Multimodality Imaging Approach to Infective Endocarditis: Current Opinion in Patients with Congenital Heart Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
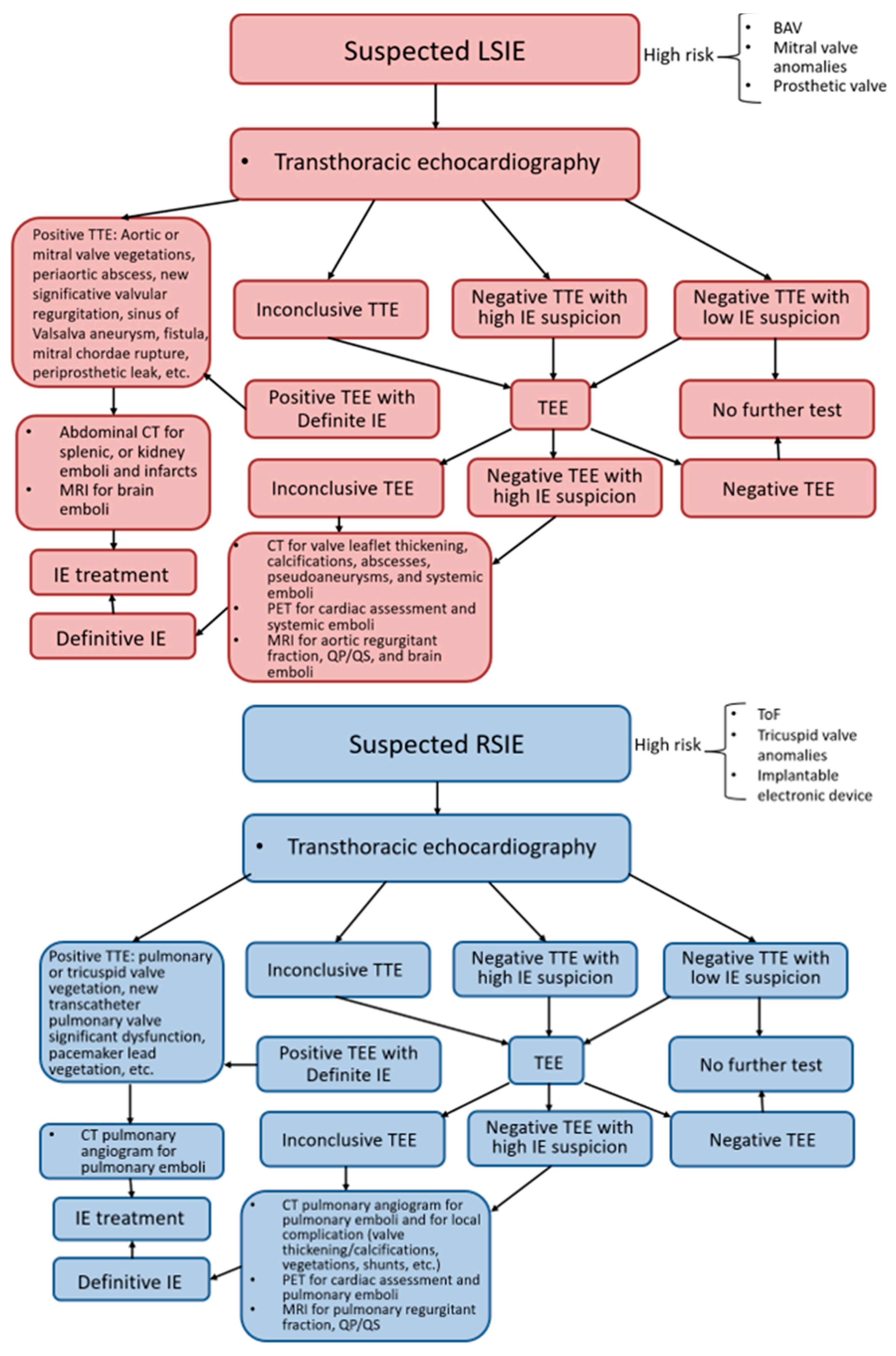
2. Left-Sided Infective Endocarditis (LSIE) in Congenital Heart Disease
2.1. Introduction to LSIE
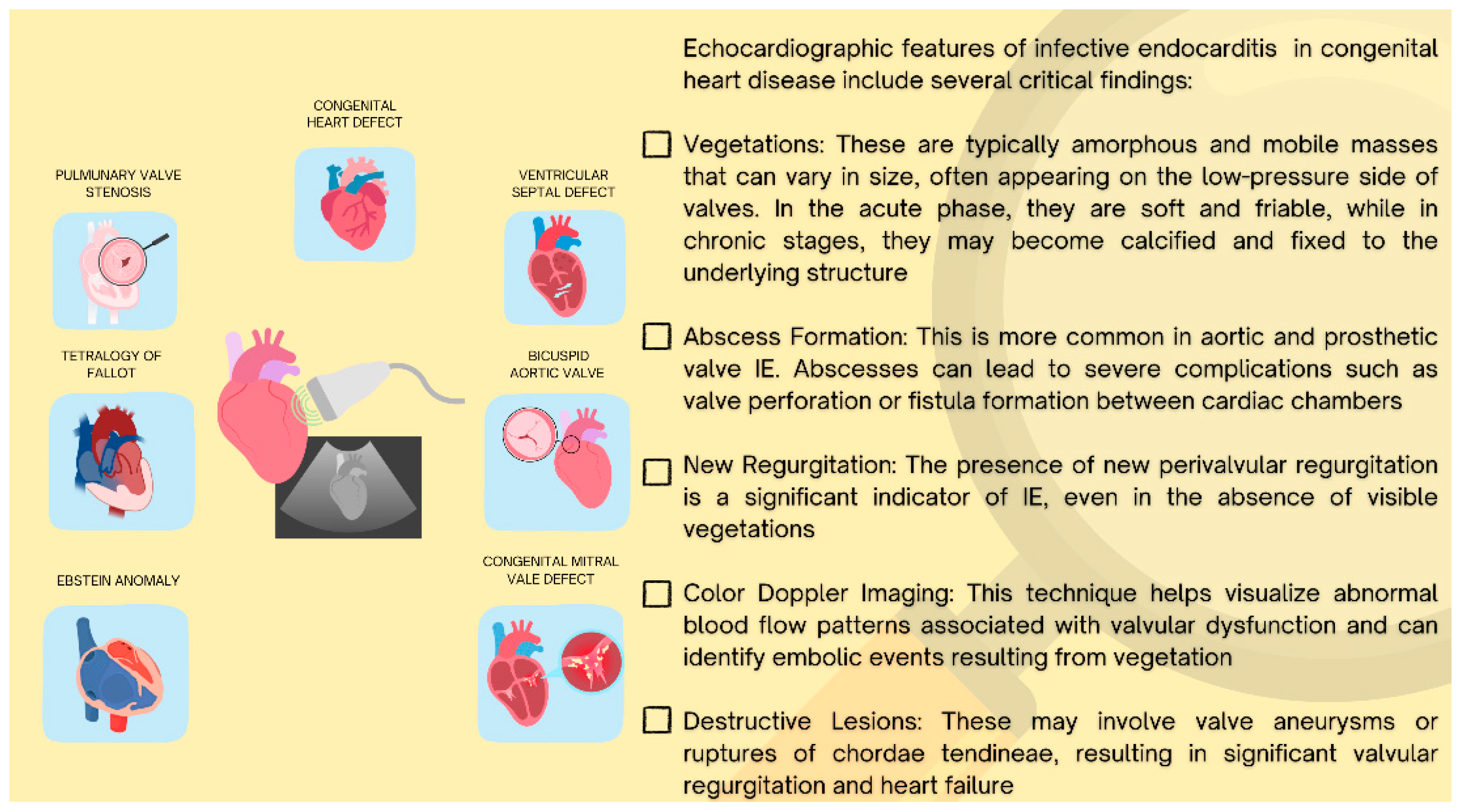
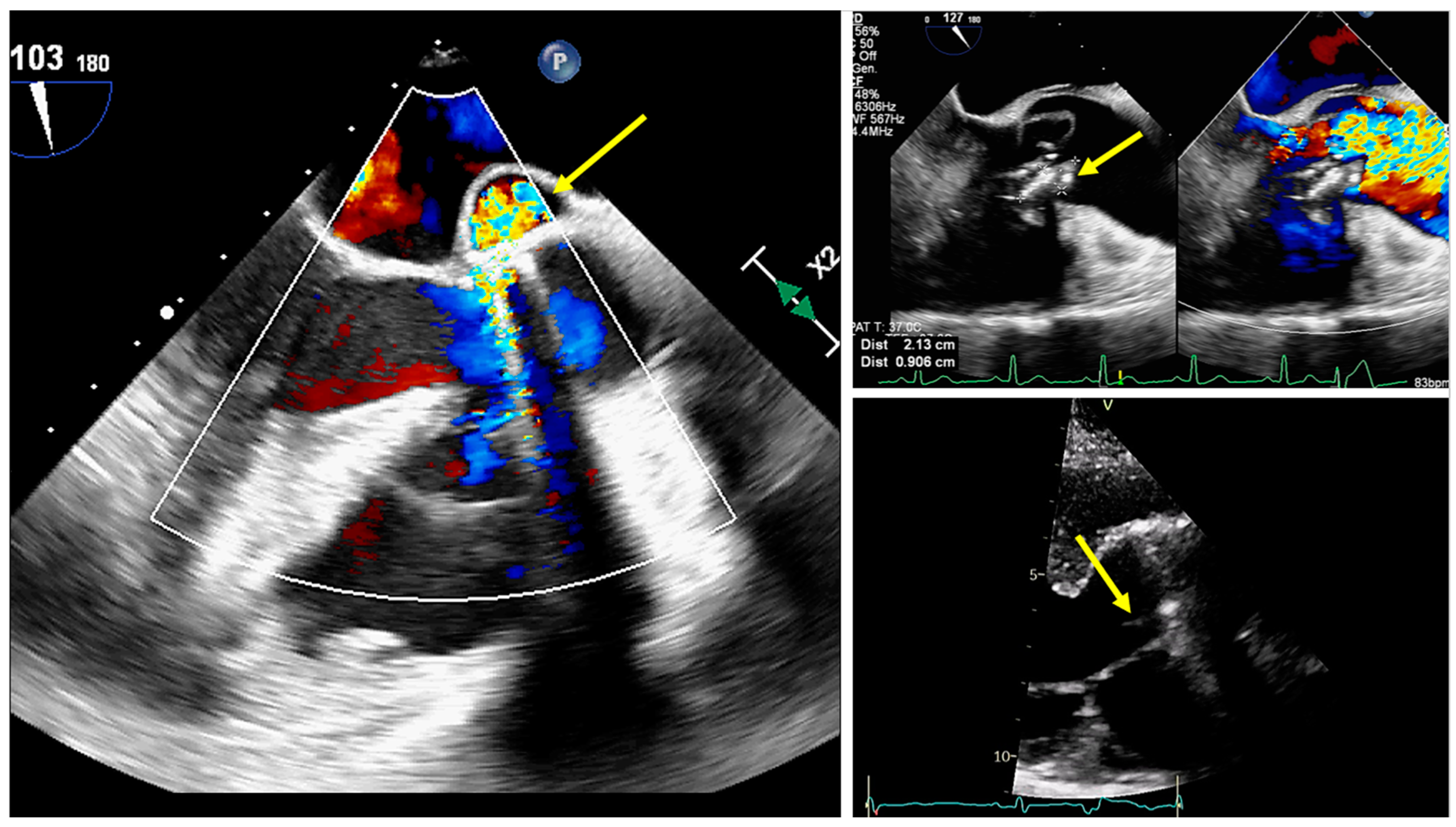
