Comparative Analysis of Neuropsychiatric Adverse Reactions Associated with Remdesivir and Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir in COVID-19 Treatment: Insights from EudraVigilance Data
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Analysis
2.2. Descriptive Analysis
2.3. Disproportionality Analysis
- Psychiatric disorders: anxiety, delirium, depressed mood disorders, thinking and perception disorders, personality and behavioral disturbances, sleep disorders, and suicidal or self-harming behavior.
- Neurological disorders: headache, mental impairment, movement disorders, seizures, and sleep disorders.
2.4. Ethics
3. Results
3.1. Descriptive Analysis of ICSRs
3.2. Disproportionality Analysis
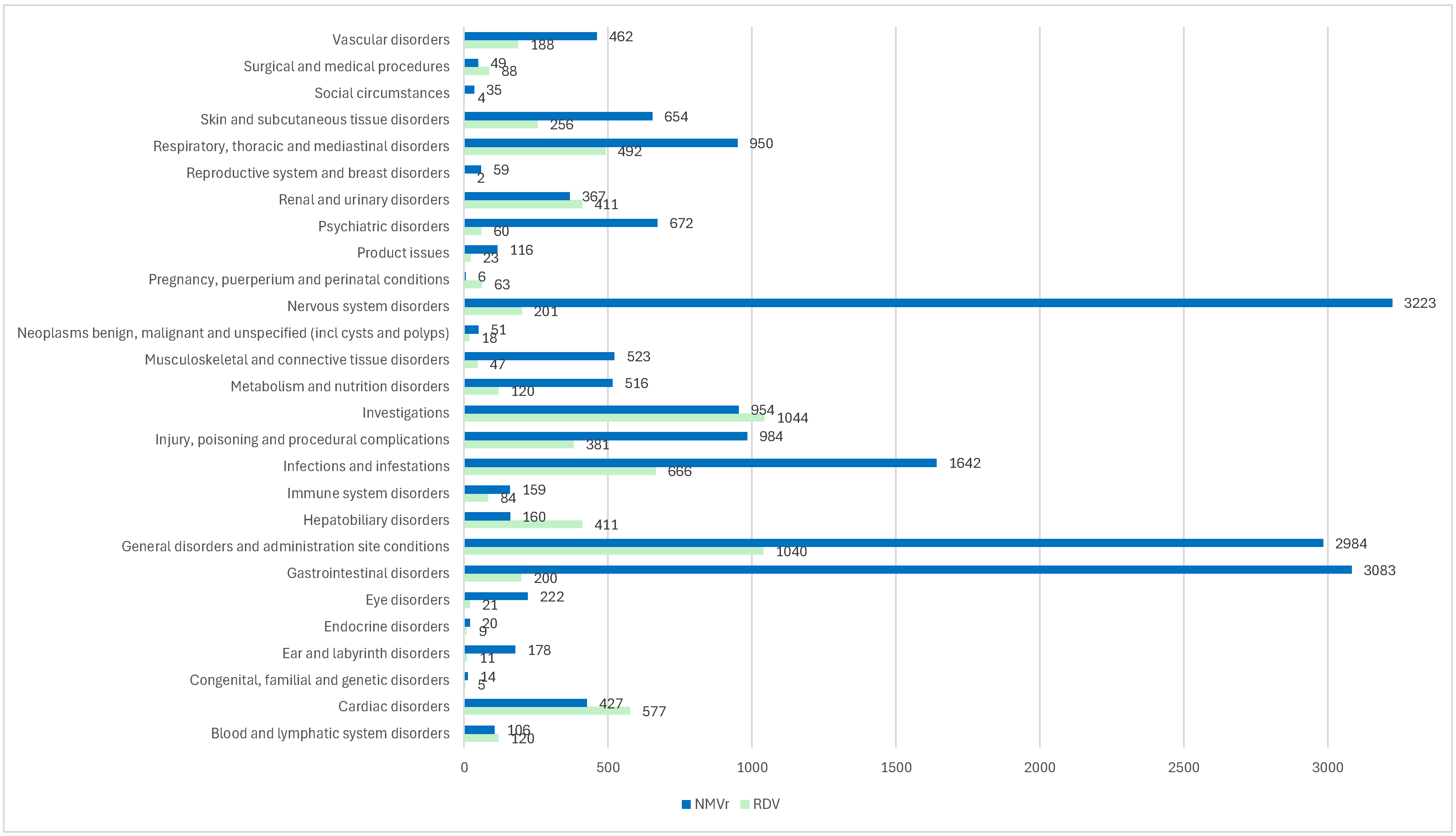
3.2.1. Disproportionality Analysis of ADRs Grouped by SOCs
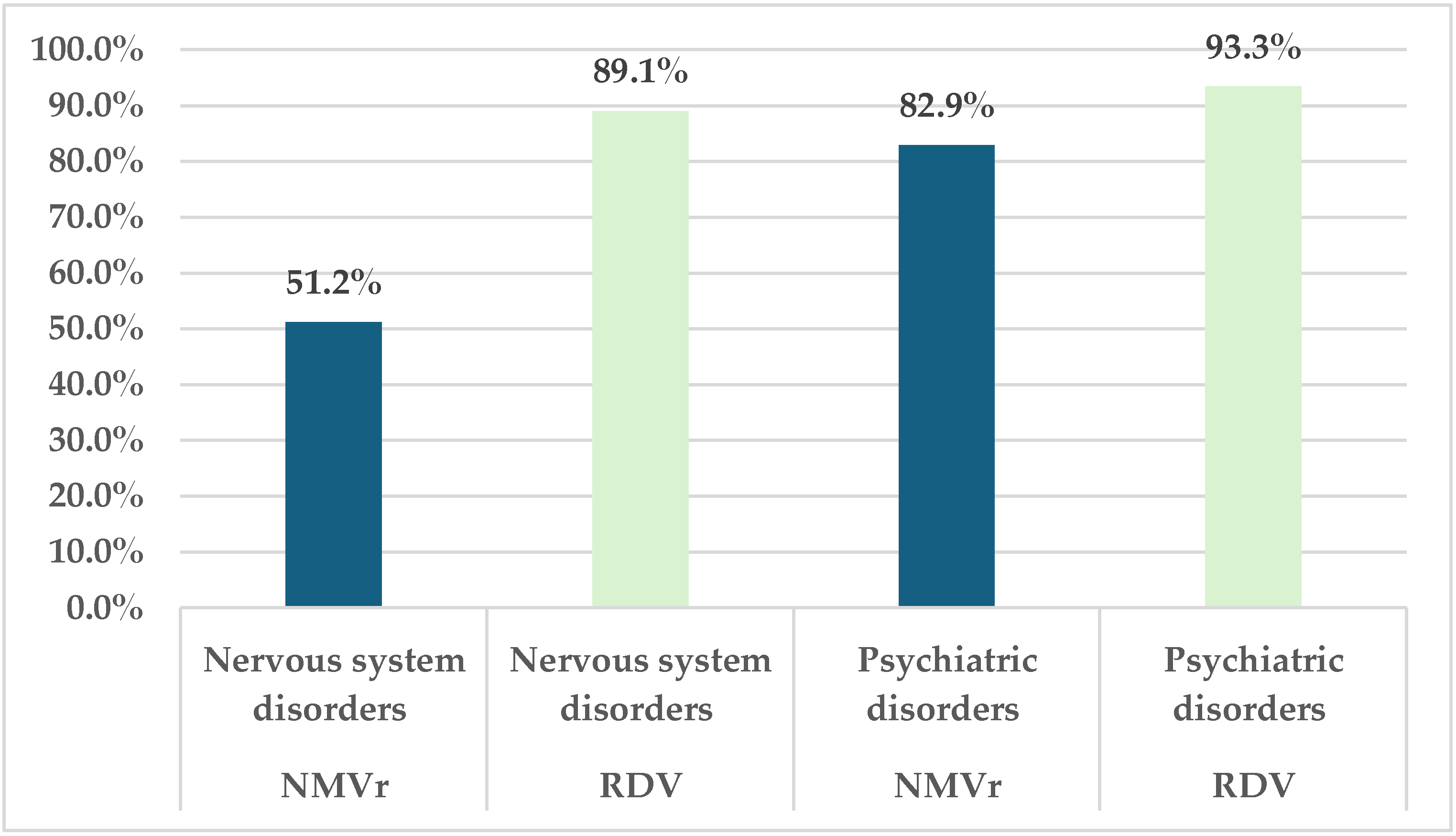
3.2.2. Disproportionality Analysis of ADRs Related to Psychiatric Disorders and Nervous System Disorders SOCs
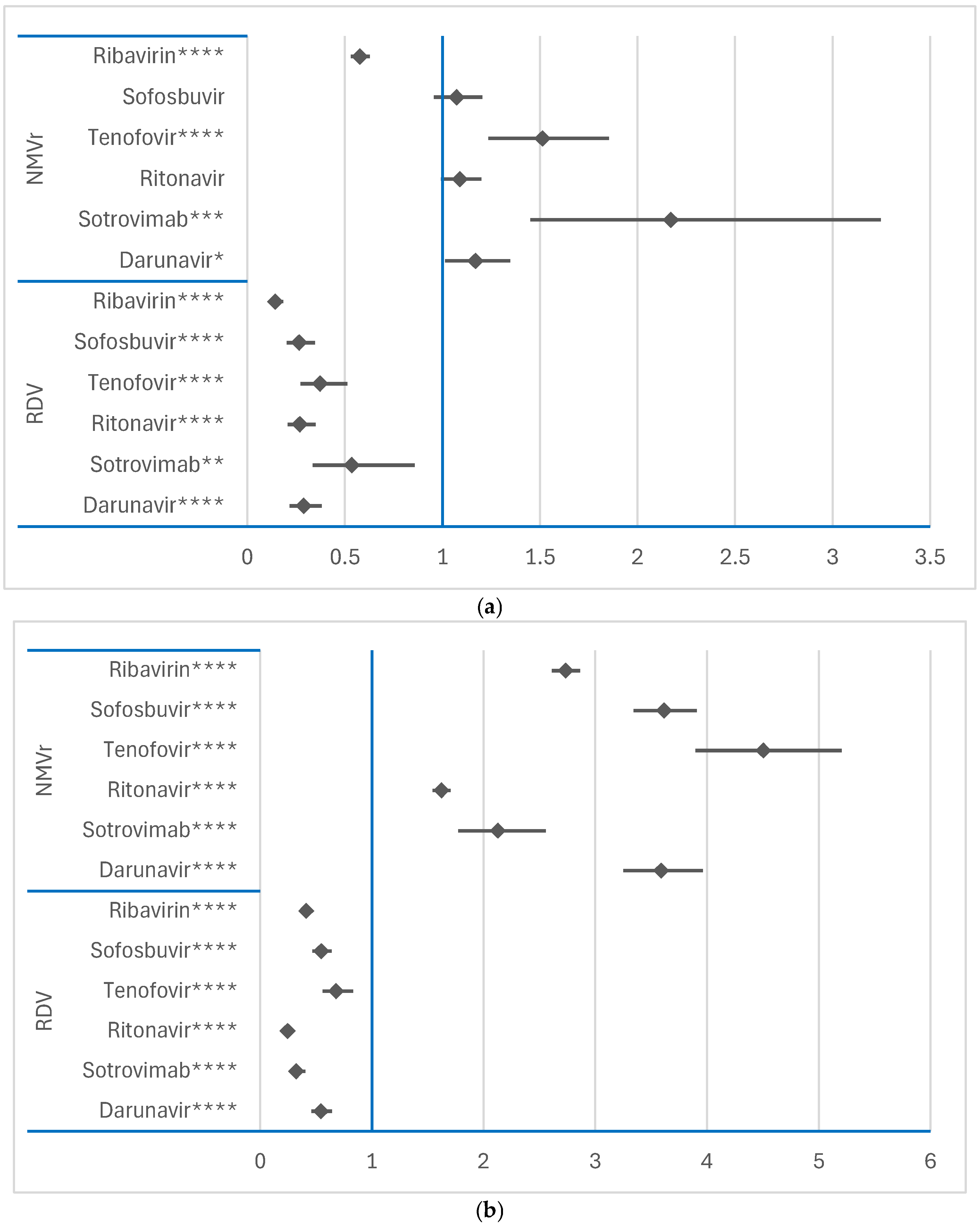
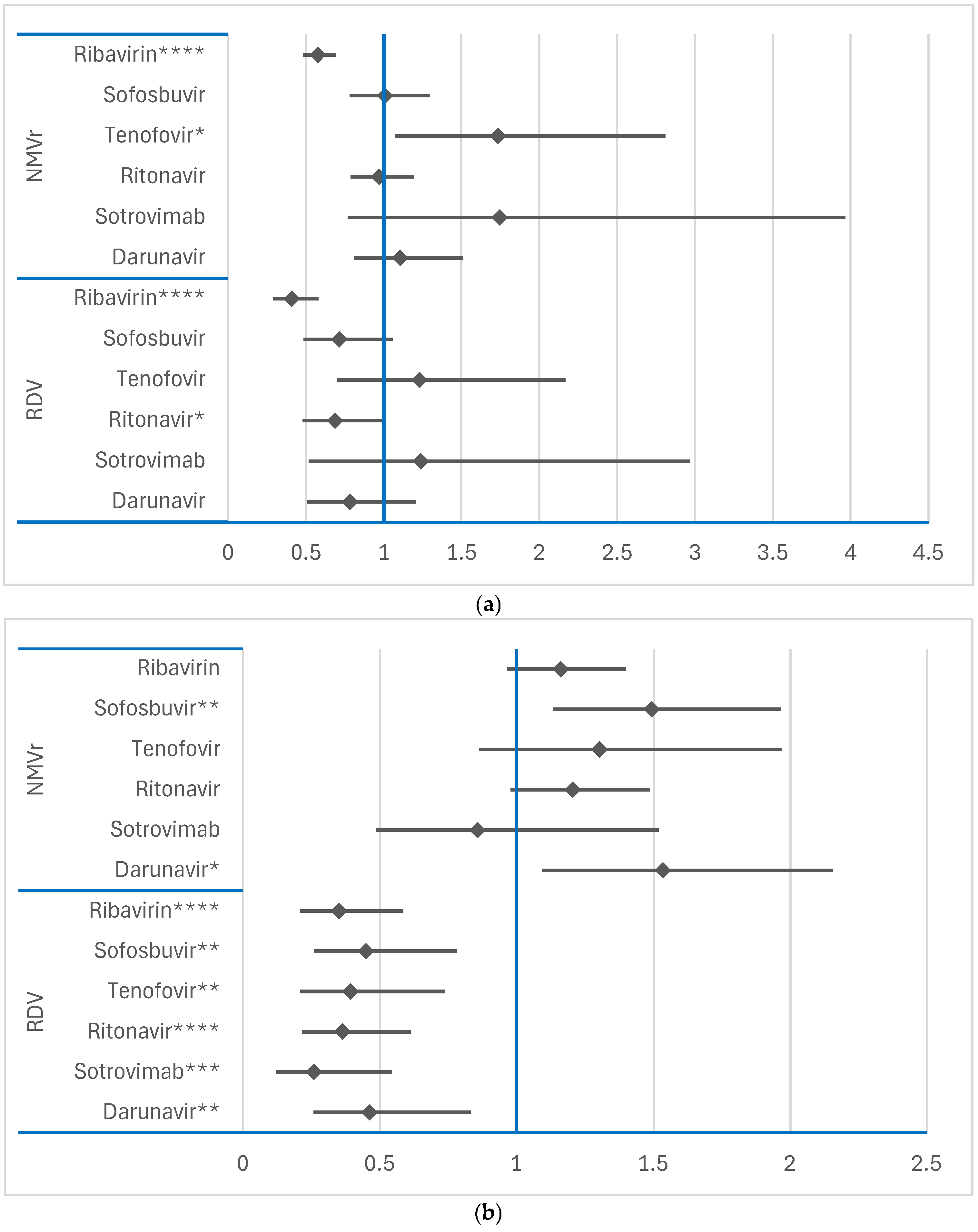
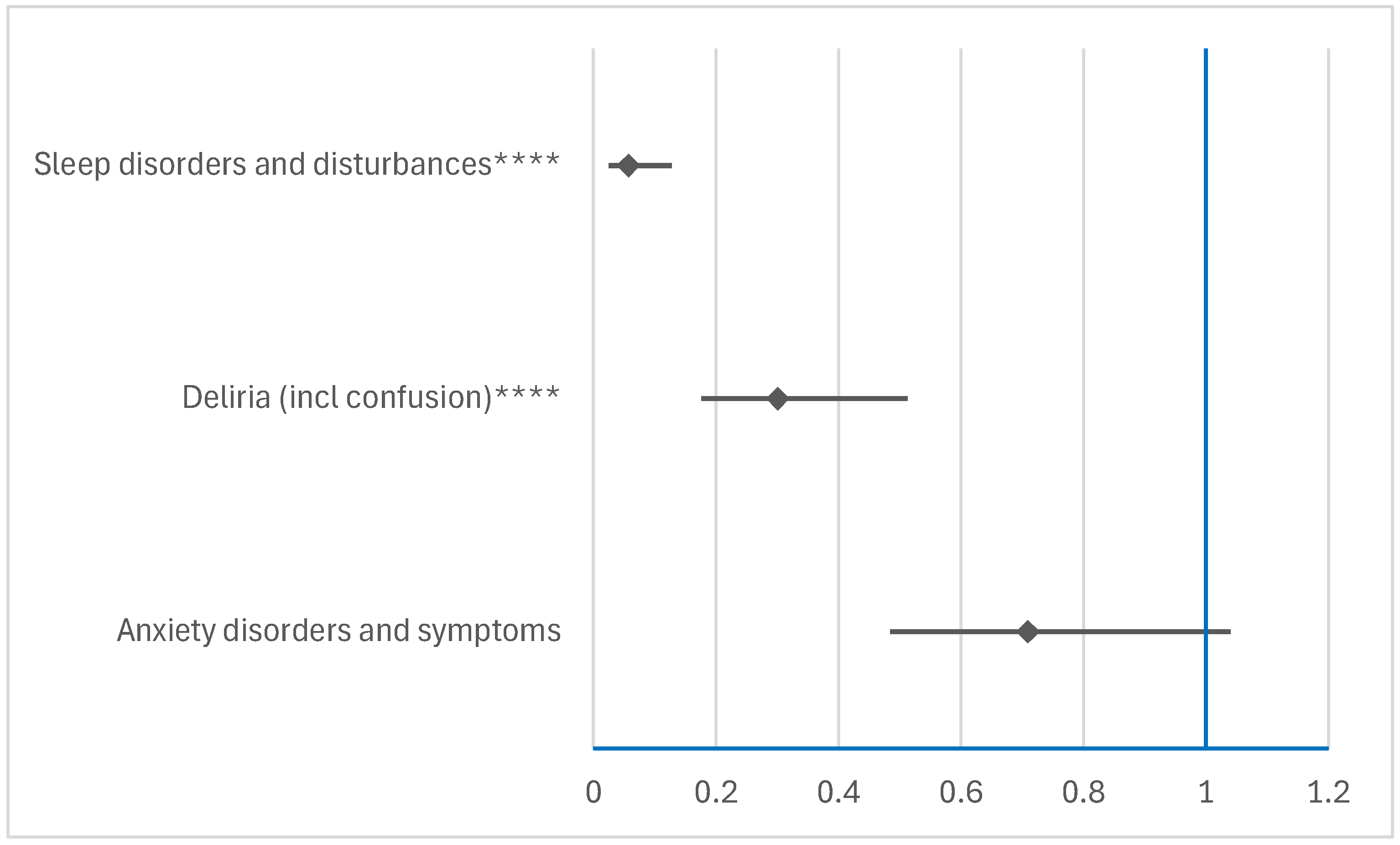
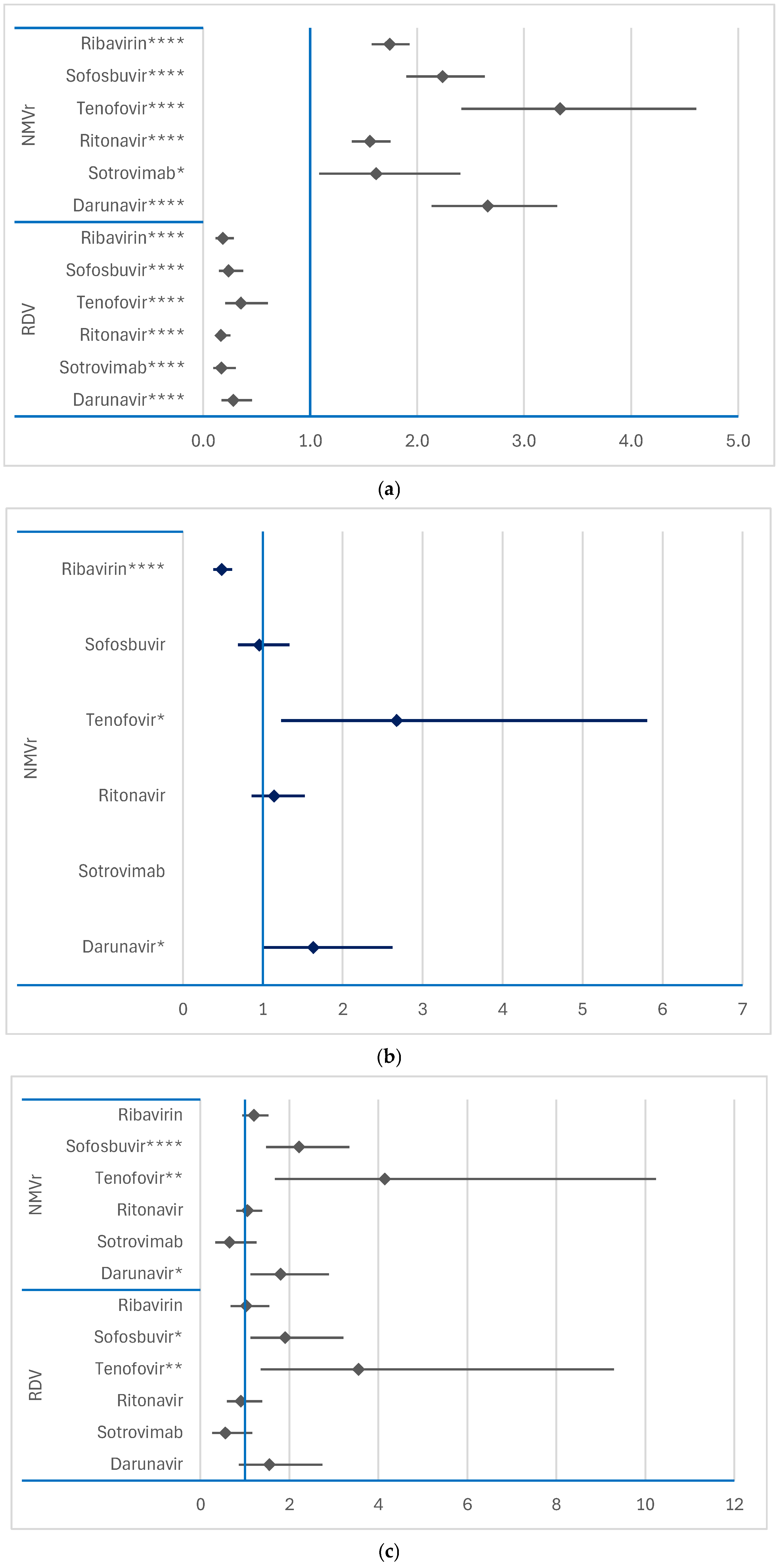
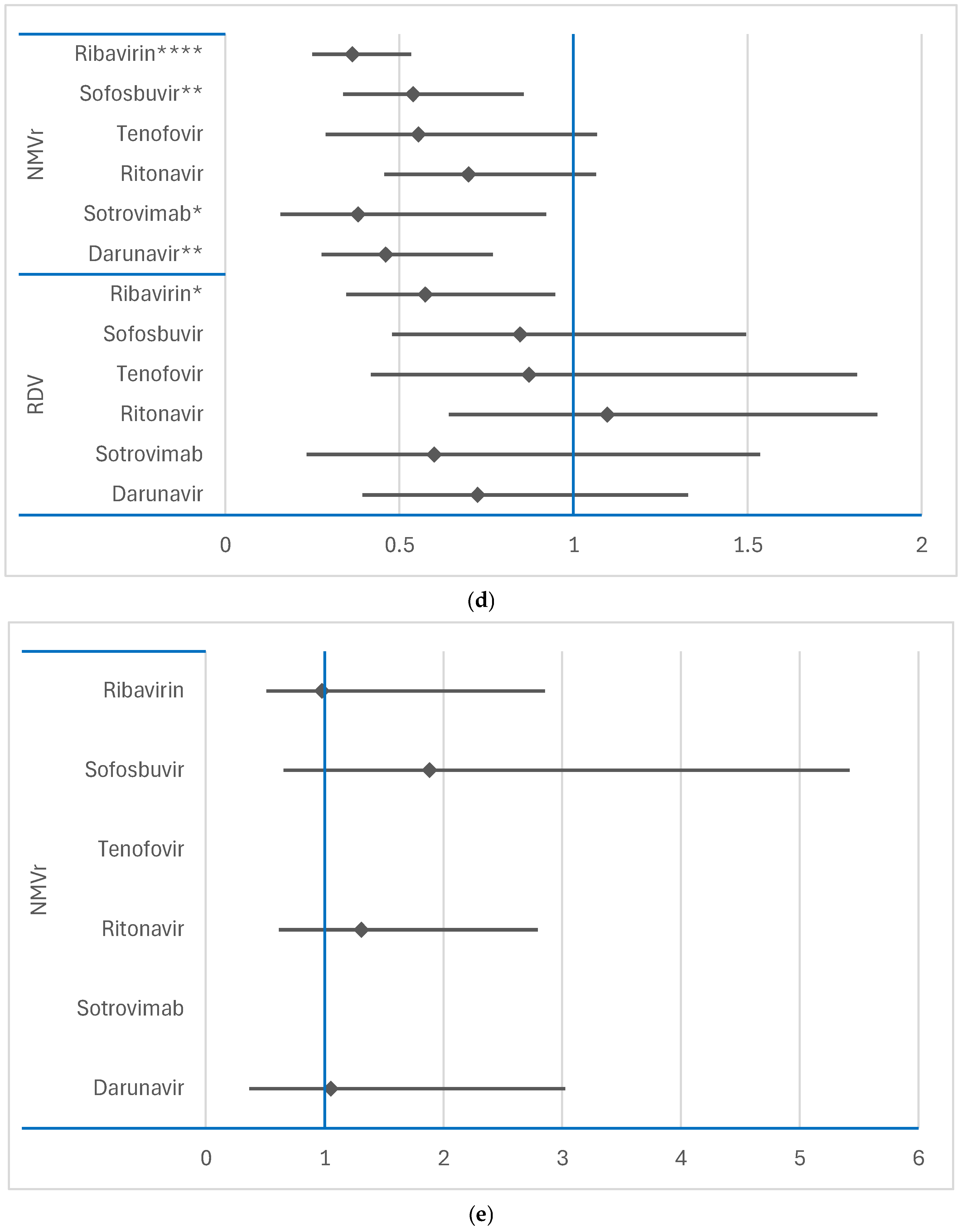
3.2.3. Disproportionality Analysis of Psychiatric ADRs
Comparison Between RDV and NMVr
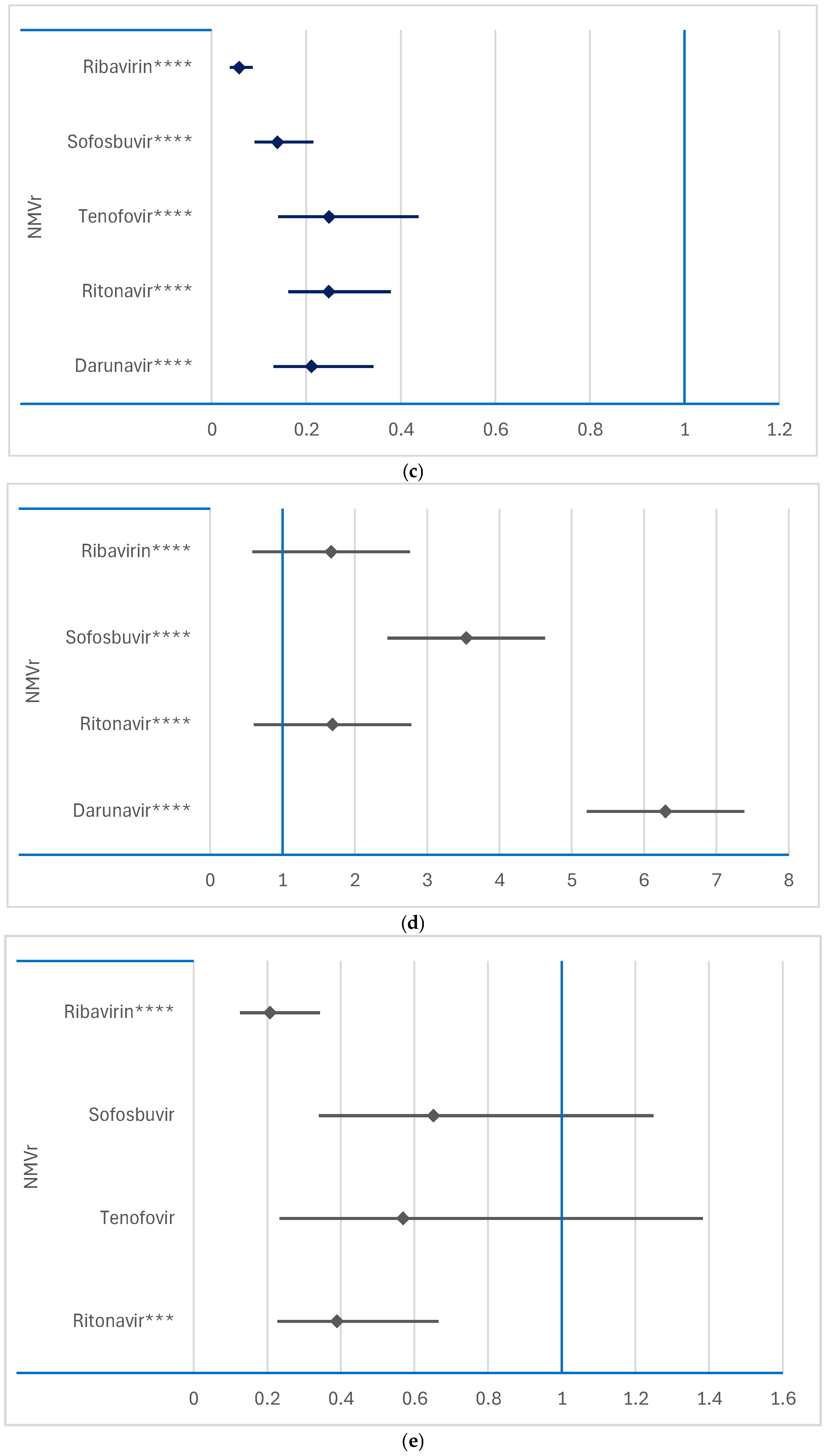
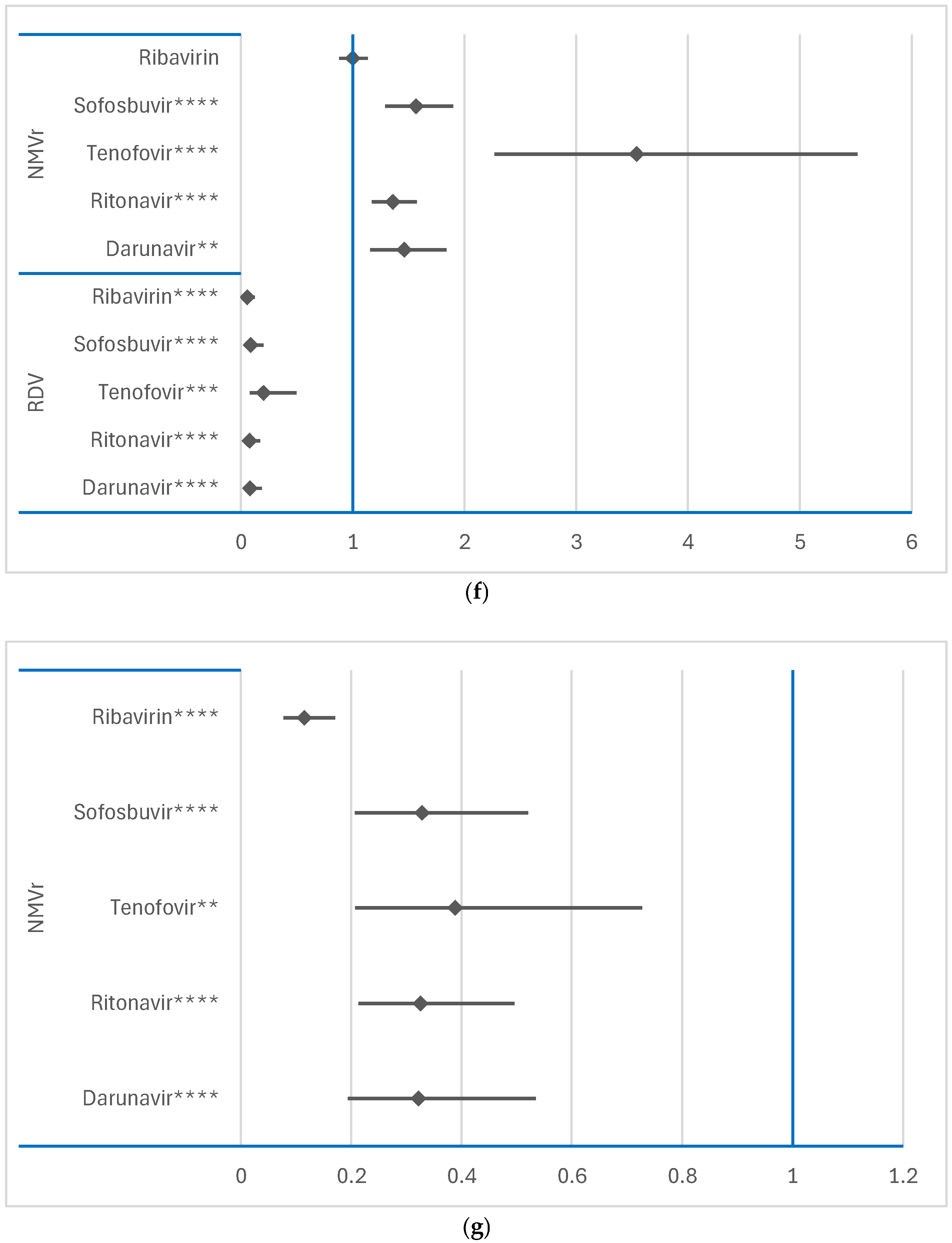
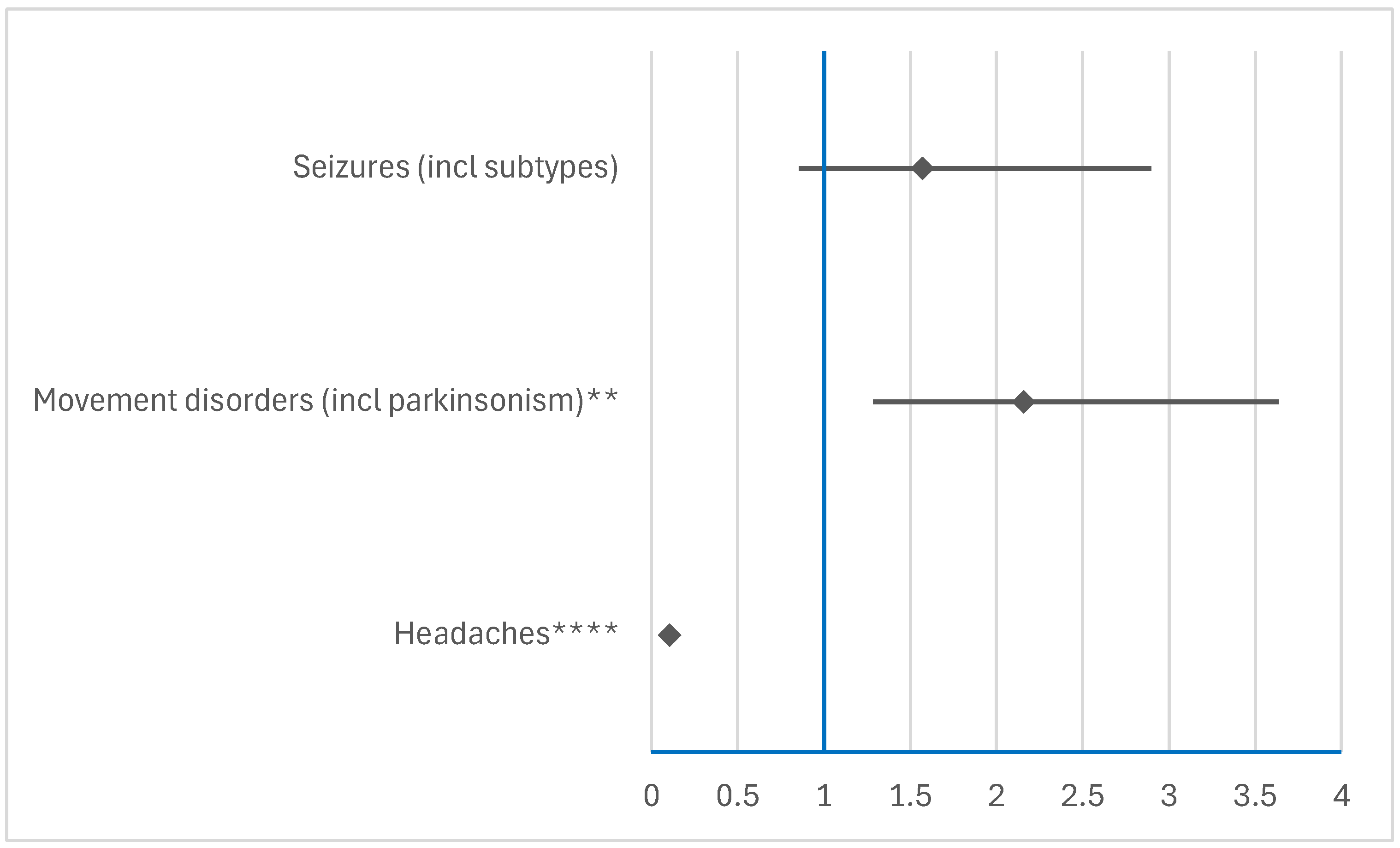
3.3. Disproportionality Analysis of Neurological ADRs
3.3.1. Comparison Between RDV or NMVr and Other Antivirals
3.3.2. Comparison Between RDV and NMVr
4. Discussion
Limitations of the Study and Future Perspectives
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ADR | Adverse drug reaction |
| CNS | Central nervous system |
| CI | Confidence interval |
| COVID-19 | Coronavirus disease 2019 |
| DNA | Deoxyribonucleic acid |
| EEA | European Economic Area |
| EMA | European Medicines Agency |
| EV | EudraVigilance |
| HCV | Hepatitis C virus |
| HLGT | High-level group term |
| HLT | High-level term |
| HP | Healthcare professional |
| HIV | Human immunodeficiency virus |
| ICSR | Individual case safety report |
| MedDRA | Medical Dictionary for Regulatory Activities |
| NEC | Not elsewhere classifiable |
| NMVr | Nirmatrelvir/ritonavir |
| NS | Not specified |
| RdRp | RNA-dependent RNA polymerase |
| RDV | Remdesivir |
| RNA | Ribonucleic acid |
| ROR | Reporting odds ratio |
| SARS-CoV-2 | Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 |
| SOC | System organ class |
References
- Huang, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Ren, L.; Zhao, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Fan, G.; Xu, J.; Gu, X.; et al. Clinical Features of Patients Infected with 2019 Novel Coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet 2020, 395, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, F.; Yu, T.; Du, R.; Fan, G.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Xiang, J.; Wang, Y.; Song, B.; Gu, X.; et al. Clinical Course and Risk Factors for Mortality of Adult Inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Lancet 2020, 395, 1054–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rochette, L.; Ghibu, S. Mechanics Insights of Alpha-Lipoic Acid against Cardiovascular Diseases during COVID-19 Infection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Punekar, M.; Kshirsagar, M.; Tellapragada, C.; Patil, K. Repurposing of Antiviral Drugs for COVID-19 and Impact of Repurposed Drugs on the Nervous System. Microb. Pathog. 