Comparative Analysis of the Histological Characteristics of Bone Tissue Following Implant Drill Preparation Under Various Parameters: An In Vitro Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation
- Paltop: 2.0 mm, 2.4 mm, 3.75 mm
- Hiossen: 2.0 mm, 2.2 mm, 3.5 mm
- AnyRidge: 2.5 mm, 2.8 mm, 3.3 mm (Figure 1)
2.2. Study Groups
- Saline at room temperaturę (n = 6)
- Saline cooled to 4 °C (n = 6)
- No cooling (n = 6)
2.3. Fluorescence Microscopy Analysis
2.4. Qualitative Evaluation Criteria
- 0–7 = Poor quality
- 8–11 = Medium quality
- 12–16 = Good quality (Table 1)
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Hiossen ET—Fluorescence Microscopy Analysis
3.2. Anyridge—Fluorescence Microscopy Analysis
3.3. Paltop—Fluorescence Microscopy Analysis
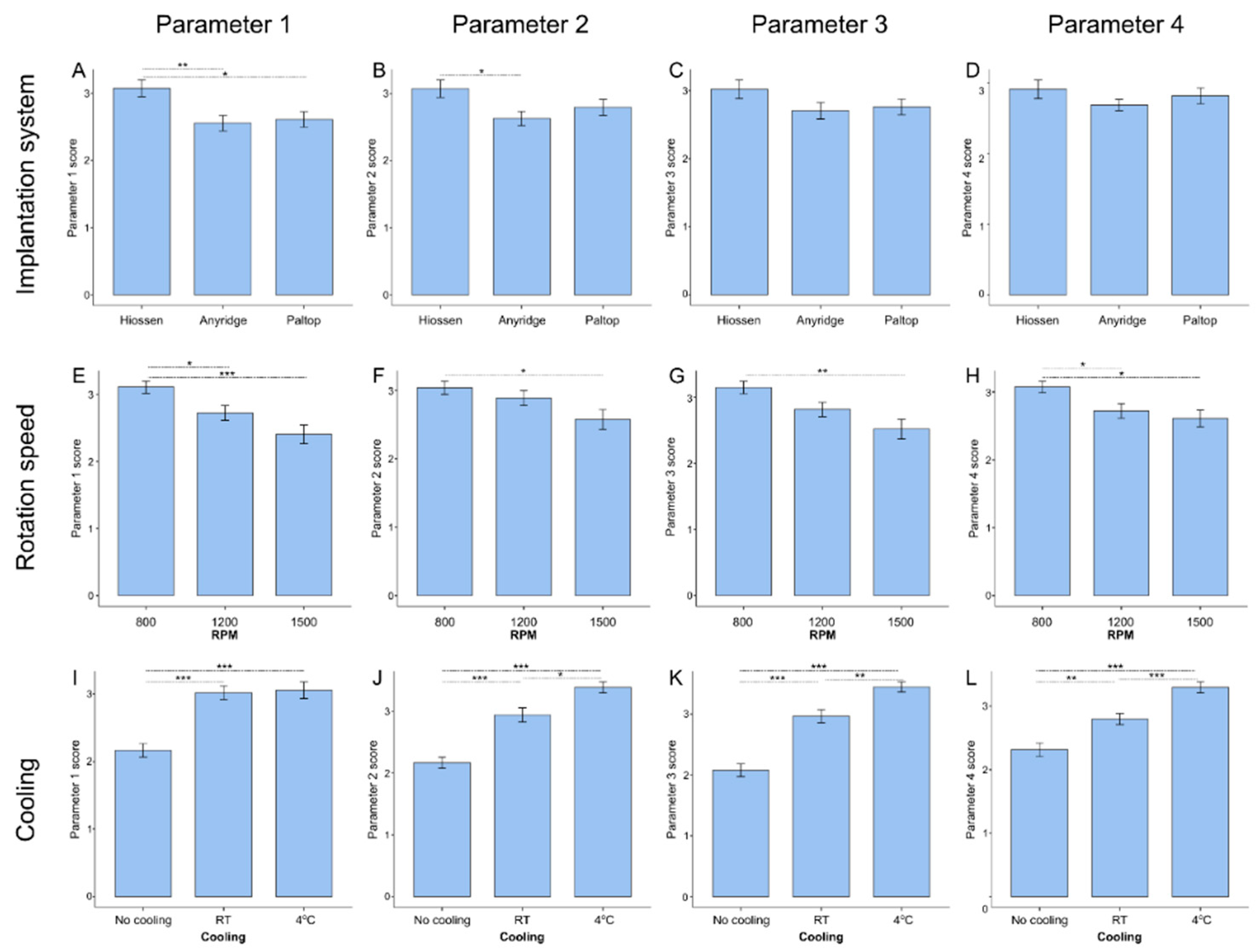
3.4. Influence of Distinct Drilling Parameters on Implantation Quality
3.5. Analysis of Optimal Combination of Drilling Parameters
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Da Silva Remísio, M.J.; Borges, T.; Castro, F.; Alexandre Gehrke, S.; Hasse Fernandes, J.C.; Vicentis de Oliveira Fernandes, G. Histologic Osseointegration Level Comparing Titanium and Zirconia Dental Implants: Meta-Analysis of Preclinical Studies. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2023, 38, 667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehrke, S.A.; Cortellari, G.C.; de Oliveira Fernandes, G.V.; Scarano, A.; Martins, R.G.; Cançado, R.M.; Mesquita, A.M.M. Randomized Clinical Trial Comparing Insertion Torque and Implant Stability of Two Different Implant Macrogeometries in the Initial Periods of Osseointegration. Medicina 2023, 59, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semez, G.; Elena Luca, R.; Cescato, A.; Faoro, V.; Emanuela Mocuţa, D.; Carmen Marilena Todea, D. Effect of the Laser Beam on Implant Site Preparation: A Preliminary Pilot Study. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol. 2018, 59, 861–867. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Makary, C.; Rebaudi, A.; Demircioglu, A.; Lahoud, P.; Naaman, N. Standard Drilling Versus Ultrasonic Implant Site Preparation: A Clinical Study at 4 Weeks after Insertion of Conical Implants. Implant Dent. 2017, 26, 547–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.H.; Coyac, B.R.; Arioka, M.; Leahy, B.; Tulu, U.S.; Aghvami, M.; Holst, S.; Hoffmann, W.; Quarry, A.; Bahat, O.; et al. A Novel Osteotomy Preparation Technique to Preserve Implant Site Viability and Enhance Osteogenesis. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vamsi, A.R.; Shenoy, S.B.; Chandran, T. Implant Practitioners’ Knowledge, Awareness and Attitudes Regarding Soft and Hard Tissue Considerations at a Single Implant Site: A Questionnaire Study. Dent. Med. Probl. 2023, 60, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, E.S.; Hall, J.L.; Handel, I.; Clements, D.N.; Ryan, J. Sequential Drilling and Drill Angulation Reduce the Accuracy of Drill Hole Start Location in a Synthetic Bone Model. Vet. Rec. 2019, 184, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, H.J.; Wikesjö, U.M.; Kang, H.S.; Ku, Y.; Eom, T.G.; Koo, K.T. Effect of Implant Drill Characteristics on Heat Generation in Osteotomy Sites: A Pilot Study. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2011, 22, 722–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettach, R.; Boukhris, G.; De Aza, P.N.; da Costa, E.M.; Scarano, A.; Fernandes, G.V.O.; Gehrke, S.A. New Strategy for Osseodensification during Osteotomy in Low-Density Bone: An in Vitro Experimental Study. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 11924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favero, V.; Sakuma, S.; Alccayhuaman, K.A.A.; Benedetto, G.A.; Bengazi, F.; Botticelli, D. Healing at Sites Prepared Using Different Drilling Protocols. An Experimental Study in the Tibiae of Sheep. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0202957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stocchero, M.; Toia, M.; Jinno, Y.; Cecchinato, F.; Becktor, J.P.; Naito, Y.; Halldin, A.; Jimbo, R. Influence of Different Drilling Preparation on Cortical Bone: A Biomechanical, Histological, and Micro-CT Study on Sheep. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2018, 29, 707–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutter, F.; Krekeler, G.; Schwammberger, A.E.; Sutter, F.J. Atraumatic Surgical Technique and Implant Bed Preparation. Quintessence Int. 1992, 23, 811. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Q.; Xia, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, C.; Hu, Y. Reduction Thermal Damage to Cortical Bone Using Ultrasonically-Assisted Drilling. Technol. Health Care 2018, 26, 843–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aghvami, M.; Brunski, J.B.; Tulu, U.S.; Chen, C.H.; Helms, J.A. A Thermal and Biological Analysis of Bone Drilling. J. Biomech. Eng. 2018, 140, 101010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharon, E.; Shapira, L.; Wilensky, A.; Abu-hatoum, R.; Smidt, A. Efficiency and Thermal Changes during Implantoplasty in Relation to Bur Type. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2013, 15, 292–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirstein, K.; Dobrzyński, M.; Kosior, P.; Chrószcz, A.; Dudek, K.; Fita, K.; Parulska, O.; Rybak, Z.; Skalec, A.; Szklarz, M.; et al. Infrared Thermographic Assessment of Cooling Effectiveness in Selected Dental Implant Systems. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 1879468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrak, I.; Joób-Fancsaly, A.; Varga, E.; Boa, K.; Piffko, J. Effect of the Combination of Low-Speed Drilling and Cooled Irrigation Fluid on Intraosseous Heat Generation during Guided Surgical Implant Site Preparation: An in Vitro Study. Implant Dent. 2017, 26, 541–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möhlhenrich, S.C.; Abouridouane, M.; Heussen, N.; Hölzle, F.; Klocke, F.; Modabber, A. Thermal Evaluation by Infrared Measurement of Implant Site Preparation between Single and Gradual Drilling in Artificial Bone Blocks of Different Densities. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2016, 45, 1478–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satpathy, M.A. Optimizing the Design of Reduced-Diameter Dental Implants to Increase Their Fatigue Lifetime. Ph.D. Thesis, The University of Mississippi Medical Center, Jackson, MS, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Bds, S.A.; Fakhouri, W.; Stylianou, P.; Angelov, N.; Pham, H. Temperature Changes for Straight Drills vs. Densah® Burs During Implant Osteotomy Preparations in Human Cadaver Tibiae. Master’s Thesis, The University of Texas School of Dentistry at Houston, Houston, TX, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, S.K.; Chowdhary, R. Heat Generated by Dental Implant Drills during Osteotomy-A Review. J. Indian Prosthodont. Soc. 2014, 14, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernabeu-Mira, J.C.; Soto-Peñaloza, D.; Peñarrocha-Diago, M.; Camacho-Alonso, F.; Rivas-Ballester, R.; Peñarrocha-Oltra, D. Low-Speed Drilling without Irrigation versus Conventional Drilling for Dental Implant Osteotomy Preparation: A Systematic Review. Clin. Oral Investig. 2021, 25, 4251–4267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalidindi, V. Optimization of Drill Design and Coolant Systems Optimization of Drill Design and Coolant Systems During Dental Implant Surgery During Dental Implant Surgery. Master’s Thesis, University of Kentucky, Lexington, KY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Möhlhenrich, S.C.; Modabber, A.; Steiner, T.; Mitchell, D.A.; Hölzle, F. Heat Generation and Drill Wear during Dental Implant Site Preparation: Systematic Review. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2015, 53, 679–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matys, J.; Flieger, R.; Dominiak, M. Assessment of Temperature Rise and Time of Alveolar Ridge Splitting by Means of Er:YAG Laser, Piezosurgery, and Surgical Saw: An Ex Vivo Study. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 9654975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matys, J.; Flieger, R.; Tenore, G.; Grzech-Leśniak, K.; Romeo, U.; Dominiak, M. Er:YAG Laser, Piezosurgery, and Surgical Drill for Bone Decortication during Orthodontic Mini-Implant Insertion: Primary Stability Analysis—An Animal Study. Lasers Med. Sci. 2018, 33, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, B.; Puthumanapully, P.K.; Amis, A.A. (Ii) Biomechanics of Implant Fixation. Orthop. Trauma 2013, 27, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Insua, A.; Galindo-Moreno, P.; Miron, R.J.; Wang, H.L.; Monje, A. Emerging Factors Affecting Peri-Implant Bone Metabolism. Periodontol 2000 2024, 94, 27–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosior, P.; Nikodem, A.; Kozuń, M.; Dudek, K.; Janeczek, M.; Dobrzyński, M. The Assessment of Temperature Amplitude Arising during the Implant Bed Formation in Relation to Variable Preparation Parameters—In Vitro Study. Acta Bioeng. Biomech. 2021, 23, 163–173. [Google Scholar]
- The Jamovi Project Jamovi—Open Statistical Software for the Desktop and Cloud (Version 2.3). Available online: https://www.jamovi.org/ (accessed on 20 February 2025).
