Prognostic Value of Chest CT Volumetric Analysis in Patients with Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. CT Acquisition Protocol
2.2. Staging
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patients’ Characteristics
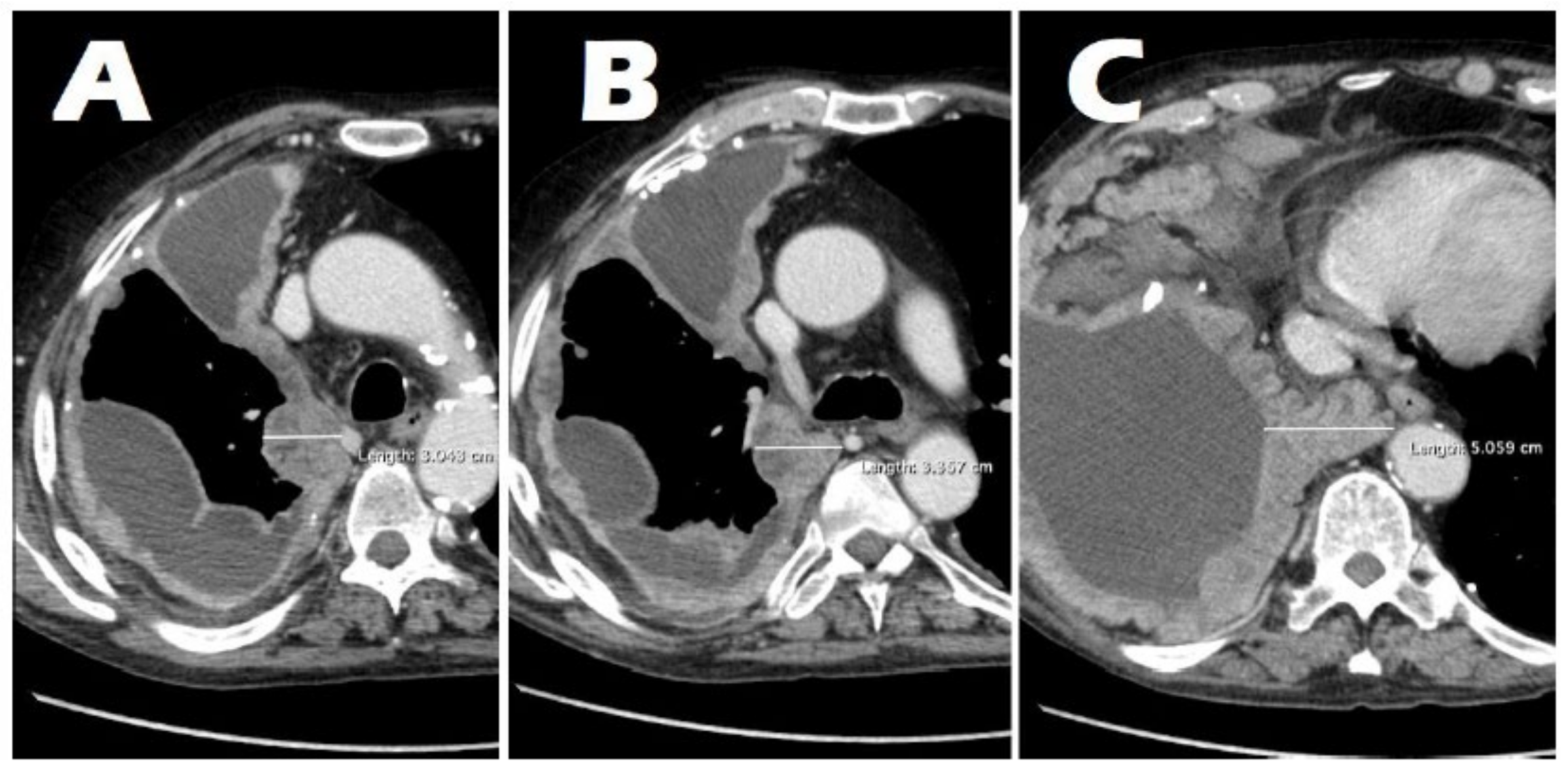
3.2. Radiological Findings on Chest CT
3.3. Correlation Between Tumor Thickness and the T Parameter
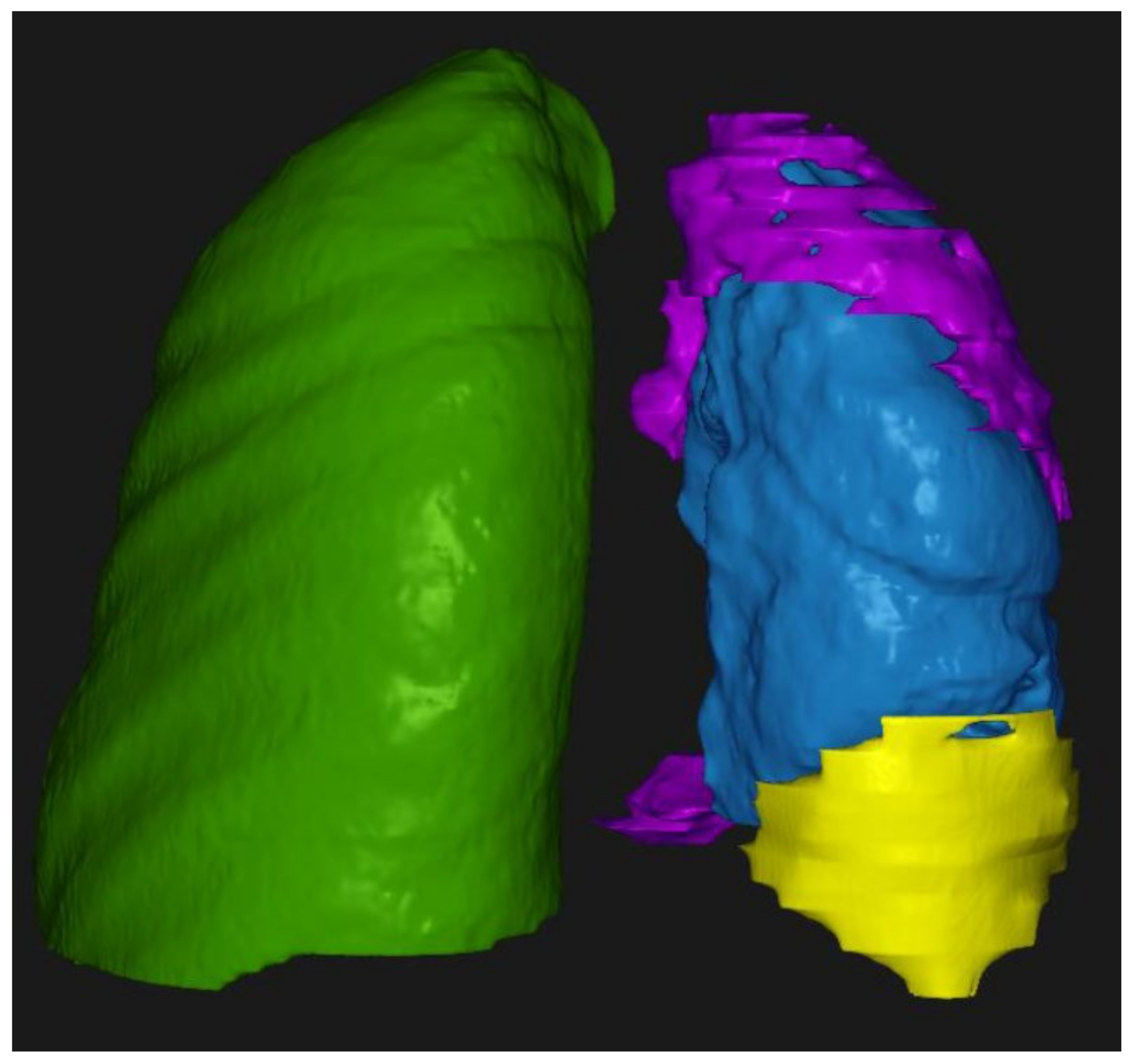
3.4. Correlation of Tumor Volume with Tumor Thickness and the T Parameter
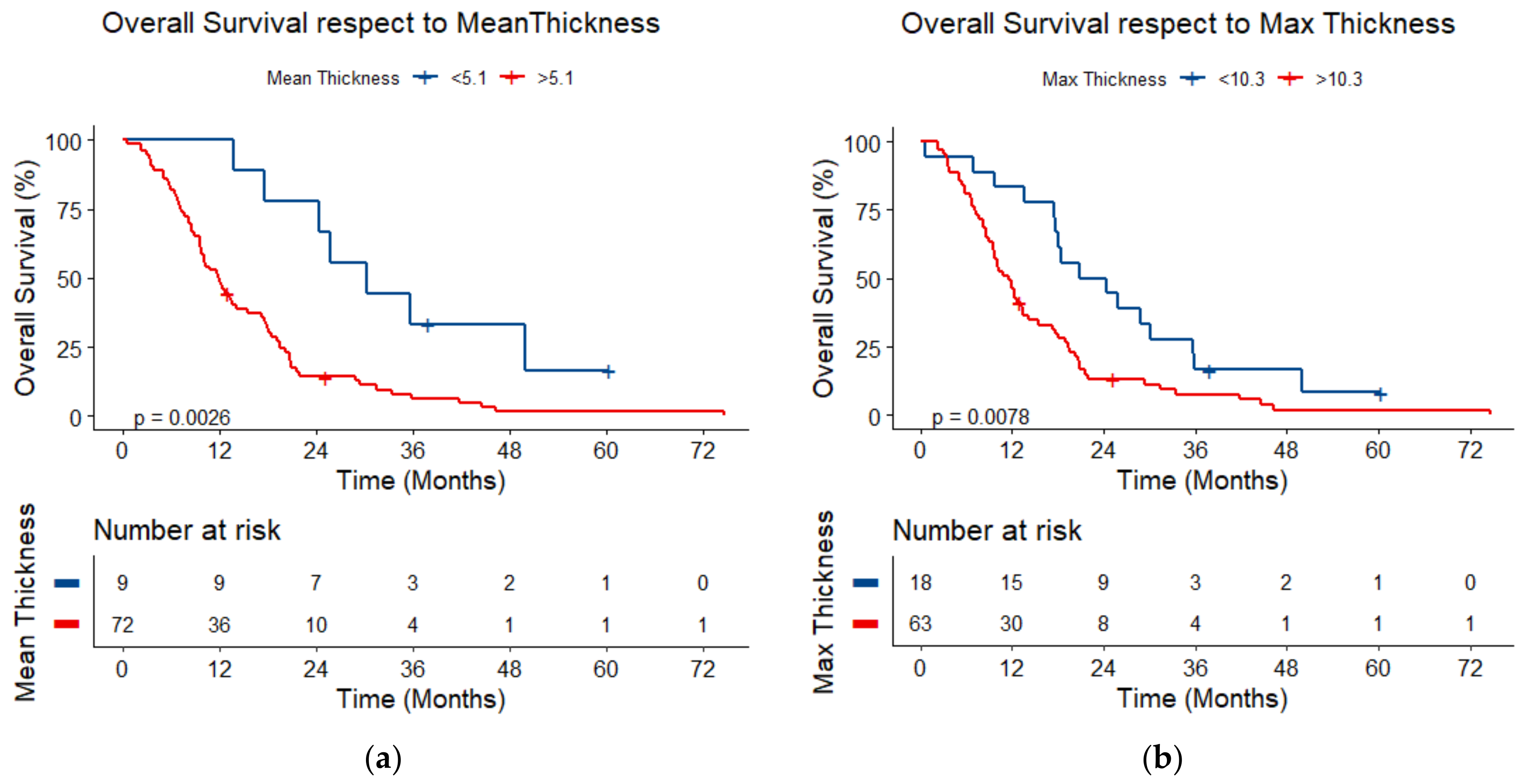
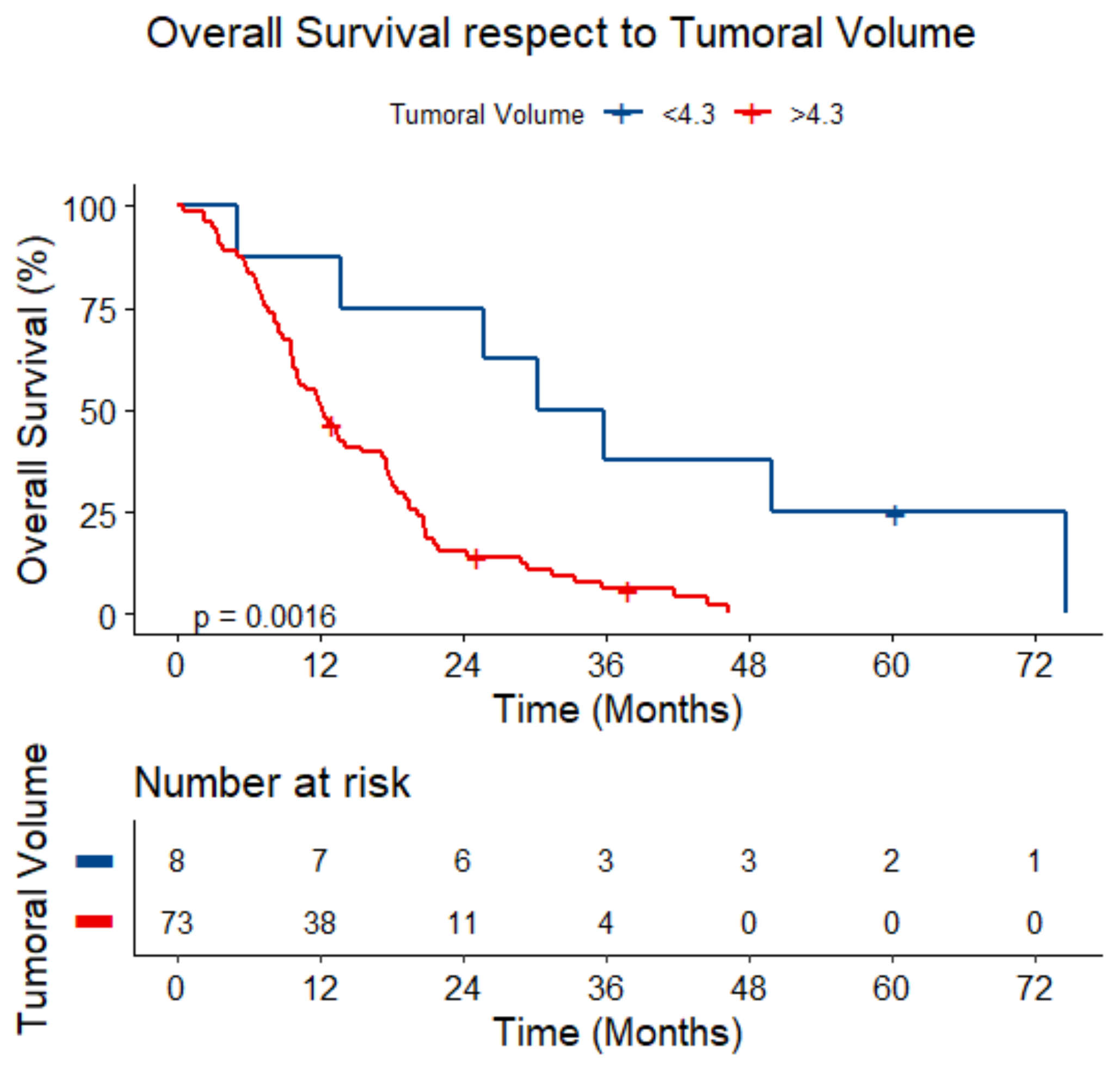
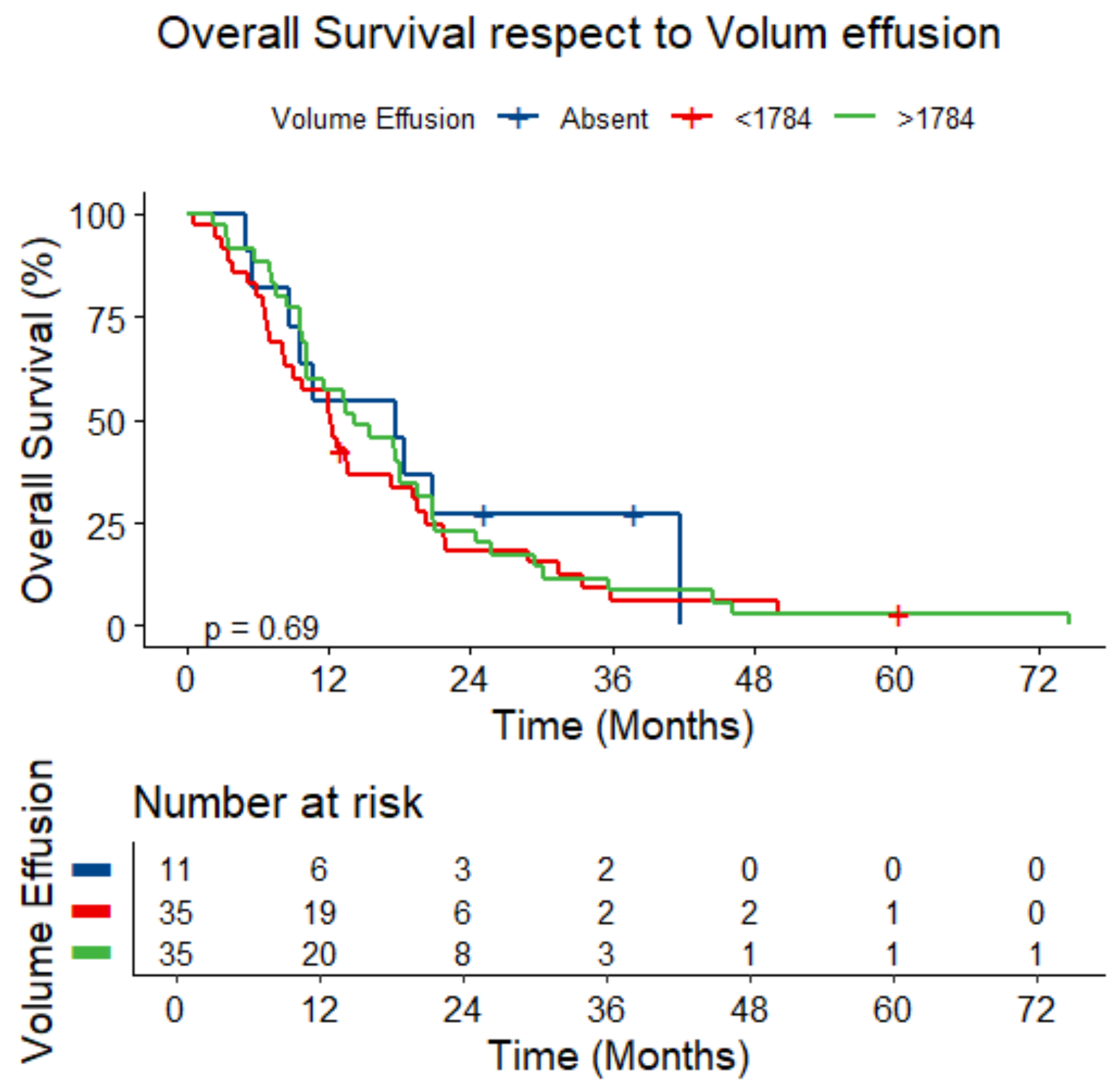
3.5. Survival Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jain, M.; Crites, M.K.; Rich, P.; Bajantri, B. Malignant pleural mesothelioma: A comprehensive review. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 5837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajj, G.N.M.; Cavarson, C.H.; Pinto, C.A.L.; Venturi, G.; Navarro, J.R.; Lima, V.C.C. Malignant pleural mesothelioma: An update. J. Bras. Pneumol. 2021, 47, e20210129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; van Gerwen, M.; Bonassi, S.; Taioli, E.; International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer Mesothelioma Task Force. Epidemiology of environmental exposure and malignant mesothelioma. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2017, 12, 1031–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Remon, J.; Hendriks, L.E.L.; Bironzo, P. Malignant pleural mesothelioma: New guidelines make us stronger for defeating this disease. Ann. Oncol. 2022, 33, 123–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fazzo, L.; Minelli, G.; De Santis, M.; Ceccarelli, E.; Iavarone, I.; Zona, A. The epidemiological surveillance of mesothelioma mortality in Italy as a tool for the prevention of asbestos exposure. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 5957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finn, R.S.; Brims, F.J.H.; Gandhi, A.; Olsen, N.; Musk, A.W.; Maskell, N.A.; Lee, Y.C.G. Postmortem findings of malignant pleural mesothelioma: A two-center study of 318 patients. Chest 2012, 142, 1267–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kindler, H.L.; Ismaila, N.; Armato, S.G., III; Bueno, R.; Hesdorffer, M.; Jahan, T.; Jones, C.M.; Miettinen, M.; Pass, H.; Rimner, A.; et al. Treatment of malignant pleural mesothelioma: American Society of Clinical Oncology Clinical Practice Guideline. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 1343–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickell, L.T., Jr.; Lichtenberger, J.P., III; Khorashadi, L.; Abbott, G.F.; Carter, B.W. Multimodality imaging for characterization, classification, and staging of malignant pleural mesothelioma. RadioGraphics 2014, 34, 1692–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, G.; Davoli, F.; Poletti, V.; Cavazza, A.; Lococo, F. When the diagnosis of mesothelioma challenges textbooks and guidelines. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherpereel, A.; Opitz, I.; Berghmans, T.; Psallidas, I.; Glatzer, M.; Rigau, D.; Astoul, P.; Bölükbas, S.; Boyd, J.; Coolen, J.; et al. ERS/ESTS/EACTS/ESTRO guidelines for the management of malignant pleural mesothelioma. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 55, 1900953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berzenji, L.; Van Schil, P.E.; Carp, L. The eight TNM classification for malignant pleural mesothelioma. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2018, 7, 543–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AIOM Linee Guida Mesotelioma Pleurico Edizione 2021. Available online: https://www.iss.it/documents/20126/8403839/LG-305-AIOM_Mesotelioma (accessed on 1 December 2024).
- Euhus, C.J.; Ripley, R.T. The staging of malignant pleural mesothelioma. Thorac. Surg. Clin. 2020, 30, 425–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonomi, M.; De Filippis, C.; Lopci, E.; Gianoncelli, L.; Rizzardi, G.; Cerchiaro, E.; Bortolotti, L.; Zanello, A.; Ceresoli, G.L. Clinical staging of malignant pleural mesothelioma: Current perspectives. Lung Cancer 2017, 8, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armato, S.G., 3rd; Nowak, A.K. Revised modified Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors for assessment of response in malignant pleural mesothelioma (Version 1.1). J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, 1012–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreto, I.; Franckenberg, S.; Frauenfelder, T.; Opitz, I.; Lauk, O. Potential advantage of magnetic resonance imaging in detecting thoracic wall infiltration in pleural mesothelioma: A retrospective single-center analysis. JTCVS Open 2024, 23, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpi, F.; D’amore, C.A.; Colligiani, L.; Milazzo, A.; Cavaliere, S.; De Liperi, A.; Neri, E.; Romei, C. The use of chest magnetic resonance imaging in malignant pleural mesothelioma diagnosis. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, S.I.; Straus, C.M.; Roshkovan, L.; Blyth, K.G.; Frauenfelder, T.; Gill, R.R.; Lalezari, F.; Erasmus, J.; Nowak, A.K.; Gerbaudo, V.H.; et al. Considerations for imaging of malignant pleural mesothelioma: A consensus statement from the International Mesothelioma Interest Group. