Clinicopathological Characteristics of Extrapulmonary Neuroendocrine Carcinomas: Treatment Responses and Survival Outcomes: Single-Center Experience
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Study Setting and Sample
2.3. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.4. Data Collection
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.6. Ethical Considerations
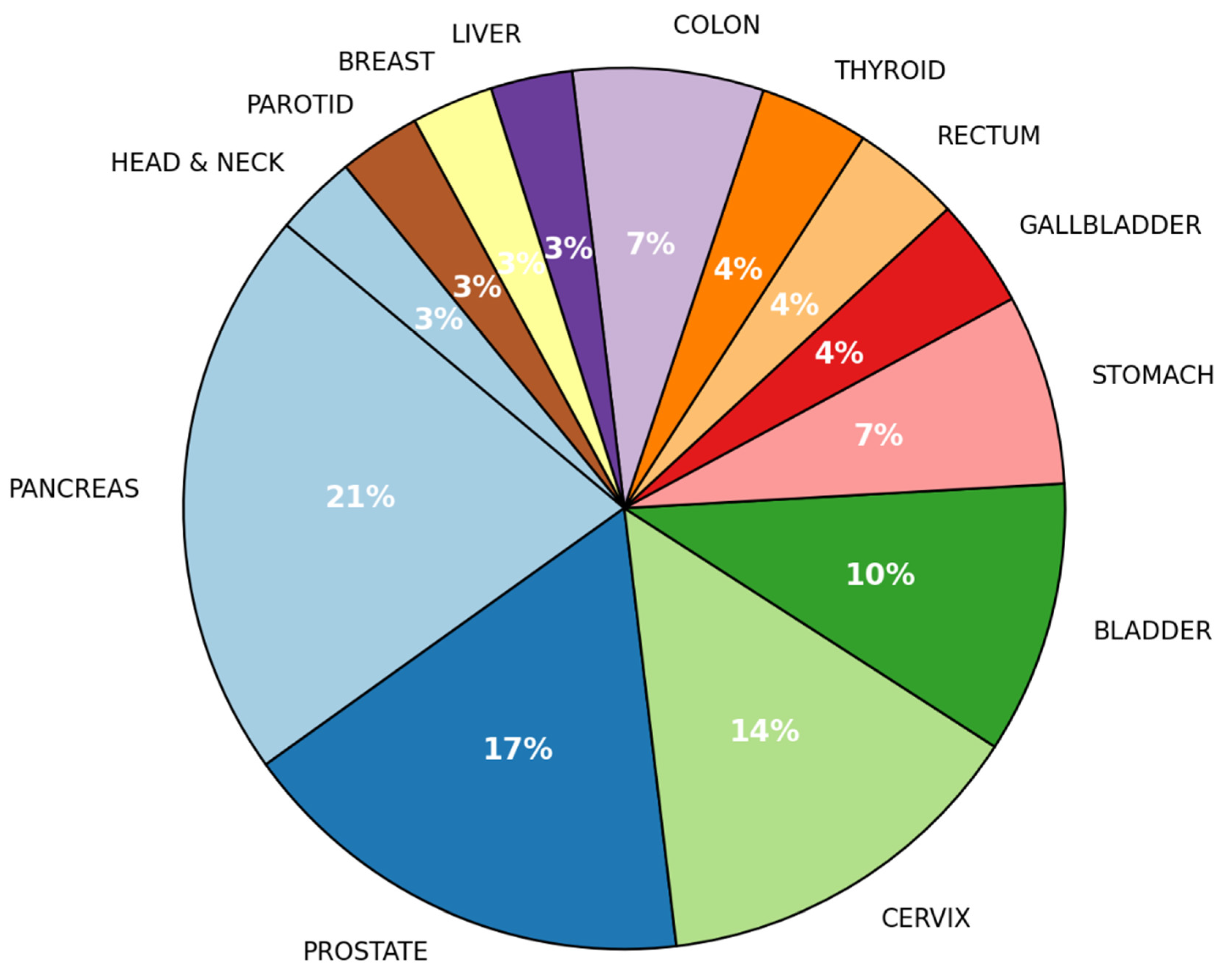
