A Clinical Probability-Based, Stepwise Algorithm for the Diagnosis of Giant Cell Arteritis: Study Protocol and Baseline Characteristics of the First 50 Patients Included in the Prospective Validation Study with Focus on Cranial Symptoms
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Study Objectives
- To determine the diagnostic accuracy of hrCS compared to temporal artery biopsy (TAB) in the diagnosis of cranial GCA.
- To determine the additional diagnostic benefit of sonographic examination of the facial and axillary arteries in the diagnosis of cranial and extracranial GCA.
- To determine the benefit of gender- and risk-adapted stratification of the cut-off values of hrCS.
- To determine the influence of clinical pre-test probability on the diagnostic accuracy of hrCS.
- To determine the impact of glucocorticoid treatment (dose and duration) on the diagnostic accuracy of the applied test procedures and the diagnostic algorithm.
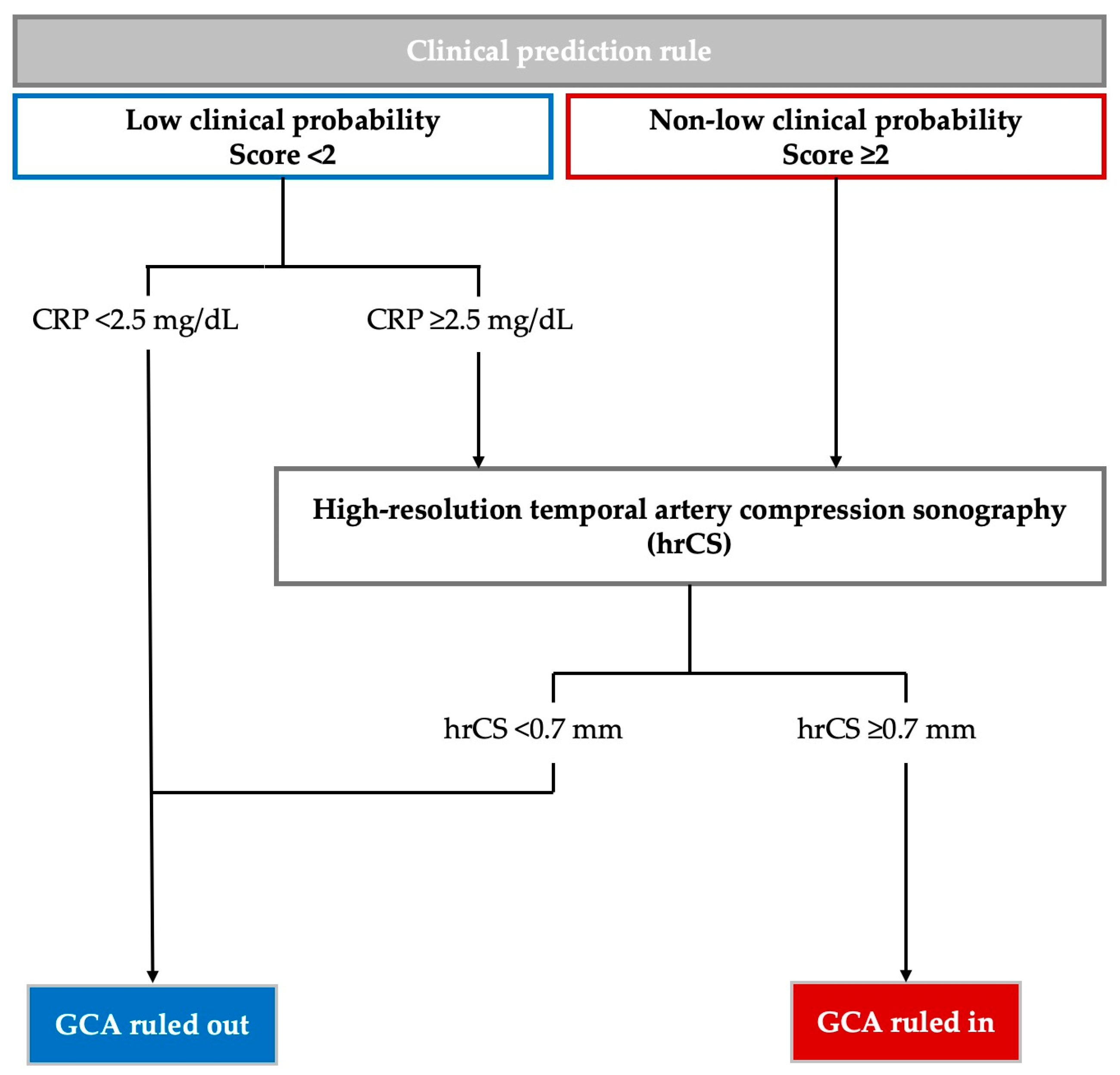
2.2. Clinical Prediction Rule and Diagnostic Algorithm
2.3. Study Population
2.4. Sonographic Protocol
2.5. Temporal Artery Biopsy and Histology
2.6. Final Reference Diagnosis
2.7. Data Handling
2.8. Statistical Considerations
2.9. Accompanying Study on Determining Reference Values of hrCS
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics of the First 50 Patients Included in PREDICT-GCA
3.2. Comparison of Patients with and Without Positive TAB
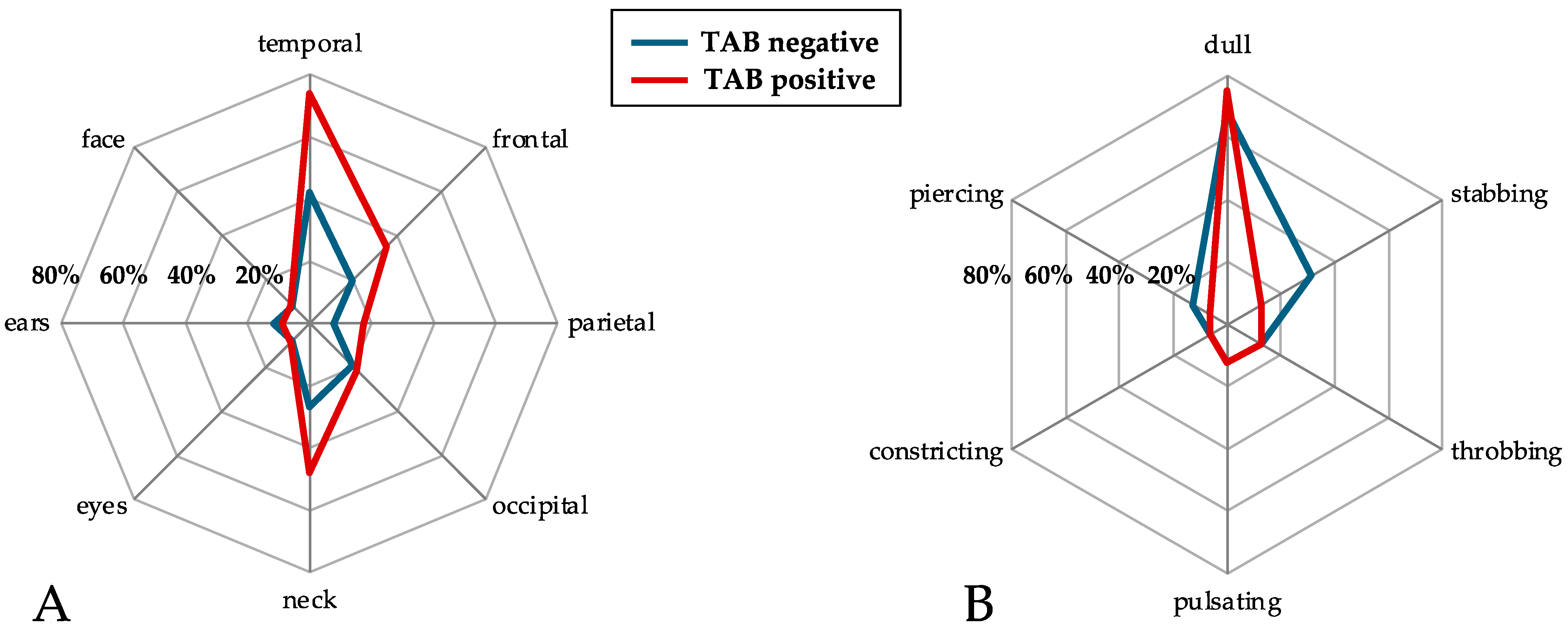
3.3. Headache Characteristics
3.4. Clinical Probability Assessment and Amendment of the Clinical Prediction Rule
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smith, S.C.M.; Al-Hashimi, M.R.; Jones, C.D.; Mukhtyar, C.B. Frequency of visual involvement in a 10-year interdisciplinary cohort of patients with giant cell arteritis. Clin. Med. 2023, 23, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Smit, E.; Palmer, A.J.; Hewitt, A.W. Projected worldwide disease burden from giant cell arteritis by 2050. J. Rheumatol. 2015, 42, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Geest, K.S.M.; Sandovici, M.; Brouwer, E.; Mackie, S.L. Diagnostic Accuracy of Symptoms, Physical Signs, and Laboratory Tests for Giant Cell Arteritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Intern. Med. 2020, 180, 1295–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, W.A.; Kraft, H.E.; Vorpahl, K.; Völker, L.; Gromnica-Ihle, E.J. Color duplex ultrasonography in the diagnosis of temporal arteritis. N. Engl. J. Med. 1997, 337, 1336–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dejaco, C.; Ramiro, S.; Bond, M.; Bosch, P.; Ponte, C.; Mackie, S.L.; Bley, T.A.; Blockmans, D.; Brolin, S.; Bolek, E.C.; et al. EULAR recommendations for the use of imaging in large vessel vasculitis in clinical practice: 2023 update. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2024, 83, 741–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebastian, A.; van der Geest, K.S.M.; Tomelleri, A.; Macchioni, P.; Klinowski, G.; Salvarani, C.; Prieto-Peña, D.; Conticini, E.; Khurshid, M.; Dagna, L.; et al. Development of a diagnostic prediction model for giant cell arteritis by sequential application of Southend Giant Cell Arteritis Probability Score and ultrasonography: A prospective multicentre study. Lancet Rheumatol. 