Markers of Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis Are Associated with Mortality in Critically Ill Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Population
2.2. Data Acquisition and Blood Sampling
2.3. Assessment of HLH Criteria
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- van der Poll, T.; Shankar-Hari, M.; Wiersinga, W.J. The immunology of sepsis. Immunity 2021, 54, 2450–2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henter, J.I.; Samuelsson-Horne, A.; Arico, M.; Egeler, R.M.; Elinder, G.; Filipovich, A.H.; Gadner, H.; Imashuku, S.; Komp, D.; Ladisch, S.; et al. Treatment of hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis with HLH-94 immunochemotherapy and bone marrow transplantation. Blood 2002, 100, 2367–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weitzman, S. Approach to hemophagocytic syndromes. Hematol. Am. Soc. Hematol. Educ. Program. 2011, 2011, 178–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauchmuller, K.; Manson, J.J.; Tattersall, R.; Brown, M.; McNamara, C.; Singer, M.; Brett, S.J. Haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in adult critical care. J. Intensive Care Soc. 2020, 21, 256–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meena, N.K.; Sinokrot, O.; Duggal, A.; Alpat, D.; Singh, Z.N.; Coviello, J.M.; Li, M.; Wang, X.; Mireles-Cabodevila, E. The Performance of Diagnostic Criteria for Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis in Critically Ill Patients. J. Intensive Care Med. 2020, 35, 1476–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valade, S.; Monseau, G.; Mariotte, E.; Darmon, M. Diagnostic Performance of Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis Criteria and HScore in Critically Ill Patients With Severe Hemophagocytic Syndrome. Crit. Care Med. 2021, 49, e874–e879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tothova, Z.; Berliner, N. Hemophagocytic Syndrome and Critical Illness: New Insights into Diagnosis and Management. J. Intensive Care Med. 2015, 30, 401–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, G.; Hererra, M.; Patel, D.; Nanchal, R.; Guddati, A.K. Outcomes of adult critically ill patients with hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in united states-analysis from an administrative database from 2007 to 2015. Am. J. Blood Res. 2020, 10, 330–338. [Google Scholar]
- Krychtiuk, K.A.; Ruhittel, S.; Hohensinner, P.J.; Koller, L.; Kaun, C.; Lenz, M.; Bauer, B.; Wutzlhofer, L.; Draxler, D.F.; Maurer, G.; et al. Mitochondrial DNA and Toll-Like Receptor-9 Are Associated With Mortality in Critically Ill Patients. Crit. Care Med. 2015, 43, 2633–2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenz, M.; Draxler, D.F.; Zhang, C.; Kassem, M.; Kastl, S.P.; Niessner, A.; Huber, K.; Wojta, J.; Heinz, G.; Speidl, W.S.; et al. Toll-like receptor 2 and 9 expression on circulating neutrophils is associated with increased mortality in critically ill patients. Shock 2020, 54, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krychtiuk, K.A.; Honeder, M.C.; Lenz, M.; Maurer, G.; Wojta, J.; Heinz, G.; Huber, K.; Speidl, W.S. Copeptin Predicts Mortality in Critically Ill Patients. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0170436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenz, M.; Krychtiuk, K.A.; Goliasch, G.; Distelmaier, K.; Wojta, J.; Heinz, G.; Speidl, W.S. N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide and high-sensitivity troponin T exhibit additive prognostic value for the outcome of critically ill patients. Eur. Heart J. Acute Cardiovasc. Care 2020, 9, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henter, J.I.; Horne, A.; Arico, M.; Egeler, R.M.; Filipovich, A.H.; Imashuku, S.; Ladisch, S.; McClain, K.; Webb, D.; Winiarski, J.; et al. HLH-2004: Diagnostic and therapeutic guidelines for hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2007, 48, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jordan, M.B.; Filipovich, A.H. Hematopoietic cell transplantation for hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: A journey of a thousand miles begins with a single (big) step. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2008, 42, 433–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, J.; Goyal, A.; Azevedo, A.M. StatPearls2023. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK430907/ (accessed on 23 January 2025).
