Description of the Risk Factors for Ischemic Stroke in the Lebanese Population: Their Association with Age at First Stroke Incidence and the Predictors of Recurrence
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Participants
2.3. Variables and Data Source Measures
- -
- Sociodemographic characteristics: Age, gender, marital status, educational level, employment, governorate, income level, and area of residency;
- -
- Previous health-related conditions: smoking, family history of stroke, hypertension (defined as having systolic blood pressure >130 mm Hg and/or diastolic blood pressure >80 mm Hg [24]), hyperlipidemia (defined as having elevated lipid levels [25]), deep vein thrombosis (DVT) or pulmonary embolism (PE) (defined as having blood clots in venous circulation or in pulmonary circulation [26]), atrial fibrillation (defined as having cardiac electricity disturbance [27]), migraine (defined as having a specific type of headache [28]), and myocardial infarction (MI) (defined as having a decreased blood flow to the myocardium [29]);
- -
- Level of disability: the modified Rankin scale was used to classify patients depending on disability levels. It ranges from 0 (no disability) to 6 (death) [30].
2.4. Ethical Considerations
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Murphy, S.J.; Werring, D.J. Stroke: Causes and Clinical Features. Med. Abingdon Engl. UK Ed. 2020, 48, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feigin, V.L.; Abate, M.D.; Abate, Y.H.; Abd ElHafeez, S.; Abd-Allah, F.; Abdelalim, A.; Abdelkader, A.; Abdelmasseh, M.; Abd-Elsalam, S.; Abdi, P.; et al. Global, Regional, and National Burden of Stroke and Its Risk Factors, 1990–2021: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet Neurol. 2024, 23, 973–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, C.; Tadi, P.; Khan Suheb, M.Z.; Patti, L. Ischemic Stroke. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Malaeb, D.; Cherri, S.; Fahs, I.; Sacre, H.; Abdallah, E.; Salameh, P.; Hosseini, H. Management of Acute Stroke Among Lebanese Patients: Assessing Adherence to International Guidelines. Curr. Drug Saf. 2023, 18, 555–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabih, A.; Tadi, P.; Kumar, A. Stroke Prevention. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- O’Donnell, M.J.; Chin, S.L.; Rangarajan, S.; Xavier, D.; Liu, L.; Zhang, H.; Rao-Melacini, P.; Zhang, X.; Pais, P.; Agapay, S.; et al. Global and Regional Effects of Potentially Modifiable Risk Factors Associated with Acute Stroke in 32 Countries (INTERSTROKE): A Case-Control Study. Lancet Lond. Engl. 2016, 388, 761–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsivgoulis, G.; Safouris, A.; Kim, D.-E.; Alexandrov, A.V. Recent Advances in Primary and Secondary Prevention of Atherosclerotic Stroke. J. Stroke 2018, 20, 145–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsanos, A.H.; Filippatou, A.; Manios, E.; Deftereos, S.; Parissis, J.; Frogoudaki, A.; Vrettou, A.-R.; Ikonomidis, I.; Pikilidou, M.; Kargiotis, O.; et al. Blood Pressure Reduction and Secondary Stroke Prevention: A Systematic Review and Metaregression Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials. Hypertens. Dallas Tex 1979 2017, 69, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Deng, H.; Shantsila, A.; Lip, G.Y.H. Rivaroxaban Versus Dabigatran or Warfarin in Real-World Studies of Stroke Prevention in Atrial Fibrillation: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Stroke 2017, 48, 970–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kernan, W.N.; Ovbiagele, B.; Black, H.R.; Bravata, D.M.; Chimowitz, M.I.; Ezekowitz, M.D.; Fang, M.C.; Fisher, M.; Furie, K.L.; Heck, D.V.; et al. Guidelines for the Prevention of Stroke in Patients with Stroke and Transient Ischemic Attack: A Guideline for Healthcare Professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 2014, 45, 2160–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitchett, D.H.; Goodman, S.G.; Langer, A. Ischemic Stroke: A Cardiovascular Risk Equivalent? Lessons Learned from the Stroke Prevention by Aggressive Reduction in Cholesterol Levels (SPARCL) Trial. Can. J. Cardiol. 2008, 24, 705–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Hajj, M.; Salameh, P.; Rachidi, S.; Hosseini, H. The Epidemiology of Stroke in the Middle East. Eur. Stroke J. 2016, 1, 180–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdo, R.; Abboud, H.; Salameh, P.; El Hajj, T.; Hosseini, H. Mortality and Predictors of Death Poststroke: Data from a Multicenter Prospective Cohort of Lebanese Stroke Patients. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. Off. J. Natl. Stroke Assoc. 2019, 28, 859–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahoud, N. A Retrospective Analysis of 254 Acute Stroke Cases Admitted to Two University Hospitals in Beirut: Classification and Associated Factors. Funct. Neurol. 2017, 32, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebanon. Available online: https://data.who.int/countries/422 (accessed on 1 March 2025).
