Does Forward Head Posture Influence Muscle Tone, Stiffness, and Elasticity in University Students?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Protocol
2.3. Data Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| FHP | Forward Head Posture |
| UT | Upper Trapezius |
| SCM | Sternocleidomastoid |
| CVA | Craniovertebral angle |
| MT | Middle Trapezius |
| LT | Lower Trapezius |
| SC | Splenius Capitis |
| PM | Pectoralis major |
| SA | Serratus Anterior |
References
- Henson, J.; De Craemer, M.; Yates, T. Sedentary behaviour and disease risk. BMC Public Health 2023, 23, 2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.-J. Neck pain and functioning in daily activities associated with smartphone usage. J. Korean Phys. Ther. 2016, 28, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szeto, G.P.; Straker, L.; Raine, S. A field comparison of neck and shoulder postures in symptomatic and asymptomatic office workers. Appl. Ergon. 2002, 33, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramalingam, V.; Subramaniam, A. Prevalence and associated risk factors of forward head posture among university students. Indian J. Public Health Res. Dev. 2019, 10, 775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, D.A. Kinesiology of the Musculoskeletal System; Mosby: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2002; pp. 25–40. [Google Scholar]
- Nishikawa, Y.; Watanabe, K.; Chihara, T.; Sakamoto, J.; Komatsuzaki, T.; Kawano, K.; Kobayashi, A.; Inoue, K.; Maeda, N.; Tanaka, S.; et al. Influence of forward head posture on muscle activation pattern of the trapezius pars descendens muscle in young adults. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 19484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alowa, Z. and W. Elsayed, The impact of forward head posture on the electromyographic activity of the spinal muscles. J. Taibah Univ. Med. Sci. 2021, 16, 224–230. [Google Scholar]
- Elizagaray-Garcia, I.; Beltran-Alacreu, H.; Angulo-Díaz, S.; Garrigós-Pedrón, M.; Gil-Martínez, A. Chronic primary headache subjects have greater forward head posture than asymptomatic and episodic primary headache sufferers: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Pain Med. 2020, 21, 2465–2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horikawa, M. Effect of visual display terminal height on the trapezius muscle hardness: Quantitative evaluation by a newly developed muscle hardness meter. Appl. Ergon. 