Transapical vs. Transaxillary Access in Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation: Comparative Mortality and Long-Term Outcomes Using Inverse Probability of Treatment Weighting Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. Statistical Analysis
4. Results
4.1. Study Population
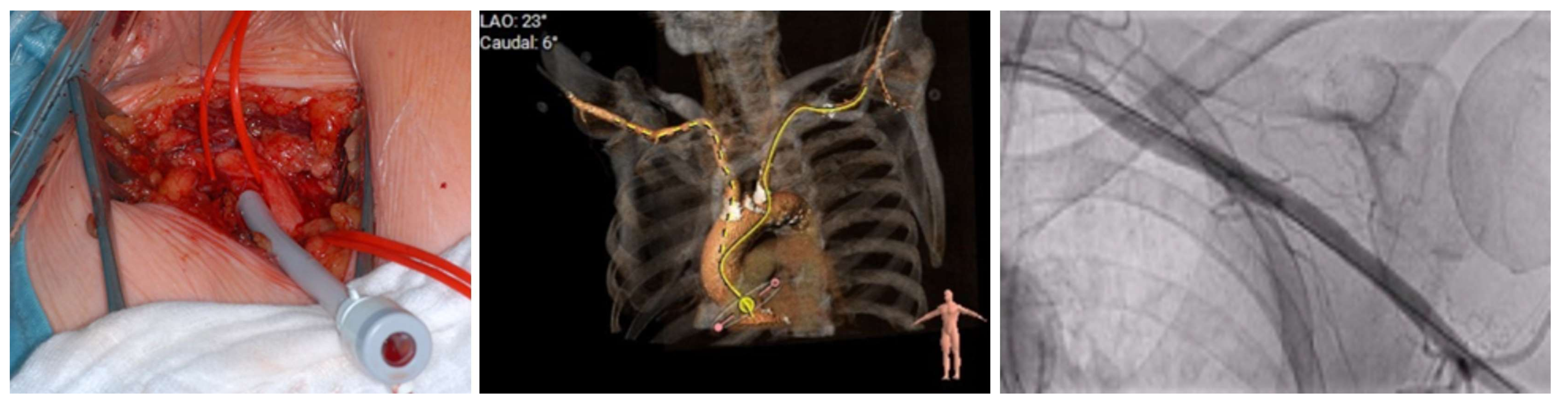
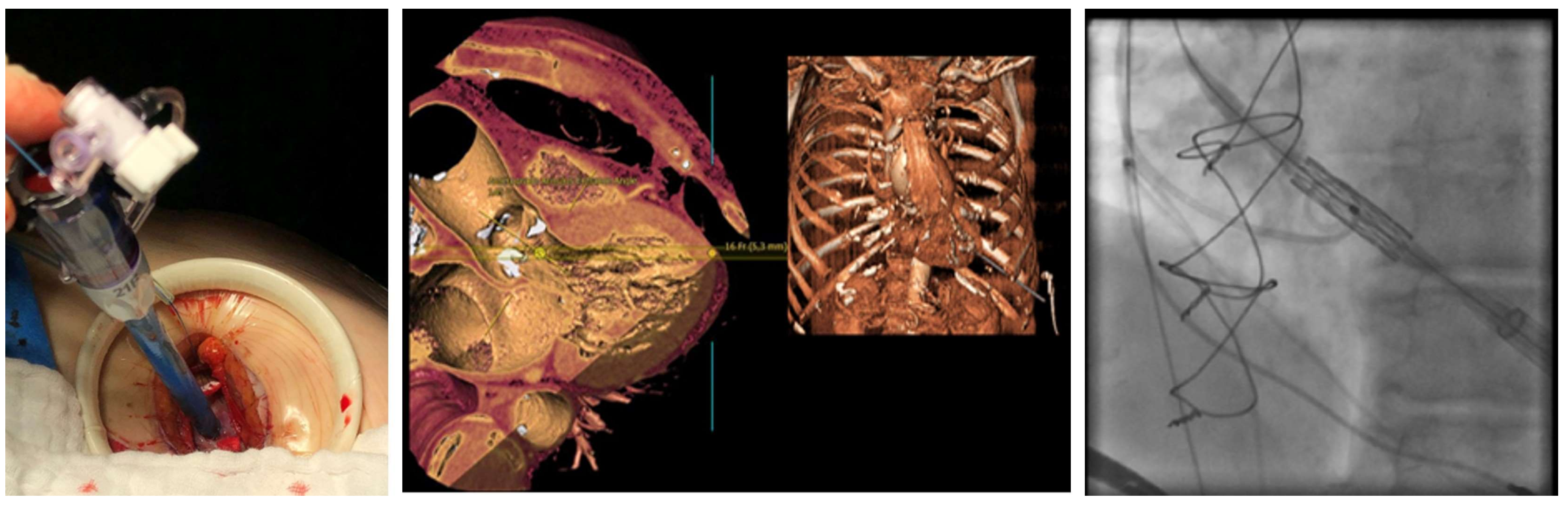
4.2. Procedural Characteristics
4.3. Procedural Outcomes, Complications, and Mortality
5. Discussion
5.1. Intrahospital and Follow-Up Mortality
5.2. Patient Characteristics, Clinical Outcomes, and Complications
6. Limitations
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Beyersdorf, F.; Vahanian, A.; Milojevic, M.; Praz, F.; Baldus, S.; Bauersachs, J.; Capodanno, D.; Conradi, L.; De Bonis, M.; De Paulis, R.; et al. Corrigendum to: 2021 ESC/EACTS Guidelines for the management of valvular heart disease. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2022, 62, ezac209. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chandrasekhar, J.; Hibbert, B.; Ruel, M.; Lam, B.-K.; Labinaz, M.; Glover, C. Transfemoral vs non transfemoral access for transcatheter aortic valve implantation: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Can. J. Cardiol. 2015, 31, 1427–1438. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jiménez-Quevedo, P.; Nombela-Franco, L.; Muñoz-García, E.; Del Valle-Fernández, R.; Trillo, R.; de la Torre Hernández, J.M.; Salido, L.; Elizaga, J.; Ojeda, S.; Sánchez Gila, J.; et al. Early clinical outcomes after transaxillary versus transfemoral TAVI. Data from the Spanish TAVI registry. Rev. Esp. Cardiol. 2022, 75, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gilard, M.; Eltchaninoff, H.; Iung, B.; Donzeau-Gouge, P.; Chevreul, K.; Fajadet, J.; Leprince, P.; Belle, E.; Laskar, M. Registry of transcatheter aortic-valve implantation in high-risk patients. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 1705–1715. [Google Scholar]
- Blackman, D.J.; Baxter, P.D.; Gale, C.P.; Moat, N.E.; Maccarthy, P.A.; Hildick-Smith, D.; Trivedi, U.; Cunningham, D.; Ludman, P.F. Do outcomes from transcatheter aortic valve implantation vary according to access route and valve type? The UK TAVI registry. J. Interv. Cardiol. 2014, 27, 86–95. [Google Scholar]
- Leon, M.B.; Smith, C.R.; Mack, M.J.; Makkar, R.R.; Svensson, L.G.; Kodali, S.K.; Thourani, V.H.; Tuzcu, E.M.; Miller, D.C.; Herrmann, H.C.; et al. Transcatheter or surgical aortic-valve replacement in intermediate-risk patients. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 1609–1620. [Google Scholar]
