Pulmonary Embolism Caused by the Combined Deficiency of Proteins C and S and Antithrombin III. J. Pulm. Respir. Med. 2015, 5, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raho, E.M.; Antonioni, A.; Cotta Ramusino, N.; Jubea, D.; Gragnaniello, D.; Franceschetti, P.; Penitenti, F.; Daniele, A.; Zatelli, M.C.; Naccarato, M.; et al. Cerebral Venous Thrombosis during Thyrotoxicosis: Case Report and Literature Update. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
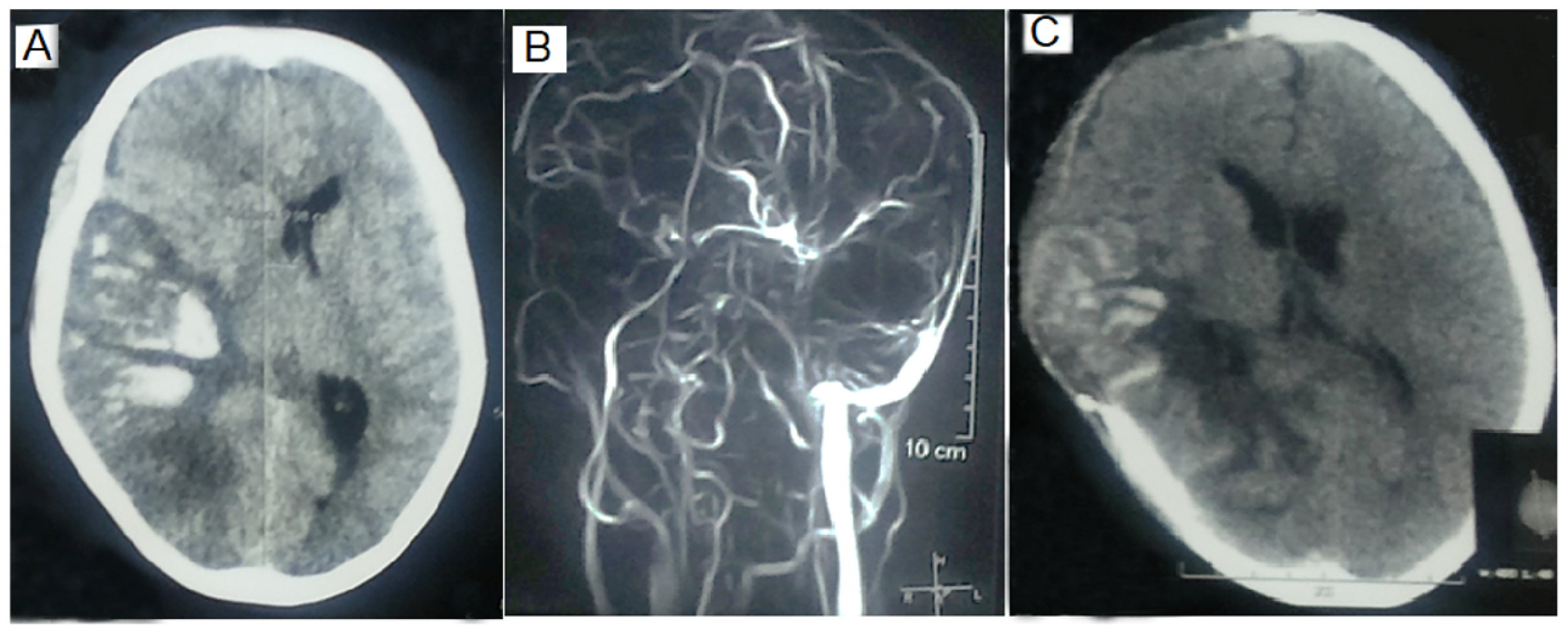
| Total (n = 98) | MV (n = 18) | Non-MV ICU (n = 27) | Non-MV Non-ICU (n = 53) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (yrs) | 32.09 ± 12.75 | 29.44 ± 11.91 | 36.67 ± 13.31 | 30.66 ± 12.36 | 0.08 |
| Females | 43 (43.9%) | 6 (33.3%) | 16 (59.3%) | 21 (39.6%) | 0.43 |
| Duration of illness (Days) | 25.92 ± 76.04 | 12.66 ± 15.02 | 10.67 ± 11.84 | 38.21 ± 101.53 | 0.22 |
| Onset | 0.02 | ||||
| Acute (≤2 days) | 8 (8.2%) | 4 (22.2%) | 3 (11.1%) | 1 (1.9%) | |
| Sub-acute (3–30 days) | 76 (77.6%) | 12 (65.7%) | 23 (85.2%) | 41 (77.4%) | |
| Chronic > 30 days | 14 (14.3%) | 2 (11.1%) | 1 (3.7%) | 11 (20.8%) | |
| Seizures | 69 (70.4%) | 10 (55.6%) | 18 (66.7%) | 41 (77.4%) | 0.20 |
| Status epilepticus | 29 (29.6%) | 8 (44.4%) | 9 (33.3%) | 12 (22.6%) | 0.25 |
| Focal deficit | 62 (63.3%) | 14 (77.8%) | 19 (70.4%) | 29 (54.7%) | 0.14 |
| GCS score | 12.11 ± 3.67 | 8.39 ± 3.22 | 9.11 ± 2.91 | 14.91 ± 0.30 | 0.001 |
| Risk factor Hereditary prothrombotic states | |||||
| MTHFR | 0.73 | ||||
| CC | 40 (67.8%) | 3 (75%) | 13 (76.5%) | 24 (64.9%) | |
| CT | 18 (30.5%) | 1 (25%) | 4 (23.5%) | 12 (32.4%) | |
| TT | 1 (1.7%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 1 (2.7%) | |
| Antithrombin III | 0.37 | ||||
| Normal | 48 (90.6%) | 9 (81.8%) | 11 (100%) | 28 (90.3%) | |
| Deficient | 5 (9.4%) | 2 (18.2%) | 0 (0%) | 3 (9.7%) | |
| Protein S | 0.11 | ||||
| Normal | 37 (52.1%) | 10 (71.4%) | 11 (61.1%) | 16 (41.0%) | |