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2023, 18, 278–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopci, E.; Castello, A.; Mansi, L. FDG PET/CT for staging and restaging malignant mesothelioma. Semin. Nucl. Med. 2022, 52, 806–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, A.K.; Francis, R.J.; Phillips, M.J.; Millward, M.J.; Van Der Schaaf, A.A.; Boucek, J.; Musk, A.W.; McCoy, M.J.; Segal, A.; Robins, P.; et al. A novel prognostic model for malignant mesothelioma incorporating quantitative FDG-PET imaging with clinical parameters. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 2409–2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, R.R.; Yeap, B.Y.; Bueno, R.; Richards, W.G. Quantitative clinical staging for patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2018, 110, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armato, S.G.; Francis, R.J.; Katz, S.I.; Ak, G.; Opitz, I.; Gudmundsson, E.; Blyth, K.G.; Gupta, A. Imaging in pleural mesothelioma: A review of the 14th International Conference of the International Mesothelioma Interest Group. Lung Cancer 2019, 130, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rusch, V.W.; Gill, R.; Mitchell, A.; Naidich, D.; Rice, D.C.; Pass, H.I.; Kindler, H.L.; Friedberg, J.; Ginsberg, M.; Erasmus, J.; et al. Malignant mesothelioma volumetric CT study group. A multicenter study of volumetric computed tomography for staging malignant pleural mesothelioma. