Serum Lipids, Inflammation, and the Risk of Atrial Fibrillation: Pathophysiological Links and Clinical Evidence
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Atrial Fibrillation Pathogenesis
2.1. Electrical Remodeling
2.2. Structural Remodeling
2.3. Contractile Remodeling
2.4. Role of the Autonomic Nervous System
3. Serum Lipids and Inflammation
3.1. Cholesterol
3.2. Triglycerides
3.3. Lipoprotein (a)
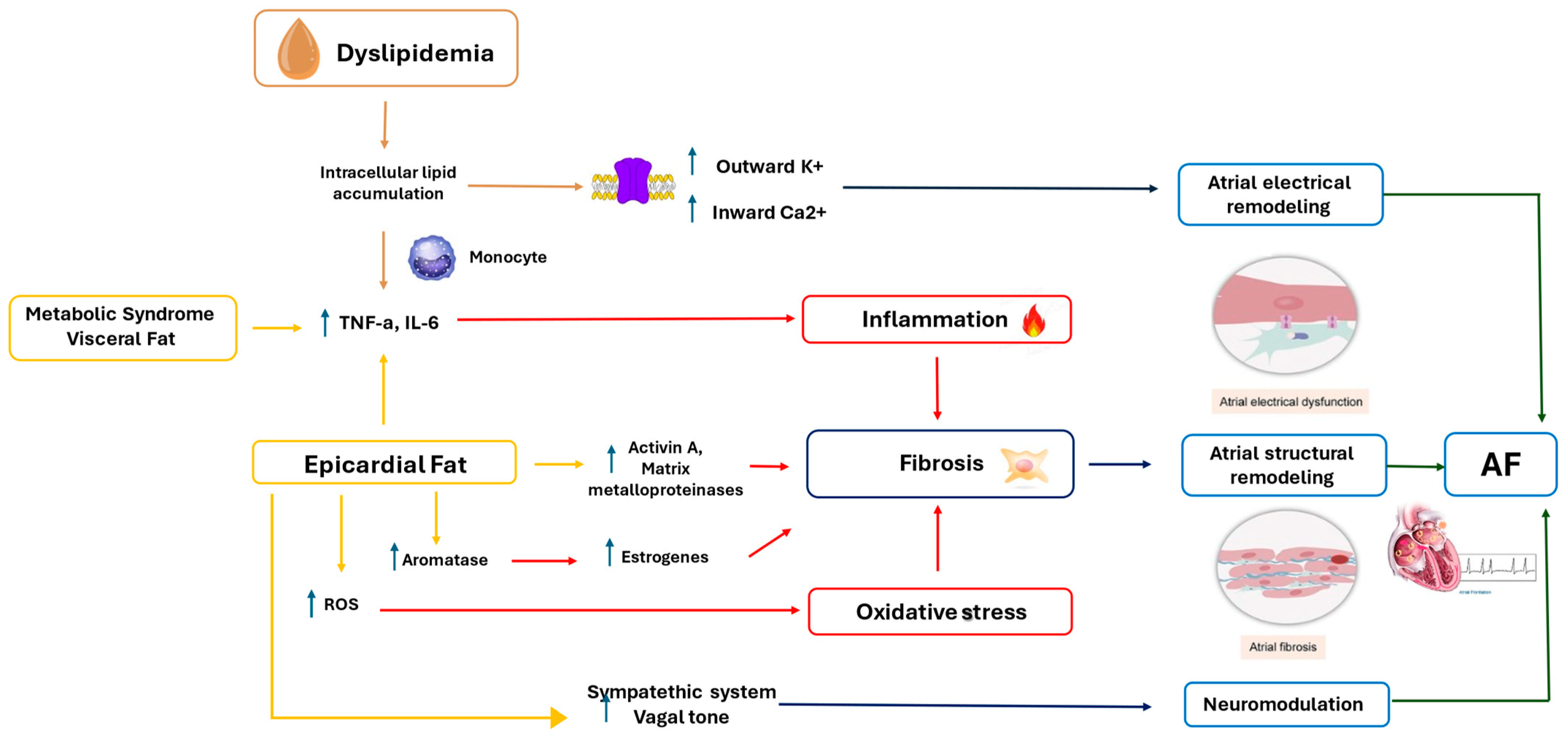
4. Epicardial Fat and Atrial Fibrillation
5. Visceral Adiposity, Metabolic Syndrome, and Atrial Fibrillation
6. Paradoxical Epidemiologic Association Between Serum Lipids and Atrial Fibrillation
7. Drugs for the Treatment of Dyslipidemia and Their Role in Atrial Fibrillation
7.1. Statins
7.2. Bempedoic Acid
7.3. Anti-Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin/Kexin Type 9
7.3.1. Evidence from Clinical Trials
Alirocumab
Evolocumab
Inclisiran
7.4. Triglyceride-Lowering Therapies
7.4.1. Icosapent Ethyl
7.4.2. Future Directions
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mach, F.; Baigent, C.; Catapano, A.L.; Koskinas, K.C.; Casula, M.; Badimon, L.; Chapman, M.J.; De Backer, G.G.; Delgado, V.; Ference, B.A.; et al. 2019 ESC/EAS Guidelines for the Management of Dyslipidaemias: Lipid Modification to Reduce Cardiovascular Risk. Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 111–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maloberti, A.; La Rosa, A.; Toscani, G.; Caccia, A.; Gualini, E.; Pezzoli, S.; Morelli, M.; Busti, A.; Colombo, V.; Tognola, C.; et al. Hypertriglyceridemia in Patients with Acute and Chronic Coronary Syndrome: Prevalence and Their Association with Extreme Cardiovascular Risk and Left Ventricular Functionhypertriglyceridemia in Patients with Acute and Chronic Coronary Syndrome: Prevalence. Eur. Heart J. Suppl. 2024, 26, ii29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abera, A.; Worede, A.; Hirigo, A.T.; Alemayehu, R.; Ambachew, S. Dyslipidemia and Associated Factors among Adult Cardiac Patients: A Hospital-Based Comparative Cross-Sectional Study. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2024, 29, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannon, C.P.; Braunwald, E.; McCabe, C.H.; Rader, D.J.; Rouleau, J.L.; Belder, R.; Joyal, S.V.; Hill, K.A.; Pfeffer, M.A.; Skene, A.M. Intensive Versus Moderate Lipid Lowering with Statins After Acute Coronary Syndromes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 350, 1495–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannon, C.P.; Blazing, M.A.; Giugliano, R.P.; McCagg, A.; White, J.A.; Theroux, P.; Darius, H.; Lewis, B.S.; Ophuis, T.O.; Jukema, J.W.; et al. Ezetimibe Added to Statin Therapy after Acute Coronary Syndromes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 2387–2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cholesterol Treatment Trialists’ (CTT). Collaboration Efficacy and Safety of More Intensive Lowering of LDL Cholesterol: A Meta-Analysis of Data from 170 000 Participants in 26 Randomised Trials. Lancet 2010, 376, 1670–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jukema, J.W.; Zijlstra, L.E.; Bhatt, D.L.; Bittner, V.A.; Diaz, R.; Drexel, H.; Goodman, S.G.; Kim, Y.-U.; Pordy, R.; Reiner, Ž.; et al. Effect of Alirocumab on Stroke in ODYSSEY OUTCOMES. Circulation 2019, 140, 2054–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, G.G.; Steg, P.G.; Szarek, M.; Bhatt, D.L.; Bittner, V.A.; Diaz, R.; Edelberg, J.M.; Goodman, S.G.; Hanotin, C.; Harrington, R.A.; et al. Alirocumab and Cardiovascular Outcomes after Acute Coronary Syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 2097–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabatine, M.S.; Giugliano, R.P.; Keech, A.C.; Honarpour, N.; Wiviott, S.D.; Murphy, S.A.; Kuder, J.F.; Wang, H.; Liu, T.; Wasserman, S.M.; et al. Evolocumab and Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Cardiovascular Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 1713–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordestgaard, B.G.; Varbo, A. Triglycerides and Cardiovascular Disease. Lancet 2014, 384, 626–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Liu, F.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z. Lipid Levels and Risk of New-Onset Atrial Fibrillation: A Systematic Review and Dose-Response Meta-Analysis. Clin. Cardiol. 2020, 43, 935–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mauriello, A.; Ascrizzi, A.; Roma, A.S.; Molinari, R.; Caturano, A.; Imbalzano, E.; D’Andrea, A.; Russo, V. Effects of Heart Failure Therapies on Atrial Fibrillation: Biological and Clinical Perspectives. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stillitano, F.; Lonardo, G.; Zicha, S.; Varro, A.; Cerbai, E.; Mugelli, A.; Nattel, S. Molecular Basis of Funny Current (If) in Normal and Failing Human Heart. J. Mol. Cell Cardiol. 2008, 45, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, Y.-H.; Wakili, R.; Qi, X.-Y.; Chartier, D.; Boknik, P.; Kääb, S.; Ravens, U.; Coutu, P.; Dobrev, D.; Nattel, S. Calcium-Handling Abnormalities Underlying Atrial Arrhythmogenesis and Contractile Dysfunction in Dogs with Congestive Heart Failure. Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 2008, 1, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzale, S.; Gollob, M.H.; Gow, R.; Birnie, D.H. Sudden Death in a Young Man with Catecholaminergic Polymorphic Ventricular Tachycardia and Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2008, 19, 1319–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasaki, Y.; Nishida, K.; Kato, T.; Nattel, S. Atrial Fibrillation Pathophysiology: Implications for Management. Circulation 2011, 124, 2264–2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauriello, A.; Correra, A.; Molinari, R.; Del Vecchio, G.E.; Tessitore, V.; D’Andrea, A.; Russo, V. Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Atrial Fibrillation: The Need for a Strong Pharmacological Approach. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 2720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, L.; Xie, J.; Nattel, S. Molecular Determinants of Cardiac Fibroblast Electrical Function and Therapeutic Implications for Atrial Fibrillation. Cardiovasc. Res. 2011, 89, 744–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauriello, A.; Correra, A.; Ascrizzi, A.; Del Vecchio, G.E.; Benfari, G.; Ilardi, F.; Lisi, M.; Malagoli, A.; Mandoli, G.E.; Pastore, M.C.; et al. Relationship Between Left Atrial Strain and Atrial Fibrillation: The Role of Stress Echocardiography. Diagnostics 2024, 15, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popescu, B.A.; Beladan, C.C.; Nagueh, S.F.; Smiseth, O.A. How to Assess Left Ventricular Filling Pressures by Echocardiography in Clinical Practice. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2022, 23, 1127–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, C.-C.; Chen, P.-S. New Concepts in Atrial Fibrillation: Neural Mechanisms and Calcium Dynamics. Cardiol. Clin. 2009, 27, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kneller, J.; Zou, R.; Vigmond, E.J.; Wang, Z.; Leon, L.J.; Nattel, S. Cholinergic Atrial Fibrillation in a Computer Model of a Two-Dimensional Sheet of Canine Atrial Cells with Realistic Ionic Properties. Circ. Res. 2002, 90, e73–e87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craig, M.; Yarrarapu, S.N.S.; Dimri, M. Biochemistry, Cholesterol; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Levitan, I.; Fang, Y.; Rosenhouse-Dantsker, A.; Romanenko, V. Cholesterol and Ion Channels. In Cholesterol Binding and Cholesterol Transport Proteins: Structure and Function in Health and Disease; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2010; pp. 509–549. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, Y.; Heybrock, S.; Neculai, D.; Saftig, P. Cholesterol Handling in Lysosomes and Beyond. Trends Cell Biol. 2020, 30, 452–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, J.K.; Cimato, T.R. Cholesterol and Hematopoietic Stem Cells: Inflammatory Mediators of Atherosclerosis. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2014, 3, 549–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerterp, M.; Fotakis, P.; Ouimet, M.; Bochem, A.E.; Zhang, H.; Molusky, M.M.; Wang, W.; Abramowicz, S.; la Bastide-van Gemert, S.; Wang, N.; et al. Cholesterol Efflux Pathways Suppress Inflammasome Activation, NETosis, and Atherogenesis. Circulation 2018, 138, 898–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yvan-Charvet, L.; Welch, C.; Pagler, T.A.; Ranalletta, M.; Lamkanfi, M.; Han, S.; Ishibashi, M.; Li, R.; Wang, N.; Tall, A.R. Increased Inflammatory Gene Expression in ABC Transporter–Deficient Macrophages. Circulation 2008, 118, 1837–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiekema, L.C.A.; Willemsen, L.; Kaiser, Y.; Prange, K.H.M.; Wareham, N.J.; Boekholdt, S.M.; Kuijk, C.; de Winther, M.P.J.; Voermans, C.; Nahrendorf, M.; et al. Impact of Cholesterol on Proinflammatory Monocyte Production by the Bone Marrow. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 4309–4320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Hagan, R.; Berg, A.R.; Hong, C.G.; Parel, P.M.; Mehta, N.N.; Teague, H.L. Systemic Consequences of Abnormal Cholesterol Handling: Interdependent Pathways of Inflammation and Dyslipidemia. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 972140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolani, S.; Pagler, T.A.; Murphy, A.J.; Bochem, A.E.; Abramowicz, S.; Welch, C.; Nagareddy, P.R.; Holleran, S.; Hovingh, G.K.; Kuivenhoven, J.A.; et al. Hypercholesterolemia and Reduced HDL-C Promote Hematopoietic Stem Cell Proliferation and Monocytosis: Studies in Mice and FH Children. Atherosclerosis 2013, 229, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerterp, M.; Murphy, A.J.; Wang, M.; Pagler, T.A.; Vengrenyuk, Y.; Kappus, M.S.; Gorman, D.J.; Nagareddy, P.R.; Zhu, X.; Abramowicz, S.; et al. Deficiency of ATP-Binding Cassette Transporters A1 and G1 in Macrophages Increases Inflammation and Accelerates Atherosclerosis in Mice. Circ. Res. 2013, 112, 1456–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baartscheer, A.; Schumacher, C.A.; Wekker, V.; Verkerk, A.O.; Veldkamp, M.W.; van Oort, R.J.; Elzenaar, I.; Ottenhoff, R.; van Roomen, C.; Aerts, H.; et al. Dyscholesterolemia Protects Against Ischemia-Induced Ventricular Arrhythmias. Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 2015, 8, 1481–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bochem, A.E.; van der Valk, F.M.; Tolani, S.; Stroes, E.S.; Westerterp, M.; Tall, A.R. Increased Systemic and Plaque Inflammation in ABCA1 Mutation Carriers with Attenuation by Statins. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2015, 35, 1663–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varbo, A.; Benn, M.; Tybjærg-Hansen, A.; Jørgensen, A.B.; Frikke-Schmidt, R.; Nordestgaard, B.G. Remnant Cholesterol as a Causal Risk Factor for Ischemic Heart Disease. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2013, 61, 427–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernelot Moens, S.J.; Verweij, S.L.; Schnitzler, J.G.; Stiekema, L.C.A.; Bos, M.; Langsted, A.; Kuijk, C.; Bekkering, S.; Voermans, C.; Verberne, H.J.; et al. Remnant Cholesterol Elicits Arterial Wall Inflammation and a Multilevel Cellular Immune Response in Humans. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2017, 37, 969–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varbo, A.; Benn, M.; Tybjærg-Hansen, A.; Nordestgaard, B.G. Elevated Remnant Cholesterol Causes Both Low-Grade Inflammation and Ischemic Heart Disease, Whereas Elevated Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Causes Ischemic Heart Disease Without Inflammation. Circulation 2013, 128, 1298–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maranhão, R.C.; Carvalho, P.O.; Strunz, C.C.; Pileggi, F. Lipoprotein (a): Structure, Pathophysiology and Clinical Implications. Arq. Bras. Cardiol. 2014, 103, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zekavat, S.M.; Ruotsalainen, S.; Handsaker, R.E.; Alver, M.; Bloom, J.; Poterba, T.; Seed, C.; Ernst, J.; Chaffin, M.; Engreitz, J.; et al. Deep Coverage Whole Genome Sequences and Plasma Lipoprotein(a) in Individuals of European and African Ancestries. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oikonomou, E.; Souvaliotis, N.; Lampsas, S.; Siasos, G.; Poulakou, G.; Theofilis, P.; Papaioannou, T.G.; Haidich, A.-B.; Tsaousi, G.; Ntousopoulos, V.; et al. Endothelial Dysfunction in Acute and Long Standing COVID−19: A Prospective Cohort Study. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2022, 144, 106975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, S.; Khan, S.; Tam, S.-P.; Koschinsky, M.; Taylor, P.; Yacoub, M. Expression of Adhesion Molecules by Lp(a): A Potential Novel Mechanism for Its Atherogenicity. FASEB J. 1998, 12, 1765–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takami, S.; Yamashita, S.; Kihara, S.; Ishigami, M.; Takemura, K.; Kume, N.; Kita, T.; Matsuzawa, Y. Lipoprotein(a) Enhances the Expression of Intercellular Adhesion Molecule-1 in Cultured Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells. Circulation 1998, 97, 721–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotiriou, S.N.; Orlova, V.V.; Al-Fakhri, N.; Ihanus, E.; Economopoulou, M.; Isermann, B.; Bdeir, K.; Nawroth, P.P.; Preissner, K.T.; Gahmberg, C.G.; et al. Lipoprotein(a) in Atherosclerotic Plaques Recruits Inflammatory Cells through Interaction with Mac-1 Integrin. FASEB J. 2006, 20, 559–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labudovic, D.; Kostovska, I.; Tosheska Trajkovska, K.; Cekovska, S.; Brezovska Kavrakova, J.; Topuzovska, S. Lipoprotein(a)—Link Between Atherogenesis and Thrombosis. Prague Med. Rep. 2019, 120, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.