Transthoracic Echocardiography in Assessing Patients with Suspected Infective Endocarditis (TEASE): An Exploratory Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
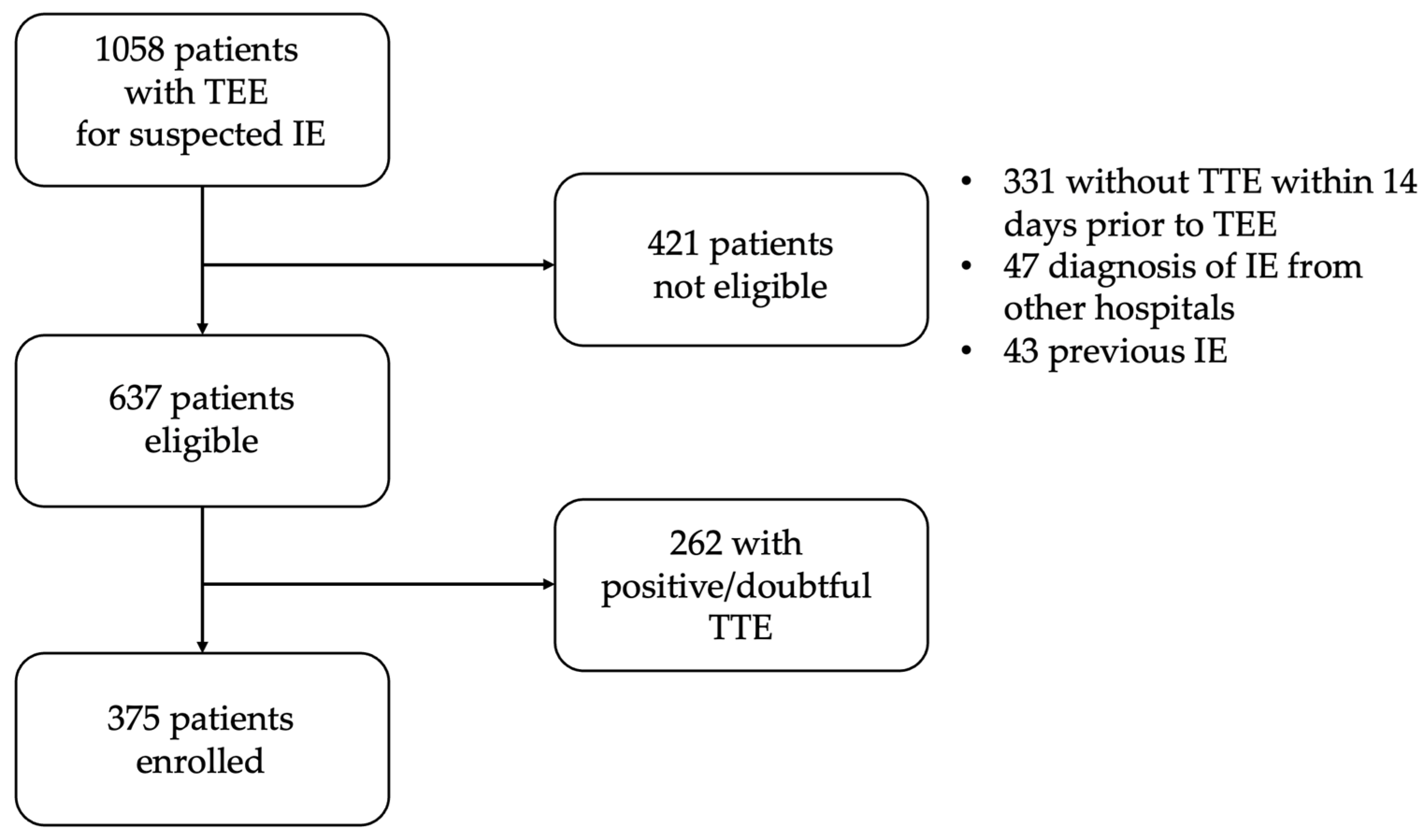
2.1. Patients
2.2. Endocarditis Diagnosis
2.3. Clinical Outcomes
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Population
3.1.1. IE Diagnosis
3.1.2. Subgroup Analysis
3.1.3. Clinical Outcomes
4. Discussion
4.1. TTE Performance and Clinical Implication
4.2. Previous Evidence on Negative TTE
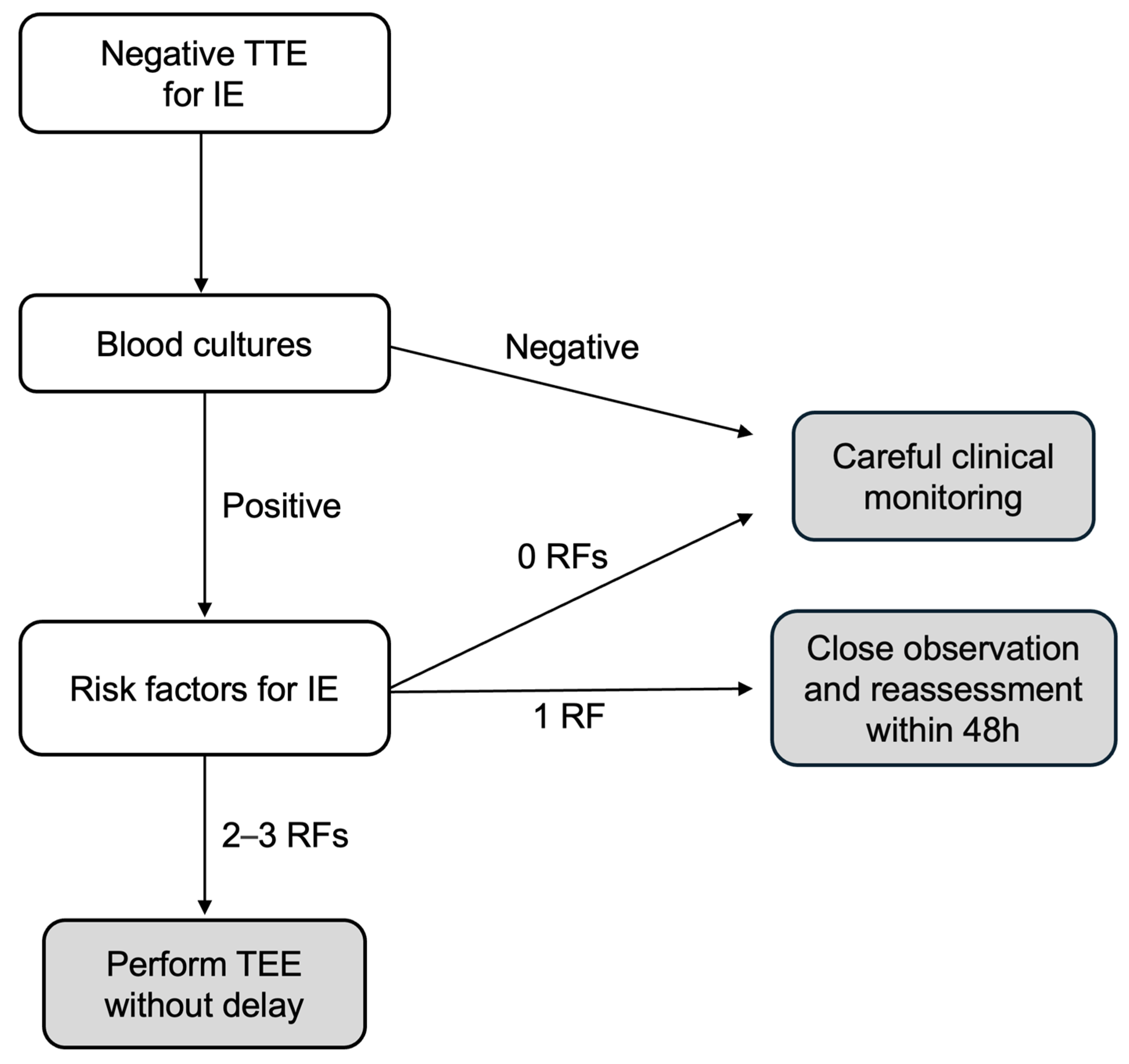
4.3. Risk Stratification and Main Predictors of IE
4.4. Clinical Outcomes and Implications for Clinical Practice
- (1)
- The low-risk group includes patients with negative BCs or positive BCs but no risk factors for IE; in these patients, TEE seems can be safely omitted but maintaining careful clinical monitoring;
- (2)
- The moderate-risk group includes patients with positive BCs but only one risk factor for IE; in these patients, close observation and short-term reassessment (within 48 h) are recommended, and TEE should be considered based on clinical/echocardiographic changes;
- (3)
- The high-risk group includes patients with positive BCs and two to three risk factors for IE; in these patients, TEE should be performed immediately.