- Gifford, A.; Biffi, A.; Gelaye, B.; Chemali, Z. Shedding Light on the Causes and Characteristics of Stroke in Lebanon: A Systematic Review of Literature. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry Neurol. 2022, 35, 655–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamal, H.; Assaf, S.; Kabalan, M.; El Maissi, R.; Salhab, D.; Rahme, D.; Lahoud, N. Evaluation of Stroke Pre-Hospital Management in Lebanon from Symptoms Onset to Hospital Arrival and Impact on Patients’ Status at Discharge: A Pilot Study. BMC Neurol. 2022, 22, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maalouf, E.; Hallit, S.; Salameh, P.; Hosseini, H. Depression, Anxiety, Insomnia, Stress, and the Way of Coping Emotions as Risk Factors for Ischemic Stroke and Their Influence on Stroke Severity: A Case-Control Study in Lebanon. Front. Psychiatry 2023, 14, 1097873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malek, E.G.; Elbejjani, M.; Abbas, R.; Abed Al Ahad, M.; Isma’eel, H.; Makki, A. TOAST Classification and Risk Factors of Ischemic Stroke in Lebanon. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2020, 141, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Hajj, M.; Ajrouche, R.; Zein, S.; Rachidi, S.; Awada, S.; Al-Hajje, A. Evaluation of Risk Factors and Drug Adherence in the Occurrence of Stroke in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation. Pharm. Pract. 2020, 18, 1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Masri, J.; Finge, H.; Afyouni, A.; Baroud, T.; Ajaj, N.; Ghazi, M.; El Masri, D.; Younes, M.; Salameh, P.; Hosseini, H. The Effects of Green Spaces and Noise Exposure on the Risk of Ischemic Stroke: A Case-Control Study in Lebanon. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2024, 21, 1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Masri, J.; Finge, H.; Baroud, T.; Ajaj, N.; Houmani, M.; Ghazi, M.; Younes, M.; Salameh, P.; Hosseini, H. Adherence to Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) Diet as a Protective Factor for Ischemic Stroke and Its Influence on Disability Level: A Case-Control Study in Lebanon. Nutrients 2024, 16, 3179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaku, A.S.; Tadi, P. Cerebrovascular Disease. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Iqbal, A.M.; Jamal, S.F. Essential Hypertension. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Hill, M.F.; Bordoni, B. Hyperlipidemia. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Office of the Surgeon General (US); National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (US). INTRODUCTION: Definitions of Deep Vein Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism. In The Surgeon General’s Call to Action to Prevent Deep Vein Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism; Office of the Surgeon General (US): Washington, DC, USA, 2008. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK44178/ (accessed on 1 March 2025).