-F.; Chen, Y.-J.; Lin, Y.-J.; Chen, S.-A. Inflammation and the Pathogenesis of Atrial Fibrillation. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2015, 12, 230–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, V.; Falco, L.; Tessitore, V.; Mauriello, A.; Catapano, D.; Napolitano, N.; Tariq, M.; Caturano, A.; Ciccarelli, G.; D’Andrea, A.; et al. Anti-Inflammatory and Anticancer Effects of Anticoagulant Therapy in Patients with Malignancy. Life 2023, 13, 1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, V.; Napolitano, N.; Ascrizzi, A.; Leonardi, S.; Pisacane, F.; Di Micco, P.; Imbalzano, E.; Sasso, F.C.; D’Andrea, A.; Caturano, A.; et al. The Lipid-Lowering Efficacy of a Nutraceutical Combination Including Leucoselect Phytosome, Red Yeast Rice, Policosanol and Folic Acid in Dyslipidaemia Patients: Real-World Insights. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conte, M.; Petraglia, L.; Poggio, P.; Valerio, V.; Cabaro, S.; Campana, P.; Comentale, G.; Attena, E.; Russo, V.; Pilato, E.; et al. Inflammation and Cardiovascular Diseases in the Elderly: The Role of Epicardial Adipose Tissue. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 844266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parisi, V.; Conte, M.; Petraglia, L.; Grieco, F.V.; Bruzzese, D.; Caruso, A.; Grimaldi, M.G.; Campana, P.; Gargiulo, P.; Paolillo, S.; et al. Echocardiographic Epicardial Adipose Tissue Thickness for Risk Stratification of Patients with Heart Failure. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacobellis, G.; Corradi, D.; Sharma, A.M. Epicardial Adipose Tissue: Anatomic, Biomolecular and Clinical Relationships with the Heart. Nat. Clin. Pract. Cardiovasc. Med. 2005, 2, 536–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, S.C.; Davidson, L.E.; Adams, T.D.; Ranson, L.; McKinlay, R.D.; Simper, S.C.; Litwin, S.E. Associations of Visceral, Subcutaneous, Epicardial, and Liver Fat with Metabolic Disorders up to 14 Years After Weight Loss Surgery. Metab. Syndr. Relat. Disord. 2021, 19, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kankaanpää, M.; Lehto, H.-R.; Pärkkä, J.P.; Komu, M.; Viljanen, A.; Ferrannini, E.; Knuuti, J.; Nuutila, P.; Parkkola, R.; Iozzo, P. Myocardial Triglyceride Content and Epicardial Fat Mass in Human Obesity: Relationship to Left Ventricular Function and Serum Free Fatty Acid Levels. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 91, 4689–4695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conte, M.; Petraglia, L.; Cabaro, S.; Valerio, V.; Poggio, P.; Pilato, E.; Attena, E.; Russo, V.; Ferro, A.; Formisano, P.; et al. Epicardial Adipose Tissue and Cardiac Arrhythmias: Focus on Atrial Fibrillation. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 932262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuta, H.; Goto, T.; Kamiya, T. Association of Epicardial Fat with Cardiac Structure and Function and Cardiovascular Outcomes: A Protocol for Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0283482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parisi, V.; Petraglia, L.; Formisano, R.; Caruso, A.; Grimaldi, M.G.; Bruzzese, D.; Grieco, F.V.; Conte, M.; Paolillo, S.; Scatteia, A.; et al. Validation of the Echocardiographic Assessment of Epicardial Adipose Tissue Thickness at the Rindfleisch Fold for the Prediction of Coronary Artery Disease. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2020, 30, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahabadi, A.A.; Berg, M.H.; Lehmann, N.; Kälsch, H.; Bauer, M.; Kara, K.; Dragano, N.; Moebus, S.; Jöckel, K.-H.; Erbel, R.; et al. Association of Epicardial Fat with Cardiovascular Risk Factors and Incident Myocardial Infarction in the General Population. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2013, 61, 1388–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.X.; Ganesan, A.N.; Selvanayagam, J.B. Epicardial Fat and Atrial Fibrillation: Current Evidence, Potential Mechanisms, Clinical Implications, and Future Directions. Eur. Heart J. 2016, 38, 1294–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salgado-Somoza, A.; Teijeira-Fernández, E.; Fernández, Á.L.; González-Juanatey, J.R.; Eiras, S. Proteomic Analysis of Epicardial and Subcutaneous Adipose Tissue Reveals Differences in Proteins Involved in Oxidative Stress. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2010, 299, H202–H209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernasochi, G.B.; Boon, W.C.; Curl, C.L.; Varma, U.; Pepe, S.; Tare, M.; Parry, L.J.; Dimitriadis, E.; Harrap, S.B.; Nalliah, C.J.; et al. Pericardial Adipose and Aromatase: A New Translational Target for Aging, Obesity and Arrhythmogenesis? J. Mol. Cell Cardiol. 2017, 111, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansaldo, A.M.; Montecucco, F.; Sahebkar, A.; Dallegri, F.; Carbone, F. Epicardial Adipose Tissue and Cardiovascular Diseases. Int. J. Cardiol. 2019, 278, 254–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, K.; Okumura, Y.; Watanabe, I.; Nagashima, K.; Sonoda, K.; Sasaki, N.; Kogawa, R.; Iso, K.; Kurokawa, S.; Ohkubo, K.; et al. Anatomical Proximity Between Ganglionated Plexi and Epicardial Adipose Tissue in the Left Atrium: Implication for 3D Reconstructed Epicardial Adipose Tissue-Based Ablation. J. Interv. Card. Electrophysiol. 2016, 47, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balcioğlu, A.S.; Çiçek, D.; Akinci, S.; Eldem, H.O.; Bal, U.A.; Okyay, K.; Müderrisoğlu, H. Arrhythmogenic Evidence for Epicardial Adipose Tissue: Heart Rate Variability and Turbulence Are Influenced by Epicardial Fat Thickness. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 2015, 38, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, D.; Zhang, S.; Yang, D.; Gao, L.; Lin, Y.; Chu, Z.; Jiang, X.; Yin, X.; Zheng, Z.; Wei, X.; et al. Effect of Epicardial Fat Pad Ablation on Acute Atrial Electrical Remodeling and Inducibility of Atrial Fibrillation. Circ. J. 2010, 74, 885–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gawałko, M.; Saljic, A.; Li, N.; Abu-Taha, I.; Jespersen, T.; Linz, D.; Nattel, S.; Heijman, J.; Fender, A.; Dobrev, D. Adiposity-Associated Atrial Fibrillation: Molecular Determinants, Mechanisms, and Clinical Significance. Cardiovasc. Res. 2023, 119, 614–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misra, A.; Vikram, N.K. Clinical and Pathophysiological Consequences of Abdominal Adiposity and Abdominal Adipose Tissue Depots. Nutrition 2003, 19, 457–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motoshima, H.; Wu, X.; Sinha, M.K.; Hardy, V.E.; Rosato, E.L.; Barbot, D.J.; Rosato, F.E.; Goldstein, B.J. Differential Regulation of Adiponectin Secretion from Cultured Human Omental and Subcutaneous Adipocytes: Effects of Insulin and Rosiglitazone. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2002, 87, 5662–5667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenkula, K.G.; Erlanson-Albertsson, C. Adipose Cell Size: Importance in Health and Disease. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2018, 315, R284–R295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.S.; White, A.; Perry, R.J.; Camporez, J.-P.; Hidalgo, J.; Shulman, G.I.; Davis, R.J. Regulation of Adipose Tissue Inflammation by Interleukin 6. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 2751–2760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberti, K.G.M.M.; Eckel, R.H.; Grundy, S.M.; Zimmet, P.Z.; Cleeman, J.I.; Donato, K.A.; Fruchart, J.-C.; James, W.P.T.; Loria, C.M.; Smith, S.C. Harmonizing the Metabolic Syndrome. Circulation 2009, 120, 1640–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engin, A. The Definition and Prevalence of Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome. In Obesity and Lipotoxicity; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Dalmas, E.; Rouault, C.; Abdennour, M.; Rovere, C.; Rizkalla, S.; Bar-Hen, A.; Nahon, J.-L.; Bouillot, J.-L.; Guerre-Millo, M.; Clément, K.; et al. Variations in Circulating Inflammatory Factors Are Related to Changes in Calorie and Carbohydrate Intakes Early in the Course of Surgery-Induced Weight Reduction. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 94, 450–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askarpour, M.; Khani, D.; Sheikhi, A.; Ghaedi, E.; Alizadeh, S. Effect of Bariatric Surgery on Serum Inflammatory Factors of Obese Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Obes. Surg. 2019, 29, 2631–2647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holdstock, C.; Lind, L.; Engstrom, B.E.; Ohrvall, M.; Sundbom, M.; Larsson, A.; Karlsson, F.A. CRP Reduction Following Gastric Bypass Surgery Is Most Pronounced in Insulin-Sensitive Subjects. Int. J. Obes. 2005, 29, 1275–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, H.