| Deficient | 34 (47.8%) | 4 (28.6%) | 7 (38.9%) | 23 (59.0%) | |
| Protein C | 0.05 | ||||
| Normal | 56 (77.8%) | 7 (53.8%) | 17 (89.5%) | 32 (77.8%) | |
| Deficient | 16 (22.2%) | 6 (46.2%) | 2 (10.5%) | 10 (20.0%) | |
| Acquired prothrombotic state | 0.50 | ||||
| Homocysteine µmol/L | |||||
| <15 | 38 (52.0%) | 4 (66.7.2%) | 13 (59.1%) | 21 (46.7%) | |
| ≥15 | 35 (47.9%) | 2 (33.3%) | 9 (40.9%) | 24 (53.3%) | |
| APLA syndrome | 0.52 | ||||
| Yes | 13 (13.3%) | 3 (16.7%) | 5 (18.5%) | 5 (9.4%) | |
| No | 85 (86.7%) | 15 (83.3%) | 22 (81.5%) | 48 (90.6%) | |
| Vitamin B12 pg/mL | 0.29 | ||||
| <200 | 28 (34.1%) | 3 (25%) | 8 (36.4%) | 17 (35.4%) | |
| 200–500 | 21 (25.6%) | 1 (8.3%) | 5 (22.7%) | 15 (31.2%) | |
| >500 | 33 (40.2%) | 8 (66.7%) | 9 (40.9%) | 16 (33.3%) | |
| Folic acid ng/mL | 0.29 | ||||
| <3.5 | 25 (25.5%) | 3 (16.7%) | 5 (18.5%) | 17 (32.1%) | |
| >3.5 | 73 (74.5%) | 15 (83.3%) | 22 (81.5%) | 36 (67.9%) | |
| Female Specific risk | 0.37 | ||||
| Puerperium | |||||
| Yes | 12 (27.9%) | 2 (33.3%) | 5 (31.3%) | 15 (48.4%) | |
| No | 31 (72.1%) | 4 (66.4%) | 11 (68.8%) | 16 (51.6%) | |
| Oral contraceptives pill | 0.40 | ||||
| Yes | 5 (11.6%) | 1 (16.7%) | 1 (6.3%) | 3 (14.3%) | |
| No | 38 (88.4%) | 5 (83.3%) | 15 (93.7%) | 18 (85.7%) | |
| Number of risk factors | 1.42 ± 1.25 | 1.38 ± 1.03 | 1.59 ± 1.45 | 1.36 ± 1.23 | 0.73 |
| No risk factor | 27 (27.6%) | 3 (16.7%) | 7 (25.9%) | 17 (32.1%) | 0.51 |
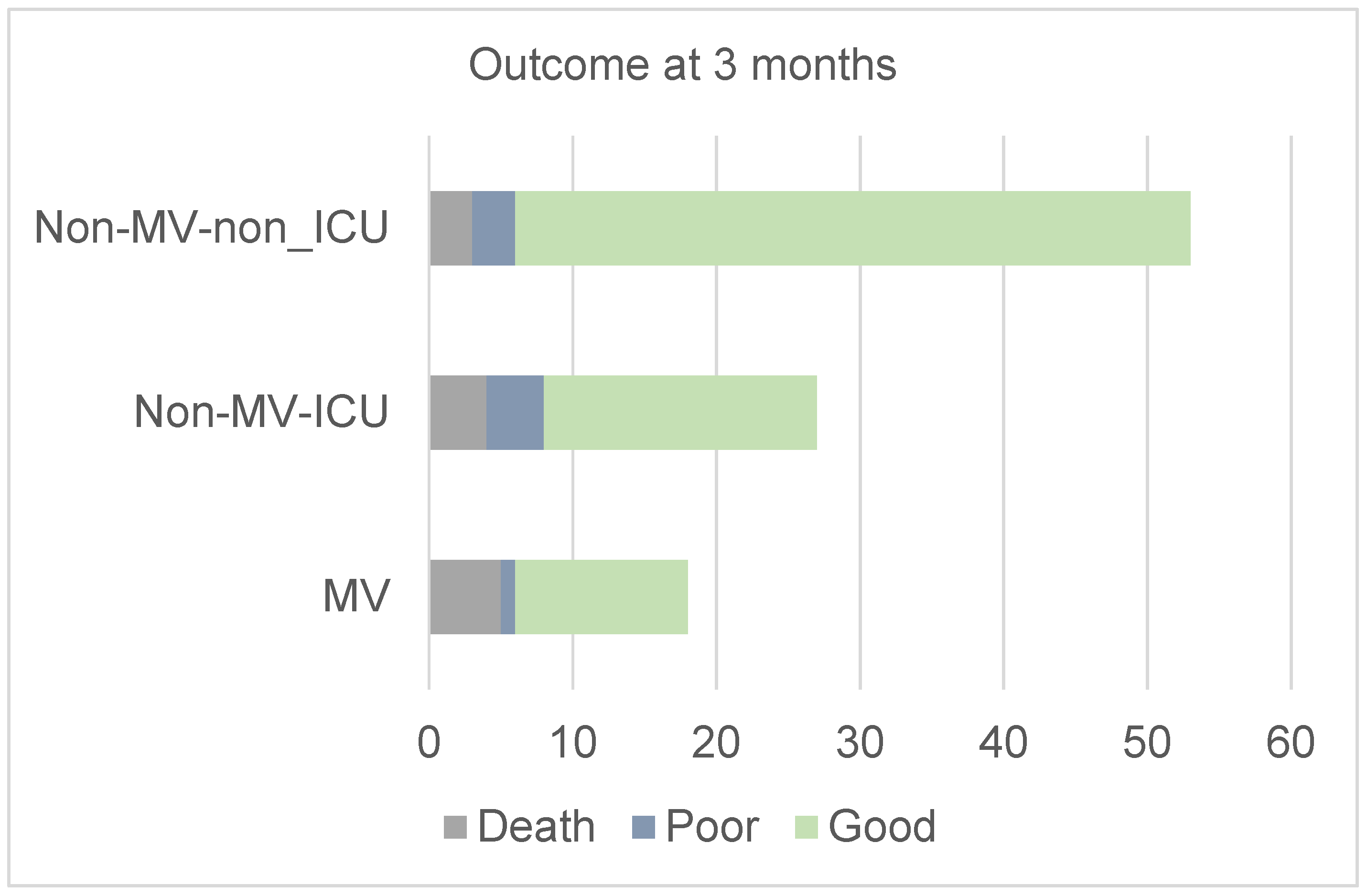
| Outcome at 3 months | 0.05 | ||||
| Good | 78 (79.6%) | 12 (66.7%) | 19 (70.4%) | 47 (88.7%) | |
| Poor | 8 (8.2%) | 1 (5.5%) | 4 (14.8%) | 3 (5.7%) | |
| Death | 12 (12.2%) | 5 (27.8%) | 4 (14.8%) | 3 (5.7%) |
| Parameter | All n = 98 | MV n = 18 | Non-MV ICU n = 27 | Non-MV Non-ICU n = 53 | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parenchymal lesion on MRI | 85 | 16 (88.9%) | 23 (85.2%) | 46 (86.8%) | 0.58 |
