Comparisons of Efficiency, Safety, and Hospital Costs of Four-Arm Robotic-Assisted Partial Nephrectomy (RAPN) Versus Three-Arm Technique: A Propensity Score–Matched Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
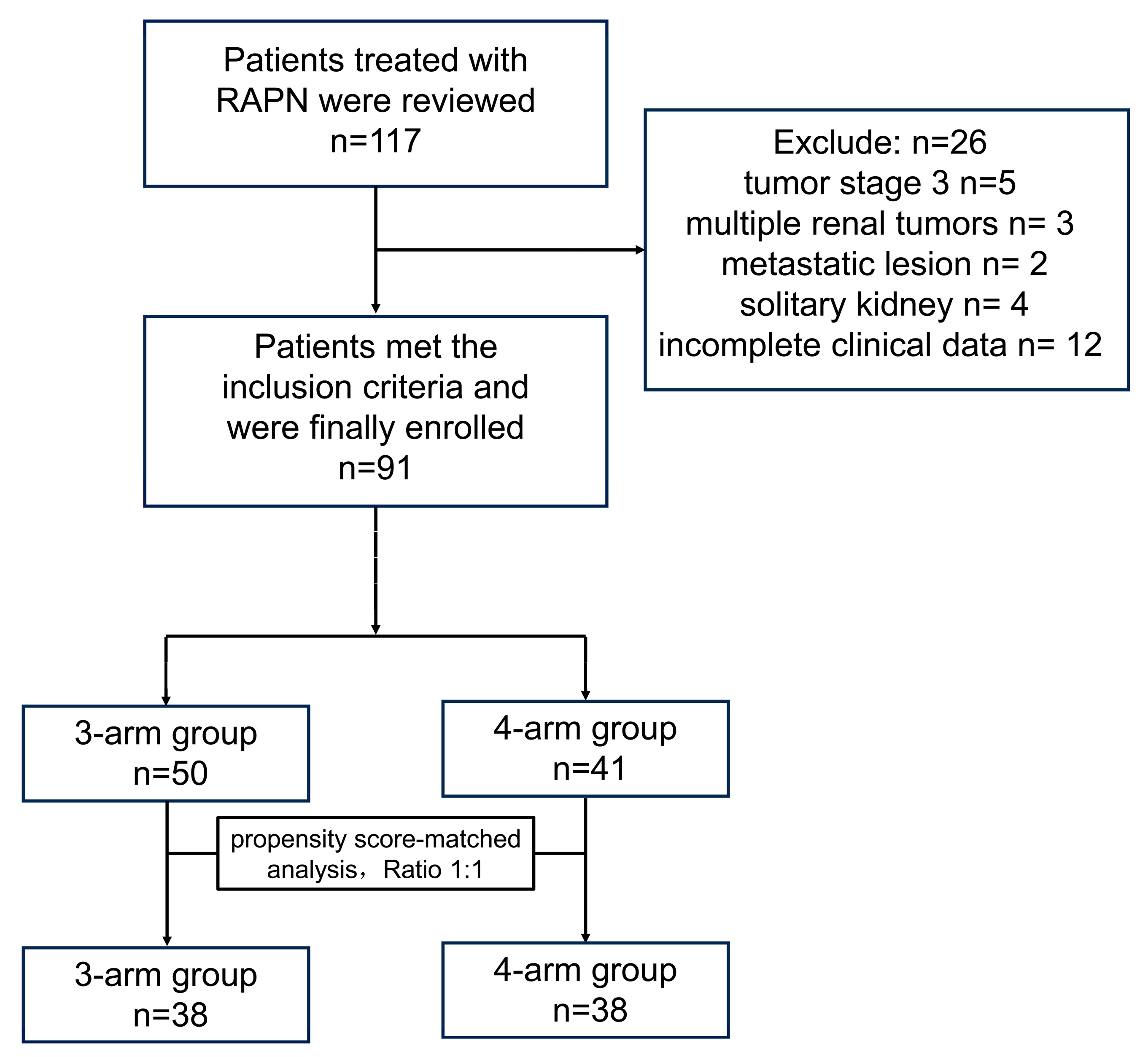
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Surgical Technique
2.3. Outcomes Measured and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographics and Tumor Characteristics
3.2. Operative Outcomes and Hospital Costs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| RCC | renal cell carcinoma |
| RAPN | Robotic-assisted partial nephrectomy |
| CNY | Chinese Yuan |
| PN | partial nephrectomy |
| IVC | inferior vena cava |
| BMI | body mass index |
| IQR | inter-quartile range |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| SD | standard deviation |
| SIRS | systemic inflammatory response syndrome |
References
- Global Burden of Disease Cancer Collaboration; Fitzmaurice, C.; Allen, C.; Barber, R.M.; Barregard, L.; Bhutta, Z.A.; Brenner, H.; Dicker, D.J.; Chimed-Orchir, O.; Dandona, R.; et al. Global, Regional, and National Cancer Incidence, Mortality, Years of Life Lost, Years Lived With Disability, and Disability-Adjusted Life-years for 32 Cancer Groups, 1990 to 2015: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study. JAMA Oncol. 2017, 3, 524–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ljungberg, B.; Campbell, S.C.; Choi, H.Y.; Jacqmin, D.; Lee, J.E.; Weikert, S.; Kiemeney, L.A. The epidemiology of renal cell carcinoma. Eur. Urol. 2011, 60, 615–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, V.; Marco, D.J.T.; Bolton, D.; Davis, I.D.; Jefford, M.; Hill, D.; Prince, H.M.; Millar, J.L.; Winship, I.M.; Coory, M.; et al. Trends in the surgical management of stage 1 renal cell carcinoma: Findings from a population-based study. BJU Int. 2017, 120 (Suppl. S3), 6–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cozar, J.M.; Tallada, M. Open partial nephrectomy in renal cancer: A feasible gold standard technique in all hospitals. Adv. Urol. 2008, 2008, 916463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, C.; Du, Y.; Wang, H.; Peng, L.; Wei, T.; Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Wang, A. Laparoscopic Versus Open Partial Nephrectomy: A Systemic Review and Meta-Analysis of Surgical, Oncological, and Functional Outcomes. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 583979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, D.C.; Hollingsworth, J.M.; Hafez, K.S.; Daignault, S.; Hollenbeck, B.K. Partial nephrectomy for small renal masses: An emerging quality of care concern? J. Urol. 2006, 175, 853–857, Discussion 858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alameddine, M.; Koru-Sengul, T.; Moore, K.J.; Miao, F.; Savio, L.F.; Nahar, B.; Prakash, N.S.; Venkatramani, V.; Jue, J.S.; Punnen, S.; et al. Trends in Utilization of Robotic and Open Partial Nephrectomy for Management of cT1 Renal Masses. Eur. Urol. Focus. 