5. Limitations of the Study
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| IE | Infective Endocarditis |
| TTE | Transthoracic Echocardiography |
| TEE | Transesophageal Echocardiography |
| BC | Blood Culture |
| LVEF | Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction |
References
- Momtazmanesh, S.; Saeedi Moghaddam, S.; Malakan Rad, E.; Azadnajafabad, S.; Ebrahimi, N.; Mohammadi, E.; Rouhifard, R.; Rezaei, N.; Masinaei, M.; Rezaei, N.; et al. Global, regional, and national burden and quality of care index of endocarditis: The global burden of disease study 1990–2019. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2022, 29, 1287–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhan, Y.; Zhang, K.; Gao, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhan, J.; Chen, Z.; Zeng, Z. The global, regional, and national burden and trends of infective endocarditis from 1990 to 2019: Results from the global burden of disease study 2019. Front. Med. Lausanne 2022, 9, 774224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delgado, V.; Ajmone Marsan, N.; de Waha, S.; Bonaros, N.; Brida, M.; Burri, H.; Caselli, S.; Doenst, T.; Ederhy, T.; Erba, P.A.; et al. ESC Scientific Document Group. 2023 ESC Guidelines for the management of endocarditis. Eur Heart J. 2023, 44, 3948–4042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birmingham, G.D.; Rahko, P.S.; Ballantyne, F., 3rd. Improved detection of infective endocarditis with transesophageal echocardiography. Am. Heart J. 1992, 123, 774–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shively, B.K.; Gurule, F.T.; Roldan, C.A.; Schiller, M.D. Diagnostic value of transesophageal compared with transthoracic echocardiography in infective endocarditis. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 1991, 18, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damlin, A.; Eriksson, M.J.; Maret, E. Can transthoracic echocardiography be used to a greater extent in the diagnostics of infective endocarditis to avoid unnecessary transoesophageal examinations without jeopardising accuracy? Cardiovasc. Ultrasound 2023, 21, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivak, J.A.; Vora, A.N.; Navar, A.M.; Schulte, P.J.; Crowley, A.L.; Kisslo, J.; Corey, J.R.; Liao, L.; Wang, A.; Velazquez, E.J.; et al. An Approach to Improve the Negative Predictive Value and Clinical Utility of Transthoracic Echocardiography in Suspected Native Valve Infective Endocarditis. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2016, 29, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taams, M.A.; Gussenhoven, E.J.; Bos, E.; de Jaegere, P.; Roelandt, J.R.; Sutherland, G.R.; Bom, N. Enhanced morphological diagnosis in infective endocarditis by transesophageal echocardiography. Br. Heart J. 1990, 63, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedersen, W.R.; Walker, M.; Olson, J.D.; Gobel, F.; Lange, H.W.; Daniel, J.A.; Rogers, J.; Longe, T.; Kane, M.; Mooney, M.R.; et al. Value of transesophageal echocardiography as an adjunct to transthoracic echocardiography in evaluation of native and prosthetic valve endocarditis. Chest 1991, 100, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindner, J.R.; Case, R.A.; Dent, J.M.; Abbott, R.D.; Scheld, W.M.; Kaul, S. Diagnostic Value of Echocardiography in Suspected Endocarditis: An Evaluation Based on the Pretest Probability of Disease. Circulation 1996, 93, 730–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roe, M.T.; Abramson, M.A.; Li, J.; Kisslo, J.; Corey, G.R.; Sexton, D.J. Clinical information determines the impact of transesophageal echocardiography on the diagnosis of infective endocarditis by the duke criteria. Am. Heart J. 2000, 139, 