Long-Term Complications Related to Cardiac Implantable Electronic Devices
Abstract
:1. Introduction
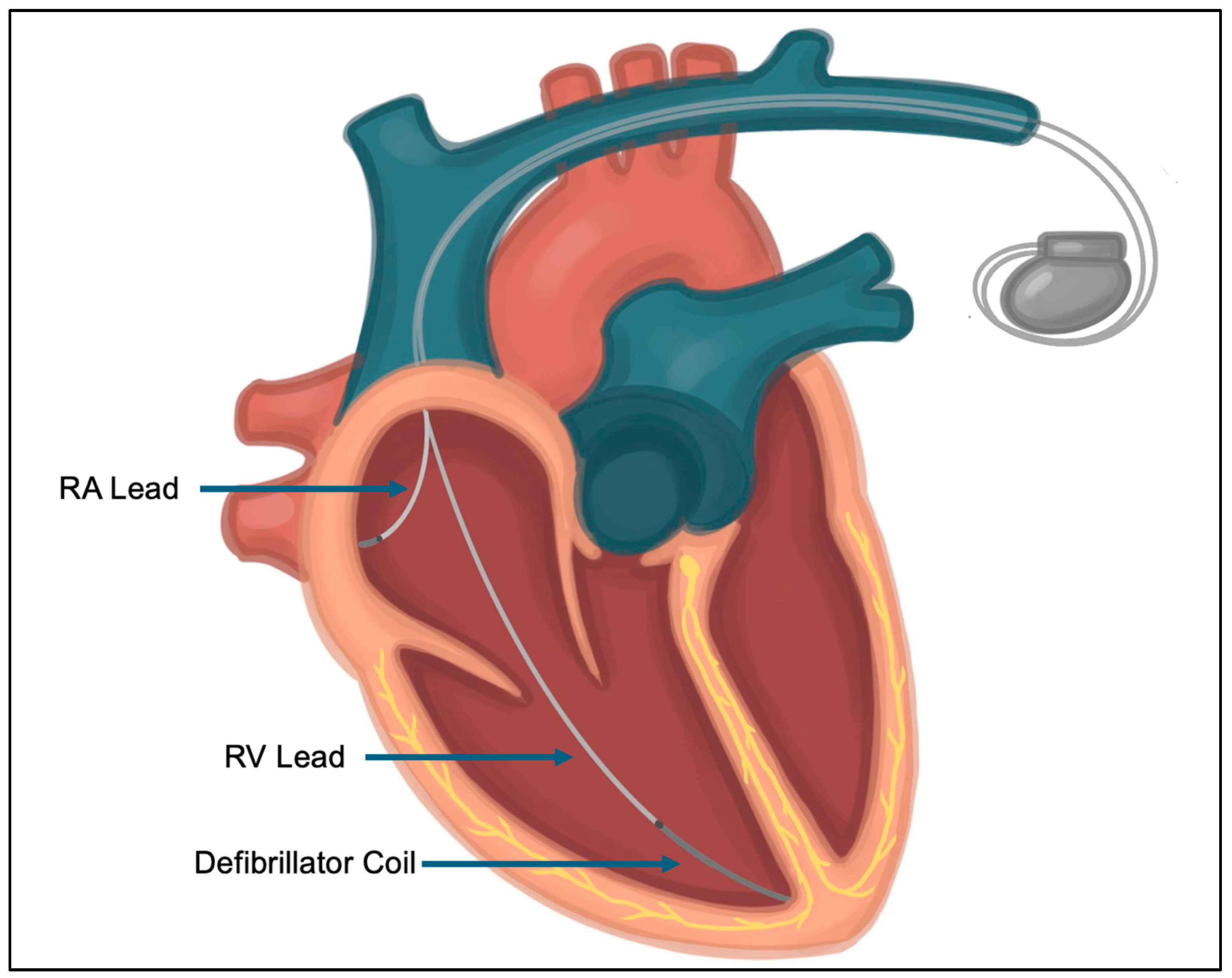
2. Lead-Related Complications
2.1. Lead Failure
| Risk Factor | Univariate HR (95% CI) | p-Value | Multivariate HR (95% CI) | p-Value | Paper |
| Age (years) | |||||
| ≥65 | 0.75 (0.66–0.85) | <0.001 | Koneru et al. 2018 [28] | ||
| <60 | 2.01 (1.15–3.53) | 0.012 | 2.33 (1.28–4.24) | 0.006 | Rordorf et al. 2013 [41] |
| Gender | |||||
| Female | 1.56 (1.18–2.08) | 0.002 | Birnie et al. 2012 [40] | ||
| Male | 0.80 (0.71–0.90) | <0.001 | Koneru et al. 2018 [28] | ||
| 0.80 (0.39–1.67) | 0.56 | Koike et al. 2023 [34] | |||
| 0.68 (0.36–1.29) | 0.26 | 0.71 (0.37–1.38) | 0.32 | Rordorf et al. 2013 [41] | |
| BMI | |||||
| 1.01 (0.92–1.10) | 0.79 | Koike et al. 2023 [34] | |||
| 0.99 (0.97–1.02) | 0.529 | Birnie et al. 2012 [40] | |||
| Cardiomyopathy class | |||||
| Ischemic | 1.68 (0.75–3.76) | 0.2 | Koike et al. 2023 [34] | ||
| 1.16 (0.67–2.00) | 0.607 | 1.97 (1.09–3.55) | 0.024 | Rordorf et al. 2013 [41] | |
| HCM | 1.08 (0.84–1.39) | 0.574 | Koneru et al. 2018 [28] | ||
| 0.29 (0.07–1.20) | 0.09 | Koike et al. 2023 [34] | |||
| 2.19 (1.03–4.64) | 0.041 | Birnie et al. 2012 [40] | |||
| Dilated | 0.63 (0.26–1.53) | 0.31 | Koike et al. 2023 [34] | ||
| ARVC | 0.91 (0.12–6.64) | 0.91 | Koike et al. 2023 [34] | ||
| Congenital heart disease | 3.16 (1.37–7.32) | 0.007 | 2.51 (1.08–5.83) | 0.03 | Koike et al. 2023 [34] |
| Other (ARVC, PED, IVF, Congenital) | 1.52 (0.93–2.49) | 0.095 | Birnie et al. 2012 [40] | ||
| History of MI | 0.84 (0.75–0.95) | 0.004 | Koneru et al. 2018 [28] | ||
| Total number of leads at implantation | 0.56 (0.32–0.95) | 0.04 | 0.59 (0.32–1.02) | 0.07 | Koike et al. 2023 [34] |
| Previous lead fracture or failure | 3.30 (2.14–5.08) | <0.001 | Birnie et al. 2012 [40] |
2.2. Venous Occlusion
2.3. Tricuspid Regurgitation
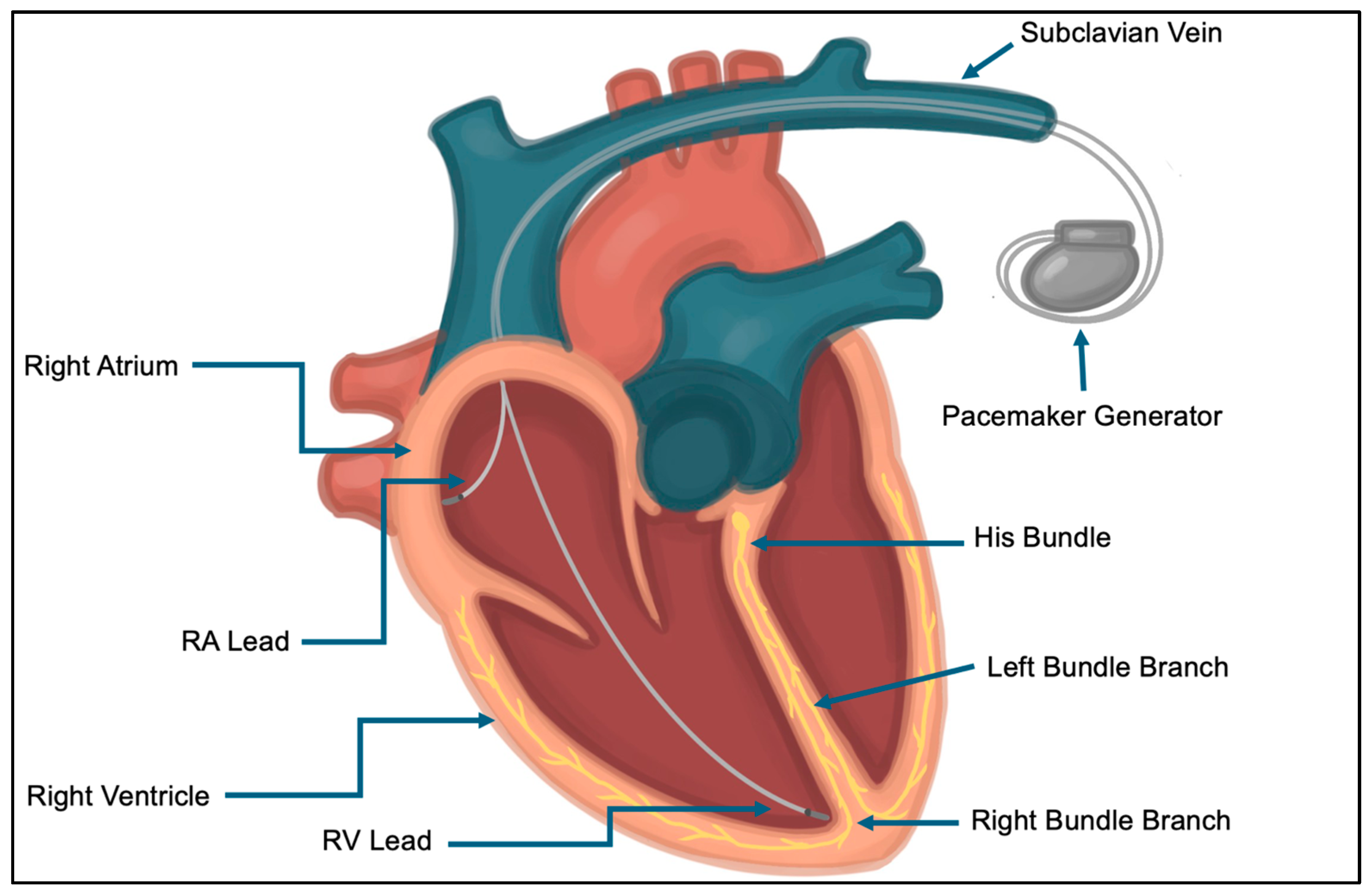
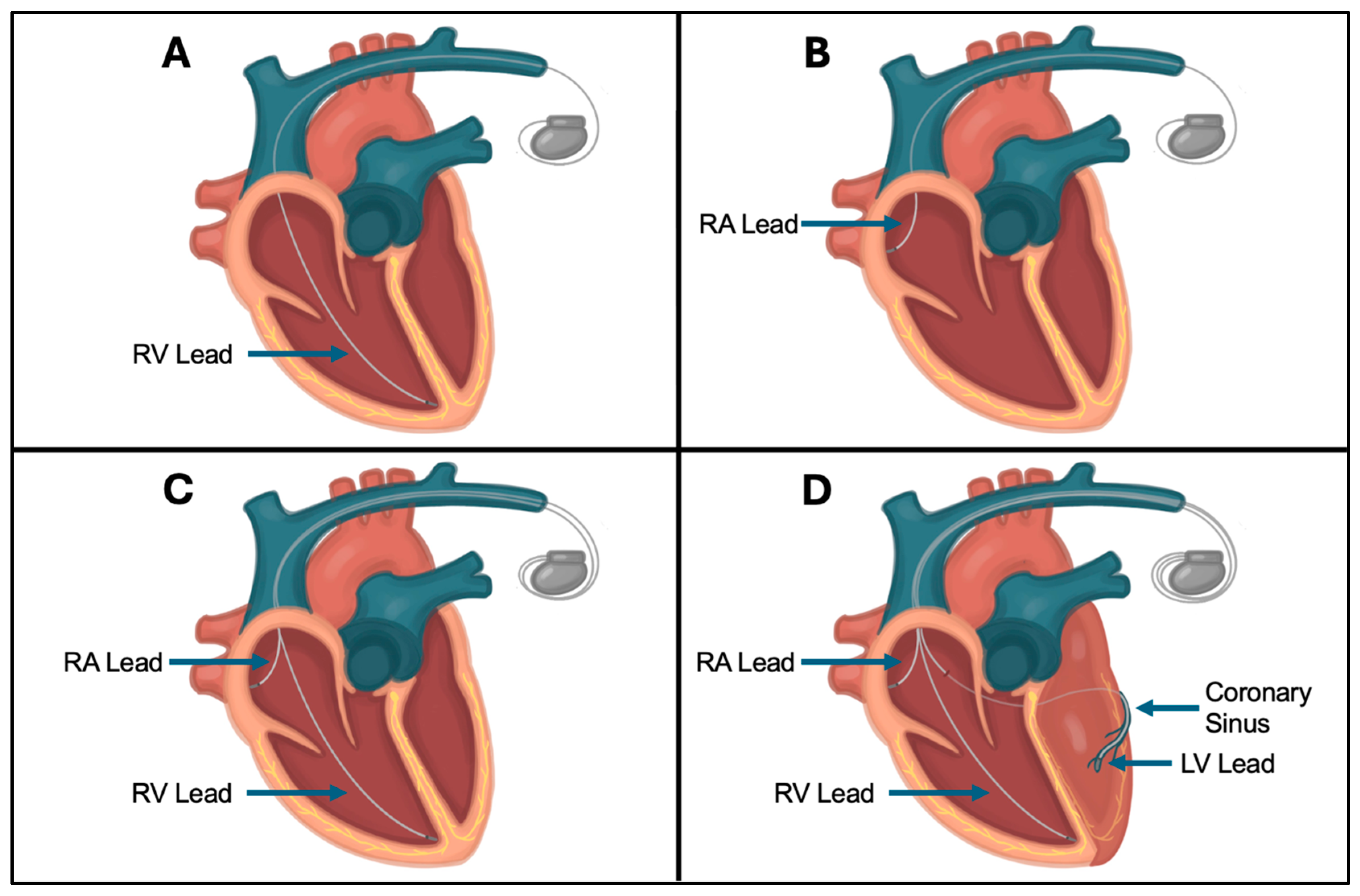
2.4. CIED Lead Placement and Fixation Techniques
2.5. Leadless Pacemakers and Emerging Technologies
3. CIED-Related Arrhythmias
3.1. Pacemaker-Induced Cardiomyopathy
3.2. Pacemaker Syndrome (Loss of AV Synchrony)
3.3. Inappropriate Device Shocks
3.4. Pacemaker-Mediated Tachycardia and Repetitive Non-Reentrant Ventriculoatrial Synchrony
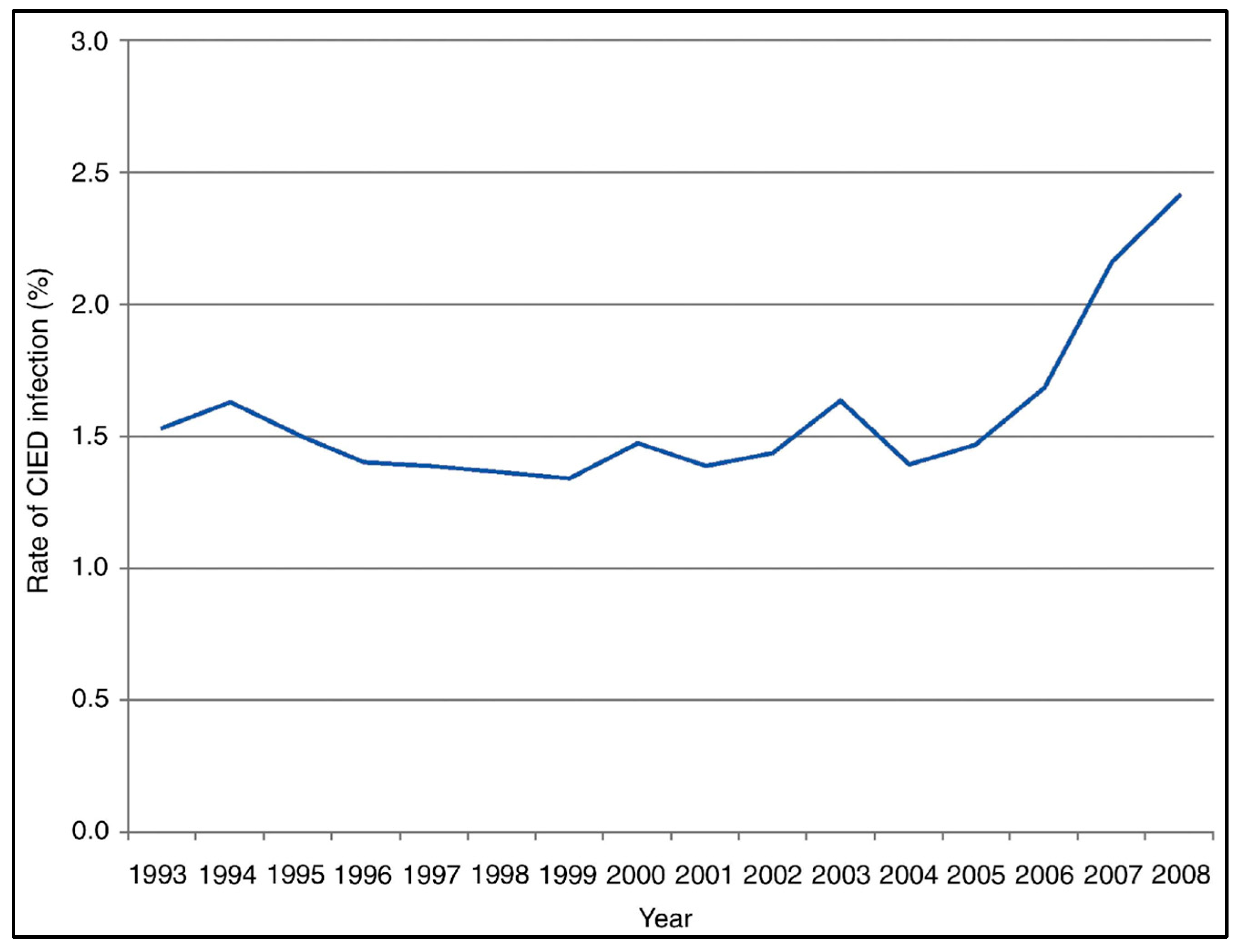
4. CIED Infections
5. Complications of Subcutaneous ICDs
5.1. Inappropriate Device Shocks
5.2. Infection
5.3. Pocket Hematoma
6. Psychological Impact of CIEDs
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AI | Aortic insufficiency. |
| ARVC | Arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy. |
| AV | Atrioventricular. |
| AVP | Axillary vein puncture. |
| BMI | Body mass index. |
| CHF | Congestive heart failure. |
| CIED | Cardiac implantable electronic device. |
| CKD | Chronic kidney disease. |
| COPD | Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. |
| CRT | Cardiac resynchronization therapy. |
| CRT-D | Cardiac resynchronization therapy defibrillator. |
| CRT-P | Cardiac resynchronization therapy pacemaker. |
| CSP | Conduction system pacing. |
| CVC | Cephalic vein cutdown. |
| CVO | Central venous obstruction. |
| CVS | Central venous stenosis. |
| DM | Diabetes mellitus. |
| ESRD | End-stage renal disease. |
| HCM | Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. |
| HV | High-voltage. |
| ICD | Implantable cardioverter–defibrillator. |
| ILR | Implantable loop recorder. |
| IVF | Idiopathic ventricular fibrillation. |
| IVUS | Intravascular ultrasound. |
| LBBB | Left bundle branch block. |
| LBBP | Left bundle branch pacing. |
| LIA | Lead Integrity Alert. |
| LL-PPM | Leadless pacemaker. |
| LNA | Lead Noise Algorithm. |
| LRL | Lower rate limit. |
| LRVO | Lead-related venous obstruction. |
| MI | Myocardial infarction. |
| PED | Primary electrical disease. |
| PiCM | Pacemaker-induced cardiomyopathy. |
| PMT | Pacemaker-mediated tachycardia. |
| PPM | Permanent pacemaker. |
| PTSD | Post-traumatic stress disorder. |
| PVARP | Post-ventricular atrial refractory period. |
| PVC | Premature ventricular contraction. |
