The Effect of Oral Semaglutide on Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Eligibility Criteria
2.3. Data Extraction
2.4. Quality Assessment
3. Results
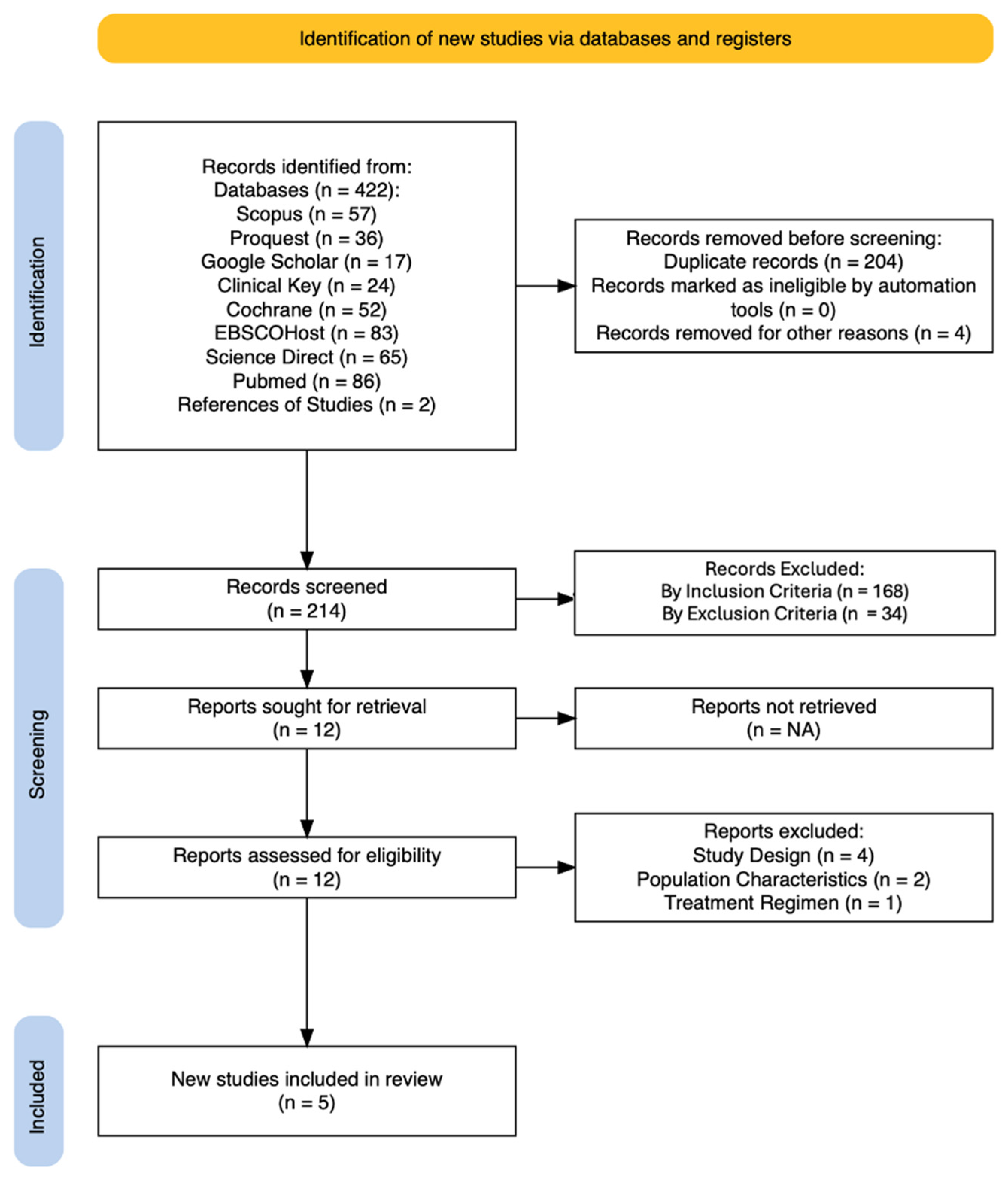
3.1. Search Results
3.2. Study Characteristics
3.3. Quality of Studies
4. Discussion
4.1. Oral Semaglutide and Blood Pressure
4.2. Oral Semaglutide and Lipid Profile
4.3. Limitations of This Review
4.4. Recommendations for Future Studies
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ABCA1 | ATP-binding cassette |
| ASCVD | Atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| CI | Confidence interval |
| CKD | Chronic kidney disease |
| CVD | Cardiovascular disease |
| DBP | Diastolic blood pressure |
| eNOS | Endothelial nitric oxide synthase |
| GLP-1 | Glucagon-like peptide-1 |
| GLP-RA | Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist |
| HDL | High-density lipoprotein |
| LDL | Low-density lipoprotein |
| NOS | Newcastle-Ottawa Scale |
| PRISMA | Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses |
| SBP | Systolic blood pressure |
| SGLT2 | Sodium glucose cotransporter 2 |
| T2DM | Type 2 diabetes mellitus |
| TC | Total cholesterol |
| TG | Triglyceride |
| VLDL | Very-low-density lipoprotein |
References
- Fan, W. Epidemiology in Diabetes Mellitus and Cardiovascular Disease. Cardiovasc. Endocrinol. 2017, 6, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zelniker, T.A.; Wiviott, S.D.; Raz, I.; Im, K.; Goodrich, E.L.; Furtado, R.H.M.; Bonaca, M.P.; Mosenzon, O.; Kato, E.T.; Cahn, A.; et al. Comparison of the Effects of Glucagon-Like Peptide Receptor Agonists and Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors for Prevention of Major Adverse Cardiovascular and Renal Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Circulation 2019, 139, 2022–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baggio, L.L.; Drucker, D.J. Biology of Incretins: GLP-1 and GIP. Gastroenterology 2007, 132, 2131–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marso, S.P.; Bain, S.C.; Consoli, A.; Eliaschewitz, F.G.; Jódar, E.; Leiter, L.A.; Lingvay, I.; Rosenstock, J.; Seufert, J.; Warren, M.L.; et al. Semaglutide and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1834–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holman, R.R.; Bethel, M.A.; Mentz, R.J.; Thompson, V.P.; Lokhnygina, Y.; Buse, J.B.; Chan, J.C.; Choi, J.; Gustavson, S.M.; Iqbal, N.; et al. Effects of Once-Weekly Exenatide on Cardiovascular Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1228–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marso, S.P.; Daniels, G.H.; Brown-Frandsen, K.; Kristensen, P.; Mann, J.F.E.; Nauck, M.A.; Nissen, S.E.; Pocock, S.; Poulter, N.R.; Ravn, L.S.; et al. Liraglutide and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, A.F.; Green, J.B.; Janmohamed, S.; D’Agostino, R.B.; Granger, C.B.; Jones, N.P.; Leiter, L.A.; Rosenberg, A.E.; Sigmon, K.N.; Somerville, M.C.; et al. Albiglutide and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Cardiovascular Disease (Harmony Outcomes): A Double-Blind, Randomised Placebo-Controlled Trial. Lancet 2018, 392, 1519–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerstein, H.C.; Colhoun, H.M.; Dagenais, G.R.; Diaz, R.; Lakshmanan, M.; Pais, P.; Probstfield, J.; Riesmeyer, J.S.; Riddle, M.C.; Rydén, L.; et al. Dulaglutide