2024, 6, e291–e299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebastian, A.; Tomelleri, A.; Kayani, A.; Prieto-Pena, D.; Ranasinghe, C.; Dasgupta, B. Probability-based algorithm using ultrasound and additional tests for suspected GCA in a fast-track clinic. RMD Open 2020, 6, e001297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laskou, F.; Coath, F.; Mackie, S.L.; Banerjee, S.; Aung, T.; Dasgupta, B. A probability score to aid the diagnosis of suspected giant cell arteritis. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2019, 37 (Suppl. S117), 104–108. [Google Scholar]
- Ing, E.B.; Miller, N.R.; Nguyen, A.; Su, W.; Bursztyn, L.; Poole, M.; Kansal, V.; Toren, A.; Albreki, D.; Mouhanna, J.G.; et al. Neural network and logistic regression diagnostic prediction models for giant cell arteritis: Development and validation. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2019, 13, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-López, J.J.; González-Moraleja, J.; Rebolleda, G.; Muñoz-Negrete, F.J. A calculator for temporal artery biopsy result prediction in giant cell arteritis suspects. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2014, 25, e98–e100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czihal, M.; Lottspeich, C.; Bernau, C.; Henke, T.; Prearo, I.; Mackert, M.; Priglinger, S.; Dechant, C.; Schulze-Koops, H.; Hoffmann, U. A Diagnostic Algorithm Based on a Simple Clinical Prediction Rule for the Diagnosis of Cranial Giant Cell Arteritis. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schäfer, V.S.; Juche, A.; Ramiro, S.; Krause, A.; Schmidt, W.A. Ultrasound cut-off values for intima-media thickness of temporal, facial and axillary arteries in giant cell arteritis. Rheumatology 2017, 56, 1479–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czihal, M.; Schröttle, A.; Baustel, K.; Lottspeich, C.; Dechant, C.; Treitl, K.M.; Treitl, M.; Schulze-Koops, H.; Hoffmann, U. B-mode sonography wall thickness assessment of the temporal and axillary arteries for the diagnosis of giant cell arteritis: A cohort study. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2017, 35 (Suppl. S103), 128–133. [Google Scholar]
- Czihal, M.; Köhler, A.; Lottspeich, C.; Prearo, I.; Hoffmann, U.; Schulze-Koops, H.; Priglinger, S.G.; Mackert, M.J.; Dechant, C. Temporal artery compression sonography for the diagnosis of giant cell arteritis in elderly patients with acute ocular arterial occlusions. Rheumatology 2020, 60, 2190–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prearo, I.; Dekorsy, F.J.; Brendel, M.; Lottspeich, C.; Dechant, C.; Schulze-Koops, H.; Hoffmann, U.; Czihal, M. Diagnostic yield of axillary artery ultrasound in addition to temporal artery ultrasound for the diagnosis of giant cell arteritis. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2022, 40, 819–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, V.; Fishbein, G.A.; Padera, R.; Seidman, M.A.; Castonguay, M.; Leduc, C.; Tan, C.D.; Rodriguez, E.R.; Maleszewski, J.J.; Miller, D.; et al. Consensus statement on the processing, interpretation and reporting of temporal artery biopsy for arteritis. Cardiovasc. Pathol. Off. J. Soc. Cardiovasc. Pathol. 