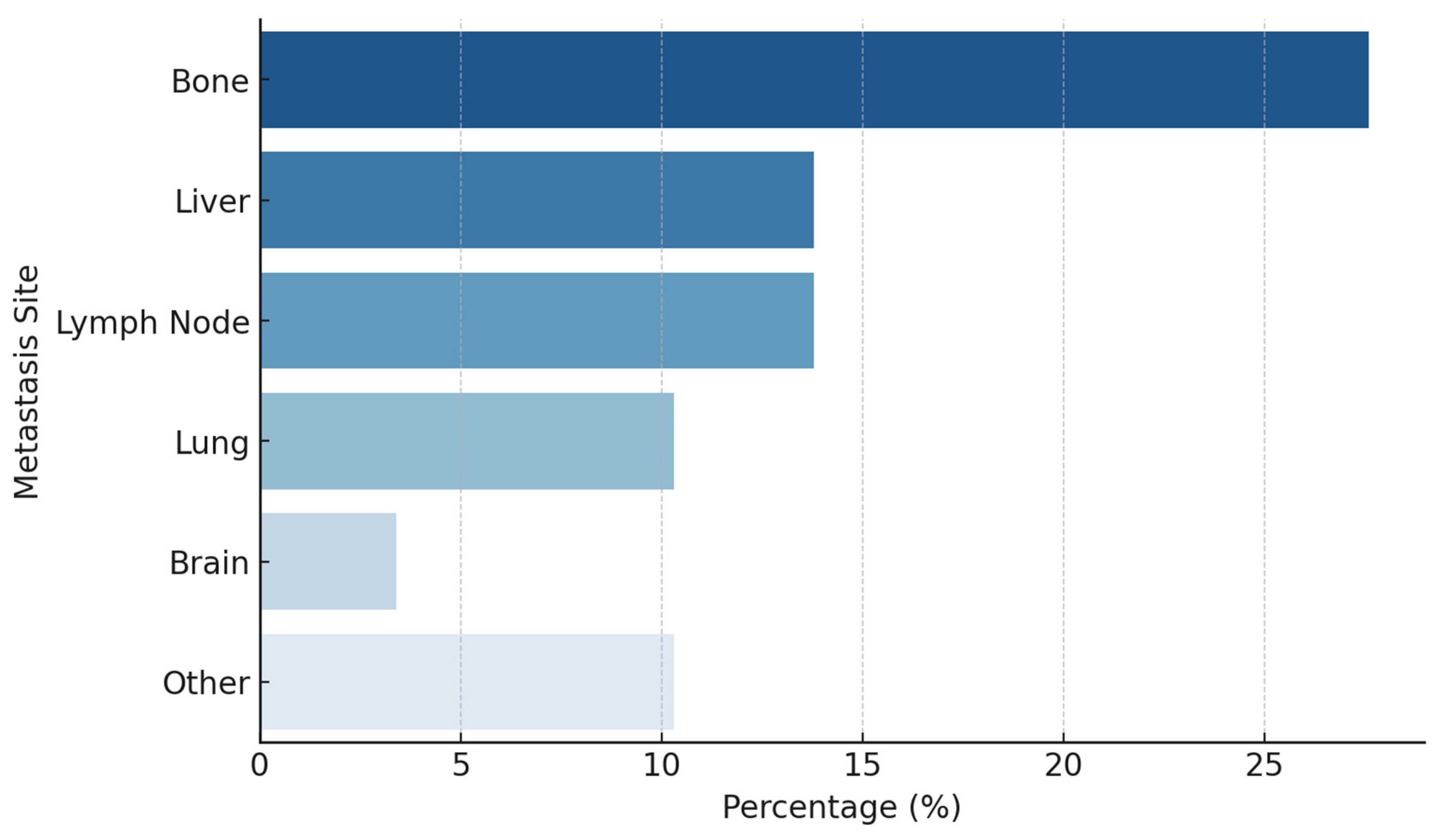
3. Results
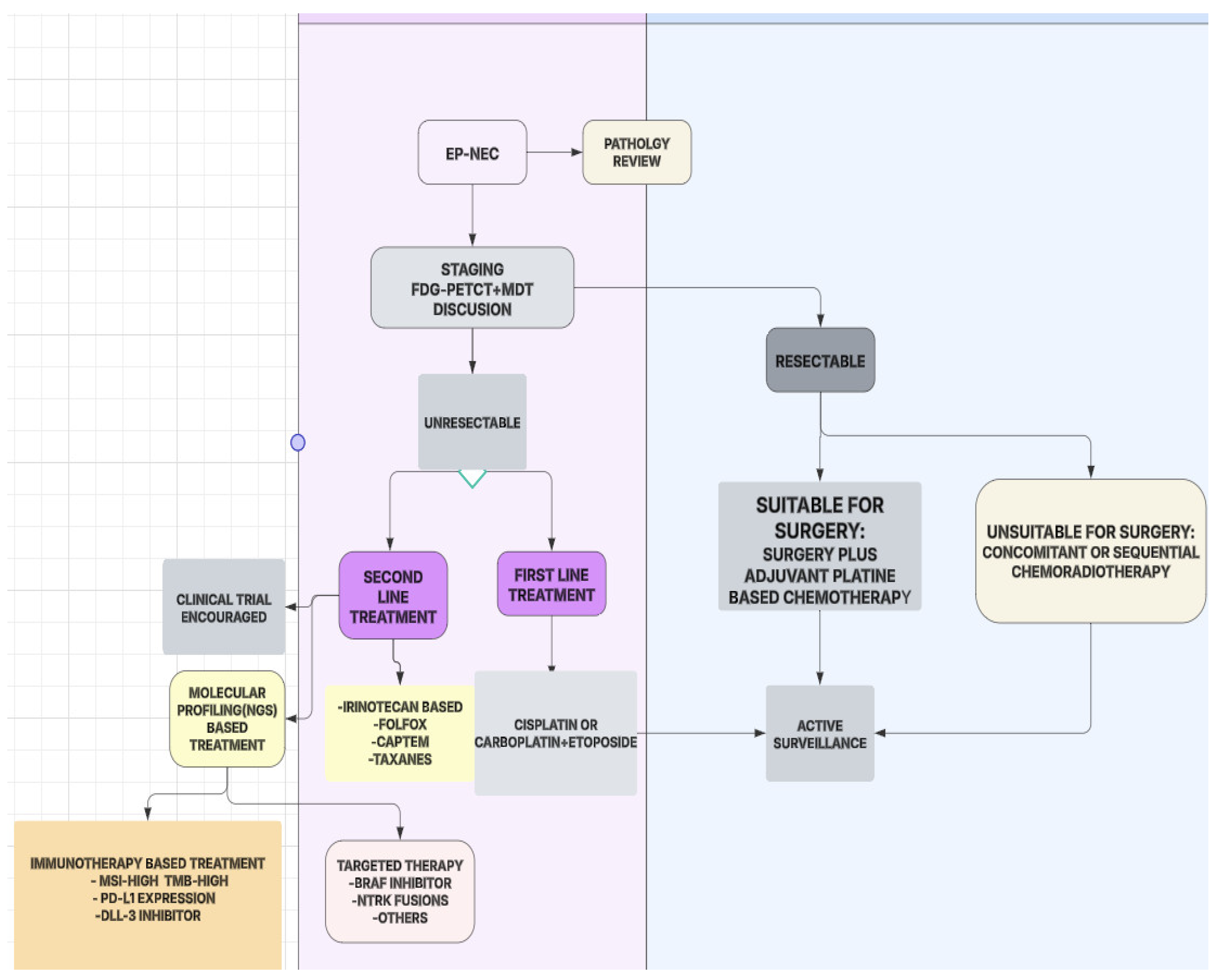
4. Discussion
- SCLC-like EP-NECs, frequently harboring TP53 and RB1 mutations, may benefit from DNA repair-targeted therapies.
- Non-neuroendocrine cancer-like EP-NECs, with frequent KRAS and BRAF mutations, could be targeted with BRAF and MEK inhibitors.
- Tumor-agnostic EP-NECs, characterized by epigenetic alterations, might respond to EZH2 inhibitors [19].
