Effects of AUC-Based Vancomycin Therapeutic Drug Monitoring on AKI Incidence and Drug Utilization: A Propensity Score-Weighted Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
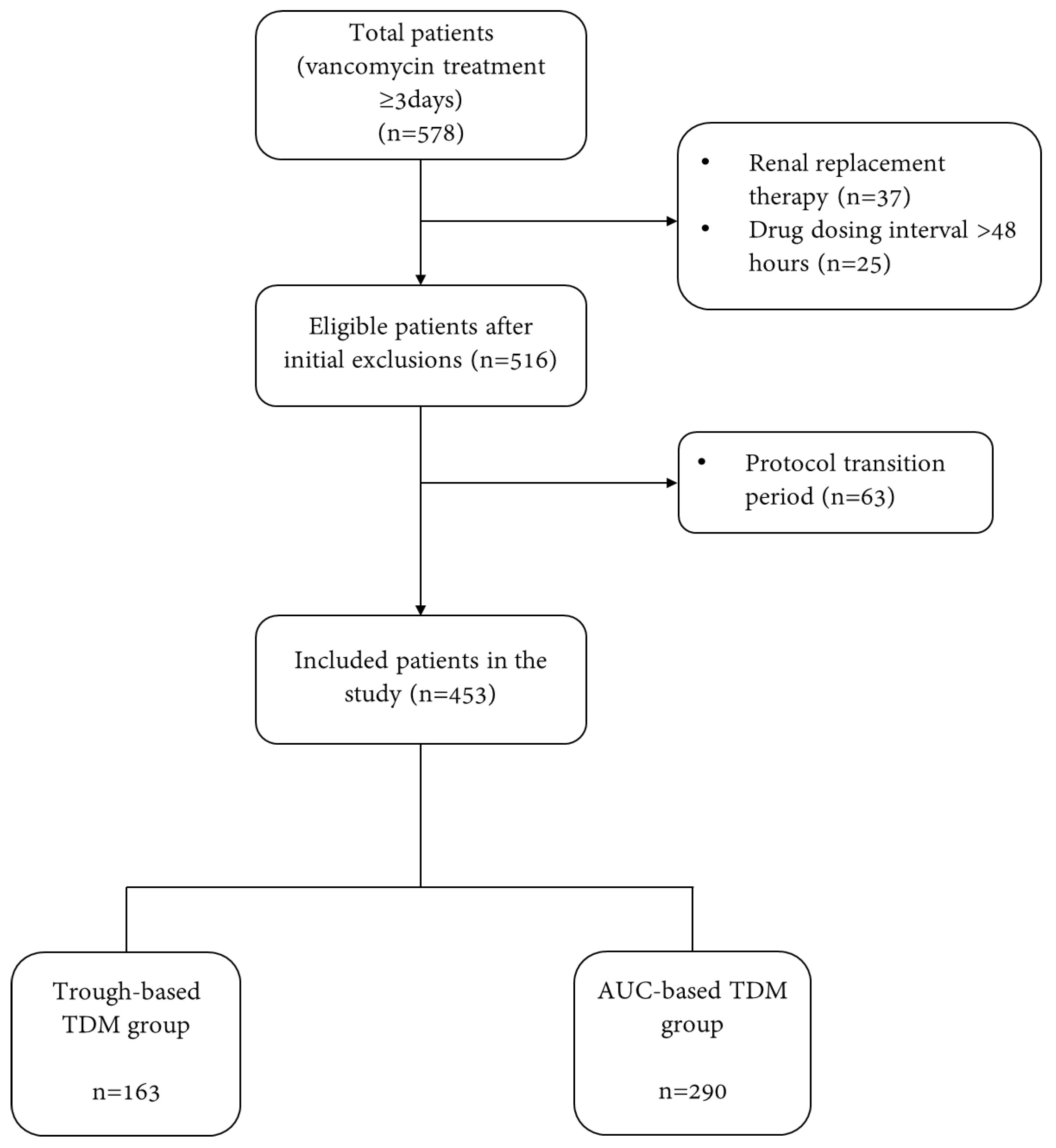
2.1. Study Subjects
2.2. Definition of Disease and Study Outcome
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Subject Characteristics
3.2. Incidence of Acute Kidney Injury
3.3. Secondary Outcomes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AKI | acute kidney injury |
| ASHP | American society of health-system pharmacists |
| AUC | area under the curve |
| BUN | blood urea nitrogen |
| CI | confidence intervals |
| CLcr | creatinine clearance |
| DM | diabetes mellitus |
| eGFR | estimated glomerular filtration rate |
| HTN | hypertension |
| IDSA | infectious diseases society of America |
| IPTW | inverse probability of treatment weighting |
| KDIGO | the kidney disease: improving global outcomes |
| MIC | minimum inhibitory concentration |
| MRSA | methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus |
| OR | odds ratio |
| SCr | serum creatinine |
| SD | standard deviation |
| SIDP | society of infectious diseases pharmacists |
| STROBE | strengthening the reporting of observational studies in epidemiology |
| TDM | therapeutic drug monitoring |
References
- Liu, C.; Bayer, A.; Cosgrove, S.E.; Daum, R.S.; Fridkin, S.K.; Gorwitz, R.J.; Kaplan, S.L.; Karchmer, A.W.; Levine, D.P.; Murray, B.E.; et al. Clinical practice guidelines by the infectious diseases society of america for the treatment of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections in adults and children: Executive summary. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2011, 52, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levine, D.P. Vancomycin: A history. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2006, 42 (Suppl 1), S5–S12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gould, F.K.; Brindle, R.; Chadwick, P.R.; Fraise, A.P.; Hill, S.; Nathwani, D.; Ridgway, G.L.; Spry, M.J.; Warren, R.E. MRSA Working Party of the British Society for Antimicrobial Chemotherapy. Guidelines (2008) for the prophylaxis and treatment of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) infections in the United Kingdom. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2009, 63, 849–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wunderink, R.G.; Niederman, M.S.; Kollef, M.H.; Shorr, A.F.; Kunkel, M.J.; Baruch, A.; McGee, W.T.; Reisman, A.; Chastre, J. Linezolid in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus nosocomial pneumonia: A randomized, controlled study. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2012, 54, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filippone, E.J.; Kraft, W.K.; Farber, J.L. The Nephrotoxicity of Vancomycin. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 102, 459–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodise, T.P.; Hall, R.G.; Scheetz, M.H. Vancomycin Area Under the Curve-guided Dosing and Monitoring: “Is the Juice Worth the Squeeze”? Pharmacotherapy 2020, 40, 1176–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybak, M.J.; Lomaestro, B.M.; Rotschafer, J.C.; Moellering, R.C.; Craig, W.A.; Billeter, M.; Dalovisio, J.R.; Levine, D.P. Vancomycin therapeutic guidelines: A summary of consensus recommendations from the infectious diseases Society of America, the American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, and the Society of Infectious Diseases Pharmacists. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2009, 49, 325–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsutsuura, M.; Moriyama, H.; Kojima, N.; Mizukami, Y.; Tashiro, S.; Osa, S.; Enoki, Y.; Taguchi, K.; Oda, K.; Fujii, S.; et al. The monitoring of vancomycin: A systematic review and meta-analyses of area under the concentration-time curve-guided dosing and trough-guided dosing. BMC Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, K.; Crumby, A.S.; Maples, H.D. Balancing vancomycin efficacy and nephrotoxicity: Should we be aiming for trough or AUC/MIC? Paediatr. Drugs 2015, 17, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybak, M.J.; Le, J.; Lodise, T.P.; Levine, D.P.; Bradley, J.S.; Liu, C.; Mueller, B.A.; Pai, M.P.; Wong-Beringer, A.; Rotschafer, J.C.; et al. Therapeutic monitoring of vancomycin for serious methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections: A revised consensus guideline and review by the American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, the Infectious Diseases Society of America, the Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society, and the Society of Infectious Diseases Pharmacists. Am. J. Health Syst. Pharm. 2020, 77, 835–864. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelmessih, E.; Patel, N.; Vekaria, J.; Crovetto, B.; SanFilippo, S.; Adams, C.; Brunetti, L. Vancomycin area under the curve versus trough only guided dosing and the risk of acute kidney injury: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Pharmacotherapy 2022, 42, 741–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nix, D.E.; Davis, L.E.; Matthias, K.R. The relationship of vancomycin 24-hour AUC and trough concentration. Am. J. Health Syst. Pharm. 2022, 79, 534–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradley, N.; Lee, Y.; Sadeia, M. Assessment of the Implementation of AUC Dosing and Monitoring Practices With Vancomycin at Hospitals Across the United States. J. Pharm. Pract. 2022, 35, 864–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, E.R.; Burgess, D.R.; Cotner, S.E.; VanHoose, J.D.; Flannery, A.H.; Gardner, B.; Autry, E.B.; Forster, D.W.; Burgess, D.S.; Wallace, K.L. Pharmacist Survey: Pharmacist Perception of Vancomycin Area Under the Curve Therapeutic Drug Monitoring. J. Pharm. Pract. 2021, 34, 272–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kufel, W.D.; Seabury, R.W.; Mogle, B.T.; Beccari, M.V.; Probst, L.A.; Steele, J.M. Readiness to implement vancomycin monitoring based on area under the concentration-time curve: A cross-sectional survey of a national health consortium. Am. J. Health Syst. Pharm. 