| RA | Right atrium. |
| RBB | Right bundle branch. |
| RBP | Right bundle pacing. |
| RNRVAS | Repetitive non-reentrant ventriculoatrial synchrony. |
| RV | Right ventricle. |
| S-ICD | Subcutaneous ICD. |
| SVC | Superior vena cava. |
| SVP | Subclavian vein puncture. |
| TV-ICD | Traditional transvenous ICD. |
| TVP | Transvenous lead extraction. |
| TR | Tricuspid regurgitation. |
| VA | Ventriculoatrial. |
| VF | Ventricular fibrillation. |
| VT | Ventricular tachycardia. |
| VUS | Venous duplex ultrasound. |
References
- Haghjoo, M. Cardiac Implantable Electronic Devices. In Practical Cardiology: Principles and Approaches; Elsevier: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2018; pp. 251–260. [Google Scholar]
- Greenspon, A.J.; Patel, J.D.; Lau, E.; Ochoa, J.A.; Frisch, D.R.; Ho, R.T.; Pavri, B.B.; Kurtz, S.M. Trends in Permanent Pacemaker Implantation in the United States from 1993 to 2009: Increasing Complexity of Patients and Procedures. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2012, 60, 1540–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kusumoto, F.M.; Schoenfeld, M.H.; Barrett, C.; Edgerton, J.R.; Ellenbogen, K.A.; Gold, M.R.; Goldschlager, N.F.; Hamilton, R.M.; Joglar, J.A.; Kim, R.J.; et al. 2018 ACC/AHA/HRS Guideline on the Evaluation and Management of Patients with Bradycardia and Cardiac Conduction Delay: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines and the Heart Rhythm Society. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 140, e382–e482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Society of Cardiology (ESC); European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA); Brignole, M.; Auricchio, A.; Baron-Esquivias, G.; Bordachar, P.; Boriani, G.; Breithardt, O.-A.; Cleland, J.; Deharo, J.-C.; et al. 2013 ESC Guidelines on Cardiac Pacing and Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy: The Task Force on Cardiac Pacing and Resynchronization Therapy of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Developed in Collaboration with the European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA). Europace 2013, 15, 1070–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Khatib, S.M.; Stevenson, W.G.; Ackerman, M.J.; Bryant, W.J.; Callans, D.J.; Curtis, A.B.; Deal, B.J.; Dickfeld, T.; Field, M.E.; Fonarow, G.C.; et al. 2017 AHA/ACC/HRS Guideline for Management of Patients with Ventricular Arrhythmias and the Prevention of Sudden Cardiac Death: Executive Summary: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines and the Heart Rhythm Society. Circulation 2018, 138, e210–e271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yancy, C.W.; Jessup, M.; Bozkurt, B.; Butler, J.; Casey, D.E.; Colvin, M.M.; Drazner, M.H.; Filippatos, G.S.; Fonarow, G.C.; Givertz, M.M.; et al. 2017 ACC/AHA/HFSA Focused Update of the 2013 ACCF/AHA Guideline for the Management of Heart Failure: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines and the Heart Failure Society of America. Circulation 2017, 136, e137–e161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Priori, S.G.; Blomström-Lundqvist, C.; Mazzanti, A.; Blom, N.; Borggrefe, M.; Camm, J.; Elliott, P.M.; Fitzsimons, D.; Hatala, R.; Hindricks, G.; et al. 2015 ESC Guidelines for the Management of Patients with Ventricular Arrhythmias and the Prevention of Sudden Cardiac Death: The Task Force for the Management of Patients with Ventricular Arrhythmias and the Prevention of Sudden Cardiac Death of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Endorsed by: Association for European Paediatric and Congenital Cardiology (AEPC). Eur. Heart J. 2015, 36, 2793–2867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DiMarco, J.P. Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillators. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 349, 1836–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FDA Approves First Leadless Pacemaker to Treat Heart Rhythm Disorders. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-approves-first-leadless-pacemaker-treat-heart-rhythm-disorders (accessed on 4 April 2024).