- Grover, F.L.; Vemulapalli, S.; Carroll, J.D.; Edwards, F.H.; Mack, M.J.; Thourani, V.H.; Brindis, R.G.; Shahian, D.M.; Ruiz, C.E.; Jacobs, J.P.; et al. 2016 annual report of the Society of Thoracic Surgeons/American College of Cardiology Transcatheter Valve Therapy registry. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2017, 69, 1215–1230. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, C.J.; Kaneko, T.; Tayal, R.; Dahle, T.G.; McCabe, J.M. Percutaneous versus surgical transaxillary access for transcatheter aortic valve replacement: A propensity-matched analysis of the US experience. EuroIntervention 2022, 17, 1514–1522. [Google Scholar]
- Kodali, S.K.; Williams, M.R.; Smith, C.R.; Svensson, L.G.; Webb, J.G.; Makkar, R.R.; Fontana, G.P.; Dewey, T.M.; Thourani, V.H.; Pichard, A.D.; et al. Two-year outcomes after transcatheter or surgical aortic-valve replacement. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 1686–1695. [Google Scholar]
- Takagi, H.; Hari, Y.; Nakashima, K.; Kuno, T.; Ando, T. Comparison of early and midterm outcomes after transsubclavian/axillary versus transfemoral, transapical, or transaortic transcatheter aortic valve implantation. Heart Lung 2019, 48, 519–529. [Google Scholar]
- Moat, N.E.; Ludman, P.; De Belder, M.A.; Bridgewater, B.; Cunningham, A.D.; Young, C.P.; Thomas, M.; Kovac, J.; Spyt, T.; MacCarthy, P.A.; et al. Long-Term Outcomes After Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation in High-Risk Patients with Severe Aortic Stenosis: The U.K. TAVI (United Kingdom Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation) Registry. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2011, 58, 2130–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilard, M.; Eltchaninoff, H.; Donzeau-Gouge, P.; Chevreul, K.; Fajadet, J.; Leprince, P.; Leguerrier, A.; Lievre, M.; Prat, A.; Teiger, E.; et al. Late outcomes of transcatheter aortic valve replacement in high-risk patients: The FRANCE-2 registry. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2016, 68, 1637–1647. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kindzelski, B.; Mick, S.L.; Krishnaswamy, A.; Kapadia, S.R.; Attia, T.; Hodges, K.; Siddiqi, S.; Lowry, A.M.; Blackstone, E.H.; Popovic, Z.; et al. Evolution of Alternative-Access Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2021, 112, 1877–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ennker, J.; Falk, V.; Photiadis, J.; Starck, C.; Weymann, A. (Eds.) Referenz Herzchirurgie; Georg Thieme Verlag KG: Stuttgart, Germany, 2023; ISBN 9783132426108/9783132431355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kappetein, A.P.; Head, S.J.; Généreux, P.; Piazza, N.; Van Mieghem, N.M.; Blackstone, E.H.; Brott, T.G.; Cohen, D.J.; Cutlip, D.E.; van Es, G.A.; et al. Updated standardized endpoint definitions for transcatheter aortic valve implantation: The Valve Academic Research Consortium-2 consensus document. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2013, 145, 6–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chesnaye, N.C.; Stel, V.S.; Tripepi, G.; Dekker, F.W.; Fu, E.L.; Zoccali, C.; Jager, K.J. An introduction to inverse probability of treatment weighting in observational research. Clin. Kidney J. 2021, 15, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lumley, T. Survey: Analysis of Complex Survey Samples; R Package Version 4.4; R Foundation For Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida, K.; Bartel, A. A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2025; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 6 February 2025).
