Inflammation-Related Markers in Pediatric Psoriasis: Resistin as a Potential Marker of Psoriasis Severity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Clinical Assessment
2.3. Laboratory Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
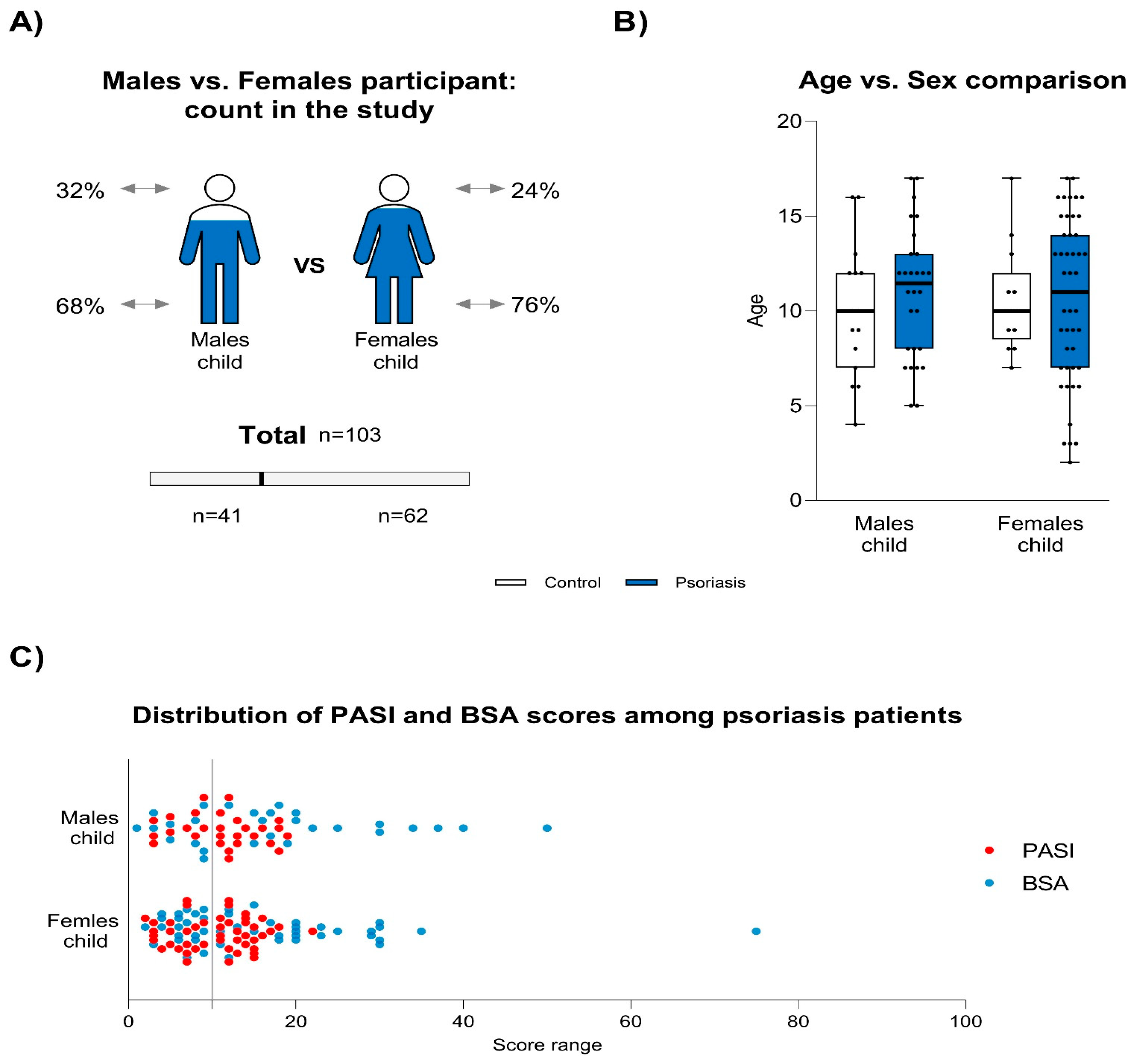
3.1. Descriptive Characteristics of Participants
3.2. Biomarker Levels
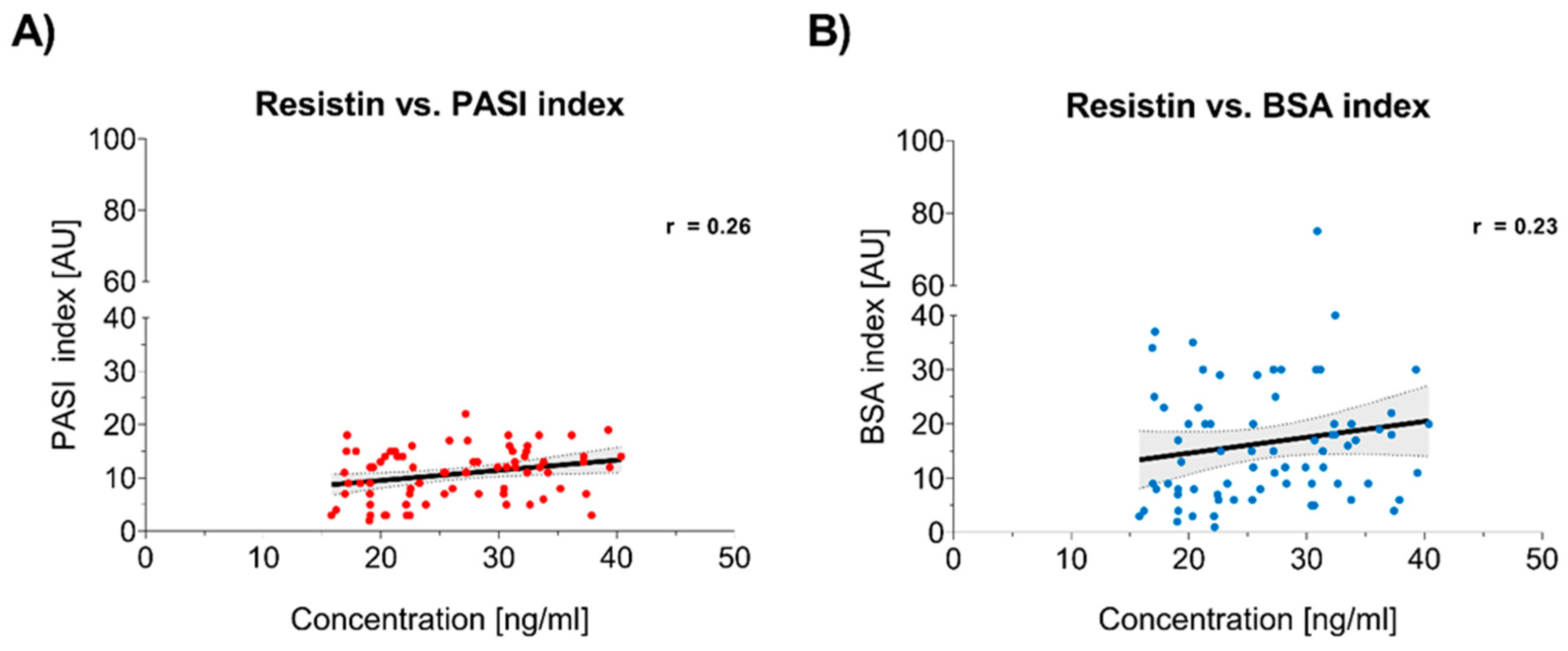
3.3. Correlation Between Resistin Levels and Psoriasis Severity
3.4. Analysis of Other Factors
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Burden-Teh, E.; Thomas, K.S.; Ratib, S.; Grindlay, D.; Adaji, E.; Murphy, R. Epidemiology of childhood psoriasis: A scoping review. Br. J. Dermatol. 2016, 174, 1242–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bronckers, I.M.; Paller, A.S.; van Geel, M.J.; van de Kerkhof, P.C.; Seyger, M.M. Psoriasis in Children and Adolescents: Diagnosis, Management and Comorbidities. Paediatr. Drugs 2015, 17, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Piekarska-Myślińska, D.; Pietrzak, A.; Myśliński, W.; Pietrzak, D.; Borysowicz, M.; Socha, M.; Krasowska, D. Childhood psoriasis. Dermatol. Rev. 2017, 104, 363–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, A.W.; Harskamp, C.T.; Armstrong, E.J. Psoriasis and metabolic syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2013, 68, 654–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caroppo, F.; Galderisi, A.; Ventura, L.; Belloni Fortina, A. Metabolic syndrome and insulin resistance in pre-pubertal children with psoriasis. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2021, 180, 1739–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Miller, I.M.; Ellervik, C.; Yazdanyar, S.; Jemec, G.B. Meta-analysis of psoriasis, cardiovascular disease, and associated risk factors. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2013, 69, 1014–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prussick, R.B.; Miele, L. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in patients with psoriasis: A consequence of systemic inflammatory burden? Br. J. Dermatol. 2018, 179, 16–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sitdikova, G.; Hermann, A. Homocysteina: Biochemia, biologia molekularna i rola w chorobie 2021. Biomolekuły 2023, 13, 1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hashimoto, T.; Shinohara, Y.; Hasegawa, H. Metabolizm homocysteiny. Yakugaku Zasshi 2007, 127, 1579–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakubowski, H. Patofizjologiczne konsekwencje nadmiaru homocysteiny. J. Nutr. 2006, 136 (Suppl. S6), 1741S–1749S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, X.; Meng, X.; Song, Z. Homocysteina i łuszczyca. Biosci. Rep. 2019, 39, BSR20190867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Menon, P.S. Childhood obesity, metabolic syndrome and Pentraxin-3. Indian J. Pediatr. 2015, 82, 3–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnston, A.; Arnadottir, S.; Gudjonsson, J.E.; Aphale, A.; Sigmarsdottir, A.A.; Gunnarsson, S.I.; Steinsson, J.T.; Elder, J.T.; Valdimarsson, H. Obesity in psoriasis: Leptin and resistin as mediators of cutaneous inflammation. Br. J. Dermatol. 