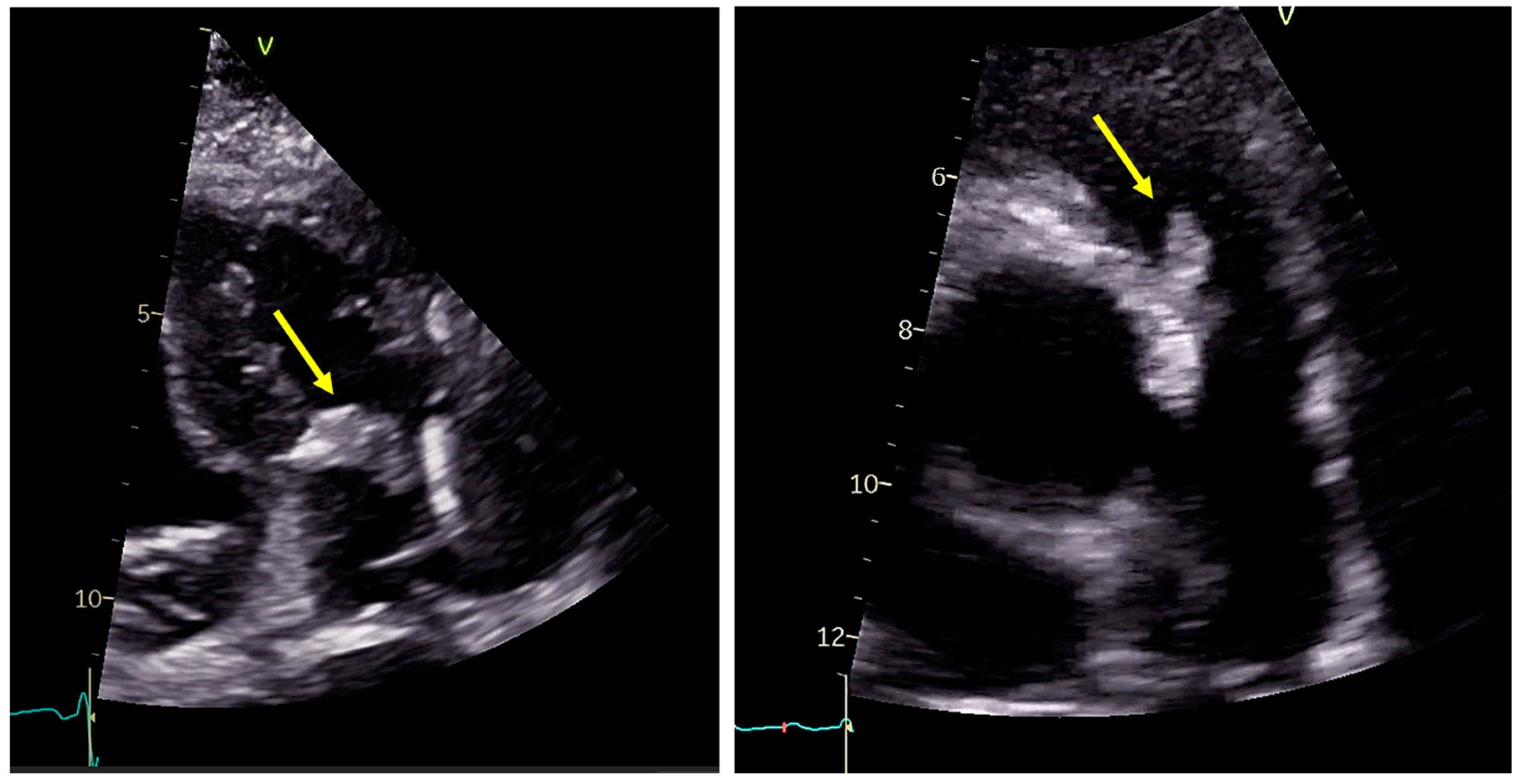
2.2. Role of Echocardiography
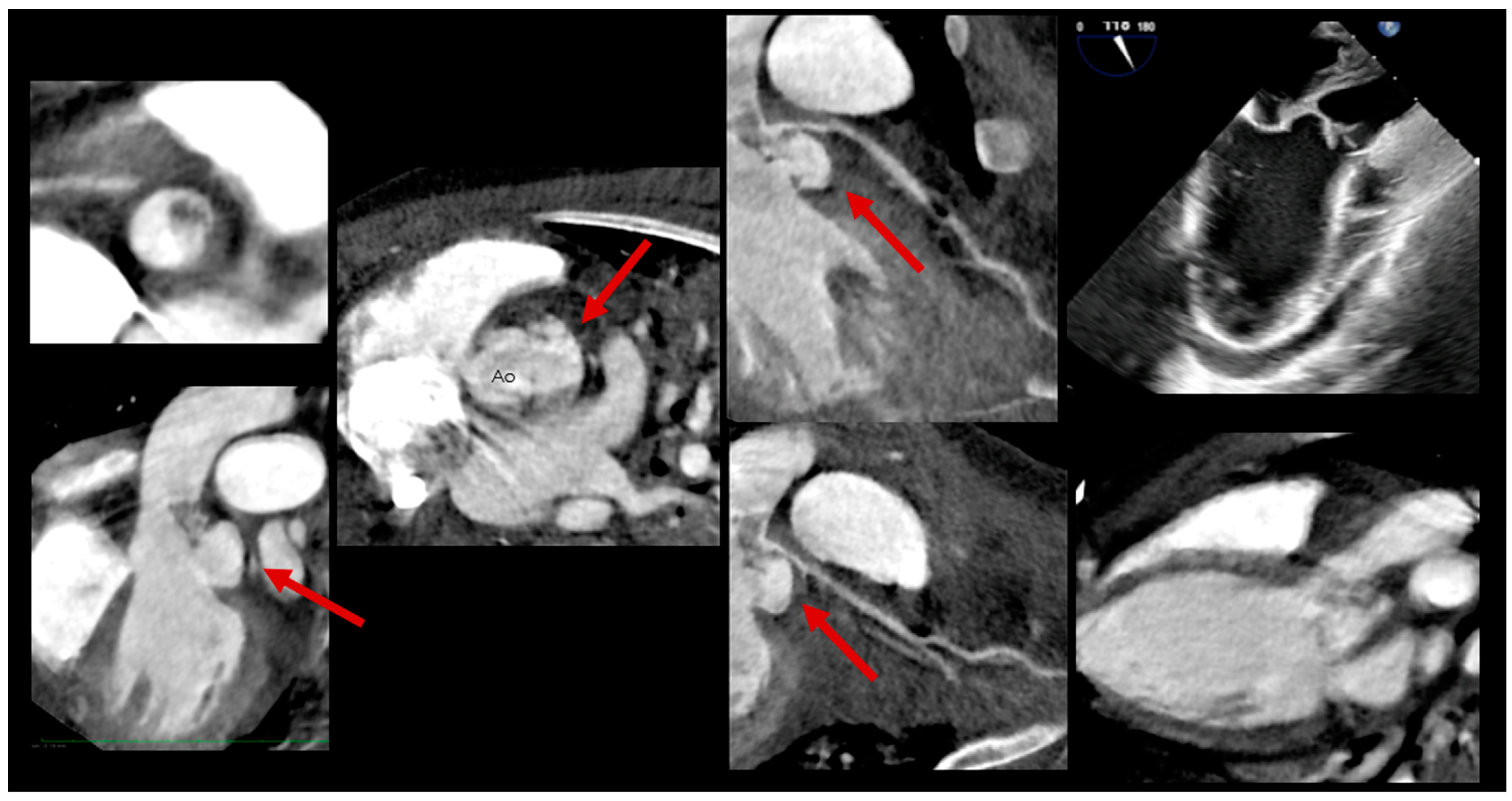
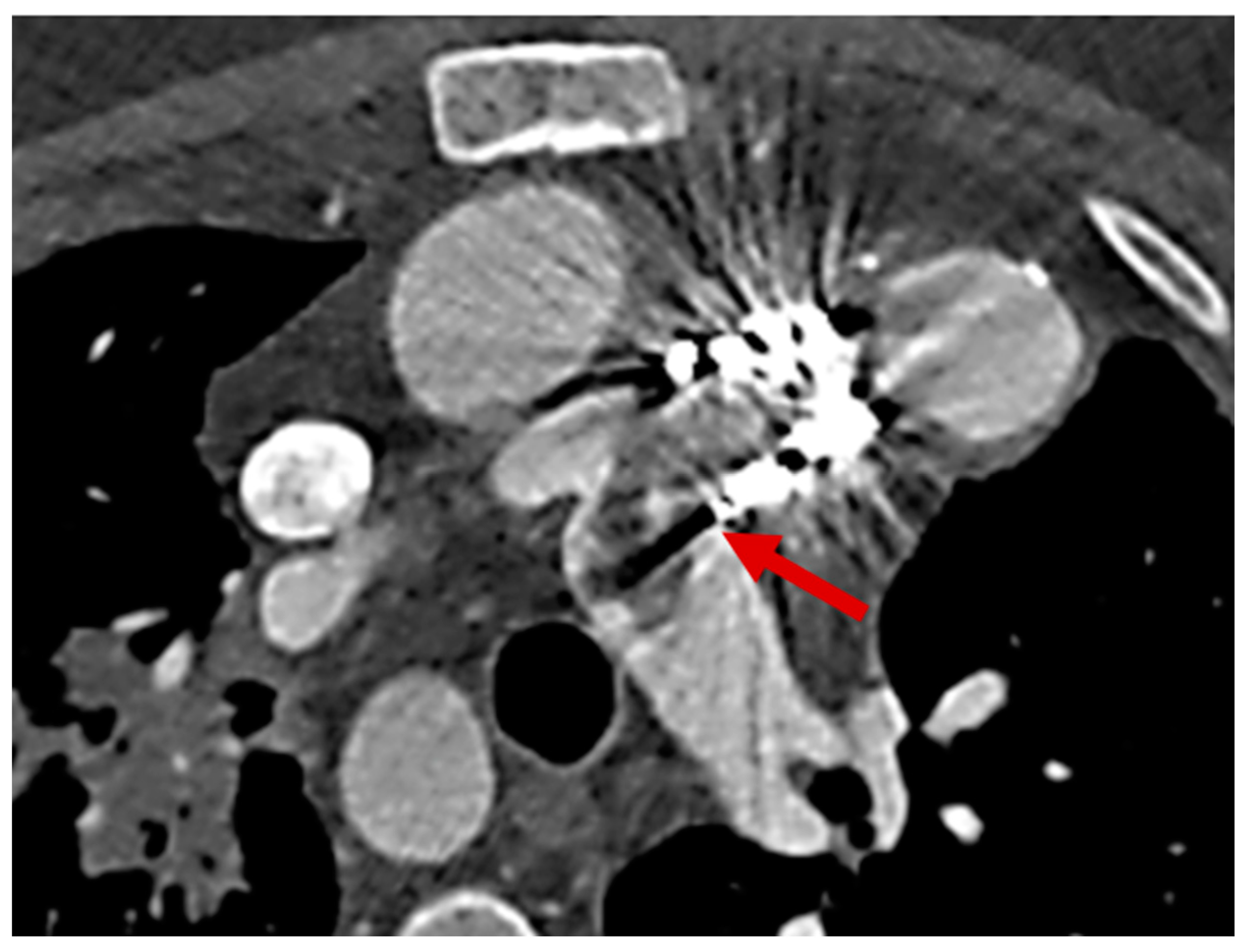
2.3. Role of Cardiac Computed Tomography
2.4. Role of Cardiac Magnetic Resonance
3. Right-Sided Infective Endocarditis (RSIE) in Congenital Heart Disease
3.1. Introduction to RSIE
3.2. Role of Echocardiography
- Upper esophageal at 0°–10°: to investigate the main pulmonary artery and pulmonary branches;
- Mid-esophageal at 0°–10° and 50°–70°: to assess the right atrium, TV, subpulmonary region, and PV;
- Transgastric at 50°–90°: this view allows for an assessment of any residual obstruction in the RVOT, as well as valvular and supravalvular areas, because the ultrasound beam often aligns with the blood flow direction.