2023, 67, 107574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schirmer, J.H.; Aries, P.M.; Balzer, K.; Berlit, P.; Bley, T.A.; Buttgereit, F.; Czihal, M.; Dechant, C.; Dejaco, C.; Garske, U.; et al. S2k guidelines: Management of large-vessel vasculitis. Z. Rheumatol. 2020, 79, 67–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czihal, M.; Köhler, A.; Prearo, I.; Hoffmann, U.; Schulze-Koops, H.; Dechant, C.; Priglinger, S.G.; Mackert, M.J.; Lottspeich, C. Hyperechogenic intimal lesions and wall thickness of the temporal and facial arteries in elderly patients with arterial occlusions of the eye. RMD Open 2021, 7, e001688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patil, P.; Williams, M.; Maw, W.W.; Achilleos, K.; Elsideeg, S.; Dejaco, C.; Borg, F.; Gupta, S.; Dasgupta, B. Fast track pathway reduces sight loss in giant cell arteritis: Results of a longitudinal observational cohort study. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2015, 33, 103–106. [Google Scholar]
- Monti, S.; Bartoletti, A.; Bellis, E.; Delvino, P.; Montecucco, C. Fast-Track Ultrasound Clinic for the Diagnosis of Giant Cell Arteritis Changes the Prognosis of the Disease but Not the Risk of Future Relapse. Front. Med. 2020, 7, 589794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamantopoulos, A.P.; Haugeberg, G.; Lindland, A.; Myklebust, G. The fast-track ultrasound clinic for early diagnosis of giant cell arteritis significantly reduces permanent visual impairment: Towards a more effective strategy to improve clinical outcome in giant cell arteritis? Rheumatology 2016, 55, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackie, S.L.; Dejaco, C.; Appenzeller, S.; Camellino, D.; Duftner, C.; Gonzalez-Chiappe, S.; Mahr, A.; Mukhtyar, C.; Reynolds, G.; de Souza, A.W.S.; et al. British Society for Rheumatology guideline on diagnosis and treatment of giant cell arteritis. Rheumatology 2020, 59, e1–e23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Gay, M.A.; Garcia-Porrua, C.; Llorca, J.; Gonzalez-Louzao, C.; Rodriguez-Ledo, P. Biopsy-negative giant cell arteritis: Clinical spectrum and predictive factors for positive temporal artery biopsy. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2001, 30, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, E.; Li, X.; Gruener, A.M.; Chang, J.R.; Eberhart, C.G.; Henderson, A.D.; Carey, A.R. Presenting Features of Giant Cell Arteritis with Active Versus Healed Arteritis on Biopsy. Neuroophthalmology 2023, 47, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincenten, S.C.; Mulleners, W.M. The quest for a headache pattern in giant cell arteritis: A cohort study. Cephalalgia Rep. 2021, 4, 25158163211024134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sargi, C.; Ducharme-Benard, S.; Benard, V.; Meunier, R.S.; Ross, C.; Makhzoum, J.P. Assessment and comparison of probability scores to predict giant cell arteritis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2024, 43, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moudrous, W.; Visser, L.H.; Yilmaz, T.; Wieringa, M.H.; Alleman, T.; Rovers, J.; Houben, M.P.W.A.; Janssen, P.M.; Janssen, J.J.B.; Rensma, P.L.; et al. A new prediction model for giant cell arteritis in patients with new onset headache and/or visual loss. Ann. Med. 2022, 54, 2770–2776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, S.; Cappa, K.G. The headache of temporal arteritis. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 1987, 35, 163–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toren, A.; Weis, E.; Patel, V.; Monteith, B.; Gilberg, S.; Jordan, D. Clinical predictors of positive temporal artery biopsy. Can. J. Ophthalmol. 2016, 51, 476–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimohama, S.; Imai, N.; Tsubata, T.; Shinohara, K.; Moriya, A.; Yagi, N.; Konishi, T.; Serizawa, M.; Tashiro, K. Headache-Related Characteristics of Biopsy-Confirmed Giant Cell Arteritis and the Relationship of Transmural Inflammation With Artery Tenderness and Chordal Thickening. Cureus 2024, 16, e56843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunder, G.G.; Bloch, D.A.; Michel, B.A.; Stevens, M.B.; Arend, W.P.; Calabrese, L.H.; Edworthy, S.M.; Fauci, A.S.; Leavitt, R.Y.; Lie, J.T.; et al. The American College of Rheumatology 1990 criteria for the classification of giant cell arteritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1990, 33, 1122–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponte, C.; Grayson, P.C.; Robson, J.C.; Suppiah, R.; Gribbons, K.B.; Judge, A.; Craven, A.; Khalid, S.; Hutchings, A.; Watts, R.A.; et al. 2022 American College of Rheumatology/EULAR classification criteria for giant cell arteritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2022, 81, 1647–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inayat, H.; Youn, S.; Bursztyn, L. Utility of online GCA risk models in predicting the result of temporal artery biopsy within a clinical setting: Study of diagnostic and screening tests. Can. J. Ophthalmol. J. Can. d’Ophtalmol. 2024, 59, e483–e488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecler, A.; Hage, R.; Charbonneau, F.; Vignal, C.; Sené, T.; Picard, H.; Leturcq, T.; Zuber, K.; Belangé, G.; Affortit, A.; et al. Validation of a multimodal algorithm for diagnosing giant cell arteritis with imaging. Diagn. Interv. Imaging 2022, 103, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Gal, G.; Righini, M.; Wells, P.S. Scoring Systems for Diagnosis of Acute Venous Thromboembolism. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2017, 43, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kermani, T.A.; Schmidt, J.; Crowson, C.S.; Ytterberg, S.R.; Hunder, G.G.; Matteson, E.L.; Warrington, K.J. Utility of erythrocyte sedimentation rate and C-reactive protein for the diagnosis of giant cell arteritis. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2012, 41, 866–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Förster, S.; Tato, F.; Weiss, M.; Czihal, M.; Rominger, A.; Bartenstein, P.; Hacker, M.; Hoffmann, U. Patterns of extracranial involvement in newly diagnosed giant cell arteritis assessed by physical examination, colour coded duplex sonography and FDG-PET. VASA Z. Fur Gefasskrankh. 