2022, 168, 105608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacnejer, A.-M.; Butuca, A.; Dobrea, C.M.; Arseniu, A.M.; Frum, A.; Gligor, F.G.; Arseniu, R.; Vonica, R.C.; Vonica-Tincu, A.L.; Oancea, C.; et al. Neuropsychiatric Burden of SARS-CoV-2: A Review of Its Physiopathology, Underlying Mechanisms, and Management Strategies. Viruses 2024, 16, 1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldman, J.D.; Lye, D.C.B.; Hui, D.S.; Marks, K.M.; Bruno, R.; Montejano, R.; Spinner, C.D.; Galli, M.; Ahn, M.-Y.; Nahass, R.G.; et al. Remdesivir for 5 or 10 Days in Patients with Severe COVID-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1827–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beigel, J.H.; Tomashek, K.M.; Dodd, L.E.; Mehta, A.K.; Zingman, B.S.; Kalil, A.C.; Hohmann, E.; Chu, H.Y.; Luetkemeyer, A.; Kline, S.; et al. Remdesivir for the Treatment of COVID-19—Final Report. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1813–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grein, J.; Ohmagari, N.; Shin, D.; Diaz, G.; Asperges, E.; Castagna, A.; Feldt, T.; Green, G.; Green, M.L.; Lescure, F.-X.; et al. Compassionate Use of Remdesivir for Patients with Severe COVID-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 2327–2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottlieb, R.L.; Vaca, C.E.; Paredes, R.; Mera, J.; Webb, B.J.; Perez, G.; Oguchi, G.; Ryan, P.; Nielsen, B.U.; Brown, M.; et al. Early Remdesivir to Prevent Progression to Severe COVID-19 in Outpatients. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scavone, C.; Mascolo, A.; Rafaniello, C.; Sportiello, L.; Trama, U.; Zoccoli, A.; Bernardi, F.F.; Racagni, G.; Berrino, L.; Castaldo, G.; et al. Therapeutic Strategies to Fight COVID-19: Which Is the Status Artis? Br. J. Pharmacol. 2022, 179, 2128–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond, J.; Leister-Tebbe, H.; Gardner, A.; Abreu, P.; Bao, W.; Wisemandle, W.; Baniecki, M.; Hendrick, V.M.; Damle, B.; Simón-Campos, A.; et al. Oral Nirmatrelvir for High-Risk, Nonhospitalized Adults with COVID-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 1397–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Du, G.; Du, R.; Zhao, J.; Jin, Y.; Fu, S.; Gao, L.; Cheng, Z.; Lu, Q.; et al. Remdesivir in Adults with Severe COVID-19: A Randomised, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Multicentre Trial. Lancet 2020, 395, 1569–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhou, F.; Zhang, D.; Zhao, J.; Du, R.; Hu, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Gao, L.; Jin, Y.; Luo, G.; et al. Evaluation of the Efficacy and Safety of Intravenous Remdesivir in Adult Patients with Severe COVID-19: Study Protocol for a Phase 3 Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Multicentre Trial. Trials 2020, 21, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spinner, C.D.; Gottlieb, R.L.; Criner, G.J.; Arribas López, J.R.; Cattelan, A.M.; Soriano Viladomiu, A.; Ogbuagu, O.; Malhotra, P.; Mullane, K.M.; Castagna, A.; et al. Effect of Remdesivir vs Standard Care on Clinical Status at 11 Days in Patients with Moderate COVID-19. JAMA 2020, 324, 1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carothers, C.; Birrer, K.; Vo, M. Acetylcysteine for the Treatment of Suspected Remdesivir-Associated Acute Liver Failure in COVID-19: A Case Series. Pharmacother. J. Hum. Pharmacol. Drug