- R Core Team R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. (Version 4.1). Available online: https://cran.r-project.org (accessed on 20 February 2025).
- Brånemark, P.I.; Zarb, G.A.; Albrektsson, T. Tissue—Integrated Prostheses. Osseointegration in Clinical Dentistry; Quintessence Publishing Co.: Chicago, IL, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Abuhussein, H.; Pagni, G.; Rebaudi, A.; Wang, H.L. The Effect of Thread Pattern upon Implant Osseointegration. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2010, 21, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dommeti, V.K.; Pramanik, S.; Roy, S. Design of Customized Coated Dental Implants Using Finite Element Analysis. Dent. Med. Probl. 2023, 60, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biju, D.; Arumugam, P.; Kannan, S.; Yadalam, P.K.; Ronsivalle, V.; Cicciù, M.; Minervini, G. Development, Characterization, and Biocompatibility and Corrosion Analyses of a Silver-Decorated Graphene Oxide and Chitosan Surface Coating for Titanium Dental Implants: A Preliminary Report. Dent. Med. Probl. 2024, 61, 627–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raines, A.L.; Berger, M.B.; Patel, N.; Hyzy, S.L.; Boyan, B.D.; Schwartz, Z. VEGF-A Regulates Angiogenesis during Osseointegration of Ti Implants via Paracrine/Autocrine Regulation of Osteoblast Response to Hierarchical Microstructure of the Surface. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2019, 107, 423–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Costa Fernandes, C.J.; Bezerra, F.J.B.; de Campos Souza, B.; Campos, M.A.; Zambuzzi, W.F. Titanium-Enriched Medium Drives Low Profile of ECM Remodeling as a Pre-Requisite to Pre-Osteoblast Viability and Proliferative Phenotype. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2018, 50, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orvalho, J.M.; Fernandes, J.C.H.; Moraes Castilho, R.; Fernandes, G.V.O. The Macrophage’s Role on Bone Remodeling and Osteogenesis: A Systematic Review. Clin. Rev. Bone Miner. Metab. 2023, 21, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosior, P.; Kuropka, P.; Janeczek, M.; Mikulewicz, M.; Zakrzewski, W.; Dobrzyński, M. The Influence of Various Preparation Parameters on the Histological Image of Bone Tissue during Implant Bed Preparation—An In Vitro Study. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coyac, B.R.; Salvi, G.; Leahy, B.; Li, Z.; Salmon, B.; Hoffmann, W.; Helms, J.A. A Novel System Exploits Bone Debris for Implant Osseointegration. J. Periodontol. 2021, 92, 716–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoegel, F.; Mueller, C.A.; Peter, R.; Pfister, U.; Suedkamp, N.P. Bone Debris: Dead Matter or Vital Osteoblasts. J. Trauma—Inj. Infect. Crit. Care 2004, 56, 363–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

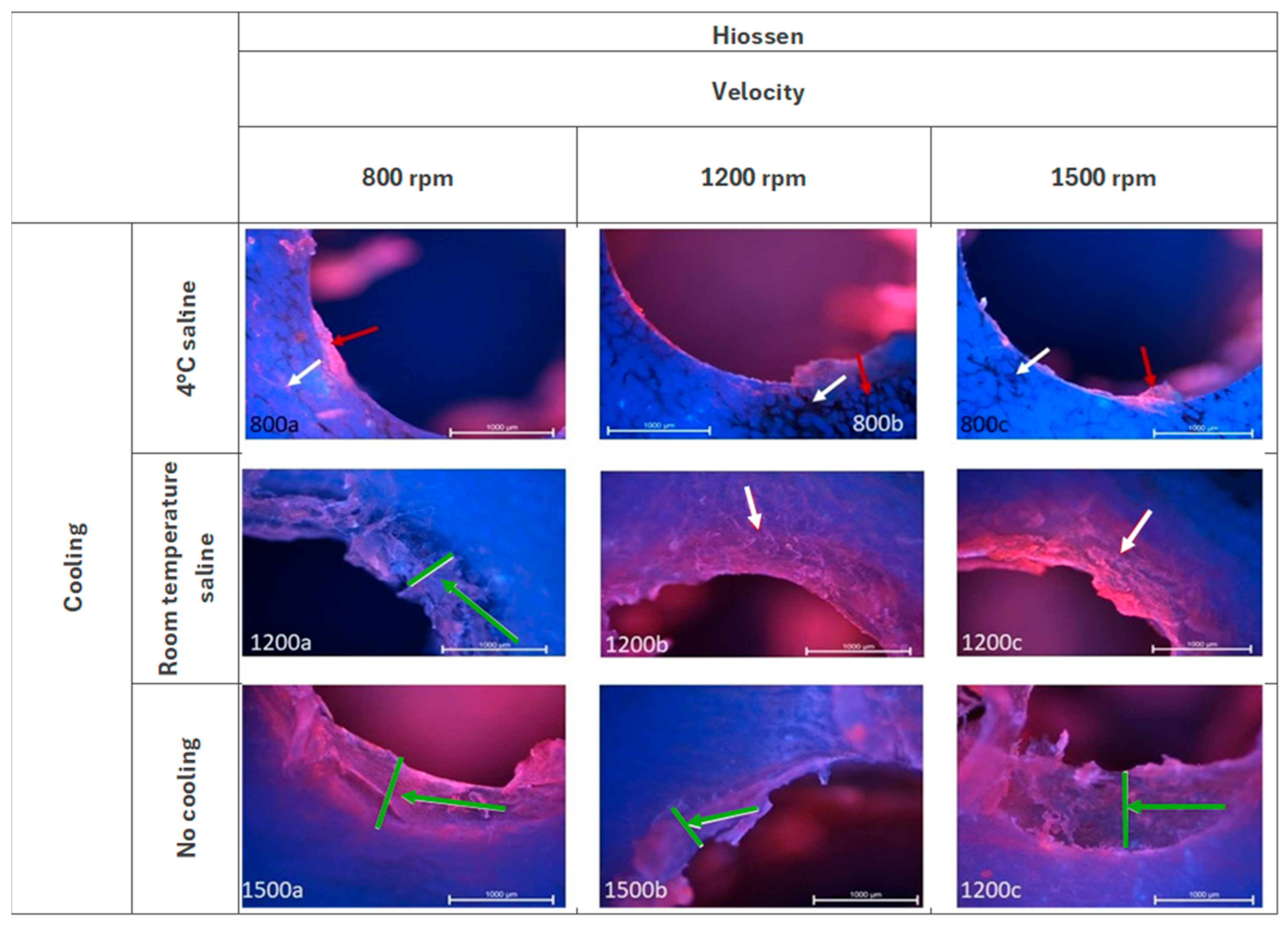
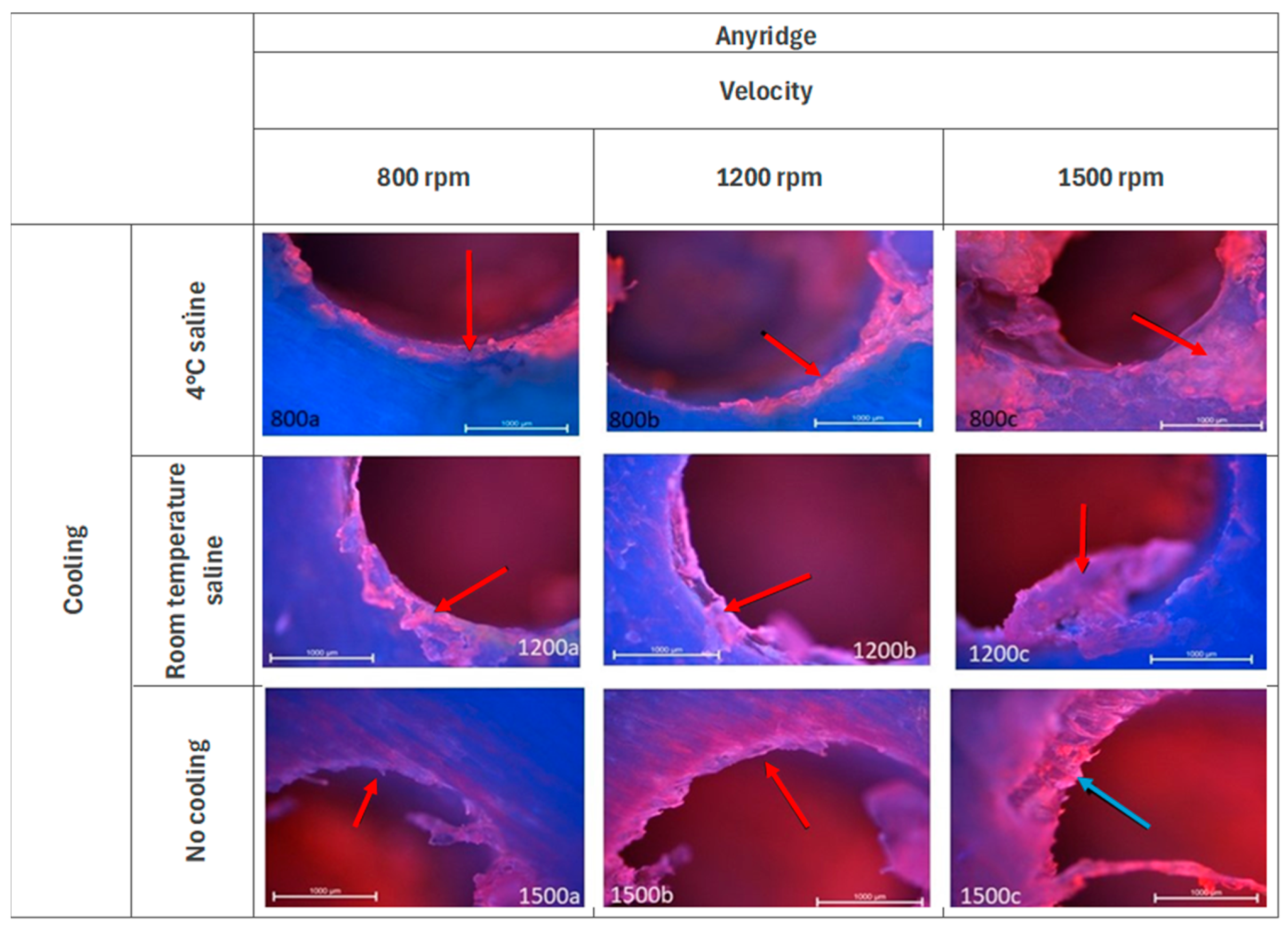
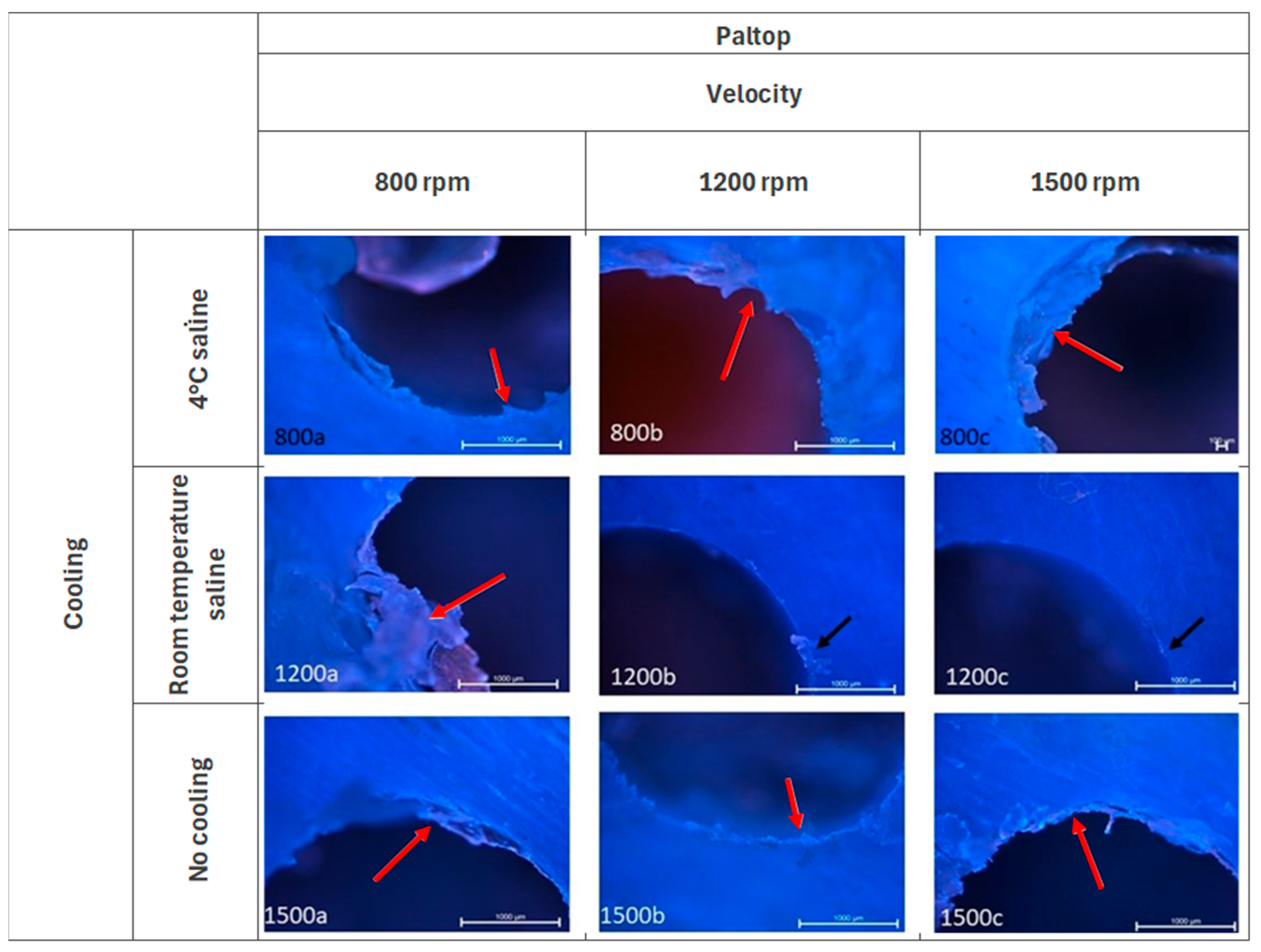

| Parameter | Score | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Surface Smoothness (torn edges, debris) | 1 | Heavily ragged edges with attached bone and soft tissue fragments filling the borehole |