- Reddy, V.Y.; Knops, R.E.; Sperzel, J.; Miller, M.A.; Petru, J.; Simon, J.; Sediva, L.; de Groot, J.R.; Tjong, F.V.Y.; Jacobson, P.; et al. Permanent Leadless Cardiac Pacing: Results of the LEADLESS Trial. Circulation 2014, 129, 1466–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auricchio, A.; Delnoy, P.-P.; Butter, C.; Brachmann, J.; Van Erven, L.; Spitzer, S.; Moccetti, T.; Seifert, M.; Markou, T.; Laszo, K.; et al. Feasibility, Safety, and Short-Term Outcome of Leadless Ultrasound-Based Endocardial Left Ventricular Resynchronization in Heart Failure Patients: Results of the Wireless Stimulation Endocardially for CRT (WiSE-CRT) Study. Europace 2014, 16, 681–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knops, R.E.; Tjong, F.V.Y.; Neuzil, P.; Sperzel, J.; Miller, M.A.; Petru, J.; Simon, J.; Sediva, L.; de Groot, J.R.; Dukkipati, S.R.; et al. Chronic Performance of a Leadless Cardiac Pacemaker: 1-Year Follow-up of the LEADLESS Trial. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2015, 65, 1497–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tjong, F.V.Y.; Knops, R.E.; Neuzil, P.; Petru, J.; Sediva, L.; Wilde, A.A.M.; Sperzel, J.; Reddy, V.Y. Midterm Safety and Performance of a Leadless Cardiac Pacemaker: 3-Year Follow-up to the LEADLESS Trial (Nanostim Safety and Performance Trial for a Leadless Cardiac Pacemaker System). Circulation 2018, 137, 633–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritter, P.; Duray, G.Z.; Steinwender, C.; Soejima, K.; Omar, R.; Mont, L.; Boersma, L.V.A.; Knops, R.E.; Chinitz, L.; Zhang, S.; et al. Early Performance of a Miniaturized Leadless Cardiac Pacemaker: The Micra Transcatheter Pacing Study. Eur. Heart J. 2015, 36, 2510–2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, M.A.; Neuzil, P.; Dukkipati, S.R.; Reddy, V.Y. Leadless Cardiac Pacemakers: Back to the Future. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2015, 66, 1179–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynolds, D.; Duray, G.Z.; Omar, R.; Soejima, K.; Neuzil, P.; Zhang, S.; Narasimhan, C.; Steinwender, C.; Brugada, J.; Lloyd, M.; et al. A Leadless Intracardiac Transcatheter Pacing System. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 533–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, V.Y.; Exner, D.V.; Cantillon, D.J.; Doshi, R.; Bunch, T.J.; Tomassoni, G.F.; Friedman, P.A.; Estes, N.A.M.; Ip, J.; Niazi, I.; et al. Percutaneous Implantation of an Entirely Intracardiac Leadless Pacemaker. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 1125–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, V.Y.; Miller, M.A.; Neuzil, P.; Søgaard, P.; Butter, C.; Seifert, M.; Delnoy, P.P.; van Erven, L.; Schalji, M.; Boersma, L.V.A.; et al. Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy with Wireless Left Ventricular Endocardial Pacing: The SELECT-LV Study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2017, 69, 2119–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckstein, J.; Koller, M.T.; Zabel, M.; Kalusche, D.; Schaer, B.A.; Osswald, S.; Sticherling, C. Necessity for Surgical Revision of Defibrillator Leads Implanted Long-Term: Causes and Management. Circulation 2008, 117, 2727–2733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kron, J.; Herre, J.; Renfroe, E.G.; Rizo-Patron, C.; Raitt, M.; Halperin, B.; Gold, M.; Goldner, B.; Wathen, M.; Wilkoff, B.; et al. Lead- and Device-Related Complications in the Antiarrhythmics versus Implantable Defibrillators Trial. Am. Heart J. 2001, 141, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleemann, T.; Becker, T.; Doenges, K.; Vater, M.; Senges, J.; Schneider, S.; Saggau, W.; Weisse, U.; Seidl, K. Annual Rate of Transvenous Defibrillation Lead Defects in Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillators Over a Period of >10 Years. Circulation 2007, 115, 2474–2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maisel, W.H.; Kramer, D.B. Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator Lead Performance. Circulation 2008, 117, 2721–2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, H.; Matheson, K.; Sapp, J.; Gardner, M.; Gray, C.; AbdelWahab, A.; Lee, D.; MacIntyre, C.; Parkash, R. Prevalence and Management of Electrical Lead Abnormalities in Cardiac Implantable Electronic Device Leads. Heart Rhythm. O2 2023, 4, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellenbogen, K.A.; Hellkamp, A.S.; Wilkoff, B.L.; Camunãs, J.L.; Love, J.C.; Hadjis, T.A.; Lee, K.L.; Lamas, G.A. Complications Arising after Implantation of DDD Pacemakers: The MOST Experience. Am. J. Cardiol. 2003, 92, 740–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauser, R.G.; Kallinen, L.M.; Almquist, A.K.; Gornick, C.C.; Katsiyiannis, W.T. Early Failure of a Small-Diameter High-Voltage Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator Lead. Heart Rhythm. 2007, 4, 892–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Rees, J.B.; van Welsenes, G.H.; Borleffs, C.J.W.; Thijssen, J.; van der Velde, E.T.; van der Wall, E.E.; van Erven, L.; Schalij, M.J. Update on Small-Diameter Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator Leads Performance. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. PACE 2012, 35, 652–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Chami, M.F.; Rao, B.; Shah, A.D.; Wood, C.; Sayegh, M.; Zakka, P.; Ginn, K.; Pallotta, L.; Evans, B.; Hoskins, M.H.; et al. Long-Term Performance of a Pacing Lead Family: A Single-Center Experience. Heart Rhythm. 2019, 16, 572–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koneru, J.N.; Jones, P.W.; Hammill, E.F.; Wold, N.; Ellenbogen, K.A. Risk Factors and Temporal Trends of Complications Associated with Transvenous Implantable Cardiac Defibrillator Leads. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2018, 7, e007691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallinen, L.M.; Hauser, R.G.; Lee, K.W.; Almquist, A.K.; Katsiyiannis, W.T.; Tang, C.Y.; Melby, D.P.; Gornick, C.C. Failure of Impedance Monitoring to Prevent Adverse Clinical Events Caused by Fracture of a Recalled High-Voltage Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator Lead. Heart Rhythm. 2008, 5, 775–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitamura, S.; Satomi, K.; Kurita, T.; Shimizu, W.; Suyama, K.; Aihara, N.; Niwaya, K.; Kobayashi, J.; Kamakura, S. Long-Term Follow-up of Transvenous Defibrillation Leads: High Incidence of Fracture in Coaxial Polyurethane Lead. Circ. J. Off. J. Jpn. Circ. Soc. 2006, 70, 273–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauser, R.G.; Cannom, D.; Hayes, D.L.; Parsonnet, V.; Hayes, J.; Ratliff, N.; Tyers, G.F.O.; Epstein, A.E.; Vlay, S.C.; Furman, S.; et al. Long-Term Structural Failure of Coaxial Polyurethane Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator Leads. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. PACE 2002, 25, 879–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aass, H.; Ilvento, J. Short and Medium Time Experience with a Tined, Multilumen Steroid Eluting Defibrillation Lead. J. Interv. Card. Electrophysiol. Int. J. Arrhythm. Pacing 2002, 6, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luria, D.; Glikson, M.; Brady, P.A.; Lexvold, N.Y.; Rasmussen, M.J.; Hodge, D.O.; Chugh, S.S.; Rea, R.F.; Hayes, D.L.; Hammill, S.C.; et al. Predictors and Mode of Detection of Transvenous Lead Malfunction in Implantable Defibrillators. Am. J. Cardiol. 2001, 87, 901–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koike, T.; Shoda, M.; Ejima, K.; Yagishita, D.; Suzuki, A.; Hasegawa, S.; Kataoka, S.; Yazaki, K.; Higuchi, S.; Kanai, M.; et al. Impact of Fracture-prone Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator Leads on Long-term Patient Mortality. J. Arrhythmia 2023, 39, 454–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrison, T.B.; Friedman, P.A.; Kallinen, L.M.; Hodge, D.O.; Crusan, D.; Kumar, K.; Hayes, D.L.; Rea, R.F.; Hauser, R.G. Impact of Implanted Recalled Sprint Fidelis Lead on Patient Mortality. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2011, 58, 278–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verlato, R.; Facchin, D.; Catanzariti, D.; Molon, G.; Zanotto, G.; Morani, G.; Brieda, M.; Zanon, F.; Delise, P.; Leoni, L.; et al. Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillators and Sprint Fidelis Leads. Heart Br. Card. Soc. 2013, 99, 799–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, M.T.; Ha, A.C.T.; Exner, D.V.; Tung, S.K.K.; Parkash, R.; Connors, S.; Coutu, B.; Crystal, E.; Champagne, J.; Philippon, F.; et al. The Canadian Experience with Durata and Riata ST Optim Defibrillator Leads: A Report from the Canadian Heart Rhythm Society Device Committee. Heart Rhythm. 2013, 10, 1478–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khattak, F.; Gupta, A.; Alluri, K.; Shariff, N.; Saba, S. Rate and Predictors of Electrical Failure in Non-Recalled Defibrillator Leads. Indian Pacing Electrophysiol. J. 2018, 19, 100–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, A.C.T.; Vezi, B.Z.; Keren, A.; Alanazi, H.; Gollob, M.H.; Green, M.S.; Lemery, R.; Nery, P.B.; Posan, E.; Birnie, D.H. Predictors of Fracture Risk of a Small Caliber Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator Lead. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. PACE 2010, 33, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birnie, D.H.; Parkash, R.; Exner, D.V.; Essebag, V.; Healey, J.S.; Verma, A.; Coutu, B.; Kus, T.; Mangat, I.; Ayala-Paredes, F.; et al. Clinical Predictors of Fidelis Lead Failure. Circulation 2012, 125, 1217–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rordorf, R.; Poggio, L.; Savastano, S.; Vicentini, A.; Petracci, B.; Chieffo, E.; Klersy, C.; Landolina, M. Failure of Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator Leads: A Matter of Lead Size? Heart Rhythm. 2013, 10, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.; Davogustto, G.; Huang, S.; Crossley, G.H.; Montgomery, J.A. Clinical and Radiographic Predictors of Cardiovascular Implantable Electronic Device Lead Failure at the Time of Initial Implantation. J. Arrhythmia 2021, 37, 1086–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauser, R.G.; Abdelhadi, R.; McGriff, D.; Retel, L.K. Deaths Caused by the Failure of Riata and Riata ST Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator Leads. Heart Rhythm. 2012, 9, 1227–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maisel, W.H. Pacemaker and ICD Generator Reliability: Meta-Analysis of Device Registries. JAMA 2006, 295, 1929–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medtronic Physician Advisory Letter-October 15th 2007. Available online: https://www.medtronic.com/us-en/healthcare-professionals/products/product-performance/sprint-fidelis-physician-10-15-2007.html (accessed on 4 April 2024).
- Class 1 Device Recall Medtronic Sprint Fidelis Lead. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cdrh/cfdocs/cfres/res.cfm?id=65383 (accessed on 12 March 2024).
- Class 1 Device Recall Riata ST Silicone Insulated Leads. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cdrh/cfdocs/cfres/res.cfm?id=105847 (accessed on 12 March 2024).
- Class 2 Device Recall Implantable Defibrillation Lead. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cdrh/cfdocs/cfres/res.cfm?id=115895 (accessed on 3 April 2024).