Ther. 2020, 40, 1166–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plasencia-García, B.O.; Rodríguez-Menéndez, G.; Rico-Rangel, M.I.; Rubio-García, A.; Torelló-Iserte, J.; Crespo-Facorro, B. Drug-Drug Interactions between COVID-19 Treatments and Antipsychotics Drugs: Integrated Evidence from 4 Databases and a Systematic Review. Psychopharmacology 2021, 238, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winston, A.; Fätkenheuer, G.; Arribas, J.; Hill, A.; van Delft, Y.; Moecklinghoff, C. Neuropsychiatric Adverse Events with Ritonavir-Boosted Darunavir Monotherapy in HIV-Infected Individuals: A Randomised Prospective Study. HIV Clin. Trials 2010, 11, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinho, M.; Novais, C.; Marques, J.; Bragança, M. Efavirenz and Neuropsychiatric Effects–When the Treatment Complicates Matter Further. Eur. Psychiatry 2017, 41, S203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lory, P.; Combret, S.; Michot, J.; Veyrac, G.; Chouchana, L.; Grandvuillemin, A. Safety Profile of the Lopinavir/Ritonavir Combination before and during the SARS-CoV-2 Pandemic. Therapies 2023, 78, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, C.A.C.; Sánchez, E.B.A.; Huerta, D.H.; Gómez-Arnau, J. Covid-19 Treatment-Induced Neuropsychiatric Adverse Effects. Gen. Hosp. Psychiatry 2020, 67, 163–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilbul, M.; Paparone, P.; Kim, A.M.; Mutalik, S.; Ernst, C.L. Psychopharmacology of COVID-19. Psychosomatics 2020, 61, 411–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Council for Harmonisation of Technical. Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use. In Introductory Guide for Standardised MedDRA Queries (SMQs) Version 24.1; International Council for Harmonisation of Technical: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Morgovan, C.; Dobrea, C.M.; Chis, A.A.; Juncan, A.M.; Arseniu, A.M.; Rus, L.L.; Gligor, F.G.; Ardelean, S.A.; Stoicescu, L.; Ghibu, S.; et al. A Descriptive Analysis of Direct Oral Anticoagulant Drugs Dosing Errors Based on Spontaneous Reports from the EudraVigilance Database. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vintila, B.I.; Arseniu, A.M.; Morgovan, C.; Butuca, A.; Sava, M.; Bîrluțiu, V.; Rus, L.L.; Ghibu, S.; Bereanu, A.S.; Roxana Codru, I.; et al. A Pharmacovigilance Study Regarding the Risk of Antibiotic-Associated Clostridioides Difficile Infection Based on Reports from the EudraVigilance Database: Analysis of Some of the Most Used Antibiotics in Intensive Care Units. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MedCalc Software Ltd. Odds Ratio Calculator. Version 23.1.3. Available online: https://www.medcalc.org/calc/odds_ratio.php (accessed on 18 January 2025).
- European Medicines Agency. Screening for Adverse Reactions in EudraVigilance. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/other/screening-adverse-reactions-eudravigilance_en.pdf (accessed on 18 January 2025).