| 2 | Ragged borehole edges with remnants of bone and soft tissue adjacent to the borehole edges | |
| 3 | Uneven borehole edges with isolated remnants of bone and soft tissue adjacent to the borehole edges | |
| 4 | Smooth surface with no noticeable remnants | |
| Compressed Tissue Presence (compaction) | 1 | Distinct tissue compression causing deformation in bone lamellae and adjacent tissues, extending up to 3 lamellae around the borehole |
| 2 | Distinct tissue compression causing deformation in bone lamellae adjacent to the borehole, extending up to 2 lamellae | |
| 3 | Slight compression of lamellae immediately adjacent to the borehole | |
| 4 | No tissue compression | |
| Carbonization (thermal damage) | 1 | Carbonization within bone lamellae extending up to 3 lamellae around the borehole |
| 2 | Carbonization within bone lamellae extending up to 2 lamellae around the borehole | |
| 3 | Carbonization within bone lamellae extending up to 1 lamella around the borehole | |
| 4 | No visible carbonization | |
| Cracking & Adjacent Tissue Damage | 1 | Cracks observed within 3 bone plates outward from the borehole |
| 2 | Cracks observed within 2 bone plates outward from the borehole | |
| 3 | Cracks observed within 1 bone plate outward from the borehole | |
| 4 | No cracks or damage to adjacent tissues |
| System-Rotation Speed-Cooling | P1 Score | P2 Score | P3 Score | P4 Score | Total Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hiossen-1200-4 °C | 3.83 | 3.83 | 3.83 | 3.83 | 15.3 |
