Custom-Made 3D-Printed Titanium Implants for Managing Segmental Distal Tibial Bone Defects: A Systematic Literature Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
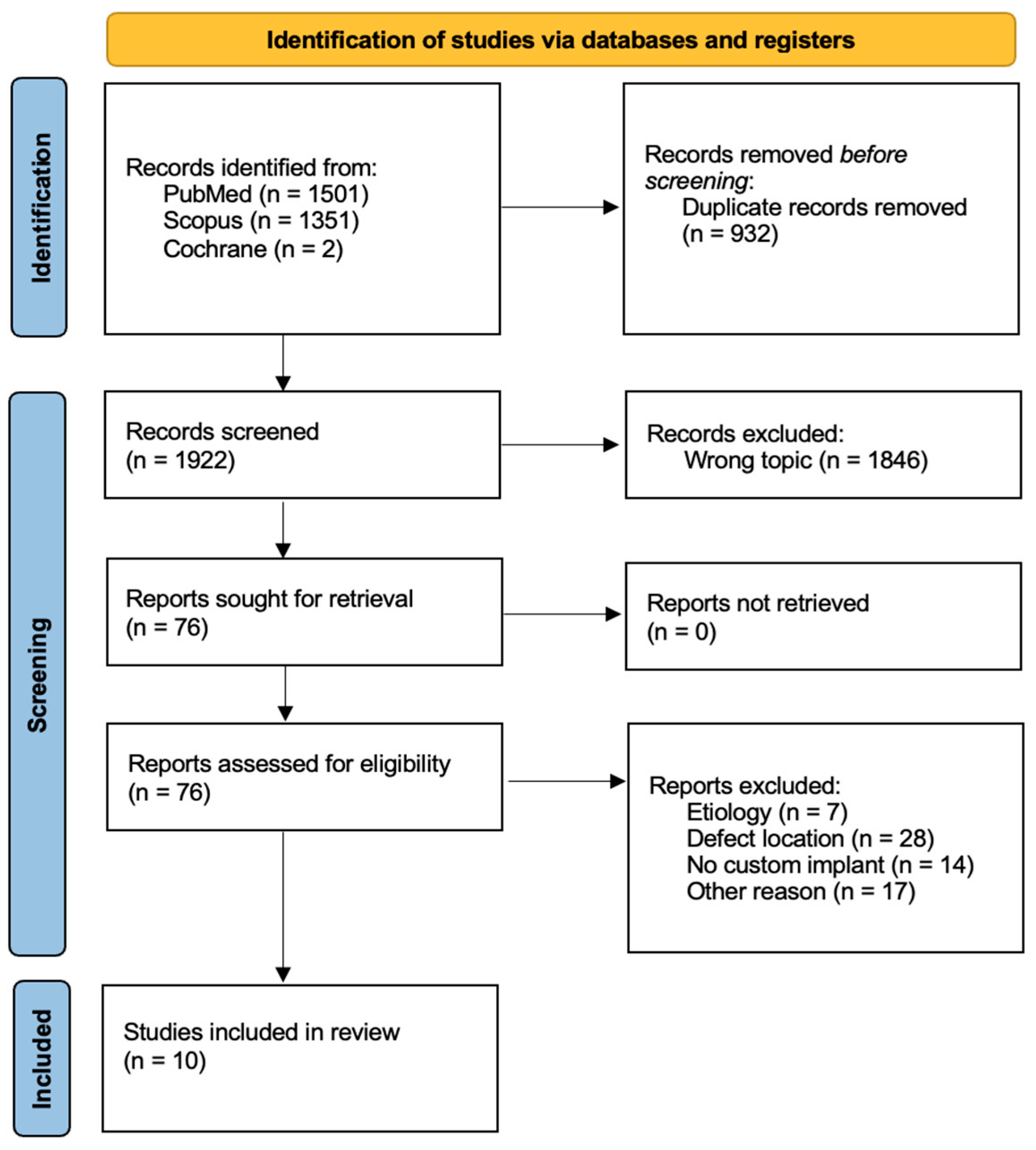
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Data Extraction
2.4. Quality Assessment
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DO | Distraction osteogenesis |
| IMT | Induced membrane technique |
| CSD | Critically sized defect |
References
- Bowers, K.M.; Anderson, D.E. Delayed Union and Nonunion: Current Concepts, Prevention, and Correction: A Review. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calori, G. Non-unions. Clin. Cases Miner. Bone Metab. 2017, 14, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melvin, S.J.; Dombroski, D.G.; Torbert, J.T.; Kovach, S.J.; Esterhai, J.L.; Mehta, S. Open Tibial Shaft Fractures: I. Evaluation and Initial Wound Management. Am. Acad. Orthop. Surg. 2010, 18, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santolini, E.; West, R.; Giannoudis, P.V. Risk factors for long bone fracture non-union: A stratification approach based on the level of the existing scientific evidence. Injury 2015, 46, S8–S19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zura, R.; Mehta, S.; Della Rocca, G.J.; Steen, R.G. Biological Risk Factors for Nonunion of Bone Fracture. JBJS Rev. 2016, 4, e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mauffrey, C.; Barlow, B.T.; Smith, W. Management of Segmental Bone Defects. J. Am. Acad. Orthop. Surg. 2015, 23, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Masquelet, A.C.; Begue, T. The Concept of Induced Membrane for Reconstruction of Long Bone Defects. Orthop. Clin. N. Am. 2010, 41, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benulic, C.; Canton, G.; Gril, I.; Murena, L.; Kristan, A. Management of acute bone loss following high grade open tibia fractures. Acta Bio Medica 2020, 91 (Suppl. 14), e2020012. [Google Scholar]
- Wakefield, S.M.; Papakostidis, C.; Giannoudis, V.P.; Mandía-Martínez, A.; Giannoudis, P.V. Distraction osteogenesis versus induced membrane technique for infected tibial non-unions with segmental bone loss: A systematic review of the literature and meta-analysis of available studies. Eur. J. Trauma Emerg. Surg. 2024, 50, 705–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrara, G.; Zampogna, B.; Schick, V.D.; Larizza, L.; Rizzo, P.; Sanzarello, I.; Nanni, M.; Leonetti, D. Post-Traumatic Segmental Tibial Defects Management: A Systematic Review of the Literature. Appl. Sci. 2024, 15, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masquelet, A.; Kanakaris, N.K.; Obert, L.; Stafford, P.; Giannoudis, P.V. Bone Repair Using the Masquelet Technique. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 2019, 101, 1024–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, C.-A.; Chen, S.-H.; Chan, S.-Y.; Yu, Y.-H. The Induced Membrane Technique for the Management of Segmental Tibial Defect or Nonunion: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Biomed. Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 5893642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, C.N.; Lin, A.S.; Leguineche, K.E.; Shekhar, S.; Walsh, W.R.; Guldberg, R.E.; Gall, K. Functional repair of criticlly sized femoral defects treated with bioinspired titanium gyroid-sheet scaffolds. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2021, 116, 104380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricles, L.M.; Coburn, J.C.; Di Prima, M.; Oh, S.S. Regulating 3D-printed medical products. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10, eaan6521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safavi, S.; Yu, Y.; Robinson, D.L.; Gray, H.A.; Ackland, D.C.; Lee, P.V.S. Additively manufactured controlled porous orthopedic joint replacement designs to reduce bone stress shielding: A systematic review. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2023, 18, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekker, T.J.; Steele, J.R.; Federer, A.E.; Hamid, K.S.; Adams, S.B. Use of Patient-Specific 3D-Printed Titanium Implants for Complex Foot and Ankle Limb Salvage, Deformity Correction, and Arthrodesis Procedures. Foot Ankle Int. 2018, 39, 916–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abar, B.; Kwon, N.; Allen, N.B.; Lau, T.; Johnson, L.G.; Gall, K.; Adams, S.B. Outcomes of Surgical Reconstruction Using Custom 3D-Printed Porous Titanium Implants for Critical-Sized Bone Defects of the Foot and Ankle. Foot Ankle Int. 2022, 43, 750–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, M.; Danilkowicz, R.; Adams, S. Patient-Specific 3D-Printed Titanium Implant for Distal Tibial Critical Bone Defect. J. 3D Print. Med. 2022, 6, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papakostidis, C.; Bhandari, M.; Giannoudis, P.V. Distraction osteogenesis in the treatment of long bone defects of the lower limbs. Bone Joint J. 2013, 95-B, 1673–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bejarano-Pineda, L.; Sharma, A.; Adams, S.B.; Parekh, S.G. Three-Dimensional Printed Cage in Patients With Tibiotalocalcaneal Arthrodesis Using a Retrograde Intramedullary Nail: Early Outcomes. Foot Ankle Spec. 2021, 14, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, A.R.; Ellington, J.K. Patient-Specific 3-Dimensional Printed Titanium Truss Cage with Tibiotalocalcaneal Arthrodesis for Salvage of Persistent Distal Tibia Nonunion. Foot Ankle Spec. 2015, 8, 483–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamid, K.S.; Parekh, S.G.; Adams, S.B. Salvage of Severe Foot and Ankle Trauma with a 3D Printed Scaffold. Foot Ankle Int. 2016, 37, 433–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slim, K.; Nini, E.; Forestier, D.; Kwiatkowski, F.; Panis, Y.; Chipponi, J. Methodological index for non-randomized studies (MINORS): Development and validation of a new instrument. ANZ J. Surg. 2003, 73, 712–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, G.; Liu, B.; Tian, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, F. Reconstruction of Ipsilateral Femoral and Tibial Bone Defect by 3D Printed Porous Scaffold Without Bone Graft. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 2022, 12, e20.00592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, K.; Day, W.; Tarpada, S.; Kahn, M.D. Treatment of an Infected Tibial Shaft Non-Union Using a Novel 3D-Printed Titanium Mesh Cage: A Case Report. Cureus 2023, 15, e34212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Hou, G.; Yang, Z.; Li, X.; Zheng, Y.; Wen, P.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, F.; Tian, Y. Repair of critical diaphyseal defects of lower limbs by 3D printed porous Ti6Al4V scaffolds without additional bone grafting: A prospective clinical study. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2022, 33, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beatti, M.A.; Zublin Guerra, C.M.; Guichet, D.M.; Pellecchia, T.S. Defectos óseos segmentarios: Uso de implantes de titanio trabecular diseñados a medida. Rev. Asoc. Argent. Ortop. Traumatol. 2022, 87, 219–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caravelli, S.; Ambrosino, G.; Vocale, E.; Di Ponte, M.; Puccetti, G.; Perisano, C.; Greco, T.; Rinaldi, V.G.; Muccioli, G.M.M.; Zaffagnini, S.; et al. Custom-Made Implants in Ankle Bone Loss: A Retrospective Assessment of Reconstruction/Arthrodesis in Sequelae of Septic Non-Union of the Tibial Pilon. Medicina 2022, 58, 1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamieldien, H.; Ferreira, N.; Birkholtz, F.F.; Hilton, T.; Campbell, N.; Laubscher, M. Filling the gap: A series of 3D-printed titanium truss cages for the management of large, lower limb bone defects in a developing country setting. Eur. J. Orthop. Surg. Traumatol. 2022, 33, 497–505. [Google Scholar]
- Kachare, A.; Goregaonkar, A.B.; Purohit, S.; Munde, K.; Renthlei, L.; Gaur, B. Surgical Planning and 3D-Printed Mesh Implant for Effective Bone Gap Management: A Case Report. J. Orthop. Case Rep. 2024, 14, 203–207. [Google Scholar]
- Nauth, A.; Schemitsch, E.; Norris, B.; Nollin, Z.; Watson, J.T. Critical-Size Bone Defects: Is There a Consensus for Diagnosis and Treatment? J. Orthop. Trauma. 2018, 32, S7–S11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giannoudis, P.V.; Faour, O.; Goff, T.; Kanakaris, N.; Dimitriou, R. Masquelet technique for the treatment of bone defects: Tips-tricks and future directions. Injury 2011, 42, 591–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mobbs, R.J.; Parr, W.C.; Choy, W.J.; McEvoy, A.; Walsh, W.R.; Phan, K. Anterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion Using a Personalized Approach: Is Custom the Future of Implants for Anterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion Surgery? World Neurosurg. 2019, 124, 452–458.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, C.N.; Miller, A.T.; Hollister, S.J.; Guldberg, R.E.; Gall, K. Design and Structure–Function Characterization of 3D Printed Synthetic Porous Biomaterials for Tissue Engineering. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2018, 7, e1701095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Luo, F.; Huang, K.; Xie, Z. Induced membrane technique for the treatment of bone defects due to post-traumatic osteomyelitis. Bone Jt. Res. 2016, 5, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labronici, P.J.; de Souza, F.C.; Pires, R.E.S.; Filho, F.C.d.S.; Gameiro, V.S.; Labronici, G.J. Posterior dislocation of the sternoclavicular joint: Report of two cases. Rev. Bras. Ortop. 2016, 51, 601–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Study | Year | Design | MINORS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Beatti et al. [27] | 2022 | RS | 10 |
| Brown et al. [18] | 2022 | CR | 8 |
| Caravelli et al. [28] | 2022 | RS | 10 |
| Gamieldien et al. [29] | 2023 | RS | 10 |
| Hamid et al. [22] | 2016 | CR | 8 |
| Hou et al. [24] | 2022 | CR | 8 |
| Hsu et al. [21] | 2015 | CR | 8 |
| Kachare et al. [30] | 2024 | CR | 8 |
| Liu et al. [26] | 2022 | PS | 12 |
| Tang et al. [25] | 2023 | CR | 8 |
| Author/s | Year | Treatment Period | Patients | Mean Age (Range) | M/F Ratio | Defect Location | Mean Follow-Up (Range) (Months) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beatti et al. [27] | 2022 | 2016–2019 | 2 | 47 (40–54) | 1/1 | 1 tibial diaphysis, 1 distal tibia | N.A. (12–N.A.) |
| Brown et al. [18] | 2022 | N.A. | 1 | 26 (N.A.) | 1/0 | Distal tibia | 36 (N.A.) |
| Caravelli et al. [28] | 2022 | 2016–2020 | 4 | 59.3 (55–64) | 3/1 | 4 distal tibia | 29.5 (18–45) |
| Gamieldien et al. [29] | 2023 | 2019–2022 | 1 | 37 (N.A.) | 1/0 | Distal tibia | 12 (N.A.) |
| Hamid et al. [22] | 2016 | N.A. | 1 | 46 (N.A.) | 0/1 | Distal tibia | 13 (N.A.) |
| Hou et al. [24] | 2022 | N.A. | 1 | 42 (N.A.) | 0/1 | Tibial diaphysis | 26 (N.A.) |
| Hsu et al. [21] | 2015 | N.A. | 1 | 63 (N.A.) | 1/0 | Distal tibia | 12 (N.A.) |
| Kachare et al. [30] | 2024 | N.A. | 1 | 38 (N.A.) | 1/0 | Distal tibia | 18 (N.A.) |
| Liu et al. [26] | 2022 | 2017–2022 | 6 | 47.2 (32–65) | 5/1 | 5 tibial diaphysis, 1 distal tibia | 21.5 (13–35) |
| Tang et al. [25] | 2023 | N.A. | 1 | 25 (N.A.) | 0/1 | Tibial diaphysis | 12 (N.A.) |
| Author/s | Year | Mean Bone Defect Size (Range) (cm) | Osteointegration Rate (%) | Time to Osteointegration (Range) (Months) | Functional Union Rate (%) | Time to Functional Union (Range) (Months) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beatti et al. [27] | 2022 | N.A. | 100% | 4.9 (N.A.) | 100% | N.A. (1.5–1.6) |
| Brown et al. [18] | 2022 | N.A. | 100% | 6 (N.A.) | 100% | 1.4 (N.A.) |
| Caravelli et al. [28] | 2022 | N.A. | 100% | N.A. (4–6) | 100% | N.A. |
| Gamieldien et al. [29] | 2023 | 3 (N.A.) | N.A. | N.A. | 100% | 2.6 (N.A.) |
| Hamid et al. [22] | 2016 | 8.5 (N.A.) | 100% | N.A. | 100% | 4.1 (N.A.) |
| Hou et al. [24] | 2022 | 8.5 (N.A.) | 100% | N.A. | 100% | 1 (N.A.) |
| Hsu et al. [21] | 2015 | N.A. | 100% | 5 (N.A.) | 100% | 3 (N.A.) |
| Kachare et al. [30] | 2024 | N.A. | 100% | N.A. | 100% | 3 (N.A.) |