- Kramer, D.B.; Hatfield, L.A.; McGriff, D.; Ellis, C.R.; Gura, M.T.; Samuel, M.; Retel, L.K.; Hauser, R.G. Transvenous Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator Lead Reliability: Implications for Postmarket Surveillance. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2015, 4, e001672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slotwiner, D.; Varma, N.; Akar, J.G.; Annas, G.; Beardsall, M.; Fogel, R.I.; Galizio, N.O.; Glotzer, T.V.; Leahy, R.A.; Love, C.J.; et al. HRS Expert Consensus Statement on Remote Interrogation and Monitoring for Cardiovascular Implantable Electronic Devices. Heart Rhythm. 2015, 12, e69–e100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kusumoto, F.M.; Schoenfeld, M.H.; Wilkoff, B.L.; Berul, C.I.; Birgersdotter-Green, U.M.; Carrillo, R.; Cha, Y.-M.; Clancy, J.; Deharo, J.-C.; Ellenbogen, K.A.; et al. 2017 HRS Expert Consensus Statement on Cardiovascular Implantable Electronic Device Lead Management and Extraction. Heart Rhythm. 2017, 14, e503–e551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swerdlow, C.D.; Kalahasty, G.; Ellenbogen, K.A. Implantable Cardiac Defibrillator Lead Failure and Management. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2016, 67, 1358–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swerdlow, C.D.; Gunderson, B.D.; Ousdigian, K.T.; Abeyratne, A.; Sachanandani, H.; Ellenbogen, K.A. Downloadable Software Algorithm Reduces Inappropriate Shocks Caused by Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator Lead Fractures. Circulation 2010, 122, 1449–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beau, S.; Greer, S.; Ellis, C.R.; Keeney, J.; Asopa, S.; Arnold, E.; Fischer, A. Performance of an ICD Algorithm to Detect Lead Noise and Reduce Inappropriate Shocks. J. Interv. Card. Electrophysiol. Int. J. Arrhythm. Pacing 2016, 45, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunderson, B.D.; Gillberg, J.M.; Wood, M.A.; Vijayaraman, P.; Shepard, R.K.; Ellenbogen, K.A. Development and Testing of an Algorithm to Detect Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator Lead Failure. Heart Rhythm. 2006, 3, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wollmann, C.G.; Böcker, D.; Löher, A.; Köbe, J.; Scheld, H.H.; Breithardt, G.E.; Gradaus, R. Incidence of Complications in Patients with Implantable Cardioverter/Defibrillator Who Receive Additional Transvenous Pace/Sense Leads. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. PACE 2005, 28, 795–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrick, A.M.; Raj, S.R.; Deneke, T.; Kojodjojo, P.; Lopez-Cabanillas, N.; Abe, H.; Boveda, S.; Chew, D.S.; Choi, J.-I.; Dagres, N.; et al. 2023 HRS/EHRA/APHRS/LAHRS Expert Consensus Statement on Practical Management of the Remote Device Clinic. Europace 2023, 25, euad123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altman, D.G.; Bland, J.M. How to Obtain the P Value from a Confidence Interval. BMJ 2011, 343, d2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimetbaum, P.; Carroll, B.J.; Locke, A.H.; Secemsky, E.; Schermerhorn, M. Lead-Related Venous Obstruction in Patients with Implanted Cardiac Devices: JACC Review Topic of the Week. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2022, 79, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duijzer, D.; de Winter, M.A.; Nijkeuter, M.; Tuinenburg, A.E.; Westerink, J. Upper Extremity Deep Vein Thrombosis and Asymptomatic Vein Occlusion in Patients with Transvenous Leads: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 698336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacko, A.; Kozyra-Pydyś, E.; Gawałko, M.; Opolski, G.; Grabowski, M. Predictors of Venous Stenosis or Occlusion Following First Transvenous Cardiac Device Implantation: Prospective Observational Study. J. Vasc. Access 2019, 20, 495–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santini, M.; Di Fusco, S.A.; Santini, A.; Magris, B.; Pignalberi, C.; Aquilani, S.; Colivicchi, F.; Gargaro, A.; Ricci, R.P. Prevalence and Predictor Factors of Severe Venous Obstruction after Cardiovascular Electronic Device Implantation. Europace 2016, 18, 1220–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haghjoo, M.; Nikoo, M.H.; Fazelifar, A.F.; Alizadeh, A.; Emkanjoo, Z.; Sadr-Ameli, M.A. Predictors of Venous Obstruction Following Pacemaker or Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator Implantation: A Contrast Venographic Study on 100 Patients Admitted for Generator Change, Lead Revision, or Device Upgrade. Europace 2007, 9, 328–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korkeila, P.; Nyman, K.; Ylitalo, A.; Koistinen, J.; Karjalainen, P.; Lund, J.; Airaksinen, K.E.J. Venous Obstruction after Pacemaker Implantation. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. PACE 2007, 30, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferro, E.G.; Kramer, D.B.; Li, S.; Locke, A.H.; Misra, S.; Schmaier, A.A.; Carroll, B.J.; Song, Y.; D’Avila, A.A.; Yeh, R.W.; et al. Incidence, Treatment, and Outcomes of Symptomatic Device Lead-Related Venous Obstruction. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2023, 81, 2328–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizi, A.H.; Shafi, I.; Shah, N.; Rosenfield, K.; Schainfeld, R.; Sista, A.; Bashir, R. Superior Vena Cava Syndrome. JACC Cardiovasc. Interv. 2020, 13, 2896–2910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, T.W.; Rodriguez, R.M.; Light, R.W. The Superior Vena Cava Syndrome: Clinical Characteristics and Evolving Etiology. Medicine 2006, 85, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horlbeck, F.W.; Eckerth, C.; Linhart, M.; Schaefer, C.; Jakob, M.; Pingel, S.; Klarmann-Schulz, U.; Nickenig, G.; Schwab, J.O. Long-Term Incidence of Upper Extremity Venous Obstruction in Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator Patients. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. PACE 2021, 44, 1027–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Costa, S.S.d.C.; Scalabrini Neto, A.; Costa, R.; Caldas, J.G.; Martinelli Filho, M. Incidence and Risk Factors of Upper Extremity Deep Vein Lesions after Permanent Transvenous Pacemaker Implant: A 6-Month Follow-up Prospective Study. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. PACE 2002, 25, 1301–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zucker, E.J.; Ganguli, S.; Ghoshhajra, B.B.; Gupta, R.; Prabhakar, A.M. Imaging of Venous Compression Syndromes. Cardiovasc. Diagn. Ther. 2016, 6, 519–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brownie, E.R.; Abuirqeba, A.A.; Ohman, J.W.; Rubin, B.G.; Thompson, R.W. False-Negative Upper Extremity Ultrasound in the Initial Evaluation of Patients with Suspected Subclavian Vein Thrombosis Due to Thoracic Outlet Syndrome (Paget-Schroetter Syndrome). J. Vasc. Surg. Venous Lymphat. Disord. 2020, 8, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lossau Née Elss, T.; Nickisch, H.; Wissel, T.; Morlock, M.; Grass, M. Learning Metal Artifact Reduction in Cardiac CT Images with Moving Pacemakers. Med. Image Anal. 2020, 61, 101655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.Y.; Merkle, E.M. Time-Resolved MR Angiography of the Central Veins of the Chest. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2008, 191, 1581–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, R.F.; Petersen, S.E.; Ferguson, J.D.; Bashir, Y. Managing Superior Vena Cava Syndrome as a Complication of Pacemaker Implantation: A Pooled Analysis of Clinical Practice. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. PACE 2010, 33, 420–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borsato, G.W.; Rajan, D.K.; Simons, M.E.; Sniderman, K.W.; Tan, K.T. Central Venous Stenosis Associated with Pacemaker Leads: Short-Term Results of Endovascular Interventions. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. JVIR 2012, 23, 363–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asif, A.; Salman, L.; Carrillo, R.G.; Garisto, J.D.; Lopera, G.; Barakat, U.; Lenz, O.; Yevzlin, A.; Agarwal, A.; Gadalean, F.; et al. Patency Rates for Angioplasty in the Treatment of Pacemaker-Induced Central Venous Stenosis in Hemodialysis Patients: Results of a Multi-Center Study. Semin. Dial. 2009, 22, 671–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, T.F.; Myers, G.R.; Cicone, J. Central Vein Stenosis or Occlusion Associated with Cardiac Rhythm Management Device Leads in Hemodialysis Patients with Ipsilateral Arteriovenous Access: A Retrospective Study of Treatment Using Stents or Stent-Grafts. J. Vasc. Access 2010, 11, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addetia, K.; Harb, S.C.; Hahn, R.T.; Kapadia, S.; Lang, R.M. Cardiac Implantable Electronic Device Lead-Induced Tricuspid Regurgitation. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2019, 12, 622–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.D.; Manning, W.J.; Ebrille, E.; Zimetbaum, P.J. Tricuspid Valve Dysfunction Following Pacemaker or Cardioverter-Defibrillator Implantation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2017, 69, 2331–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delling, F.N.; Hassan, Z.K.; Piatkowski, G.; Tsao, C.W.; Rajabali, A.; Markson, L.J.; Zimetbaum, P.J.; Manning, W.J.; Chang, J.D.; Mukamal, K.J. Tricuspid Regurgitation and Mortality in Patients with Transvenous Permanent Pacemaker Leads. Am. J. Cardiol. 2016, 117, 988–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.B.; Spevack, D.M.; Tunick, P.A.; Bullinga, J.R.; Kronzon, I.; Chinitz, L.A.; Reynolds, H.R. The Effect of Transvenous Pacemaker and Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator Lead Placement on Tricuspid Valve Function: An Observational Study. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. Off. Publ. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2008, 21, 284–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klutstein, M.; Balkin, J.; Butnaru, A.; Ilan, M.; Lahad, A.; Rosenmann, D. Tricuspid Incompetence Following Permanent Pacemaker Implantation. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. PACE 2009, 32 (Suppl. S1), S135–S137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, G.; Nishimura, R.A.; Connolly, H.M.; Dearani, J.A.; Sundt, T.M.; Hayes, D.L. Severe Symptomatic Tricuspid Valve Regurgitation Due to Permanent Pacemaker or Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator Leads. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2005, 45, 1672–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paniagua, D.; Aldrich, H.R.; Lieberman, E.H.; Lamas, G.A.; Agatston, A.S. Increased Prevalence of Significant Tricuspid Regurgitation in Patients with Transvenous Pacemakers Leads. Am. J. Cardiol. 1998, 82, 1130–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, G.; Margossian, R.; Alexander, M.E.; Cecchin, F.; Triedman, J.K.; Walsh, E.P.; Berul, C.I. Impact of Transvenous Ventricular Pacing Leads on Tricuspid Regurgitation in Pediatric and Congenital Heart Disease Patients. J. Interv. Card. Electrophysiol. Int. J. Arrhythm. Pacing 2008, 21, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höke, U.; Auger, D.; Thijssen, J.; Wolterbeek, R.; van der Velde, E.T.; Holman, E.R.; Schalij, M.J.; Bax, J.J.; Delgado, V.; Marsan, N.A. Significant Lead-Induced Tricuspid Regurgitation Is Associated with Poor Prognosis at Long-Term Follow-Up. Heart Br. Card. Soc. 2014, 100, 960–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Bawardy, R.; Krishnaswamy, A.; Rajeswaran, J.; Bhargava, M.; Wazni, O.; Wilkoff, B.; Tuzcu, E.M.; Martin, D.; Thomas, J.; Blackstone, E.; et al. Tricuspid Regurgitation and Implantable Devices. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. PACE 2015, 38, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arabi, P.; Özer, N.; Ateş, A.H.; Yorgun, H.; Oto, A.; Aytemir, K. Effects of Pacemaker and Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator Electrodes on Tricuspid Regurgitation and Right Sided Heart Functions. Cardiol. J. 2015, 22, 637–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fanari, Z.; Hammami, S.; Hammami, M.B.; Hammami, S.; Shuraih, M. The Effects of Right Ventricular Apical Pacing with Transvenous Pacemaker and Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator on Mitral and Tricuspid Regurgitation. J. Electrocardiol. 2015, 48, 791–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, R.C.; Friedman, S.E.; Kono, A.T.; Greenberg, M.L.; Palac, R.T. Tricuspid Regurgitation Following Implantation of Endocardial Leads: Incidence and Predictors. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. PACE 2015, 38, 1267–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, Y.; Ishizu, T.; Nakajima, H.; Sekiguchi, Y.; Watanabe, S.; Aonuma, K. Clinical Utility of 3-Dimensional Echocardiography in the Evaluation of Tricuspid Regurgitation Caused by Pacemaker Leads. Circ. J. Off. J. Jpn. Circ. Soc. 2008, 72, 1465–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, J.; Kim, D.-Y.; Cho, I.; Hong, G.-R.; Ha, J.-W.; Shim, C.Y. Prevalence, Predictors, and Prognosis of Tricuspid Regurgitation Following Permanent Pacemaker Implantation. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0235230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tatum, R.; Maynes, E.J.; Wood, C.T.; Deb, A.K.; Austin, M.A.; O’Malley, T.J.; Choi, J.H.; Massey, H.T.; Morris, R.J.; Pavri, B.B.; et al. Tricuspid Regurgitation Associated with Implantable Electrical Device Insertion: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. PACE 2021, 44, 1297–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-X.; Wei, M.; Xiang, R.; Lu, Y.-M.; Zhang, L.; Li, Y.-D.; Zhang, J.-H.; Xing, Q.; Tu-Erhong, Z.K.; Tang, B.