2008, 159, 342–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wisse, B.E. The inflammatory syndrome: The role of adipose tissue cytokines in metabolic disorders linked to obesity. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2004, 15, 2792–2800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiyang, B.; Panayi, A.; Ruifang, W.; Peng, Z.; Siqi, F. Adiponectin in psoriasis and its comorbidities: A review. Lipids Health Dis. 2021, 20, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Dessie, G.; Ayelign, B.; Akalu, Y.; Shibabaw, T.; Molla, M.D. Effect of Leptin on Chronic Inflammatory Disorders: Insights to Therapeutic Target to Prevent Further Cardiovascular Complication. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2021, 14, 3307–3322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Karampinis, E.; Goudouras, G.; Ntavari, N.; Bogdanos, D.P.; Roussaki-Schulze, A.V.; Zafiriou, E. Serum vitamin D levels can be predictive of psoriasis flares up after COVID-19 vaccination: A retrospective case control study. Front. Med. 2023, 10, 1203426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Giannoni, M.; Consales, V.; Campanati, A.; Ganzetti, G.; Giuliodori, K.; Postacchini, V.; Liberati, G.; Azzaretto, L.; Vichi, S.; Guanciarossa, F.; et al. Poziomy homocysteiny w osoczu u pacjentów z łuszczycą: Nasze doświadczenia i przegląd piśmiennictwa. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2015, 29, 1781–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.E.; Lee, H.J.; Lee, J.S.; Whang, K.U.; Park, Y.L.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, H.J. Związek między poziomem homocysteiny a łuszczycą: Metaanaliza. Ann. Dermatol. 2019, 31, 378–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Arias-Santiago, S.; Orgaz-Molina, J.; Castellote-Caballero, L.; Arrabal-Polo, M.Á.; García-Rodriguez, S.; Perandrés-López, R.; Ruiz, J.C.; Naranjo-Sintes, R.; Zubiaur, M.; Sancho, J.; et al. Atheroma plaque, metabolic syndrome and inflammation in patients with psoriasis. Eur. J. Dermatol. 2012, 22, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, X.; Wang, Z.; Lei, W.; Shen, M.; Tang, J.; Xu, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, H. Pentraxin 3: A promising therapeutic target for cardiovascular diseases. Ageing Res. Rev. 2024, 93, 102163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cieślik, P.; Hrycek, A. Long pentraxin 3 (PTX3) in the light of its structure, mechanism of action and clinical implications. Autoimmunity 2012, 45, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mantovani, A.; Valentino, S.; Gentile, S.; Inforzato, A.; Bottazzi, B.; Garlanda, C. The long pentraxin PTX3: A paradigm for humoral pattern recognition molecules. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2013, 1285, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mantovani, A.; Garlanda, C.; Doni, A.; Bottazzi, B. Pentraksyny w odporności wrodzonej: Od białka C-reaktywnego do długiej pentraksyny PTX3. J. Clin. Immunol. 