- Waterford, S.D.; Trujillo, J.F. Outcomes of Alternative Access Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement Procedures. Innovations 2023, 18, 326–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomala, O.; Zamvar, V.; Bing, R.; Pessotto, R.; Cruden, N. Comparison of outcomes of trans-subclavian versus trans-apical approaches in transcatheter aortic valve implantation. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2022, 17, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciuca, C.; Tarantini, G.; Latib, A.; Gasparetto, V.; Savini, C.; Di Eusanio, M.; Napodano, M.; Maisano, F.; Gerosa, G.; Sticchi, A.; et al. Trans-subclavian versus transapical access for transcatheter aortic valve implantation: A multicenter study. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2016, 87, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamo, M.; Fiorina, C.; Curello, S.; Maffeo, D.; Chizzola, G.; Di Matteo, G.; Mastropierro, R.; Nardi, M.; Cervi, E.; De Cicco, G.; et al. Role of different vascular approaches on transcatheter aortic valve implantation outcome: A single-center study. J. Cardiovasc. Med. 2015, 16, 279–285. [Google Scholar]
- Fröhlich, G.M.; Baxter, P.D.; Malkin, C.J.; Scott, D.J.A.; Moat, N.E.; Hildick-Smith, D.; Cunningham, D.; MacCarthy, P.A.; Trivedi, U.; de Belder, M.A.; et al. Comparative survival after transapical, direct aortic, and subclavian transcatheter aortic valve implantation (Data from the UK TAVI Registry). Am. J. Cardiol. 2015, 116, 1555–1559. [Google Scholar]
- Ludman, P.F. UK TAVI registry. Heart 2019, 105, S2–S5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranka, S.; Lahan, S.; Chhatriwalla, A.K.; Allen, K.B.; Chiang, M.; O’Neill, B.; Verma, S.; Wang, D.D.; Lee, J.; Frisoli, T.; et al. Network Meta-Analysis Comparing the Short- and Long-Term Outcomes Of Alternative Access for transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement. Cardiovasc. Revasc. Med. 2022, 40, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, D.C.; Benjo, A.; Cardoso, R.N.; Macedo, F.Y.; Chavez, P.; Aziz, E.F.; Herzog, E.; Alam, M.; de Marchena, E. Device-stratified comparison among transfemoral, transapical, and trans-subclavian access for transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR): A meta-analysis. Int. J. Cardiol. 2014, 172, e318–e321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taramasso, M.; Maisano, F.; Cioni, M.; Denti, P.; Godino, C.; Montorfano, M.; Colombo, A.; Alfieri, O. Trans-apical and trans-axillary percutaneous aortic valve implantation as alternatives to the femoral route: Short- and middle-term results. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2011, 40, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eric, V.B.; Françis, J.; Sophie, S.; André, V.; Bernard, I.; Jean, D.; Eltchaninoff, H.; Laskar, M.; Leprince, P.; Lievre, M.; et al. Postprocedural aortic regurgitation in balloon-expandable and self-expandable transcatheter aortic valve replacement procedures. Circulation 2014, 129, 1415–1427. [Google Scholar]
- Deharo, P.; Bisson, A.; Herbert, J.; Lacour, T.; Saint Etienne, C.; Grammatico-Guillon, L.; Porto, A.; Collart, F.; Bourguignon, T.; Cuisset, T.; et al. Impact of Sapien 3 balloon-expandable versus Evolut R self-expandable transcatheter aortic valve implantation in patients with aortic stenosis. Circulation 2020, 141, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjursten, H.; Rasmussen, M.; Nozohoor, S.; Götberg, M.; Olaison, L.; Rück, A.; Ragnarsson, S. Infective endocarditis after transcatheter aortic valve implantation: A nationwide study. Eur. Heart J. 2019, 40, 3263–3269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, J.; Bob-Manuel, T.; Tafur, J.; Joury, A.; Aymond, J.; Duran, A.; Almusawi, H.; Cloninger, A.; Parrino, P.; Ramee, S. Transaxillary TAVR Leads to Shorter Ventilator Duration and Hospital Length of Stay Compared to Transapical TAVR. Curr. Probl. Cardiol. 2021, 46, 100624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Before IPTW | After IPTW | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TAP (N = 26) | TAX (N = 50) | p-Value | TAP (N = 26) | TAX (N = 50) | Weighted p-Value | |
| Female | 11 (42.3%) | 25 (50.0%) | 0.693 | 11 (41.3%) | 20 (40.4%) | 0.950 |
| Age (years) | 75.9 (6.69) | 81.8 (6.00) | <0.001 * | 78.1 (1.03) | 78.0 (2.28) | 0.989 |
| Arterial hypertension | 23 (88.5%) | 47 (94.0%) | 0.688 | 23 (90.3%) | 48 (95.6%) | 0.350 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 26.3 (4.35) | 24.1 (3.33) | 0.031 * | 26.4 (0.93) | 24.78 (0.92) | 0.226 |
| NYHA I, II | 4 (20.0%) | 6 (15.8%) | 0.97 | 3 (10.6%) | 3 (5.6%) | 0.445 |
| NYHA III, IV | 16 (80.0%) | 32 (84.2%) | 0.97 | 20 (77.9%) | 43 (86.4%) | 0.445 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 7 (26.9%) | 12 (24.0%) | 1 | 2 (9.3%) | 5 (10.7%) | 0.471 |
| Coronary heart disease | 22 (84.6%) | 43 (86.0%) | 1 | 22 (83.9%) | 44 (87.7%) | 0.660 |
| History of atrial fibrillation | 12 (46.2%) | 21 (42.0%) | 0.918 | 12 (45.8%) | 17 (33.0%) | 0.326 |
| Renal insufficiency | 15 (57.7%) | 20 (40.0%) | 0.22 | 16 (62.8%) | 21 (42.7%) | 0.157 |
| Euro Score II | 10.5 [0.810, 32.0] | 7.20 [1.94, 37.2] | 0.259 | 10.55 [1.95, 18.00] | 7.2 [1.03, 18.11] | 0.951 |
| STS Score | 4.97 [1.60, 16.9] | 6.00 [1.89, 18.9] | 0.25 | 5.14 [3.98, 7.4] | 6.00 [4.4, 8.0] | 0.771 |