2019, 5, 482–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gettman, M.T.; Blute, M.L.; Chow, G.K.; Neururer, R.; Bartsch, G.; Peschel, R. Robotic-assisted laparoscopic partial nephrectomy: Technique and initial clinical experience with DaVinci robotic system. Urology 2004, 64, 914–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, G.; Bahadori, A.; Mao, D.; Ranasinghe, S.; Tracey, C. Benefits of Robotic Assisted vs. Traditional Laparoscopic Partial Nephrectomy: A Single Surgeon Comparative Study. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 6974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaouk, J.H.; Khalifeh, A.; Hillyer, S.; Haber, G.P.; Stein, R.J.; Autorino, R. Robot-assisted laparoscopic partial nephrectomy: Step-by-step contemporary technique and surgical outcomes at a single high-volume institution. Eur. Urol. 2012, 62, 553–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, K.; Furukawa, J.; Shigemura, K.; Hinata, N.; Ishimura, T.; Muramaki, M.; Miyake, H.; Fujisawa, M. Surgery-related outcomes and postoperative split renal function by scintigraphy evaluation in robot-assisted partial nephrectomy in complex renal tumors: An initial case series. J. Endourol. 2015, 29, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, C.G.; Laungani, R.; Bhandari, A.; Krane, L.S.; Eun, D.; Patel, M.N.; Boris, R.; Shrivastava, A.; Menon, M. Maximizing console surgeon independence during robot-assisted renal surgery by using the Fourth Arm and TilePro. J. Endourol. 2009, 23, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhayani, S.B. da Vinci robotic partial nephrectomy for renal cell carcinoma: An atlas of the four-arm technique. J. Robot. Surg. 2008, 1, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, Y.; Du, C.; Josephson, D.Y.; Wilson, T.G.; Nelson, R. Four-arm robotic partial nephrectomy for complex renal cell carcinoma. World J. Urol. 2010, 28, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ener, K.; Canda, A.E.; Altinova, S.; Atmaca, A.F.; Alkan, E.; Asil, E.; Ozcan, M.F.; Akbulut, Z.; Balbay, M.D. Robotic partial nephrectomy for clinical stage T1 tumors: Experience in 42 cases. Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci. 2016, 32, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Asmar, J.M.; Sebaaly, R.; Mailhac, A.; Bulbul, M.; Khauli, R.; Tamim, H.; El Hajj, A. Use of Bariatric Ports in 4-Arm Robotic Partial Nephrectomy: A Comparative Study With the Standard 3-Arm Technique. Cureus 2021, 13, e16461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, B.A.; Crivelli, J.; Sorokin, I.; Gahan, J.; Cadeddu, J.A. Surgical Outcomes of Three vs Four Arm Robotic Partial Nephrectomy: Is the Fourth Arm Necessary? Urology 2019, 123, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulze, L.; Dubeux, V.T.; Milfont, J.C.A.; Pecanha, G.; Ferrer, P.; Cavalcanti, A.G. Analysis of surgical and histopathological results of robot-assisted partial nephrectomy with use of three or four robotic arms: An early series results. Int. Braz. J. Urol. 2022, 48, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sforza, S.; Tellini, R.; Grosso, A.A.; Zaccaro, C.; Viola, L.; Di Maida, F.; Mari, A.; Carini, M.; Minervini, A.; Masieri, L. Can we predict the development of symptomatic lymphocele following robot-assisted radical prostatectomy and lymph node dissection? Results from a tertiary referral Centre. Scand. J. Urol. 2020, 54, 328–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutikov, A.; Uzzo, R.G. The R.E.N.A.L. nephrometry score: A comprehensive standardized system for quantitating renal tumor size, location and depth. J. Urol. 2009, 182, 844–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dindo, D.; Demartines, N.; Clavien, P.A. Classification of surgical complications: A new proposal with evaluation in a cohort of 6336 patients and results of a survey. Ann. Surg. 2004, 240, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiroki, R.; Fukami, N.; Fukaya, K.; Kusaka, M.; Natsume, T.; Ichihara, T.; Toyama, H. Robot-assisted partial nephrectomy: Superiority over laparoscopic partial nephrectomy. Int. J. Urol. 2016, 23, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alemozaffar, M.; Chang, S.L.; Kacker, R.; Sun, M.; DeWolf, W.C.; Wagner, A.A. Comparing costs of robotic, laparoscopic, and open partial nephrectomy. J. Endourol. 2013, 27, 560–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Q.; Gu, L.; Zhu, J.; Peng, C.; Du, S.; Liu, Q.; Chen, J.; Wang, B.; Fan, Y.; Gao, Y.; et al. A three-dimensional, anatomy-based nephrometry score to guide nephron-sparing surgery for renal sinus tumors. Cancer 2020, 126 (Suppl. S9), 2062–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanagho, Y.S.; Figenshau, R.S.; Bhayani, S.B. Technique, outcomes, and evolving role of extirpative laparoscopic and robotic surgery for renal cell carcinoma. Surg. Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 2013, 22, 91–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriarty, M.A.; Nepple, K.G.; Tracy, C.R.; Strigenz, M.E.; Lee, D.K.; Brown, J.A. Impact of Robotic Fellowship Experience on Perioperative Outcomes of Robotic-Assisted Laparoscopic Partial Nephrectomy. Curr. Urol. 2016, 9, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larcher, A.; Muttin, F.; Peyronnet, B.; De Naeyer, G.; Khene, Z.E.; Dell’Oglio, P.; Ferreiro, C.; Schatteman, P.; Capitanio, U.; D’Hondt, F.; et al. The Learning Curve for Robot-assisted Partial Nephrectomy: Impact of Surgical Experience on Perioperative Outcomes. Eur. Urol. 2019, 75, 253–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harke, N.N.; Kuczyk, M.A.; Huusmann, S.; Schiefelbein, F.; Schneller, A.; Schoen, G.; Wiesinger, C.; Pfuner, J.; Ubrig, B.; Gloger, S.; et al. Impact of Surgical Experience Before Robot-assisted Partial Nephrectomy on Surgical Outcomes: A Multicenter Analysis of 2500 Patients. Eur. Urol. Open Sci. 2022, 46, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kira, S.; Mitsui, T.; Sawada, N.; Nakagomi, H.; Ihara, T.; Takahashi, N.; Takeda, M. Feasibility and necessity of the fourth arm of the da Vinci Si surgical system for robot-assisted partial nephrectomy. Int. J. Med. Robot. 2020, 16, e2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel Raheem, A.; Sheikh, A.; Kim, D.K.; Alatawi, A.; Alabdulaali, I.; Han, W.K.; Choi, Y.D.; Rha, K.H. Da Vinci Xi and Si platforms have equivalent perioperative outcomes during robot-assisted partial nephrectomy: Preliminary experience. J. Robot. Surg. 2017, 11, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Before Propensity Score Maching | After Propensity Score Maching | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | 3-Arm Group (n = 50) | 4-Arm Group (n = 41) | p | 3-Arm Group (n = 38) | 4-Arm Group (n = 38) | p |
| Age (years), median (IQR) | 56.0 (49.8, 60.3) | 56.0 (48.0, 63.0) | 0.838 | 56.5 (49.3, 65.0) | 55.5 (48.0, 60.5) | 0.659 |
| Male, n (%) | 36 (72.0%) | 29 (70.7%) | 0.894 | 26 (68.4%) | 27 (71.1%) | 1.000 |
| BMI (kg/m2), mean (SD) | 24.7 (3.2) | 23.9 (2.6) | 0.181 | 24.1 (3.1) | 24.1 (6.8) | 0.995 |
| Left, n (%) | 24 (48.0%) | 15 (36.6%) | 0.141 | 17 (44.7%) | 13 (34.2%) | 0.348 |
| RENAL score, median (IQR) | 7.0 (6.0, 9.0) | 7.0 (7.0, 9.0) | 0.761 | 7.0 (6.0, 8.0) | 7.0 (6.8, 9.0) | 0.970 |
| Tumor stage, n (%) | 0.277 | 0.373 | ||||
| T1a | 43 (86.0%) | 31 (75.6%) | 32 (84.2%) | 28 (73.7%) | ||
| T1b | 3 (6.0%) | 8 (19.5%) | 2 (5.3%) | 8 (21.0%) | ||
| T2a | 3 (6.0%) | 2 (4.9%) | 3 (7.9%) | 2 (5.3%) | ||
| T2b | 1 (2.0%) | 0 (%) | 1 (2.6%) | 0 (0%) | ||
| Pathological grade (WHO), n (%) | 0.375 | 0.986 | ||||
| 1 | 14 (28.0%) | 17 (41.5%) | 13 (34.2%) | 15 (39.5%) | ||
| 2 | 32 (64.0%) | 19 (46.3%) | 23 (60.5%) | 18 (47.4%) | ||
| 3 | 3 (6.0%) | 5 (12.2%) | 2 (5.3%) | 5 (13.1%) | ||
| 4 | 1 (2.0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (%) | 0 (%) | ||