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2016, 102, 1059–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kidd, A.C.; Anderson, O.; Cowell, G.W.; Weir, A.J.; Voisey, J.P.; Evison, M.; Tsim, S.; A Goatman, K.; Blyth, K.G. Fully automated volumetric measurement of malignant pleural mesothelioma by deep learning AI: Validation and comparison with modified RECIST response criteria. Thorax 2022, 77, 1251–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellini, A.; Dell’amore, A.; Giraudo, C.; Modugno, A.; Bernardinello, N.; Terzi, S.; Zambello, G.; Pasello, G.; Zuin, A.; Rea, F. Computed tomography and spirometry can predict unresectability in malignant pleural mesothelioma. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 4407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Entwisle, J. The use of magnetic resonance imaging in malignant mesothelioma. Lung Cancer 2004, 45 (Suppl. 1), S69–S71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, A.K.; Chansky, K.; Rice, D.C.; Pass, H.I.; Kindler, H.L.; Shemanski, L.; Billé, A.; Rintoul, R.C.; Batirel, H.F.; Thomas, C.F.; et al. The IASLC Mesothelioma Staging Project: Proposals for revisions of the T descriptors in the forthcoming eight edition of the TNM classification for pleural mesothelioma. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2016, 11, 2089–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Du, J.; Wang, Y.S.; Kang, H.Y.; Zhai, K.; Shi, H.Z. Prognostic impact of pleural effusion in patients with malignancy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Transl. Sci. 2022, 15, 1340–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| T1 | Tumor involving the ipsilateral parietal or visceral pleura only. | ||
| T2 | Tumor involving ipsilateral pleura (parietal or visceral pleura) with invasion involving at least one of the following: diaphragmatic muscle; pulmonary parenchyma. | ||