2001, 32, 473–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-de-Las-Penas, C.; Alonso-Blanco, C.; Cuadrado, M.; Pareja, J. Neck mobility and forward head posture are not related to headache parameters in chronic tension-type headache. Cephalalgia 2007, 27, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simons, D.; Mense, S. Understanding and measurement of muscle tone as related to clinical muscle pain. Pain 1998, 75, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocur, P.; Tomczak, M.; Wiernicka, M.; Goliwąs, M.; Lewandowski, J.; Łochyński, D. Relationship between age, BMI, head posture and superficial neck muscle stiffness and elasticity in adult women. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 8515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pille, V.; Reinhold, K.; Tint, P.; Hartšenko, J. Musculoskeletal disorders caused by the static posture of office and garment workers. Int. J. Biol. Biomed. Eng. 2016, 10, 191–201. [Google Scholar]
- Urrejola-Contreras, G.P.; Martínez, J.M.; Rodríguez-Bagó, M.; Ronda, E. Myotonometry in machinery operators and its relationship with postural ergonomic risk. Ann. Work Expo. Health 2024, 68, 605–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viir, R.; Virkus, A.; Laiho, K.; Rajaleid, K.; Selart, A.; Mikkelsson, M. Trapezius muscle tone and viscoelastic properties in sitting and supine positions. Scand. J. Work. Environ. Health 2007, 33, 76–80. [Google Scholar]
- Kisner, C.; Colby, L. Therapeutic Exercise Therapy Foundation; F.A. Davis Co.: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Wendt, M.; Waszak, M. Assessment of the stiffness of the upper trapezius muscle in a group of asymptomatic people with cervical spine rotation asymmetry. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0298544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocur, P.; Wilski, M.; Goliwąs, M.; Lewandowski, J.; Łochyński, D. Influence of forward head posture on myotonometric measurements of superficial neck muscle tone, elasticity, and stiffness in asymptomatic individuals with sedentary jobs. J. Manip. Physiol. Ther. 2019, 42, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yip, C.H.T.; Chiu, T.T.W.; Poon, A.T.K. The relationship between head posture and severity and disability of patients with neck pain. Man. Ther. 2008, 13, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moustafa, I.M.; Youssef, A.; Ahbouch, A.; Tamim, M.; Harrison, D.E. Is forward head posture relevant to autonomic nervous system function and cervical sensorimotor control? Cross sectional study. Gait Posture 2020, 77, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deniz, V.; Sariyildiz, A.; Buyuktas, B.; Basaran, S. Comparison of the activation and mechanical properties of scapulothoracic muscles in young tennis players with and without scapular dyskinesis: An observational comparative study. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2024, 33, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullix, J.; Warner, M.; Stokes, M. Testing muscle tone and mechanical properties of rectus femoris and biceps femoris using a novel hand held MyotonPRO device: Relative ratios and reliability. Work. Pap. Health Sci. 2012, 1, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Guduru, R.K.R.; Domeika, A.; Domeikienė, A. Effect of rounded and hunched shoulder postures on myotonometric measurements of upper body muscles in sedentary workers. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 3333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.-H.; Lee, C.-H. Immediate effects of vibrating foam rollers on neck pain, muscle stiffness, and cervical proprioception in patients with forward head posture. Ann. Rom. Soc. Cell Biol. 2021, 25, 889–894. [Google Scholar]
- Weon, J.-H.; Oh, J.-S.; Cynn, H.-S.; Kim, Y.-W.; Kwon, O.-Y.; Yi, C.-H. Influence of forward head posture on scapular upward rotators during isometric shoulder flexion. J. Bodyw. Mov. Ther. 2010, 14, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiatkulanusorn, S.; Luangpon, N.; Tudpor, K. Increased upper and lower trapezius muscle activities during rest in side-lying position in young adults with forward head posture. Indian J. Physiother. Occup. Ther. 2020, 14, 266–271. [Google Scholar]
- Alnaqeeb, M.; Al Zaid, N.; Goldspink, G. Connective tissue changes and physical properties of developing and ageing skeletal muscle. J. Anat. 1984, 139 Pt 4, 677. [Google Scholar]
- Baumgart, E. Stiffness—An unknown world of mechanical science. Injury 2000, 31 (Suppl. 2), B14–B23. [Google Scholar]
- Gavronski, G.; Veraksitš, A.; Vasar, E.; Maaroos, J. Evaluation of viscoelastic parameters of the skeletal muscles in junior triathletes. Physiol. Meas. 2007, 28, 625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kocur, P.; Grzeskowiak, M.; Wiernicka, M.; Goliwas, M.; Lewandowski, J.; Łochyński, D. Effects of aging on mechanical properties of sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles during transition from lying to sitting position—A cross-sectional study. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2017, 70, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khayatzadeh, S.; Kalmanson, O.A.; Schuit, D.; Havey, R.M.; Voronov, L.I.; Ghanayem, A.J.; Patwardhan, A.G. Cervical spine muscle-tendon unit length differences between neutral and forward head postures: Biomechanical study using human cadaveric specimens. Phys. Ther. 2017, 97, 756–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, J.F.; Baber, C. Neck muscle activity and perceived pain and discomfort due to variations of head load and posture. Aviat. Space Environ. Med. 2004, 75, 123–131. [Google Scholar]