3.3. Role of Cardiac Computed Tomography
3.4. Role of Cardiac Magnetic Resonance
4. Role of SPECT/CT and PET/CT in CHD Patients with IE
4.1. SPECT/CT
4.2. PET/CT
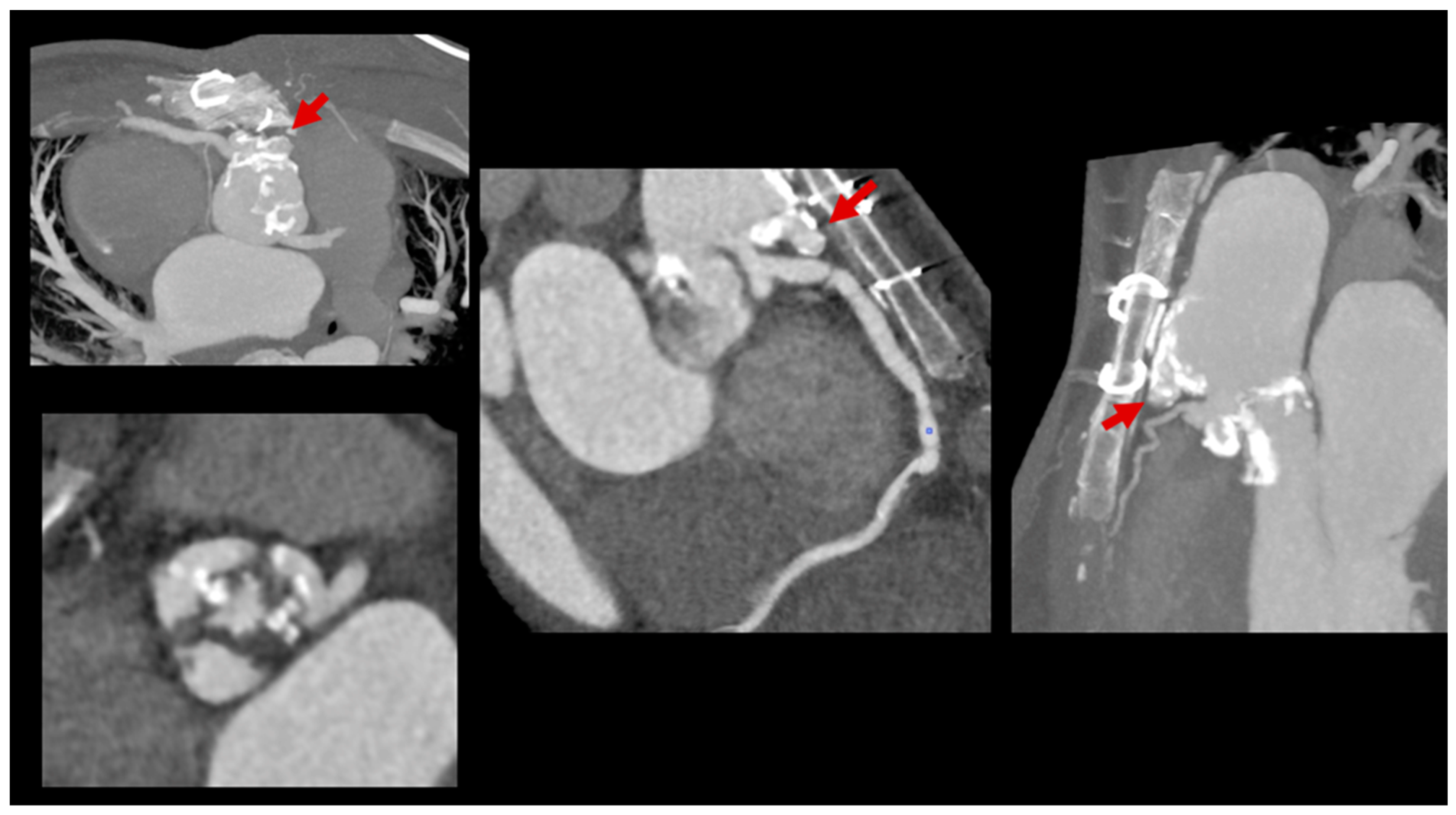
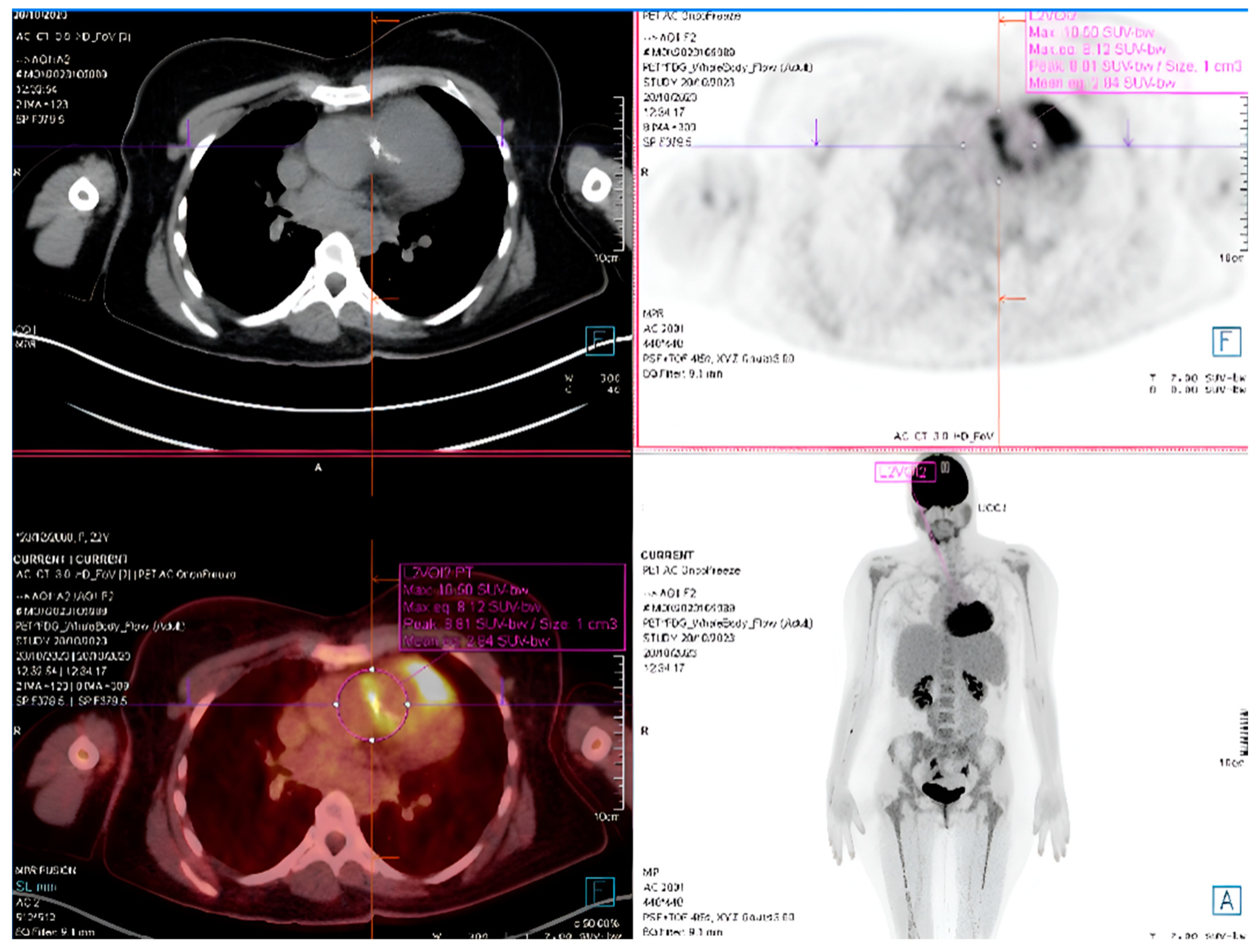
- Detecting Device-Related Infections: PET/CT is highly effective for evaluating infections involving prosthetic valves, pacemaker leads, and other intracardiac devices (Figure 7). It offers unmatched sensitivity in visualizing device pockets and lead tracks, helping differentiate sterile thrombi from infectious vegetations. This is critical in CHD patients, who frequently require surgical implants as part of their treatment.
- Enhancing Diagnostic Accuracy with the Duke Criteria: PET/CT significantly improves the sensitivity of the Duke Criteria for IE diagnoses, increasing it from 52 to 70% to 87–97%. By combining PET/CT findings with clinical and microbiological evidence, cases previously classified as “possible IE” can often be reclassified as either “definite” or “rejected”, reducing diagnostic ambiguity [27,98].
- Integration with CT Angiography (PET/CTA): When PET is paired with CT angiography, the resulting hybrid imaging achieves remarkable diagnostic precision. This combination leverages PET’s sensitivity for detecting metabolic activity in infected tissues and CTA’s detailed visualization of structural abnormalities. For instance, PET/CTA achieves a sensitivity of 91% and a positive predictive value of 93% for diagnosing infections involving prosthetic valves and intracardiac devices, significantly enhancing diagnostic confidence [99].
4.3. Detection of Extra-Cardiac Pathologies
4.4. Therapeutic Impact
- Avoiding Unnecessary Procedures: PET/CT’s ability to distinguish active infections from sterile inflammation helps prevent unwarranted removal of prosthetic devices or unnecessary surgical interventions.
- Guiding Surgical Interventions: In cases where PET/CT identifies active infections such as abscesses or large vegetations with embolic potential, surgical interventions can be prioritized to mitigate risks.
- Monitoring Treatment Response: PET/CT is also invaluable in evaluating the efficacy of antibiotic therapy by tracking changes in metabolic activity at infected sites. This early assessment allows for timely adjustments to therapeutic regimens, optimizing patient outcomes.