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shia, J.; Tang, L.H.; Weiser, M.R.; Brenner, B.; Adsay, N.V.; Stelow, E.B.; Saltz, L.B.; Qin, J.; Landmann, R.; Leonard, G.D.; et al. Is nonsmall cell type high-grade neuroendocrine carcinoma of the tubular gastrointestinal tract a distinct disease entity? Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2008, 32, 719–731. [Google Scholar]
- Qubaiah, O.; Devesa, S.S.; Platz, C.E.; Huycke, M.M.; Dores, G.M. Small intestinal cancer: A population-based study of incidence and survival patterns in the United States, 1992 to 2006. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2010, 19, 1908–1918. [Google Scholar]
- Walenkamp, A.M.; Sonke, G.S.; Sleijfer, D.T. Clinical and therapeutic aspects of extrapulmonary small cell carcinoma. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2009, 35, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Strosberg, J.R.; Coppola, D.; Klimstra, D.S.; Phan, A.T.; Kulke, M.H.; Wiseman, G.A.; Kvols, L.K. The NANETS consensus guidelines for the diagnosis and management of poorly differentiated (high-grade) extrapulmonary neuroendocrine carcinomas. Pancreas 2010, 39, 799–800. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yao, J.C.; Hassan, M.; Phan, A.; Dagohoy, C.; Leary, C.; Mares, J.E.; Abdalla, E.K.; Fleming, J.B.; Vauthey, J.-N.; Rashid, A.; et al. One hundred years after “carcinoid”: Epidemiology of and prognostic factors for neuroendocrine tumors in 35,825 cases in the United States. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 3063–3072. [Google Scholar]
- McNamara, M.G.; Frizziero, M.; Jacobs, T.; Lamarca, A.; Hubner, R.A.; Valle, J.W.; Amir, E. Second-line treatment in patients with advanced extra-pulmonary poorly differentiated neuroendocrine carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2020, 12, 1758835920915299. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Carbonero, R.; Sorbye, H.; Baudin, E.; Raymond, E.; Wiedenmann, B.; Niederle, B.; Sedlackova, E.; Toumpanakis, C.; Anlauf, M.; Cwikla, J.M.; et al. ENETS consensus guidelines for high-grade gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumors and neuroendocrine carcinomas. Neuroendocrinology 2016, 103, 186–194. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura, M.; Seki, K.; Bychkov, A.; Fukuoka, J. Molecular pathology of pulmonary large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma: Novel concepts and treatments. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 671799. [Google Scholar]
- Hiroshima, K.; Iyoda, A.; Shida, T.; Shibuya, K.; Iizasa, T.; Kishi, H.; Tanizawa, T.; Fujisawa, T.; Nakatani, Y. Distinction of pulmonary large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma from small cell lung carcinoma: A morphological, immunohistochemical, and molecular analysis. Mod. Pathol. 2006, 19, 1358–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasari, A.; Shen, C.; Halperin, D.; Zhao, B.; Zhou, S.; Xu, Y.; Shih, T.; Yao, J.C. Trends in the incidence, prevalence, and survival outcomes in patients with neuroendocrine tumors in the United States. JAMA Oncol. 2017, 3, 1335–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rindi, G.; Klimstra, D.S.; Abedi-Ardekani, B.; Asa, S.L.; Bosman, F.T.; Brambilla, E.; Busam, K.J.; De Krijger, R.R.; Dietel, M.; El-Naggar, A.K.; et al. A common classification framework for neuroendocrine neoplasms: An International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) and World Health Organization (WHO) expert consensus proposal. Mod. Pathol. 2018, 31, 1770–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dowlati, A.; Lipka, M.B.; McColl, K.; Dabir, S.; Behtaj, M.; Kresak, A.; Miron, A.; Yang, M.; Sharma, N.; Fu, P.; et al. Clinical correlation of extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer genomics. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27, 642–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNamara, M.G.; Scoazec, J.-Y.; Walter, T. Extrapulmonary poorly differentiated NECs, including molecular and immune aspects. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2020, 27, R219–R238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pea, A.; Hruban, R.H.; Wood, L.D. Genetics of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors: Implications for the clinic. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 9, 1407–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, T.; Tougeron, D.; Baudin, E.; Le Malicot, K.; Lecomte, T.; Malka, D.; Miron, A.; Yang, M.; Sharma, N.; Fu, P.; et al. Poorly differentiated gastro-entero-pancreatic neuroendocrine carcinomas: Are they really heterogeneous? Insights from the FFCD-GTE national cohort. Eur. J. Cancer 2017, 79, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heetfeld, M.; Chougnet, C.N.; Olsen, I.H.; Rinke, A.; Borbath, I.; Crespo, G.; Barriuso, J.; Pavel, M.; O’Toole, D.; Walter, T. Characteristics and treatment of patients with G3 gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2015, 22, 657–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorbye, H.; Baudin, E.; Borbath, I.; Caplin, M.; Chen, J.; Cwikla, J.B.; Frilling, A.; Grossman, A.; Kaltsas, G.; Scarpa, A.; et al. Unmet needs in high-grade gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms (WHO G3). Neuroendocrinology 2019, 108, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yachida, S.; Totoki, Y.; Noë, M.; Nakatani, Y.; Horie, M.; Kawasaki, K.; Nakamura, H.; Saito-Adachi, M.; Suzuki, M.; Takai, E.; et al. Comprehensive genomic profiling of neuroendocrine carcinomas of the gastrointestinal system. Cancer Discov. 2022, 12, 692–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frizziero, M.; Kilgour, E.; Simpson, K.L.; Rothwell, D.G.; Moore, D.A.; Frese, K.K.; Galvin, M.; Lamarca, A.; Hubner, R.A.; Valle, J.W.; et al. Expanding therapeutic opportunities for extrapulmonary neuroendocrine carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 28, 1999–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lantuejoul, S.; Fernandez-Cuesta, L.; Damiola, F.; Girard, N.; McLeer, A. New molecular classification of large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma and small cell lung carcinoma with potential therapeutic impacts. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2020, 9, 2233–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Travis, W.D.; Brambilla, E.; Burke, A.P.; Marx, A.; Nicholson, A.G. Introduction to the 2015 World Health Organization classification of tumors of the lung, pleura, thymus, and heart. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2015, 10, 1240–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, M.B.; Edge, S.B.; Greene, F.L.; Byrd, D.R.; Brookland, R.K.; Washington, M.K.; Gershenwald, J.E.; Compton, C.C.; Hess, K.R.; Sullivan, D.C.; et al. AJCC Cancer Staging Manual; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Eisenhauer, E.A.; Therasse, P.; Bogaerts, J.; Schwartz, L.H.; Sargent, D.; Ford, R.; Dancey, J.; Arbuck, S.; Gwyther, S.; Mooney, M.; et al. New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours: Revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur. J. Cancer 2009, 45, 228–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moertel, C.G.; Kvols, L.K.; O’Connell, M.J.; Rubin, J. Treatment of neuroendocrine carcinomas with combined etoposide and cisplatin. Evidence of major therapeutic activity in the anaplastic variants of these neoplasms. Cancer 1991, 68, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Terashima, T.; Morizane, C.; Hiraoka, N.; Tsuda, H.; Tamura, T.; Shimada, Y.; Kaneko, S.; Kushima, R.; Ueno, H.; Kondo, S.; et al. Comparison of chemotherapeutic treatment outcomes of advanced extrapulmonary neuroendocrine carcinomas and advanced small-cell lung carcinoma. Neuroendocrinology 2012, 96, 324–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, T.; Machida, N.; Morizane, C.; Kasuga, A.; Takahashi, H.; Sudo, K.; Nishina, T.; Tobimatsu, K.; Ishido, K.; Furuse, J.; et al. Multicenter retrospective analysis of systemic chemotherapy for advanced neuroendocrine carcinoma of the digestive system. Cancer Sci. 2014, 105, 1176–1181. [Google Scholar]