| Paltop-800-4 °C | 3.67 | 3.83 | 3.83 | 3.83 | 15.2 |
| Hiossen-1500-4 °C | 3.83 | 3.67 | 3.67 | 3.5 | 14.7 |
| Hiossen-1200-RT | 3.5 | 3.83 | 3.67 | 3 | 14 |
| Hiossen-1500-RT | 3.33 | 3.33 | 3.5 | 3.83 | 14 |
| Anyridge-800-4 °C | 3.33 | 3.33 | 3.67 | 3.33 | 13.7 |
| Hiossen-800-4 °C | 3.33 | 3.33 | 3.67 | 3.33 | 13.7 |
| Paltop-800-RT | 3.5 | 3.17 | 3.5 | 3.17 | 13.3 |
| Hiossen-800-RT | 3.5 | 3.5 | 3 | 2.83 | 12.8 |
| Anyridge-1200-4 °C | 2.83 | 3 | 3.17 | 3 | 12 |
| Anyridge-800-RT | 3 | 2.67 | 3 | 2.83 | 11.5 |
| Paltop-1500-4 °C | 2 | 3.33 | 3 | 3.17 | 11.5 |
| Anyridge-1500-4 °C | 2 | 3.33 | 3.17 | 2.83 | 11.3 |
| Paltop-1200-4 °C | 2.67 | 2.83 | 3 | 2.83 | 11.3 |
| Anyridge-800-No cooling | 2.67 | 2.5 | 2.67 | 2.83 | 10.7 |
| Hiossen-800-No cooling | 2.5 | 2.67 | 2.5 | 2.67 | 10.3 |
| Paltop-1200-RT | 2.67 | 2.83 | 2.33 | 2.5 | 10.3 |
| Anyridge-1200-RT | 2.67 | 2.5 | 2.5 | 2.5 | 10.2 |
| Paltop-800-No cooling | 2.5 | 2.33 | 2.5 | 2.83 | 10.2 |
| Anyridge-1500-RT | 2.5 | 2.33 | 2.67 | 2.17 | 9.67 |
| Paltop-1200-No cooling | 2 | 2.5 | 2.5 | 2.67 | 9.67 |
| Paltop-1500-RT | 2.5 | 2.33 | 2.5 | 2.33 | 9.67 |
| Anyridge-1200-No cooling | 2 | 2.5 | 2.17 | 2.5 | 9.17 |
| Hiossen-1200-No cooling | 2.33 | 2.17 | 2.17 | 1.67 | 8.33 |
| Paltop-1500-No cooling | 2 | 2 | 1.67 | 2 | 7.67 |
| Anyridge-1500-No cooling | 2 | 1.5 | 1.33 | 2.17 | 7 |