| T3 | Tumor involving ipsilateral pleura (parietal or visceral pleura) with invasion involving at least one of the following: endothoracic fascia; mediastinal fat; chest wall, with or without associated rib destruction (solitary, resectable); pericardium (non-transmural invasion). | ||
| T4 | Tumor involving ipsilateral pleura (parietal or visceral pleura) with invasion involving at least one of the following: chest wall, with or without associated rib destruction (diffuse or multifocal, unresectable); peritoneum (via direct transdiaphragmatic extension); contralateral pleura; mediastinal organs (esophagus, trachea, heart, great vessels); vertebrae, neuroforamen, spinal cord, or brachial plexus; pericardium (transmural invasion with or without pericardial effusion). | ||
| NX | Regional lymph nodes cannot be assessed. | ||
| N0 | No regional lymph node metastases. | ||
| N1 | Metastases to ipsilateral intrathoracic lymph nodes (including ipsilateral bronchopulmonary, hilar, subcarinal, paratracheal, aortopulmonary, paraesophageal, peridiaphragmatic, pericardial, intercostals, and internal mammary nodes). | ||
| N2 | Metastases to contralateral intrathoracic lymph nodes, metastases to ipsilateral or contralateral supraclavicular lymph nodes. | ||
| M0 | No distant metastasis. | ||
| M1 | Distant metastases present. | ||
| Stage I A | T1 | N0 | M0 |
| Stage I B | T2, T3 | N0 | M0 |
| Stage II | T1, T2 | N1 | M0 |
| Stage III A | T3 | N1 | M0 |
| Stage III B | T1, T2, T3 | N2 | M0 |
| T4 | Any N | M0 | |
| Stage IV | Any T | Any N | M1 |
| Covariate | Total (n = 81) |
|---|---|
| Age (median [range]), years | 73 [69–78] |