| Liu et al. [26] | 2022 | N.A. (6–N.A.) | 100% | N.A. | 83.3% | 0.4 (0.2–0.5) |
| Tang et al. [25] | 2023 | 5 (N.A.) | N.A. | N.A. | 100% | 1 (N.A.) |
| Author/s | Pts | DU or NU | AD > 5° | Deep, Persistent, or Recurrent Infection | IL or Breakage | LLD > 2.5 cm | Joint Related Complication | Other Complications | Complications per Patient |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beatti et al. [27] | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 (0/2) |
| Brown et al. [18] | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 (0/1) |
| Caravelli et al. [28] | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 wound-healing delay 1 nail removal due to intolerance | 0.5 (2/4) |
| Gamieldien et al. [29] | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 (0/1) |
| Hamid et al. [22] | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 (0/1) |
| Hou et al. [24] | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | 0 (0/1) |
| Hsu et al. [21] | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 (0/1) |
| Kachare et al. [30] | 1 | 0 | N.A. | N.A. | 0 | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | 0 (0/1) |
| Liu et al. [26] | 6 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | N.A. | N.A. | 0.2 (1/6) |
| Tang et al. [25] | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | N.A. | 0 (0/1) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schick, V.D.; Zampogna, B.; Marrara, G.; Siracusano, L.; Larizza, L.; Calaciura, S.; Sanzarello, I.; Marinozzi, A.; Leonetti, D. Custom-Made 3D-Printed Titanium Implants for Managing Segmental Distal Tibial Bone Defects: A Systematic Literature Review. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 1796. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14061796
Schick VD, Zampogna B, Marrara G, Siracusano L, Larizza L, Calaciura S, Sanzarello I, Marinozzi A, Leonetti D. Custom-Made 3D-Printed Titanium Implants for Managing Segmental Distal Tibial Bone Defects: A Systematic Literature Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(6):1796. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14061796
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchick, Viktor Dietrich, Biagio Zampogna, Giovanni Marrara, Lorenza Siracusano, Leone Larizza, Salvatore Calaciura, Ilaria Sanzarello, Andrea Marinozzi, and Danilo Leonetti. 2025. "Custom-Made 3D-Printed Titanium Implants for Managing Segmental Distal Tibial Bone Defects: A Systematic Literature Review" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 6: 1796. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14061796
APA StyleSchick, V. D., Zampogna, B., Marrara, G., Siracusano, L., Larizza, L., Calaciura, S., Sanzarello, I., Marinozzi, A., & Leonetti, D. (2025). Custom-Made 3D-Printed Titanium Implants for Managing Segmental Distal Tibial Bone Defects: A Systematic Literature Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(6), 1796. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14061796