-P.; et al. Incidence, Risk Factors, and Prognosis of Tricuspid Regurgitation After Cardiac Implantable Electronic Device Implantation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Cardiothorac. Vasc. Anesth. 2022, 36, 1741–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mutlak, D.; Aronson, D.; Lessick, J.; Reisner, S.A.; Dabbah, S.; Agmon, Y. Functional Tricuspid Regurgitation in Patients with Pulmonary Hypertension: Is Pulmonary Artery Pressure the Only Determinant of Regurgitation Severity? Chest 2009, 135, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.W.; Gwag, H.B.; Hwang, J.K.; Chun, K.J.; Park, K.-M.; On, Y.K.; Kim, J.S.; Park, S.-J. Clinical Features, Predictors, and Long-Term Prognosis of Pacing-Induced Cardiomyopathy. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2019, 21, 643–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Cock, C.C.; Vinkers, M.; Van Campe, L.C.; Verhorst, P.M.; Visser, C.A. Long-Term Outcome of Patients with Multiple (> or = 3) Noninfected Transvenous Leads: A Clinical and Echocardiographic Study. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. PACE 2000, 23, 423–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Postaci, N.; Ekşi, K.; Bayata, S.; Yeşil, M. Effect of the Number of Ventricular Leads on Right Ventricular Hemodynamics in Patients with Permanent Pacemaker. Angiology 1995, 46, 421–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celiker, C.; Küçükoglu, M.S.; Arat-Ozkan, A.; Yazicioglu, N.; Uner, S. Right Ventricular and Tricuspid Valve Function in Patients with Two Ventricular Pacemaker Leads. Jpn. Heart J. 2004, 45, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krupa, W.; Kozłowski, D.; Derejko, P.; Swiatecka, G. Permanent Cardiac Pacing and Its Influence on Tricuspid Valve Function. Folia Morphol. 2001, 60, 249–257. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, T.-E.; Wang, C.-C.; Chern, M.-S.; Chu, J.-J. Entrapment of Permanent Pacemaker Lead as the Cause of Tricuspid Regurgitation. Circ. J. Off. J. Jpn. Circ. Soc. 2007, 71, 1169–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Champagne, J.; Poirier, P.; Dumesnil, J.G.; Desaulniers, D.; Boudreault, J.R.; O’Hara, G.; Gilbert, M.; Philippon, F. Permanent Pacemaker Lead Entrapment: Role of the Transesophageal Echocardiography. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. PACE 2002, 25, 1131–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mediratta, A.; Addetia, K.; Yamat, M.; Moss, J.D.; Nayak, H.M.; Burke, M.C.; Weinert, L.; Maffessanti, F.; Jeevanandam, V.; Mor-Avi, V.; et al. 3D Echocardiographic Location of Implantable Device Leads and Mechanism of Associated Tricuspid Regurgitation. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2014, 7, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miglioranza, M.H.; Becker, D.; Jiménez-Nácher, J.-J.; Moya, J.L.; Golfin, C.F.; Zamorano, J.L. A New View of an Unusual Pacemaker Complication: Role of Three-Dimensional Transthoracic Echocardiography. Echocardiogr. Mt. Kisco N 2013, 30, E164–E166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayan, R.L.; Vaishnava, P.; Goldman, M. Three-Dimensional Transthoracic Echocardiography in the Diagnosis of Device Lead-Related Tricuspid Leaflet Entrapment. Tex. Heart Inst. J. 2012, 39, 906–907. [Google Scholar]
- Nucifora, G.; Badano, L.P.; Allocca, G.; Gianfagna, P.; Proclemer, A.; Cinello, M.; Fioretti, P.M. Severe Tricuspid Regurgitation Due to Entrapment of the Anterior Leaflet of the Valve by a Permanent Pacemaker Lead: Role of Real Time Three-Dimensional Echocardiography. Echocardiogr. Mt. Kisco N 2007, 24, 649–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polewczyk, A.; Kutarski, A.; Tomaszewski, A.; Brzozowski, W.; Czajkowski, M.; Polewczyk, M.; Janion, M. Lead Dependent Tricuspid Dysfunction: Analysis of the Mechanism and Management in Patients Referred for Transvenous Lead Extraction. Cardiol. J. 2013, 20, 402–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazmul, M.N.; Cha, Y.-M.; Lin, G.; Asirvatham, S.J.; Powell, B.D. Percutaneous Pacemaker or Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator Lead Removal in an Attempt to Improve Symptomatic Tricuspid Regurgitation. Europace 2013, 15, 409–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, C.M.; Nishimura, R.A.; Bonow, R.O.; Carabello, B.A.; Erwin, J.P.; Gentile, F.; Jneid, H.; Krieger, E.V.; Mack, M.; McLeod, C.; et al. 2020 ACC/AHA Guideline for the Management of Patients With Valvular Heart Disease: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation 2021, 143, e72–e227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vahanian, A.; Beyersdorf, F.; Praz, F.; Milojevic, M.; Baldus, S.; Bauersachs, J.; Capodanno, D.; Conradi, L.; De Bonis, M.; De Paulis, R.; et al. 2021 ESC/EACTS Guidelines for the Management of Valvular Heart Disease. Eur. Heart J. 2022, 43, 561–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, J.; Kusumoto, F.M.; Zhou, X.; Elayi, C.S. How to Perform Extrathoracic Venous Access for Cardiac Implantable Electronic Device Placement: Detailed Description of Techniques. Heart Rhythm. 2022, 19, 1184–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bongiorni, M.G.; Proclemer, A.; Dobreanu, D.; Marinskis, G.; Pison, L.; Blomstrom-Lundqvist, C.; Scientific Initiative Committee; European Heart Rhythm Association. Preferred Tools and Techniques for Implantation of Cardiac Electronic Devices in Europe: Results of the European Heart Rhythm Association Survey. Europace 2013, 15, 1664–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Littleford, P.O.; Parsonnet, V.; Spector, S.D. Method for the Rapid and Atraumatic Insertion of Permanent Endocardial Pacemaker Electrodes through the Subclavian Vein. Am. J. Cardiol. 1979, 43, 980–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallik, D.M.; Ben-Zur, U.M.; Gross, J.N.; Furman, S. Lead Fracture in Cephalic versus Subclavian Approach with Transvenous Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator Systems. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. PACE 1996, 19, 1089–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atti, V.; Turagam, M.K.; Garg, J.; Koerber, S.; Angirekula, A.; Gopinathannair, R.; Natale, A.; Lakkireddy, D. Subclavian and Axillary Vein Access Versus Cephalic Vein Cutdown for Cardiac Implantable Electronic Device Implantation: A Meta-Analysis. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2020, 6, 661–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunbayo, G.O.; Charnigo, R.; Darrat, Y.; Morales, G.; Kotter, J.; Olorunfemi, O.; Elbadawi, A.; Sorrell, V.L.; Smyth, S.S.; Elayi, C.S. Incidence, Predictors, and Outcomes Associated with Pneumothorax during Cardiac Electronic Device Implantation: A 16-Year Review in over 3.7 Million Patients. Heart Rhythm. 2017, 14, 1764–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotter, J.; Lolay, G.; Charnigo, R.; Leung, S.; McKibbin, C.; Sousa, M.; Jimenez, L.; Gurley, J.; Biase, L.D.; Natale, A.; et al. Predictors, Morbidity, and Costs Associated with Pneumothorax during Electronic Cardiac Device Implantation. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. PACE 2016, 39, 985–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anagnostopoulos, I.; Kossyvakis, C.; Kousta, M.; Verikokkou, C.; Lakka, E.; Karakanas, A.; Deftereos, G.; Spanou, P.; Giotaki, S.; Vrachatis, D.; et al. Different Venous Approaches for Implantation of Cardiac Electronic Devices. A Network Meta-Analysis. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. PACE 2022, 45, 717–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charles, P.; Ditac, G.; Montoy, M.; Thenard, T.; Courand, P.-Y.; Lantelme, P.; Harbaoui, B.; Fareh, S. Intra-Pocket Ultrasound-Guided Axillary Vein Puncture vs. Cephalic Vein Cutdown for Cardiac Electronic Device Implantation: The ACCESS Trial. Eur. Heart J. 2023, 44, 4847–4858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerontitis, D.; Diab, I.; Chow, A.W.C.; Hunter, R.J.; Leyva, F.; Turley, A.J.; Williams, I.; Ullah, W.; other members of the Attain Stability Study Group/Consortium. UK Multicenter Retrospective Comparison of Novel Active versus Conventional Passive Fixation Coronary Sinus Leads. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2020, 31, 2948–2953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-S.; Chen, T.-H.; Hung, S.-P.; Chen, D.Y.; Mao, C.-T.; Tsai, M.-L.; Chang, S.-T.; Wang, C.-C.; Wen, M.-S.; Chen, M.-C. Impact of Pacemaker Lead Characteristics on Pacemaker Related Infection and Heart Perforation: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0128320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robertson, C.; Duffey, O.; Tang, P.-T.; Fairhurst, N.; Monteiro, C.; Green, P.; Grogono, J.; Davies, M.; Lewis, A.; Wijesurendra, R.; et al. An Active Fixation Quadripolar Left Ventricular Lead for Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy with Reduced Postoperative Complication Rates. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2022, 33, 458–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, Y.; Li, Y.; Liao, D.; Yang, L.; Liu, F. A Comparative Analysis of the Effectiveness of Active versus Passive Atrial Lead Fixation in Chinese Patients with Cardiac Implantable Electrical Devices: A Long Term, Retrospective, Observational, Single-Center Study. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2017, 33, 573–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Tang, J.; Peng, H.; Wu, S.; Lin, C.; Chen, D.; Zhang, Q.; Liang, Y.; Chen, S.; Chen, Y.; et al. A Long-Term, Prospective, Cohort Study on the Performance of Right Ventricular Pacing Leads: Comparison of Active-Fixation with Passive-Fixation Leads. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 7662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levi, N.; Bongiorni, M.G.; Rav Acha, M.; Tovia-Brodie, O.; Kennergren, C.; Auricchio, A.; Maggioni, A.P.; Rinaldi, C.A.; Nof, E.; Ilan, M.; et al. Lead Fixation Mechanism Impacts Outcome of Transvenous Lead Extraction: Data from the European Lead Extraction ConTRolled Registry. Europace 2022, 24, 817–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahapatra, S.; Bybee, K.A.; Bunch, T.J.; Espinosa, R.E.; Sinak, L.J.; McGoon, M.D.; Hayes, D.L. Incidence and Predictors of Cardiac Perforation after Permanent Pacemaker Placement. Heart Rhythm. 2005, 2, 907–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cano, Ó.; Andrés, A.; Alonso, P.; Osca, J.; Sancho-Tello, M.-J.; Olagüe, J.; Martínez-Dolz, L. Incidence and Predictors of Clinically Relevant Cardiac Perforation Associated with Systematic Implantation of Active-Fixation Pacing and Defibrillation Leads: A Single-Centre Experience with over 3800 Implanted Leads. Europace 2017, 19, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crossley, G.H.; Piccini, J.P.; Longacre, C.; Higuera, L.; Stromberg, K.; El-Chami, M.F. Leadless versus Transvenous Single-Chamber Ventricular Pacemakers: 3 Year Follow-up of the Micra CED Study. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2023, 34, 1015–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantillon, D.J.; Dukkipati, S.R.; Ip, J.H.; Exner, D.V.; Niazi, I.K.; Banker, R.S.; Rashtian, M.; Plunkitt, K.; Tomassoni, G.F.; Nabutovsky, Y.; et al. Comparative Study of Acute and Mid-Term Complications with Leadless and Transvenous Cardiac Pacemakers. Heart Rhythm. 2018, 15, 1023–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piccini, J.P.; El-Chami, M.; Wherry, K.; Crossley, G.H.; Kowal, R.C.; Stromberg, K.; Longacre, C.; Hinnenthal, J.; Bockstedt, L. Contemporaneous Comparison of Outcomes Among Patients Implanted with a Leadless vs. Transvenous Single-Chamber Ventricular Pacemaker. JAMA Cardiol. 2021, 6, 1187–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Fazia, V.M.; Lepone, A.; Pierucci, N.; Gianni, C.; Barletta, V.; Mohanty, S.; Della Rocca, D.G.; La Valle, C.; Torlapati, P.G.; Al-Ahmad, M.; et al. Low Prevalence of New-Onset Severe Tricuspid Regurgitation Following Leadless Pacemaker Implantation in a Large Series of Consecutive Patients. Heart Rhythm. 2024, 21, 2603–2604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhuarrat, M.A.D.; Kharawala, A.; Renjithlal, S.; Magdi Eid, M.; Varrias, D.; Mohammed, M.; Grushko, M.; Di Biase, L. Comparison of In-Hospital Outcomes and Complications of Leadless Pacemaker and Traditional Transvenous Pacemaker Implantation. Europace 2023, 25, euad269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haddadin, F.; Majmundar, M.; Jabri, A.; Pecha, L.; Scott, C.; Daher, M.; Kumar, A.; Kalra, A.; Fram, R.; Haddadin, F.; et al. Clinical Outcomes and Predictors of Complications in Patients Undergoing Leadless Pacemaker Implantation. Heart Rhythm. 2022, 19, 1289–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vouliotis, A.I.; Roberts, P.R.; Dilaveris, P.; Gatzoulis, K.; Yue, A.; Tsioufis, K. Leadless Pacemakers: Current Achievements and Future Perspectives. Eur. Cardiol. Rev. 2023, 18, e49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crossley, G.H.; Sanders, P.; De Filippo, P.; Tarakji, K.G.; Hansky, B.; Shah, M.; Mason, P.; Maus, B.; Holloman, K. Rationale and Design of the Lead Evaluation for Defibrillation and Reliability Study: Safety and Efficacy of a Novel ICD Lead Design. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2023, 34, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.S.; Yin, R.T.; Pfenniger, A.; Koo, J.; Avila, R.; Lee, K.B.; Chen, S.W.; Lee, G.; Li, G.; Qiao, Y.; et al. Fully Implantable and Bioresorbable Cardiac Pacemakers Without Leads or Batteries. Nat. Biotechnol. 