- Nesheiwat, Z.; Goyal, A.; Jagtap, M. Atrial Fibrillation. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Pescador Ruschel, M.A.; De Jesus, O. Migraine Headache. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Ojha, N.; Dhamoon, A.S. Myocardial Infarction. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Pożarowszczyk, N.; Kurkowska-Jastrzębska, I.; Sarzyńska-Długosz, I.; Nowak, M.; Karliński, M. Reliability of the Modified Rankin Scale in Clinical Practice of Stroke Units and Rehabilitation Wards. Front. Neurol. 2023, 14, 1064642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto-Cámara, R.; González-Bernal, J.J.; González-Santos, J.; Aguilar-Parra, J.M.; Trigueros, R.; López-Liria, R. Age-Related Risk Factors at the First Stroke Event. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, A.J.S.; Werring, D.J. New Insights Into Cerebrovascular Pathophysiology and Hypertension. Stroke 2022, 53, 1054–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveros, E.; Patel, H.; Kyung, S.; Fugar, S.; Goldberg, A.; Madan, N.; Williams, K.A. Hypertension in Older Adults: Assessment, Management, and Challenges. Clin. Cardiol. 2020, 43, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guthmann, R.; Davis, N.; Brown, M.; Elizondo, J. Visit Frequency and Hypertension. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2007, 7, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machaalani, M.; Seifeddine, H.; Ali, A.; Bitar, H.; Briman, O.; Chahine, M.N. Knowledge, Attitude, and Practice Toward Hypertension Among Hypertensive Patients Residing in Lebanon. Vasc. Health Risk Manag. 2022, 18, 541–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bou Sanayeh, E.; El Chamieh, C. The Fragile Healthcare System in Lebanon: Sounding the Alarm about Its Possible Collapse. Health Econ. Rev. 2023, 13, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, G. Antiplatelet Therapy and Anticoagulation in Patients with Hypertension. Am. Fam. Physician 2005, 71, 897–899. [Google Scholar]
- Prasad, M.; Khanna, P.; Katyal, V.K.; Verma, R. Acute Psychological Stress Is a Trigger for Stroke: A Case-Crossover Study. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2020, 29, 104799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddin, C.; Murphy, R.; Hankey, G.J.; Judge, C.; Xavier, D.; Rosengren, A.; Ferguson, J.; Alvarez-Iglesias, A.; Oveisgharan, S.; Iversen, H.K.; et al. Association of Psychosocial Stress With Risk of Acute Stroke. JAMA Netw. Open 2022, 5, e2244836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guiraud, V.; Touzé, E.; Rouillon, F.; Godefroy, O.; Mas, J.