and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes (REWIND): A Double-Blind, Randomised Placebo-Controlled Trial. Lancet 2019, 394, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lingvay, I.; Deanfield, J.; Kahn, S.E.; Weeke, P.E.; Toplak, H.; Scirica, B.M.; Rydéen, L.; Rathor, N.; Plutzky, J.; Morales, C.; et al. Semaglutide and Cardiovascular Outcomes by Baseline HbA1c and Change in HbA1c in People With Overweight or Obesity but Without Diabetes in SELECT. Diabetes Care 2024, 47, 1360–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikirica, M.; Martin, A.; Wood, R.; Leith, A.; Piercy, J.; Higgins, V. Reasons for Discontinuation of GLP1 Receptor Agonists: Data from a Real-World Cross-Sectional Survey of Physicians and Their Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2017, 10, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy Chowdhury, S.; Sadouki, F.; Collins, E.; Keen, F.; Bhagi, R.; Lim, Y.S.J.; Cozma, S.L.; Bain, S.C. Real-World Use of Oral and Subcutaneous Semaglutide in Routine Clinical Practice in the UK: A Single-Centre, Retrospective Observational Study. Diabetes Ther. 2024, 15, 869–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isaacs, D.M.; Kruger, D.F.; Spollett, G.R. Optimizing Therapeutic Outcomes With Oral Semaglutide: A Patient-Centered Approach. Diabetes Spectrum. 2021, 34, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallwitz, B.; Giorgino, F. Clinical Perspectives on the Use of Subcutaneous and Oral Formulations of Semaglutide. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 645507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horii, T.; Masudo, C.; Takayanagi, Y.; Oikawa, Y.; Shimada, A.; Mihara, K. Adherence and Treatment Discontinuation of Oral Semaglutide and Once-weekly Semaglutide Injection at 12 Month Follow-up: Japanese Real-world Data. J. Diabetes Investig. 2024, 15, 1578–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.-D.; Yang, Y.-Y. Clinical Pharmacokinetics of Semaglutide: A Systematic Review. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2024, 18, 2555–2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husain, M.; Birkenfeld, A.L.; Donsmark, M.; Dungan, K.; Eliaschewitz, F.G.; Franco, D.R.; Jeppesen, O.K.; Lingvay, I.; Mosenzon, O.; Pedersen, S.D.; et al. Oral Semaglutide and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 841–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantanetti, P.; Ronconi, V.; Sguanci, M.; Palomares, S.M.; Mancin, S.; Tartaglia, F.C.; Cangelosi, G.; Petrelli, F. Oral Semaglutide in Type 2 Diabetes: Clinical–Metabolic Outcomes and Quality of Life in Real-World Practice. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 4752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aroda, V.R.; Aberle, J.; Bardtrum, L.; Christiansen, E.; Knop, F.K.; Gabery, S.; Pedersen, S.D.; Buse, J.B. Efficacy and Safety of Once-Daily Oral Semaglutide 25 Mg and 50 Mg Compared with 14 Mg in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes (PIONEER PLUS): A Multicentre, Randomised, Phase 3b Trial. Lancet 2023, 402, 693–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpe, S.; Lisco, G.; Fanelli, M.; Racaniello, D.; Colaianni, V.; Lavarra, V.; Triggiani, D.; Crudele, L.; Triggiani, V.; Sabbà, C.; et al. Oral Semaglutide Improves Body Composition and Preserves Lean Mass in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A 26-Week Prospective Real-Life Study. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1240263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunati, M.E.; Cimino, V.; Bernasconi, D.; Gandolfi, A.; Morpurgo, P.S.; Tinari, C.; Lazzaroni, E.; Baruffaldi, L.; Muratori, M.; Montefusco, L.; et al. Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Pharmacological Remission with Dapagliflozin plus Oral Semaglutide. Pharmacol. Res. 2024, 199, 107040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandzari, D.E.; Mahfoud, F.; Weber, M.A.; Townsend, R.; Parati, G.; Fisher, N.D.L.; Lobo, M.D.; Bloch, M.; Böhm, M.; Sharp, A.S.P.; et al. Clinical Trial Design Principles and Outcomes Definitions for Device-Based Therapies for Hypertension: A Consensus Document From the Hypertension Academic Research Consortium. Circulation 2022, 145, 847–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liakos, C.I.; Papadopoulos, D.P.; Sanidas, E.A.; Markou, M.I.; Hatziagelaki, E.E.; Grassos, C.A.; Velliou, M.L.; Barbetseas, J.D. Blood Pressure-Lowering Effect of Newer Antihyperglycemic Agents (SGLT-2 Inhibitors, GLP-1 Receptor Agonists, and DPP-4 Inhibitors). Am. J. Cardiovasc. Drugs 2021, 21, 123–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro-Silva, J.C.; Tavares, C.A.M.; Girardi, A.C.C. The Blood Pressure Lowering Effects of Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists: A Mini-Review of the Potential Mechanisms. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2023, 69, 102355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowlands, J.; Heng, J.; Newsholme, P.; Carlessi, R. Pleiotropic Effects of GLP-1 and Analogs on Cell Signaling, Metabolism, and Function. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraiva, J.F.K.; Franco, D. Oral GLP-1 Analogue: Perspectives and Impact on Atherosclerosis in Type 2 Diabetic Patients. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2021, 20, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, R.; Nguyen, M.T.; Allahwala, M.A.; Psaltis, J.P.; Marathe, C.S.; Marathe, J.A.; Psaltis, P.J. Cardiovascular Protective Properties of GLP-1 Receptor Agonists: More than Just Diabetic and Weight Loss Drugs. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 4674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meier, J.J.; Gethmann, A.; Götze, O.; Gallwitz, B.; Holst, J.J.; Schmidt, W.E.; Nauck, M.A. Glucagon-like Peptide 1 Abolishes the Postprandial Rise in Triglyceride Concentrations and Lowers Levels of Non-Esterified Fatty Acids in Humans. Diabetologia 2006, 49, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Zong, Y.; Ma, Y.; Tian, Y.; Pang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Gao, J. Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor: Mechanisms and Advances in Therapy. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsuyama, H.; Hakoshima, M.; Kaji, E.; Mino, M.; Kakazu, E.; Iida, S.; Adachi, H.; Kanto, T.; Yanai, H. Effects of Once-Weekly Semaglutide on Cardiovascular Risk Factors and Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease in Japanese Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Retrospective Longitudinal Study Based on Real-World Data. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hjerpsted, J.B.; Flint, A.; Brooks, A.; Axelsen, M.B.; Kvist, T.; Blundell, J. Semaglutide Improves Postprandial Glucose and Lipid Metabolism, and Delays First-hour Gastric Emptying in Subjects with Obesity. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2018, 20, 610–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilding, J.P.H.; Batterham, R.L.; Calanna, S.; Davies, M.; Van Gaal, L.F.; Lingvay, I.; McGowan, B.M.; Rosenstock, J.; Tran, M.T.D.; Wadden, T.A.; et al. Once-Weekly Semaglutide in Adults with Overweight or Obesity. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 989–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sattar, N.; Lee, M.M.Y.; Kristensen, S.L.; Branch, K.R.H.; Del Prato, S.; Khurmi, N.S.; Lam, C.S.P.; Lopes, R.D.; McMurray, J.J.V.; Pratley, R.E.; et al. Cardiovascular, Mortality, and Kidney Outcomes with GLP-1 Receptor Agonists in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomised Trials. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2021, 9, 653–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Study | Participants | Control | Therapy | Blood Pressure | Lipid Profile | Study Period | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SBP | DBP | Total C | HDL-C | LDL-C | TG | |||||
| Husain M. et al. (2019) [16] Double-blind, randomized controlled trial | Age ≥ 50 years old + established CVD/CKD, or age ≥ 60 years old + had CV risk factors only 3172 patients (1347 with oral semaglutide and 1435 with placebo) | Placebo + standard of care | Once-daily oral semaglutide 14 mg † + standard of care | Treatment difference (95% CI): −2.6 (−3.7; −1.5) | Treatment difference (95% CI): 0.7 (0.0; 1.3) | Statistically significant reduction at 50 weeks (exact value not reported) | No statistically significant change at 50 weeks | Statistically significant reduction at 50 weeks (exact value not reported) | Statistically significant reduction at 50 weeks (exact value not reported) | 83 weeks |
| Aroda VR. et al. (2023) [18] Double-blind randomized controlled trial | Age ≥ 18 years with T2DM, HbA1c 8.0–10.5%, BMI ≥ 25.0 kg/m2, on stable daily doses of 1 to 3 of the following drugs: metformin, SU, SGLT2i, or DPP-4i At trial completion, the number of participants was 507 for 14 mg ‡ | No control group Results are compared with baseline values as a part of treatment intensification | Once-daily oral semaglutide 14 mg † | Change from baseline: −4.2 mmHg (p = N.A.) | Change from baseline: −2.4 mmHg (p = N.A.) | Ratio to baseline: 0.99 (p = N.A.) | Ratio to baseline: 1.06 (p = N.A.) | Ratio to baseline: 1.02 (p = N.A.) | Ratio to baseline: 0.82 (p = N.A.) | 68 weeks |
| Volpe S. et al. (2023) [19] Prospective, open-label study | Age ≥ 18 years old, T2DM 32 participants | No control group The results are compared with baseline values (on top of metformin) | Once-daily oral semaglutide 7 mg (starting 3 mg daily for the first 4 weeks, then escalating to 7 mg daily afterwards) | 128.7 ± 2.3 to 121.9 ± 2.6 (p < 0.05). | 74.9 ± 1.7 to 75.4 ± 1.7 (p = N.S.). | 154.4 ± 4.8 to 139.2 ± 3.6 (p < 0.001) | 55.6 ± 2.5 to 51.6 ± 2.2 (p < 0.05) | 75.7 ± 4.2 to 65.7 ± 2.7 (p < 0.05) | 122.6 ± 12 to 111.6 ± 9.0 (p = N.S.) | 26 weeks |