2011, 40, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czihal, M.; Tatò, F.; Rademacher, A.; Kuhlencordt, P.; Schulze-Koops, H.; Hoffmann, U. Involvement of the femoropopliteal arteries in giant cell arteritis: Clinical and color duplex sonography. J. Rheumatol. 2012, 39, 314–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czihal, M.; Piller, A.; Schroettle, A.; Kuhlencordt, P.; Bernau, C.; Schulze-Koops, H.; Hoffmann, U. Impact of cranial and axillary/subclavian artery involvement by color duplex sonography on response to treatment in giant cell arteritis. J. Vasc. Surg. 2015, 61, 1285–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czihal, M.; Piller, A.; Schroettle, A.; Kuhlencordt, P.J.; Schulze-Koops, H.; Hoffmann, U. Outcome of giant cell arteritis of the arm arteries managed with medical treatment alone: Cross-sectional follow-up study. Rheumatology 2013, 52, 282–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Inclusion Criteria | Exclusion Criteria |
|---|---|
| Age > 50 years | Age < 50 years |
| Substantiated clinical suspicion of GCA | Pre-existing diagnosis of GCA |
| Signed informed consent | Glucocorticoid treatment with a daily dose of at least 20 mg prednisolone for >7 days |
| Previous glucocorticoid treatment with a daily dose of >20 mg for at least 30 days within the preceding 3 months | |
| Previous therapy with the interleukin-6 receptor antagonist tocilizumab |
| Variables | Overall Cohort, n = 50 |
|---|---|
| Female sex | 27 (54) |
| Age ≥ 70 years | 32 (64) |
| New onset headache | 37 (74) |
| Jaw claudication | 26 (52) |
| Scalp tenderness | 19 (38) |
| Temporal artery tenderness | 25 (50) |
| Diplopia | 10 (20) |
| Amaurosis fugax | 10 (20) |
| Permanent visual impairment | 26 (52) |
| Bilateral visual impairment | 8 (16) |
| Anterior ischemic optic neuropathy | 18 (36) |
| Polymyalgia rheumatica | 5 (10) |
| Constitutional symptoms | 21 (42) |
| Extremity claudication | 3 (6) |
| Manifest cardiovascular disease 1 | 15 (30) |
| Arterial hypertension | 26 (52) |
| Diabetes mellitus | 11 (22) |
| Active or former smoking | 24 (48) |
| Dyslipidemia | 23 (46) |
| Known rheumatic disease 2 | 9 (18) |
| History of cancer | 4 (8) |
| Temporal artery swelling | 18 (36) |
| Temporal artery tenderness on palpation | 24 (48) |
| Temporal artery induration | 23 (46) |
| Pre-existing low-dose glucocorticoid treatment | 4 (8) |
| Pre-existing treatment with glucocorticoid sparing agents | 3 (6) |
| Glucocorticoid treatment started for suspected GCA | 34 (68) |
| Daily (methyl-)prednisolone dose (mg) | 237 ± 361 |
| Time interval between start of glucocorticoid treatment and TAB (days) | 3.5 ± 3.3 |
| C-reactive protein (mg/dL) | 4.3 ± 5.7 |
| C-reactive protein elevated | |
| >0.5 mg/dL | 37 (74) |
| >2.5 mg/dL | 21 (42) |
| Variable | Odds Ratio (95% CI) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| Cranial symptoms | ||
| Bilateral headache | 3.5 (1.1–11.4) | 0.05 |
| Headache in >3 regions | 2.0 (0.5–7.1) | 0.35 |