-L. Stressful Life Events as Triggers of Ischemic Stroke: A Case-Crossover Study. Int. J. Stroke Off. J. Int. Stroke Soc. 2013, 8, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamczyk, K. Voluntary and Involuntary Singlehood and Young Adults’ Mental Health: An Investigation of Mediating Role of Romantic Loneliness. Curr. Psychol. 2017, 36, 888–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, H.T.; Lai, A.J.X.; Sun, J.; Hoang, M.T.; Vu, L.G.; Pham, H.Q.; Nguyen, T.H.; Tran, B.X.; Latkin, C.A.; Le, X.T.T.; et al. Anxiety and Depression Among People Under the Nationwide Partial Lockdown in Vietnam. Front. Public Health 2020, 8, 589359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rink, L.C.; Oyesanya, T.O.; Adair, K.C.; Humphreys, J.C.; Silva, S.G.; Sexton, J.B. Stressors Among Healthcare Workers: A Summative Content Analysis. Glob. Qual. Nurs. Res. 2023, 10, 23333936231161127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto-Cámara, R.; González-Bernal, J.; Aguilar-Parra, J.M.; Trigueros, R.; López-Liria, R.; González-Santos, J. Factors Related to Prehospital Time in Caring for Patients with Stroke. Emergencias 2021, 33, 454–463. [Google Scholar]
- Stubberud, A.; Buse, D.C.; Kristoffersen, E.S.; Linde, M.; Tronvik, E. Is There a Causal Relationship between Stress and Migraine? Current Evidence and Implications for Management. J. Headache Pain 2021, 22, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawless, M.H.; Harrison, K.A.; Grandits, G.A.; Eberly, L.E.; Allen, S.S. Perceived Stress and Smoking-Related Behaviors and Symptomatology in Male and Female Smokers. Addict. Behav. 2015, 51, 80–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, B.T.; Brown, R.C.; Davis, T.P. Smoking and Ischemic Stroke: A Role for Nicotine? Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2002, 23, 78–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oza, R.; Rundell, K.; Garcellano, M. Recurrent Ischemic Stroke: Strategies for Prevention. Am. Fam. Physician 2017, 96, 436–440. [Google Scholar]
- Flach, C.; Muruet, W.; Wolfe, C.D.A.; Bhalla, A.; Douiri, A. Risk and Secondary Prevention of Stroke Recurrence. Stroke 2020, 51, 2435–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saade, S.; Hallit, S.; Salameh, P.; Hosseini, H. Knowledge and Response to Stroke Among Lebanese Adults: A Population-Based Survey. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 891073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saade, S.; Kobeissy, R.; Sandakli, S.; Malaeb, D.; Lahoud, N.; Hallit, S.; Hosseini, H.; Salameh, P. Medication Adherence for Secondary Stroke Prevention and Its Barriers among Lebanese Survivors: A Cross-Sectional Study. Clin. Epidemiol. Glob. Health 2021, 9, 338–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busch, M.A.; Schienkiewitz, A.; Nowossadeck, E.; Gößwald, A. Prevalence of stroke in adults aged 40 to 79 years in Germany: Results of the German Health Interview and Examination Survey for Adults (DEGS1). Bundesgesundheitsblatt Gesundheitsforschung Gesundheitsschutz 2013, 56, 656–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stahmeyer, J.T.; Stubenrauch, S.; Geyer, S.; Weissenborn, K.; Eberhard, S. The Frequency and Timing of Recurrent Stroke. Dtsch. Ärztebl. Int. 2019, 116, 711–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

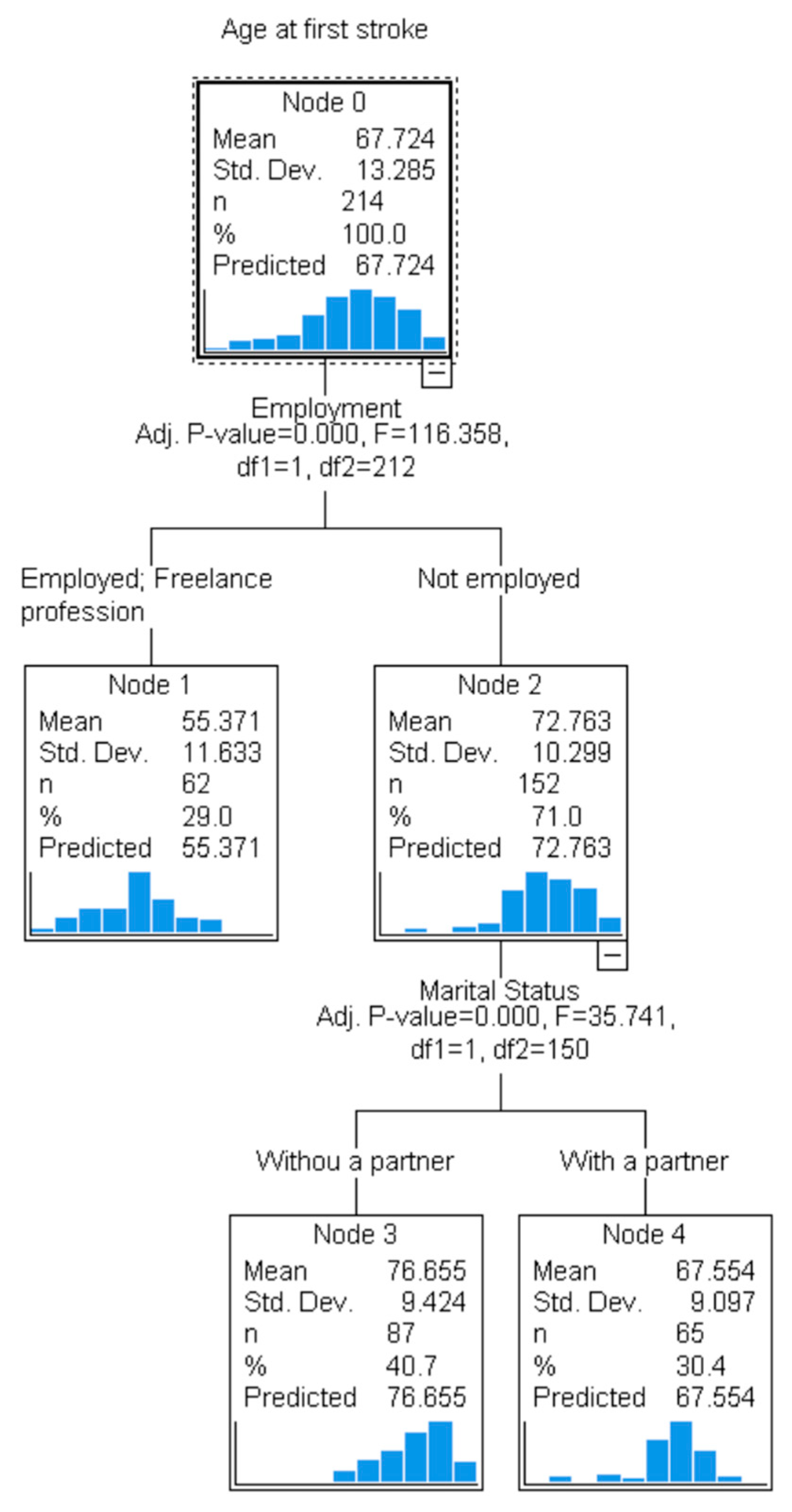
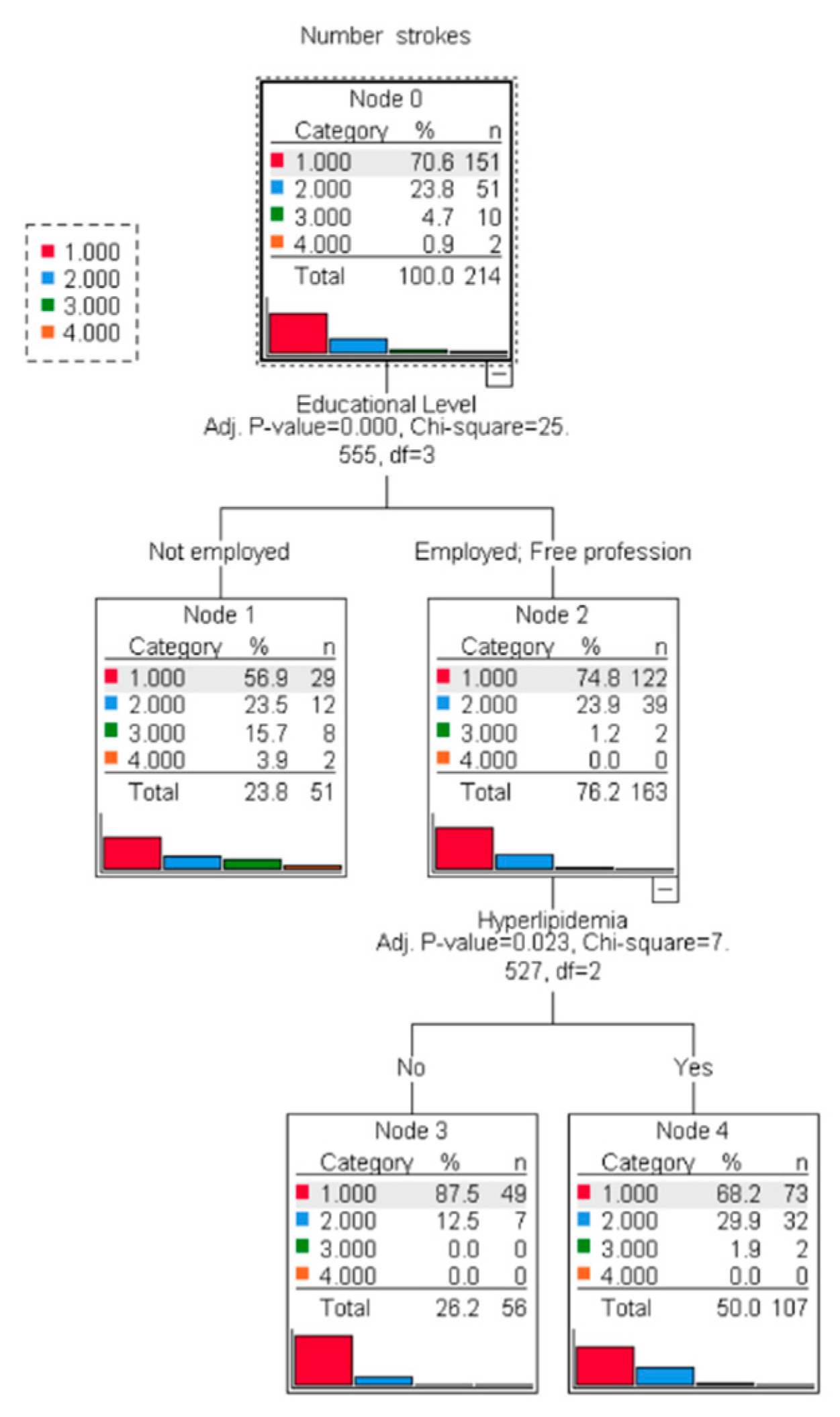
| Factor | Category | Number | Percentage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | Mean ± SD | 68.589 ± 13.436 | |
| Gender | Female | 103 | 48.13 |
| Male | 111 | 51.86 | |
| Marital status | With a partner | 119 | 55.6 |
| Without a partner | 95 | 44.4 | |
| Governorate | North | 11 | 5.1 |
| Beirut | 99 | 46.3 | |
| South | 57 | 26.6 | |
| Mount Leb | 20 | 9.3 | |
| Bekaa | 27 | 12.6 | |
| Education | Not educated | 51 | 23.83 |
| School education | 99 | 46.26 | |
| University education | 64 | 29.91 | |
| Employment | Not employed | 152 | 71.03 |
| Employed | 31 | 14.48 | |
| Freelance profession | 31 | 14.48 | |
| Income | Low | 71 | 33.2 |
| Moderate | 129 | 60.3 | |
| High | 28 | 6.5 | |
| Residency location | Rural | 55 | 25.7 |
| Urban | 159 | 74.3 | |
| Factor | Category | Number | Percentage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Smoking | Yes | 126 | 58.88 |
| No | 88 | 41.12 | |
| Family history | Yes | 105 | 49.06 |
| No | 109 | 50.94 | |
| Hypertension | Yes | 194 | 90.65 |
| No | 20 | 9.35 | |
| Hyperlipidemia | Yes | 151 | 70.56 |
| No | 63 | 29.44 | |
| DVT or PE | Yes | 27 | 11.21 |
| No | 187 | 87.39 | |
| Atrial fibrillation | Yes | 74 | 34.58 |
| No | 140 | 65.42 | |
| Migraine | Yes | 28 | 13.08 |
| No | 186 | 86.92 | |
| Myocardial infarction | Yes | 49 | 22.9 |
| No | 165 | 77.1 |
| Factor | Category | Age at 1st Stroke | Number of Strokes | Stroke Recurrence | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD | p-Value | Mean ± SD | p-Value | Yes | No | p-Value | ||