945–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greaves, K.; Mou, D.; Patel, A.; Celermajer, D.S. Clinical criteria and the appropriate use of transthoracic ecocardiography for the exclusion of infective endocarditis. Heart 2003, 89, 273–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durack, D.T.; Lukes, A.S.; Bright, D.K. New criteria for diagnosis of infective endocarditis: Utilization of specific echocardiographic findings. Duke Endocarditis Service. Am. J. Med. 1994, 96, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, H.; Badano, L.; Tribouilloy, C.; Vilacosta, I.; Zamorano, J.L.; Galderisi, M. Recommendations for the practice of echocardiography in infective endocarditis. Eur. J. Echocardiogr. 2010, 11, 202–219. [Google Scholar]
- Hahn, R.T.; Abraham, T.; Adams, M.S.; Bruce, C.J.; Glas, K.E.; Lang, R.L.; Reeves, S.T.; Shanewise, J.S.; Siu, S.C.; Stewart, W.; et al. Guidelines for Performing a Comprehensive Transesophageal Echocardiographic Examination: Recommendations from the American Society of Echocardiography and the Society of Cardiovascular Anesthesiologists. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2013, 26, 921–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irani, W.N.; Grayburn, P.A.; Afridi, I. A negative transthoracic echocardiogram obviates the need for transesophageal echocardiography in patients with suspected native valve active infective endocarditis. Am. J. Cardiol. 1996, 78, 101–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barton, T.L.; Mottram, P.M.; Stuart, R.L.; Cameron, J.D.; Stuart Moir, S. Transthoracic Echocardiography Is Still Useful in the Initial Evaluation of Patients with Suspected Infective Endocarditis: Evaluation of a Large Cohort at a Tertiary Referral Center. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2014, 89, 799–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, A.D.; Steinberg, M.; Showler, A.; Burry, L.; Bhatia, R.S.; Tomlinson, G.A.; Bell, C.M.; Morris, A.M. Diagnostic accuracy of transthoracic echocardiography for infective endocarditis findings using transesophageal echocardiography as the reference standard: A meta-analysis. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2017, 30, 639–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonzi, M.; Cernuschi, G.; Solbiati, M. Diagnostic accuracy of transthoracic echocardiography to identify native valve infective endocarditis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2018, 13, 937–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamy, B.; Dargere, S.; Arendrup, M.C.; Parienti, J.; Tattevin, P. How to optimize the use of blood cultures for the diagnosis of bloodstream infections? A state-of-the art. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, W.K.F.; Salsano, A.; Giacobbe, D.R.; Popescu, B.A.; Laroche, C.; Duval, X.; Schueler, R.; Moreo, A.; Colonna, P.; Piper, C.; et al. Outcomes of culture-negative vs. culture-positive infective endocarditis: The ESC-EORP EURO-ENDO registry. Eur. Heart J. 2022, 43, 2770–2780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuervo, G.; Quintana, E.; Regueiro, A.; Perissinotti, A.; Vidal, B.; Miro, J.M.; Baddour, L.M. The Clinical Challenge of Prosthetic Valve Endocarditis: JACC Focus Seminar 3/4. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2024, 83, 1418–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayer, M.J.; Quintero-Martinez, J.A.; Thornhill, M.H.; Chambers, J.B.; Pettersson, G.B.; Baddour, L.M. Recent Insights into Native Valve Infective Endocarditis: JACC Focus Seminar 4/4. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2024, 83, 1431–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornhill, M.H.; Jones, S.; Prendergast, B.; Baddour, L.M.; Chambers, J.B.; Lockhart, P.B.; Dayer, M.J. Quantifying infective endocarditis risk in patients with predisposing cardiac conditions. Eur. Heart J. 2018, 39, 586–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anantha-Narayanan, M.; Reddy, Y.N.V.; Sundaram, V.; Murad, M.H.; Erwin, P.J.; Baddour, L.M.; Schaff, H.V.; Nishimura, R.A. Endocarditis risk with bioprosthetic and mechanical valves: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Heart 2020, 106, 1413–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hubert, S.; Thuny, F.; Resseguier, N.; Giorgi, R.; Tribouilloy, C.; Le Dolley, Y.; Casalta, J.; Riberi, A.; Chevalier, F.; Rusinaru, D.; et al. Prediction of symptomatic infarct in infective endocarditis: Construction and validation of a risk calculator in a multicenter cohort. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2013, 62, 1384–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, H.A.; Thompson, E.C.; Laureno, R.; Fuisz, A.; Mark, A.S.; Lin, M.; Goldstein, S.A. Subclinical brain embolization in left-sided infective endocarditis: Results from the evaluation by MRI of the brains of patients with left-sided intracardiac solid masses (INFARCT) pilot study. Circulation 2009, 120, 585–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambola, A.; Lozano-Torres, J.; Boersma, E.; Olmos, C.; Ternacle, J.; Calvo, F.; Tribouilloy, C.; Reskovic-Luksic, V.; Separovic-Hanzevacki, J.; ESC EORP EURO-ENDO Registry Investigator Group; et al. Predictors of infarct and death in left-sided infective endocarditis: The European Society of Cardiology EURObservational Research Programme European Infective Endocarditis registry. Eur. Heart J. 2023, 44, 4566–4575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, M.; Adhikari, B.; Devkota, A.; Mohebtash, M. Severe Thrombocytopenia in Infective Endocarditis. J. Community Hosp. Intern. Med. Perspect. 2023, 13, 80–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrera, C.; Vilacosta, I.; Fernandez, C.; López, J.; Sarriá, C.; Olmos, C.; Vivas, D.; Sáez, C.; Sánchez-Enrique, C.; Ortiz, C.; et al. Usefulness of thrombocytopenia at admission as a prognostic marker in native valve left-sided infective endocarditis. Am. J. Cardiol. 2015, 115, 950–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sy, R.W.; Chawantanpipat, C.; Richmond, D.R.; Kritharides, L. Thrombocytopenia and mortality in infective endocarditis. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2008, 51, 1824–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangner, N.; Panagides, V.; Del Val, D.; Abdel-Wahab, M.; Crusius, L.; Durand, E.; Ihlemann, N.; Urena, M.; Pellegrini, C.; Giannini, F.; et al. Incidence, Clinical Characteristics, and Impact of Absent Echocardiographic Signs in Patients with Infective Endocarditis After Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2023, 76, 1003–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Cabrera, E.; Fernandez-Hidalgo, N.; Almirante, B.; Ivanova-Georgieva, R.; Noureddine, M.; Plata, A.; Lomas, J.M.; Gálvez-Acebal, J.; Hidalgo-Tenorio, C.; Ruíz-Morales, J.; et al. Neurological complications of infective endocarditis: Risk factors, outcome, and impact of cardiac surgery: A multicenter observational study. Circulation 2013, 127, 2272–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selton-Suty, C.; Delahaye, F.; Tattevin, P.; Federspiel, C.; Le Moing, V.; Chirouze, C.; Nazeyrollas, P.; Vernet-Garnier, V.; Bernard, Y.; Chocron, S.; et al. Symptomatic and asymptomatic neurological complications of infective endocarditis: Impact on surgical management and prognosis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0158522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreß, S.; Reischmann, K.; Markovic, S.; Rohlmann, F.; Hay, B.; Rottbauer, W.; Buckert, D.; d’Almeida, S. Men’s more frequent predisposing factors in infectious endocarditis facilitate improvement of outcomes by shortening of diagnostic delay. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2025, 11, 1517288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naderi, H.R.; Sheybani, F.; Erfani, S.S. Errors in diagnosis infective endocarditis. Epidemiol. Infect. 2018, 146, 394–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickerman, S.A.; Abrutyn, E.; Barsic, B.; Bouza, E.; Cecchi, E.; Moreno, A.; Doco-Lecompte, T.; Eisen, D.P.; Fortes, C.Q.; Fowler, V.G., Jr.; et al. The relationship between the initiation of antimicrobial therapy and the incidence of stroke in infective endocarditis: An analysis from the ICE Prospective Cohort Study (ICE-PCS). Am. Heart J. 2007, 154, 1086–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Infective Endocarditis (n = 56) | No Infective Endocarditis (n = 319) | Odds Ratio (95% CI) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 69 ± 13 | 67 ± 15 | 1.01 (0.99–1.03) | 0.39 |
| Male | 37 (66%) | 209 (66%) | 1.03 (0.56–1.89) | 0.94 |
| Body mass index (Kg/m2) | 56 ± 26 | 316 ± 25 | 1.01 (0.98–1.03) | 0.57 |
| Diabetes | 20 (37%) | 81 (25%) | 1.63 (0.89–2.98) | 0.11 |
| Positive blood cultures | 47 (84%) | 201 (63%) | 3.07 (1.45–6.48) | 0.003 |
| Gram-positive | 44 (79%) | 167 (80%) | 3.43 (1.55–7.56) | 0.002 |
| Gram-negative | 3 (5%) | 34 (16%) | 0.41 (0.12–1.40) | 0.16 |
| Staph. Aureus | 16 (31%) | 105 (39%) | 0.70 (0.37–1.33) | 0.28 |
| Staph. Epidermidis | 4 (8%) | 14 (5%) | 1.53 (0.48–4.85) | 0.47 |
| Str. Viridans | 1 (2%) | 2 (1%) | 2.64 (0.24–29.63) | 0.43 |
| Str. Gallolyticus | 4 (8%) | 9 (3%) | 2.43 (0.72–8.20) | 0.15 |
| E. Faecalis | 9 (18%) | 18 (7%) | 2.93 (1.24–6.95) | 0.015 |
| HACEK | 0 (0%) | 1 (0.4%) | 1.88 (0.08–46.71) | 0.99 |
| Fungal | 1 (2%) | 12 (4%) | 0.42 (0.05–3.33) | 0.41 |
| Fever | 37 (66%) | 191 (60%) | 1.30 (0.71–2.35) | 0.40 |
| Urinary tract infection | 5 (9%) | 61 (19%) | 0.42 (0.16–1.08) | 0.072 |
| Respiratory tract infection | 14 (25%) | 47 (15%) | 1.93 (0.98–3.81) | 0.06 |
| Gastro-intestinal tract infection | 3 (5%) | 31 (10%) | 0.53 (0.16–1.78) | 0.30 |
| Skin/soft tissue infection | 12 (21%) | 102 (32%) | 0.58 (0.29–1.15) | 0.12 |
| Embolism | 21 (38%) | 16 (5%) | 11.36 (5.43–23.78) | <0.001 |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 10.7 ± 1.7 | 11.5 ± 4.4 | 0.87 (0.75–0.99) | 0.048 |
| White blood cells (×109/L) | 13.8 ± 7.7 | 12.5 ± 6.4 | 1.83 (1.02–3.28) | 0.042 |
| Platelets (×109/L) | 191 ± 114 | 256 ± 137 | 0.99 (0.992–0.998) | <0.001 |
| Platelets < 150 × 109/L | 21 (38%) | 56 (18%) | 2.82 (1.53–5.20) | <0.001 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 1.28 ± 1.1 | 1.54 ± 1.7 | 0.88 (0.70–1.11) | 0.28 |
| Bilirubin (mg/dL) | 0.94 ± 0.8 | 1.03 ± 1.56 | 0.95 (0.74–1.22) | 0.68 |
| C-reactive protein (mg/L) | 142 ± 88 | 157 ± 202 | 0.99 (0.99–1.00) | 0.58 |
| Procalcitonin (ng/mL) | 5 ± 10 | 10 ± 34 | 0.99 (0.97–1.01) | 0.31 |
| Infective Endocarditis (n = 56) | No Infective Endocarditis (n = 319) | Odds Ratio (95% CI) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Days between TTE and TEE | 5 ± 3 | 6 ± 4 | 0.075 | |
| LVEF (%) | 54 ± 12 | 54 ± 11 | 1.00 (0.98–1.03) | 0.94 |
| Aortic regurgitation | 11 (20%) | 29 (9%) | 2.44 (1.14–5.22) | 0.022 |
| Aortic stenosis | 6 (11%) | 17 (5%) | 2.13 (0.80–5.65) | 0.13 |
| Mitral regurgitation | 17 (30%) | 54 (17%) | 2.13 (1.12–4.04) | 0.021 |
| Mitral stenosis | 2 (4%) | 3 (1%) | 3.89 (0.64–23.82) | 0.14 |
| Tricuspid regurgitation | 14 (25%) | 54 (17%) | 1.63 (0.83–3.19) | 0.15 |