5. Gaps in Evidence and New Perspectives
- Standardization of imaging protocols
- Assessment fluid dynamics
- Role of hybrid technologies
- Risk models
- Telemedicine
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CHD | Congenital heart disease |
| IE | Infective endocarditis |
| CCT | Cardiac Computed Tomography |
| CMR | Cardiac Magnetic Resonance |
| BAV | Bicuspid aortic valve |
| LSIE | Left-sided infective endocarditis |
| MVP | Mitral valve prolapse |
| MV | Mitral valve |
| TEE | Transesophageal echocardiography |
| 3D | Three-dimensional |
| 2D | Two-dimensional |
| TTE | Transthoracic echocardiography |
| RSIE | Right-sided infective endocarditis |
| TV | Tricuspid valve |
| ToF | Tetralogy of Fallot |
| PV | Pulmonary valve |
| RVOT | Right ventricular outflow tract |
| 4D | Four-dimensional |
References
- Rushani, D.; Kaufman, J.S.; Ionescu-Ittu, R.; Mackie, A.S.; Pilote, L.; Therrien, J.; Marelli, A.J. Infective Endocarditis in Children with Congenital Heart Disease. Circulation 2013, 128, 1412–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuijpers, J.M.; Koolbergen, D.R.; Groenink, M.; Peels, K.C.H.; Reichert, C.L.A.; Post, M.C.; Bosker, H.A.; Wajon, E.M.C.J.; Zwinderman, A.H.; Mulder, B.J.M.; et al. Incidence, Risk Factors, and Predictors of Infective Endocarditis in Adult Congenital Heart Disease: Focus on the Use of Prosthetic Material. Eur. Heart J. 2017, 38, 2048–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delgado, V.; Ajmone Marsan, N.; de Waha, S.; Bonaros, N.; Brida, M.; Burri, H.; Caselli, S.; Doenst, T.; Ederhy, S.; Erba, P.A.; et al. 2023 ESC Guidelines for the management of endocarditis. Eur. Heart J. 2023, 44, 3948–4042, Erratum in Eur. Heart J. 2023, 44, 4780. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehad625. Erratum in Eur. Heart J. 2024, 45, 56. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehad776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Melle, J.P.; Roos-Hesselink, J.W.; Bansal, M.; Kamp, O.; Meshaal, M.; Pudich, J.; Luksic, V.R.; Rodriguez-Alvarez, R.; Sadeghpour, A.; Hanzevacki, J.S.; et al. Infective endocarditis in adult patients with congenital heart disease. Int. J. Cardiol. 2023, 370, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, P.T.; Uy, F.M.; Foo, J.S.; Tan, J.L. Increased Incidence of Infective Endocarditis in Patients with Ventricular Septal Defect. Congenit. Heart Dis. 2018, 13, 1005–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moscatelli, S.; Leo, I.; Bianco, F.; Surkova, E.; Pezel, T.; Donald, N.A.; Triumbari, E.K.A.; Bassareo, P.P.; Pradhan, A.; Cimini, A.; et al. The Role of Multimodality Imaging in Patients with Congenital Heart Disease and Infective Endocarditis. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 3638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havers-Borgersen, E.; Østergaard, L.; Holgersson, C.K.; Stahl, A.; Schmidt, M.R.; Smerup, M.; Køber, L.; Fosbøl, E.L. Infective Endocarditis with or without Congenital Heart Disease: Clinical Features and Outcomes. Eur. Heart J. 2024, 45, 4704–4715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brida, M.; Balint, H.O.; Bence, A.; Panfile, E.; Prokšelj, K.; Kačar, P.; Lebid, I.H.; Šimkova, I.; Bobocka, K.; Meidrops, K.; et al. Infective Endocarditis in Adults with Congenital Heart Disease: Contemporary Management and Related Outcomes in Central and South-Eastern European Region. Int. J. Cardiol. 2023, 377, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltimore, R.S.; Gewitz, M.; Baddour, L.M.; Beerman, L.B.; Jackson, M.A.; Lockhart, P.B.; Pahl, E.; Schutze, G.E.; Shulman, S.T.; Willoughby, R.; et al. Infective Endocarditis in Childhood: 2015 Update. Circulation 2015, 132, 1487–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahill, T.J.; Jewell, P.D.; Denne, L.; Franklin, R.C.; Frigiola, A.; Orchard, E.; Prendergast, B.D. Contemporary epidemiology of infective endocarditis in patients with congenital heart disease: A UK prospective study. Am. Heart J. 2019, 215, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, B.; Cao, J.; Kotchetkova, I.; Celermajer, D.S. Incidence, predictors and outcomes of infective endocarditis in a contemporary adult congenital heart disease population. Int. J. Cardiol. 2017, 249, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mylonakis, E.; Calderwood, S.B. Infective endocarditis in adults. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 345, 1318–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishimura, R.A.; McGoon, M.D. Perspectives on mitral-valve prolapse. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 341, 48–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katan, O.; Michelena, H.I.; Avierinos, J.F.; Mahoney, D.W.; DeSimone, D.C.; Baddour, L.M.; Suri, R.M.; Enriquez-Sarano, M. Incidence and Predictors of Infective Endocarditis in Mitral Valve Prolapse: A Population-Based Study. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2016, 91, 336–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zegri-Reiriz, I.; de Alarcón, A.; Muñoz, P.; Martínez Sellés, M.; González-Ramallo, V.; Miro, J.M.; Falces, C.; Gonzalez Rico, C.; Kortajarena Urkola, X.; Lepe, J.A.; et al. Infective Endocarditis in Patients with Bicuspid Aortic Valve or Mitral Valve Prolapse. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 71, 2731–2740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeSimone, D.C.; DeSimone, C.V.; Tleyjeh, I.M.; Correa de Sa, D.D.; Anavekar, N.S.; Lahr, B.D.; Sohail, M.R.; Steckelberg, J.M.; Wilson, W.R.; Baddour, L.M. Association of Mitral Valve Prolapse with Infective Endocarditis Due to Viridans Group Streptococci. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2015, 61, 623–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Calcaterra, G.; Crisafulli, A.; Guccione, P.; Di Salvo, G.; Bassareo, P.P. Infective endocarditis triangle. Is it the time to revisit infective endocarditis susceptibility and indications for its antibiotic prophylaxis? Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2019, 26, 1771–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.A.; Wu, V.C.; Chan, Y.S.; Cheng, Y.T.; Lee, J.K.; Chu, P.H.; Chen, S.W. Infective endocarditis after surgical aortic or mitral valve replacement: A nationwide population-based study. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2023, 166, 1056–1068.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dillon, J.C.; Feigenbaum, H.; Konecke, L.L.; Davis, R.H.; Chang, S. Echocardiographic Manifestations of Valvular Vegetations. Am. Heart J. 1973, 86, 698–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, G.; Badano, L.; Tribouilloy, C.; Vilacosta, I.; Zamorano, J.L.; Galderisi, M.; Voigt, J.-U.; Sicari, R.; Cosyns, B.; Fox, K.; et al. Recommendations for the Practice of Echocardiography in Infective Endocarditis. Eur. J. Echocardiogr. 2010, 11, 202–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltodano-Arellano, R.; Huaman-Carrasco, D.; Cupe-Chacalcaje, K.; Cachicatari-Beltran, A.; Benites-Yshpilco, L.; Urdanivia-Ruiz, D.; Rafael-Horna, E.; Falcón-Quispe, L.; Demarini-Orellana, A.; Velarde-Acosta, K.; et al. Role of 3D transoesophageal echocardiography in the study of infective endocarditis. Demonstration in a case collection. Eur. Heart J. Imaging Methods Pract. 2024, 2, qyae085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanovic, B.; Trifunovic, D.; Matic, S.; Petrovic, J.; Sacic, D.; Tadic, M. Prosthetic Valve Endocarditis—A Trouble or a Challenge? J. Cardiol. 2019, 73, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horstkotte, D.; Follath, F.; Gutschik, E.; Lengyel, M.; Oto, A.; Pavie, A.; Soler-Soler, J.; Thiene, G.; von Graevenitz, A.; Priori, S.G.; et al. Guidelines on Prevention, Diagnosis and Treatment of Infective Endocarditis Executive Summary: The Task Force on Infective Endocarditis of the European Society of Cardiology. Eur. Heart J. 2004, 25, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepi, M.; Muratori, M. Challenges in Cardiology: Diagnosis of Native and Prosthetic Valve Endocarditis. Eur. Heart J. Suppl. 2023, 25 (Suppl. B), B131–B135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knirsch, W.; Nadal, D. Infective Endocarditis in Congenital Heart Disease. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2011, 170, 1111–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erba, P.A.; Pizzi, M.N.; Roque, A.; Salaun, E.; Lancellotti, P.; Tornos, P.; Habib, G. Multimodality Imaging in Infective Endocarditis. Circulation 2019, 140, 1753–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horgan, S.J.; Mediratta, A.; Gillam, L.D. Cardiovascular Imaging in Infective Endocarditis: A Multimodality Approach. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2020, 13, e008956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kort, S. Real-Time 3-Dimensional Echocardiography for Prosthetic Valve Endocarditis: Initial Experience. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2006, 19, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangner, N.; Panagides, V.; Del Val, D.; Abdel-Wahab, M.; Crusius, L.; Durand, E.; Ihlemann, N.; Urena, M.; Pellegrini, C.; Giannini, F.; et al. Incidence, Clinical Characteristics, and Impact of Absent Echocardiographic Signs in Patients with Infective Endocarditis After Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2023, 76, 1003–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagiub, M.; Fares, M.; Ganigara, M.; Ullah, S.; Hsieh, N.; Jaquiss, R.; Dillenbeck, J.; Hussain, T. Value of Time-Resolved Cardiac CT in Children and Young Adults with Congenital Heart Disease and Infective Endocarditis. Pediatr. Cardiol. 2024, 45, 1267–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, G.; Lancellotti, P.; Antunes, M.J.; Bongiorni, M.G.; Casalta, J.P.; Del Zotti, F.; Dulgheru, R.; El Khoury, G.; Erba, P.A.; Iung, B.; et al. 2015 ESC Guidelines for the Management of Infective Endocarditis. Eur. Heart J. 2015, 36, 3075–3128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Festa, P.; Lovato, L.; Bianco, F.; Alaimo, A.; Angeli, E.; Baccano, G.; Barbi, E.; Bennati, E.; Bonhoeffer, P.; Bucciarelli, V.; et al. Recommendations for cardiovascular magnetic resonance and computed tomography in congenital heart disease: A consensus paper from the CMR/CCT Working Group of the Italian Society of Pediatric Cardiology and the Italian College of Cardiac Radiology endorsed by the Italian Society of Medical and Interventional Radiology (Part II). J. Cardiovasc. Med. 2024, 25, 473–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thaler, C.; Witt, D.; Casey, S.; Kelle, A.M.; Garcia, S.; Lesser, J.; Han, B.K. Diagnostic Value of Computed Tomography Angiography for Infective Endocarditis After Right Ventricle Outflow Tract Repair. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. Case Rep. 2023, 23, 102011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fowler, V.G.; Durack, D.T.; Selton-Suty, C.; Athan, E.; Bayer, A.S.; Chamis, A.L.; Dahl, A.; DiBernardo, L.; Durante-Mangoni, E.; Duval, X.; et al. The 2023 Duke-ISCVID Criteria for Infective Endocarditis: Updating the Modified Duke Criteria. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2023, 77, 518–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valsangiacomo Buechel, E.R.; Grosse-Wortmann, L.; Fratz, S.; Eichhorn, J.; Sarikouch, S.; Greil, G.F.; Beerbaum, P.; Bucciarelli-Ducci, C.; Bonello, B.; Sieverding, L.; et al. Indications for cardiovascular magnetic resonance in children with congenital and acquired heart disease: An expert consensus paper of the Imaging Working Group of the AEPC and the Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance Section of the EACVI. Cardiol. Young 2015, 25, 819–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basso, C.; Boschello, M.; Perrone, C.; Mecenero, A.; Cera, A.; Bicego, D.; Thiene, G.; De Dominicis, E. An echocardiographic survey of primary school children for bicuspid aortic valve. Am. J. Cardiol. 2004, 93, 661–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, C. Clinical significance of the bicuspid aortic valve. Heart 2000, 83, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Gleeson, T.G.; Mwangi, I.; Horgan, S.J.; Cradock, A.; Fitzpatrick, P.; Murray, J.G. Steady-state free-precession (SSFP) cine MRI in distinguishing normal and bicuspid aortic valves. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2008, 28, 873–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leo, I.; Sabatino, J.; Avesani, M.; Moscatelli, S.; Bianco, F.; Borrelli, N.; De Sarro, R.; Leonardi, B.; Calcaterra, G.; Surkova, E.; et al. Non-Invasive Imaging Assessment in Patients with Aortic Coarctation: A Contemporary Review. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 13, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lancellotti, P.; Tribouilloy, C.; Hagendorff, A.; Popescu, B.A.; Edvardsen, T.; Pierard, L.A.; Badano, L.; Zamorano, J.L.; Scientific Document Committee of the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging. Recommendations for the echocardiographic assessment of native valvular regurgitation: An executive summary from the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2013, 14, 611–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moscatelli, S.; Leo, I.; Bianco, F.; Borrelli, N.; Beltrami, M.; Garofalo, M.; Milano, E.G.; Bisaccia, G.; Iellamo, F.; Bassareo, P.P.; et al. The Role of Multimodality Imaging in Pediatric Cardiomyopathies. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 4866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hadji-Turdeghal, K.; Jensen, A.D.; Bruun, N.E.; Iversen, K.K.; Bundgaard, H.; Smerup, M.; Kober, L.; Østergaard, L.; Fosbøl, E.L. Temporal trends in the incidence of infective endocarditis in patients with a prosthetic heart valve. Open Heart 2023, 10, e002269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sachdev, M.; Peterson, G.E.; Jollis, J.G. Imaging techniques for diagnosis of infective endocarditis. Infect. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2002, 16, 319–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sverdlov, A.L.; Taylor, K.; Elkington, A.G.; Zeitz, C.J.; Beltrame, J.F. Images in cardiovascular medicine. Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging identifies the elusive perivalvular abscess. Circulation 2008, 118, e1–e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajiah, P.; Moore, A.; Saboo, S.; Goerne, H.; Ranganath, P.; MacNamara, J.; Joshi, P.; Abbara, S. Multimodality Imaging of Complications of Cardiac Valve Surgeries. Radiographics 2019, 39, 932–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eder, M.D.; Upadhyaya, K.; Park, J.; Ringer, M.; Malinis, M.; Young, B.D.; Sugeng, L.; Hur, D.J. Multimodality Imaging in the Diagnosis of Prosthetic Valve Endocarditis: A Brief Review. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 750573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Remenyi, B.; Gentles, T.L. Congenital mitral valve lesions: Correlation between morphology and imaging. Ann. Pediatr. Cardiol. 2012, 5, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Schaverien, M.V.; Freedom, R.M.; McCrindle, B.W. Independent factors associated with outcomes of parachute mitral valve in 84 patients. Circulation 2004, 109, 2309–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figliozzi, S.; Georgiopoulos, G.; Lopes, P.M.; Bauer, K.B.; Moura-Ferreira, S.; Tondi, L.; Mushtaq, S.; Censi, S.; Pavon, A.G.; Bassi, I.; et al. Myocardial Fibrosis at Cardiac MRI Helps Predict Adverse Clinical Outcome in Patients with Mitral Valve Prolapse. Radiology 2023, 306, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McElhinney, D.B.; Zhang, Y.; Aboulhosn, J.A.; Morray, B.H.; Biernacka, E.K.; Qureshi, A.M.; Torres, A.J.; Shahanavaz, S.; Goldstein, B.H.; Cabalka, A.K.; et al. Multicenter Study of Endocarditis After Transcatheter Pulmonary Valve Replacement. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2021, 78, 575–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Havers-Borgersen, E.; Butt, J.H.; Smerup, M.; Gislason, G.H.; Torp-Pedersen, C.; Gröning, M.; Schmidt, M.R.; Søndergaard, L.; Køber, L.; Fosbøl, E.L. Incidence of Infective Endocarditis Among Patients with Tetralogy of Fallot. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2021, 10, e022445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Slouha, E.; Johnson, L.L.; Thirunavukarasu, A.; Al-Geizi, H.; Clunes, L.A.; Kollias, T.F. Risk of Infective Endocarditis Post-transcatheter Pulmonary Valve Replacement Versus Surgical Pulmonary Valve Replacement: A Systematic Review. Cureus 2023, 15, e48022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Van Dijck, I.; Budts, W.; Cools, B.; Eyskens, B.; Boshoff, D.E.; Heying, R.; Frerich, S.; Vanagt, W.Y.; Troost, E.; Gewillig, M. Infective endocarditis of a transcatheter pulmonary valve in comparison with surgical implants. Heart 2015, 101, 788–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bos, D.; De Wolf, D.; Cools, B.; Eyskens, B.; Hubrechts, J.; Boshoff, D.; Louw, J.; Frerich, S.; Ditkowski, B.; Rega, F.; et al. Infective endocarditis in patients after percutaneous pulmonary valve implantation with the stent-mounted bovine jugular vein valve: Clinical experience and evaluation of the modified Duke criteria. Int. J. Cardiol. 