- Sjoberg, B.P.; Menias, C.O.; Lubner, M.G.; Mellnick, V.M.; Pickhardt, P.J. Splenomegaly: A Combined Clinical and Radiologic Approach to the Differential Diagnosis. Gastroenterol. Clin. N. Am. 2018, 47, 643–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curovic Rotbain, E.; Lund Hansen, D.; Schaffalitzky de Muckadell, O.; Wibrand, F.; Meldgaard Lund, A.; Frederiksen, H. Splenomegaly—Diagnostic validity, work-up, and underlying causes. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0186674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinacher, E.; Lenz, M.; Krychtiuk, K.A.; Hengstenberg, C.; Huber, K.; Wojta, J.; Heinz, G.; Niessner, A.; Speidl, W.S.; Koller, L. Decreased percentages of plasmacytoid dendritic cells predict survival in critically ill patients. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2024, 115, 902–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLong, E.R.; DeLong, D.M.; Clarke-Pearson, D.L. Comparing the areas under two or more correlated receiver operating characteristic curves: A nonparametric approach. Biometrics 1988, 44, 837–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Bahr Greenwood, T.; Palmkvist-Kaijser, K.; Chiang, S.C.; Tesi, B.; Bryceson, Y.T.; Hjelmqvist, H.; Henter, J.-I. Elevated ferritin and soluble CD25 in critically ill patients are associated with parameters of (hyper) inflammation and lymphocyte cytotoxicity. Minerva Anestesiol. 2019, 85, 1289–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.M.; Xu, X.J.; Qi, W.Q.; Ge, Q.M. Prognostic significance of soluble CD25 in patients with sepsis: A prospective observational study. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2022, 60, 952–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knaak, C.; Schuster, F.S.; Spies, C.; Vorderwulbecke, G.; Nyvlt, P.; Schenk, T.; Balzer, F.; La Rosée, P.; Janka, G.; Brunkhorst, F.M.; et al. Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis in Critically Ill Patients. Shock 2020, 53, 701–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, E.; Lee, J.H.; Lim, H.J.; Oh, S.W.; Jo, S.K.; Cho, W.Y.; Kim, H.; Lee, S.Y. Soluble CD25 is increased in patients with sepsis-induced acute kidney injury. Nephrology 2014, 19, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bursa, D.; Bednarska, A.; Pihowicz, A.; Paciorek, M.; Horban, A. Analysis of the occurrence of hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH) features in patients with sepsis: A prospective study. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 10529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarczak, D.; Nierhaus, A. Cytokine Storm-Definition, Causes, and Implications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fajgenbaum, D.C.; June, C.H. Cytokine Storm. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2255–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metcalf, T.U.; Wilkinson, P.A.; Cameron, M.J.; Ghneim, K.; Chiang, C.; Wertheimer, A.M.; Hiscott, J.B.; Nikolich-Zugich, J.; Haddad, E.K. Human Monocyte Subsets Are Transcriptionally and Functionally Altered in Aging in Response to Pattern Recognition Receptor Agonists. J. Immunol. 