- Ferracini, G.N.; Chaves, T.C.; Dach, F.; Bevilaqua-Grossi, D.; Fernández-De-Las-Peñas, C.; Speciali, J.G. Relationship between active trigger points and head/neck posture in patients with migraine. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2016, 95, 831–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, K.T.; Cheung, K.Y.; Chan, K.B.; Chan, M.H.; Lo, K.Y.; Chiu, T.T.W. Relationships between sagittal postures of thoracic and cervical spine, presence of neck pain, neck pain severity and disability. Man. Ther. 2010, 15, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinesiology, O. The Mechanics and Pathomechanics of Human Movement; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Baltimore, MD, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Brandt, L.P.A.; Andersen, J.H.; Lassen, C.F.; Kryger, A.; Overgaard, E.; Vilstrup, I.; Mikkelsen, S.; Lpa, B. Neck and shoulder symptoms and disorders among Danish computer workers. Scand. J. Work. Environ. Health 2004, 30, 399–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szeto, G.P.; Straker, L.M.; O’Sullivan, P.B. A comparison of symptomatic and asymptomatic office workers performing monotonous keyboard work—1: Neck and shoulder muscle recruitment patterns. Man. Ther. 2005, 10, 270–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
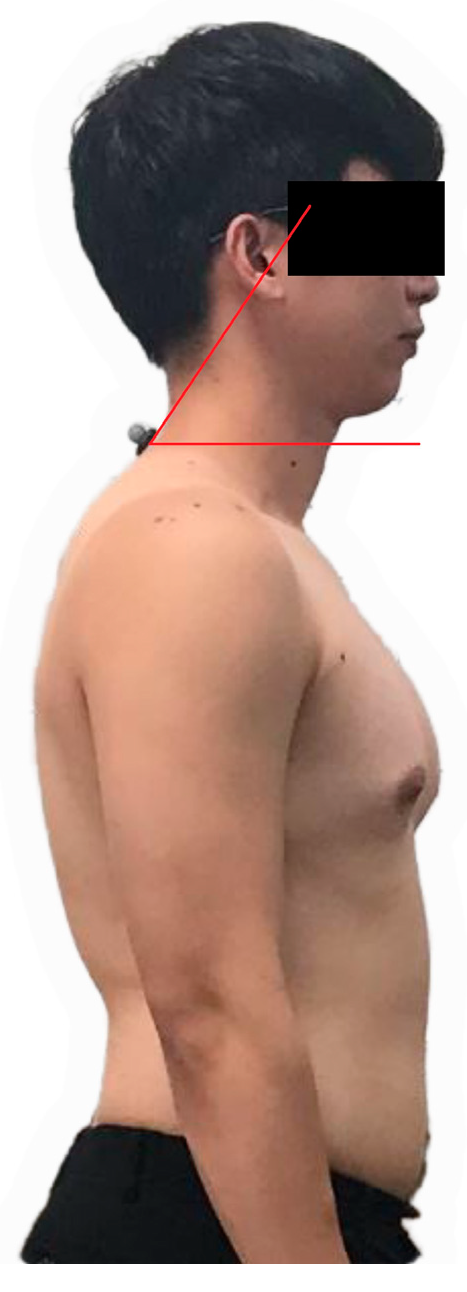
| Variables | FHP (n = 13) | CON (n = 11) |
|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 21.87 ± 0.83 | 21.57 ± 1.39 |
| Height (cm) | 172.25 ± 4.89 | 176.28 ± 5.18 |
| Weight (kg) | 69.62 ± 6.09 | 68.74 ± 5.42 |
| CVA (°) | 47.46 ± 1.31 | 57.08 ± 3.90 |
| Muscle | Variables | FHP | CON | t | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
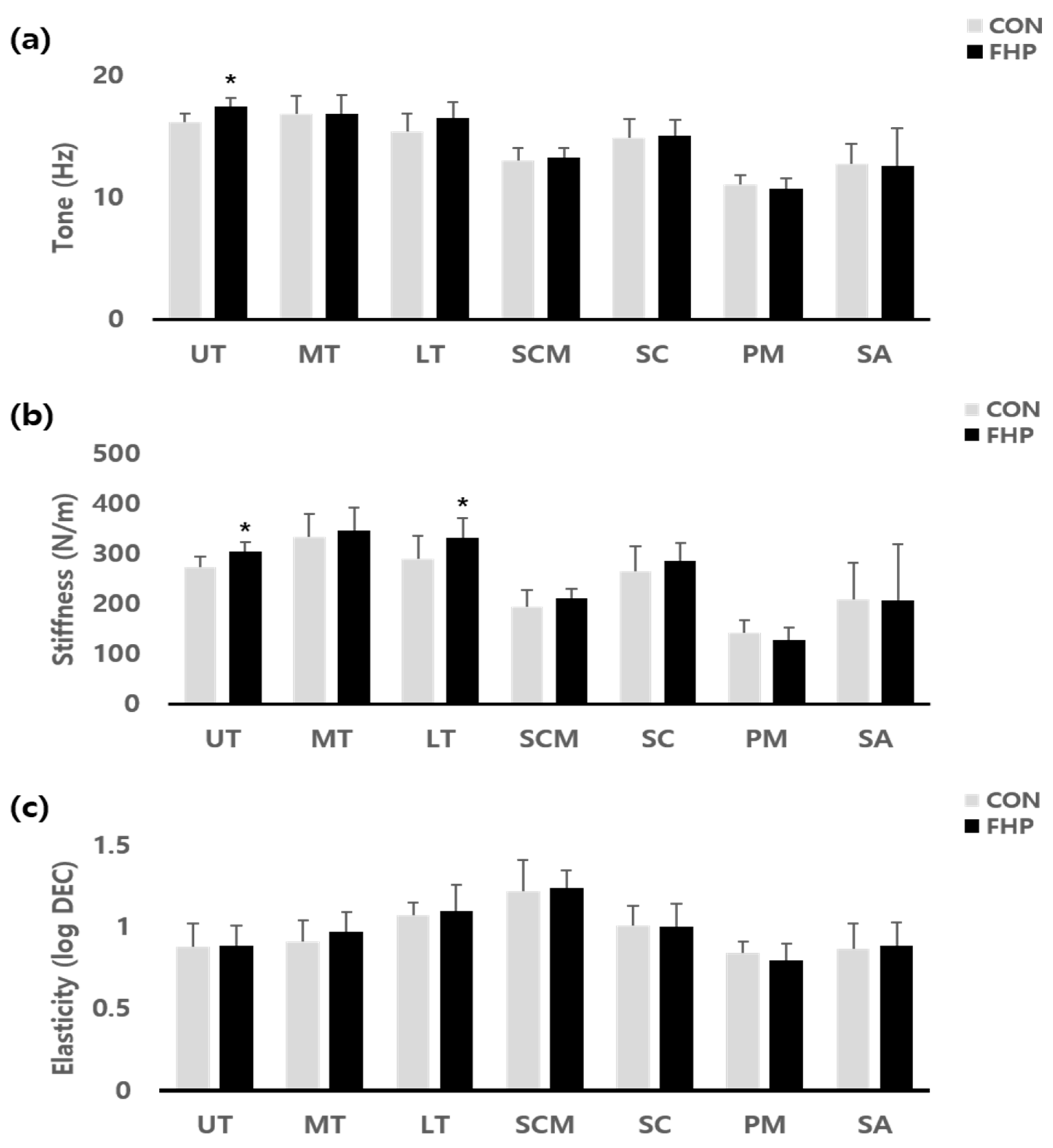
| UT | tone | 17.41 ± 0.70 | 16.11 ± 0.70 | 4.49 | 0.00 * |
| stiffness | 304.16 ± 21.55 | 272.48 ± 19.82 | 3.72 | 0.00 * | |
| elasticity | 0.89 ± 0.14 | 0.88 ± 0.12 | 0.03 | 0.97 | |
| MT | tone | 16.83 ± 1.46 | 16.85 ± 1.57 | −0.03 | 0.97 |
| stiffness | 346.06 ± 45.50 | 332.96 ± 45.20 | 0.70 | 0.48 | |
| elasticity | 0.97 ± 0.13 | 0.91 ± 0.12 | 1.62 | 0.11 | |
| LT | tone | 16.51 ± 1.44 | 15.39 ± 1.29 | 1.98 | 0.06 |
| stiffness | 331.99 ± 45.66 | 290.75 ± 39.37 | 2.34 | 0.02 * | |
| elasticity | 1.10 ± 0.08 | 1.07 ± 0.16 | 0.55 | 0.58 | |