2021, 323, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McElhinney, D.B.; Benson, L.N.; Eicken, A.; Kreutzer, J.; Padera, R.F.; Zahn, E.M. Infective endocarditis after transcatheter pulmonary valve replacement using the Melody valve: Combined results of 3 prospective North American and European studies. Circ. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2013, 6, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machanahalli Balakrishna, A.; Dilsaver, D.B.; Aboeata, A.; Gowda, R.M.; Goldsweig, A.M.; Vallabhajosyula, S.; Anderson, J.H.; Simard, T.; Jhand, A. Infective Endocarditis Risk with Melody versus Sapien Valves Following Transcatheter Pulmonary Valve Implantation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Prospective Cohort Studies. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 4886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chimoriya, R.; Awasthy, N.; Kumar, G. COVID-19 infection with delayed presentation of infective endocarditis of the prosthetic pulmonary valve. Cardiol. Young 2021, 31, 2045–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Li, Y.J.; Ma, L.; Pan, X. Infective Endocarditis in a Patient with Transcatheter Pulmonary Valve Implantation. Int. Heart J. 2019, 60, 983–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munawar, F.; Ahmed, I. Right-sided infective endocarditis with ventricular septal defect. Pak. J. Med. Sci. 2024, 40, 1587–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Al-Senaidi, K.S.; Abdelmogheth, A.A.; Balkhair, A.A. Complicated subacute bacterial endocarditis in a patient with ventricular septal defect. Sultan Qaboos Univ. Med. J. 2014, 14, e130–e133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Moazez, C.; Zeitjian, V.; Breburda, C.; Roy, R. A Rare Manifestation of Asymptomatic Ebstein’s Anomaly with Tricuspid Valve Endocarditis. Case Rep. Cardiol. 2017, 2017, 7630915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bilge, A.K.; Adalet, K.; Ozyiğit, T.; Ozben, B.; Yilmaz, E. Tricuspid endocarditis in an adult patient with Ebstein’s anomaly who has a residual pacemaker lead. Int. J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2005, 21, 641–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, W.J.; Kaisbain, N.; Kim, H.S. Septic pulmonary emboli in pulmonary valve endocarditis with concurrent ventricular septal defect and coronary artery disease: A case report. Eur. Heart J. Case Rep. 2022, 6, ytac162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Fusco, F.; Scognamiglio, G.; Correra, A.; Merola, A.; Colonna, D.; Palma, M.; Romeo, E.; Sarubbi, B. Pulmonary valve endocarditis in adults with congenital heart disease: The role of echocardiography in a case series. Eur. Heart J. Case Rep. 2020, 4, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caiati, C.; Pollice, P.; Lepera, M.E.; Favale, S. Pacemaker lead endocarditis investigated with intracardiac echocardiography: Factors modulating the size of vegetations and larger vegetation embolic risk during lead extraction. Antibiotics 2019, 8, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San Román, J.A.; Vilacosta, I.; López, J.; Revilla, A.; Arnold, R.; Sevilla, T.; Rollán, M.J. Role of transthoracic and transesophageal echocardiography in right-sided endocarditis: One echocardiographic modality does not fit all. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2012, 25, 807–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawhney, N.; Palakodeti, V.; Raisinghani, A.; Rickman, L.S.; DeMaria, A.N.; Blanchard, D.G. Eustachian valve endocarditis: A case series and analysis of the literature. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2001, 14, 1139–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelghani, M.; Nassif, M.; Blom, N.A.; Van Mourik, M.S.; Straver, B.; Koolbergen, D.R.; Kluin, J.; Tijssen, J.G.; Mulder, B.J.M.; Bouma, B.J.; et al. Infective Endocarditis After Melody Valve Implantation in the Pulmonary Position: A Systematic Review. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2018, 7, e008163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Salvo, G.; Pozza, A.; Castaldi, B.; Galzerano, D.; Pergola, V. Pediatric Three-dimensional Transesophageal Echocardiography: A Game Changer in Congenital Heart Disease. J. Cardiovasc. Echogr. 2024, 34, 203–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puchalski, M.D.; Lui, G.K.; Miller-Hance, W.C.; Brook, M.M.; Young, L.T.; Bhat, A.; Roberson, D.A.; Mercer-Rosa, L.; Miller, O.I.; Parra, D.A.; et al. Guidelines for Performing a Comprehensive Transesophageal Echocardiographic: Examination in Children and All Patients with Congenital Heart Disease: Recommendations from the American Society of Echocardiography. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2019, 32, 173–215, Erratum in J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2019, 32, 681. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.echo.2019.03.007. Erratum in J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2019, 32, 1373–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narducci, M.L.; Pelargonio, G.; Russo, E.; Marinaccio, L.; Di Monaco, A.; Perna, F.; Bencardino, G.; Casella, M.; Di Biase, L.; Santangeli, P.; et al. Usefulness of intracardiac echocardiography for the diagnosis of cardiovascular implantable electronic device-related endocarditis. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2013, 61, 1398–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, J.; Liu, S.; Yang, J.; Xu, J.; Zhu, G. Inaccuracy of transthoracic echocardiography for the identification of right-sided vegetation in patients with no history of intravenous drug abuse or cardiac device insertion. J. Int. Med. Res. 2014, 42, 837–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moscatelli, S.; Pozza, A.; Leo, I.; Ielapi, J.; Scatteia, A.; Piana, S.; Cavaliere, A.; Reffo, E.; Di Salvo, G. Importance of Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance Applied to Congenital Heart Diseases in Pediatric Age: A Narrative Review. Children 2024, 11, 878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fratz, S.; Chung, T.; Greil, G.F.; Samyn, M.M.; Taylor, A.M.; Valsangiacomo Buechel, E.R.; Yoo, S.-J.; Powell, A.J. Guidelines and Protocols for Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance in Children and Adults with Congenital Heart Disease: SCMR Expert Consensus Group on Congenital Heart Disease. J. Cardiovasc. Magn. Reson. 2013, 15, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zatorska, K.; Michalowska, I.; Duchnowski, P.; Szymanski, P.; Kusmierczyk, M.; Hryniewiecki, T. The Usefulness of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in the Diagnosis of Infectious Endocarditis. J. Heart Valve Dis. 2015, 24, 767–775. [Google Scholar]
- Bhuta, S.; Patel, N.J.; Ciricillo, J.A.; Haddad, M.N.; Khokher, W.; Mhanna, M.; Patel, M.; Burmeister, C.; Malas, H.; Kammeyer, J.A. Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Imaging for the Diagnosis of Infective Endocarditis in the COVID-19 Era. Curr. Probl. Cardiol. 2023, 48, 101396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozza, A.; Reffo, E.; Castaldi, B.; Cattapan, I.; Avesani, M.; Biffanti, R.; Cavaliere, A.; Cerutti, A.; Di Salvo, G. Utility of Fetal Cardiac Resonance Imaging in Prenatal Clinical Practice: Current State of the Art. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 3523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dursun, M.; Yilmaz, S.; Yilmaz, E.; Yilmaz, R.; Onur, I.; Oflaz, H.; Dindar, A. The Utility of Cardiac MRI in Diagnosis of Infective Endocarditis: Preliminary Results. Diagn. Interv. Radiol. 2015, 21, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogel, M.A.; Anwar, S.; Broberg, C.; Browne, L.; Chung, T.; Johnson, T.; Muthurangu, V.; Taylor, M.; Valsangiacomo-Buechel, E.; Wilhelm, C. Society for Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance/European Society of Cardiovascular Imaging/American Society of Echocardiography/Society for Pediatric Radiology/North American Society for Cardiovascular Imaging Guidelines for the Use of Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance in Pediatric Congenital and Acquired Heart Disease. J. Cardiovasc. Magn. Reson. 2022, 24, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isorni, M.-A.; Moisson, L.; Moussa, N.B.; Monnot, S.; Raimondi, F.; Roussin, R.; Boet, A.; Van Aerschot, I.; Fournier, E.; Cohen, S.; et al. 4D Flow Cardiac Magnetic Resonance in Children and Adults with Congenital Heart Disease: Clinical Experience in a High Volume Center. Int. J. Cardiol. 