- Govindan, R.; Aggarwal, C.; Antonia, S.J.; Davies, M.; Dubinett, S.M.; Ferris, A.; Forde, P.M.; Garon, E.B.; Goldberg, S.B.; Hassan, R.; et al. Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer (SITC) clinical practice guideline on immunotherapy for the treatment of lung cancer and mesothelioma. J. Immunother. Cancer 2022, 10, e003956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de M Rêgo, J.F.; de Medeiros, R.S.S.; Braghiroli, M.I.; Galvão, B.; Neto, J.E.B.; Munhoz, R.R.; Guerra, J.; Nonogaki, S.; Kimura, L.; Pfiffer, T.E.; et al. Expression of ERCC1, Bcl-2, Lin28a, and Ki-67 as biomarkers of response to first-line platinum-based chemotherapy in patients with high-grade extrapulmonary neuroendocrine carcinomas or small cell lung cancer. Ecancermedicalscience 2017, 11, 767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jesinghaus, M.; Konukiewitz, B.; Keller, G.; Kloor, M.; Steiger, K.; Reiche, M.; Penzel, R.; Endris, V.; Arsenic, R.; Hermann, G.; et al. Colorectal mixed adenoneuroendocrine carcinomas and neuroendocrine carcinomas are genetically closely related to colorectal adenocarcinomas. Mod. Pathol. 2017, 30, 610–619. [Google Scholar]
- Cicin, I.; Karagol, H.; Uzunoglu, S.; Uygun, K.; Usta, U.; Kocak, Z.; Caloglu, M.; Saynak, M.; Tokatli, F.; Uzal, C. Extrapulmonary small-cell carcinoma compared with small-cell lung carcinoma: A retrospective single-center study. Cancer 2007, 110, 1068–1076. [Google Scholar]
- Vijayvergia, N.; Boland, P.M.; Handorf, E.; Gustafson, K.S.; Gong, Y.; Cooper, H.S.; Sheriff, F.; Astsaturov, I.; Cohen, S.J.; Engstrom, P.F. Molecular Profiling of Neuroendocrine Malignancies to İdentify Prognostic and Therapeutic Markers: A Fox Chase Cancer Center Pilot Study. Br. J. Cancer 2016, 115, 564–570. [Google Scholar]
- Regalla, D.K.R.; Deep, O.; Paluri, R.K. Advances in understanding and management of high-grade pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasm: A comprehensive review. Chin. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 12, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefàno, E.; De Castro, F.; Ciccarese, A.; Muscella, A.; Marsigliante, S.; Benedetti, M.; Fanizzi, F.P. An Overview of Altered Pathways Associated with Sensitivity to Platinum-Based Chemotherapy in Neuroendocrine Tumors: Strengths and Prospects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 8568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stumpo, S.; Formelli, M.G.; Persano, I.; Parlagreco, E.; Lauricella, E.; Rodriquenz, M.G.; Guerrera, L.P.; Zurlo, I.V.; Campana, D.; Brizzi, M.P.; et al. Extrapulmonary Neuroendocrine Carcinomas: Current Management and Future Perspectives. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 7715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, S.P.; Othus, M.; Chae, Y.K.; Giles, F.J.; Hansel, D.E.; Singh, P.P.; Fontaine, A.; Shah, M.H.; Kasi, A.; Al Baghdadi, T.; et al. A Phase II Basket Trial of Dual Anti-CTLA-4 and Anti-PD-1 Blockade in Rare Tumors (DART SWOG 1609) in Patients with Nonpancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 2290–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgensztern, D.; Besse, B.; Greillier, L.; Santana-Davila, R.; Ready, N.; Hann, C.L.; Glisson, B.S.; Farago, A.F.; Dowlati, A.; Rudin, C.M.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Rovalpituzumab Tesirine in Third-Line and Beyond Patients with DLL3-Expressing, Relapsed/Refractory Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Results from the Phase II TRINITY Study. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 6958–6966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, M.D.; Livesey, D.; Hubner, R.A.; Valle, J.W.; McNamara, M.G. Future therapeutic strategies in the treatment of extrapulmonary neuroendocrine carcinoma: A review. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2023, 15, 17588359231156870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frizziero, M.; Durand, A.; Taboada, R.G.; Zaninotto, E.; Luchini, C.; Chakrabarty, B.; Hervieu, V.; Claro, L.C.L.; Zhou, C.; Cingarlini, S.; et al. Is the morphological subtype of extra-pulmonary neuroendocrine carcinoma clinically relevant? Cancers 2021, 13, 4152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohmoto, A.; Fujiwara, Y.; Horita, N.; Nakano, K.; Takahashi, S. Platinum-doublet chemotherapy for advanced gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Discov. Oncol. 2022, 13, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celik, E.; Samanci, N.S.; Derin, S.; Bedir, S.; Degerli, E.; Oruc, K.; Oztas, N.S.; Alkan, G.; Senyigit, A.; Turna, H. A single center’s experience of the extrapulmonary neuroendocrine carcinomas. North. Clin. Istanb. 2022, 9, 35–40. [Google Scholar]