| LVEF (%) | 47.1 (13.7) | 52.1 (14.0) | 0.183 | 47.5 (2.77) | 46.4 (5.22) | 0.857 |
| Aortic valve area (cm2) | 0.724 (0.197) | 0.710 (0.161) | 0.775 | 0.723 (0.046) | 0.682 (0.059) | 0.577 |
| Aortic valve mean gradient (mmHG) | 34.3 (14.3) | 33.2 (12.4) | 0.808 | 35.16 (3.21) | 31.48 (2.24) | 0.353 |
| Aortic valve peak gradient (mmHG) | 57.1 (22.0) | 53.8 (17.6) | 0.6 | 58.49 (5.33) | 53.72 (3.15) | 0.445 |
| AV Vmax (m/s) | 3.73 (0.688) | 3.63 (0.571) | 0.597 | 3.77 (0.170) | 3.55 (0.105) | 0.288 |
| Before IPTW | After IPTW | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TAP (N = 26) | TAX (N = 50) | p-Value | TAP (N = 26) | TAX (N = 50) | Weighted p-Value | |
| Procedural duration (min) | 138 (50.1) | 139 (40.7) | 0.648 | 137 (10.67) | 138 (6.34) | 0.998 |
| Peri-operative anaethesia | ||||||
| Analog sedation | 1 (4.0%) | 3 (7.0%) | 1 | 1 (2.7%) | 2 (4.6%) | 0.651 |
| General anesthesia | 24 (96.0%) | 40 (93.0%) | 1 | 25 (97.3%) | 48 (95.4%) | 0.651 |
| Valve prosthesis system | ||||||
| CoreValve Evolut | 0 (0%) | 47 (94.0%) | NA | 0 (0%) | 47 (94.0%) | NA |
| Edwards Sapien 3 | 26 (100%) | 2 (4.0%) | NA | 26 (100%) | 2 (4.0%) | NA |
| Portico | 0 (0%) | 1 (2.0%) | NA | 0 (0%) | 1 (2.0%) | NA |
| Contrast medium volume (mL) | 90.4 (61.7) | 129 (41.6) | <0.001 * | 97.8 (16.07) | 134.57 (7.45) | 0.041 * |
| Radiation exposure (min) | 7.77 (4.50) | 16.6 (8.52) | <0.001 * | 8.24 (1.12) | 16.06 (1.14) | <0.001 * |
| Radiation dose (Gy/cm2) | 23.9 (15.8) | 30.0 (18.6) | 0.225 | 25.11 (3.48) | 34.61 (3.88) | 0.073 |
| Valze size (mm) | 25.7 (2.13) | 28.2 (2.48) | <0.001 * | 25.57 (0.42) | 28.68 (0.65) | <0.001 * |
| Valvuloplastie | 3 (11.5%) | 23 (47.9%) | 0.004 * | 3 (13.3%) | 29 (57.6%) | 0.002 * |
| Valve implantation success | 26 (100%) | 50 (100%) | NA | 26 (100%) | 50 (100%) | NA |
| Before IPTW | After IPTW | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TAP (N = 26) | TAX (N = 50) | p-Value | TAP (N = 26) | TAX (N = 50) | Weighted p-Value | |
| Safety composite | 2 (7.7%) | 4 (8.0%) | 1 | 2 (9.5%) | 3 (6.2%) | 0.649 |
| In-hospital mortality | 0 (0%) | 1 (2.0%) | 1 | 0 (0%) | 1 (2.1%) | 0.388 |
| 30-day mortality | 1 (3.8%) | 2 (4.0%) | 1 | 1 (3.4%) | 2 (3.5%) | 0.957 |
| Postprocedural myocardial infarct | ||||||
| <72 h periprocedural | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | NA | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | NA |
| >72 h postprocedural | 0 (0%) | 1 (2.0%) | 1 | 0 (0%) | 1 (1.4%) | 0.393 |
| AKIN | ||||||
| 1 | 1 (3.8%) | 1 (2.0%) | 1 | 1 (1.7%) | 1 (1.4%) | 0.921 |
| 2 | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | NA | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | NA |
| 3 | 2 (7.7%) | 1 (2.0%) | 0.532 | 2 (9.5%) | 1 (1.4%) | 0.087 |
| Stroke (non-diabling or disabling) | 0 (0%) | 2 (4.0%) | 0.8 | 0 (0%) | 2 (3.3%) | 0.244 |
| Bleeding type | ||||||
| Life-threatening | 0 (0%) | 1 (2.0%) | 1 | 0 (0%) | 1 (2.1%) | 0.388 |