| Gender | Female | 68.75 ± 14.039 | 0.281 | 1.34 ± 0.57 | 0.884 | 30 (23.07%) | 73 (76.93%) | 0.923 |
| Male | 66.77 ± 12.533 | 1.38 ± 0.661 | 33 (29.73%) | 78 (70.27%) | ||||
| Marital status | With a partner | 74.87 ± 11.508 | <0.001 * | 1.37 ± 0.62 | 0.891 | 28 (29.47%) | 67 (70.53%) | 0.992 |
| Without a partner | 62.02 ± 11.793 | 1.35 ± 0.619 | 35 (29.41) | 84 (70.59%) | ||||
| Governorate | North | 70.45 ± 12.421 | 0.15 | 1.18 ± 0.405 | 0.381 | 2 (18.18%) | 9 (81.82%) | 0.317 |
| Beirut | 68.34 ± 13.313 | 1.39 ± 0.667 | 31 (31.31%) | 68 (68.69%) | ||||
| South | 69.63 ± 12.059 | 1.28 ± 0.59 | 12 (21.05%) | 45 (78.95%) | ||||
| Mount Lebanon | 63.95 ± 13.847 | 1.35 ± 0.489 | 7 (35%) | 13 (65%) | ||||
| Bekaa | 63.11 ± 14.813 | 1.48 ± 0.643 | 11 (40.74%) | 16 (59.26%) | ||||
| Education | Not educated | 75.92 ± 9.718 | <0.001 * | 1.67 ± 0.887 | <0.001 * | 22 (43.14 | 29 (56.86%) | 0.027 * |
| School education | 69.13 ± 10.558 | 1.3 ± 0.504 | 28 (28.28%) | 71 (71.72%) | ||||
| University education | 59.02 ± 14.622 | 1.2 ± 0.406 | 13 (20.31%) | 51 (79.69%) | ||||
| Employment | Not employed | 72.76 ± 10.299 | <0.001 * | 1.44 ± 0.668 | 0.004 * | 54 (35.53%) | 98 (64.47%) | 0.004 * |
| Employed | 51.13 ± 12.005 | 1.23 ± 0.425 | 7 (22.58%) | 24 (77.42%) | ||||
| Freelance profession | 59.61 ± 9.625 | 1.1 ± 0.396 | 2 (6.45%) | 29 (93.55%) | ||||
| Income | Low | 67.83 ± 10.191 | 0.15 | 1.41 ± 0.667 | 0.767 | 23 (32.39%) | 48 (67.61%) | 0.799 |
| Moderate | 68.02 ± 14.061 | 1.33 ± 0.591 | 36 (27.91%) | 93 (72.09%) | ||||
| High | 64.5 ± 14.867 | 1.36 ± 0.633 | 4 (28.57%) | 10 (71.43%) | ||||
| Residency location | Rural | 66.49 ± 12.993 | 0.42 | 1.45 ± 0.689 | 0.241 | 19 (34.55%) | 36 (65.45%) | 0.335 |
| Urban | 68.15 ± 13.398 | 1.33 ± 0.59 | 44 (27.67%) | 115 (72.33%) | ||||
| Factor | Category | Age at First Stroke | Number of Strokes | Stroke Recurrence | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD | p-Value | Mean ± SD | p-Value | Yes | No | p-Value | ||
| Smoking | Yes | 64.5 ± 11.43 | <0.001 * | 1.33 ± 0.645 | 0.176 | 32 (25.4%) | 94 (74.6%) | 0.121 |
| No | 72.34 ± 14.414 | 1.4 ± 0.578 | 31 (35.23%) | 57 (64.77%) | ||||
| Family history | Yes | 65.5 ± 14.685 | 0.016 * | 1.48 ± 0.681 | 0.005 * | 40 (38.1%) | 65 (61.9%) | 0.006 * |
| No | 69.87 ± 11.442 | 1.25 ± 0.53 | 23 (21.1%) | 86 (78.9%) | ||||
| Hypertension | Yes | 69.42 ± 11.267 | <0.001 * | 1.39 ± 0.637 | 0.012 * | 62 (31.96%) | 132 (68.04%) | 0.012 * |