2019, 76, 889–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flannery, A.H.; Hammond, D.A.; Oyler, D.R.; Li, C.; Wong, A.; Smith, A.P.; Yeo, Q.M.; Chaney, W.; Pfaff, C.E.; Plewa-Rusiecki, A.M.; et al. Vancomycin Dosing Practices among Critical Care Pharmacists: A Survey of Society of Critical Care Medicine Pharmacists. Infect. Dis. 2020, 13, 1178633720952078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.; Patel, D.; Vega, A.; Claeys, K.C.; Heil, E.L.; Scheetz, M.H. Does calculation method matter for targeting vancomycin area under the curve? J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2022, 77, 2245–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khwaja, A. KDIGO clinical practice guidelines for acute kidney injury. Nephron Clin. Pract. 2012, 120, c179–c184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Hal, S.J.; Paterson, D.L.; Lodise, T.P. Systematic review and meta-analysis of vancomycin-induced nephrotoxicity associated with dosing schedules that maintain troughs between 15 and 20 milligrams per liter. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 734–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha Ray, A.; Haikal, A.; Hammoud, K.A.; Yu, A.S.L. Vancomycin and the Risk of AKI: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2016, 11, 2132–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laou, E.; Mavridis, T.; Papagiannakis, N.; Pais, G.; Chighine, A.; Chang, J.; Locci, E.; D’Aloja, E.; Scheetz, M.; Chalkias, A.; et al. Blood Biomarkers and Metabolomic Profiling for the Early Diagnosis of Vancomycin-Associated Acute Kidney Injury: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Experimental Studies. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Patient Characteristics | Before Weighted by Propensity Score | After Weighted by Propensity Score | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trough-Based TDM Group (n = 163), n (%) | AUC-Based TDM Group (n = 290), n (%) | p-Value | Variance Ratio | Trough-Based TDM Group (n = 455), n (%) | AUC-Based TDM Group (n = 452), n (%) | p-Value | Variance Ratio | |
| Age (year) † | 63.7 ± 16.73 | 62.7 ± 14.07 | 0.5503 | 0.7070 | 63.1 ± 28.04 | 63.0 ± 17.42 | 0.9551 | 0.7035 |
| Body weight (kg) † | 63.3 ± 19.39 | 63.6 ± 16.63 | 0.8677 | 0.7351 | 64.1 ± 34.16 | 63.7 ± 20.61 | 0.8238 | 0.6289 |
| Sex | 0.7293 | 0.9767 | 0.9598 | 0.9970 | ||||
| Men | 107 (65.6) | 195 (67.2) | 303 (66.6) | 300 (66.4) | ||||
| Women | 56 (34.4) | 95 (32.8) | 152 (33.4) | 152 (33.6) | ||||
| SCr (mg/dL) † | 0.78 ± 0.41 | 0.77 ± 0.36 | 0.7780 | 0.7685 | 0.77 ± 0.61 | 0.78 ± 0.49 | 0.8277 | 1.1256 |
| BUN (mg/dL) † | 19.4 ± 11.33 | 17.2 ± 8.27 | 0.0265 * | - | 19.1 ± 18.38 | 17.5 ± 10.65 | 0.1133 | - |
| CLcr (mL/min) † | 74.2 ± 26.42 | 76.2 ± 25.88 | 0.5317 | - | 75.6 ± 43.43 | 75.4 ± 32.59 | 0.9548 | - |
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) † | 91.5 ± 18.91 | 94.3 ± 15.21 | 0.1040 | - | 92.31 ± 29.04 | 93.99 ± 19.97 | 0.3084 | - |
| High-risk medication use | 21 (12.9) | 17 (5.9) | 0.0097 * | 0.4917 | 38 (8.4) | 37 (8.3) | 0.9511 | 1.0016 |
| Low-risk medication use | 117 (71.78) | 190 (65.5) | 0.1711 | 1.1153 | 307 (67.5) | 306 (67.6) | 0.9750 | 0.9947 |
| Indication for vancomycin | ||||||||
| Bloodstream infection | 50 (30.7) | 94 (32.4) | 0.7028 | 1.0302 | 139 (30.5) | 143 (31.6) | 0.7548 | 1.0323 |
| Pneumonia | 23 (14.1) | 22 (7.6) | 0.0259 * | 0.5785 | 45 (9.9) | 44 (9.7) | 0.9837 | 1.0117 |