| Major | 2 (7.7%) | 0 (0%) | 0.205 | 1 (5.4%) | 0 (0%) | 0.140 |
| Minor | 1 (3.8%) | 4 (8.0%) | 0.87 | 2 (7.2%) | 8 (15.1%) | 0.492 |
| Bleeding (all types) | 3 (11.5%) | 5 (10.0%) | 1 | 0.684 | ||
| Postprocedural higher AV-block | 0 (0%) | 5 (10.0%) | 0.252 | 0 (0%) | 9 (17.7%) | 0.091 |
| Postprocedural BB block | 3 (12.0%) | 15 (30.0%) | 0.152 | 3 (10.9%) | 16 (32.4%) | 0.055 |
| New pacemaker device | 0 (0%) | 8 (16.0%) | 0.085 | 0 (0%) | 11 (22.6%) | 0.032 * |
| Coronary obstruction | 0 (0%) | 1 (2.0%) | 1 | 0 (0%) | 1 (1.4%) | 0.393 |
| Major vascular complication | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | NA | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | NA |
| Peri-interventional BB block | ||||||
| Left BB block | 5 (20.0%) | 7 (14.6%) | 0.737 | 4 (14.4%) | 7 (13.5%) | 0.946 |
| Right BB block | 1 (4.0%) | 1 (2.1%) | 1 | 2 (7.5%) | 1 (1.7%) | 0.247 |
| Paravalvular leakage | ||||||
| 1 | 7 (26.9%) | 20 (40.0%) | 0.444 | 7 (26.6%) | 22 (44.2%) | 0.189 |
| 2 | 0 (0%) | 5 (10.0%) | 0.252 | 0 (0%) | 4 (8.2%) | 0.078 |
| 3 | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | NA | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | NA |
| Access site complication type | ||||||
| Major | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | NA | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | NA |
| Minor | 1 (3.8%) | 1 (2.0%) | 1 | 1 (5.0%) | 1 (1.3%) | 0.298 |
| Pleural effusion | 4 (15.4%) | 3 (6.0%) | 0.652 | 4 (15.7%) | 3(4.9%) | 0.070 |
| Prosthesis endocarditis | 1 (3.8%) | 1 (2.0%) | 1 | 1 (3.4%) | 1 (1.7%) | 0.635 |
| Total hospital days | 19.0 [5.00, 54.0] | 9.50 [5.00, 32.0] | 0.002 * | 19.0 [13.00, 28.00] | 10 [8.00, 21.00] | 0.016 * |
| Before IPTW | After IPTW | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TAP (N = 26) | TAX (N = 50) | p-Value | TAP (N = 26) | TAX (N = 50) | Weighted p-Value | |
| Safety composite | 3 (11.5%) | 4 (8.0%) | 0.930 | 4 (13.8%) | 5 (9.0%) | 0.518 |
| All-cause death | 2 (7.7%) | 3 (6.0%) | 1 | 2 (6.7%) | 2 (4.8%) | 0.709 |
| Rehospitalization | 14 (53.8%) | 35 (70%) | 0.253 | 10 (37.0%) | 22 (43.0%) | 0.667 |
| Cardiac decompensation | 0 (0.0%) | 3 (6.0%) | 0.513 | 0 (0.0%) | 8 (15.2%) | 0.152 |
| Resusication | 1 (3.8%) | 1 (2.0%) | 1 | 1 (3.6%) | 1 (2.1%) | 0.702 |
| Postprocedural myocardial infarct | 0 (0%) | 1 (2.0%) | 1 | 0 (0.0%) | 1 (1.4%) | 0.393 |
| AKIN | ||||||
| 1 | 5 (19.2%) | 7 (14.0%) | 0.794 | 4 (16.1%) | 14 (28.8%) | 0.335 |
| 2 | 1 (3.8%) | 1 (2.0%) | 1 | 4 (1.6%) | 1 (1.5%) | 0.975 |
| 3 | 2 (7.7%) | 1 (2.0%) | 0.556 | 2 (9.0%) | 1 (1.1%) | 0.087 |
| Stroke (non-diabling or disabling) | 1 (3.8%) | 2 (4.0%) | 1 | 1 (3.2%) | 2 (3.2%) | 0.988 |
| Bleeding type | ||||||
| Life-threatening | 0 (0.0%) | 1 (2.0%) | 1 | 0 (0.0%) | 1 (2.0%) | 0.388 |
| Major | 2 (7.7%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0.210 | 1 (5.3%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0.140 |