| Jaw claudication | 8.1 (2.2–29.6) | <0.01 |
| Scalp tenderness | 4.1 (1.2–14.2) | 0.04 |
| Temporal artery tenderness | 4.3 (1.3–14.3) | 0.04 |
| Physical examination findings | ||
| Temporal artery tenderness (on palpation) | 2.1 (0.66–6.5) | 0.26 |
| Temporal artery induration | 4.2 (1.3–14.0) | 0.02 |
| Temporal artery swelling | 8.5 (2.2–33.2) | <0.01 |
| Variable | Description | Score |
|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | <70 years | 0 |
| ≥70 years | 1 | |
| New onset headache | No | 0 |
| Yes | 1 | |
| Symptoms of cranial ischemia (jaw claudication, scalp tenderness) and/or temporal artery swelling 1 | No | 0 |
| Yes | 2 | |
| Permanent visual impairment due to anterior ischemic optic neuropathy | No | 0 |
| Unilateral | 1 | |
| Bilateral | 2 | |
| Score (range 0–6) | Low clinical probability | Score < 2 |
| Non-low clinical probability | Score ≥ 2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Thielmann, L.-C.; Findik-Kilinc, M.; Füeßl, L.; Lottspeich, C.; Löw, A.; Henke, T.; Hasmann, S.; Prearo, I.; von Bismarck, A.; Reik, L.U.; et al. A Clinical Probability-Based, Stepwise Algorithm for the Diagnosis of Giant Cell Arteritis: Study Protocol and Baseline Characteristics of the First 50 Patients Included in the Prospective Validation Study with Focus on Cranial Symptoms. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 2254. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14072254
Thielmann L-C, Findik-Kilinc M, Füeßl L, Lottspeich C, Löw A, Henke T, Hasmann S, Prearo I, von Bismarck A, Reik LU, et al. A Clinical Probability-Based, Stepwise Algorithm for the Diagnosis of Giant Cell Arteritis: Study Protocol and Baseline Characteristics of the First 50 Patients Included in the Prospective Validation Study with Focus on Cranial Symptoms. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(7):2254. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14072254
Chicago/Turabian StyleThielmann, Lukas-Caspar, Melike Findik-Kilinc, Louise Füeßl, Christian Lottspeich, Anja Löw, Teresa Henke, Sandra Hasmann, Ilaria Prearo, Amanda von Bismarck, Lilly Undine Reik, and et al. 2025. "A Clinical Probability-Based, Stepwise Algorithm for the Diagnosis of Giant Cell Arteritis: Study Protocol and Baseline Characteristics of the First 50 Patients Included in the Prospective Validation Study with Focus on Cranial Symptoms" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 7: 2254. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14072254
APA StyleThielmann, L.-C., Findik-Kilinc, M., Füeßl, L., Lottspeich, C., Löw, A., Henke, T., Hasmann, S., Prearo, I., von Bismarck, A., Reik, L. U., Wirthmiller, T., Nützel, A., Mackert, M. J., Priglinger, S., Schulz, H., Mayr, D., Haas-Lützenberger, E., Gebhardt, C., Schulze-Koops, H., & Czihal, M. (2025). A Clinical Probability-Based, Stepwise Algorithm for the Diagnosis of Giant Cell Arteritis: Study Protocol and Baseline Characteristics of the First 50 Patients Included in the Prospective Validation Study with Focus on Cranial Symptoms. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(7), 2254. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14072254