- Weaver, J.M.J.; Hubner, R.A.; Valle, J.W.; McNamara, M.G. Selection of Chemotherapy in Advanced Poorly Differentiated Extra-Pulmonary Neuroendocrine Carcinoma. Cancers 2023, 15, 4951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGarrah, P.W.; Leventakos, K.; Hobday, T.J.; Molina, J.R.; Finnes, H.D.; Westin, G.F.; Halfdanarson, T.R. Efficacy of Second-Line Chemotherapy in Extrapulmonary Neuroendocrine Carcinoma. Pancreas 2020, 49, 529–533. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cai, L.; DeBerardinis, R.J.; Xiao, G.; Minna, J.D.; Xie, Y. A Pan-Cancer Assessment of RB1/TP53 Co-Mutations. Cancers 2022, 14, 4199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melhorn, P.; Spitzer, J.; Adel, T.; Wolff, L.; Mazal, P.; Raderer, M.; Kiesewetter, B. Patterns and outcomes of current antitumor therapy for high-grade neuroendocrine neoplasms: Perspective of a tertiary referral center. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2025, 151, 86. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Howlader, N.; Noone, A.; Krapcho, M.; Garshell, J.; Miller, D.; Altekruse, S. Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) Program; SEER* Stat Database; NCI: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Sorbye, H.; Welin, S.; Langer, S.W.; Vestermark, L.W.; Holt, N.; Osterlund, P.; Dueland, S.; Hofsli, E.; Guren, M.G.; Ohrling, K.; et al. Predictive and prognostic factors for treatment and survival in 305 patients with advanced gastrointestinal neuroendocrine carcinoma (WHO G3): The NORDIC NEC study. Ann. Oncol. 2013, 24, 152–160. [Google Scholar]
- Machida, N.; Yamaguchi, T.; Kasuga, A.; Takahashi, H.; Sudo, K.; Nishina, T.; Tobimatsu, K.; Ishido, K.; Furuse, J.; Boku, N. Multicenter retrospective analysis of systemic chemotherapy for advanced poorly differentiated neuroendocrine carcinoma of the digestive system. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 15. [Google Scholar]
- Bernick, P.; Klimstra, D.; Shia, J.; Minsky, B.; Saltz, L.; Shi, W.; Thaler, H.; Guillem, J.; Paty, P.; Cohen, A.M.; et al. Neuroendocrine carcinomas of the colon and rectum. Dis. Colon Rectum 2004, 47, 163–169. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, J.D.; Reidy, D.L.; Goodman, K.A.; Shia, J.; Nash, G.M. A retrospective review of 126 high-grade neuroendocrine carcinomas of the colon and rectum. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2014, 21, 2956–2962. [Google Scholar]
- Fujii, H.; Aotake, T.; Horiuchi, T.; Chiba, Y.; Imamura, Y.; Tanaka, K. Small cell carcinoma of the gallbladder: A case report and review of 53 cases in the literature. Hepatogastroenterology 2001, 48, 1588–1593. [Google Scholar]
- Strosberg, J.R.; Cheema, A.; Weber, J.; Han, G.; Coppola, D.; Kvols, L.K. Prognostic validity of a novel American Joint Committee on Cancer Staging Classification for pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 3044–3049. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Carbonero, R.; Capdevila, J.; Crespo-Herrero, G.; Díaz-Pérez, J.; Del Prado, M.M.; Orduña, V.A.; Sevilla-García, I.; Villabona-Artero, C.; Beguiristain-Gómez, A.; Llanos-Muñoz, M.; et al. Incidence, patterns of care and prognostic factors for outcome of gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (GEP-NETs): Results from the National Cancer Registry of Spain (RGETNE). Ann. Oncol. 2010, 21, 1794–1803. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Toubah, T.; Cives, M.; Strosberg, J. Novel immunotherapy strategies for treatment of neuroendocrine neoplasms. Transl. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 5, 54. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bösch, F.; Brüwer, K.; Altendorf-Hofmann, A.; Auernhammer, C.J.; Spitzweg, C.; Westphalen, C.B.; Boeck, S.; Schubert-Fritschle, G.; Werner, J.; Heinemann, V.; et al. Immune checkpoint markers in gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasia. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2019, 26, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Marabelle, A.; Le, D.T.; Ascierto, P.A.; Di Giacomo, A.M.; De Jesus-Acosta, A.; Delord, J.-P.; Geva, R.; Gottfried, M.; Penel, N.; Hansen, A.R.; et al. Efficacy of pembrolizumab in patients with noncolorectal high microsatellite instability/mismatch repair–deficient cancer: Results from the phase II KEYNOTE-158 study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Frenel, J.S.; Le Tourneau, C.; O’Neil, B.; Ott, P.A.; Piha-Paul, S.A.; Gomez-Roca, C.; van Brummelen, E.M.J.; Rugo, H.S.; Thomas, S.; Saraf, S.; et al. Safety and efficacy of pembrolizumab in advanced, programmed death ligand 1-positive cervical cancer: Results from the phase Ib KEYNOTE-028 trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 4035–4041. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yao, J.C.; Strosberg, J.; Fazio, N.; Pavel, M.E.; Bergsland, E.; Ruszniewski, P.; Halperin, D.M.; Li, D.; Tafuto, S.; Raj, N.; et al. Spartalizumab in metastatic, well/poorly-differentiated neuroendocrine neoplasms. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2021, 28, 161–172. [Google Scholar]