| Infarct | 16 | 1 (5.6%) | 6 (22.2%) | 9 (16.9%) | |
| Hemorrhagic | 69 | 15 83.3.%) | 17 (62.9%) | 37 (69.8%) | |
| Thrombosis on MRV | 0.95 | ||||
| Superficial system | 84 | 15 (83.3%) | 22 (81.5%) | 47 (88.7%) | |
| Deep system | 4 | 1 (5.6%) | 1 (3.7%) | 2 (3.8%) | |
| Both | 10 | 2 (11.1%) | 4 (14.8%) | 4 (75.5%) | |
| Superior sagittal sinus | 68 | 13 (72.2%) | 18 (66.7%) | 37 (69.8%) | 0.91 |
| Inferior sagittal sinus | 4 | 0 (0%) | 2 (7.4%) | 2 (3.8%) | 0.55 |
| Transverse sinus | 63 | 13 (72.2%) | 16 (59.2%) | 34 (64.1%) | 0.69 |
| Sigmoid sinus | 46 | 9 (50.0%) | 10 (37.0%) | 27 (50.9%) | 0.52 |
| Number of sinuses involved | 1.63 ± 0.74 | 1.33 ± 0.48 | 1.63 ± 0.69 | 1.73 ± 0.81 | 0.13 |
| Death N = 12 | Survived N = 86 | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (yrs) | 30.25 ± 12.17 | 32.35 ± 12.87 | 0.59 |
| Gender (Male/Female) | 8 (66.7%)/4 (33.3%) | 47 (54.7%)/39 (45.3%) | 0.42 |
| Duration (days) | 9.00 ± 8.58 | 28.29 ± 80.89 | 0.43 |
| Acute | 3 (25.0%) | 5 (5.8%) | 0.03 |
| Sub | 9 (75.0%) | 67 (77.9%) | |
| chronic | 0 (0%) | 14 (16.3%) | |
| Status epilepticus | 3 (25.0%) | 27 (31.4%) | 0.75 |
| Motor deficit | 10 (83.3%) | 52 (60.5%) | 0.20 |
| Number of risk factors | 0.83 ± 0.71 | 1.51 ± 1.29 | 0.08 |
| MRI parenchymal lesion | 12 (100%) | 73 (84.9%) | 0.05 |
| MRV | 0.38 | ||
| Deep | 0 (0.0%) | 4 (4.7%) | |
| Superficial | 10 (83.3%) | 74 (86.0%) | |
| Both | 2 (16.7%) | 8 (9.3%) | |
| GCS score | 8.92 ± 4.29 | 12.56 ± 3.37 | 0.01 |
| Requirement of mechanical ventilation (MV)/Intensive care unit (ICU) | 0.04 | ||
| MV | 5 (27.8%) | 13 (72.2%) | |
| Non-MV ICU | 4 (14.8%) | 23 (85.2%) | |
| Non-MV non-ICU | 3 (5.7%) | 50 (94.3%) |
| Poor N = 20 | Good N = 78 | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (yrs) | 35.00 ± 14.49 | 31.39 ± 12.28 | 0.27 |
| Gender (Male/Female) | 12 (63.1%)/7 (36.8%) | 43 (54.4%)/36 (45.5%) | 0.60 |
| Duration (days) | 12.79 ± 14.53 | 29.08 ± 84.21 | 0.40 |