2021, 39, 1228–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khurshid, S.; Frankel, D.S. Pacing-Induced Cardiomyopathy. Card. Electrophysiol. Clin. 2021, 13, 741–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khurshid, S.; Epstein, A.E.; Verdino, R.J.; Lin, D.; Goldberg, L.R.; Marchlinski, F.E.; Frankel, D.S. Incidence and Predictors of Right Ventricular Pacing-Induced Cardiomyopathy. Heart Rhythm. 2014, 11, 1619–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiehl, E.L.; Makki, T.; Kumar, R.; Gumber, D.; Kwon, D.H.; Rickard, J.W.; Kanj, M.; Wazni, O.M.; Saliba, W.I.; Varma, N.; et al. Incidence and Predictors of Right Ventricular Pacing-Induced Cardiomyopathy in Patients with Complete Atrioventricular Block and Preserved Left Ventricular Systolic Function. Heart Rhythm. 2016, 13, 2272–2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tops, L.F.; Schalij, M.J.; Bax, J.J. The Effects of Right Ventricular Apical Pacing on Ventricular Function and Dyssynchrony Implications for Therapy. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2009, 54, 764–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leclercq, C.; Gras, D.; Le Helloco, A.; Nicol, L.; Mabo, P.; Daubert, C. Hemodynamic Importance of Preserving the Normal Sequence of Ventricular Activation in Permanent Cardiac Pacing. Am. Heart J. 1995, 129, 1133–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Somma, V.; Ha, F.J.; Palmer, S.; Mohamed, U.; Agarwal, S. Pacing-Induced Cardiomyopathy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Definition, Prevalence, Risk Factors, and Management. Heart Rhythm. 2023, 20, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.D.; Rizo-Patron, C.; Hallstrom, A.P.; O’Neill, G.P.; Rothbart, S.; Martins, J.B.; Roelke, M.; Steinberg, J.S.; Greene, H.L. Percent Right Ventricular Pacing Predicts Outcomes in the DAVID Trial. Heart Rhythm. 2005, 2, 830–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.-M.; Fang, F.; Luo, X.-X.; Zhang, Q.; Azlan, H.; Razali, O. Long-Term Follow-up Results of the Pacing to Avoid Cardiac Enlargement (PACE) Trial. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2014, 16, 1016–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Chen, X.; Su, L.; Wu, S.; Xia, X.; Vijayaraman, P. A Beginner’s Guide to Permanent Left Bundle Branch Pacing. Heart Rhythm. 2019, 16, 1791–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshmukh, P.; Casavant, D.A.; Romanyshyn, M.; Anderson, K. Permanent, Direct His-Bundle Pacing: A Novel Approach to Cardiac Pacing in Patients with Normal His-Purkinje Activation. Circulation 2000, 101, 869–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lustgarten, D.L.; Crespo, E.M.; Arkhipova-Jenkins, I.; Lobel, R.; Winget, J.; Koehler, J.; Liberman, E.; Sheldon, T. His-Bundle Pacing Versus Biventricular Pacing in Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy Patients: A Crossover Design Comparison. Heart Rhythm. 2015, 12, 1548–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.; Su, L.; Wu, S.; Xu, L.; Xiao, F.; Zhou, X.; Ellenbogen, K.A. Benefits of Permanent His Bundle Pacing Combined with Atrioventricular Node Ablation in Atrial Fibrillation Patients with Heart Failure with Both Preserved and Reduced Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2017, 6, e005309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelrahman, M.; Subzposh, F.A.; Beer, D.; Durr, B.; Naperkowski, A.; Sun, H.; Oren, J.W.; Dandamudi, G.; Vijayaraman, P. Clinical Outcomes of His Bundle Pacing Compared to Right Ventricular Pacing. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 71, 2319–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.; Su, L.; Wu, S.; Xu, L.; Xiao, F.; Zhou, X.; Mao, G.; Vijayaraman, P.; Ellenbogen, K.A. Long-Term Outcomes of His Bundle Pacing in Patients with Heart Failure with Left Bundle Branch Block. Heart Br. Card. Soc. 2019, 105, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijayaraman, P.; Chung, M.K.; Dandamudi, G.; Upadhyay, G.A.; Krishnan, K.; Crossley, G.; Bova Campbell, K.; Lee, B.K.; Refaat, M.M.; Saksena, S.; et al. His Bundle Pacing. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 72, 927–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanon, F.; Ellenbogen, K.A.; Dandamudi, G.; Sharma, P.S.; Huang, W.; Lustgarten, D.L.; Tung, R.; Tada, H.; Koneru, J.N.; Bergemann, T.; et al. Permanent His-Bundle Pacing: A Systematic Literature Review and Meta-Analysis. Europace 2018, 20, 1819–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subzposh, F.A.; Vijayaraman, P. Long-Term Results of His Bundle Pacing. Card. Electrophysiol. Clin. 2018, 10, 537–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barba-Pichardo, R.; Moriña-Vázquez, P.; Fernández-Gómez, J.M.; Venegas-Gamero, J.; Herrera-Carranza, M. Permanent His-Bundle Pacing: Seeking Physiological Ventricular Pacing. Europace 2010, 12, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.S.; Dandamudi, G.; Herweg, B.; Wilson, D.; Singh, R.; Naperkowski, A.; Koneru, J.N.; Ellenbogen, K.A.; Vijayaraman, P. Permanent His-Bundle Pacing as an Alternative to Biventricular Pacing for Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy: A Multicenter Experience. Heart Rhythm. 2018, 15, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, G.A.; Vijayaraman, P.; Nayak, H.M.; Verma, N.; Dandamudi, G.; Sharma, P.S.; Saleem, M.; Mandrola, J.; Genovese, D.; Tung, R.; et al. His Corrective Pacing or Biventricular Pacing for Cardiac Resynchronization in Heart Failure. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 74, 157–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Li, Y.; Dai, Y.; Sun, Q.; Luo, B.; Li, C.; Zhang, S. Comparison of Electrocardiogram Characteristics and Pacing Parameters between Left Bundle Branch Pacing and Right Ventricular Pacing in Patients Receiving Pacemaker Therapy. EP Eur. 2019, 21, 673–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Chen, K.; Dai, Y.; Li, C.; Sun, Q.; Chen, R.; Gold, M.R.; Zhang, S. Left Bundle Branch Pacing for Symptomatic Bradycardia: Implant Success Rate, Safety, and Pacing Characteristics. Heart Rhythm. 2019, 16, 1758–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.; Su, L.; Wu, S.; Xu, L.; Xiao, F.; Zhou, X.; Ellenbogen, K.A. A Novel Pacing Strategy with Low and Stable Output: Pacing the Left Bundle Branch Immediately Beyond the Conduction Block. Can. J. Cardiol. 2017, 33, 1736.e1–1736.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayaraman, P.; Cano, Ó.; Koruth, J.S.; Subzposh, F.A.; Nanda, S.; Pugliese, J.; Ravi, V.; Naperkowski, A.; Sharma, P.S. His-Purkinje Conduction System Pacing Following Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement: Feasibility and Safety. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2020, 6, 649–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Li, H.; Ma, W.; Ning, X.; Liang, E.; Pang, K.; Yao, Y.; Hua, W.; Zhang, S.; Fan, X. Permanent Left Bundle Branch Area Pacing for Atrioventricular Block: Feasibility, Safety, and Acute Effect. Heart Rhythm. 2019, 16, 1766–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Zhou, X.; Gold, M.R. Left Bundle Branch Pacing: JACC Review Topic of the Week. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 74, 3039–3049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, P.S.; Patel, N.R.; Ravi, V.; Zalavadia, D.V.; Dommaraju, S.; Garg, V.; Larsen, T.R.; Naperkowski, A.M.; Wasserlauf, J.; Krishnan, K.; et al. Clinical Outcomes of Left Bundle Branch Area Pacing Compared to Right Ventricular Pacing: Results from the Geisinger-Rush Conduction System Pacing Registry. Heart Rhythm. 2022, 19, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bednarek, A.; Kiełbasa, G.; Moskal, P.; Ostrowska, A.; Bednarski, A.; Sondej, T.; Kusiak, A.; Rajzer, M.; Jastrzębski, M. Left Bundle Branch Area Pacing Prevents Pacing Induced Cardiomyopathy in Long-Term Observation. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. PACE 2023, 46, 629–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rademakers, L.M.; Bouwmeester, S.; Mast, T.P.; Dekker, L.; Houthuizen, P.; Bracke, F.A. Feasibility, Safety and Outcomes of Upgrading to Left Bundle Branch Pacing in Patients with Right Ventricular Pacing Induced Cardiomyopathy. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. PACE 2022, 45, 726–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wei, L.; Bai, J.; Wang, W.; Qin, S.; Wang, J.; Liang, Y.; Su, Y.; Ge, J. Procedure-Related Complications of Left Bundle Branch Pacing: A Single-Center Experience. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 645947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayaraman, P.; Subzposh, F.A.; Naperkowski, A.; Panikkath, R.; John, K.; Mascarenhas, V.; Bauch, T.D.; Huang, W. Prospective Evaluation of Feasibility and Electrophysiologic and Echocardiographic Characteristics of Left Bundle Branch Area Pacing. Heart Rhythm. 2019, 16, 1774–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz, J.C.; Sauer, W.H.; Duque, M.; Koplan, B.A.; Braunstein, E.D.; Marín, J.E.; Aristizabal, J.; Niño, C.D.; Bastidas, O.; Martinez, J.M.; et al. Left Bundle Branch Area Pacing Versus Biventricular Pacing as Initial Strategy for Cardiac Resynchronization. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2023, 9, 1568–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jastrzębski, M.; Kiełbasa, G.; Cano, O.; Curila, K.; Heckman, L.; De Pooter, J.; Chovanec, M.; Rademakers, L.; Huybrechts, W.; Grieco, D.; et al. Left Bundle Branch Area Pacing Outcomes: The Multicentre European MELOS Study. Eur. Heart J. 2022, 43, 4161–4173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shali, S.; Wu, W.; Bai, J.; Wang, W.; Qin, S.; Wang, J.; Liang, Y.; Chen, H.; Su, Y.; Chen, X.; et al. Current of Injury Is an Indicator of Lead Depth and Performance during Left Bundle Branch Pacing Lead Implantation. Heart Rhythm. 2022, 19, 1281–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, E.S.J.; Lee, J.-Y.; Boey, E.; Soh, R.; Seow, S.-C.; Teo, L.J.T.; Yeo, C.; Tan, V.H.; Kojodjojo, P. Predictors of Loss of Capture in Left Bundle Branch Pacing: A Multicenter Experience. Heart Rhythm. 2022, 19, 1757–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahajan, A.; Pokharel, P.; Vijayaraman, P. Lead-to-Lead Interaction Leading to Left Bundle Branch Area Pacing Lead Failure. Hear. Case Rep. 2023, 9, 72–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, R.; Wu, S.; Wang, S.; Su, L.; Ellenbogen, K.A.; Huang, W. Case Report: Interventricular Septal Hematoma Complicating Left Bundle Branch Pacing Lead Implantation. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 744079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, R.; Rattigan, E.; Bauch, T.D.; Mascarenhas, V.; Ahmad, T.; Subzposh, F.A.; Vijayaraman, P. Giant Interventricular Septal Hematoma Complicating Left Bundle Branch Pacing: A Cautionary Tale. JACC Case Rep. 2023, 16, 101887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Lu, H.; Xu, L.; Chen, H.; Xu, Y.; Xu, S.; Wang, Q.; Qian, J.; Ge, J. Interventricular Septal Hematoma with Pericardial Effusion After Left Bundle Branch Pacing Implantation. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2023, 9, 142–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Ye, Y.; Wang, Z.; Jin, Q.; Qiu, Z.; Wang, J.; Qin, S.; Bai, J.; Wang, W.; Liang, Y.; et al. Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy via Left Bundle Branch Pacing vs. Optimized Biventricular Pacing with Adaptive Algorithm in Heart Failure with Left Bundle Branch Block: A Prospective, Multi-Centre, Observational Study. Europace 2022, 24, 807–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponnusamy, S.S.; Arora, V.; Namboodiri, N.; Kumar, V.; Kapoor, A.; Vijayaraman, P. Left Bundle Branch Pacing: A Comprehensive Review. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2020, 31, 2462–2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, L.; Wang, S.; Wu, S.; Xu, L.; Huang, Z.; Chen, X.; Zheng, R.; Jiang, L.; Ellenbogen, K.A.; Whinnett, Z.I.; et al. Long-Term Safety and Feasibility of Left Bundle Branch Pacing in a Large Single-Center Study. Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 2021, 14, e009261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padala, S.K.; Master, V.M.; Terricabras, M.; Chiocchini, A.; Garg, A.; Kron, J.; Shepard, R.; Kalahasty, G.; Azizi, Z.; Tsang, B.; et al. Initial Experience, Safety, and Feasibility of Left Bundle Branch Area Pacing: A Multicenter Prospective Study. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2020, 6, 1773–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, W.; Fan, X.; Li, X.; Niu, H.; Gu, M.; Ning, X.; Hu, Y.; Gold, M.R.; Zhang, S. Comparison of Left Bundle Branch and His Bundle Pacing in Bradycardia Patients. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2020, 6, 1291–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Pooter, J.; Calle, S.; Timmermans, F.; Van Heuverswyn, F. Left Bundle Branch Area Pacing Using Stylet-Driven Pacing Leads with a New Delivery Sheath: A Comparison with Lumen-Less Leads. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2021, 32, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmisano, P.; Ziacchi, M.; Dell’Era, G.; Donateo, P.; Ammendola, E.; Coluccia, G.; Guido, A.; Piemontese, G.P.; Lazzeri, M.; Ghiglieno, C.; et al. Rate and Nature of Complications of Conduction System Pacing Compared with Right Ventricular Pacing: Results of a Propensity Score-Matched Analysis from a Multicenter Registry. Heart Rhythm. 2023, 20, 984–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Link, M.S.; Hellkamp, A.S.; Estes, N.A.M.; Orav, E.J.; Ellenbogen, K.A.; Ibrahim, B.; Greenspon, A.; Rizo-Patron, C.; Goldman, L.; Lee, K.L.; et al. High Incidence of Pacemaker Syndrome in Patients with Sinus Node Dysfunction Treated with Ventricular-Based Pacing in the Mode Selection Trial (MOST). J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2004, 43, 2066–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillis, A.M.; Russo, A.M.; Ellenbogen, K.A.; Swerdlow, C.D.; Olshansky, B.; Al-Khatib Sana, M.; Beshai, J.F.; McComb, J.M.; Nielsen, J.C.; Philpott, J.M.; et al. HRS/ACCF Expert Consensus Statement on Pacemaker Device and Mode Selection. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2012, 60, 682–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamas, G.A.; Lee, K.L.; Sweeney, M.O.; Silverman, R.; Leon, A.; Yee, R.; Marinchak, R.A.; Flaker, G.; Schron, E.; Orav, E.J.; et al. Ventricular Pacing or Dual-Chamber Pacing for Sinus-Node Dysfunction. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 346, 1854–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furman, S. Pacemaker Syndrome. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 1994, 17, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamas, G.A.; Orav, E.J.; Stambler, B.S.; Ellenbogen, K.A.; Sgarbossa, E.B.; Huang, S.K.S.; Marinchak, R.A.; Estes, N.A.M.; Mitchell, G.F.; Lieberman, E.H.; et al. Quality of Life and Clinical Outcomes in Elderly Patients Treated with Ventricular Pacing as Compared with Dual-Chamber Pacing. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998, 338, 1097–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah Syed, A.R.; Akram, A.; Azam, M.S.; Ansari, A.I.; Muzammil, M.A.; Ahad Syed, A.; Ahmed, S.; Zakir, S.J. Dual-Chamber versus Single Chamber Pacemakers, a Systemic Review and Meta-Analysis on Sick Sinus Syndrome and Atrioventricular Block Patients. Heliyon 2024, 10, e23877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connolly, S.J.; Kerr, C.R.; Gent, M.; Roberts, R.S.; Yusuf, S.; Gillis, A.M.; Sami, M.H.; Talajic, M.; Tang, A.S.L.; Klein, G.J.; et al. Effects of Physiologic Pacing Versus Ventricular Pacing on the Risk of Stroke and Death Due to Cardiovascular Causes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 342, 1385–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiegand, U.K.H.; Bode, F.; Bonnemeier, H.; Eberhard, F.; Schlei, M.; Peters, W. Long-Term Complication Rates in Ventricular, Single Lead VDD, and Dual Chamber Pacing. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 2003, 26, 1961–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Rees, J.B.; Borleffs, C.J.W.; de Bie, M.K.; Stijnen, T.; van Erven, L.; Bax, J.J.; Schalij, M.J. Inappropriate Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator Shocks: Incidence, Predictors, and Impact on Mortality. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2011, 57, 556–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daubert, J.P.; Zareba, W.; Cannom, D.S.; McNitt, S.; Rosero, S.Z.; Wang, P.; Schuger, C.; Steinberg, J.S.; Higgins, S.L.; Wilber, D.J.; et al. Inappropriate Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator Shocks in MADIT II: Frequency, Mechanisms, Predictors, and Survival Impact. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2008, 51, 1357–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambiase, P.D.; Theuns, D.A.; Murgatroyd, F.; Barr, C.; Eckardt, L.; Neuzil, P.; Scholten, M.; Hood, M.; Kuschyk, J.; Brisben, A.J.; et al. Subcutaneous Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillators: Long-Term Results of the EFFORTLESS Study. Eur. Heart J. 2022, 43, 2037–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louise Olde Nordkamp; Pepplinkhuizen, S.; Ghani, A.; Boersma, L.V.A. Inappropriate Therapy and Shock Rates Between the Subcutaneous and Transvenous Implantable Cardiac Defibrillator: A Secondary Analysis of the PRAETORIAN Trial. Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 2024, 17, e012836. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez, R.; Mihos, C.G.; Torres, J.L.; Tolentino, A.O. Inappropriate Pacing Due to T-Wave Oversensing. J. Thorac. Dis. 2020, 12, 2983–2985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vollmann, D.; Lüthje, L.; Vonhof, S.; Unterberg, C. Inappropriate Therapy and Fatal Proarrhythmia by an Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator. Heart Rhythm. 2005, 2, 307–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hreybe, H.; Ezzeddine, R.; Barrington, W.; Bazaz, R.; Jain, S.; Ngwu, O.; Saba, S. Relation of Advanced Heart Failure Symptoms to Risk of Inappropriate Defibrillator Shocks. Am. J. Cardiol. 2006, 97, 544–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poole, J.E.; Johnson, G.W.; Hellkamp, A.S.; Anderson, J.; Callans, D.J.; Raitt, M.H.; Reddy, R.K.; Marchlinski, F.E.; Yee, R.; Guarnieri, T.; et al. Prognostic Importance of Defibrillator Shocks in Patients with Heart Failure. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 1009–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ezekowitz, J.A.; Armstrong, P.W.; McAlister, F.A. Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillators in Primary and Secondary Prevention. Ann. Intern. Med. 2003, 138, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almehmadi, F.; Porta-Sánchez, A.; Ha, A.C.T.; Fischer, H.D.; Wang, X.; Austin, P.C.; Lee, D.S.; Nanthakumar, K. Mortality Implications of Appropriate Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator Therapy in Secondary Prevention Patients: Contrasting Mortality in Primary Prevention Patients From a Prospective Population-Based Registry. J. Am. Heart Assoc. Cardiovasc. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2017, 6, e006220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moss, A.J.; Schuger, C.; Beck, C.A.; Brown, M.W.; Cannom, D.S.; Daubert, J.P.; Estes, N.A.M.; Greenberg, H.; Hall, W.J.; Huang, D.T.; et al. Reduction in Inappropriate Therapy and Mortality through ICD Programming. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 2275–2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, J.C.; Lin, Y.-J.; de Oliveira Figueiredo, M.J.; Sepehri Shamloo, A.; Alfie, A.; Boveda, S.; Dagres, N.; Di Toro, D.; Eckhardt, L.L.; Ellenbogen, K.; et al. European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA)/Heart Rhythm Society (HRS)/Asia Pacific Heart Rhythm Society (APHRS)/Latin American Heart Rhythm Society (LAHRS) Expert Consensus on Risk Assessment in Cardiac Arrhythmias: Use the Right Tool for the Right Outcome, in the Right Population. J. Arrhythmia 2020, 36, 553–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theuns, D.A.M.J.; Klootwijk, A.P.J.; Goedhart, D.M.; Jordaens, L.J.L.M. Prevention of Inappropriate Therapy in Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillators. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2004, 44, 2362–2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deisenhofer, I.; Kolb, C.; Ndrepepa, G.; Schreieck, J.; Karch, M.; Schmieder, S.; Zrenner, B.; Schmitt, C. Do Current Dual Chamber Cardioverter Defibrillators Have Advantages over Conventional Single Chamber Cardioverter Defibrillators in Reducing Inappropriate Therapies? A Randomized, Prospective Study. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2001, 12, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshmukh, A.; Friedman, P. Can We Avoid Inappropriate Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator Shocks. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2019, 5, 716–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, D.L.; Levine, P.A. Pacemaker Timing Cycles. In Cardiac Pacing and ICDs; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005; pp. 265–321. ISBN 978-0-470-75067-4. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, P.S.; Kaszala, K.; Tan, A.Y.; Koneru, J.N.; Shepard, R.; Ellenbogen, K.A.; Huizar, J.F. Repetitive Nonreentrant Ventriculoatrial Synchrony: An Underrecognized Cause of Pacemaker-Related Arrhythmia. Heart Rhythm. 2016, 13, 1739–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klementowicz, P.T.; Furman, S. Selective Atrial Sensing in Dual Chamber Pacemakers Eliminates Endless Loop Tachycardia. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 1986, 7, 590–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sane, M.; Marjamaa, A.; Kuusisto, J.; Raatikainen, P.; Karvonen, J. “PVC Response Atrial-Pace”, an Algorithm Designed for Preventing Pacemaker-Induced Tachycardia after Premature Ventricular Contractions, Triggers Atrial High Rate Episodes. Heart Rhythm. 2024, 21, 495–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-haniyeh, A.; Hajouli, S. Pacemaker Mediated Tachycardia. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Sohail, M.R.; Uslan, D.Z.; Khan, A.H.; Friedman, P.A.; Hayes, D.L.; Wilson, W.R.; Steckelberg, J.M.; Jenkins, S.M.; Baddour, L.M. Infective Endocarditis Complicating Permanent Pacemaker and Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator Infection. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2008, 83, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenspon, A.J.; Patel, J.D.; Lau, E.; Ochoa, J.A.; Frisch, D.R.; Ho, R.T.; Pavri, B.B.; Kurtz, S.M. 16-Year Trends in the Infection Burden for Pacemakers and Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillators in the United States 1993 to 2008. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2011, 58, 1001–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uslan, D.Z.; Sohail, M.R.; St Sauver, J.L.; Friedman, P.A.; Hayes, D.L.; Stoner, S.M.; Wilson, W.R.; Steckelberg, J.M.; Baddour, L.M. Permanent Pacemaker and Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator Infection: A Population-Based Study. Arch. Intern. Med. 2007, 167, 669–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsen, T.; Jørgensen, O.D.; Nielsen, J.C.; Thøgersen, A.M.; Philbert, B.T.; Johansen, J.B. Incidence of Device-Related Infection in 97,750 Patients: Clinical Data from the Complete Danish Device-Cohort (1982–2018). Eur. Heart J. 2019, 40, 1862–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, V.; Chen, H.; Hsia, H.; Zei, P.; Wang, P.; Al-Ahmad, A. Cardiac Device Infections Complicated by Erosion. J. Interv. Card. Electrophysiol. 2007, 19, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyzos, K.A.; Konstantelias, A.A.; Falagas, M.E. Risk Factors for Cardiac Implantable Electronic Device Infection: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Europace 2015, 17, 767–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohail, M.R.; Corey, G.R.; Wilkoff, B.L.; Poole, J.E.; Mittal, S.; Kennergren, C.; Greenspon, A.J.; Cheng, A.; Lande, J.D.; Lexcen, D.R.; et al. Clinical Presentation, Timing, and Microbiology of CIED Infections: An Analysis of the WRAP-IT Trial. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2021, 7, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vujadinovic, N.; Radovanovic, N.; Milasinovic, G.; Pavlovic, S.; Kircanski, B.; Brankovic, N.; Sajic, V.; Milasinovic, A.; Zivkovic, M.; Bisenic, V. Incidence of Pocket Infection during Long-Term Follow-Up. EP Eur. 2021, 23, euab116.482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohail, M.R.; Hussain, S.; Le, K.Y.; Dib, C.; Lohse, C.M.; Friedman, P.A.; Hayes, D.L.; Uslan, D.Z.; Wilson, W.R.; Steckelberg, J.M.; et al. Risk Factors Associated with Early- Versus Late-Onset Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator Infections. J. Interv. Card. Electrophysiol. 2011, 31, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Sajadi, M.M.; Dilsizian, V. Merits of FDG PET/CT and Functional Molecular Imaging Over Anatomic Imaging with Echocardiography and CT Angiography for the Diagnosis of Cardiac Device Infections. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2018, 11, 1679–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarrazin, J.-F.; Philippon, F.; Tessier, M.; Guimond, J.; Molin, F.; Champagne, J.; Nault, I.; Blier, L.; Nadeau, M.; Charbonneau, L.; et al. Usefulness of Fluorine-18 Positron Emission Tomography/Computed Tomography for Identification of Cardiovascular Implantable Electronic Device Infections. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2012, 59, 1616–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohail, M.R.; Uslan, D.Z.; Khan, A.H.; Friedman, P.A.; Hayes, D.L.; Wilson, W.R.; Steckelberg, J.M.; Stoner, S.M.; Baddour, L.M. Risk Factor Analysis of Permanent Pacemaker Infection. Clin. Infect. Dis. Off. Publ. Infect. Dis. Soc. Am. 2007, 45, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mateos Gaitán, R.; Boix-Palop, L.; Muñoz García, P.; Mestres, C.A.; Marín Arriaza, M.; Pedraz Prieto, Á.; de Alarcón Gonzalez, A.; Gutiérrez Carretero, E.; Hernández Meneses, M.; Goenaga Sánchez, M.Á.; et al. Infective Endocarditis in Patients with Cardiac Implantable Electronic Devices: A Nationwide Study. Europace 2020, 22, 1062–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klug, D.; Wallet, F.; Kacet, S.; Courcol, R.J. Involvement of Adherence and Adhesion Staphylococcus Epidermidis Genes in Pacemaker Lead-Associated Infections. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003, 41, 3348–3350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viganego, F.; O’Donoghue, S.; Eldadah, Z.; Shah, M.H.; Rastogi, M.; Mazel, J.A.; Platia, E.V. Effect of Early Diagnosis and Treatment with Percutaneous Lead Extraction on Survival in Patients with Cardiac Device Infections. Am. J. Cardiol. 2012, 109, 1466–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arabia, G.; Mitacchione, G.; Cersosimo, A.; Calvi, E.; Salghetti, F.; Bontempi, L.; Giacopelli, D.; Cerini, M.; Curnis, A. Long-Term Outcomes Following Transvenous Lead Extraction: Data from a Tertiary Referral Center. Int. J. Cardiol. 