| SCM | tone | 13.25 ± 1.01 | 13.02 ± 0.75 | 0.62 | 0.54 |
| stiffness | 210.85 ± 31.99 | 195.24 ± 19.30 | 1.41 | 0.17 | |
| elasticity | 1.24 ± 0.19 | 1.22 ± 0.11 | 0.34 | 0.73 | |
| SC | tone | 15.07 ± 1.51 | 14.91 ± 1.21 | 0.29 | 0.77 |
| stiffness | 284.70 ± 51.63 | 264.03 ± 36.30 | 1.11 | 0.27 | |
| elasticity | 1.00 ± 0.12 | 1.01 ± 0.14 | −0.28 | 0.78 | |
| PM | tone | 10.67 ± 0.72 | 11.05 ± 0.88 | −1.15 | 0.26 |
| stiffness | 127.06 ± 23.09 | 143.36 ± 24.73 | −1.66 | 0.10 | |
| elasticity | 0.80 ± 0.07 | 0.84 ± 0.10 | −1.22 | 0.23 | |
| SA | tone | 12.60 ± 1.63 | 12.76 ± 3.06 | −0.15 | 0.87 |
| stiffness | 206.60 ± 74.38 | 207.93 ± 111.37 | −0.03 | 0.97 | |
| elasticity | 0.89 ± 0.15 | 0.87 ± 0.14 | 0.26 | 0.79 |
| Muscle | Variables | R | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| UT | tone | −0.731 | 0.000 ** |
| stiffness | −0.749 | 0.000 ** | |
| elasticity | −0.143 | 0.506 | |
| MT | tone | 0.031 | 0.886 |
| stiffness | −0.154 | 0.472 | |
| elasticity | −0.369 | 0.076 | |
| LT | tone | −0.303 | 0.150 |
| stiffness | −0.369 | 0.076 | |
| elasticity | −0.245 | 0.249 | |
| SCM | tone | −0.123 | 0.566 |
| stiffness | −0.286 | 0.175 | |
| elasticity | −0.148 | 0.491 | |
| SC | tone | −0.121 | 0.573 |
| stiffness | −0.301 | 0.153 | |
| elasticity | −0.022 | 0.920 | |
| PM | tone | 0.329 | 0.116 |
| stiffness | 0.311 | 0.140 | |
| elasticity | 0.077 | 0.721 | |
| SA | tone | 0.105 | 0.624 |
| stiffness | 0.057 | 0.793 | |
| elasticity | −0.074 | 0.732 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yong, M.-S.; Lee, H.-Y. Does Forward Head Posture Influence Muscle Tone, Stiffness, and Elasticity in University Students? J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 1888. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14061888
Yong M-S, Lee H-Y. Does Forward Head Posture Influence Muscle Tone, Stiffness, and Elasticity in University Students? Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(6):1888. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14061888
Chicago/Turabian StyleYong, Min-Sik, and Hae-Yong Lee. 2025. "Does Forward Head Posture Influence Muscle Tone, Stiffness, and Elasticity in University Students?" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 6: 1888. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14061888
APA StyleYong, M.-S., & Lee, H.-Y. (2025). Does Forward Head Posture Influence Muscle Tone, Stiffness, and Elasticity in University Students? Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(6), 1888. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14061888