2017, 199, 1405–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Maeyer, R.P.H.; Chambers, E.S. The impact of ageing on monocytes and macrophages. Immunol. Lett. 2021, 230, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, K.; Tsujita, Y.; Yamane, T.; Eguchi, Y. Decreasing Plasma Fibrinogen Levels in the Intensive Care Unit Are Associated with High Mortality Rates in Patients with Sepsis-Induced Coagulopathy. Clin. Appl. Thromb. Hemost. 2022, 28, 10760296221101386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, N.; Li, R.; Sun, S.; Zhang, L.; Xia, Y.; Chen, S.; Sun, J.; Chen, M. Fibrinogen Is Associated with Prognosis of Critically Ill Patients with Sepsis: A Study Based on Cox Regression and Propensity Score Matching. Mediators Inflamm. 2023, 2023, 7312822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fricault, P.; Piot, J.; Estève, C.; Savan, V.; Sebesteyn, A.; Durand, M.; Chavanon, O.; Albaladejo, P. Preoperative fibrinogen level and postcardiac surgery morbidity and mortality rates. Ann. Card. Anaesth. 2022, 25, 485–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davalos, D.; Akassoglou, K. Fibrinogen as a key regulator of inflammation in disease. Semin. Immunopathol. 2012, 34, 43–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lachmann, G.; Knaak, C.; Vorderwulbecke, G.; La Rosee, P.; Balzer, F.; Schenk, T.; Schuster, F.S.; Nyvlt, P.; Janka, G.; Brunkhorst, F.M.; et al. Hyperferritinemia in Critically Ill Patients. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 48, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusu, D.; Blaj, M.; Ristescu, I.; Patrascanu, E.; Gavril, L.; Lungu, O.; Siriopol, I.; Buzincu, I.; Grigoraș, I. Outcome Predictive Value of Serum Ferritin in ICU Patients with Long ICU Stay. Medicina 2020, 57, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, M.; Deng, H.; Mao, W.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Fan, J.; Li, W.; Liu, D. U-shaped association between serum triglyceride levels and mortality among septic patients: An analysis based on the MIMIC-IV database. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0294779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
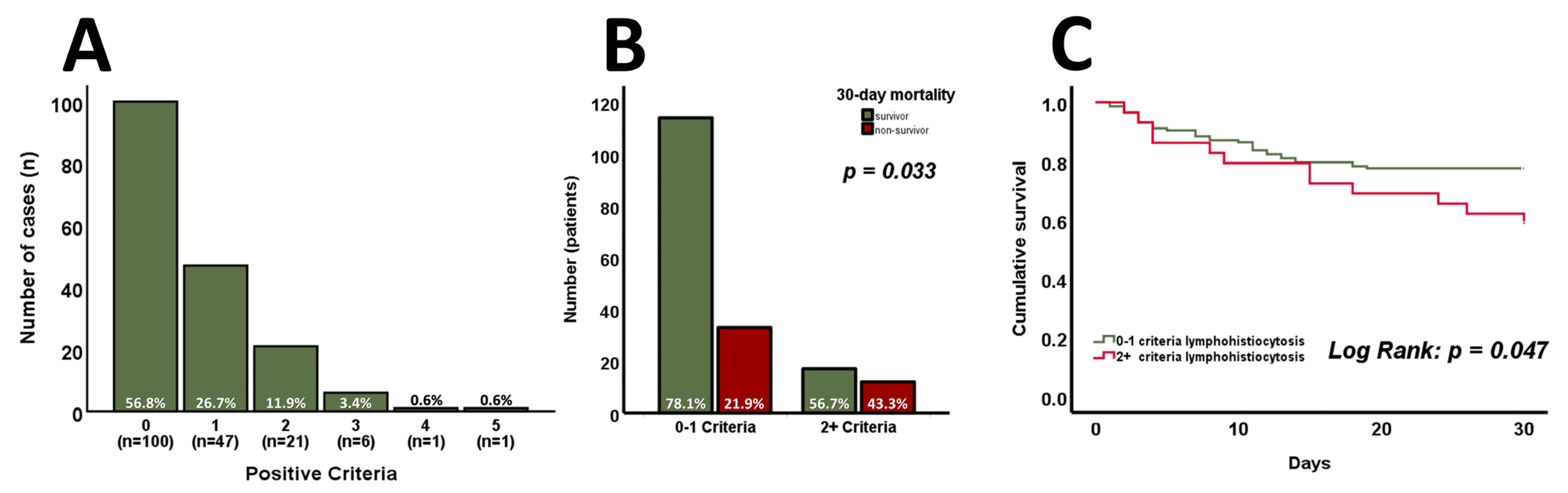
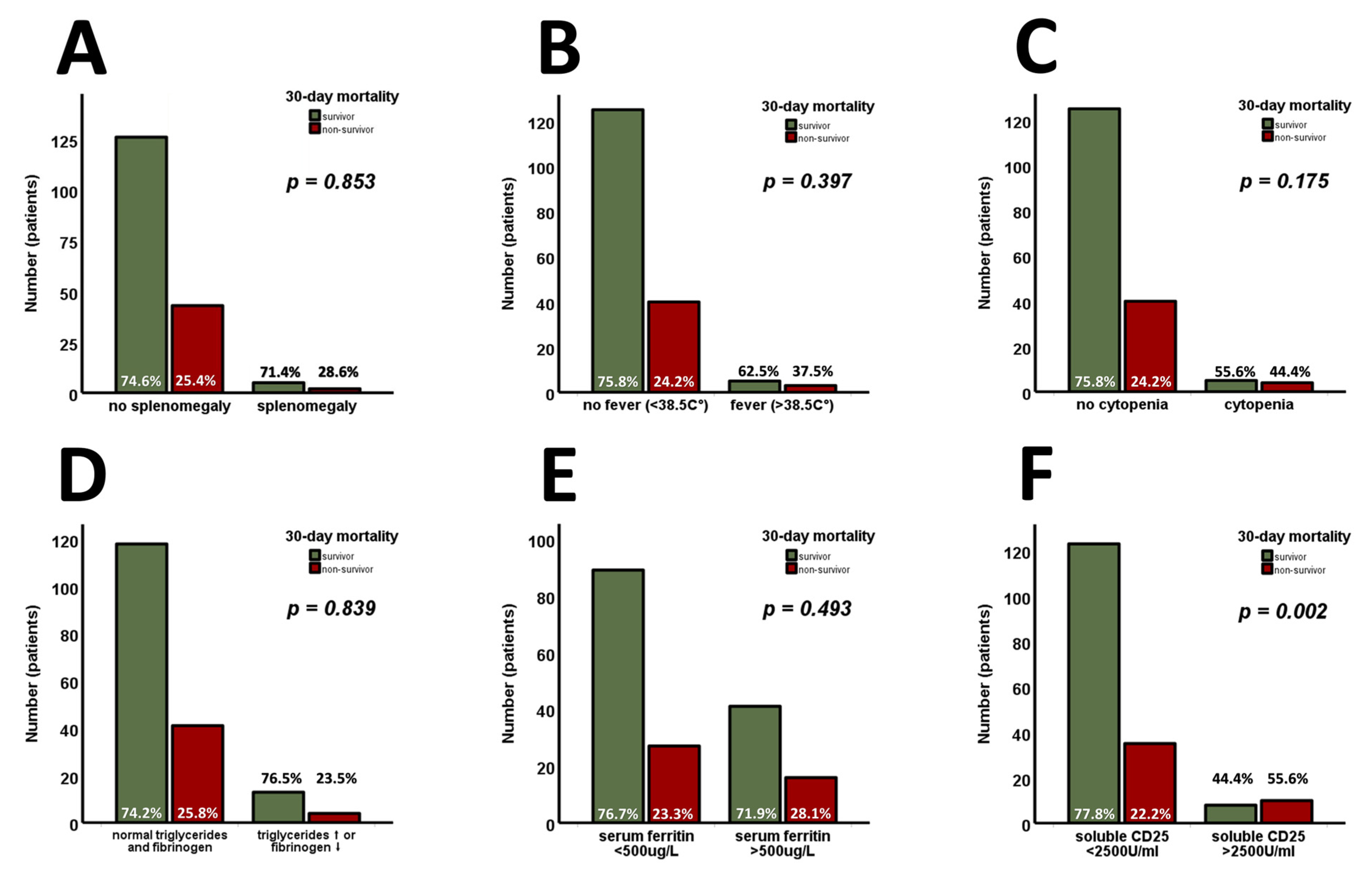
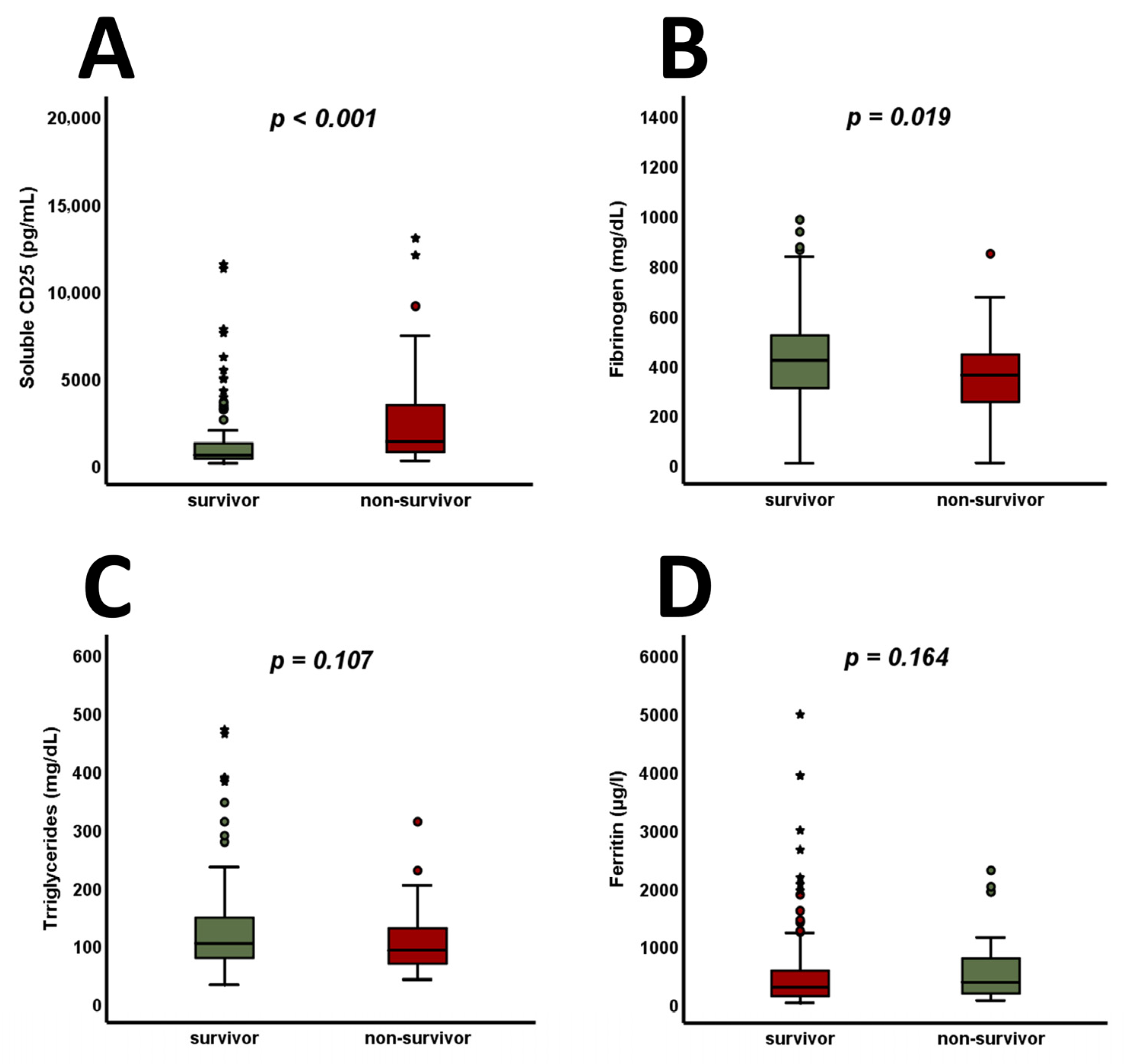
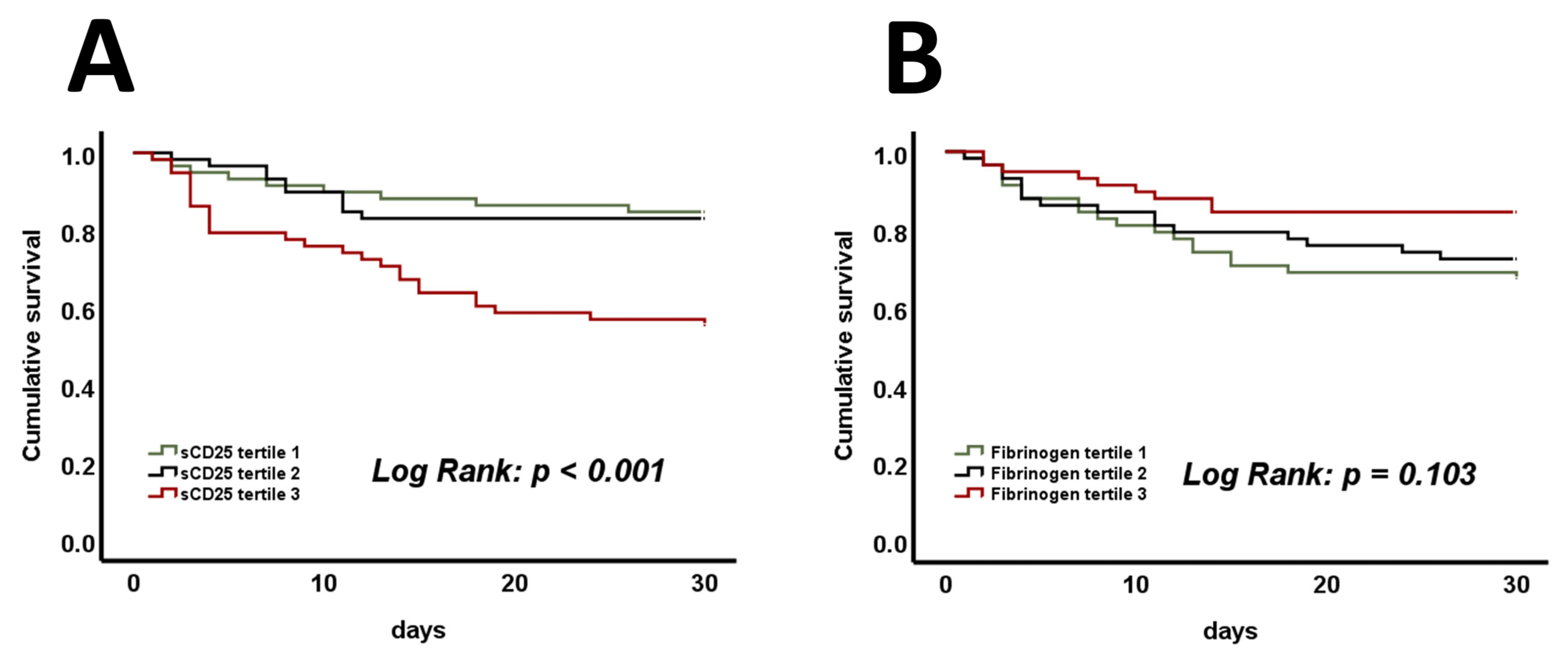
| Total n = 176 (100%) | 30-Day Survivors n = 131 (74.4%) | 30-Day Non-Survivors n = 45 (25.6%) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patient characteristics: | ||||
| Age [years] | 67.5 (57.5–77.4) | 65.8 (52.8–76.5) | 71.0 (61.1–78.5) | 0.218 |
| Male sex, n (%) | 108 (61.4%) | 79 (60.3%) | 29 (64.4%) | 0.723 |
| Vasopressors, n (%) | 103 (58.5%) | 69 (52.7%) | 34 (75.6%) | 0.004 |
| Mechanical ventilation, n (%) | 102 (58.0%) | 71 (54.2%) | 31 (68.9%) | 0.025 |
| C-reactive protein [mg/dL] Leukocytes max [G/L] | 4.10 (1.02–10.67) 11.21 (7.69–16.17) | 4.00 (0.89–10.68) 11.20 (7.69–16.43) | 4.42 (1.53–10.42) 11.34 (7.71–16.11) | 0.897 0.976 |
| Fibrinogen [mg/dL] | 392.0 (286.3–507.5) | 416.0 (304.8–517.3) | 358.0 (247.3–441.8) | 0.019 |
| Creatinine [mg/dL] | 1.15 (0.87–1.85) | 1.06 (0.86–1.68) | 1.55 (1.11–2.70) | <0.001 |
| Lactate [mmol/L] | 1.9 (1.3–3.2) | 1.8 (1.3–2.7) | 2.7 (1.30–6.8) | 0.012 |