2008, 28, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uysal, S.; Yılmaz, F.M.; Karatoprak, K.; Artüz, F.; Cumbul, N.U. The levels of serum pentraxin3, CRP, fetuin-A, and insulin in patients with psoriasis. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2014, 18, 3453–3458. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bevelacqua, V.; Libra, M.; Mazzarino, M.C.; Gangemi, P.; Nicotra, G.; Curatolo, S.; Massimino, D.; Plumari, A.; Merito, P.; Valente, G.; et al. Long pentraxin 3: A marker of inflammation in untreated psoriatic patients. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2006, 18, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Sterry, W.; Strober, B.E.; Menter, A.; International Psoriasis Council. Obesity in psoriasis: The metabolic, clinical and therapeutic implications. Report of an interdisciplinary conference and review. Br. J. Dermatol. 2007, 157, 649–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiełbowski, K.; Bakinowska, E.; Ostrowski, P.; Pala, B.; Gromowska, E.; Gurazda, K.; Dec, P.; Modrzejewski, A.; Pawlik, A. The Role of Adipokines in the Pathogenesis of Psoriasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Folco, E.J.; Rocha, V.Z.; López-Ilasaca, M.; Libby, P. Adiponectin inhibits pro-inflammatory signaling in human macrophages independent of interleukin-10. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 25569–25575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kaushik, A.; Chopra, D.; Kaur, K.; Gupta, S.; Chopra, P. Serum Adiponectin Levels as an Independent Marker of Severity of Psoriasis: A Cross-Sectional Analysis. J. Psoriasis Psoriatic Arthritis 2023, 8, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sereflican, B.; Goksugur, N.; Bugdayci, G.; Polat, M.; Haydar Parlak, A. Serum Visfatin, Adiponectin, and Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha (TNF-α) Levels in Patients with Psoriasis and their Correlation with Disease Severity. Acta Dermatovenerol. Croat. 2016, 24, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bai, F.; Zheng, W.; Dong, Y.; Wang, J.; Garstka, M.A.; Li, R.; An, J.; Ma, H. Serum levels of adipokines and cytokines in psoriasis patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Oncotarget 2017, 9, 1266–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Huang, H.; Shen, E.; Tang, S.; Tan, X.; Guo, X.; Wang, Q.; Ding, H. Increased serum resistin levels correlate with psoriasis: A meta-analysis. Lipids Health Dis. 2015, 14, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Askin, L.; Abus, S.; Tanriverdi, O. Resistin and Cardiovascular Disease: A Review of the Current Literature Regarding Clinical and Pathological Relationships. Curr. Cardiol. Rev. 2022, 18, e290721195114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Jamaluddin, M.S.; Weakley, S.M.; Yao, Q.; Chen, C. Resistin: Functional roles and therapeutic considerations for cardiovascular disease. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 165, 622–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Vachatova, S.; Andrys, C.; Krejsek, J.; Salavec, M.; Ettler, K.; Rehacek, V.; Cermakova, E.; Malkova, A.; Fiala, Z.; Borska, L. Metabolic Syndrome and Selective Inflammatory Markers in Psoriatic Patients. J. Immunol. Res. 2016, 2016, 5380792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Robati, R.M.; Partovi-Kia, M.; Haghighatkhah, H.R.; Younespour, S.; Abdollahimajd, F. Increased serum leptin and resistin levels and increased carotid intima-media wall thickness in patients with psoriasis: Is psoriasis associated with atherosclerosis? J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2014, 71, 642–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coimbra, S.; Oliveira, H.; Reis, F.; Belo, L.; Rocha, S.; Quintanilha, A.; Figueiredo, A.; Teixeira, F.; Castro, E.; Rocha-Pereira, P.; et al. Circulating adipokine levels in Portuguese patients with psoriasis vulgaris according to body mass index, severity and therapy. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2010, 24, 1386–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajappa, M.; Rathika, S.; Munisamy, M.; Chandrashekar, L.; Thappa, D.M. Effect of treatment with methotrexate and coal tar on adipokine levels and indices of insulin resistance and sensitivity in patients with psoriasis vulgaris. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2015, 29, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyriakou, A.; Patsatsi, A.; Sotiriadis, D.; Goulis, D.G. Effects of treatment for psoriasis on circulating levels of leptin, adiponectin and resistin: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Br. J. Dermatol. 2018, 179, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brodell, R.T. JAAD Game Changers: “Increased serum leptin and resistin levels and increased carotid intima-media wall thickness in patients with psoriasis: Is psoriasis associated with atherosclerosis”? J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2024, 91, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, X.; Cheng, Y.; Chang, D. The Important Role of Leptin in Modulating the Risk of Dermatological Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2021, 11, 593564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Toussirot, E.; Aubin, F.; Dumoulin, G. Relationships between Adipose Tissue and Psoriasis, with or without Arthritis. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhu, K.J.; Zhang, C.; Li, M.; Zhu, C.Y.; Shi, G.; Fan, Y.M. Leptin levels in patients with psoriasis: A meta-analysis. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2013, 38, 478–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.J.; Wu, C.Y.; Shen, J.L.; Chu, S.Y.; Chen, C.K.; Chang, Y.T.; Chen, C.M. Psoriasis independently associated with hyperleptinemia contributing to metabolic syndrome. Arch. Dermatol. 2008, 144, 1571–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, S.; Zilmer, K.; Leping, V.; Zilmer, M. The levels of adiponectin and leptin and their relation to other markers of cardiovascular risk in patients with psoriasis. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2011, 25, 1328–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Biomarker | Effect of Group | Effect of Age | Effect of Sex | Interaction (Group × Age) | Interaction (Group × Sex) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Homocysteine | F = 45.67, p < 0.001 (Significant) | F = 1.12, p = 0.29 (ns) | F = 0.89, p = 0.35 (ns) | F = 0.72, p = 0.39 (ns) | F = 0.45, p = 0.50 (ns) |