| Sex, n (%) | |
| Male | 73 (90.1%) |
| Female | 8 (9.9%) |
| Asbestos exposure, n (%) | |
| Yes | 67 (82.7%) |
| No | 4 (4.9%) |
| Uncertain | 10 (12.3%) |
| Tobacco use, n (%) | |
| Yes | 30 (37.1%) |
| No | 15 (18.5%) |
| N/A | 36 (44.4%) |
| Diabetes, n (%) | |
| Yes | 21 (25.9%) |
| No | 59 (72.8%) |
| N/A | 1 (1.2%) |
| Arterial hypertension, n (%) | |
| Yes | 48 (51.9%) |
| No | 32 (46.9%) |
| N/A | 1 (1.2%) |
| Coronary artery disease, n (%) | |
| Yes | 15 (18.5%) |
| No | 65 (80.3%) |
| N/A | 1 (1.2%) |
| Tumor side, n (%) | |
| Right side | 40 (49.4%) |
| Left side | 41 (50.6%) |
| Histologic subtype, n (%) | |
| Epithelioid | 60 (74.1%) |
| Sarcomatoid | 8 (9.9%) |
| Biphasic | 12 (14.8%) |
| Desmoplastic | 1 (1.2%) |
| Tumor growth pattern, n (%) | |
| Minimal | 28 (34.6%) |
| Nodular | 42 (51.9%) |
| Circumferential | 11 (13.6%) |
| Pleural effusion, n (%) | |
| Yes | 70 (86.4%) |
| No | 11 (13.6%) |
| Treatment, n (%) | |
| None treatment | 12 (14.8%) |
| Only CT | 16 (19.8%) |
| P/D | 8 (9.9%) |
| CT + RT | 7 (8.6%) |
| P/D + Chemotherapy | 22 (27.2%) |
| P/D + CT + RT | 16 (19.8%) |
| T parameter, n (%) | |
| T1 | 19 (23.5%) |
| T2 | 11 (13.6%) |
| T3 | 26 (32.1%) |
| T4 | 16 (19.8) |
| N/A | 9 (11.1) |
| Average tumor thickness (median [range]), mm | 12.4 [7.9–17.9] |
| Maximum tumor thickness (median [range]), mm | 18.3 [10.8–26.3] |
| Tumor volume (median [range]), mL | 27.7 [15.7–88.1] |
| Pleural effusion volume (median [range]), mL | 1784.1 [821.6–2697.0] |
| Follow-up (median [range]), months | 31.6 [22.2–43.6] |
| Univariable Model | Multivariable Model | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable a | Hazard Ratio (95%CI) | p-Value | Hazard Ratio (95%CI) b | p-Value |