| Arterial pH | 7.38 (7.28–7.48) | 7.40 (7.30–7.48) | 7.31 (7.22–7.48) | 0.036 |
| Bilirubin [mg/dL] | 0.90 (0.60–1.40) | 0.83 (0.52–1.22) | 0.60 (1.05–1.80) | 0.089 |
| SIRS, n (%) | 129 (73.3%) | 90 (68.7%) | 39 (86.7%) | 0.019 |
| SAPS II | 45 (31–59) | 39 (29–52) | 61 (47–70) | <0.001 |
| SOFA | 8 (5–11) | 7 (4–10) | 12 (8–14) | <0.001 |
| Cause of admission: | ||||
| Cardiac arrest, n (%) | 40 (22.7%) | 22 (16.8%) | 18 (40.0%) | <0.001 |
| ADHF, n (%) | 16 (9.1%) | 13 (9.9%) | 3 (6.7%) | 0.512 |
| Cardiogenic shock, n (%) | 25 (14.2%) | 14 (10.7%) | 11 (24.4%) | 0.023 |
| Sepsis/septic shock, n (%) | 16 (9.1%) | 12 (9.2%) | 4 (8.9%) | 0.956 |
| Respiratory failure, n (%) | 14 (8.0%) | 10 (7.6%) | 4 (8.9%) | 0.788 |
| Cardiac-surgery/valve intervention, n (%) | 59 (33.5%) | 55 (42.0%) | 4 (8.9%) | <0.001 |
| Other reasons, n (%) | 6 (3.4%) | 5 (3.8%) | 1 (2.2%) | 0.611 |
| Total n = 176 (100%) | 0–1 Criterion n = 147 (83.5%) | 2+ Criteria n = 29 (16.5%) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patient characteristics: | ||||
| Age [years] | 67.5 (57.5–77.4) | 69.8 (58.8–77.5) | 60.0 (48.6–72.1) | 0.031 |
| Male sex, n (%) | 108 (61.4%) | 92 (62.6%) | 16 (55.2%) | 0.454 |
| BMI [kg/m2] | 26.6 (23.9–30.1) | 26.6 (24.0–30.9) | 26.4 (21.3–29.7) | 0.481 |
| Heart rate [beats/min] | 96 (81–111) | 95 (81–110) | 107 (88–120) | 0.137 |
| Mean blood pressure [mmHg] | 64 (58–72) | 65 (59–72) | 65 (59–72) | 0.148 |
| Vasopressors, n (%) | 103 (58.5%) | 83 (56.5%) | 19 (65.5%) | 0.279 |
| Mechanical ventilation, n (%) | 102 (58.0%) | 87 (59.2%) | 15 (51.7%) | 0.554 |