| Hiossen-1500-No cooling | 1.5 | 1.33 | 1.17 | 1.5 | 5.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kosior, P.; Dobrzyński, M.; Wiśniewska, K.; Kulus, M.; Struzik, N.; Matys, J.; Kuropka, P. Comparative Analysis of the Histological Characteristics of Bone Tissue Following Implant Drill Preparation Under Various Parameters: An In Vitro Study. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 2161. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14072161
Kosior P, Dobrzyński M, Wiśniewska K, Kulus M, Struzik N, Matys J, Kuropka P. Comparative Analysis of the Histological Characteristics of Bone Tissue Following Implant Drill Preparation Under Various Parameters: An In Vitro Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(7):2161. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14072161
Chicago/Turabian StyleKosior, Piotr, Maciej Dobrzyński, Kamila Wiśniewska, Michał Kulus, Natalia Struzik, Jacek Matys, and Piotr Kuropka. 2025. "Comparative Analysis of the Histological Characteristics of Bone Tissue Following Implant Drill Preparation Under Various Parameters: An In Vitro Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 7: 2161. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14072161
APA StyleKosior, P., Dobrzyński, M., Wiśniewska, K., Kulus, M., Struzik, N., Matys, J., & Kuropka, P. (2025). Comparative Analysis of the Histological Characteristics of Bone Tissue Following Implant Drill Preparation Under Various Parameters: An In Vitro Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(7), 2161. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14072161