2023, 378, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandoe, J.A.T.; Barlow, G.; Chambers, J.B.; Gammage, M.; Guleri, A.; Howard, P.; Olson, E.; Perry, J.D.; Prendergast, B.D.; Spry, M.J.; et al. Guidelines for the Diagnosis, Prevention and Management of Implantable Cardiac Electronic Device Infection. Report of a Joint Working Party Project on Behalf of the British Society for Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (BSAC, Host Organization), British Heart Rhythm Society (BHRS), British Cardiovascular Society (BCS), British Heart Valve Society (BHVS) and British Society for Echocardiography (BSE). J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2015, 70, 325–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gold, M.R.; Aasbo, J.D.; Weiss, R.; Burke, M.C.; Gleva, M.J.; Knight, B.P.; Miller, M.A.; Schuger, C.D.; Carter, N.; Leigh, J.; et al. Infection in Patients with Subcutaneous Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator: Results of the S-ICD Post Approval Study. Heart Rhythm. 2022, 19, 1993–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blomstrom-Lundqvist, C.; Ostrowska, B. Prevention of Cardiac Implantable Electronic Device Infections: Guidelines and Conventional Prophylaxis. Europace 2021, 23, iv11–iv19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarakji, K.G.; Mittal, S.; Kennergren, C.; Corey, R.; Poole, J.E.; Schloss, E.; Gallastegui, J.; Pickett, R.A.; Evonich, R.; Philippon, F.; et al. Antibacterial Envelope to Prevent Cardiac Implantable Device Infection. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 1895–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asbeutah, A.A.A.; Salem, M.H.; Asbeutah, S.A.; Abu-Assi, M.A. The Role of an Antibiotic Envelope in the Prevention of Major Cardiac Implantable Electronic Device Infections: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Medicine 2020, 99, e20834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeitler, E.P.; Friedman, D.J.; Loring, Z.; Campbell, K.B.; Goldstein, S.A.; Wegermann, Z.K.; Schutz, J.; Smith, N.; Black-Maier, E.; Al-Khatib, S.M.; et al. Complications Involving the Subcutaneous Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator: Lessons Learned from MAUDE. Heart Rhythm. 2020, 17, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iavarone, M.; Rago, A.; Nigro, G.; Golino, P.; Russo, V. Inappropriate Shocks Due to Air Entrapment in Patients with Subcutaneous Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator: A Meta-Summary of Case Reports. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. PACE 2022, 45, 1210–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knops, R.E.; Nordkamp, L.R.A.O.; Delnoy, P.-P.H.M.; Boersma, L.V.A.; Kuschyk, J.; El-Chami, M.F.; Bonnemeier, H.; Behr, E.R.; Brouwer, T.F.; Kääb, S.; et al. Subcutaneous or Transvenous Defibrillator Therapy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 526–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knops, R.E.; Pepplinkhuizen, S.; Delnoy, P.P.H.M.; Boersma, L.V.A.; Kuschyk, J.; El-Chami, M.F.; Bonnemeier, H.; Behr, E.R.; Brouwer, T.F.; Kaab, S.; et al. Device-Related Complications in Subcutaneous versus Transvenous ICD: A Secondary Analysis of the PRAETORIAN Trial. Eur. Heart J. 2022, 43, 4872–4883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baddour, L.M.; Weiss, R.; Mark, G.E.; El-Chami, M.F.; Biffi, M.; Probst, V.; Lambiase, P.D.; Miller, M.A.; McClernon, T.; Hansen, L.K.; et al. Diagnosis and Management of Subcutaneous Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator Infections Based on Process Mapping. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. PACE 2020, 43, 958–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brouwer, T.F.; Driessen, A.H.G.; Olde Nordkamp, L.R.A.; Kooiman, K.M.; de Groot, J.R.; Wilde, A.A.M.; Knops, R.E. Surgical Management of Implantation-Related Complications of the Subcutaneous Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2016, 2, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birnie, D.H.; Healey, J.S.; Wells, G.A.; Verma, A.; Tang, A.S.; Krahn, A.D.; Simpson, C.S.; Ayala-Paredes, F.; Coutu, B.; Leiria, T.L.L.; et al. Pacemaker or Defibrillator Surgery Without Interruption of Anticoagulation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 2084–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldon, S.H.; Cunnane, R.; Lavu, M.; Parikh, V.; Atkins, D.; Reddy, Y.M.; Berenbom, L.D.; Emert, M.P.; Pimentel, R.; Dendi, R.; et al. Perioperative Hematoma with Subcutaneous ICD Implantation: Impact of Anticoagulation and Antiplatelet Therapies. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. PACE 2018, 41, 799–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knops, R.E.; Brouwer, T.F.; Barr, C.S.; Theuns, D.A.; Boersma, L.; Weiss, R.; Neuzil, P.; Scholten, M.; Lambiase, P.D.; Leon, A.R.; et al. The Learning Curve Associated with the Introduction of the Subcutaneous Implantable Defibrillator. Europace 2016, 18, 1010–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magyar-Russell, G.; Thombs, B.D.; Cai, J.X.; Baveja, T.; Kuhl, E.A.; Singh, P.P.; Montenegro Braga Barroso, M.; Arthurs, E.; Roseman, M.; Amin, N.; et al. The Prevalence of Anxiety and Depression in Adults with Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillators: A Systematic Review. J. Psychosom. Res. 2011, 71, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghezzi, E.S.; Sharman, R.L.S.; Selvanayagam, J.B.; Psaltis, P.J.; Sanders, P.; Astley, J.M.; Knayfati, S.; Batra, V.; Keage, H.A.D. Burden of Mood Symptoms and Disorders in Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of 39 954 Patients. Europace 2023, 25, euad130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bostwick, J.M.; Sola, C.L. An Updated Review of Implantable Cardioverter/Defibrillators, Induced Anxiety, and Quality of Life. Heart Fail. Clin. 2011, 7, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, S.; Becker, R.; Wilke, S.; Hartmann, M.; Herzog, W.; Löwe, B. Anxiety Disorders in Patients with Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillators: Frequency, Course, Predictors, and Patients’ Requests for Treatment. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. PACE 2014, 37, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thylén, I.; Dekker, R.L.; Jaarsma, T.; Strömberg, A.; Moser, D.K. Characteristics Associated with Anxiety, Depressive Symptoms, and Quality-of-Life in a Large Cohort of Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator Recipients. J. Psychosom. Res. 2014, 77, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sola, C.L.; Bostwick, J.M. Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillators, Induced Anxiety, and Quality of Life. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2005, 80, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, S.A.; Friedmann, E.; Kao, C.W.; Inguito, P.; Metcalf, M.; Kelley, F.J.; Gottlieb, S.S. Quality of Life and Psychological Status of Patients with Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillators. Am. J. Crit. Care Off. Publ. Am. Assoc. Crit.-Care Nurses 2006, 15, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godemann, F.; Butter, C.; Lampe, F.; Linden, M.; Werner, S.; Behrens, S. Determinants of the Quality of Life (QoL) in Patients with an Implantable Cardioverter/Defibrillator (ICD). Qual. Life Res. Int. J. Qual. Life Asp. Treat. Care Rehabil. 2004, 13, 411–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leosdottir, M.; Sigurdsson, E.; Reimarsdottir, G.; Gottskalksson, G.; Torfason, B.; Vigfusdottir, M.; Eggertsson, S.; Arnar, D.O. Health-Related Quality of Life of Patients with Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillators Compared with That of Pacemaker Recipients. Europace 2006, 8, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newall, E.G.; Lever, N.A.; Prasad, S.; Hornabrook, C.; Larsen, P.D. Psychological Implications of ICD Implantation in a New Zealand Population. Europace 2007, 9, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haugaa, K.H.; Potpara, T.S.; Boveda, S.; Deharo, J.-C.; Chen, J.; Dobreanu, D.; Fumagalli, S.; Lenarczyk, R.; Hernandez Madrid, A.; Larsen, T.B.; et al. Patients’ Knowledge and Attitudes Regarding Living with Implantable Electronic Devices: Results of a Multicentre, Multinational Patient Survey Conducted by the European Heart Rhythm Association. Europace 2018, 20, 386–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fumagalli, S.; Pieragnoli, P.; Haugaa, K.H.; Potpara, T.S.; Rasero, L.; Ramacciati, N.; Ricciardi, G.; Solimene, F.; Mascia, G.; Mascioli, G.; et al. The Influence of Age on the Psychological Profile of Patients with Cardiac Implantable Electronic Devices: Results from the Italian Population in a Multicenter Study Conducted by the European Heart Rhythm Association. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2019, 31, 1219–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Chami, M.F.; Garweg, C.; Clementy, N.; Al-Samadi, F.; Iacopino, S.; Martinez-Sande, J.L.; Roberts, P.R.; Tondo, C.; Johansen, J.B.; Vinolas-Prat, X.; et al. Leadless Pacemakers at 5-Year Follow-up: The Micra Transcatheter Pacing System Post-Approval Registry. Eur. Heart J. 2024, 45, 1241–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Risk Factor | Univariate (95% CI) | p-Value | Multivariate (95% CI) | p-Value | Paper |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (per 1 year increase) | |||||
| 1.01 (0.99–1.02) | 0.09 | Somma et al. 2022 [142] | |||
| 1.00 (0.98–1.02) | 0.9 | Kurshid et al. 2014 [138] | |||
| BMI (per 1 kg/m2 increase) | |||||
| 0.99 (0.95–1.03) | 0.6 | Kurshid et al. 2014 [138] | |||
| Male Sex | |||||
| 1.23 (1.12–1.35) | <0.001 | Somma et al. 2022 [142] | |||
| 1.8 (1.13–2.86) | <0.01 | 1.24 (0.69–2.21) | 0.48 | Cho et al. 2019 [96] | |
| 2.38 (1.28–4.41) | <0.01 | 2.15 (1.14–4.02) | 0.02 | Kurshid et al. 2014 [138] | |
| Baseline QRS duration (per msec increase) | |||||
| 1.02 (1.01–1.03) | <0.01 | Somma et al. 2022 [142] | |||
| 1.01 (1.004–1.016) a | <0.01 | 1.00 (0.99–1.01) a | 0.61 | Cho et al. 2019 [96] | |
| 1.03 (1.02–1.05) | <0.001 | 1.03 (1.01–1.05) | <0.001 | Kurshid et al. 2014 [138] | |
| Paced QRS duration (per msec increase) | |||||
| 1.02 (1.01–1.03) | <0.001 | Somma et al. 2022 [142] | |||
| 1.013 (1.008–1.019) a | <0.001 | 1.01 (1.00–1.02) a | 0.03 | Cho et al. 2019 [96] | |
| 1.01 (0.99–1.03) | 0.3 | 1.01 (0.99–1.03) | Kurshid et al. 2014 [138] | ||
| Baseline EF | |||||
| 0.95 (0.93–0.97) | <0.001 | Somma et al. 2022 [142] | |||
| 0.96 (0.94–0.98) | <0.01 | 0.98 (0.90–1.07) | 0.001 | Cho et al. 2019 [96] | |
| 0.97 (0.94–1.00) | 0.05 | 0.97 (0.95–1.00) | 0.09 | Kurshid et al. 2014 [138] | |
| Ventricular pacing frequency (per 1% increase) | |||||
| 1.02 (1.01–1.02) | <0.001 | Somma et al. 2022 [142] | |||
| 1.02 (1.01–1.03) | <0.001 | 1.01 (1.00–1.02) | 0.02 | Cho et al. 2019 [96] | |
| 1.00 (0.99–1.02) | 0.7 | Kurshid et al. 2014 [138] | |||
| Atrial Fibrillation | |||||
| 1.32 (1.23–1.42) | <0.001 | Somma et al. 2022 [142] | |||
| 0.97 (0.56–1.69) | 0.9 | Kurshid et al. 2014 [138] | |||
| History of MI | |||||
| 1.81 (1.54–2.12) | <0.001 | Somma et al. 2022 [142] | |||
| 3.2 (1.17–8.78) | 0.02 | 3.31 (0.94–11.7) | 0.06 | Cho et al. 2019 [96] | |
| CKD | |||||
| 1.66 (1.32–2.01) | <0.001 | Somma et al. 2022 [142] | |||
| Diabetes | |||||
| 0.86 (0.69–1.06) | 0.14 | Somma et al. 2022 [142] | |||
| 1.28 (0.68–1.24) | 0.8 | Kurshid et al. 2014 [138] |
| Risk Factor | Number of Studies (N) | Pooled Effect | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Host-related | |||
| COPD | 03 | 3.35 [1.73, 6.50] | <0.01 |
| CHF | 6 | 1.60 [1.08, 2.36] | 0.02 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 12 | 2.00 [1.52, 2.64] | <0.01 |
| ESRD a | 8 | 6.27 [2.86, 13.75] | <0.01 |
| Malignancy | 6 | 2.23 [1.26, 3.95] | <0.01 |
| Renal insufficiency b | 5 | 2.64 [1.17, 5.97] | 0.02 |
| Corticosteroid use | 7 | 5.28 [2.29, 12.18] | <0.01 |
| History of device infection | 4 | 7.84 [1.94, 31.60] | <0.01 |
| Procedure-related | |||
| Antibiotic prophylaxis used | 15 | 0.37 [0.21, 0.64] | <0.01 |
| Device revision/upgrade | 17 | 2.00 [1.39, 2.89] | <0.01 |
| Generator change | 16 | 1.74 [1.15, 2.63] | <0.01 |
| Hematoma development | 8 | 9.78 [3.70, 25.84] | <0.01 |
| Lead dislodgment/repositioning | 4 | 8.71 [3.86, 19.64] | <0.01 |
| Temporary pacing | 7 | 2.05 [1.02, 4.12] | 0.04 |
| <100 procedures by operator | 2 | 2.85 [1.23, 6.58] | 0.01 |
| Device-related | |||
| Dual-chamber device | 10 | 1.70 [1.11, 2.59] | 0.01 |
| Presence of epicardial leads | 3 | 8.09 [3.46, 18.92] | <0.01 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Simpson, J.; Yoder, M.; Christian-Miller, N.; Wheat, H.; Kovacs, B.; Cunnane, R.; Ghannam, M.; Liang, J.J. Long-Term Complications Related to Cardiac Implantable Electronic Devices. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 2058. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14062058
Simpson J, Yoder M, Christian-Miller N, Wheat H, Kovacs B, Cunnane R, Ghannam M, Liang JJ. Long-Term Complications Related to Cardiac Implantable Electronic Devices. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(6):2058. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14062058
Chicago/Turabian StyleSimpson, Jamie, Mason Yoder, Nathaniel Christian-Miller, Heather Wheat, Boldizsar Kovacs, Ryan Cunnane, Michael Ghannam, and Jackson J. Liang. 2025. "Long-Term Complications Related to Cardiac Implantable Electronic Devices" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 6: 2058. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14062058
APA StyleSimpson, J., Yoder, M., Christian-Miller, N., Wheat, H., Kovacs, B., Cunnane, R., Ghannam, M., & Liang, J. J. (2025). Long-Term Complications Related to Cardiac Implantable Electronic Devices. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(6), 2058. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14062058