- Rubin, D.; Chan-Tack, K.; Farley, J.; Sherwat, A. FDA Approval of Remdesivir—A Step in the Right Direction. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2598–2600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohl, M.E.; Miller, D.R.; Lund, B.C.; Kobayashi, T.; Richardson Miell, K.; Beck, B.F.; Alexander, B.; Crothers, K.; Vaughan Sarrazin, M.S. Association of Remdesivir Treatment with Survival and Length of Hospital Stay Among US Veterans Hospitalized with COVID-19. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e2114741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, D.-Y.; Abi Fadel, F.; Huang, S.; Milinovich, A.T.; Sacha, G.L.; Bartley, P.; Duggal, A.; Wang, X. Nirmatrelvir or Molnupiravir Use and Severe Outcomes from Omicron Infections. JAMA Netw. Open 2023, 6, e2335077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, N.R.; Beaty, L.E.; Bennett, T.D.; Fish, L.E.; Jacobs, J.R.; Mayer, D.A.; Molina, K.C.; Peers, J.L.; Richardson, D.B.; Russell, S.; et al. Real-World Use of Nirmatrelvir-Ritonavir in COVID-19 Outpatients during BQ.1, BQ.1.1., and XBB.1.5 Predominant Omicron Variants in Three U.S. Health Systems: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Lancet Reg. Health Am. 2024, 31, 100693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrer, K.; Rakhmanina, N. Neuropsychiatric Effects of Tenofovir in Comparison with Other Antiretroviral Drugs. Neurobehav. HIV Med. 2013, 5, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allavena, C.; Le Moal, G.; Michau, C.; Chiffoleau, A.; Raffi, F. Neuropsychiatric Adverse Events after Switching from an Antiretroviral Regimen Containing Efavirenz without Tenofovir to an Efavirenz Regimen Containing Tenofovir: A Report of Nine Cases. Antivir. Ther. 2006, 11, 263–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.S.Y.; Masur, J.; Sims, Z.; Nelson, A.; Osinusi, A.; Kohli, A.; Kattakuzhy, S.; Polis, M.; Kottilil, S. Safe and Effective Sofosbuvir-Based Therapy in Patients with Mental Health Disease on Hepatitis C Virus Treatment. World J. Hepatol. 2016, 8, 1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iriana, S.; Curry, M.P.; Afdhal, N.H. Neurologic Manifestations of Hepatitis C Virus Infection. Clin. Liver Dis. 2017, 21, 535–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zareifopoulos, N.; Lagadinou, M.; Karela, A.; Kyriakopoulou, O.; Velissaris, D. Neuropsychiatric Effects of Antiviral Drugs. Cureus 2020, 12, e9536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Back, D.; Sekar, V.; Hoetelmans, R.M.W. Darunavir: Pharmacokinetics and Drug Interactions. Antivir. Ther. 2008, 13, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moltó, J.; Valle, M.; Clotet, B. Interacciones Medicamentosas de Darunavir. Enferm. Infecc. Microbiol. Clin. 2008, 26, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, R.-C.; Behl, T.; Negrut, N.; Bungau, S. Management of Antiretroviral Therapy with Boosted Protease Inhibitors—Darunavir/Ritonavir or Darunavir/Cobicistat. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhang, Q.-S.; Liu, X.-L.; Wang, H.-L.; Liu, W. Adverse Events Associated with Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir: A Pharmacovigilance Analysis Based on FAERS. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Chang, L.; Yang, Y.; Wang, X.; Xie, Y.; Shen, J.; Tan, B.; Liu, J. Pharmacokinetics and Tissue Distribution of Remdesivir and Its Metabolites Nucleotide Monophosphate, Nucleotide Triphosphate, and Nucleoside in Mice. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2021, 42, 1195–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.K.H.; Au, I.C.H.; Cheng, W.Y.; Man, K.K.C.; Lau, K.T.K.; Mak, L.Y.; Lui, S.L.; Chung, M.S.H.; Xiong, X.; Lau, E.H.Y.; et al. Remdesivir Use and Risks of Acute Kidney Injury and Acute Liver Injury among Patients Hospitalised with COVID-19: A Self-Controlled Case Series Study. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2022, 56, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Laar, S.A.; de Boer, M.G.J.; Gombert-Handoko, K.B.; Guchelaar, H.-J.; Zwaveling, J. LUMC-Covid-19 research group Liver and Kidney Function in Patients with Covid-19 Treated with Remdesivir. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2021, 87, 4450–4454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamsick, M.L.; Gandhi, R.G.; Bidell, M.R.; Elshaboury, R.H.; Bhattacharyya, R.P.; Kim, A.Y.; Nigwekar, S.; Rhee, E.P.; Sise, M.E. Remdesivir in Patients with Acute or Chronic Kidney Disease and COVID-19. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2020, 31, 1384–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panahi, Y.; Gorabi, A.M.; Talaei, S.; Beiraghdar, F.; Akbarzadeh, A.; Tarhriz, V.; Mellatyar, H. An Overview on the Treatments and Prevention against COVID-19. Virol. J. 2023, 20, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakamaki, A.; Kamimura, K.; Fukui, N.; Watanabe, H.; Sakai, N.; Tominaga, K.; Mizuno, K.; Takamura, M.; Kawai, H.; Sugai, T.; et al. A Case Report of Psychiatric Symptoms Following Direct-Acting Antiviral and Ribavirin Combination Therapy for Chronic Hepatitis C in a Patient with Innate Anxiety. BMC Gastroenterol. 2019, 19, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Focosi, D.; Casadevall, A.; Franchini, M.; Maggi, F. Sotrovimab: A Review of Its Efficacy against SARS-CoV-2 Variants. Viruses 2024, 16, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, A.; Gonzalez-Rojas, Y.; Juarez, E.; Crespo Casal, M.; Moya, J.; Rodrigues Falci, D.; Sarkis, E.; Solis, J.; Zheng, H.; Scott, N.; et al. Effect of Sotrovimab on Hospitalization or Death Among High-Risk Patients with Mild to Moderate COVID-19. JAMA 2022, 327, 1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patone, M.; Snelling, A.J.; Tibble, H.; Coupland, C.; Sheikh, A.; Hippisley-Cox, J. Uptake and Safety of Sotrovimab for Prevention of Severe COVID-19 in a Cohort and Self-Controlled Case Series Study. Commun. Med. 2025, 5, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amani, B.; Amani, B. Efficacy and Safety of Sotrovimab in Patients with COVID-19: A Rapid Review and Meta-analysis. Rev. Med. Virol. 2022, 32, e2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.Z.; Vashistha, V.; Kaur, S.; Houchens, N.W. Serotonin Syndrome: Preventing, Recognizing, and Treating It. Cleve Clin. J. Med. 2016, 83, 810–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majerová, T.; Konvalinka, J. Viral Proteases as Therapeutic Targets. Mol. Asp. Med. 2022, 88, 101159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matt, S.M.; Gaskill, P.J. Dopaminergic Impact of CART and Anti-Depressants on HIV Neuropathogenesis in Older Adults. Brain Res. 2019, 1723, 146398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, S.; Caster, O.; Rochon, P.A.; den Ruijter, H. Reported Adverse Drug Reactions in Women and Men: Aggregated Evidence from Globally Collected Individual Case Reports during Half a Century. EClinicalMedicine 2019, 17, 100188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Yang, J.W.; Jung, S.Y.; Kim, M.S.; Yon, D.K.; Lee, S.W.; Kang, H.-C.; Dragioti, E.; Tizaoui, K.; Jacob, L.; et al. Neuropsychological Adverse Drug Reactions of Remdesivir: Analysis Using VigiBase, the WHO Global Database of Individual Case Safety Reports. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2021, 25, 7390–7397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strohbehn, I.A.; Ouyang, T.; Lee, M.D.; Zhao, S.; Harden, D.; Mejia, S.M.; Cao, A.; Bhattacharyya, R.P.; Sise, M.E. The Effect of Nirmatrelvir-Ritonavir on Short- and Long-Term Adverse Outcomes from COVID-19 Among Patients with Kidney Disease: A Propensity Score–Matched Study. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2024, 12, ofae756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Deng, X.; Huang, J.; He, G.; Huang, S. Data Mining of Adverse Drug Event Signals with Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir from FAERS. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0316573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonçalves de Andrade, E.; Šimončičová, E.; Carrier, M.; Vecchiarelli, H.A.; Robert, M.-È.; Tremblay, M.-È. Microglia Fighting for Neurological and Mental Health: On the Central Nervous System Frontline of COVID-19 Pandemic. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 647378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, R.L.; Benjamin, L.; Lunn, M.P.; Bharucha, T.; Zandi, M.S.; Hoskote, C.; McNamara, P.; Manji, H. Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, and Management of Neuroinflammation in COVID-19. BMJ 2023, 382, e073923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
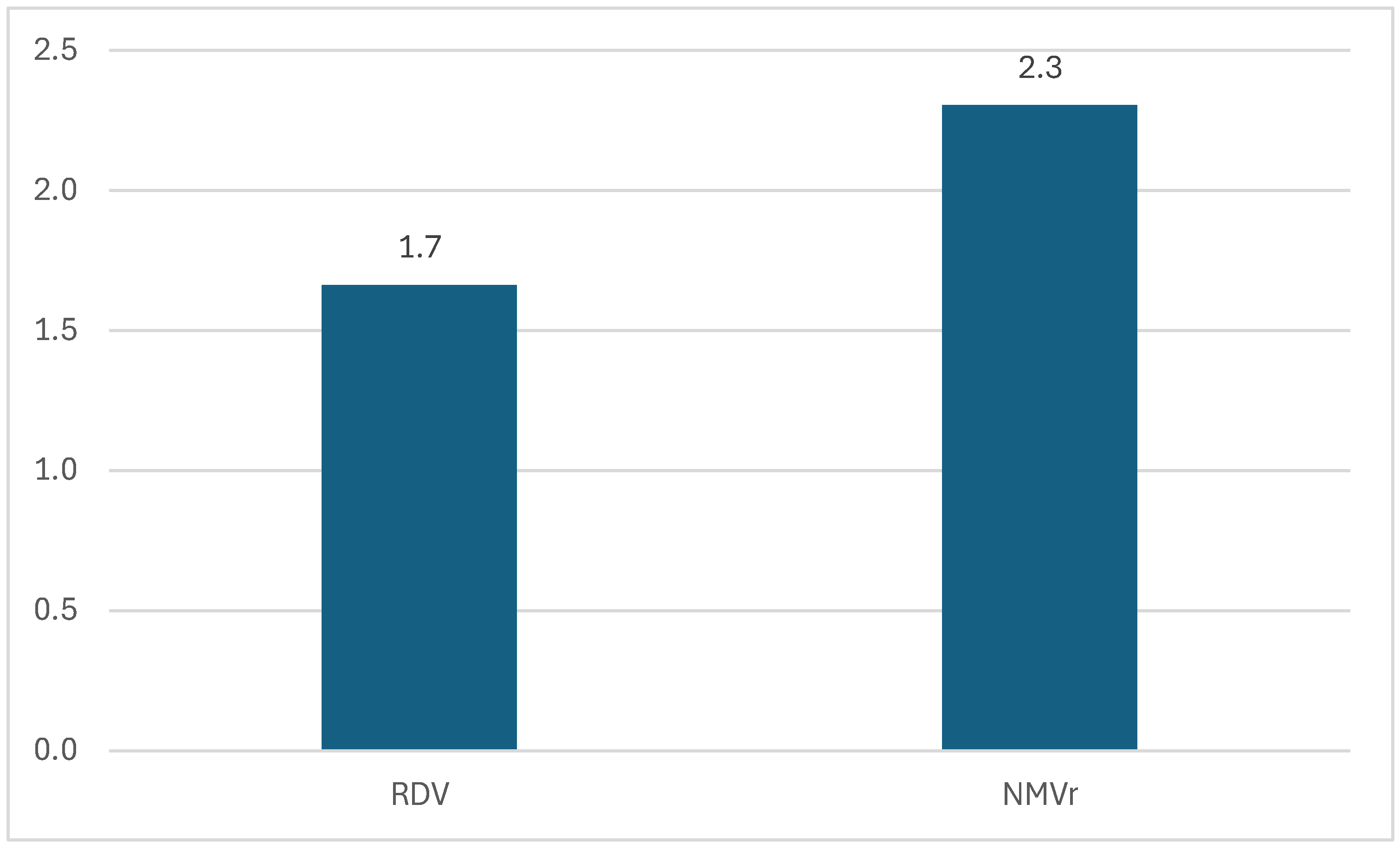
| Antiviral Agent | Pharmacological Class | Mechanism of Action |
|---|---|---|
| Remdesivir (RDV) | RNA-dependent RNA polymerase inhibitor | Inhibits viral RNA polymerase, blocking viral replication. |
| Nirmatrelvir/ritonavir (NMVr) | Protease inhibitor + pharmacokinetic booster | Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 main protease; ritonavir boosts nirmatrelvir’s bioavailability. |
| Ribavirin | Nucleoside analog antiviral | Mimics natural nucleosides, inducing lethal mutagenesis in viral RNA. |
| Sofosbuvir | Nucleotide RNA polymerase inhibitor | Inhibits HCV RNA polymerase, leading to inhibition of viral replication. |
| Tenofovir | Nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitor | Blocks reverse transcriptase, preventing viral DNA synthesis in retroviruses. |
| Darunavir | HIV-1 protease inhibitor | Inhibits HIV protease, preventing the cleavage of polyproteins necessary for viral maturation. |
| Sotrovimab | Neutralizing monoclonal antibody | Targets the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2, preventing cell entry and viral replication. |
| ADR Category | HLT | PT |
|---|---|---|
| Psychiatric disorders | Anxiety disorders and symptoms | Agitation |
| Anxiety | ||
| Fear | ||
| Nervousness | ||
| Panic attack | ||
| Phobia of driving | ||
| Stress | ||
| Deliria (including confusion) | Confusional state | |
| Delirium | ||
| Disorientation | ||
| Depressed mood disorders and disturbances | Depressed mood | |
| Depression | ||
| Depression suicidal | ||
| Disturbances in thinking and perception | Autoscopy | |
| Bradyphrenia | ||
| Delusion | ||
| Hallucination | ||
| Hallucination, auditory | ||
| Hallucination, visual | ||
| Tachyphrenia | ||
| Thinking abnormal | ||
| Mood disorders and disturbances NEC | Emotional distress | |
| Euphoric mood | ||
| Frustration tolerance decreased | ||
| Irritability | ||
| Mood altered | ||
| Mood swings | ||
| Personality disorders and disturbances in behavior | Aggression | |
| Paranoia | ||
| Sleep disorders and disturbances | Abnormal dreams | |