| Hemoglobin [g/dL] | 10.4 (9.3–11.8) | 10.5 (9.5–11.9) | 9.55 (8.3–10.28) | 0.001 |
| Thrombocytes [G/L] | 171 (122–218) | 184 (135–224) | 98 (48–142.8) | <0.001 |
| Leukocytes max [G/L] | 11.21 (7.69–16.17) | 11.83 (7.96–16.13) | 10.05 (7.38–16.5) | 0.678 |
| C-reactive protein [mg/dL] | 4.10 (1.02–10.67) | 3.50 (0.89–10.07) | 7.45 (3.85–20.63) | 0.003 |
| Fibrinogen [mg/dL] | 392.0 (286.3–507.5) | 396.5 (296.3–507.5) | 380.5 (193.0–514.5) | 0.436 |
| Creatinine [mg/dL] | 1.15 (0.87–1.85) | 1.10 (0.86–1.68) | 1.84 (1.04–2.95) | 0.006 |
| Lactate [mmol/L] | 1.9 (1.3–3.2) | 1.8 (1.2–3.1) | 2.1 (1.5–3.7) | 0.690 |
| Arterial pH | 7.38 (7.28–7.48) | 7.38 (7.28–7.48) | 7.36 (7.25–7.49) | 0.489 |
| Bilirubin [mg/dL] | 0.90 (0.60–1.40) | 0.83 (0.52–1.20) | 1.59 (0.73–2.88) | 0.001 |
| SIRS, n (%) | 129 (73.3%) | 105 (71.4%) | 24 (82.8%) | 0.208 |
| SAPS II | 45 (31–59) | 44 (30–57) | 47.0 (37.5–60.0) | 0.166 |
| SOFA | 8.0 (5.0–11.0) | 7.0 (4.8–11.0) | 10.0 (8.0–14.0) | 0.001 |
| Cause of admission: | ||||
| Cardiac arrest, n (%) | 40 (22.7%) | 35 (23.8%) | 5 (17.2%) | 0.440 |
| ADHF, n (%) | 16 (9.1%) | 13 (8.8%) | 3 (10.3%) | 0.797 |
| Cardiogenic shock, n (%) | 25 (14.2%) | 18 (12.2%) | 7 (24.1%) | 0.094 |
| Sepsis/septic shock, n (%) | 16 (9.1%) | 10 (6.8%) | 6 (20.7%) | 0.017 |
| Respiratory failure, n (%) | 14 (8.0%) | 10 (6.8%) | 4 (13.8%) | 0.204 |
| Cardiac surgery/valve intervention, n (%) | 59 (33.5%) | 56 (38.1%) | 3 (10.3%) | 0.004 |