2020, 320, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nussbaumer, C.; Bouchardy, J.; Blanche, C.; Piccini, D.; Pavon, A.; Hugelshofer, S.; Monney, P.; Stuber, M.; Schwitter, J.; Rutz, T. 2D Cine vs. 3D Free-Breathing Self-Navigated Whole Heart for Aortic Root Measurements in Congenital Heart Disease. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2021, 22, jeaa356.404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Knobelsdorff-Brenkenhoff, F.; Schulz-Menger, J. Role of Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance in the Guidelines of the European Society of Cardiology. J. Cardiovasc. Magn. Reson. 2016, 18, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moscatelli, S.; Avesani, M.; Borrelli, N.; Sabatino, J.; Pergola, V.; Leo, I.; Montanaro, C.; Contini, F.; Gaudieri, G.; Ielapi, J.; et al. Complete Transposition of the Great Arteries in the Pediatric Field: A Multimodality Imaging Approach. Children 2024, 11, 626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corey, K.M.; Campbell, M.J.; Hill, K.D.; Hornik, C.P.; Krasuski, R.; Barker, P.C.; Jaquiss, R.D.B.; Li, J.S. Pulmonary Valve Endocarditis: The Potential Utility of Multimodal Imaging Prior to Surgery. World J. Pediatr. Congenit. Heart Surg. 2020, 11, 192–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, A.K.M.M.; Sayami, L.A.; Zaman, S. Chiari Network: A Case Report and Brief Overview. J. Saudi Heart Assoc. 2013, 25, 225–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammash, N.M.; Warnes, C.A.; Connolly, H.M.; Danielson, G.K.; Seward, J.B. Mimics of Ebstein’s Anomaly. Am. Heart J. 1997, 134, 508–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.H.; Oh, Y.-W. Assessment of Cor Triatriatum Dexter and Giant Eustachian Valve with Cardiac Magnetic Resonance. Circulation 2014, 130, 1727–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.H.; Teo, L.L.S.; Hia, C.P.P. Double Outlet Right Ventricle with Infective Endocarditis. Singap. Med. J. 2012, 53, e176–e178. [Google Scholar]
- Moscatelli, S.; Pergola, V.; Motta, R.; Fortuni, F.; Borrelli, N.; Sabatino, J.; Leo, I.; Avesani, M.; Montanaro, C.; Surkova, E.; et al. Multimodality Imaging Assessment of Tetralogy of Fallot: From Diagnosis to Long-Term Follow-Up. Children 2023, 10, 1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Moscatelli, S.; Borrelli, N.; Sabatino, J.; Leo, I.; Avesani, M.; Montanaro, C.; Di Salvo, G. Role of Cardiovascular Imaging in the Follow-Up of Patients with Fontan Circulation. Children 2022, 9, 1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Taksande, A.; Bhanushali, K.; Taksande, A.; Damam, S.; Lohakare, A. Pulmonary Valve Endocarditis With Tetralogy of Fallot: A Comprehensive Exploration. Cureus 2024, 16, e58013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ojha, V.; Pandey, N.N.; Sharma, A.; Ganga, K.P. Spectrum of Changes on Cardiac Magnetic Resonance in Repaired Tetralogy of Fallot: Imaging According to Surgical Considerations. Clin. Imaging 2021, 69, 102–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonardi, B.; Perrone, M.; Calcaterra, G.; Sabatino, J.; Leo, I.; Aversani, M.; Bassareo, P.P.; Pozza, A.; Oreto, L.; Moscatelli, S.; et al. Repaired Tetralogy of Fallot: Have We Understood the Right Timing of PVR? J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galea, N.; Bandera, F.; Lauri, C.; Autore, C.; Laghi, A.; Erba, P.A. Multimodality Imaging in the Diagnostic Work-Up of Endocarditis and Cardiac Implantable Electronic Device (CIED) Infection. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, V.; Wang, T.K.M.; Bansal, A.; Farwati, M.; Gad, M.; Montane, B.; Kaur, S.; Bolen, M.A.; Grimm, R.; Griffin, B.; et al. Diagnostic performance of cardiac computed tomography versus transesophageal echocardiography in infective endocarditis: A contemporary comparative meta-analysis. J. Cardiovasc. Comput. Tomogr. 2021, 15, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erba, P.A.; Lancellotti, P.; Vilacosta, I.; Gaemperli, O.; Rouzet, F.; Hacker, M.; Signore, A.; Slart, R.H.J.A.; Habib, G. Recommendations on nuclear and multimodality imaging in IE and CIED infections. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2018, 45, 1795–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouzet, F.; Iung, B.; Duval, X. 18 F-FDG PET/CT in Infective Endocarditis: New Perspectives for Improving Patient Management. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 74, 1041–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzi, M.N.; Dos-Subirà, L.; Roque, A.; Fernández-Hidalgo, N.; Cuéllar-Calabria, H.; Pijuan Domènech, A.; Gonzàlez-Alujas, M.T.; Subirana-Domènech, M.T.; Miranda-Barrio, B.; Ferreira-González, I.; et al. 18 F-FDG-PET/CT angiography in the diagnosis of infective endocarditis and cardiac device infection in adult patients with congenital heart disease and prosthetic material. Int. J. Cardiol. 2017, 248, 396–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzi, M.N.; Roque, A.; Fernández-Hidalgo, N.; Cuéllar-Calabria, H.; Ferreira-González, I.; Gonzàlez-Alujas, M.T.; Oristrell, G.; Gracia-Sánchez, L.; González, J.J.; Rodríguez-Palomares, J.; et al. Improving the Diagnosis of Infective Endocarditis in Prosthetic Valves and Intracardiac Devices with 18F-Fluordeoxyglucose Positron Emission Tomography/Computed Tomography Angiography: Initial Results at an Infective Endocarditis Referral Center. Circulation 2015, 132, 1113–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Riet, J.; Hill, E.E.; Gheysens, O.; Dymarkowski, S.; Herregods, M.C.; Herijgers, P.; Peetermans, W.E.; Mortelmans, L. (18)F-FDG PET/CT for early detection of embolism and metastatic infection in patients with infective endocarditis. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2010, 37, 1189–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauridsen, T.K.; Iversen, K.K.; Ihlemann, N.; Hasbak, P.; Loft, A.; Berthelsen, A.K.; Dahl, A.; Dejanovic, D.; Albrecht-Beste, E.; Mortensen, J.; et al. Clinical utility of 18 F-FDG positron emission tomography/computed tomography scan vs. 99m Tc-HMPAO white blood cell single-photon emission computed tomography in extra-cardiac work-up of infective endocarditis. Int. J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2017, 33, 751–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borrelli, N.; Avesani, M.; Sabatino, J.; Ibrahim, A.; Josen, M.; Paredes, J.; Di Salvo, G. Blood speckle imaging: A new echocardiographic approach to study fluid dynamics in congenital heart disease. Int. J. Cardiol. Congenit. Heart Dis. 2021, 2, 100079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrelli, N.; Grimaldi, N.; Papaccioli, G.; Fusco, F.; Palma, M.; Sarubbi, B. Telemedicine in Adult Congenital Heart Disease: Usefulness of Digital Health Technology in the Assistance of Critical Patients. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 5775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Borrelli, N.; Sabatino, J.; Gimelli, A.; Avesani, M.; Pergola, V.; Leo, I.; Moscatelli, S.; Abbate, M.; Motta, R.; De Sarro, R.; et al. Multimodality Imaging Approach to Infective Endocarditis: Current Opinion in Patients with Congenital Heart Disease. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 1862. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14061862
Borrelli N, Sabatino J, Gimelli A, Avesani M, Pergola V, Leo I, Moscatelli S, Abbate M, Motta R, De Sarro R, et al. Multimodality Imaging Approach to Infective Endocarditis: Current Opinion in Patients with Congenital Heart Disease. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(6):1862. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14061862
Chicago/Turabian StyleBorrelli, Nunzia, Jolanda Sabatino, Alessia Gimelli, Martina Avesani, Valeria Pergola, Isabella Leo, Sara Moscatelli, Massimiliana Abbate, Raffaella Motta, Rosalba De Sarro, and et al. 2025. "Multimodality Imaging Approach to Infective Endocarditis: Current Opinion in Patients with Congenital Heart Disease" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 6: 1862. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14061862
APA StyleBorrelli, N., Sabatino, J., Gimelli, A., Avesani, M., Pergola, V., Leo, I., Moscatelli, S., Abbate, M., Motta, R., De Sarro, R., Ielapi, J., Sicilia, F., Perrone, M. A., Bassareo, P. P., Sarubbi, B., & Di Salvo, G., on behalf of the Working Group on Congenital Heart Disease, Cardiovascular Prevention in Paediatric Age of the Italian Society of Cardiology (SIC). (2025). Multimodality Imaging Approach to Infective Endocarditis: Current Opinion in Patients with Congenital Heart Disease. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(6), 1862. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14061862