| Central venous catheter | 7 (13%) | 56 (18%) | 0.67 (0.29–1.56) | 0.35 |
| Cardiac electronic device | 15 (27%) | 69 (22%) | 1.33 (0.69–2.54) | 0.39 |
| Mechanical heart valve | 5 (9%) | 20 (6%) | 1.47 (0.53–4.08) | 0.46 |
| Bioprosthetic heart valve | 21 (37%) | 44 (14%) | 3.75 (2.00–7.03) | <0.001 |
| Odds Ratio (95% Confidence Interval) | p | |
|---|---|---|
| Systemic/pulmonary embolism | 13.25 (5.49–31.98) | <0.001 |
| Bioprosthetic valve | 3.79 (1.76–8.16) | <0.001 |
| Platelets < 150 × 109/L | 2.50 (1.20–5.22) | 0.014 |
| Positive blood cultures | 3.79 (1.27–11.34) | 0.017 |
| Urinary tract infection | 0.39 (0.13–1.12) | 0.08 |
| Respiratory tract infection | 1.76 (0.76–4.07) | 0.18 |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 0.89 (0.75–1.07) | 0.24 |
| White blood cells (×109/L) | 0.92 (0.38–2.21) | 0.85 |
| Aortic regurgitation | 1.74 (0.66–4.54) | 0.26 |
| Mitral regurgitation | 2.01 (0.89–4.55) | 0.09 |
| No. Patients | % of Patients | IE Diagnosis | Risk for IE | IE-Related Mortality | Non IE-Related Mortality | Heart Surgery | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR | CI 95% | p | |||||||
| Negative BCs | 127 | 34% | 9 (7.1%) | 1.00 * | - | - | 0 (0%) | 6 (4.6%) | 2 (1.6%) |
| 0 RF | 81 | 22% | 1 (1.2%) | 1.00 † | - | - | 0 (0%) | 3 (3.7%) | 1 (1.2%) |
| 1 RF | 38 | 10% | 3 (7.9%) | 1.2 | 0.28–5.00 | 0.82 | 0 (0%) | 3 (7.9%) | 1 (1.2%) |
| 2–3 RF | 8 | 2% | 5 (62.5%) | 48.0 | 8.37–275 | <0.001 | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) |
| Positive BCs | 248 | 66% | 47 (19%) | 3.1 | 1.45–6.48 | 0.003 | 13 (5.2%) | 34 (13.8%) | 13 (5.2%) |
| 0 RF | 148 | 39% | 16 (10.8%) | 1.6 | 0.68–3.73 | 0.29 | 4 (2.7%) | 20 (13.5%) | 5 (3.4%) |
| 1 RF | 79 | 21% | 16 (20.3%) | 3.3 | 1.39–7.96 | 0.007 | 3 (3.8%) | 14 (17.7%) | 5 (6.3%) |
| 2–3 RF | 21 | 6% | 15 (71.4%) | 33.0 | 10.2–105 | <0.001 | 6 (28.6%) | 0 (0%) | 3 (14.3%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cambise, N.; Tremamunno, S.; Marino, A.G.; Lenci, L.; De Benedetto, F.; Belmusto, A.; Tinti, L.; Di Renzo, A.; Di Perna, F.; Buonamassa, G.; et al. Transthoracic Echocardiography in Assessing Patients with Suspected Infective Endocarditis (TEASE): An Exploratory Study. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 2195. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14072195
Cambise N, Tremamunno S, Marino AG, Lenci L, De Benedetto F, Belmusto A, Tinti L, Di Renzo A, Di Perna F, Buonamassa G, et al. Transthoracic Echocardiography in Assessing Patients with Suspected Infective Endocarditis (TEASE): An Exploratory Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(7):2195. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14072195
Chicago/Turabian StyleCambise, Nello, Saverio Tremamunno, Angelo Giuseppe Marino, Ludovica Lenci, Fabio De Benedetto, Antonietta Belmusto, Lorenzo Tinti, Antonio Di Renzo, Federico Di Perna, Giacomo Buonamassa, and et al. 2025. "Transthoracic Echocardiography in Assessing Patients with Suspected Infective Endocarditis (TEASE): An Exploratory Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 7: 2195. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14072195
APA StyleCambise, N., Tremamunno, S., Marino, A. G., Lenci, L., De Benedetto, F., Belmusto, A., Tinti, L., Di Renzo, A., Di Perna, F., Buonamassa, G., Pontecorvo, S., De Vita, A., Camilli, M., Gabrielli, F. A., Graziani, F., Lamendola, P., Locorotondo, G., Natali, R., Lombardo, A., & Lanza, G. A. (2025). Transthoracic Echocardiography in Assessing Patients with Suspected Infective Endocarditis (TEASE): An Exploratory Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(7), 2195. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14072195