| Other reasons, n (%) | 6 (3.4%) | 5 (3.4%) | 1 (3.4%) | 0.990 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lenz, M.; Haider, P.; Steinacher, E.; Gatterer, C.; Zilberszac, R.; Demyanets, S.; Hengstenberg, C.; Wojta, J.; Heinz, G.; Speidl, W.S.; et al. Markers of Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis Are Associated with Mortality in Critically Ill Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 1970. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14061970
Lenz M, Haider P, Steinacher E, Gatterer C, Zilberszac R, Demyanets S, Hengstenberg C, Wojta J, Heinz G, Speidl WS, et al. Markers of Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis Are Associated with Mortality in Critically Ill Patients. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(6):1970. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14061970
Chicago/Turabian StyleLenz, Max, Patrick Haider, Eva Steinacher, Constantin Gatterer, Robert Zilberszac, Svitlana Demyanets, Christian Hengstenberg, Johann Wojta, Gottfried Heinz, Walter S. Speidl, and et al. 2025. "Markers of Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis Are Associated with Mortality in Critically Ill Patients" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 6: 1970. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14061970
APA StyleLenz, M., Haider, P., Steinacher, E., Gatterer, C., Zilberszac, R., Demyanets, S., Hengstenberg, C., Wojta, J., Heinz, G., Speidl, W. S., & Krychtiuk, K. A. (2025). Markers of Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis Are Associated with Mortality in Critically Ill Patients. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(6), 1970. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14061970