| Acute | 4 (21.1%) | 4 (5.0%) | 0.02 |
| Sub acute chronic | 14 (73.7%) 1 (5.2%) | 62 (78.5%) 13 (16.5%) | |
| Status epilepticus | 7 (23.3%) | 23 (76.7%) | 0.58 |
| Motor deficit | 16 (25.8%) | 46 (74.2%) | 0.04 |
| Number of risk factors | 1.00 ± 1.00 | 1.53 ± 1.29 | 0.10 |
| MRI parenchymal lesion | 18 (21.2%) | 67 (78.8%) | 0.30 |
| MRV | 0.05 | ||
| Deep | 0 (0.0%) | 4 (5.1%) | |
| Superficial | 14 (73.7%) | 70 (88.6%) | |
| Both | 5 (26.3%) | 5 (6.3%) | |
| GCS score | 6.89 ± 2.62 | 9.31 ± 2.95 | 0.03 |
| Requirement of mechanical ventilation (MV)/Intensive care unit (ICU) | 0.09 | ||
| Mechanical ventilation | 6 (33.3%) | 12 (66.7%) | |
| Non-MV ICU | 8 (29.6%) | 19 (70.4%) | |
| Non-MV Non-ICU | 5 (9.4%) | 48 (90.6%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kalita, J.; Pandey, P.C.; Gutti, N.B.; Das, K.K.; Kumar, S.; Singh, V.K. Outcome of Cerebral Venous Thrombosis Requiring Mechanical Ventilation. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 2930. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14092930
Kalita J, Pandey PC, Gutti NB, Das KK, Kumar S, Singh VK. Outcome of Cerebral Venous Thrombosis Requiring Mechanical Ventilation. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(9):2930. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14092930
Chicago/Turabian StyleKalita, Jayantee, Prakash C. Pandey, Nagendra B. Gutti, Kuntal K. Das, Sunil Kumar, and Varun K. Singh. 2025. "Outcome of Cerebral Venous Thrombosis Requiring Mechanical Ventilation" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 9: 2930. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14092930
APA StyleKalita, J., Pandey, P. C., Gutti, N. B., Das, K. K., Kumar, S., & Singh, V. K. (2025). Outcome of Cerebral Venous Thrombosis Requiring Mechanical Ventilation. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(9), 2930. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14092930