| Maximum thickness (continuous) | 1.55 (1.22–1.96) | <0.001 | 1.97 (1.40–2.77) | <0.001 |
| Mean thickness (continuous) | 1.54 (1.21–1.95) | <0.001 | 2.23 (1.56–3.20) | <0.001 |
| Tumoral Volume (continuous) | 1.19 (1.08–1.32) | <0.001 | 1.26 (1.10–1.45) | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baratella, E.; Ercolani, E.; Segalotti, A.; Troian, M.; Lovadina, S.; Giudici, F.; Minelli, P.; Ruaro, B.; Salton, F.; Cova, M.A. Prognostic Value of Chest CT Volumetric Analysis in Patients with Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 1547. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14051547
Baratella E, Ercolani E, Segalotti A, Troian M, Lovadina S, Giudici F, Minelli P, Ruaro B, Salton F, Cova MA. Prognostic Value of Chest CT Volumetric Analysis in Patients with Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(5):1547. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14051547
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaratella, Elisa, Eleonora Ercolani, Antonio Segalotti, Marina Troian, Stefano Lovadina, Fabiola Giudici, Pierluca Minelli, Barbara Ruaro, Francesco Salton, and Maria Assunta Cova. 2025. "Prognostic Value of Chest CT Volumetric Analysis in Patients with Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 5: 1547. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14051547
APA StyleBaratella, E., Ercolani, E., Segalotti, A., Troian, M., Lovadina, S., Giudici, F., Minelli, P., Ruaro, B., Salton, F., & Cova, M. A. (2025). Prognostic Value of Chest CT Volumetric Analysis in Patients with Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(5), 1547. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14051547








