Direct Innominate Artery Cannulation for Thoracic Aortic Surgery
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Variables
2.2. Statistical Analysis
2.3. Surgical Technique
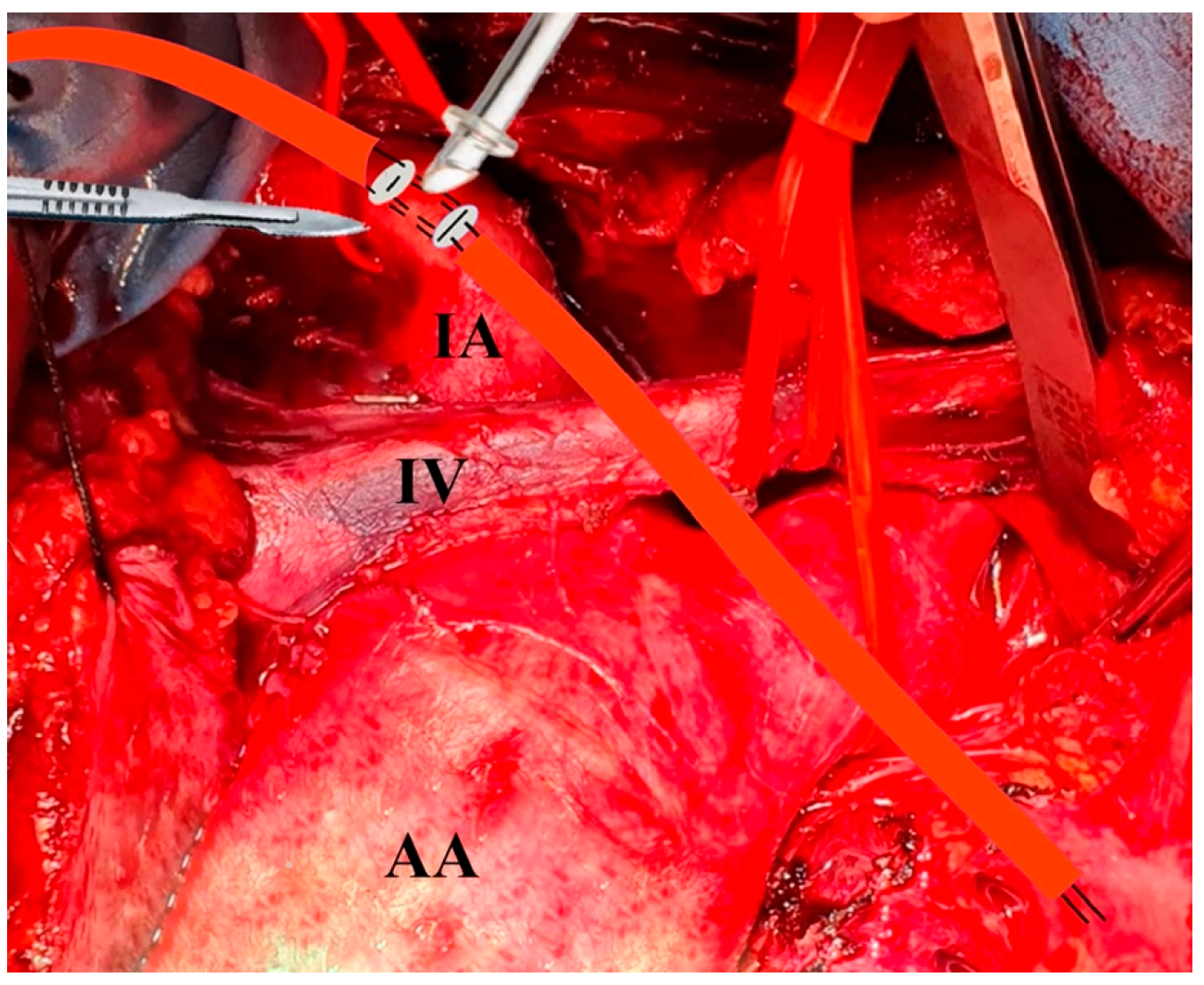
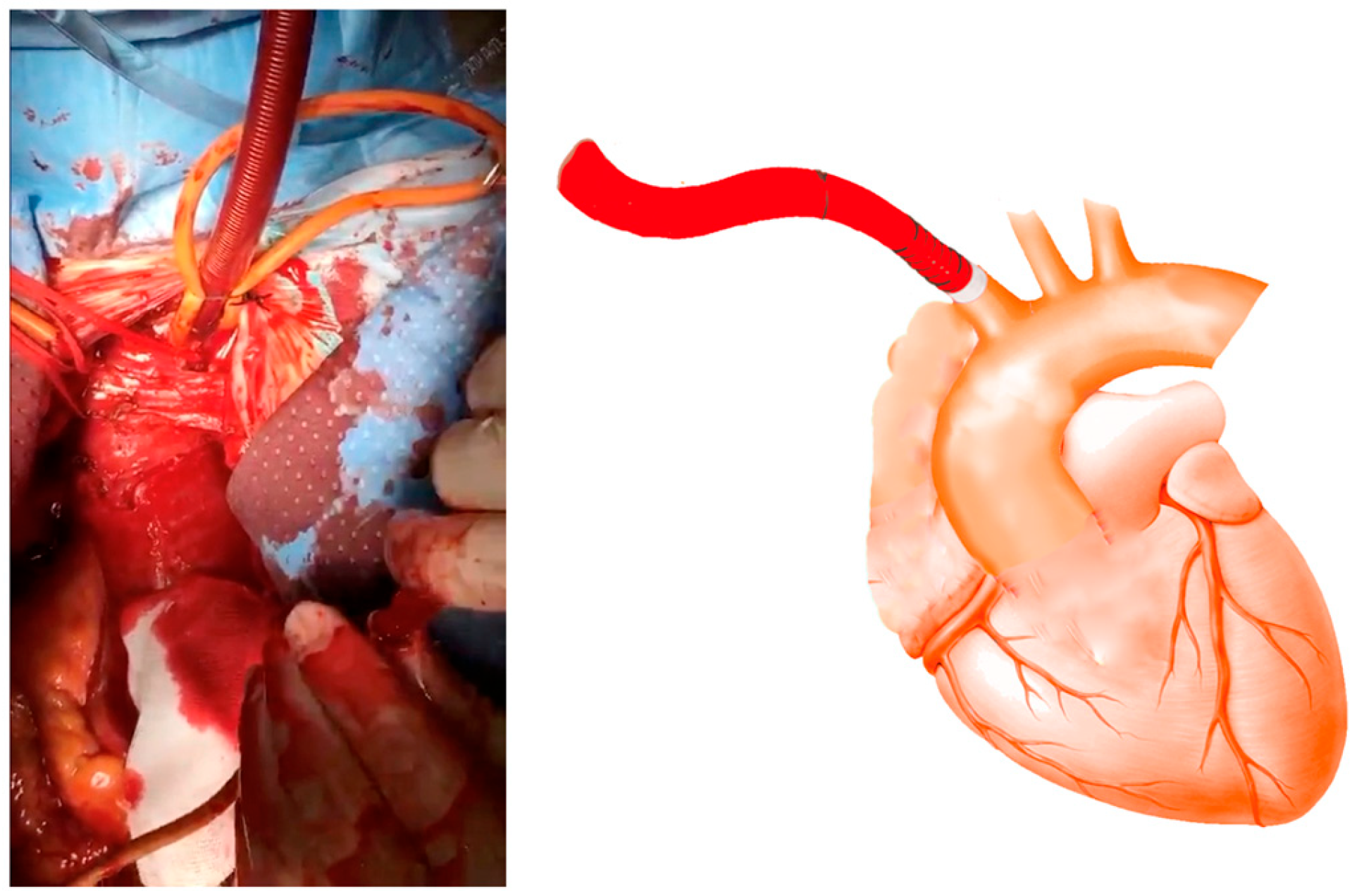
Cannulation
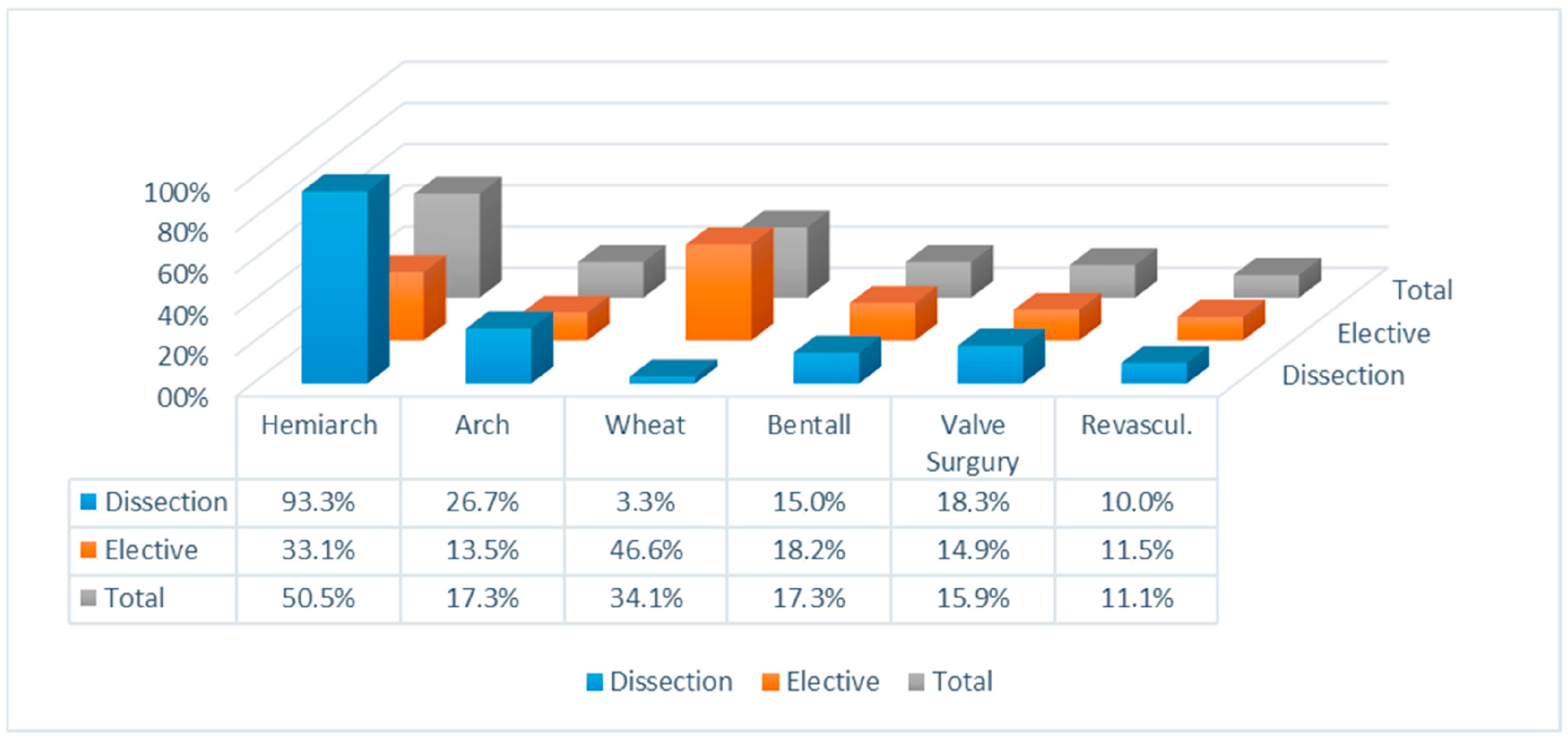
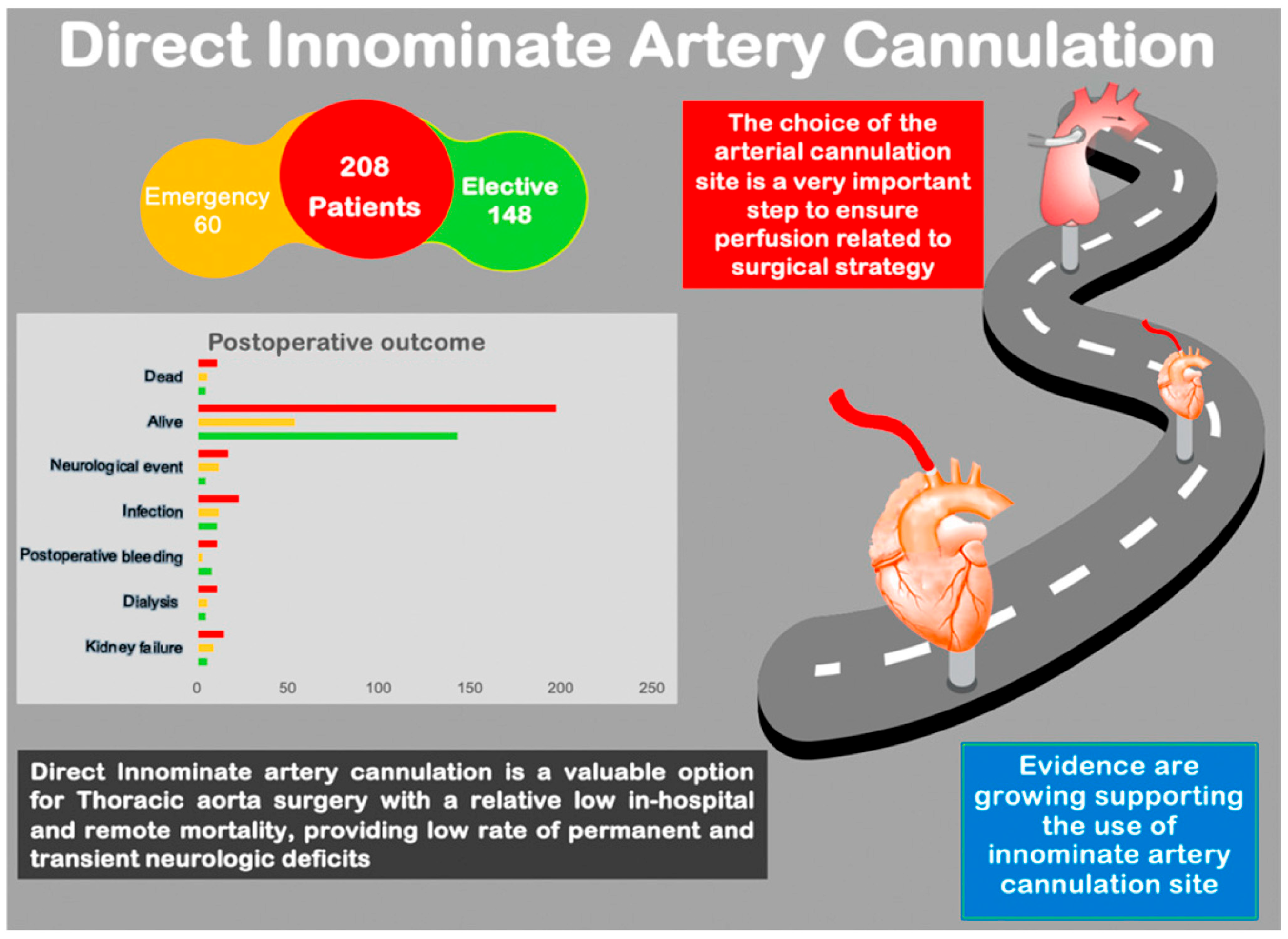
3. Results
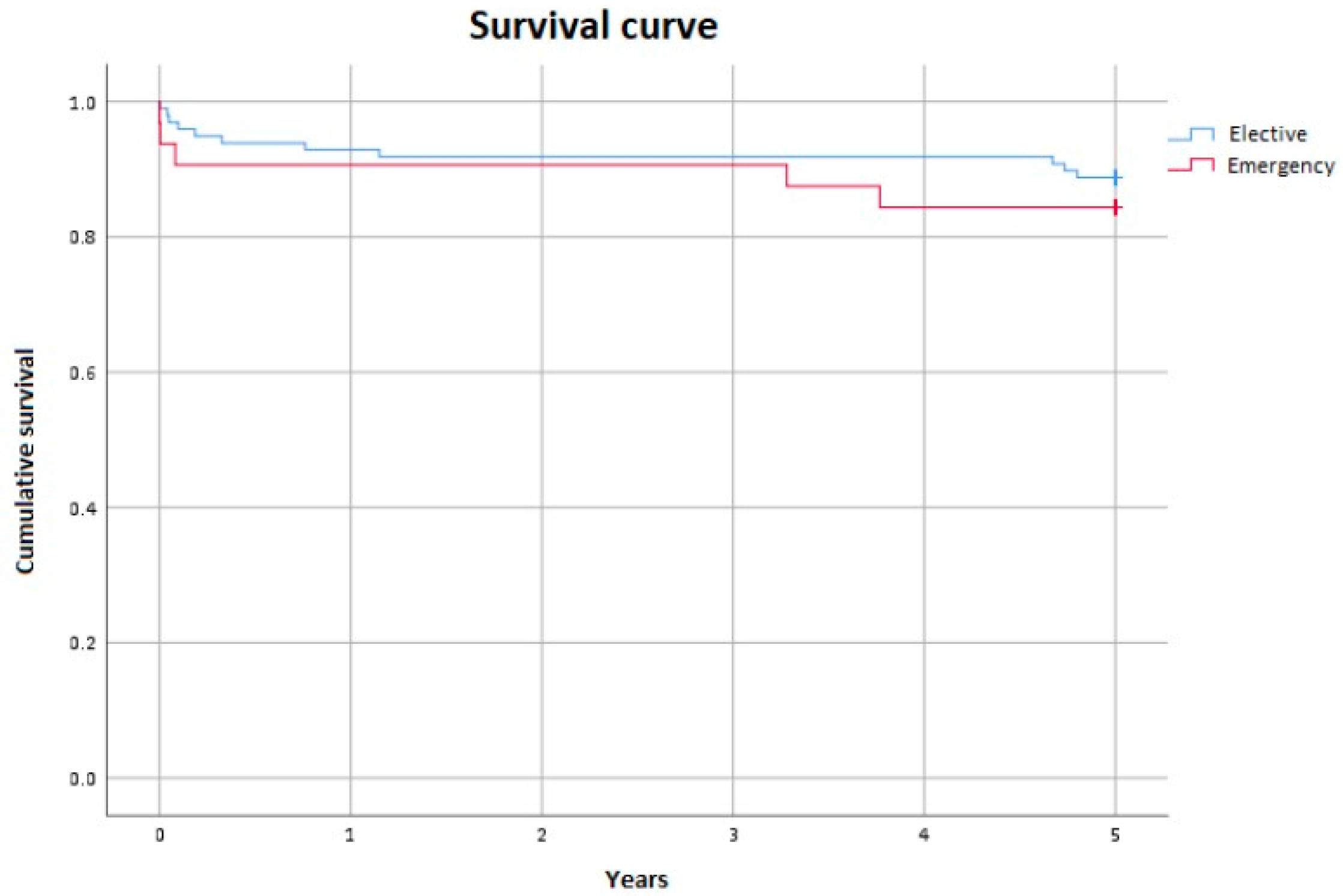
3.1. Mortality
3.2. Neurological Events
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
Abbreviations
| IA | innominate artery |
| SCP | antegrade selective cerebral perfusion |
| ACP | antegrade cerebral perfusion |
| HCA | hypothermic circulatory arrest |
| CPB | cardiopulmonary bypass |
| ACC | aortic cross-clamping |
| CT | computed tomography |
| EEG | electroencephalogram |
| PND | permanent neurological dysfunction |
| TND | transient neurological dysfunction |
| IQR | interquartile range |
| OR | odds ratio |
| NIRS | near-infrared spectroscopy |
| rSO2 | regional oxygen saturation |
| CW | circle of Willis |
References
- Abe, T.; Usui, A. The Cannulation Strategy in Surgery for Acute Type A Dissection. Gen. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2017, 65, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montisci, A.; Maj, G.; Cavozza, C.; Audo, A.; Benussi, S.; Rosati, F.; Cattaneo, S.; Di Bacco, L.; Pappalardo, F. Cerebral Perfusion and Neuromonitoring during Complex Aortic Arch Surgery: A Narrative Review. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 3470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harky, A.; Oo, S.; Gupta, S.; Field, M. Proximal arterial cannulation in thoracic aortic surgery—A literature review. J. Card. Surg. 2019, 34, 598–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedetto, U.; Raja, S.G.; Amrani, M.; Pepper, J.R.; Zeinah, M.; Tonelli, E.; Biondi-Zoccai, G.; Frati, G. The impact of arterial cannulation strategy on operative outcomes in aortic surgery: Evidence from a comprehensive meta-analysis of comparative studies on 4476 patients. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2014, 148, 2936–2943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, S.K.; Reddy, P.R. Cannulation strategies in aortic surgery: Techniques and decision making. Indian J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2022, 38 (Suppl 1), 132–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwari, K.K.; Murzi, M.; Bevilacqua, S.; Glauber, M. Which cannulation (ascending aortic cannulation or peripheral arterial cannulation) is better for acute type A aortic dissection surgery? Interact. Cardiovasc. Thorac. Surg. 2010, 10, 797–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preventza, O.; Price, M.D.; Hiruni, S.; Amarasekara, H.S.; Cornwell, L.D.; Omer, S.; De la Cruz, K.I.; Zhang, Q.; Green, S.Y.; LeMaire, S.A.; et al. In elective arch surgery with circulatory arrest, does the arterial cannulation site matter? A propensity score analysis of right axillary and innominate artery cannulation. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2018, 155, 1953–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogino, H.; Sasaki, H.; Minatoya, K.; Matsuda, H.; Tanaka, H.; Watanuki, H.; Ando, M.; Kitamura, S. Evolving arch surgery using integrated antegrade selective cerebral perfusion: Impact of axillary artery perfusion. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2008, 136, 641–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayyash, B.; Tranquilli, M.; Elefteriades, J.A. Femoral artery cannulation for thoracic aortic surgery: Safe under transesophageal echocardiographic control. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2011, 142, 1478–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etz, C.D.; Plestis, K.A.; Kari, F.A.; Silovitz, D.; Bodian, C.A.; Spielvogel, D.; Griepp, R.B. Axillary cannulation significantly improves survival and neurologic outcomes after atherosclerotic aneurysm repair of the aortic root and ascending aorta. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2008, 86, 441–446; discussion 446–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, D.R.; Coselli, J.S.; Palmero, L.; Bozinovski, J.; Carter, S.A.; Murariu, D.; LeMaire, S.A. Axillary artery cannulation in surgery for acute or subacute ascending aortic dissections. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2010, 90, 731–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preventza, O.; Garcia, A.; Tuluca, A.; Henry, M.; Cooley, D.A.; Simpson, K.; Bakaeen, F.G.; Cornwell, L.D.; Omer, S.; Coselli, J.S. Innominate artery cannulation for proximal aortic surgery: Outcomes and neurological events in 263 patients. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2015, 48, 937–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Eusanio, M.; Ciano, M.; Labriola, G.; Lionetti, G.; Di Eusanio, G. Cannulation of the innominate artery during surgery of the thoracic aorta: Our experience in 55 patients. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2007, 32, 270–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, K.M.; Li, S.J.; Lin, T.Y.; Chan, C.Y.; Chu, S.H. Innominate artery cannulation for aortic surgery. Asian Cardiovasc. Thorac. Ann. 2007, 15, 348–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banbury, M.K.; Cosgrove, D.M., III. Arterial cannulation of the innominate artery. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2000, 69, 957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.J.; Wu, Q.; Ren, C.W.; Lai, Y.Q.; Yang, S.; Rui, Q.J.; Xu, S.D. Cannulation of the innominate artery with a side graft in arch surgery. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2010, 89, 800–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehran, R.; Hadi, S.; Ali, N.; Taban-Sadeghi, M.; Khalili, A.; Hamzehzadeh, S.; Khoei, R.A.A.; Hosseinifard, H.; Sulague, R.M.; Kpodonu, J. Cerebral protection in acute type A aortic dissection surgery: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Thorac. Dis. 2024, 16, 1289–1312. [Google Scholar]
- Urbanski, P.P.; Lenos, A.; Blume, J.C.; Ziegler, V.; Griewing, B.; Schmitt, R.; Diegeler, A.; Dinkel, M. Does anatomical completeness of the circle of Willis correlate with sufficient cross-perfusion during unilateral cerebral perfusion? Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2008, 33, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoksbergen, A.W.J.; Legemate, D.A.; Ubbink, D.T.; Jacobs, M.J.H.M. Collateral variations in the circle of Willis in atherosclerotic population were assessed using transcranial colour-coded duplex ultrasonography. Stroke 2000, 31, 1656–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, S.L. Collateral Circulation. Stroke 2003, 34, 2279–2284. [Google Scholar]
- Svensson, L.G.; Blackstone, E.H.; Rajeswaran, J.; Sabik, J.F., 3rd; Lytle, B.W.; Gonzalez-Stawinski, G.; Varvitsiotis, P.; Banbury, M.K.; McCarthy, P.M.; Pettersson, G.B.; et al. Does the arterial cannulation site for circulatory arrest influence stroke risk? Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2004, 78, 1274–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, M.W.; Losenno, K.L.; Gelinas, J.J.; Garg, V.; Dickson, J.; Harrington, A.; Verma, S.; Peterson, M.D. Innominate and Axillary Cannulation in Aortic Arch Surgery Provide Similar Neuroprotection. Can. J. Cardiol. 2016, 32, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garg, V.; Tsirigotis, D.N.; Dickson, J.; Dalamagas, C.; Latter, D.A.; Verma, S.; Peterson, M.D. Direct innominate artery cannulation for selective antegrade cerebral perfusion during deep hypothermic circulatory arrest in aortic surgery. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2014, 148, 2920–2924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterson, M.D.; Garg, V.; Mazer, C.D.; Chu, M.W.A.; Bozinovski, J.; Dagenais, F.; MacArthur, R.G.G.; Ouzounian, M.; Quan, A.; Jüni, P.; et al. A randomized trial comparing axillary versus innominate artery cannulation for aortic arch surgery. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2022, 164, 1426–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isselbacher, E.M.; Preventza, O.; Hamilton Black, J.; Augoustides, J.G.; Beck, A.W.; Bolen, M.A.; Braverman, A.C.; Bray, B.E.; Brown-Zimmerman, M.M.; Chen, E.P.; et al. 2022 ACC/AHA Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of Aortic Disease: A Report of the American Heart Association/American College of Cardiology Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2022, 146, e334–e482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabik, J.F.; Lytle, B.W.; McCarthy, P.M.; Cosgrove, D.M. Axillary artery: An alternative arterial cannulation site for patients with extensive aortic and peripheral vascular disease. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 1995, 109, 885–890; discussion 890–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldeiry, M.; Ghincea, C.; Aftab, M.; Cleveland, J.C.; Fullerton, D.; Reece, T.B. Innominate Versus Axillary Artery Cannulation for the Hemiarch Repair. J. Surg. Res. 2018, 232, 234–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamou, S.C.; Gartner, D.; Kouchoukos, N.T.; Lobdell, K.W.; Khabbaz, K.; Murphy, E.; Murphy, E.; Hagberg, R.C. Axillary Versus Femoral Arterial Cannulation During Repair of Type A Aortic Dissection?: An Old Problem Seeking New Solutions. Aorta 2016, 4, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angeloni, E.; Benedetto, U.; Takkenberg, J.J.; Stigliano, I.; Roscitano, A.; Melina, G.; Sinatra, R. Unilateral versus bilateral antegrade cerebral protection during circulatory arrest in aortic surgery: A meta-analysis of 5100 patients. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2014, 147, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zierer, A.; Risteski, P.; El-Sayed Ahmad, A.; Moritz, A.; Diegeler, A.; Urbanski, P.P. The impact of unilateral versus bilateral antegrade cerebral perfusion on surgical outcomes after aortic arch replacement: A propensity-matched analysis. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2014, 147, 1212–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harky, A.; Wong, C.H.M.; Chan, J.S.K.; Zaki, S.; Froghi, S.; Bashir, M. Innominate artery cannulation in aortic surgery: A systematic review. J. Card. Surg. 2018, 33, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| n | % | |
|---|---|---|
| Male | 133 | 63.9 |
| Female | 75 | 36.1 |
| Median Age [IQR] | 69.00 | [59.25–76] |
| Smoking | 91 | 43.8 |
| Hypertension | 173 | 83.2 |
| Diabetes Mellitus | 12 | 5.8 |
| Dysilipidemia | 73 | 35.1 |
| COPD | 21 | 10.1 |
| Peripheral Vascular Disease | 65 | 31.3 |
| History of Myocardial Infarction | 3 | 1.4 |
| Renal Failure | 19 | 9.1 |
| Median EF% [IQR] | 59 [55–60] | |
| EuroSCORE % [IQR] | 4.04 [2.27–8.93] |
| Median [IQR] | |
|---|---|
| CPB | 140.50 [107.75–184] |
| Aortic Cross-Clamping | 97 [77–138.25] |
| ACP (n = 110) | 31.50 [22–56.25] |
| Total | Elective | Dissection Type A | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patients | 208 | 148 | 60 |
| Kidney Failure | 7.2% | 4.1% | 15% |
| 15 | 6 | 9 | |
| Dialysis | 5.3% | 3.4% | 10% |
| 11 | 5 | 6 | |
| Postoperative Bleeding | 5.3% | 5.4% | 5% |
| 11 | 8 | 3 | |
| Infections | 11.1% | 7.4% | 20% |
| 23 | 11 | 12 | |