| No | 51.25 ± 19.336 | 1.05 ± 0.224 | 1 (5%) | 19 (95%) | ||||
| Hyperlipidemia | Yes | 71.15 ± 10.471 | <0.001 * | 1.46 ± 0.681 | <0.001 * | 55 (36.42%) | 96 (63.57%) | 0.001 * |
| No | 59.51 ± 15.614 | 1.13 ± 0.336 | 8 (12.7%) | 55 (87.3%) | ||||
| DVT or PE | Yes | 73.07 ± 12.764 | 0.025 * | 1.63 ± 0.839 | 0.041 * | 51 (44.44) | 136 (55.56%) | 0.067 |
| No | 66.95 ± 13.213 | 1.32 ± 0.571 | 12 (27.27%) | 15 (72.73) | ||||
| Atrial fibrillation | Yes | 69.95 ± 10.994 | 0.075 | 1.57 ± 0.76 | 0.001 * | 31 (43.24%) | 109 (56.76%) | 0.001 * |
| No | 66.55 ± 14.246 | 1.25 ± 0.496 | 32 (22.14%) | 42 (77.86%) | ||||
| Migraine | Yes | 54.71 ± 14.616 | <0.001 * | 1.25 ± 0.441 | 0.472 | 56 (25%) | 130 (75%) | 0.58 |
| No | 69.68 ± 11.939 | 1.38 ± 0.639 | 7 (30.1%) | 21 (69.9%) | ||||
| Myocardial infarction | Yes | 71.12 ± 9.482 | 0.041 * | 1.45 ± 0.679 | 0.220 | 45 (36.73%) | 120 (63.27%) | 0.202 |
| No | 66.72 ± 14.086 | 1.33 ± 0.598 | 18 (27.27) | 31 (72.73) | ||||
| Factor | Category | Age at First Stroke | Number of Strokes | Stroke Recurrence | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD | p-Value | Mean ± SD | p-Value | Yes | No | p-Value | ||
| mRS category | Mild disability or no symptoms | 62.7 ± 15.66 | <0.001 * | 1.18 ± 0.39 | 0.05 * | 11 (18.33%) | 49 (81.66%) | 0.082 |
| Moderate disability | 68.43 ± 11.743 | 1.42 ± 0.64 | 38 (34.23%) | 73 (65.77%) | ||||
| Severe disability or death | 72.91 ± 11.156 | 1.44 ± 0.765 | 14 (32.56%) | 29 (67.44%) | ||||
| Parameter | B | Std. Error | p-Value | 95% Confidence Interval | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower Bound | Upper Bound | ||||
| Intercept | 54.753 | 2.733 | 0.000 | 49.365 | 60.141 |
| Marital status | |||||
| With partner vs. no partner * | 6.058 | 1.385 | 0.000 | 3.326 | 8.789 |
| Education | |||||
| Not educated vs. university education * | 5.512 | 1.828 | 0.003 | 1.906 | 9.117 |
| School vs. university education * | 2.246 | 1.561 | 0.152 | −0.832 | 5.324 |
| Employment status | |||||
| Not employed vs. freelancer * | 7.983 | 1.896 | 0.000 | 4.244 | 11.721 |
| Employed vs. freelancer * | −4.518 | 2.246 | 0.046 | −8.947 | −0.088 |
| Other lifestyle factors and comorbidities | |||||
| Smoking | −2.929 | 1.316 | 0.027 | −5.525 | −0.334 |
| Family history of stroke | −2.303 | 1.170 | 0.050 | −4.611 | 0.004 |
| Hypertension | 5.064 | 2.256 | 0.026 | 0.615 | 9.513 |
| Hyperlipidemia | 3.378 | 1.455 | 0.021 | 0.509 | 6.248 |
| DVT or PE | −0.939 | 1.808 | 0.604 | −4.504 | 2.626 |
| Atrial fibrillation | −1.337 | 1.271 | 0.294 | −3.844 | 1.170 |