| Abnormal sleep-related event | ||
| Hypnagogic hallucination | ||
| Initial insomnia | ||
| Insomnia | ||
| Middle insomnia | ||
| Nightmare | ||
| Parasomnia | ||
| Poor quality sleep | ||
| Sleep disorder | ||
| Sleep talking | ||
| Sleep terror | ||
| Sleep-related eating disorder | ||
| Somnambulism | ||
| Suicidal and self-injurious behaviors NEC | Completed suicide | |
| Suicidal ideation | ||
| Suicide attempt | ||
| Neurologic disorders | Headaches | Headache |
| Migraine | ||
| Migraine with aura | ||
| Mental impairment disorders | Amnesia | |
| Disturbance in attention | ||
| Memory impairment | ||
| Movement disorders | Bradykinesia | |
| Dyskinesia | ||
| Freezing phenomenon | ||
| Paralysis | ||
| Psychomotor hyperactivity | ||
| Resting tremor | ||
| Tremor | ||
| Seizures | Seizure | |
| Seizure like phenomena |
| RDV | NMVr | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | % | n | % | ||
| Total | 3934 | 100.0% | 8078 | 100.0% | |
| Age category | NS | 580 | 14.7% | 1269 | 15.7% |
| 0–1 month | 4 | 0.1% | 5 | 0.1% | |
| 2 months–2 years | 22 | 0.6% | 0 | 0.0% | |
| 3–11 years | 26 | 0.7% | 0 | 0.0% | |
| 12–17 years | 28 | 0.7% | 18 | 0.2% | |
| 18–64 years | 1483 | 37.7% | 3072 | 38.0% | |
| 65–85 years | 1398 | 35.5% | 3110 | 38.5% | |
| More than 85 years | 393 | 10.0% | 604 | 7.5% | |
| Sex | Female | 1448 | 36.8% | 4996 | 61.8% |
| Male | 2310 | 58.7% | 2735 | 33.9% | |
| NS | 176 | 4.5% | 347 | 4.3% | |
| Geographic region | EEA | 1406 | 35.7% | 3912 | 48.4% |
| NON-EEA | 2528 | 64.3% | 4166 | 51.6% | |
| NS | 0 | 0.0% | 0 | 0.0% | |
| Reporter | HP | 3673 | 93.4% | 4445 | 55.0% |
| Non-HP | 261 | 6.6% | 3633 | 45.0% | |
| NS | 0 | 0.0% | 0 | 0.0% | |
| Seriousness | Non serious | 621 | 15.8% | 3239 | 40.1% |
| NS | 0 | 0.0% | 0 | 0.0% | |
| Serious | 3313 | 84.2% | 4839 | 59.9% | |
| ADRs of RDV | Other ADRs of RDV | ADRs of NMVr | Other ADRs of NMVr | ROR | 95% CI Minimum | 95% CI Maximum | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blood and lymphatic system disorders **** | 120 | 6422 | 106 | 18,510 | 3.263 | 2.5089 | 4.2437 | p < 0.0001 |
| Cardiac disorders **** | 577 | 5965 | 427 | 18,189 | 4.1205 | 3.6236 | 4.6854 | p < 0.0001 |
| Congenital, familial, and genetic disorders | 5 | 6537 | 14 | 18,602 | 1.0163 | 0.3659 | 2.8227 | p = 0.9752 |
| Ear and labyrinth disorders **** | 11 | 6531 | 178 | 18,438 | 0.1745 | 0.0948 | 0.3210 | p < 0.0001 |
| Endocrine disorders | 9 | 6533 | 20 | 18,596 | 1.2809 | 0.5830 | 2.8145 | p = 0.5376 |
| Eye disorders **** | 21 | 6521 | 222 | 18,394 | 0.2668 | 0.1704 | 0.4178 | p < 0.0001 |
| Gastrointestinal disorders **** | 200 | 6342 | 3083 | 15,533 | 0.1589 | 0.1373 | 0.1839 | p < 0.0001 |
| General disorders and administration site conditions | 1040 | 5502 | 2984 | 15,632 | 0.9902 | 0.9169 | 1.0694 | p = 0.8022 |
| Hepatobiliary disorders **** | 411 | 6131 | 160 | 18,456 | 7.7326 | 6.4272 | 9.3032 | p < 0.0001 |
| Immune system disorders ** | 84 | 6458 | 159 | 18,457 | 1.5099 | 1.1574 | 1.9698 | p = 0.0024 |
| Infections and infestations ** | 666 | 5876 | 1642 | 16,974 | 1.1717 | 1.0657 | 1.2882 | p = 0.0011 |
| Injury, poisoning, and procedural complications | 381 | 6161 | 984 | 17,632 | 1.1081 | 0.9811 | 1.2516 | p = 0.0985 |
| Investigations **** | 1044 | 5498 | 954 | 17,662 | 3.5155 | 3.2038 | 3.8576 | p < 0.0001 |
| Metabolism and nutrition disorders **** | 120 | 6422 | 516 | 18,100 | 0.6555 | 0.5363 | 0.8011 | p < 0.0001 |
| Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders **** | 47 | 6495 | 523 | 18,093 | 0.2503 | 0.1855 | 0.3379 | p < 0.0001 |
| Neoplasms benign, malignant, and unspecified (including cysts and polyps) | 18 | 6524 | 51 | 18,565 | 1.0043 | 0.5864 | 1.7202 | p = 0.9874 |
| Nervous system disorders **** | 201 | 6341 | 3223 | 15,393 | 0.1514 | 0.1309 | 0.1751 | p < 0.0001 |
| Pregnancy, puerperium, and perinatal conditions **** | 63 | 6479 | 6 | 18,610 | 30.1597 | 13.0479 | 69.7131 | p < 0.0001 |
| Product issues * | 23 | 6519 | 116 | 18,500 | 0.5627 | 0.3594 | 0.8809 | p = 0.0119 |
| Psychiatric disorders **** | 60 | 6482 | 672 | 17,944 | 0.2472 | 0.1895 | 0.3224 | p < 0.0001 |
| Renal and urinary disorders **** | 411 | 6131 | 367 | 18,249 | 3.3334 | 2.8872 | 3.8485 | p < 0.0001 |
| Reproductive system and breast disorders | 2 | 6540 | 59 | 18,557 | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Respiratory, thoracic, and mediastinal disorders **** | 492 | 6050 | 950 | 17,666 | 1.5123 | 1.3511 | 1.6927 | p < 0.0001 |
| Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders | 256 | 6286 | 654 | 17,962 | 1.1185 | 0.9653 | 1.2961 | p = 0.1362 |
| Social circumstances | 4 | 6538 | 35 | 18,581 | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Surgical and medical procedures **** | 88 | 6454 | 49 | 18,567 | 5.1665 | 3.6389 | 7.3354 | p < 0.0001 |
| Vascular disorders | 188 | 6354 | 462 | 18,154 | 1.1626 | 0.9790 | 1.3808 | p = 0.0859 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pacnejer, A.-M.; Negru, M.C.; Arseniu, A.M.; Trandafirescu, C.; Oancea, C.; Gligor, F.G.; Morgovan, C.; Butuca, A.; Dehelean, C.A. Comparative Analysis of Neuropsychiatric Adverse Reactions Associated with Remdesivir and Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir in COVID-19 Treatment: Insights from EudraVigilance Data. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 1886. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14061886
Pacnejer A-M, Negru MC, Arseniu AM, Trandafirescu C, Oancea C, Gligor FG, Morgovan C, Butuca A, Dehelean CA. Comparative Analysis of Neuropsychiatric Adverse Reactions Associated with Remdesivir and Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir in COVID-19 Treatment: Insights from EudraVigilance Data. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(6):1886. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14061886
Chicago/Turabian StylePacnejer, Aliteia-Maria, Mihaela Cristina Negru, Anca Maria Arseniu, Cristina Trandafirescu, Cristian Oancea, Felicia Gabriela Gligor, Claudiu Morgovan, Anca Butuca, and Cristina Adriana Dehelean. 2025. "Comparative Analysis of Neuropsychiatric Adverse Reactions Associated with Remdesivir and Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir in COVID-19 Treatment: Insights from EudraVigilance Data" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 6: 1886. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14061886
APA StylePacnejer, A.-M., Negru, M. C., Arseniu, A. M., Trandafirescu, C., Oancea, C., Gligor, F. G., Morgovan, C., Butuca, A., & Dehelean, C. A. (2025). Comparative Analysis of Neuropsychiatric Adverse Reactions Associated with Remdesivir and Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir in COVID-19 Treatment: Insights from EudraVigilance Data. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(6), 1886. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14061886