| Pentraxin 3 | F = 18.24, p < 0.001 (Significant) | F = 0.54, p = 0.46 (ns) | F = 0.62, p = 0.43 (ns) | F = 0.31, p = 0.58 (ns) | F = 0.23, p = 0.63 (ns) |
| Adiponectin | F = 22.18, p < 0.001 (Significant) | F = 0.92, p = 0.34 (ns) | F = 0.71, p = 0.40 (ns) | F = 0.56, p = 0.45 (ns) | F = 0.48, p = 0.49 (ns) |
| Resistin | F = 39.34, p < 0.001 (Significant) | F = 0.87, p = 0.35 (ns) | F = 0.53, p = 0.47 (ns) | F = 0.49, p = 0.49 (ns) | F = 0.36, p = 0.55 (ns) |
| Leptin | F = 27.89, p < 0.001 (Significant) | F = 0.67, p = 0.42 (ns) | F = 0.78, p = 0.38 (ns) | F = 0.41, p = 0.52 (ns) | F = 0.28, p = 0.60 (ns) |
| Variable | Biomarkers Tested | Statistical Test | Test Statistic (Range) | p-Value (Range) | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender (Male/Female) | Homocysteine, PTX3, Adiponectin, Resistin, Leptin | Mann-Whitney U Test | U = 925.5–1056.0 | 0.23–0.68 | ns |
| Family History | Homocysteine, PTX3, Adiponectin, Resistin, Leptin | Chi- square/Fisher Test | χ2 = 2.14–4.08 | 0.12–0.26 | ns |
| Obesity (BMI ≥ 30) | Homocysteine, PTX3, Adiponectin, Resistin, Leptin | T-test/Mann- Whitney U | t = −1.13–0.94, U = 530.0–620.5 | 0.19–0.57 | ns |
| Itching (Yes/No) | Homocysteine, PTX3, Adiponectin, Resistin, Leptin | Mann-Whitney U Test | U = 910.5–1025.5 | 0.21–0.63 | ns |
| Joint Pain (Yes/No) | Homocysteine, PTX3, Adiponectin, Resistin, Leptin | Mann-Whitney U Test | U = 885.5–1012.0 | 0.18–0.59 | ns |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Szczegielniak, M.; Lesiak, A.; Reich, A.; Opalińska, A.; Zakrzewski, B.; Arasiewicz, H.; Grabowski, K.; Nolberczak, D.; Narbutt, J. Inflammation-Related Markers in Pediatric Psoriasis: Resistin as a Potential Marker of Psoriasis Severity. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 1689. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14051689
Szczegielniak M, Lesiak A, Reich A, Opalińska A, Zakrzewski B, Arasiewicz H, Grabowski K, Nolberczak D, Narbutt J. Inflammation-Related Markers in Pediatric Psoriasis: Resistin as a Potential Marker of Psoriasis Severity. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(5):1689. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14051689
Chicago/Turabian StyleSzczegielniak, Magdalena, Aleksandra Lesiak, Adam Reich, Aleksandra Opalińska, Bartosz Zakrzewski, Hubert Arasiewicz, Kamil Grabowski, Daniel Nolberczak, and Joanna Narbutt. 2025. "Inflammation-Related Markers in Pediatric Psoriasis: Resistin as a Potential Marker of Psoriasis Severity" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 5: 1689. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14051689
APA StyleSzczegielniak, M., Lesiak, A., Reich, A., Opalińska, A., Zakrzewski, B., Arasiewicz, H., Grabowski, K., Nolberczak, D., & Narbutt, J. (2025). Inflammation-Related Markers in Pediatric Psoriasis: Resistin as a Potential Marker of Psoriasis Severity. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(5), 1689. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14051689