| Minor | 1 (3.8%) | 4 (8.0%) | 0.837 | 2 (7.1%) | 8 (15.4%) | 0.492 |
| Higher-grade AV block | 1 (3.8%) | 5 (10.0%) | 0.620 | 1 (5.0%) | 9 (17.9%) | 0.223 |
| Onset of atrial fibrillation | 3 (11.5%) | 1 (2.0%) | 0.220 | 2 (8.9%) | 1 (2.0%) | 0.164 |
| Pacemaker device | 1 (3.8%) | 10 (20.0%) | 0.120 | 1 (2.7%) | 13 (26.7%) | 0.0067 * |
| Valve intervention | 1 (3.8%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0.738 | 1 (3.1%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0.265 |
| Coronary angiography | 1 (3.8%) | 2 (4.0%) | 1 | 1 (3.1%) | 2 (4.1%) | 0.815 |
| Coronary obstruction | 1 (3.8%) | 1 (2.0%) | 1 | 1 (3.1%) | 1 (1.4%) | 0.578 |
| Bacteremia | 4 (15.4%) | 1 (2.0%) | 0.081 | 4 (13.4%) | 1 (1.6%) | 0.027 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schrader, H.; Wiedenhofer, J.M.; Berlinghof, S.; Ducaruge, J.; Brand, A.; Spethmann, S.; Landmesser, U.; Blaschke, F.; Grubitzsch, H.; Falk, V.; et al. Transapical vs. Transaxillary Access in Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation: Comparative Mortality and Long-Term Outcomes Using Inverse Probability of Treatment Weighting Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 2235. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14072235
Schrader H, Wiedenhofer JM, Berlinghof S, Ducaruge J, Brand A, Spethmann S, Landmesser U, Blaschke F, Grubitzsch H, Falk V, et al. Transapical vs. Transaxillary Access in Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation: Comparative Mortality and Long-Term Outcomes Using Inverse Probability of Treatment Weighting Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(7):2235. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14072235
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchrader, Helene, Julia M. Wiedenhofer, Sophie Berlinghof, Juliane Ducaruge, Anna Brand, Sebastian Spethmann, Ulf Landmesser, Florian Blaschke, Herko Grubitzsch, Volkmar Falk, and et al. 2025. "Transapical vs. Transaxillary Access in Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation: Comparative Mortality and Long-Term Outcomes Using Inverse Probability of Treatment Weighting Analysis" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 7: 2235. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14072235
APA StyleSchrader, H., Wiedenhofer, J. M., Berlinghof, S., Ducaruge, J., Brand, A., Spethmann, S., Landmesser, U., Blaschke, F., Grubitzsch, H., Falk, V., Klein, C., Unbehaun, A., Sherif, M., Dreger, H., Trippel, T. D., Primessnig, U., & Sündermann, S. H. (2025). Transapical vs. Transaxillary Access in Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation: Comparative Mortality and Long-Term Outcomes Using Inverse Probability of Treatment Weighting Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(7), 2235. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14072235