| Migraine | −9.109 | 1.817 | 0.000 | −12.693 | −5.525 |
| Myocardial infarction | 2.477 | 1.434 | 0.086 | −0.351 | 5.304 |
| Parameter | p-Value | ORa [Exp(B)] | 95% Confidence Interval | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | |||
| Employment status | 0.018 | |||
| Employed vs. Not employed * | 0.005 | 9.591 | 1.976 | 46.56 |
| Freelancer vs. Not employed * | 0.044 | 6.036 | 1.053 | 34.61 |
| Partner vs. No partner * | 0.036 | 2.136 | 1.05 | 4.345 |
| Family history of stroke | 0.001 | 3.251 | 1.625 | 6.505 |
| Hyperlipidemia | 0.004 | 3.710 | 1.515 | 9.085 |
| Atrial fibrillation | 0.008 | 2.521 | 1.272 | 4.999 |
| Constant | 0.000 | 0.011 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
El Masri, J.; El Masri, D.; Ghazi, M.; Afyouni, A.; Finge, H.; El Ahdab, J.; Tlayss, M.; Al Chaar, S.; Abou-Kheir, W.; Salameh, P.; et al. Description of the Risk Factors for Ischemic Stroke in the Lebanese Population: Their Association with Age at First Stroke Incidence and the Predictors of Recurrence. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 2034. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14062034
El Masri J, El Masri D, Ghazi M, Afyouni A, Finge H, El Ahdab J, Tlayss M, Al Chaar S, Abou-Kheir W, Salameh P, et al. Description of the Risk Factors for Ischemic Stroke in the Lebanese Population: Their Association with Age at First Stroke Incidence and the Predictors of Recurrence. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(6):2034. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14062034
Chicago/Turabian StyleEl Masri, Jad, Diala El Masri, Maya Ghazi, Ahmad Afyouni, Hani Finge, Jad El Ahdab, Maryam Tlayss, Soltan Al Chaar, Wassim Abou-Kheir, Pascale Salameh, and et al. 2025. "Description of the Risk Factors for Ischemic Stroke in the Lebanese Population: Their Association with Age at First Stroke Incidence and the Predictors of Recurrence" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 6: 2034. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14062034
APA StyleEl Masri, J., El Masri, D., Ghazi, M., Afyouni, A., Finge, H., El Ahdab, J., Tlayss, M., Al Chaar, S., Abou-Kheir, W., Salameh, P., & Hosseini, H. (2025). Description of the Risk Factors for Ischemic Stroke in the Lebanese Population: Their Association with Age at First Stroke Incidence and the Predictors of Recurrence. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(6), 2034. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14062034