-J.; Han, K.-D.; Choi, E.-K.; Jung, J.-H.; Kwon, S.; Lee, S.-R.; Oh, S.; Lip, G.Y.H. Cumulative Burden of Metabolic Syndrome and Its Components on the Risk of Atrial Fibrillation: A Nationwide Population-Based Study. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2021, 20, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Lee, S.; Choi, E.; Kwon, S.; Yang, S.; Park, J.; Choi, Y.; Lee, H.; Moon, I.; Lee, E.; et al. Association Between Change in Metabolic Syndrome Status and Risk of Incident Atrial Fibrillation: A Nationwide Population-Based Study. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2021, 10, e020901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Gao, L.; Wang, Z.; Guan, B.; Guan, X.; Wang, B.; Han, X.; Xiao, X.; Waleed, K.B.; Chandran, C.; et al. Lipid Profile and Incidence of Atrial Fibrillation: A Prospective Cohort Study in China. Clin. Cardiol. 2018, 41, 314–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iguchi, Y.; Kimura, K.; Aoki, J.; Kobayashi, K.; Terasawa, Y.; Sakai, K.; Shibazaki, K. Prevalence of Atrial Fibrillation in Community-Dwelling Japanese Aged 40 Years or Older in Japan Analysis of 41,436 Non-Employee Residents in Kurashiki-City. Circ. J. 2008, 72, 909–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walldius, G.; Malmström, H.; Jungner, I.; de Faire, U.; Lambe, M.; Van Hemelrijck, M.; Hammar, N. Cohort Profile: The AMORIS Cohort. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2017, 46, 1103–1103i. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Qin, D.; Yang, L.; Lin, Y.; Zhai, L.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, G.; Wang, K.; Tong, D.; Li, X.; et al. Causal Effects of Plasma Lipids on the Risk of Atrial Fibrillation: A Multivariable Mendelian Randomization Study. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2021, 31, 1569–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Baars, D.P.; Desai, R.; Singh, D.; Pinto-Sietsma, S.-J. Association Between Lipoprotein (a) and Risk of Atrial Fibrillation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Mendelian Randomization Studies. Curr. Probl. Cardiol. 2024, 49, 102024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stancu, C.; Sima, A. Statins: Mechanism of Action and Effects. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2001, 5, 378–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cholesterol Treatment Trialists’ (CTT) Collaborators. Efficacy and Safety of Cholesterol-Lowering Treatment: Prospective Meta-Analysis of Data from 90,056 Participants in 14 Randomised Trials of Statins. Lancet 2005, 366, 1267–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oesterle, A.; Laufs, U.; Liao, J.K. Pleiotropic Effects of Statins on the Cardiovascular System. Circ. Res. 2017, 120, 229–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauthier, T.W.; Scalia, R.; Murohara, T.; Guo, J.; Lefer, A.M. Nitric Oxide Protects Against Leukocyte-Endothelium Interactions in the Early Stages of Hypercholesterolemia. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 1995, 15, 1652–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozai, T.; Eto, M.; Yang, Z.; Shimokawa, H.; Luscher, T. Statins Prevent Pulsatile Stretch-Induced Proliferation of Human Saphenous Vein Smooth Muscle Cells via Inhibition of Rho/Rho-Kinase Pathway. Cardiovasc. Res. 2005, 68, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dichtl, W.; Dulak, J.; Frick, M.; Alber, H.F.; Schwarzacher, S.P.; Ares, M.P.S.; Nilsson, J.; Pachinger, O.; Weidinger, F. HMG-CoA Reductase Inhibitors Regulate Inflammatory Transcription Factors in Human Endothelial and Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2003, 23, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, I.; Aoki, N.; Kawano, K.; Shimoyama, K.; Maki, A.; Homori, M.; Yanagisawa, A.; Yamamoto, M.; Kawai, Y.; Ishikawa, K. Platelet-Dependent Thrombin Generation in Patients with Hyperlipidemia. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 1997, 30, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oraii, A.; Vasheghani-Farahani, A.; Oraii, S.; Roayaei, P.; Balali, P.; Masoudkabir, F. Update on the Efficacy of Statins in Primary and Secondary Prevention of Atrial Fibrillation. Rev. Port. Cardiol. 2021, 40, 509–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.S.; Wu, J.H.; Cui, J.; Hua, C.; Xia, S.J.; He, L.; Li, X.; Ning, M.; Hu, R.; Du, X.; et al. Analysis of Dyslipidemia Management Status in Atrial Fibrillation Patients with Very High and High Risk of Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease. Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi 2023, 51, 642–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinkosky, S.L.; Groot, P.H.E.; Lalwani, N.D.; Steinberg, G.R. Targeting ATP-Citrate Lyase in Hyperlipidemia and Metabolic Disorders. Trends Mol. Med. 2017, 23, 1047–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nissen, S.E.; Lincoff, A.M.; Brennan, D.; Ray, K.K.; Mason, D.; Kastelein, J.J.P.; Thompson, P.D.; Libby, P.; Cho, L.; Plutzky, J.; et al. Bempedoic Acid and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Statin-Intolerant Patients. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 1353–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bays, H.E.; Bloedon, L.T.; Lin, G.; Powell, H.A.; Louie, M.J.; Nicholls, S.J.; Lincoff, A.M.; Nissen, S.E. Safety of Bempedoic Acid in Patients at High Cardiovascular Risk and with Statin Intolerance. J. Clin. Lipidol. 2024, 18, e59–e69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, E.M.; Davidson, M.H. PCSK9 Inhibitors: Mechanism of Action, Efficacy, and Safety. Rev. Cardiovasc. Med. 2018, 19, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momtazi-Borojeni, A.A.; Sabouri-Rad, S.; Gotto, A.M.; Pirro, M.; Banach, M.; Awan, Z.; Barreto, G.E.; Sahebkar, A. PCSK9 and Inflammation: A Review of Experimental and Clinical Evidence. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacother. 2019, 5, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Z.; Pothineni, N.V.K.; Goel, A.; Lüscher, T.F.; Mehta, J.L. PCSK9 and Inflammation: Role of Shear Stress, Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines, and LOX-1. Cardiovasc. Res. 2020, 116, 908–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, X.; Gao, Y.; He, M.; Luo, Y.; Wei, Y.; Duan, Y.; Zhang, S.; Yu, H.; Kan, J.; Hou, T.; et al. Evolocumab Prevents Atrial Fibrillation in Rheumatoid Arthritis Rats through Restraint of PCSK9 Induced Atrial Remodeling. J. Adv. Res. 2024, 61, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes, R.D.; Guimarães, P.O.; Schwartz, G.G.; Bhatt, D.L.; Bittner, V.A.; Budaj, A.; Dalby, A.J.; Diaz, R.; Goodman, S.G.; Harrington, R.A.; et al. Effect of Alirocumab on Incidence of Atrial Fibrillation After Acute Coronary Syndromes: Insights from the ODYSSEY OUTCOMES Trial. Am. J. Med. 2022, 135, 915–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Mei, Y.; Wu, Q.; Wu, X. Drug Target Mendelian Randomization Study of PCSK9 and HMG-CoA Reductase Inhibition and Atrial Fibrillation. Cardiology 2024, 149, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Shen, W.; Zhang, H.-Z.; Wang, C.-X.; Yang, P.-P.; Wu, Q.-H. Effect of PCSK9 Monoclonal Antibody Versus Placebo/Ezetimibe on Atrial Fibrillation in Patients at High Cardiovascular Risk: A Meta-Analysis of 26 Randomized Controlled Trials. Cardiovasc. Drugs Ther. 2023, 37, 927–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raal, F.J.; Kallend, D.; Ray, K.K.; Turner, T.; Koenig, W.; Wright, R.S.; Wijngaard, P.L.J.; Curcio, D.; Jaros, M.J.; Leiter, L.A.; et al. Inclisiran for the Treatment of Heterozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1520–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, K.K.; Wright, R.S.; Kallend, D.; Koenig, W.; Leiter, L.A.; Raal, F.J.; Bisch, J.A.; Richardson, T.; Jaros, M.; Wijngaard, P.L.J.; et al. Two Phase 3 Trials of Inclisiran in Patients with Elevated LDL Cholesterol. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1507–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, K.K.; Kallend, D.; Leiter, L.A.; Raal, F.J.; Koenig, W.; Jaros, M.J.; Schwartz, G.G.; Landmesser, U.; Garcia Conde, L.; Wright, R.S. Effect of Inclisiran on Lipids in Primary Prevention: The ORION-11 Trial. Eur. Heart J. 2022, 43, 5047–5057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capece, U.; Gugliandolo, S.; Morciano, C.; Avolio, A.; Splendore, A.; Di Giuseppe, G.; Ciccarelli, G.; Soldovieri, L.; Brunetti, M.; Mezza, T.; et al. Erythrocyte Membrane Fluidity and Omega-3 Fatty Acid Intake: Current Outlook and Perspectives for a Novel, Nutritionally Modifiable Cardiovascular Risk Factor. Nutrients 2024, 16, 4318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, R.P.; Libby, P.; Bhatt, D.L. Emerging Mechanisms of Cardiovascular Protection for the Omega-3 Fatty Acid Eicosapentaenoic Acid. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2020, 40, 1135–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, W.S.; Miller, M.; Tighe, A.P.; Davidson, M.H.; Schaefer, E.J. Omega-3 Fatty Acids and Coronary Heart Disease Risk: Clinical and Mechanistic Perspectives. Atherosclerosis 2008, 197, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiffel, J.A.; McDonald, A. Antiarrhythmic Effects of Omega-3 Fatty Acids. Am. J. Cardiol. 2006, 98, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calder, P.C. Omega-3 Fatty Acids and Inflammatory Processes: From Molecules to Man. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2017, 45, 1105–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, S.C.; Kumlin, M.; Ingelman-Sundberg, M.; Wolk, A. Dietary Long-Chain N−3 Fatty Acids for the Prevention of Cancer: A Review of Potential Mechanisms. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 79, 935–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardi, M.; Chiabrando, J.G.; Vescovo, G.M.; Bressi, E.; Del Buono, M.G.; Carbone, S.; Koenig, R.A.; Van Tassell, B.W.; Abbate, A.; Biondi-Zoccai, G.; et al. Impact of Different Doses of Omega-3 Fatty Acids on Cardiovascular Outcomes: A Pairwise and Network Meta-Analysis. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2020, 22, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilbring, M.; Ploetze, K.; Bormann, S.; Waldow, T.; Matschke, K. Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids Reduce the Incidence of Postoperative Atrial Fibrillation in Patients with History of Prior Myocardial Infarction Undergoing Isolated Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2014, 62, 569–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Costanzo, A.; Indolfi, C.; Sorrentino, S.; Esposito, G.; Spaccarotella, C.A.M. The Effects of Statins, Ezetimibe, PCSK9-Inhibitors, Inclisiran, and Icosapent Ethyl on Platelet Function. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bäck, M. Icosapent Ethyl in Cardiovascular Prevention: Resolution of Inflammation through the Eicosapentaenoic Acid—Resolvin E1—ChemR23 Axis. Pharmacol. Ther. 2023, 247, 108439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayah, N.; Bhatt, D.L.; Miller, M.; Brinton, E.A.; Jacobson, T.A.; Ketchum, S.B.; Jiao, L.; Pineda, A.L.; Doyle, R.T.; Tardif, J.C.; et al. Icosapent Ethyl Following Acute Coronary Syndrome: The REDUCE-IT Trial. Eur. Heart J. 2024, 45, 1173–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olshansky, B.; Bhatt, D.L.; Miller, M.; Steg, P.G.; Brinton, E.A.; Jacobson, T.A.; Ketchum, S.B.; Doyle, R.T.; Juliano, R.A.; Jiao, L.; et al. Cardiovascular Benefits of Icosapent Ethyl in Patients with and Without Atrial Fibrillation in REDUCE-IT. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2023, 12, e026756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stankov, S.; Cuchel, M. Gene Editing for Dyslipidemias: New Tools to “Cut” Lipids. Atherosclerosis 2023, 368, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mauriello, A.; Correra, A.; Maratea, A.C.; Caturano, A.; Liccardo, B.; Perrone, M.A.; Giordano, A.; Nigro, G.; D’Andrea, A.; Russo, V. Serum Lipids, Inflammation, and the Risk of Atrial Fibrillation: Pathophysiological Links and Clinical Evidence. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 1652. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14051652
Mauriello A, Correra A, Maratea AC, Caturano A, Liccardo B, Perrone MA, Giordano A, Nigro G, D’Andrea A, Russo V. Serum Lipids, Inflammation, and the Risk of Atrial Fibrillation: Pathophysiological Links and Clinical Evidence. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(5):1652. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14051652
Chicago/Turabian StyleMauriello, Alfredo, Adriana Correra, Anna Chiara Maratea, Alfredo Caturano, Biagio Liccardo, Marco Alfonso Perrone, Antonio Giordano, Gerardo Nigro, Antonello D’Andrea, and Vincenzo Russo. 2025. "Serum Lipids, Inflammation, and the Risk of Atrial Fibrillation: Pathophysiological Links and Clinical Evidence" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 5: 1652. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14051652
APA StyleMauriello, A., Correra, A., Maratea, A. C., Caturano, A., Liccardo, B., Perrone, M. A., Giordano, A., Nigro, G., D’Andrea, A., & Russo, V. (2025). Serum Lipids, Inflammation, and the Risk of Atrial Fibrillation: Pathophysiological Links and Clinical Evidence. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(5), 1652. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14051652