- Krauss, T.; Ferrara, A.M.; Links, T.P.; Wellner, U.; Bancos, I.; Kvachenyuk, A.; Heras, K.V.G.d.L.; Yukina, M.Y.; Petrov, R.; Bullivant, G.; et al. Preventive medicine of von Hippel–Lindau disease-associated pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2018, 25, 783–793. [Google Scholar]
- Åkerström, G.; Hessman, O.; Skogseid, B. Timing and extent of surgery in symptomatic and asymptomatic neuroendocrine tumors of the pancreas in MEN 1. Langenbecks Arch. Surg. 2002, 386, 558–569. [Google Scholar]
- Pavel, M.; Öberg, K.; Falconi, M.; Krenning, E.; Sundin, A.; Perren, A.; Berruti, A. Gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 844–860. [Google Scholar]
- Morizane, C.; Machida, N.; Honma, Y.; Okusaka, T.; Boku, N.; Kato, K.; Mizusawa, J.; Katayama, H.; Hiraoka, N.; Taniguchi, H.; et al. Randomized phase III study of etoposide plus cisplatin versus irinotecan plus cisplatin in advanced neuroendocrine carcinoma of the digestive system: A Japan Clinical Oncology Group study (JCOG1213). Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 15. [Google Scholar]
- Jeong, H.; Shin, J.; Jeong, J.; Kim, K.-p.; Hong, S.-M.; Kim, Y.-i.; Ryu, J.-S.; Ryoo, B.-Y.; Yoo, C. Capecitabine plus temozolomide in patients with grade 3 unresectable or metastatic gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms with Ki-67 index < 55%: Single-arm phase II study. ESMO Open 2021, 6, 100119. [Google Scholar]
- Dasari, A.; Shen, C.; Devabhaktuni, A.; Nighot, R.; Sorbye, H. Survival according to primary tumor location, stage, and treatment patterns in locoregional gastroenteropancreatic high-grade neuroendocrine carcinomas. Oncologist 2022, 27, 299–306. [Google Scholar]
| Variable | (%) |
|---|---|
| Age | |
| Median Age (Range) | 60.14 (29–82) |
| ECOG-PS | |
| 0 | 82.8 |
| 1 | 10.3 |
| 2 | 6.9 |
| Sex | |
| Female | 48.3 |
| Male | 51.7 |
| Smoking | |
| Yes | 31.0 |
| No | 69.0 |
| Stage at first diagnosis | |
| Localized | 10.3 |
| Locoregional | 34.5 |
| Metastatic | 55.2 |
| Ki-67 | |
| >80 | 75.0 |
| 60–80 | 25.0 |
| Surgery | |
| Yes | 31.0 |
| No | 69.0 |
| Curative RT | |
| Yes | 39.3 |
| No | 58.6 |
| Concurrent CRT | |
| Yes | 25.0 |
| No | 75.0 |
| Liver-Directed Therapy | |
| Yes | 6.9 |
| No | 93.1 |
| First-line Chemotherapy | |
| Cisplatin + Etoposide | 51.7 |
| Carboplatin + Etoposide | 48.3 |
| Second-line Chemotherapy | |
| Cisplatin + Etoposide | 6.9 |
| Irinotecan | 17.2 |
| Paclitaxel | 3.4 |
| CAPOX | 3.4 |
| Third-line Therapy | |
| Chemotherapy | 34.5 |
| Immunotherapy | 10.3 |
| Therapy Line | N (%) |
|---|---|
| 1st Line | |
| Complete Response (CR) | 12 (42.9%) |
| Partial Response (PR) | 11 (39.3%) |
| Progressive Disease (PD) | 5 (17.9%) |
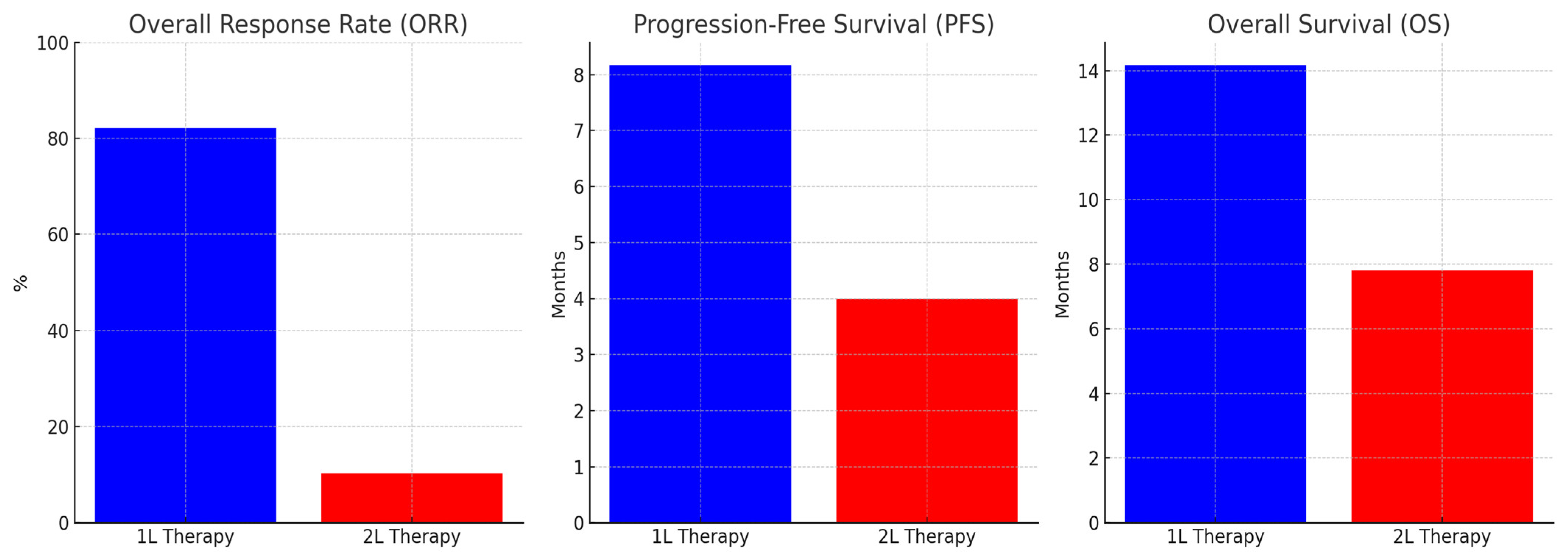
| Objective Response Rate (ORR) | %82.1 |
| Second Line | |
| Partial Response (PR) | 3 (10.3%) |
| Stable Disease (SD) | 1 (3.4%) |
| Progressive Disease (PD) | 7 (24.1%) |
| Third Line | |
| Partial Response (PR) | 0(0%) |
| Stable Disease (SD) | 2 (6.9%) |
| Progressive Disease (PD) | 3 (10.3%) |
| Immunotherapy | |
| Partial Response (PR) | 0 (0%) |
| Stable Disease (SD) | 1 (33.3%) |
| Progressive Disease (PD) | 2 (66.6%) |
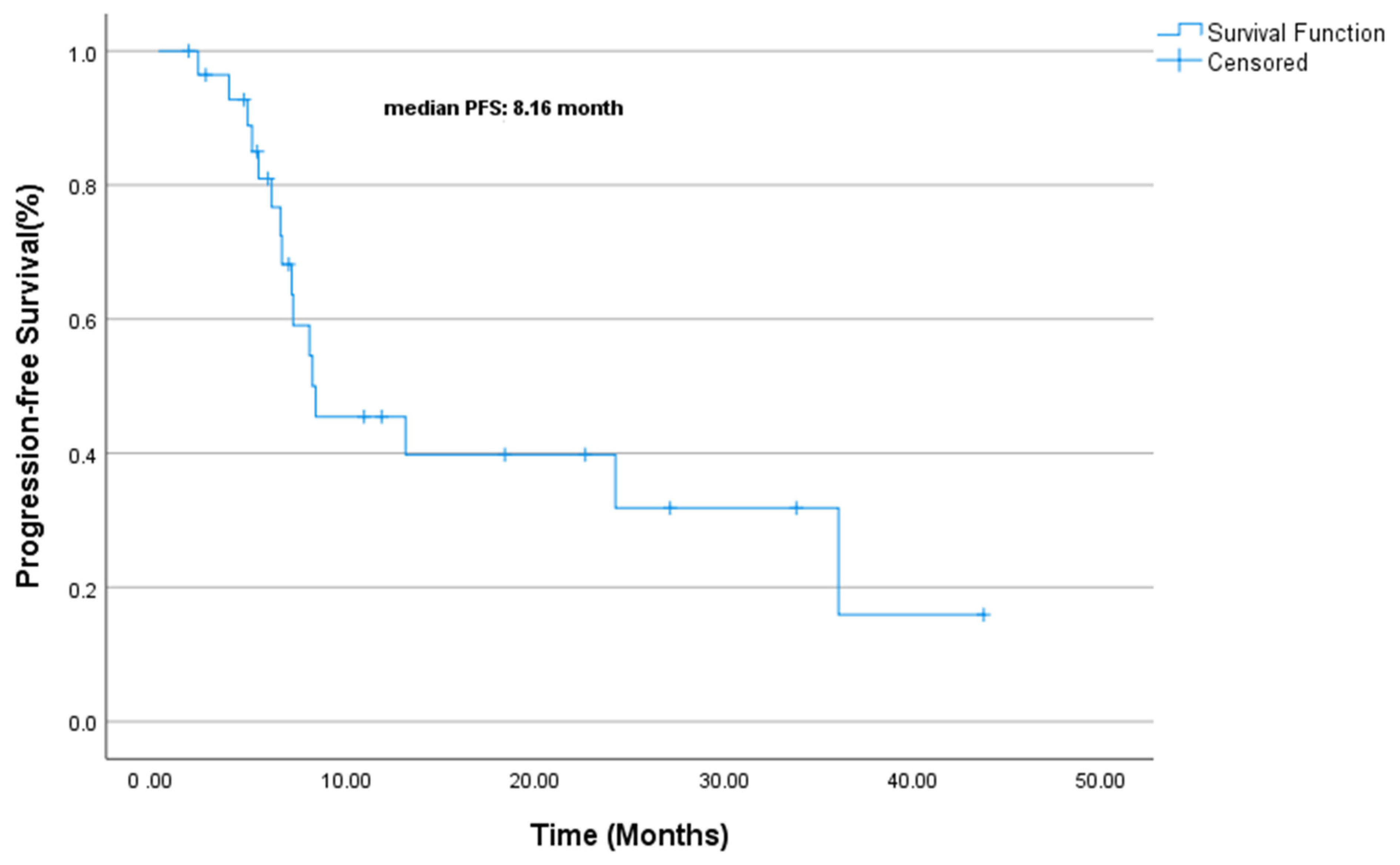
| Variable | PFS Duration (Median, Months) | Univariate p-Value | Multivariate HR (95% CI) | Multivariate p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | 0.747 | - | - | |
| Male | 8.3 mo. | |||
| Female | 8 mo. | |||
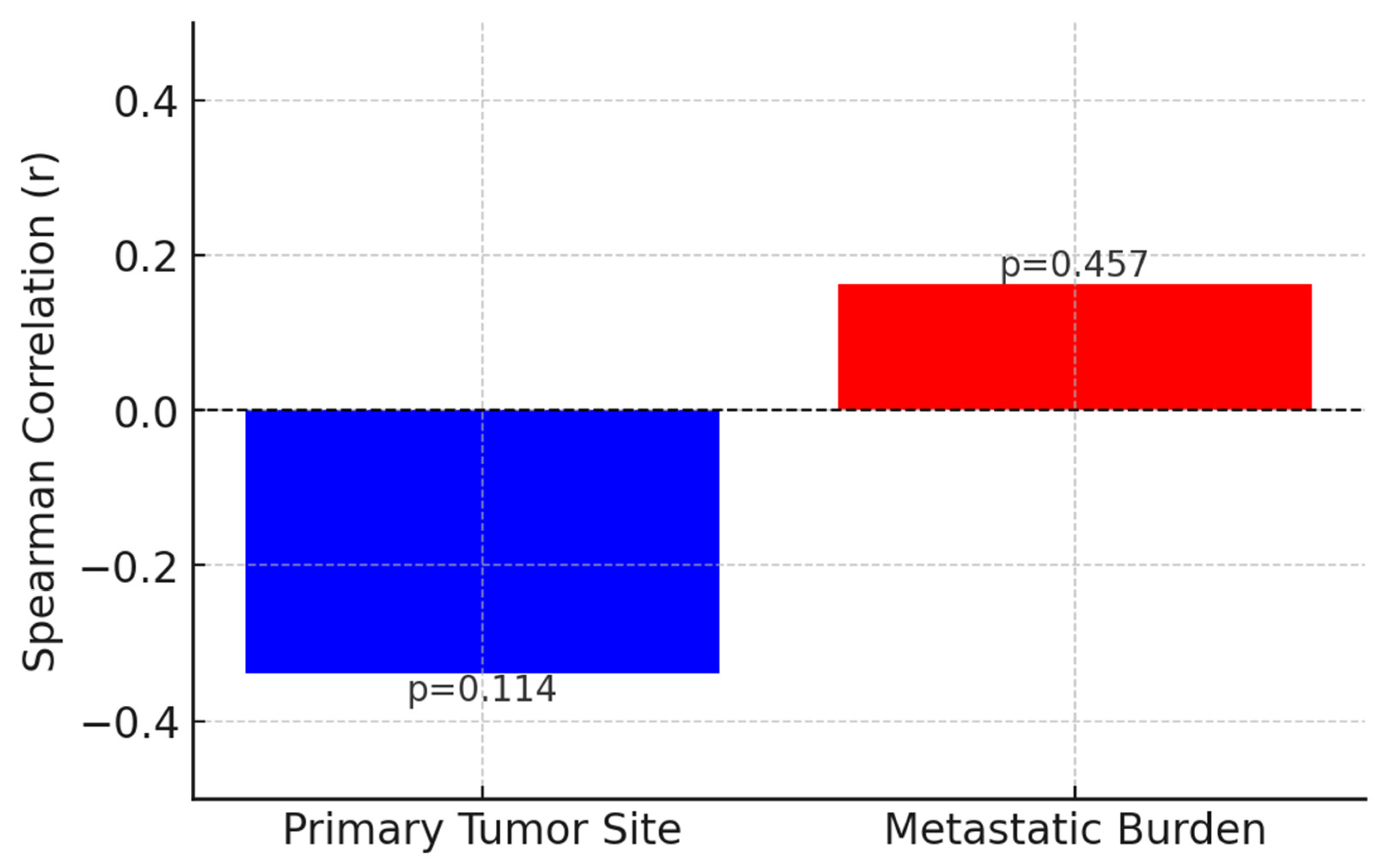
| Stage | 0.442 | - | - | |
| Local | 24.2 mo. | |||
| Locoregional | 8.1 mo. | |||
| Metastatic | 8 mo. | |||
| ECOG-PS | 0.005 | 1.452 (0.537–3.926) | 0.463 | |
| ECOG PS-0 | 8.1 mo. | |||
| ECOG PS-1 | 8.3 mo. | |||
| ECOG PS-2 | 2.1 mo. | |||
| Smoking Status | 0.539 | - | - | |
| Non-smoker | 8.1 mo. | |||
| Smoker | 7.1 mo. | |||
| Surgical History | 0.02 | 7.291 (1.212–43.862) | 0.03 | |
| No Surgery | 8 mo. | |||