| Variables | 3-Arm Group (n = 38) | 4-Arm Group (n = 38) | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Preparative time (min) | 11.5 (10.0, 15.0) | 15.0 (10.0, 20.0) | 0.080 |
| Total operative time (min) | 120.0 (100.0, 135.0) | 146.5 (101.5, 177.8) | 0.068 |
| Warm ischemia time (min) | 28.0 (21.8, 33.3) | 30.0 (25.8, 39.3) | 0.106 |
| Estimated blood loss (mL) | 150.0 (100.0, 300.0) | 200.0 (100.0, 362.5) | 0.447 |
| Blood transfusion, n (%) | 5 (13.2%) | 5 (13.2%) | 1.000 |
| Positive surgical margin, n (%) | 1 (2.6%) | 1 (2.6%) | 1.000 |
| Post-operative analgesic use (days) | 3.0 (2.0, 3.0) | 3.0 (3.0, 4.0) | 0.201 |
| Post-operative stay (days) | 6.0 (5.0, 7.0) | 5.0 (5.0, 7.0) | 0.694 |
| Hospital costs (CNY) | 68,406.7 (66,284.4, 74,542.7) | 76,922.5 (68,474.3, 87,432.4) | 0.006 * |
| Variables | 3-Arm Group (n = 38) | 4-Arm Group (n = 38) | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Complications | 9 (23.7%) | 8 (21.1%) | 1.000 |
| Clavien Grade | 0.673 | ||
| 1 | 6 (15.8%) | 3 (7.9%) | |
| 2 | 2 (5.3%) | 2 (5.3%) | |
| 3 | 1 (2.6%) | 3 (7.9%) | |
| SIRS | 2 (5.3%) | 3 (7.9%) | 1.000 |
| Post-operative bleeding | 1 (2.6%) | 1 (2.6%) | 1.000 |
| Wound infection | 2 (5.3%) | 1 (2.6%) | 1.000 |
| Thrombosis | 4 (10.5%) | 3 (7.9%) | 1.000 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Li, F.; Guo, W.; Zhang, Z.; Li, H.; Guan, W. Comparisons of Efficiency, Safety, and Hospital Costs of Four-Arm Robotic-Assisted Partial Nephrectomy (RAPN) Versus Three-Arm Technique: A Propensity Score–Matched Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 2739. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14082739
Zhang Y, Li F, Guo W, Zhang Z, Li H, Guan W. Comparisons of Efficiency, Safety, and Hospital Costs of Four-Arm Robotic-Assisted Partial Nephrectomy (RAPN) Versus Three-Arm Technique: A Propensity Score–Matched Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(8):2739. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14082739
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yan, Fan Li, Wenhao Guo, Zongbiao Zhang, Heng Li, and Wei Guan. 2025. "Comparisons of Efficiency, Safety, and Hospital Costs of Four-Arm Robotic-Assisted Partial Nephrectomy (RAPN) Versus Three-Arm Technique: A Propensity Score–Matched Analysis" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 8: 2739. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14082739
APA StyleZhang, Y., Li, F., Guo, W., Zhang, Z., Li, H., & Guan, W. (2025). Comparisons of Efficiency, Safety, and Hospital Costs of Four-Arm Robotic-Assisted Partial Nephrectomy (RAPN) Versus Three-Arm Technique: A Propensity Score–Matched Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(8), 2739. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14082739