| Lunati ME. et al. (2024) [20] Observational, prospective study | Age > 18 years old; T2DM; dapagliflozin or dapagliflozin + oral semaglutide. The final analysis includes 959 participants: 415 dapagliflozin and 544 dapagliflozin + semaglutide | Dapagliflozin + standard therapy (rapid-acting insulin, basal insulin, or SU/glinides) | Dapagliflozin + oral semaglutide (mean dose 12.76 mg/day) + standard therapy | * Treatment difference: −5.40 ± 0.20 (p < 0.0001) | * Treatment difference: −4.30 ± 0.22 (p < 0.0001) | * Treatment difference: −8.8 ± 0.5 (p < 0.0001) | * Treatment difference: +0.90 ± 0.12 (p < 0.0001) | * Treatment difference: −7.60 ± 0.49 p < 0.0001) | * Treatment difference: +18.20 ± 0.82 (p < 0.0001) | 24 weeks (6 months) |
| Pantanetti P. et al. (2024) [17] Observational prospective study | Age ≥ 18 years old with T2DM The initial 100 participants and the final analysis includes 61 participants | No control group | Once-daily oral semaglutide 14 mg † | −12.74 mmHg; SD = 16.53; p < 0.05 | −6.39 mmHg; SD = 12.04; p < 0.05 | −22.19 mg/dL; SD = 46.26; p < 0.05 | 0.77 mg/dL; SD = 6.14; p = 0.31 | −18.00 mg/dL; SD = 34.51; p < 0.05 | −40.13 mg/dL; SD = 8.01; p < 0.05 | 24 weeks (6 months) |
| No. | Study | Selection (Max *) | Comparability (Max **) | Outcome (Max *) | Score | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Representativeness of Exposed Cohort | Selection of Exposed Cohort | Ascertainment of Exposure | No Outcome of Interest at Start | Comparability of Cohorts Based on Design or Analysis | Assessment of Outcome | Was Followed Up Long Enough for Outcomes to Occur | Adequacy of Follow-Up of Cohorts | |||
| 1 | Volpe S. et al., 2023 [19] | - | * | * | * | ** | * | * | - | 7 |
| 2 | Pantanetti P. et al., 2024 [17] | - | * | * | * | ** | * | * | * | 8 |
| 3 | Lunati M.E. et al., 2024 [20] | * | N.A. | * | - | * | * | * | * | 6 |
| No. | Study | Randomization | Blinding | Account of All Patients’ | Score | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Randomization Mentioned | Appropriate Method of Randomization | Blinding Mentioned | Appropriate Method of Blinding | Fate (Withdrawn or Drop-Outs) of All Patients in Trial is Known | |||
| 1 | Husain, M. et al., 2019 [16] | * | * | * | * | * | 5 |
| 2 | Aroda, V.R. et al., 2023 [18] | * | * | * | * | * | 5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Krishnanda, S.I.; Christabelle, M.; Yausep, O.E.; Sugiharto, C.; Vincent, L.D.; Agarwal, R.; Damara, I.; Harbuwono, D.S. The Effect of Oral Semaglutide on Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 2239. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14072239
Krishnanda SI, Christabelle M, Yausep OE, Sugiharto C, Vincent LD, Agarwal R, Damara I, Harbuwono DS. The Effect of Oral Semaglutide on Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(7):2239. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14072239
Chicago/Turabian StyleKrishnanda, Stanislaus Ivanovich, Marie Christabelle, Oliver Emmanuel Yausep, Caroline Sugiharto, Leroy David Vincent, Raksheeth Agarwal, Ivan Damara, and Dante Saksono Harbuwono. 2025. "The Effect of Oral Semaglutide on Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 7: 2239. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14072239
APA StyleKrishnanda, S. I., Christabelle, M., Yausep, O. E., Sugiharto, C., Vincent, L. D., Agarwal, R., Damara, I., & Harbuwono, D. S. (2025). The Effect of Oral Semaglutide on Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(7), 2239. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14072239