| Surgery | NR | |||
| Concurrent CRT | 0.847 | - | - | |
| No Concurrent CRT | 8.3 mo. | |||
| Concurrent CRT | 8.1 mo. | |||
| First-line CT (Cis-Eto vs. Carbo-Eto) | 0.182 | - | - | |
| Cis-Eto: | 13.1 mo. | |||
| Carbo-Eto | 7.1 mo. | |||
| Ki-67 | 0.032 | NE | 0.0 | |
| Ki-67 < 80 | 36 mo. | |||
| Ki-67 ≥ 80:8 mo. | 8 mo. | |||
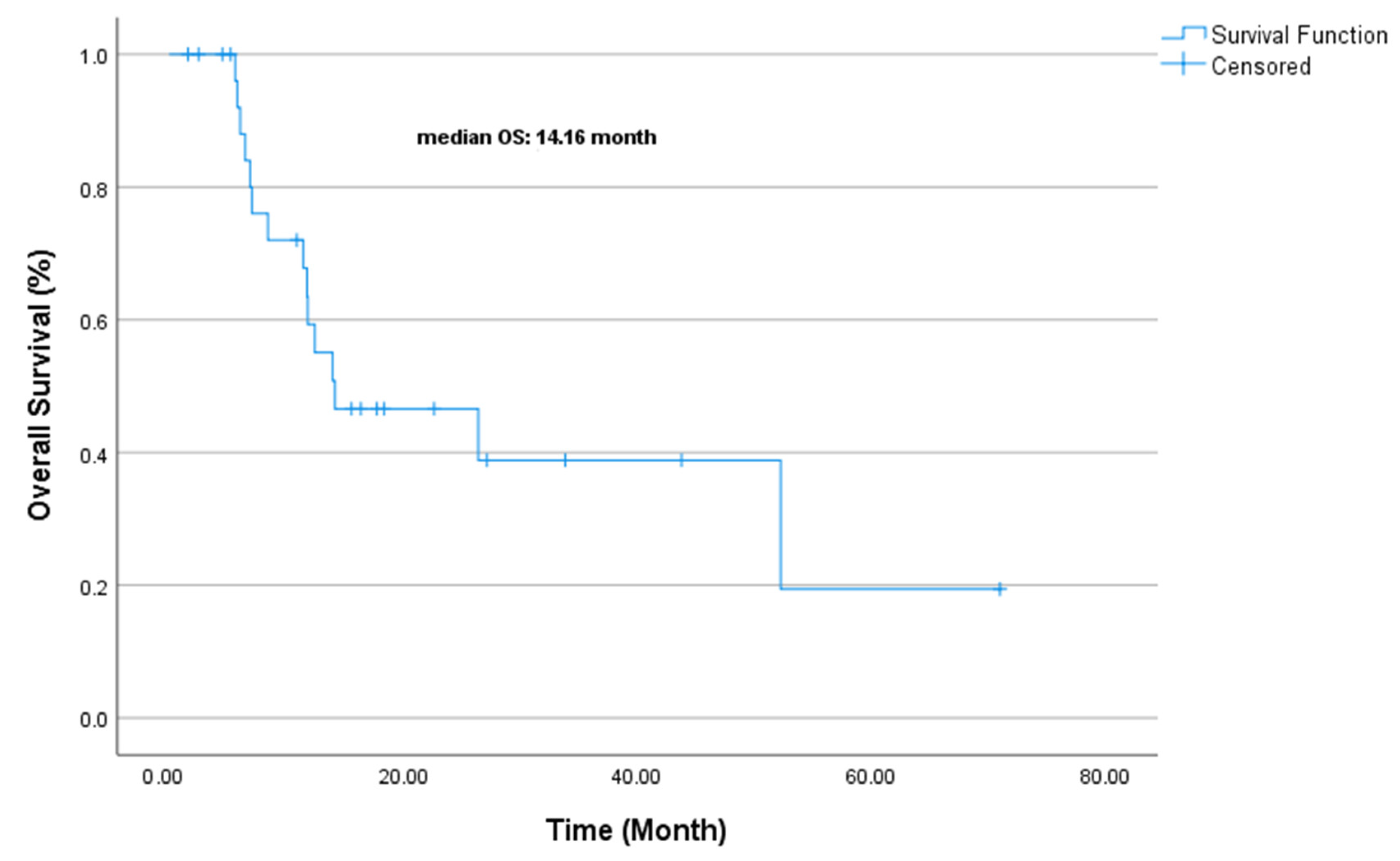
| Variable | OS Duration (Median, Months) | Univariate p-Value | Multivariate Exp(B) | Multivariate p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | 0.451 | - | - | |
| Male | 11.8 mo. | |||
| Female | 26.4 mo. | |||
| Stage | 0.520 | - | - | |
| Local | 52.2 mo. | |||
| Locoregional | 12.4 mo. | |||
| Metastatic | 11.8 mo. | |||
| ECOG-PS | 0.448 | 1.106 | 0.825 | |
| ECOG PS-0 | 13.9 mo. | |||
| ECOG PS-1 | NR | |||
| ECOG PS-2 | 6.5 mo. | |||
| Smoking Status | 0.418 | - | - | |
| Non-smoker | 26.4 mo. | |||
| Smoker | 11.7 mo. | |||
| Surgical History | 0.385 | 1.324 | 0.705 | |
| No Surgery | 11.8 mo. | |||
| Surgery | 26.4 mo. | |||
| Concurrent CRT | 0.581 | - | - | |
| No Concurrent CRT | 14.1 mo. | |||
| Concurrent CRT | 14.1 mo. | |||
| First-line CT (Cis-Eto vs. Carbo-Eto) | 0.180 | 0.508 | 0.331 | |
| Cis-Eto: | 26.4 mo. | |||
| Carbo-Eto | 11.7 mo. | |||
| Ki-67 | 0.959 | 1.405 | 0.645 | |
| Ki-67 < 80 | 26.4 mo. | |||
| Ki-67 ≥ 80:8 mo. | 11.8 mo. | |||
| Reference | No. of Patients | Cohort | Primary Site | Median PFS (months) | Median OS (months) | 2-Year Survival (%) | 3-Year Survival (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yao 2008 [5] | 2027 | All NEC (including Lung) | Mixed | - | 5 (4.5–5.5) | - | - |
| SEER Program 2013 [45] | 1389 | GEP-NEC | GEP | - | 5 (4.7–5.4) | 11 | 8 |
| Sorbye 2013 [46] | 252 | GEP-NEC (chemotherapy treated) | GEP | - | 11 (9.4–12.6) | 14 | 9.5 |
| Sorbye 2013 [46] | 53 | GEP-NEC (no treatment) | GEP | - | 1 (0.3–1.8) | - | - |
| Machida 2012 [47] | 258 | GEP-NEC (chemotherapy treated) | GEP | - | 11.5 | - | - |
| Bernick 2004 [48] | 38 | colorectal small-cell NEC | Colon and rectum | - | 10.5 (6.7–19) | 26 | 13 |
| Smith 2013 [49] | 126 | Colorectal NEC | Colon and rectum | - | 13 | 5 | - |
| Fujii 2001 [50] | 53 | Gallbladder, small-cell NEC (chemotherapy treated) | Gallbladder | - | 8 | 0 | - |
| Strosberg 2011 [51] | 32 | Pancreatic NEC | Pancreas | - | 21 | - | - |
| Garcia-Carbonero 2010 [52] | 85 | GEP-NEC | GEP | - | 1.7 | - | - |
| Celik et al. (2022) [40] | 47 | EP-NEC (chemotherapy treated) | Stomach (27.6%), Unknown Primary (23.4%), Pancreas (10.6%) | 5.83 (4.46–7.20) | 13.6 (9.01–18.18) | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Muğlu, H.; Sünger, E.; Mıldanoğlu, M.M.; Engin Delipoyraz, E.; Yücel, M.H.; Özçelik, H.; Hamdard, J.; Açıkgöz, Ö.; Ölmez, Ö.F.; Yıldız, Ö.; et al. Clinicopathological Characteristics of Extrapulmonary Neuroendocrine Carcinomas: Treatment Responses and Survival Outcomes: Single-Center Experience. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 2264. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14072264
Muğlu H, Sünger E, Mıldanoğlu MM, Engin Delipoyraz E, Yücel MH, Özçelik H, Hamdard J, Açıkgöz Ö, Ölmez ÖF, Yıldız Ö, et al. Clinicopathological Characteristics of Extrapulmonary Neuroendocrine Carcinomas: Treatment Responses and Survival Outcomes: Single-Center Experience. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(7):2264. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14072264
Chicago/Turabian StyleMuğlu, Harun, Erdem Sünger, Maral Martin Mıldanoğlu, Ebru Engin Delipoyraz, Mehmet Haluk Yücel, Hakan Özçelik, Jamshid Hamdard, Özgür Açıkgöz, Ömer Fatih Ölmez, Özcan Yıldız, and et al. 2025. "Clinicopathological Characteristics of Extrapulmonary Neuroendocrine Carcinomas: Treatment Responses and Survival Outcomes: Single-Center Experience" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 7: 2264. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14072264
APA StyleMuğlu, H., Sünger, E., Mıldanoğlu, M. M., Engin Delipoyraz, E., Yücel, M. H., Özçelik, H., Hamdard, J., Açıkgöz, Ö., Ölmez, Ö. F., Yıldız, Ö., & Bilici, A. (2025). Clinicopathological Characteristics of Extrapulmonary Neuroendocrine Carcinomas: Treatment Responses and Survival Outcomes: Single-Center Experience. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(7), 2264. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14072264