| Neurological Events | 8.2% | 3.4% | 20% |
| (PND and TND) | 17 | 5 | 12 |
| Total | Elective | Dissection Type A | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patients | 208 | 148 | 60 |
| Alive | 94.7% | 96.6% | 90% |
| 197 | 143 | 54 | |
| Dead | 5.3% | 3.4% | 10% |
| 11 | 5 | 6 | |
| Total | 100% | 100% | 100% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cavozza, C.; Scarongella, R.; Policastro, G.; Maj, G.; Cassinari, A.; Penpa, S.; Maconi, A.; Audo, A. Direct Innominate Artery Cannulation for Thoracic Aortic Surgery. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 2684. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14082684
Cavozza C, Scarongella R, Policastro G, Maj G, Cassinari A, Penpa S, Maconi A, Audo A. Direct Innominate Artery Cannulation for Thoracic Aortic Surgery. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(8):2684. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14082684
Chicago/Turabian StyleCavozza, Corrado, Rossella Scarongella, Giulia Policastro, Giulia Maj, Antonella Cassinari, Serena Penpa, Antonio Maconi, and Andrea Audo. 2025. "Direct Innominate Artery Cannulation for Thoracic Aortic Surgery" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 8: 2684. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14082684
APA StyleCavozza, C., Scarongella, R., Policastro, G., Maj, G., Cassinari, A., Penpa, S., Maconi, A., & Audo, A. (2025). Direct Innominate Artery Cannulation for Thoracic Aortic Surgery. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(8), 2684. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14082684