| Neutropenic fever | 12 (7.3) | 16 (5.5) | 0.4339 | 0.7643 | 29 (6.4) | 29 (6.4) | 0.9515 | 0.9434 |
| Osteomyelitis | 20 (12.3) | 69 (23.8) | 0.0031 * | 1.6844 | 94 (20.7) | 89 (19.7) | 0.7180 | 0.9563 |
| Others | 58 (35.6) | 89 (30.7) | 0.2857 | 0.9280 | 148 (32.5) | 147 (32.5) | 0.9635 | 1.0008 |
| Comorbidity | ||||||||
| HTN | 20 (12.3) | 51 (17.6) | 0.1352 | 1.3464 | 73 (16.1) | 71 (15.8) | 0.9067 | 0.9740 |
| DM | 24 (14.7) | 57 (19.7) | 0.1887 | 1.2577 | 84 (18.5) | 82 (18.1) | 0.8860 | 0.9678 |
| Before Weighted by Propensity Score | After Weighted by Propensity Score | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trough-Based TDM Group (n = 163) n (%) | AUC-Based TDM Group (n = 290) n (%) | OR (95% CI) | p-Value | Trough-Based TDM Group (n = 455) n (%) | AUC-Based TDM Group (n = 452) n (%) | OR (95% CI) | p-Value | |
| no AKI | 154 (94.48) | 287 (98.97) | 0.18 (0.05–0.67) | 0.0107 * | 432 (94.92) | 447 (98.80) | 0.23 (0.09–0.59) | 0.0021 * |
| AKI | 9 (5.52) | 3 (1.03) | 23 (5.08) | 5 (1.20) | ||||
| Before Weighted by Propensity Score | After Weighted by Propensity Score | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trough-Based TDM Group (n = 163) mean ± SD | AUC-Based TDM Group (n = 290) mean ± SD | p-Value | Trough-Based TDM Group (n = 455) mean ± SD | AUC-Based TDM Group (n = 452) mean ± SD | p-Value | |
| Total dose of vancomycin administered (mg) | 29,092 ± 33,512.8 | 21,093 ± 25,478.3 | 0.0086 * | 29,530 ± 54,671.7 | 20,987 ± 33,124.1 | 0.0047 * |
| Total duration of vancomycin treatment (days) | 13.47 ± 13.54 | 12.35 ± 14.85 | 0.4280 | 13.59 ± 22.91 | 12.35 ± 19.54 | 0.3811 |
| The number of modifications to the vancomycin regimen | 1.08 ± 1.56 | 1.07 ± 1.52 | 0.9427 | 1.09 ± 2.66 | 1.06 ± 1.89 | 0.8695 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, H.Y.; Kim, B.Y.; Song, J.Y.; Seo, K.H.; Lee, S.H.; Choi, S.; Rhew, K. Effects of AUC-Based Vancomycin Therapeutic Drug Monitoring on AKI Incidence and Drug Utilization: A Propensity Score-Weighted Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 1863. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14061863
Park HY, Kim BY, Song JY, Seo KH, Lee SH, Choi S, Rhew K. Effects of AUC-Based Vancomycin Therapeutic Drug Monitoring on AKI Incidence and Drug Utilization: A Propensity Score-Weighted Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(6):1863. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14061863
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Hye Young, Bo Young Kim, Joon Young Song, Kyung Hee Seo, So Hyun Lee, Seeun Choi, and Kiyon Rhew. 2025. "Effects of AUC-Based Vancomycin Therapeutic Drug Monitoring on AKI Incidence and Drug Utilization: A Propensity Score-Weighted Analysis" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 6: 1863. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14061863
APA StylePark, H. Y., Kim, B. Y., Song, J. Y., Seo, K. H., Lee, S. H., Choi, S., & Rhew, K. (2025). Effects of AUC-Based Vancomycin Therapeutic Drug Monitoring on AKI Incidence and Drug Utilization: A Propensity Score-Weighted Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(6), 1863. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14061863






